Abstract
Computational approaches in immune-oncology therapies focus on using data-driven methods to identify potential immune targets and develop novel drug candidates. In particular, the search for PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) has enlivened the field, leveraging the use of cheminformatics and bioinformatics tools to analyze large datasets of molecules, gene expression and protein–protein interactions. Up to now, there is still an unmet clinical need for improved ICIs and reliable predictive biomarkers. In this review, we highlight the computational methodologies applied to discovering and developing PD-1/PD-L1 ICIs for improved cancer immunotherapies with a greater focus in the last five years. The use of computer-aided drug design structure- and ligand-based virtual screening processes, molecular docking, homology modeling and molecular dynamics simulations methodologies essential for successful drug discovery campaigns focusing on antibodies, peptides or small-molecule ICIs are addressed. A list of recent databases and web tools used in the context of cancer and immunotherapy has been compilated and made available, namely regarding a general scope, cancer and immunology. In summary, computational approaches have become valuable tools for discovering and developing ICIs. Despite significant progress, there is still a need for improved ICIs and biomarkers, and recent databases and web tools have been compiled to aid in this pursuit.
1. Introduction
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are a main breakthrough in immunotherapy due to their capacity to help the body’s immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells [1]. They work by blocking the pathways that allow tumors to evade detection and activation of the immune system. The immune checkpoints are expressed on the surface of immune cells and tumor cells and can either be upregulated or downregulated depending on the setting of the immune response and tissue environment. In cancer, when these checkpoints are upregulated, tumor cells can evade detection by the immune system, dampen their elimination by cytotoxic T cells and, subsequently, continue to grow [2]. The ICIs target these checkpoints and block their interaction expression, allowing the immune system to detect and fight the cancer cells.
As illustrated in Figure 1, immune oncology and, in particular, ICIs in cancer have become a markedly pursued subject of research in the last ten years.
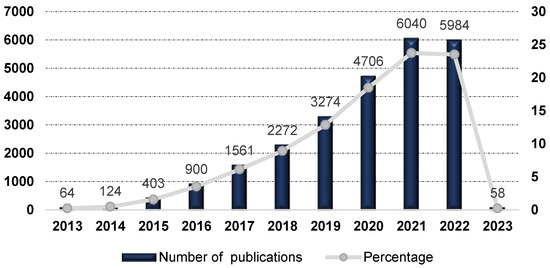
Figure 1.
Number of publications and percentages per year covering ICIs in cancer topics, period 2013–2023. Data source from Web of Science™ Core Collection.
The PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint axis is crucial in regulating the immune response. Programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) is a receptor protein found on the surface of specific immune cells, including T-cells [3]. PD-1 binds to its ligand, programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1), and triggers an inhibitory signal that halts T-cell activity against the target cell. PD-L1 is often overexpressed on the surface of cancer cells, and this is one way that cancer cells can evade destruction by the immune system [4].
Therefore, drugs that target the PD-1/PD-L1 axis can block this interaction and allow the immune cells to continue setting up a response against the cancer cells. These drugs are known as ICIs, and they have shown great promise in treating various cancers, including melanoma, lung cancer and bladder cancer. The present review aims to provide an overview of different computational approaches used to identify ICIs targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 axis or to ameliorate their efficacy or critical characteristics as therapeutics.
1.1. Methods
The literature used was indexed in Web of Science™ Core Collection, Current Contents Connect®, Derwent Innovations Index℠, KCI-Korean Journal Database™, MEDLINE® and SciELO Citation before 18 January 2023. A total of 25,458 publications (13,901 articles, 91 proceedings, 2016 meeting abstracts, 671 editorials and 8517 reviews) were retrieved. This section describes the methods used to carry out the statistical analysis.
Data Collection: The data for this study were obtained by searching the aforementioned databases using the search terms “cancer” and “immune checkpoint inhibitor” prior to 18 January 2023. A total of 25,458 publications were identified and included in the analysis, comprising 13,901 articles, 91 proceedings, 2016 meeting abstracts, 671 editorials and 8517 reviews.
1.2. Publication Trends from 2013 to 2022 on ICIs
From 2013 until 2016 there was a steady increase in the number of publications related to ICIs per year, rising from 64 in 2013 to 900 during 2016. However, since 2016, we observed a notable increase in the number of reports. In the last five years, there was a nearly 94% increase in publications, with 6040 and 5984 publications in 2021 and 2022, respectively. The awarding of the 2018 Nobel Prize for Medicine in this area to James P. Allison and Tasuku Honjo may have contributed to the significant growth of interest in ICIs. The American immunologist James P. Allison contributed to the discovery of mechanisms underlying T-cell activation and was a pioneer in the development of immune checkpoint therapy for cancer, specifically using cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4) blockade. The Japanese immunologist Tasuku Honjo contributed to the discovery of mechanisms and proteins critical to the regulation of immune responses, which led to the development of novel immunotherapies against cancer, namely the development of anti-programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) cancer immunotherapies.
Worldwide, more than three-quarters of the publications (i.e., 21,372 out of 25,400, corresponding to 84%) since 2013 have been linked to five countries: USA, China, Japan, Italy and France. The most productive country in this field has been the USA, contributing 9486 outputs across this period (37%). However, it is necessary to consider that the publications may include researchers from several countries.
Over 2000 journals have been selected as containing publications relating to ICIs in cancer since 2013. The top twenty-five journals reporting the above theme are listed in Figure 2.
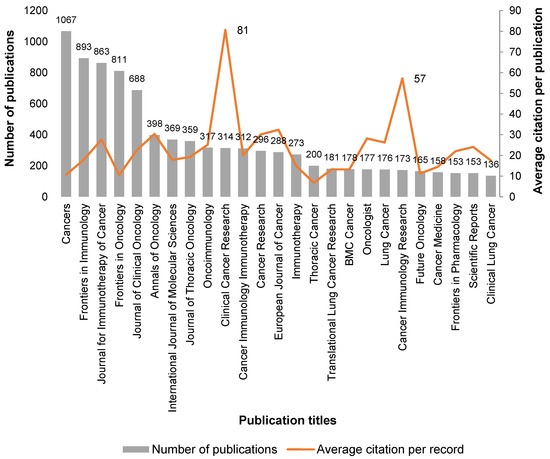
Figure 2.
Analysis of the 25 selected journals reporting ICIs in cancer topics, by number of records and average citation per record, since 2013. Data source from Web of Science™ Core Collection.
The four most-published journals are all open access, namely Cancers from MDPI, Frontiers in Immunology and Frontiers in Oncology from Frontiers and Journal for Immunotherapy of Cancer from Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) (Figure 2), which also contributed to the wide dissemination of this subject. The first generalist journal to appear is the International Journal of Molecular Sciences (IJMS) of the MDPI publisher; in positions 23rd and 24th are Frontiers in Pharmacology (Frontiers publisher) and Scientific Reports (Nature publisher), respectively (see Figure 2). Although we perceive that, in general, older publications accumulate more citations, and the publications analyzed in this theme are mostly very recent (representing 94% in the period of 2017–2022), there are clearly two journals that stand out with numbers of citations per publication of 81 and 57 for Clinical Cancer Research and Cancer Immunology Research, respectively (see Figure 2). Interestingly, these two most-cited journals are both from the American Association for Cancer Research publisher.
1.3. From Antibodies to Small Molecules: The Advancements in PD-1/PD-L1 ICIs
In 2011, cancer treatment was revolutionized with the first approval of an ICI by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), Ipilimumab [5], establishing a new field of research–immuno-oncology. Ipilimumab is a monoclonal antibody (mAb) against the immune checkpoint CTLA-4 developed by the Nobel Prize winner James P. Allison. Regarding the PD-1–PD-L1 axis, the first anti-PD-1 Ab, pembrolizumab, developed following the findings of Nobel Prize winner Tasuku Honjo, was approved by the FDA in 2014 to treat advanced melanoma. Two years later, in 2016, the first anti-PD-L1 Ab, atezolizumab, was approved for the treatment of bladder cancer. To date, the FDA has approved seven ICIs mAbs for the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway: four anti-PD-1 (nivolumab, pembrolizumab, cemiplimab and dostarlimab) and three anti-PD-L1 (atezolizumab, avelumab and durvalumab) [6,7]. Small molecule ICIs of the PD-1/PD-L1 interaction have been explored to obviate the drawbacks of mAbs such as lack of oral bioavailability, prolonged retention in the tissues and poor permeability [7]. Although no small molecules have yet been approved as PD-1/PD-L1 ICIs, eight small molecules are already in clinical trials, mostly in the early stages [8], as shown in Table 1. The small molecules navtemadlin (3) and ciforadenant (5), shown in Table 1, are also being tested in combination clinical trials with mAbs avelumab and atezolizumab [8]. In addition to these two small molecules, there are ten more small molecules (9–18) being used in combination clinical trials with mAbs, as shown in Figure 3.

Table 1.
Small molecule (1–8) ICIs targeting PD-1/PD-L1 in clinical trials.
Figure 3.
Small molecule (9–18) ICIs targeting PD-1/PD-L1 in combination clinical trials with mAbs.
The development of a drug from concept to market currently takes 13–15 years [9] with an average investment of $2–3 billion [9]. To reduce the length and cost of the drug discovery and development process, drug designers have been exploring computer-aided drug design (CADD) tools [10,11,12,13,14] over the past few decades to design and identify new drug-like chemical entities that can overcome clinical attrition and lack of efficiency.
In this review, we highlight the computational methodologies applied to the discovery and development of PD-1/PD-L1 ICIs for improved cancer immunotherapies, with greater focus in the last five years. The use of CADD structure- and ligand-based virtual screening processes, molecular docking, homology modeling and molecular dynamics (MD) simulations methodologies essential for successful drug discovery campaigns focusing on small molecule ICIs will be addressed. Databases and web tools in the context of cancer and immunotherapy will be also reported in this review and in the Supplementary Material. In this review, the most relevant current computational methodologies for binding mode and binding affinity prediction of the PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint are highlighted.
2. Databases and Web Tools in the Context of Cancer and Immunotherapy
When developing immunotherapies for cancer, databases are a valuable resource that provide researchers and clinicians with access to a wealth of information about cancer cells’ genetic and molecular characteristics and the immune system. These databases collect and store a vast amount of data from various sources, such as clinical trials, genomic sequencing and gene expression profiling.
The most-used databases are the global repositories for nucleotide sequences of the International Nucleotide Database Consortium [15,16,17], as they harbor almost all the relevant sequences known until now, excluding the databases of reads that are not individually annotated. Even if they present different names, addresses or user interfaces, they share the very same body of data regarding the sequences. These databases are usually served by a specific database for translated coding sequences (CDS) and their annotation. Apart from the NCBI Peptide [15], the most popular database is UniProtKB from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) [18]. The latter cooperates closely with InterPro [19] regarding the functional annotation and provides a fully integrated view of the knowledge of a given sequence, especially regarding entries for its Swiss-Prot division. It may be the ideal entry point for obtaining annotation for a given protein or the underlying family/domain architecture.
