Molecular Advances in Sinusoidal Obstruction Syndrome/Veno-Occlusive Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
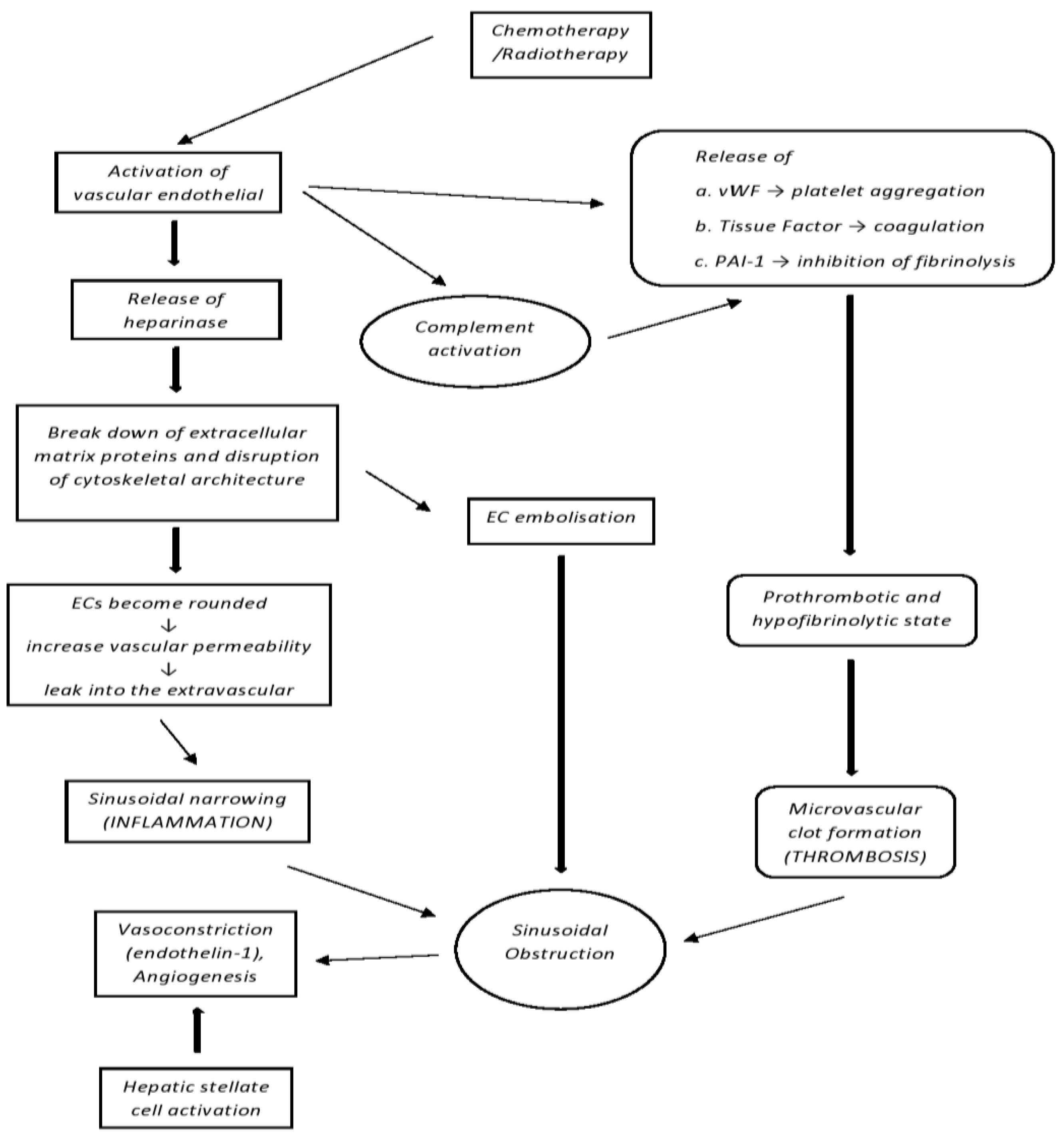
2. Pathophysiology
3. Clinical Presentation, Diagnostic Criteria and Risk Stratification
4. Risk Factors
5. Prophylaxis
5.1. Prostaglandin E1
5.2. Pentoxifylline, Antithrombin
5.3. Ursodeoxycholic Acid (UDCA)
5.4. Defibrotide
6. SOS/VOD Management
6.1. Defibrotide
6.2. Tissue Plasminogen Activator (TPA)
6.3. n-Acetyl-l-cysteine (NAC)
6.4. Recombinant Human Soluble Thrombomodulin Alpha (rhTM)
7. Complement Activation in SOS/VOD
Advances in Other Endothelial Injury Syndromes
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SOS/VOD | Sinusoidal Obstruction Syndrome/Veno-Occlusive Disease |
| HSCT | Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation |
| MOD | Multi-Organ Dysfunction |
| HCT | Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation |
| EBMT | European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation |
| SEC | Sinusoidal Endothelial Cell |
| AML | Acute Myeloid Leukemia |
| B-ALL | B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia |
| ECs | Endothelial Cells |
| VWF | Von Willebrand Factor |
| PAI-I | Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-I |
| PH | Portal Hypertension |
| DILI | Drug-Induced Liver Injury |
| GVHD | Graft-Versus-Host Disease |
| RT | Refractory Thrombocytopenia |
| HVPG | Hepatic Vein Pressure Gradient |
| US | Ultrasound |
| CIBMTR | Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research |
| EASIX | Endothelial Activation and Stress Index |
| LDH | Lactate Dehydrogenase |
| AlloSCT | Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation |
| GM | Gut Microbiome |
| BSI | Bloodstream Infection |
| LSM | Liver Stiffness Measurement |
| TE | Transient Elastography |
| MAC | Myeloablative Conditioning |
| GO | Gemtuzumab Ozogamicin |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| IO | Inotuzumab Ozogamicin |
| UFH | Unfractionated Heparin |
| LMWH | Low Molecular Weight Heparin |
| UDCA | Ursodeoxycholic Acid |
| BCSH | British Committee for Standards in Haematology |
| BSBMT | British Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation |
| VOD | Veno-Occlusive Disease |
| CR | Complete Remission |
| TPA | Tissue Plasminogen Activator |
| NAC | n-Acetyl-l-Cysteine |
| RhTM | Recombinant human soluble Thrombomoduline alpha |
| HELLP | Hemolysis, Elevated Liver enzymes, and Low Platelet number syndrome |
| TA-TMA | Transplant-Associated Thrombotic Microangiopathy |
| ADAMTS13 | A Disintegrin and Metalloproteinase with Thrombospondin motifs |
| C1-INH-C | C1 Esterase Inhibitor |
| CFH | Complement Factor H |
| CFI | Complement Factor I |
| HLH | Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis |
| HUS | Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome |
| MASP-2 | Mannan-binding lectin-associated Serine Protease-2 |
References