Functional annotation is, nowadays, enabled by a set of different and concurrent databases with their specific models. Being different in nature and source sequence sets, the concurrency of matches imparts significance, and probably detail, to the annotation of a novel sequence. In this field, InterPro (and InterProScan) shines due to its meta-database structure, the models (“signatures”) belong to the federated partners [20,21,22] and the InterPro matches are accompanied by a consolidated annotation that makes it the resource of choice for functional annotation. Regarding proteins and their role in the cell, structural information is of paramount importance, even if it is not always known. Nowadays, there is an ever-increasing volume of available structures, and they are mostly stored at Protein Data Bank (PDB) [23]; this database comprises both experimentally derived structures and a growing amount of results from homology modeling.
Databases of annotated genes comprise the next level of information consolidation, as they connect the individual sequences, plus their annotation to the genomic assembly and the genomic variability or even gene expression. The largest database of this scope by far is Gene from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), and it connects almost seamlessly with Genome, the NCBI database for genomic assemblies [15]. Its entries are also present, through the all-pervasive body of cross references, in other databases such as the University of California, Santa Cruz, Genomes (UCSC) [24]. Individual genes are of limited use when dealing with the physiological conditions of the cell or other high-level phenomena to address the requirements of dealing with huge pools of genes, and their expression ontologies were developed into group genes according to their function and process and the localization of the product. The Gene Ontology (GO) project has been the main reference in this role [25], and there are derivatives and subsets, even if the rationale remains. Other classification approaches may be used, such as the one used by Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery (DAVID) [26], using functional annotation on large sets of genes. Other ways of classification are possible, and available, based on increased levels of data integration, such as the Molecular Signatures Database (MSigDB) [27], the PRO [28] or the Human Protein Atlas [29].
Regarding the gene expression study results, the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database [30] is the main destiny for experimental data. The deposited information, and new datasets gained through insight when they are crossed with known interactions, are available through STRING [31] or the even more detailed content of GeneMANIA [32]. In any case, the accepted reference for mapping a given set of genes to a pathway has been, for a long time, the KEGG Pathway database [33]. The Online Catalog of Human Genes and Genetic Disorders (OMIM) bridges the gap between the genotype and the phenotype while focusing on the field of human mendelian disorders [34].
Departing from the general point of view and looking into cancer situations, there are a multitude of avenues and resources, depending on the required scale. Mutations and their putative outcomes can be inferred with the help of both divisions of the FannsDB [35,36]. Looking into the cell and their mutation repertoire in an integrated fashion, databases such as the Broad’s Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia [37], the Cancer Genome Atlas [38];,the cBioPortal [39], TIMER [40], GTEx portal [41] and GEPIA [42] may be relevant stops for finding expression data analysis, pharmacologic impact characterization or epigenetic information. Those projects incorporate and analyze an ever-increasing number of results according to stable pipelines that highlight specific aspects of the data.
Other relevant sources of database stored data are dedicated portals that centralize different sources and facilitate in different degrees the processes of querying and data retrieval. The Genomic Data Commons (GDC) of the National Cancer Institute [43] or the Broad’s GDAC—Firehose are good examples for the kind of facilities alluded. The ability to associate medical imaging results with clinical and molecular data is well represented by the Cancer Digital Slide Archive [44]; in this case, the connection with the Cancer Genome Atlas is established through the images’ meta-data.
The interactions between tumors, the immune system and pharmacology are addressed in portals such the Tumor Immune System Interactions and Drug Bank (TISIDB) [45]. Regarding the work on ICIs, the availability of T-cell receptor-related databases is important. Databases such as VDJDB [46] or PIRD [47] are complemented by much smaller but manually curated resources such as McPAS-TCR [48] or TBAdb [47], where the latter group trades quantity for quality. Other databases are more ambitious in their scope, integrating a more diverse dataset. This is the case for the Human Primary Cell Atlas [49] and The international ImMunoGeneTics information system® [50].
Importantly, databases serve as essential resources for identifying potential drug targets and understanding the molecular mechanisms of drug action. Several critical databases in this context are described in Table S1 of the Supplementary Materials.
3. Computational Methods for Predicting Checkpoint Inhibitors
3.1. Small Molecules
Small molecule-based immunotherapies, compared to peptide- and especially Ab-based therapies, offer advantages such as a higher oral bioavailability, overall lower costs and a relative shorter half-life, which leads to less potential toxicity and adverse effects [51]. However, despite the pharmacokinetic benefits, small molecules have been receiving limited attention, probably due to the intrinsic difficulty of mimicking conventionally complex protein–protein interactions (PPIs) [52]. It was only recently that small molecules started receiving attention, taking on a more relevant role in immune checkpoint therapies, especially as inhibitors of the PD-1/PD-L1 interaction. This late and complex investigation might be due to the PD-1/PD-L1 large binding interface, spanning ~1970 Å2, devoid of well-defined binding pockets [53]. The first small molecules with a promising inhibitory activity against PD-L1, a series of compounds containing a biphenyl group, were disclosed by Bristol-Myers Squibb (BMS) in 2015 [54]. However, the binding mechanism was found by Holak’s group, who discovered that the BMS compounds induced the dimerization of the PD-L1 protein. The unveiling of two co-crystal structures of PD-L1 in complex with small molecule inhibitors, BMS-202 (19) and BMS-200 (20) (PDB ID: 5N2F and PDB ID: 5J89, respectively), brought light to structure-based drug design [55,56]. Mittal et al. [57] applied molecular docking studies to a PD-1/PD-L1 complex with BMS inhibitors against the PD-L1 protein and discovered that the residues Tyr56, Asp122 and Lys124 play crucial roles in ligand binding to the PD-L1 protein (Figure 4), an important piece of information for the design of inhibitors of PD-L1. These findings also led to the development of different molecules containing a biaryl moiety, following a ligand-based approach.
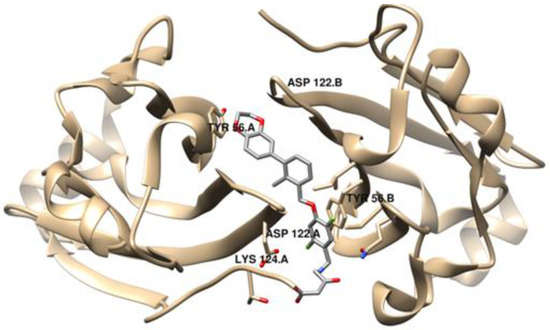
Figure 4.
Visualization of the co-crystal dimer structure of PD-L1 in complex with BMS-200 (Protein Data Bank, PDB ID: 5N2F), highlighted with the critical residues for ligand binding, using UCSF Chimera [57,58].
Qin et al. discovered and explored the structure activity relationships (SARs) of a series of [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyridines scaffold inhibitors, showing that a ring fusion strategy could be employed for designing analogues of the Bristol-Myers Squibb chemical compounds such as BMS-202 (19) and BMS-200 (20), as shown in Figure 5 [59]. In the following work, they also developed and studied SARs of indoline scaffold compounds [60], and, afterwards, 4-arylindolines containing a thiazole moiety [61], with one of them, A30 (21) in Figure 5, reaching an IC50 value of 11.2 nM. This showed that compounds bearing a thiazole moiety exhibited significantly increased activity compared to compounds containing a thiophene group. The authors applied molecular docking to confirm the binding mode of A30 (21) to PD-L1 binding sites using the BMS-200/PD-L1 complex as a template, showing that A30 (21) fit well within the inhibitor binding pocket [61]. Cheng et al. [62] chose a combined structure and ligand-based approach and started with docking-based virtual screening. The hit compound was then improved through SAR studies, and a series of resorcinol dibenzyl ethers were synthetized, with compound NP19 (22) in Figure 5 inhibiting the PD-1/PD-L1 interaction with an IC50 value of 12.5 nM in Homogeneous Time-Resolved Fluorescence (HTRF) binding assays. Also based on the pharmacophoric model of BMS compounds, and with the use of molecular docking as a corroborative technique [63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73], Dai and co-workers [74] obtained 1-methyl-1H-pyrazolo [4,3-b] pyridine derivatives, with the best compound, D38 (23) (Figure 5), having an IC50 value of 9.6 nM. Liu et al. [75] reported benzo[c][1,2,5]oxadiazole derivatives, with molecule L7 (24) in Figure 5 exhibiting an IC50 value of 1.8 nM. Wang et al. [76] designed biphenyl pyridine derivatives, with the most potent compound (25) showing an IC50 value of 3.8 nM [59].
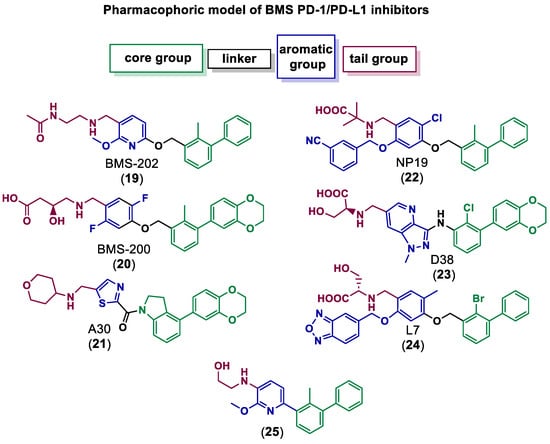
Figure 5.
Small molecule inhibitors of PD-1/PD-L1 based on the BMS pharmacophoric model [59,61,62,74,75,76].
In 2022, DiFrancesco and co-workers [51] began a high-throughput virtual screening of approximately 3.7 million lead-like molecules from the ZINC online repository using a rigid-receptor docking approach against both human PD-1 and PD-L1. This first step showed possible small molecule tractability of only the PD-1 binding. This lead-like dataset followed, as criteria, a molecular weight between ≥250 and ≤350 g/mol, an XlogP value ≤3.5 and a number of rotatable bonds ≤7. The next step involved molecular docking of the National Cancer Institute (NCI) compound dataset only against the PD-1 binding pocket. The top ~0.1–5% of molecules obtained from both datasets were clustered into separate bins using the ChemMine server binning tools. Considering the cost, commercial availability and binding to key residues of PD-1 and PD-L1, 40 top hit compounds were selected. The dynamic binding performance of these compounds was further investigated using long 100 ns MD simulation with the Desmond Molecular Dynamics package. Despite its low molecular weight (415.5 g/mol), compound NSC631535 (26) in Figure 6 reveals itself to be a potentially stable binder at the PD-1 interface pocket, exhibiting an experimental IC50 of 15 µM.
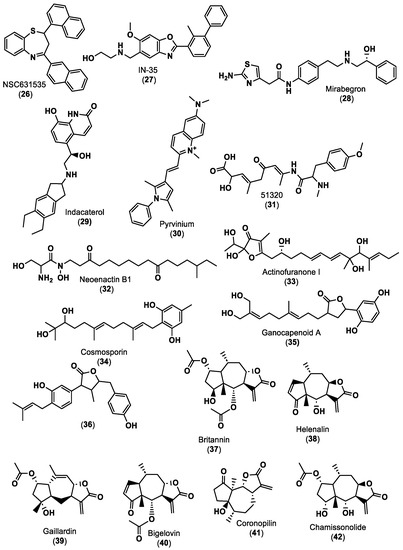
Figure 6.
Small molecule inhibitors of PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint [51,65,77,78,80,81,82].
Chandrasekaran et al. [77] used a drug repurposing approach consisting of e-Pharmacophore modeling, molecular docking and then MD simulation. All the in silico preparations, such as protein and ligand preparation, molecular docking and MD, were performed using the Maestro 12.6 modeling package. The three-dimensional crystal structure of human PD-L1 (PDB ID: 5J89) co-crystallised with a small molecule inhibitor, BMS-202 (19), was retrieved from the PDB. The treated PD-L1 protein was docked with INCB086550 (5) in Table 1, an Incyte corporation hit molecule for PD-L1 inhibition. Based on the observed interactions, an e-Pharmacophore hypothesis with six crucial characteristics was determined, comprising two acceptors of hydrogen bonds, one donor of hydrogen bonds, one positively ionizable group and two aromatic rings. To reveal FDA-approved candidates that can be repurposed against PD-L1, the pharmacophore characteristics were introduced into the PHASE module with a matching threshold of four out of six features. The screening retrieved 324 FDA-approved drugs with a fitness score of ≥1. The ten top hits were then compared with a clinical trial candidate, IN-35 (27) in Figure 6. Compounds with a fitness score greater than one were selected for extra-precise flexible docking at the PD-L1 dimer interface. Mirabegron (28) and indacaterol (29), shown in Figure 6, exhibited docking scores against the PD-L1 dimer (PDB: 5J89) of −9.213 kcal/mol and −8.023 kcal/mol, respectively. The binding-free energy of mirabegron (28) and indacaterol (29) was determined by MM-GBSA analyses, suggesting that mirabegron (28) uses less energy to create a more stable complex. MD simulation confirmed that the mirabegron (28) complex demonstrated a similar pattern of deviation in correlation with IN-35 (27), maintaining the interaction with the active key amino acids during the simulation period. Fattakhova and co-workers [78] reported a drug repurposing strategy, using a structure and ligand-based screening of ZINC15 database, that includes ~10,000 approved and investigational drugs. The AutoDock Vina docking algorithm was used to carry out structure-based docking of the drug molecules to all PD-L1 dimer interfaces (PDB IDs: 5N2F, 5NIU, 6R3K, 5J89, 5J8O, 5N2D, 6NM8). The top 1000 molecules with the best docking scores were selected. The ligand-based virtual screening of ZINC15 was performed using ROCS 3.4.1.0 (Open Eye Scientific Software, Santa Fe, NM. http://www.eye-sopen.com (accessed on 28 February 2023)), a database that aligns and ranks drugs based on the similarity to a given 3D structure. The compounds with a higher similarity, as indicated by higher Tanimoto Combo scores across the seven crystal ligands, were then combined with the previously obtained 1000 molecules. These top ROCS hits were then further subjected to docking against the high-resolution PD-L1 crystal structure (PDB: 5N2F). After studying MD and performing HTRF binding assays, pyrvinium (30) in Figure 6, an FDA-approved anthelmintic drug, showed the highest activity, with an IC50 value of approximately 29.66 μM. Since pyrvinium (30) is an approved drug, it may be a good starting point for the design of even more potent analogues as PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors.
Similarly, Urban et al. [79] also employed a pharmacophore-based virtual screening (PBVS) approach. The structure-based pharmacophore model was obtained with the crystal structures of the PD-L1 dimer in complex with BMS-8 (PDB ID 5J89), BMS-202 (PDB ID 5J8O) in Figure 5, BMS-1001 (PDB ID 5NIU) and BMS-1166 (PDB ID 6R3K) by Pharmit server software. PBVS was performed in the PubChem database, which contains over 90 million chemical structures, and the matching compounds were docked to the PD-L1 dimer using the AutoDock Vina program. The PD-L1/inhibitor complexes were subjected to energy minimization using the Smina minimization feature of the same program, and complexes with energies lower than 8 kcal/mol were selected for further screening. Screening was performed using pharmaceutically relevant descriptors and properties of lead-like drugs. The first screening was performed using the QikProp program and the second after docking optimization by the SwissADME web tool. After molecular docking screening using the Glide module of the Schrödinger Suite, the MD simulations showed that nine out of ten compounds established stable complexes with the PD-L1 dimer, as shown by the analysis of MD trajectories. Additionally, molecular mechanics Poisson–Boltzmann surface area (MM-PBSA) calculations revealed low binding energies for the interactions of these ligands with the PD-L1 dimer, indicating that the identified molecules could be used for the design of novel inhibitors of PD-1/PD-L1 interactions.
Luo and co-workers [80] also used a structure-based PBVS approach, applying Discovery Studio 4.5 to establish a pharmacophore model using PD-L1/small molecule inhibitors downloaded from PDB after screening marine small molecule databases such as the Comprehensive Marine Natural Products Database (CMNPD, https://www.cmnpd.org/ (accessed on 28 February 2023)) and the Seaweed Metabolite Database (SWMD, http://www.swmd.co.in/ (accessed on 28 February 2023)) according to the properties of the pharmacophore. The compounds matched from the different databases were transferred to a list for another virtual screening based on pharmacophore characteristics, yielding a total of 12 hits. Then, two compounds were selected for further evaluation based on their molecular docking scores. Afterward, ADME (absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion), toxicity and docking studies were performed using the SwissADME, ProTox-II and CDOCKER programs, respectively. Molecule 51320 (31) in Figure 6 was selected for MD analysis using GROMACS. Moreover, molecule 51320 (31) maintained a steady conformation with PD-L1, indicating that the compound could be used or improved to potentially become an inhibitor of PD-L1.
On the other hand, Kumar and co-workers [81] began with a virtual screening of 32,552 compounds from the Natural Product Atlas database for PD-L1 inhibitors. First, all ligands were filtered using ADME and drug-likeness criteria using the QikProp tool, and then the filtered ligands were virtually screened via three subsequent steps, including (i) high-throughput virtual screening (HTVS), (ii) standard precision (SP) screening and (iii) extra precision (XP) screening protocols. Five natural compounds, namely neoenactin B1 (31), actinofuranone I (33), cosmosporin (34), ganocapenoid A (35) and 3-[3-hydroxy-4-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)-2-methylidene-cyclohexanone (36), shown in Figure 6, were collected, and the joint results of binding free energy calculation and MD simulation support the use and further development of these compounds as PD-L1 ICIs in cancer immunotherapy.
With a study based on molecular docking using GOLD software (GOLD 5.3 release, Cambridge Crystallographic Data Center, Cambridge, UK), Vergoten et al. [82] showed the potential of pseudoguaianolide sesquiterpene lactones, especially BRT (37), to interact with PD-L1 homo and dimer forms. Besides BRT (37), 15 other pseudoguaianolide sesquiterpene lactone analogues to BRT (37), including helenalin (38), gaillardin (39), bigelovin (40) and coronopilin (41), as shown in Figure 6, were docked to PD-L1 homo and dimer forms. BRT (37) seemed to form a more stable complex with the dimeric form, with a calculated empirical energy of interaction (ΔE) value of −63.1 kcal/mol, similar to the ΔE of PD-L1/BMS-202 (19), shown in Figure 5 (−73.4 kcal/mol) under the same conditions. The docking analysis of chamissonolide (42), shown in Figure 6, also yielded good results, with a ΔE of −64.8 kcal/mol, providing a direction for the design of novel PD-L1 binders incorporating an SL-like tricyclic scaffold. The structure of the ligands was optimized before docking using a classical Monte Carlo conformational searching procedure, as established in the BOSS software [83].
Lessons from Small Molecules Targeting Other Immune Checkpoints
Although the most recent studies involving cancer immunotherapy and computer methods mainly target PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoints, computer approaches have also been useful for discovering novel small molecules for other immune checkpoints. Qayed and co-workers [84] reported a combination of ligand- and structure-based modeling studies, designing and synthetizing novel hybrids of 2-indolinone-thiazolidinone, a well-known scaffold with anticancer activity. Twenty-six hybrids were tested in vitro for CDK2 inhibition, a key checkpoint enzyme, and compared to the reference enzyme inhibitors, such as sunitinib (43), nintedanib (44) and semaxanib (45) (Figure 7). To support their biological activities, broad docking and MD simulations were performed. In addition to the confirmed consistency between the in vitro and in silico studies, ADME and Tox studies using SwissADME and pkCSM also predicted good pharmacokinetic properties and low toxicity.
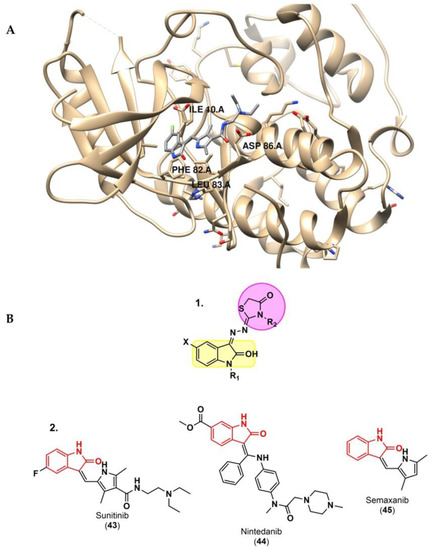
Figure 7.
(A) 3D interactions of sunitinib with CDK2 (PDB code: 3Ti1) using UCSF Chimera [58,84]. (B) 1. Structure of the designed hybridized molecules. 2. 2-indolinone pharmacophore motifs in CDK2 inhibitor commercially marketed drugs [58,84].
CD73, a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-linked cell surface enzyme, has been receiving increasing attention in the past decade. Although some inhibitors have been identified through in vitro assays, none of them have passed preliminary clinical trials. Lyu et al. [85] aimed to identify novel inhibitors by using a structure-based virtual screening approach, retrieving about 500 molecules with a high binding affinity from the Chemdiv-Plus database. These molecules were filtered by drug properties and pharmacokinetics using the Stardrop program (Release 6.5.0, Optibrium Ltd., Cambridge, UK), resulting in 68 small molecules. Phelligrin-based compounds showed the best experimental inhibition activities and may serve as lead compounds for the development of better analogues with the insight provided by the docking studies.
3.2. Peptides
In addition to small molecules, computational methods also played a crucial role in the discovery of novel peptides as immunotherapeutic drugs.
Li et al. [86] designed several PD-1 binding peptides using a computational de novo design method, which was divided into four steps: (1) identification of key anchor residues and building of a scaffold library; (2) screening of the scaffold to identify fragments in which the identified anchor residues are present; (3) transfer of the fragments onto the scaffold; and finally (4) sequence design and structure optimization using the Rosetta modeling package (https://www.rosettacommons.org/software (accessed on 28 February 2023)). The best peptides were then selected for in vitro studies.