- Mohty, M.; Malard, F.; Abecassis, M.M.; Aerts, E.; Alaskar, A.S.; Aljurf, M.; Arat, M.; Bader, P.; Baron, F.; Bazarbachi, A.; et al. Sinusoidal obstruction syndrome/veno-occlusive disease: Current situation and perspectives—A position statement from the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT). Bone Marrow Transplant. 2015, 50, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, P.; Miller, J.L.; Uys, C.J.; Dietrich, B.E. Fatal veno-occlusive disease of the liver after chemotherapy, whole-body irradiation and bone marrow transplantation for refractory acute leukaemia. S. Afr. Med. J. 1979, 55, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carreras, E.; Diaz-Ricart, M. The role of the endothelium in the short-term complications of hematopoietic SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2011, 46, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohty, M.; Malard, F.; Abecassis, M.; Aerts, E.; Alaskar, A.S.; Aljurf, M.; Arat, M.; Bader, P.; Baron, F.; Bazarbachi, A.; et al. Revised diagnosis and severity criteria for sinusoidal obstruction syndrome/veno-occlusive disease in adult patients: A new classification from the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2016, 51, 906–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kernan, N.A.; Grupp, S.; Smith, A.R.; Arai, S.; Triplett, B.; Antin, J.H.; Lehmann, L.; Shore, T.; Ho, V.T.; Bunin, N.; et al. Final results from a defibrotide treatment-IND study for patients with hepatic veno-occlusive disease/sinusoidal obstruction syndrome. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 181, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppell, J.A.; Richardson, P.G.; Soiffer, R.; Martin, P.L.; Kernan, N.A.; Chen, A.; Guinan, E.; Vogelsang, G.; Krishnan, A.; Giralt, S.; et al. Hepatic Veno-Occlusive Disease following Stem Cell Transplantation: Incidence, Clinical Course, and Outcome. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2010, 16, 157–168. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/art-cle/pii/S1083879109004182 (accessed on 10 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Haeger, M.; Unander, M.; Bengtsson, A. Enhanced anaphylatoxin and terminal C5b-9 complement complex formation in patients with the syndrome of hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count. Obstet. Gynecol. 1990, 76, 698–702. [Google Scholar]
- Burwick, R.M.; Fichorova, R.N.; Dawood, H.Y.; Yamamoto, H.S.; Feinberg, B.B. Urinary excretion of C5b-9 in severe preeclampsia: Tipping the balance of complement activation in pregnancy. Hypertension 2013, 62, 1040–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaught, A.J.; Gavriilaki, E.; Hueppchen, N.; Blakemore, K.; Yuan, X.; Seifert, S.M.; York, S.; Brodsky, R.A. Direct evidence of complement activation in HELLP syndrome: A link to atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. Exp. Hematol. 2016, 44, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmon, J.E.; Heuser, C.; Triebwasser, M.; Liszewski, M.K.; Kavanagh, D.; Roumenina, L.; Branch, D.W.; Goodship, T.; Fremeaux-Bacchi, V.; Atkinson, J.P. Mutations in Complement Regulatory Proteins Predispose to Preeclampsia: A Genetic Analysis of the PROMISSE Cohort. PLoS Med. 2011, 8, e1001013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaught, A.J.; Braunstein, E.M.; Jasem, J.; Yuan, X.; Makhlin, I.; Eloundou, S.; Baines, A.C.; Merrill, S.A.; Chaturvedi, S.; Blakemore, K.; et al. Germline mutations in the alternative pathway of complement predispose to HELLP syndrome. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e99128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masetti, R.; Biagi, E.; Zama, D.; Muratore, E.; D’Amico, F.; Leardini, D.; Turroni, S.; Prete, A.; Brigidi, P.; Pession, A. Early modifications of the gut microbiome in children with hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, K.R.; Jannin, A.; Ho, V. The Contribution of Endothelial Activation and Injury to End-Organ Toxicity following Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2008, 14, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salat, C.; Holler, E.; Kolb, H.