The scaffold library was built by extracting scaffold fragments from 22,912 protein crystal structures in the PDB. The key PD-L1 anchor residues, Tyr56, Arg113, Ala121, Asp122 and Tyr123, were identified using three prediction tools, Robetta, KFC2 and PredHS, with the PD-1/PD-L1 complex (PDB ID 4ZQK) as the input structure. Scaffold screening was performed by superposing each fragment from the library onto the anchor residues using the Cealign algorithm in the Pymol program. The scaffold fragments with a root-mean-square deviation (RMSD) inferior to 2.0 Å were kept for the next step. Since one scaffold was unable to accommodate all five key residues due to their relative positions and structural properties, two scaffold fragments were selected. To transform the two scaffolds into a continuous peptide, Rosetta module Kinematic loop modeling was applied, and the optimization of the sequence design and structure minimization was performed employing the Backrub module. Finally, the resulting peptides in complex with PD-1 were enhanced using Rosetta’s Relax module and scored using the InterfaceAnalyzer module of Rosetta. The most potent peptide, Ar5Y_4 (46), as seen in Figure 8, showed a KD value of 1.38 ± 0.39 μM, comparable to the binding affinity of the cognate PD-L1.
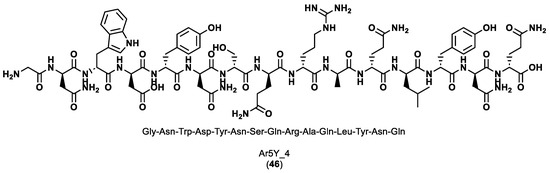
Figure 8.
Sequence and structure of the most potent peptide designed, Ar5Y_4 [86].
On the other hand, Manavalan and co-workers [87] created a web server, PIP-EL (www.thegleelab.org/PIP-EL (accessed on 28 February 2023)), a free access automated computational method that allows a faster identification of novel Proinflammatory Inducing Peptides (PIPs) using the strategy of ensemble learning (EL). PIPs have the ability to induce proinflammatory cytokines and have been used as an antitumor agent, an antibacterial agent and a vaccine in immunotherapies.
To build the dataset, experimental validated positive and negative peptides were extracted from IEDB (https://www.iedb.org/ (accessed on 28 February 2023)). A peptide was considered positive if it induced any one of the proinflammatory cytokines (i.e., IL1α, IL1β, TNFα, IL6, IL8, IL12, IL17, IL18 and IL23) in T-cell assays of human and mouse. Since the dataset was imbalanced, a random under-sampling technique to generate 10 balanced models for each composition was applied, leading to the combination of 50 random forest models. PIP-EL reached a Matthews’ correlation coefficient (MCC) of 0.435 in a 5-fold cross-validation test, which is ~2–5% higher than that of the individual classifiers. Additionally, the performance of PIP-EL was tested on an independent dataset, resulting in an MCC of 0.454. Therefore, PIP-EL can be a useful tool for researchers working in the field of peptide therapeutics and immunotherapy.
Another web server, PDL1Binder (http://i.uestc.edu.cn/pdl1binder/cgi-bin/PDL1Binder.pl (accessed on 28 February 2023)), was developed by He and co-workers [88]. The dataset is composed of 80 PD-L1 binding peptides obtained by next-generation phage display (NGPD) and is used for the development of computational models for identifying PD-L1 binding peptides. Instead of random forest-based models, as in the previous work, a Support Vector Machine-based model composed of four different peptide descriptors and an optimal feature selection approach chosen from five feature selection strategies outperformed the models developed with eleven other machine learning (ML) algorithms. This work offers promising PD-L1 binding peptide candidates for further investigations.
Antunes et al. [89] also implemented a new platform using Jupyter Notebook and the Docker program called HLA-Arena, which allows the analysis and even structural modeling of peptide–HLA complexes. This platform enables the use of computational tools such as APE-Gen, DINC, MODELLER and MHCflurry. This environment can be used to perform structural analyses for personalized cancer immunotherapy, neoantigen discovery or vaccine development.
Li and co-workers [90] described an in silico virtual screening and biomolecular interaction analysis (BIAcore) against an internal peptide library to discover novel PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor peptides. Screening was performed using molecular docking and RRQWFW-NH2 (47) and RRWWRR-NH2 (48), which were found to have the best docking scores, as shown in Figure 9. Next, MD simulations and surface plasmon resonance (SPR) were used to further corroborate their predictions. The in vitro studies were consistent with the computational data, providing some insight on new candidate peptide drugs for cancer immunotherapy.
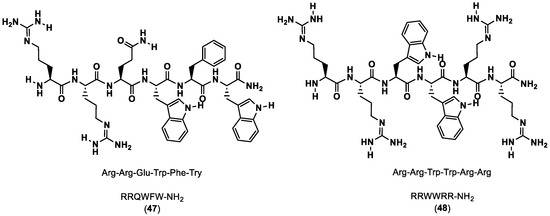
Figure 9.
Sequence and structure of RRQWFW-NH2 and RRWWRR-NH2 [90].
On the other hand, Bojko and co-workers [91] designed and synthetized potential blockers/inhibitors of the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway. The sequences of the peptides were based on the binding sites of PD-1 to PD-L1, as shown by the crystal structure of the complex, and also on molecular mechanics with generalized Born and surface area solvation (MM/GBSA). The computational results were confirmed by in vitro and cell assays, such as Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR), which studies the interactions, and cell assays that study their inhibitory activity.
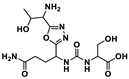
PD-1(122–138) C123-S137C (49) in Figure 10 has been shown to have the best inhibitory activity, so its 3D NMR structure was established and the binding site to PD-L1 was determined using molecular modeling methods. These results showed that the peptides synthetized are able to mimic the PD-1 interactions and block the PD-1/PD-L1 interaction.
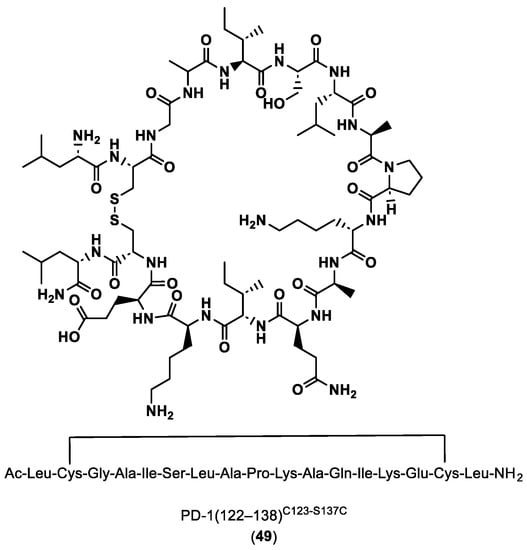
Figure 10.
Sequence and structure of PD-1(122–138)C123-S137C [91].
One of the most recently developed computational methods, AlphaFold, has revolutionized structural biology by predicting highly accurate structures of proteins and their complexes with peptides, antibodies and proteins [92,93,94]. In addition to that, AlphaFold can also be useful for protein–peptide systems and drug discovery, as it can help identify the highest affinity binder among a set of peptides. Chang and Perez [92] presented a new competitive binding assay using AlphaFold to predict the structures of the receptor in the presence of peptides. The authors tested the application on six protein receptors for which they possessed the experimental binding affinities to several peptides and obtained the predicted structures (bound form) for the higher affinity peptides [92]. They concluded that this assay had a better prediction score for identifying stronger peptide binders that also adopt stable secondary structures upon binding [92]. Johansson-Åkhe et al. [93] also show the importance of AlphaFold, in this case, AlphaFold-Multimer. AlphaFold-Multimer is shown to be capable of predicting the structure of peptide–protein complexes with acceptable or better accuracy than previous models and also has the capacity to predict whether a peptide and a protein will interact, thus improving peptide–protein docking [93].
3.3. Antibodies (Abs)
The recent advances on computational approaches to improve immunotherapies for cancer are mostly based on the discovery of novel small molecule and peptide/peptidomimetic inhibitors of immune checkpoints [95,96]. On the other hand, in the area of Abs, recent investigations have had a greater focus on the discovery and better elucidation of the binding modes of Abs onto antigens that can guide the development of variants with higher affinity and specificity. The computational approaches may also improve pharmacokinetic properties of mAbs, which tend to be worse compared to peptides and small molecules.
On the other hand, the study of mechanisms and binding modes, especially of already approved Abs for the treatment of cancer, can help elucidate the mechanisms of smaller molecules and even lead to the discovery of potential novel molecules.
In this context, Tavares et al. [97,98] investigated in silico, by employing quantum chemistry methods based on the Density Functional Theory (DFT), the binding energy features of the receptor PD-1 in complex with pembrolizumab, an FDA-approved Ab for advanced melanoma (see Figure 11). Their computational findings allowed for a greater knowledge of the binding mechanisms, helping in the development of better Ab-based drugs or even small molecules.
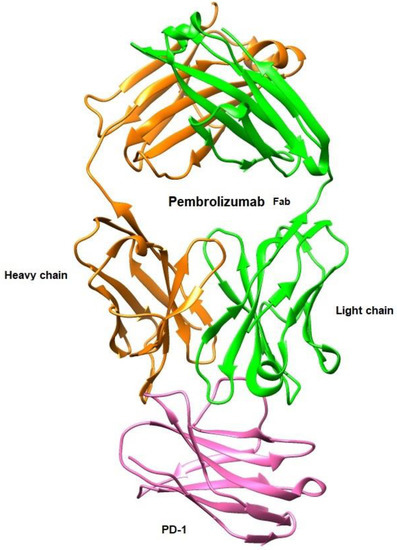
Figure 11.
Structural representation of the antigen-binding fragment (Fab) of pembrolizumab (PDB ID: 5GGS) in complex with the extracellular domain of human PD-1 receptor using UCSF Chimera [58,97,98].
Wen et al. [99] also studied the binding mechanism of Abs against PD-L1. They used the computational alanine scanning method (MM/GB/ASIE method) to calculate residue-specific binding energy contributions for five systems: PD-L1/KN035 (Figure 12), PD-L1/atezolizumab, PD-L1/avelumab, PD-L1/durvalumab and PD-L1/BMS-936559 (PDB IDs: 5JDS, 5XXM, 5GRJ, 5X8M and 5GGT, respectively). Their hotspots were predicted, and their results showed that PD-L1 Met115 and PD-L1 Tyr123 are important hotspots for all five complexes. In addition, it also showed that the crucial mAbs residues binding to PD-L1 Met115 and PD-L1 Tyr123 are very similar to each other. The experimental measurements available for KN035 and atezolizumab are in agreement with the computational results, with a correlation coefficient of 0.87 for PD-L1/KN035 and 0.6 for PD-L1/atezolizumab. The computational results also found more interactions on PD-L1/KN035, which is also in agreement with the experimental results.
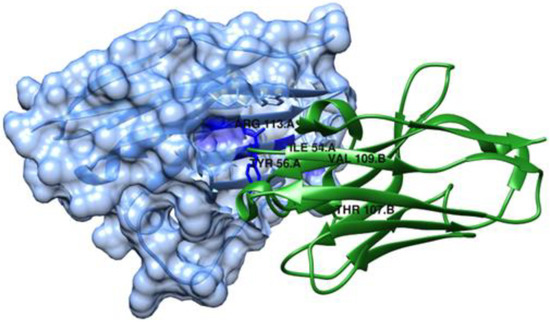
Figure 12.
Structure of the KN035/ PD-L1 complex (PDB ID: 5JDS) represented using UCSF Chimera [58,99]. PD-L1 is shown as a slate, semi-transparent surface.
In terms of Ab–antigen interactions, Myung and co-workers [100] developed a free access web server named CSM-AB (http://biosig.unimelb.edu.au/csm_ab/datasets (accessed on 28 February 2023)), an ML method with the capacity to predict binding affinity. This is made possible by considering structural features such as graph-based signatures and atomic interactions of Ab–antigen interface residues. CSM-AB achieved a Person’s correlation of 0.64 on blind tests and also works as a docking score function, accurately ranking poses.
4. Binding Mode and Binding Affinity Prediction of the PD-1/PD-L1 Immune Checkpoint
4.1. Target Predictions of Small Molecules and Peptides
Several small molecules targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 interaction have been identified in the last years, some of them comprising moieties such as urea (e.g., CA-170 (1)), guanidine (e.g., abemaciclib (4), ciforadenant (6), 6-thio-2′-deoxyguanosine (10), SF1126 (15)), sulfone (e.g., navtemadlin (3), vismodegib (11)), biphenyl (e.g., INCB086550 (5)) and N-heterocycle (e.g., tomivosertib (2), pexidantinib (9), carbozanitinib (12), cediranib and olaparib (13), itacitinib (14), sitravatinib (16), talazopanib (17), apatinib (18)), which are already in the clinical phases (Table 1 and Figure 3). However, the clinical results of targeting multiple immune-related targets still need to be elucidated; therefore, some works have recently been reported to identify small molecule targets using computational approaches in this regard [101,102,103]. Zhang et al. [101] reported using the PharmMapper database [104] to identify the targets of the small molecule lomustine (a nitrosourea derivative, 50), which is investigated for the treatment of primary glioblastoma (see Figure 13). Pan et al. [102] used the BATMAN-TCM web tool [105] to identify 288 targets and 53 bioactive compounds from Qingfei Jiedu decoction (QFJDD, an empirical Chinese prescription prepared from several herbals) that regulates PD-L1 expression in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD). In the end, six flavonoid derivatives, including quercetin (51), luteolin (52), kaempferol (53), wogonin (54), baicalein (55) and acacetin (56), and 22 hub genes were identified (Figure 13). Huang et al. [103] reported the use of PASS web resources for the validation of MYC/CXCL8 (C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 8)/TIMP1 (TIMP metallopeptidase inhibitor 1) oncogenes, which regulate immune response in an antitumor direction by mediating PD-L1, as potential drug targets for RV59 (57), an anthraquinone derivative with anticancer activity against NCI human colon cancer cell lines (Figure 13). Mittal et al. [57] developed an in silico structure-driven approach to screen and classify small molecules from the Asinex Signature library for the investigation of the inhibition of the PPIs between PD-L1 and PD-1/CD80 and its overexpression on cancer cells. In the end, two molecules, H5 (58) and H12 (59), were proposed as ICIs (Figure 13). The intersection between the two predicted targets, lomustine (50) and glioblastoma-related targets, was 59 active targets [101]. PPI, gene enrichment analysis, gene difference analysis, molecular docking and MD simulation have been used by the authors to screen out three effective targets of lomustine (50): HMOX1 (heme oxygenase 1), AKT1(AKT serine/threonine kinase 1) and EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) [101]. The same target, EGFR, was proposed by a different approach for QFJDD bioactive compounds (51–56) through a network construction and analysis comprising PPI, GO, KEGG and DAVID pathway analyses and molecular docking [102]. Several selected targets were associated with numerous human cancers, e.g., AKT1 [101], EGFR [101,102], HIF-1 (hypoxia inducible factor 1 subunit alpha) [102], MYC [103] and CXCL8 [103]. Furthermore, some of the selected targets seem to be related to an inflammatory response (CXCL8 [103]) or responses to viral infection (JUN [102], NFκB [102], and CD80 [57]).
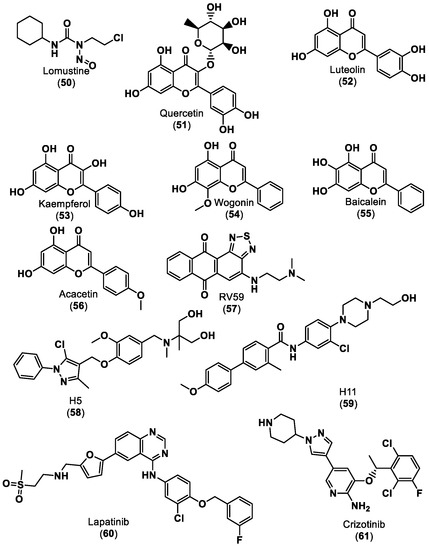
Figure 13.
Small molecule ICIs predict targets that regulate PD-L1 expression [101,102,103,106,107].
Molecular docking simulations were used by the three works [101,102,103] to evaluate the potential interactions of the small molecule ICIs with the proposed targets. For example, in the molecular docking of lomustine (50) [101] and quercetin (51) [102] with an EGFR target, hydrogen bonds between lomustine (50) and Asp855 and Thr854 residues [101] and between quercetin (51) and Lys745 residue [102] were observed, all of which are in the binding active pocket of the EGFR protein (Figure 14).
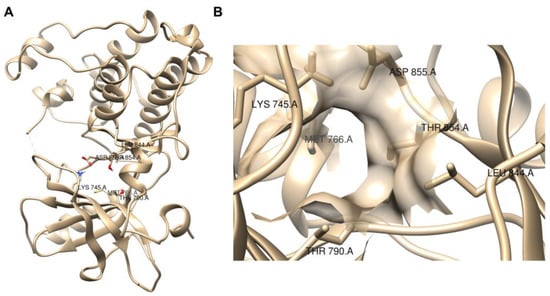
Figure 14.
Visualization of EGFR protein (PDB, ID 3W2S) with UCSF Chimera [58]. (A) Full view; (B) binding active pocket region [101,102].
In recent years, computational modeling tools for peptides have advanced significantly [108,109,110,111,112]. Similar to mAbs, peptides exhibit large and chemically diverse binding interfaces, but they show better biodistribution and tissue penetration than mAbs. Most current computational methods are based on building a model to predict whether peptides bind to antigens based on their sequences [111,113,114,115,116]. Some models were developed using ML techniques such as NetMHC [116], which trains a neural network to classify binders/non-binders using a dataset of experimental binding affinity measurements, NetMHCpan [117], which relies on neural networks and mass spectrometry (MS) data of peptides, and Abella et al.’s model [111], which uses a random forest algorithm to classify binders from non-binders and the Anchored Peptide-MHC Ensemble Generator (APE-Gen) tool [115] to model peptides–antigen complex structures. More computationally expensive molecular simulations of peptides–antigen complex structures have produced accurate binding predictions, e.g., MD (PB/GBSA) [118] and Monte Carlo simulations (available in the Rosetta modeling suite) [110].
Guardiola et al. [110] reported the exploitation of the computational power of the Rosetta modeling suite (https://www.rosettacommons.org/software (accessed on 28 February 2023)) in terms of large-scale backbone sampling (Monte Carlo simulations), side-chain composition and energy scoring to design heterochiral cyclic peptides that bind to a protein surface of PD-1. The authors designed a library of seven cyclic peptides (PD-i1- PD-i7) from those two peptides, PD-i3 (61) and PD-i6 (62). PD-i3 and PD-i6 showed mid-micromolar binding affinity to the target PD-1 and outcompeted endogenous PD-1 ligands for disrupting the PD-1/PD-L1 interaction, as shown in Figure 15.
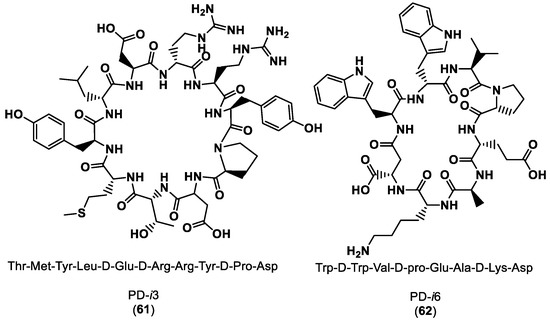
Figure 15.
Structures and sequences of the designed peptide inhibitors of PD-1 [110].
A very important stage in the peptide de novo design developed by Guardiola et al. [110] was the hotspot selection. Two approaches were carried out, first for the peptides PD-i1 to PD-i4 and second for the peptides PD-i5 to PD-i7. These two groups of peptides were designed based on the X-ray structure of the PD-1/PD-L1 complex (PDB ID:4ZQK) and the apo-PD-1 form of the protein (PDB ID: 3RRQ), respectively [110]. The residues Tyr and Trp were selected as main hotspot residues of the interaction for the first and second approaches, using the in silico Ala scan and the FTMap algorithm (https://ftmap.bu.edu (accessed on 28 February 2023)), respectively [110].
AlphaFold, which was already mentioned in Section 3.2, is Alphabet’s DeepMind entry in the CASP13 competition as an artificial intelligence system designed to predict protein–protein or protein–peptide structures [119,120]. Recently, DeepMind and EMBL-EBI developed the AlphaFold Protein Structure Database (https://alphafold.com/ (accessed on 17 March 2023)), leading to an unprecedented number of reliable protein structure predictions that are easily accessible to the scientific community. Varadi et al. [121] provided a brief overview and highlighted how beneficial this influx of protein structure data can be for the fields of bioinformatics, structural biology and drug discovery.
4.2. Target Predictions of mAbs
In silico design methods typically involve molecular modeling and simulation techniques to predict the effects of point mutations on the Ab–antigen interactions. This can include methods such as MD simulations, which use classical mechanics to simulate the movement of atoms and molecules. To improve binding modes and affinity, models of mutational dynamics of the mAb variable regions can be used, considering all the complexities associated with mAb diversity, such as the natural V(D)J rearrangement process. In this regard, adapted Markov Chain Monte Carlo simulations have been used to simulate the effects of mutations on the population of Ab molecules and to predict the most likely route to the high-affinity binding [122].
5. Targeted Therapies for PD-1/PD-L1 ICIs
Nowadays, targeted-tailored and personalized medicine, focused on the individual characteristics of each patient’s cancer, has become an extremely topical topic. The use of computational modeling for PD-1/PD-L1 ICIs [106,107] provides a unique tool for the prediction of responses to immunotherapeutic treatments, which can be used to integrate robust data input—big data—from genomic and transcriptomic studies, clinical data and in vivo and in vitro experimental models. Jiang et al. [106] reported a computational analysis of resistance (CARE), a computational method focused on targeted therapies, to infer genome-wide transcriptomic signatures of drug efficacy from cell line compound screens. The authors predicted PRKD3 (protein kinase D3) as a potential regulator of anti-HER2 breast cancer cell resistance and validated it as a promising target to increase lapatinib (60), as shown in Figure 13, and trastuzumab (mAb) efficacy through combinatorial treatment with PRKD inhibitors, which can be associated with an anti-PD-1 clinical response. Furthermore, Lombardo et al. [107] carried out a similar approach in neuroblastoma, creating a computational network model simulating the different intracellular pathways involved in neuroblastoma using the COPASI software. The authors showed that ALK (anaplastic lymphoma kinase) is an important factor in PD-L1 expression since treatment with crizotinib (a known ALK inhibitor) (61), as shown in Figure 13, decreased PD-L1 concentrations [107].