-J.; Reinhardt, B.; Pihusch, R.; Wilmanns, W.; Hiller, E. Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 Confirms the Diagnosis of Hepatic Veno-Occlusive Disease in Patients With Hyperbilirubinemia After Bone Marrow Transplantation. Blood 1997, 89, 2184–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohty, M.; Malard, F.; Abecasis, M.; Aerts, E.; Alaskar, A.S.; Aljurf, M.; Arat, M.; Bader, P.; Baron, F.; Basak, G.; et al. Prophylactic, preemptive, and curative treatment for sinusoidal obstruction syndrome/veno-occlusive disease in adult patients: A position statement from an international expert group. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2019, 55, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.J.; Lee, K.S.K.; Beschorner, W.E.; Vogel, V.G.; Grochow, L.B.; Braine, H.G.; Vogelsang, G.B.; Sensenbrenner, L.L.; Santos, G.W.; Saral, R. Venoocclusive disease of the liver following bone marrow transplantation. Transplantation 1987, 44, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcdonald, G.B.; Sharma, P.; Matthews, D.E.; Shulman, H.M.; Thomas, E.D. Venocclusive Disease of the Liver after Bone Marrow Transplantation: Diagnosis, Incidence, and Predisposing Factors. Hepatology 1984, 4, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbacioglu, S.; Carreras, E.; Ansari, M.; Balduzzi, A.; Cesaro, S.; Dalle, J.-H.; Dignan, F.; Gibson, B.; Guengoer, T.; Gruhn, B.; et al. Diagnosis and severity criteria for sinusoidal obstruction syndrome/veno-occlusive disease in pediatric patients: A new classification from the European society for blood and marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2018, 53, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embaby, M.; Rangarajan, H.G.; Abu-Arja, R.; Auletta, J.J.; Stanek, J.; Pai, V.; Nicol, K.K.; Bajwa, R.S. Refractory Thrombocytopenia Is a Valid Early Diagnostic Criteria for Hepatic Veno-Occlusive Disease in Children. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2020, 26, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dignan, F.L.; Wynn, R.F.; Hadzic, N.; Karani, J.; Quaglia, A.; Pagliuca, A.; Veys, P.; Potter, M.N. BCSH/BSBMT guideline: Diagnosis and management of veno-occlusive disease (sinusoidal obstruction syndrome) following haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 163, 444–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravaioli, F.; Colecchia, A.; Alemanni, L.V.; Vestito, A.; Dajti, E.; Marasco, G.; Sessa, M.; Pession, A.; Bonifazi, F.; Festi, D. Role of imaging techniques in liver veno-occlusive disease diagnosis: Recent advances and literature review. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 13, 463–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, S.S.; Colecchia, A.; Duarte, R.F.; Bonifazi, F.; Ravaioli, F.; Bourhis, J.H. Imaging in Hepatic Veno-Occlusive Disease/Sinusoidal Obstruction Syndrome. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2020, 26, 1770–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strouse, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.-J.; Digilio, A.; Pasquini, M.; Horowitz, M.M.; Lee, S.; Ho, V.; Ramanathan, M.; Chinratanalab, W.; et al. Risk Score for the Development of Veno-Occlusive Disease after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplant. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018, 24, 2072–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Penack, O.; Terzer, T.; Schult, D.; Majer-Lauterbach, J.; Radujkovic, A.; Blau, I.W.; Bullinger, L.; Müller-Tidow, C.; Dreger, P.; et al. Predicting sinusoidal obstruction syndrome after allogeneic stem cell transplantation with the EASIX biomarker panel. Haematologica 2021, 106, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peled, J.U.; Gomes, A.L.; Devlin, S.M.; Littmann, E.R.; Taur, Y.; Sung, A.D.; Weber, D.; Hashimoto, D.; Slingerland, A.E.; Slingerland, J.B.; et al. Microbiota as Predictor of Mortality in Allogeneic Hematopoietic-Cell Transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 822–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, M.S.; Ward, D.V.; Severyn, C.J.; Arshad, M.; Heston, S.M.; Jenkins, K.; Martin, P.L.; McGill, L.; Stokhuyzen, A.; Bhattarai, S.K.; et al. Gut Colonization Preceding Mucosal Barrier Injury Bloodstream Infection in Pediatric Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Recipients. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019, 25, 2274–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagi, E.; Zama, D.; Rampelli, S.; Turroni, S.; Brigidi, P.; Consolandi, C.; Severgnini, M.; Picotti, E.; Gasperini, P.; Merli, P.; et al. Early gut microbiota signature of aGvHD in children given allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for hematological disorders. BMC Med Genom. 2019, 12, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zama, D.; Biagi, E.; Masetti, R.; Gasperini, P.; Prete, A.; Candela, M.; Brigidi, P.; Pession, A. Gut microbiota and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: Where do we stand? Bone Marrow Transplant. 2017, 52, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özkan, S.G.; Pata, C.; Şekuri, A.; Çınar, Y.; Özkan, H.A. Transient elastography of liver: Could it be a guide for diagnosis and management strategy in hepatic veno-occlusive disease (sinusoidal obstruction syndrome)? Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2022, 61, 103370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbacioglu, S.; Jabbour, E.J.; Mohty, M. Risk Factors for Development of and Progression of Hepatic Veno-Occlusive Disease/Sinusoidal Obstruction Syndrome. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019, 25, 1271–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeker, L.; Kim, H.T.; Glotzbecker, B.; Nageshwar, P.; Nikiforow, S.; Koreth, J.; Armand, P.; Cutler, C.; Alyea, E.P.; Antin, J.H.; et al. Early Clinical Predictors of Hepatic Veno-Occlusive Disease/Sinusoidal Obstruction Syndrome after Myeloablative Stem Cell Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019, 25, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakushijin, K.; Atsuta, Y.; Doki, N.; Yokota, A.; Kanamori, H.; Miyamoto, T.; Ohwada, C.; Miyamura, K.; Nawa, Y.; Kurokawa, M.; et al. Sinusoidal obstruction syndrome after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: Incidence, risk factors and outcomes. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2016, 51, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, D.Y.; Kim, S.-J.; Cheong, J.