Considering the target predictions of small molecules and peptides with important intracellular pathways is also relevant, indeed, while it is essential to understand direct bindings of new candidates to PD-1 and PD-L1, it is equally important to identify how molecules could bind and influence intracellular pathways and result in meaningful efficacy of ICIs. In the field of chemical interaction with the cell pathways, and pathway cross-talk, the PubChem Pathway [123], the successor to the legacy Pathway Interaction Database (PID), constitutes a suitable analysis entry point as it strive to connect the pharmacology to physiology. Pathway cross-talk can be assessed by bridging global databases such as KEGG Pathways [33] or Reactome [124] to any of the more focused ones, such as NetPah [125] or HumanCyc [126]. This bridging effort is being eased by the development of common formats and collaborative platforms, as it is in the case of WikiPathways [127].
6. Conclusions
We would like to emphasize the need for computational approaches to immune oncology therapies. We focused on using data-driven methods to identify potential targets for PD-1/PD-L1 ICIs and to develop novel drug candidates such as antibodies, peptides or small molecules. We highlighted the use of cheminformatics and bioinformatics tools to analyze large datasets of molecules, gene expression and protein–protein interaction data to identify potential biomarkers that can be used to predict response to PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. We also discussed the use of computer-aided drug design structure- and ligand-based virtual screening processes, molecular docking, homology modeling and MD simulation methodologies essential for successful drug discovery campaigns focusing on small molecule ICIs. We compiled a list of databases and web tools used in the context of cancer and immunotherapy, which is available as Supplementary Materials for this review. This includes databases and tools of a general scope, cancer and immunology.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijms24065908/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.P.; data curation, P.S.S., J.M.G.C.F.A. and F.P.; writing—original draft preparation, P.S.S., J.M.G.C.F.A., P.A.V. and F.P.; writing—review and editing, P.S.S., V.C.C.L., J.M.G.C.F.A., P.A.V. and F.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia (FCT) Portugal, grant number UIDB/50006/2020 (LAQV-REQUIMTE), UIDP/04378/2020 and UIDB/04378/2020 (UCIBIO) and LA/P/0140/2020 (i4HB), the European Commission GLYCOTwinning (GA 101079417), the EJPRD ProDGNE (EJPRD/0001/2020 EU 825575) and SI I&DT, DCMatters (AVISO Nº 17/SI/2019) REF 47212. F.P. gratefully acknowledges FCT for an Assistant Research Position (CEECIND/01649/2021).
Data Availability Statement
The databases and web tools reported in this review are available as Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bagchi, S.; Yuan, R.; Engleman, E.G. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for the Treatment of Cancer: Clinical Impact and Mechanisms of Response and Resistance. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2021, 16, 223–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobosz, P.; Stepien, M.; Golke, A.; Dzieciatkowski, T. Challenges of the Immunotherapy: Perspectives and Limitations of the Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Long, S.; Shi, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wu, W.; Han, L.; Wang, S. The role of PD-1/PD-L1 and application of immune-checkpoint inhibitors in human cancers. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 964442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiravand, Y.; Khodadadi, F.; Kashani, S.M.A.; Hosseini-Fard, S.R.; Hosseini, S.; Sadeghirad, H.; Ladwa, R.; O’Byrne, K.; Kulasinghe, A. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 3044–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, F.; Whiteside, G.; Perry, C. Ipilimumab First Global Approval. Drugs 2011, 71, 1093–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhaya, S.; Neftelinov, S.T.; Hodge, J.; Campbell, J. Challenges and opportunities in the PD1/PDL1 inhibitor clinical trial landscape. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 482–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, B.X.; Yang, H.Y.; Hu, S.Q.; Dong, X.W. If small molecules immunotherapy comes, can the prime be far behind? Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 218, 113356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The ClinicalTrials.gov Results Database. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on 24 February 2023).
- Nosengo, N. New tricks for old drugs. Nature 2016, 534, 314–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nantasenamat, C.; Prachayasittikul, V. Maximizing computational tools for successful drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2015, 10, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, J. Chemoinformatics: Achievements and Challenges, a Personal View. Molecules 2016, 21, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliwoski, G.; Kothiwale, S.; Meiler, J.; Lowe, E.W. Computational Methods in Drug Discovery. Pharmacol. Rev. 2014, 66, 334–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsila, T.; Spyroulias, G.A.; Patrinos, G.P.; Matsoukas, M.-T. Computational approaches in target identification and drug discovery. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabe, V.T.; Ntombela, T.; Jhamba, L.A.; Maguire, G.E.M.; Govender, T.; Naicker, T.; Kruger, H.G. Current trends in computer aided drug design and a highlight of drugs discovered via computational techniques: A review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 224, 113705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayers, E.W.; Bolton, E.E.; Brister, J.R.; Canese, K.; Chan, J.; Comeau, D.C.; Connor, R.; Funk, K.; Kelly, C.; Kim, S.; et al. Database resources of the national center for biotechnology information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D20–D26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amid, C.; Alako, B.T.F.; Kadhirvelu, V.B.; Burdett, T.; Burgin, J.; Fan, J.; Harrison, P.W.; Holt, S.; Hussein, A.; Ivanov, E.; et al. The European Nucleotide Archive in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D70–D76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, A.; Kodama, Y.; Mashima, J.; Fujisawa, T.; Ogasawara, O. DDBJ update: Streamlining submission and access of human data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D71–D75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coudert, E.; Gehant, S.; de Castro, E.; Pozzato, M.; Baratin, D.; Neto, T.; Sigrist, C.J.A.; Redaschi, N.; Bridge, A.; UniProt, C. Annotation of biologically relevant ligands in UniProtKB using ChEBI. Bioinformatics 2023, 39, btac793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, M.; Chang, H.-Y.; Chuguransky, S.; Grego, T.; Kandasaamy, S.; Mitchell, A.; Nuka, G.; Paysan-Lafosse, T.; Qureshi, M.; Raj, S.; et al. The InterPro protein families and domains database: 20 years on. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D344–D354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, J.; Chuguransky, S.; Williams, L.; Qureshi, M.; Salazar, G.A.; Sonnhammer, E.L.L.; Tosatto, S.C.E.; Paladin, L.; Raj, S.; Richardson, L.J.; et al. Pfam: The protein families database in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D412–D419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Khedkar, S.; Bork, P. SMART: Recent updates, new developments and status in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D458–D460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigrist, C.J.A.; de Castro, E.; Cerutti, L.; Cuche, B.A.; Hulo, N.; Bridge, A.; Bougueleret, L.; Xenarios, I. New and continuing developments at PROSITE. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, E344–E347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burley, S.K.; Berman, H.M.; Bhikadiya, C.; Bi, C.; Chen, L.; Di Costanzo, L.; Christie, C.; Duarte, J.M.; Dutta, S.; Feng, Z.; et al. Protein Data Bank: The single global archive for 3D macromolecular structure data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D520–D528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, W.J.; Sugnet, C.W.; Furey, T.S.; Roskin, K.M.; Pringle, T.H.; Zahler, A.M.; Haussler, D. The human genome browser at UCSC. Genome Res. 2002, 12, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene Ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, B.T.; Hao, M.; Qiu, J.; Jiao, X.; Baseler, M.W.; Lane, H.C.; Imamichi, T.; Chang, W. DAVID: A web server for functional enrichment analysis and functional annotation of gene lists (2021 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W216–W221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natale, D.A.; Arighi, C.N.; Blake, J.A.; Bona, J.; Chen, C.; Chen, S.-C.; Christie, K.R.; Cowart, J.; D’Eustachio, P.; Diehl, A.D.; et al. Protein Ontology (PRO): Enhancing and scaling up the representation of protein entities. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D339–D346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlen, M.; Fagerberg, L.; Hallstroem, B.M.; Lindskog, C.; Oksvold, P.; Mardinoglu, A.; Sivertsson, A.; Kampf, C.; Sjoestedt, E.; Asplund, A.; et al. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science 2015, 347, 1260419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, T.; Wilhite, S.E.; Ledoux, P.; Evangelista, C.; Kim, I.F.; Tomashevsky, M.; Marshall, K.A.; Phillippy, K.H.; Sherman, P.M.; Holko, M.; et al. NCBI GEO: Archive for functional genomics data sets-update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D991–D995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Nastou, K.C.; Lyon, D.; Kirsch, R.; Pyysalo, S.; Doncheva, N.T.; Legeay, M.; Fang, T.; Bork, P.; et al. The STRING database in 2021: Customizable protein-protein networks, and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D605–D612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warde-Farley, D.; Donaldson, S.L.; Comes, O.; Zuberi, K.; Badrawi, R.; Chao, P.; Franz, M.; Grouios, C.; Kazi, F.; Lopes, C.T.; et al. The GeneMANIA prediction server: Biological network integration for gene prioritization and predicting gene function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, W214–W220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M.; Sato, Y.; Morishima, K. KEGG: New perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D353–D361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amberger, J.S.; Bocchini, C.A.; Scott, A.F.; Hamosh, A. OMIM.org: Leveraging knowledge across phenotype-gene relationships. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D1038–D1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Perez, A.; Lopez-Bigas, N. Improving the Assessment of the Outcome of Nonsynonymous SNVs with a Consensus Deleteriousness Score, Condel. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 88, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Perez, A.; Deu-Pons, J.; Lopez-Bigas, N. Improving the prediction of the functional impact of cancer mutations by baseline tolerance transformation. Genome Med. 2012, 4, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barretina, J.; Caponigro, G.; Stransky, N.; Venkatesan, K.; Margolin, A.A.; Kim, S.; Wilson, C.J.; Lehar, J.; Kryukov, G.V.; Sonkin, D.; et al. The Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia enables predictive modelling of anticancer drug sensitivity. Nature 2012, 483, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutter, C.; Zenklusen, J.C. The Cancer Genome Atlas: Creating Lasting Value beyond Its Data. Cell 2018, 173, 283–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The cBio Cancer Genomics Portal: An Open Platform for Exploring Multidimensional Cancer Genomics Data. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Fan, J.; Wang, B.; Traugh, N.; Chen, Q.; Liu, J.S.; Li, B.; Liu, X.S. TIMER: A Web Server for Comprehensive Analysis of Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, E108–E110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguet, F.; Barbeira, A.N.; Bonazzola, R.; Brown, A.; Castel, S.E.; Jo, B.; Kasela, S.; Kim-Hellmuth, S.; Liang, Y.; Parsana, P.; et al. The GTEx Consortium atlas of genetic regulatory effects across human tissues. Science 2020, 369, 1318–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.F.; Li, C.W.; Kang, B.X.; Gao, G.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z.M. GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W98–W102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, R.L.; Heath, A.P.; Ferretti, V.; Varmus, H.E.; Lowy, D.R.; Kibbe, W.A.; Staudt, L.M. Toward a Shared Vision for Cancer Genomic Data. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1109–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutman, D.A.; Khalilia, M.; Lee, S.; Nalisnik, M.; Mullen, Z.; Beezley, J.; Chittajallu, D.R.; Manthey, D.; Cooper, L.A.D. The Digital Slide Archive: A Software Platform for Management, Integration, and Analysis of Histology for Cancer Research. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, E75–E78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ru, B.; Wong, C.N.; Tong, Y.; Zhong, J.Y.; Zhong, S.S.W.; Wu, W.C.; Chu, K.C.; Wong, C.Y.; Lau, C.Y.; Chen, I.; et al. TISIDB: An integrated repository portal for tumor-immune system interactions. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 4200–4202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagaev, D.V.; Vroomans, R.M.A.; Samir, J.; Stervbo, U.; Rius, C.; Dolton, G.; Greenshields-Watson, A.; Attaf, M.; Egorov, E.S.; Zvyagin, I.V.; et al. VDJdb in 2019: Database extension, new analysis infrastructure and a T-cell receptor motif compendium. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D1057–D1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, L.; Liu, K.; Wei, X.; Yang, K.; Du, W.; Wang, S.; Guo, N.; Ma, C.; Luo, L.; et al. PIRD: Pan Immune Repertoire Database. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tickotsky, N.; Sagiv, T.; Prilusky, J.; Shifrut, E.; Friedman, N. McPAS-TCR: A manually curated catalogue of pathology-associated T cell receptor sequences. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2924–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabbott, N.A.; Baillie, J.K.; Brown, H.; Freeman, T.C.; Hume, D.A. An expression atlas of human primary cells: Inference of gene function from coexpression networks. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefranc, M.-P.; Giudicelli, V.; Duroux, P.; Jabado-Michaloud, J.; Folch, G.; Aouinti, S.; Carillon, E.; Duvergey, H.; Houles, A.; Paysan-Lafosse, T.; et al. IMGT (R), the international ImMunoGeneTics information system (R) 25 years on. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D413–D422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiFrancesco, M.; Hofer, J.; Aradhya, A.; Rufinus, J.; Stoddart, J.; Finocchiaro, S.; Mani, J.; Tevis, S.; Visconti, M.; Walawender, G.; et al. Discovery of small-molecule PD-1/PD-L1 antagonists through combined virtual screening and experimental validation. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2022, 102, 107804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, J.A.; McClendon, C.L. Reaching for high-hanging fruit in drug discovery at protein-protein interfaces. Nature 2007, 450, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zak, K.M.; Kitel, R.; Przetocka, S.; Golik, P.; Guzik, K.; Musielak, B.; Domling, A.; Dubin, G.; Holak, T.A. Structure of the Complex of Human Programmed Death 1, PD-1, and Its Ligand PD-L1. Structure 2015, 23, 2341–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chupak, L.S.; Zheng, X. Bristol-Myers Squibb Company Assignee. Compounds Useful as Immunomodulators. International Patent WO 034820 Al, 12 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zak, K.M.; Grudnik, P.; Guzik, K.; Zieba, B.J.; Musielak, B.; Domling, A.; Dubin, G.; Holak, T.A. Structural basis for small molecule targeting of the programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1). Oncotarget 2016, 7, 30323–30335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzik, K.; Zak, K.M.; Grudnik, P.; Magiera, K.; Musielak, B.; Torner, R.; Skalniak, L.; Domling, A.; Dubin, G.; Holak, T.A. Small-Molecule Inhibitors of the Programmed Cell Death-1/Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-1/PD-L1) Interaction via Transiently Induced Protein States and Dimerization of PD-L1. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 5857–5867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, L.; Tonk, R.K.; Awasthi, A.; Asthana, S. Targeting cryptic-orthosteric site of PD-L1 for inhibitor identification using structure-guided approach. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2021, 713, 109059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.Z.; Cao, Q.; Zheng, S.S.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, H.T.; Xie, J.; Xie, H.B.; Liu, Y.J.; Zhao, Y.F.; Gong, P. Discovery of 1,2,4 Triazolo 4,3-a pyridines as Potent Inhibitors Targeting the Programmed Cell Death-1/Programmed Cell Death-Ligand 1 Interaction. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 4703–4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.Z.; Cao, Q.; Wu, X.; Liu, C.Y.; Zheng, S.S.; Xie, H.B.; Tian, Y.; Xie, J.; Zhao, Y.F.; Hou, Y.L.; et al. Discovery of the programmed cell death-1/programmed cell death-ligand 1 interaction inhibitors bearing an indoline scaffold. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 186, 111856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.Z.; Meng, Y.Y.; Yang, H.S.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.T.; Wang, S.M.; Liu, C.Y.; Wu, X.; Wu, D.; Tian, Y.; et al. Discovery of 4-Arylindolines Containing a Thiazole Moiety as Potential Antitumor Agents Inhibiting the Programmed Cell Death-1/Programmed Cell Death-Ligand 1 Interaction. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 5519–5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.B.; Ren, Y.C.; Niu, X.G.; Wang, W.; Wang, S.H.; Tu, Y.F.; Liu, S.W.; Wang, J.; Yang, D.Y.; Liao, G.C.; et al. Discovery of Novel Resorcinol Dibenzyl Ethers Targeting the Programmed Cell Death-1/Programmed Cell Death-Ligand 1 Interaction as Potential Anticancer Agents. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 8338–8358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butera, R.; Wazynska, M.; Magiera-Mularz, K.; Plewka, J.; Musielak, B.; Surmiak, E.; Sala, D.; Kitel, R.; de Bruyn, M.; Nijman, H.W.; et al. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Imidazopyridines as PD-1/PD-L1 Antagonists. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konieczny, M.; Musielak, B.; Kocik, J.; Skalniak, L.; Sala, D.; Czub, M.; Magiera-Mularz, K.; Rodriguez, I.; Myrcha, M.; Stec, M.; et al. Di-bromo-Based Small-Molecule Inhibitors of the PD-1/PD-L1 Immune Checkpoint. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 11271–11285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Qi, Z.H.; Wang, T.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhang, K.J.; Wang, K.Z.; Cheng, Y.; Xiao, Y.B.; Li, Z.; Jiang, S. Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of PD-1/PD-L1 Antagonists Bearing a Benzamide Scaffold. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muszak, D.; Surmiak, E.; Plewka, J.; Magiera-Mularz, K.; Kocik-Krol, J.; Musielak, B.; Sala, D.; Kitel, R.; Stec, M.; Weglarczyk, K.; et al. Terphenyl-Based Small-Molecule Inhibitors of Programmed Cell Death-1/Programmed Death-Ligand 1 Protein-Protein Interaction. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 11614–11636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Liu, B.; Peng, X.; Gu, W.; Sun, Y.; Xing, L.; Xu, Y.; Geng, M.; Ai, J.; Zhang, A. Design, Synthesis, and Pharmacological Evaluation of Biaryl-Containing PD-1/PD-L1 Interaction Inhibitors Bearing a Unique Difluoromethyleneoxy Linkage. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 16687–16702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Cai, S.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, M.; Sun, H.; Guo, B.; Li, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Jiang, S. Discovery of Small-Molecule Inhibitors of the PD-1/PD-L1 Axis That Promote PD-L1 Internalization and Degradation. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 3879–3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.L.; Wang, H.X.; Shen, L.L.; Xu, H.Q.; Deng, M.H.; Cheng, M.S.; Wang, J. Discovery of benzo[d]isothiazole derivatives as novel scaffold inhibitors targeting the programmed cell death-1/programmed cell death-ligand 1 (PD-1/PD-L1) interaction through “ring fusion” strategy. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 123, 105769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.Y.; Chu, C.P.; Niu, X.Y.; Cheng, L.Y.; Wu, D.; Liu, L.; Zhang, S.P.; Li, T.Q.; Hou, Y.L.; Liu, Y.J.; et al. Discovery of 4-phenylindolines containing a (5-cyanopyridin-3-yl)methoxy moiety as potent inhibitors of the PD-1/PD-L1 interaction. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2022, 63, 128647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, K.; Gao, Y.L.; Yuan, D.D.; Ling, L.; Liu, J.Q.; Wu, S.H.; Chen, R.F.; Li, H.; Xiong, Y.Z.; et al. Discovery of quinazoline derivatives as novel small-molecule inhibitors targeting the programmed cell death-1/programmed cell death-ligand 1 (PD-1/PD-L1) interaction. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 229, 113998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.P.; Chen, H.; Dai, X.Y.; Xu, M.Q.; Wang, K.; Feng, Z.Q. Design, synthesis, and structure-activity relationship of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors with a benzo[d]isoxazole scaffold. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 52, 128403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russomanno, P.; Assoni, G.; Amato, J.; D’Amore, V.M.; Scaglia, R.; Brancaccio, D.; Pedrini, M.; Polcaro, G.; La Pietra, V.; Orlando, P.; et al. Interfering with the Tumor-Immune Interface: Making Way for Triazine-Based Small Molecules as Novel PD-L1 Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 16020–16045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.Y.; Wang, K.; Chen, H.; Huang, X.P.; Feng, Z.Q. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of 1-methyl-1H-pyrazolo 4,3-b pyridine derivatives as novel small-molecule inhibitors targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 interaction. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 114, 105034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Yao, Z.Y.; Wang, S.J.; Xie, T.; Wu, G.Q.; Zhang, H.H.; Zhang, P.; Wu, Y.J.; Yuan, H.L.; Sun, H.B. Syntheses, Biological Evaluations, and Mechanistic Studies of Benzo c 1,2,5 oxadiazole Derivatives as Potent PD-L1 Inhibitors with In Vivo Antitumor Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 8391–8409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.Y.; Cai, S.; Wang, M.M.; Zhang, W.H.; Zhang, K.J.; Chen, D.; Li, Z.; Jiang, S. Novel Biphenyl Pyridines as Potent Small-Molecule Inhibitors Targeting the Programmed Cell Death-1/Programmed Cell Death-Ligand 1 Interaction. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 7390–7403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, J.; Elumalai, S.; Murugesan, V.; Kunjiappan, S.; Pavadai, P.; Theivendren, P. Computational design of PD-L1 small molecule inhibitors for cancer therapy. Mol. Divers. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattakhova, E.; Hofer, J.; DiFlumeri, J.; Cobb, M.; Dando, T.; Romisher, Z.; Wellington, J.; Oravic, M.; Radnoff, M.; Patil, S.P. Identification of the FDA-Approved Drug Pyrvinium as a Small-Molecule Inhibitor of the PD-1/PD-L1 Interaction. ChemMedChem 2021, 16, 2769–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, V.A.; Davidovskii, A.I.; Veresov, V.G. Computational discovery of small drug-like compounds as potential inhibitors of PD-1/PD-L1 interactions. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 13, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.X.; Zhong, A.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, T.Y. Structure-Based Pharmacophore Modeling, Virtual Screening, Molecular Docking, ADMET, and Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulation of Potential Inhibitors of PD-L1 from the Library of Marine Natural Products. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.S.; Moustafa, M.; Sahoo, A.K.; Maly, P.; Bharadwaj, S. Computational Investigations on the Natural Small Molecule as an Inhibitor of Programmed Death Ligand 1 for Cancer Immunotherapy. Life 2022, 12, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergoten, G.; Bailly, C. Molecular docking study of britannin binding to PD-L1 and related anticancer pseudoguaianolide sesquiterpene lactones. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. 2022, 42, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Tirado-Rives, J. Molecular modeling of organic and biomolecular systems using BOSS and MCPRO. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1689–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qayed, W.S.; Hassan, M.A.; El-Sayed, W.M.; Silva, J.R.A.; Aboul-Fadl, T. Novel Azine Linked Hybrids of 2-Indolinone and Thiazolodinone Scaffolds as CDK2 Inhibitors with Potential Anticancer Activity: In Silico Design, Synthesis, Biological, Molecular Dynamics and Binding Free Energy Studies. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 126, 105884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, S.F.; Zhao, Y.S.; Zeng, X.; Chen, X.T.; Meng, Q.Q.; Ding, Z.; Zhao, W.S.; Qi, Y.M.; Gao, Y.F.; Du, J.F. Identification of Phelligridin-Based Compounds as Novel Human CD73 Inhibitors. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 1275–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Quan, L.N.; Lyu, J.K.; He, Z.H.; Wang, X.; Meng, J.J.; Zhao, Z.J.; Zhu, L.L.; Liu, X.F.; Li, H.L. Discovery of peptide inhibitors targeting human programmed death 1 (PD-1) receptor. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 64967–64976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manavalan, B.; Shin, T.H.; Kim, M.O.; Lee, G. PIP-EL: A New Ensemble Learning Method for Improved Proinflammatory Peptide Predictions. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Li, B.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, C.; Yang, S.; Long, J.; Ning, L.; Chen, H.; Huang, J. PDL1Binder: Identifying programmed cell death ligand 1 binding peptides by incorporating next-generation phage display data and different peptide descriptors. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 928774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, D.A.; Abella, J.R.; Hall-Swan, S.; Devaurs, D.; Conev, A.; Moll, M.; Lizee, G.; Kavraki, L.E. HLA-Arena: A Customizable Environment for the Structural Modeling and Analysis of Peptide-HLA Complexes for Cancer Immunotherapy. JCO Clin. Cancer Inform. 2020, 4, 623–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.P.; Guo, H.Q.; Zhao, L.A.; Feng, H.X.; He, H.W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Lin, Z.H. Discovery of modulators for the PD-1/PD-L1 interaction by molecular simulation and bioassay. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 18497–18508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojko, M.; Wegrzyn, K.; Sikorska, E.; Kocikowski, M.; Parys, M.; Battin, C.; Steinberger, P.; Kogut, M.M.; Winnicki, M.; Sieradzan, A.K.; et al. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of PD-1 derived peptides as inhibitors of PD-1/PD-L1 complex formation for cancer therapy. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 128, 106047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Perez, A. Ranking Peptide Binders by Affinity with AlphaFold. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2023, 62, e202213362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson-Akhe, I.; Wallner, B. Improving peptide-protein docking with AlphaFold-Multimer using forced sampling. Front. Bioinform. 2022, 2, 959160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Zidek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acurcio, R.C.; Scomparin, A.; Satchi-Fainaro, R.; Florindo, H.F.; Guedes, R.C. Computer-aided drug design in new druggable targets for the next generation of immune-oncology therapies. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Mol. Sci. 2019, 9, e1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Jiang, L.; Li, S.C.; He, Q.J.; Yang, B.; Cao, J. Small molecule inhibitors targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 signaling pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021, 42, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavares, A.; Neto, J.X.L.; Fulco, U.L.; Albuquerque, E.L. Inhibition of the checkpoint protein PD-1 by the therapeutic antibody pembrolizumab outlined by quantum chemistry. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavares, A.B.M.L.A.; Neto, J.X.L.; Fulco, U.L.; Albuquerque, E.L. Blockade of the checkpoint PD-1 by its ligand PD-L1 and the immuno-oncological drugs pembrolizumab and nivolumab. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2021, 23, 21207–21217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, W.; Huang, D.D.; Bao, J.X.; Zhang, J.Z.H. Residue Specific Binding Mechanisms of PD-1 to Its Monoclonal Antibodies by Computational Alanine Scanning. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 2021, 42, 2161–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myung, Y.; Pires, D.E.V.; Ascher, D.B. CSM-AB: Graph-based antibody-antigen binding affinity prediction and docking scoring function. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 1141–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.Y.; Zhang, D.D.; Shi, F. Silico analysis of the target and possible mechanism of lomustine in the treatment of primary glioblastoma. J. Mol. Model. 2023, 29, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.J.; Yang, H.K.; Zhu, L.H.; Lou, Y.F.; Jin, B. Qingfei Jiedu decoction inhibits PD-L1 expression in lung adenocarcinoma based on network pharmacology analysis, molecular docking and experimental verification. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 897966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.H.; Mokgautsi, N.; Huang, Y.J.; Wu, A.T.H.; Huang, H.S. Comprehensive Omics Analysis of a Novel Small-Molecule Inhibitor of Chemoresistant Oncogenic Signatures in Colorectal Cancer Cell with Antitumor Effects. Cells 2021, 10, 1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Shen, Y.H.; Wang, S.W.; Li, S.L.; Zhang, W.L.; Liu, X.F.; Lai, L.H.; Pei, J.F.; Li, H.L. PharmMapper 2017 update: A web server for potential drug target identification with a comprehensive target pharmacophore database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W356–W360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Guo, F.F.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.L.; Li, H.L.; Diao, L.H.; Gu, J.Y.; Wang, W.; Li, D.; et al. BATMAN-TCM: A Bioinformatics Analysis Tool for Molecular mechANism of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, P.; Lee, W.; Li, X.J.; Johnson, C.; Liu, J.S.; Brown, M.; Aster, J.C.; Liu, X.S. Genome-Scale Signatures of Gene Interaction from Compound Screens Predict Clinical Efficacy of Targeted Cancer Therapies. Cell Syst. 2018, 6, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, S.D.; Presti, M.; Mangano, K.; Petralia, M.C.; Basile, M.S.; Libra, M.; Candido, S.; Fagone, P.; Mazzon, E.; Nicoletti, F.; et al. Prediction of PD-L1 Expression in Neuroblastoma via Computational Modeling. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanda, S.K.; Usmani, S.S.; Agrawal, P.; Nagpal, G.; Gautam, A.; Raghava, G.P.S. Novel in silico tools for designing peptide-based subunit vaccines and immunotherapeutics. Brief. Bioinform. 2017, 18, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, D.A.; Devaurs, D.; Moll, M.; Lizee, G.; Kavraki, L.E. General Prediction of Peptide-MHC Binding Modes Using Incremental Docking: A Proof of Concept. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardiola, S.; Varese, M.; Roig, X.; Sanchez-Navarro, M.; Garcia, J.; Giralt, E. Target-templated de novo design of macrocyclic d-/l-peptides: Discovery of drug-like inhibitors of PD-1. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 5164–5170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abella, J.R.; Antunes, D.A.; Clementi, C.; Kavraki, L.E. Large-Scale Structure-Based Prediction of Stable Peptide Binding to Class I HLAs Using Random Forests. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherafat, E.; Force, J.; Mandoiu, I.I. Semi-supervised learning for somatic variant calling and peptide identification in personalized cancer immunotherapy. BMC Bioinform. 2020, 21, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.L.; Sher, X.W. Systematically benchmarking peptide-MHC binding predictors: From synthetic to naturally processed epitopes. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2018, 14, e1006457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, T.J.; Rubinsteyn, A.; Bonsack, M.; Riemer, A.B.; Laserson, U.; Hammerbacher, J. MHCflurry: Open-Source Class I MHC Binding Affinity Prediction. Cell Syst. 2018, 7, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abella, J.R.; Antunes, D.A.; Clementi, C.; Kavraki, L.E. APE-Gen: A Fast Method for Generating Ensembles of Bound Peptide-MHC Conformations. Molecules 2019, 24, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, M.; Lundegaard, C.; Worning, P.; Lauemoller, S.L.; Lamberth, K.; Buus, S.; Brunak, S.; Lund, O. Reliable prediction of T-cell epitopes using neural networks with novel sequence representations. Protein Sci. 2003, 12, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurtz, V.; Paul, S.; Andreatta, M.; Marcatili, P.; Peters, B.; Nielsen, M. NetMHCpan-4.0: Improved Peptide-MHC Class I Interaction Predictions Integrating Eluted Ligand and Peptide Binding Affinity Data. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 3360–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.Z.; Knapp, B.; Wright, D.W.; Deane, C.M.; Coveney, P.V. Rapid, Precise, and Reproducible Prediction of Peptide-MHC Binding Affinities from Molecular Dynamics That Correlate Well with Experiment. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2015, 11, 3346–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcu, S.B.; Tabirca, S.; Tangney, M. An Overview of Alphafold’s Breakthrough. Front. Artif. Intell. 2022, 5, 875587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlQuraishi, M. AlphaFold at CASP13. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 4862–4865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varadi, M.; Velankar, S. The impact of AlphaFold Protein Structure Database on the fields of life sciences. Proteomics 2022, e2200128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, D.; Melhem, M.; Gandhi, Y.; Lu, S.; Visser, S. Comparative analysis of PD-1 target engagement of dostarlimab and pembrolizumab in advanced solid tumors using ex vivo IL-2 stimulation data. CPT Pharmacomet. Syst. Pharmacol. 2023, 12, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Cheng, T.; He, S.; Thiessen, P.A.; Li, Q.; Gindulyte, A.; Bolton, E.E. PubChem Protein, Gene, Pathway, and Taxonomy Data Collections: Bridging Biology and Chemistry through Target-Centric Views of PubChem Data. J. Mol. Biol. 2022, 434, 167514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillespie, M.; Jassal, B.; Stephan, R.; Milacic, M.; Rothfels, K.; Senff-Ribeiro, A.; Griss, J.; Sevilla, C.; Matthews, L.; Gong, C.; et al. The reactome pathway knowledgebase 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D687–D692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandasamy, K.; Mohan, S.S.; Raju, R.; Keerthikumar, S.; Kumar, G.S.S.; Venugopal, A.K.; Telikicherla, D.; Navarro, J.D.; Mathivanan, S.; Pecquet, C.; et al. NetPath: A public resource of curated signal transduction pathways. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caspi, R.; Altman, T.; Billington, R.; Dreher, K.; Foerster, H.; Fulcher, C.A.; Holland, T.A.; Keseler, I.M.; Kothari, A.; Kubo, A.; et al. The MetaCyc database of metabolic pathways and enzymes and the BioCyc collection of Pathway/Genome Databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D459–D471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, M.; Ammar, A.; Riutta, A.; Waagmeester, A.; Slenter, D.N.; Hanspers, K.; Miller, R.A.; Digles, D.; Lopes, E.N.; Ehrhart, F.; et al. WikiPathways: Connecting communities. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D613–D621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).