-W.; Kim, Y.; Jang, J.E.; Lee, J.Y.; Min, Y.H.; Yang, W.I.; Kim, J.S. High pre-transplant serum ferritin and busulfan-thiotepa conditioning regimen as risk factors for hepatic sinusoidal obstructive syndrome after autologous stem cell transplantation in patients with malignant lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2016, 57, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, I.D.; Singer, J.; Andrews, R.G.; Keating, A.; Powell, J.S.; Bjornson, B.H.; Cuttner, J.; Najfeld, V.; Reaman, G.; Raskind, W. Treatment of acute myeloid leukemia cells in vitro with a monoclonal antibody recognizing a myeloid differentiation antigen allows normal progenitor cells to be expressed. J. Clin. Investig. 1987, 79, 1153–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norsworthy, K.J.; Ko, C.-W.; Lee, J.E.; Liu, J.; John, C.S.; Przepiorka, D.; Farrell, A.T.; Pazdur, R. FDA Approval Summary: Mylotarg for Treatment of Patients with Relapsed or Refractory CD33-Positive Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Oncologist 2018, 23, 1103–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Mylotarg (Gemtuzumab Ozogamicin) [Prescribing Information]. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/761060s004lbl.pdf (accessed on 2 January 2023).
- Rajvanshi, P.; Shulman, H.M.; Sievers, E.; McDonald, G.B. Hepatic sinusoidal obstruction after gemtuzumab ozogamicin (Mylotarg) therapy. Blood 2002, 99, 2310–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaigne, S.; Pautas, C.; Terré, C.; Raffoux, E.; Bordessoule, D.; Bastie, J.-N.; Legrand, O.; Thomas, X.; Turlure, P.; Reman, O.; et al. Effect of gemtuzumab ozogamicin on survival of adult patients with de-novo acute myeloid leukaemia (ALFA-0701): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet 2012, 379, 1508–1516, Erratum in Lancet 2018, 391, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battipaglia, G.; Labopin, M.; Candoni, A.; Fanin, R.; El Cheikh, J.; Blaise, D.; Michallet, M.; Ruggeri, A.; Contentin, N.; Ribera, J.-M.; et al. Risk of sinusoidal obstruction syndrome in allogeneic stem cell transplantation after prior gemtuzumab ozogamicin treatment: A retrospective study from the Acute Leukemia Working Party of the EBMT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2017, 52, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantarjian, H.M.; DeAngelo, D.J.; Advani, A.S.; Stelljes, M.; Kebriaei, P.; Cassaday, R.D.; Merchant, A.A.; Fujishima, N.; Uchida, T.; Calbacho, M.; et al. Hepatic adverse event profile of inotuzumab ozogamicin in adult patients with relapsed or refractory acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: Results from the open-label, randomised, phase 3 INO-VATE study. Lancet Haematol. 2017, 4, e387–e398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batsis, I.; Yannaki, E.; Kaloyannidis, P.; Sakellari, I.; Smias, C.; Georgoulis, I.; Fassas, A.; Anagnostopoulos, A. Veno-occlusive disease prophylaxis with fresh frozen plasma and heparin in bone marrow transplantation. Thromb. Res. 2006, 118, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, H.; Tleyjeh, I.; Zirakzadeh, A.; Rodriguez, V.; Khan, S.P. Use of prophylactic anticoagulation and the risk of hepatic veno-occlusive disease in patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2006, 37, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bearman, S.I.; Shen, D.D.; Hinds, M.S.; Hill, H.A.; McDonald, G.B. A phase I/II study of prostaglandin E1 for the prevention of hepatic venocclusive disease after bone marrow transplantation. Br. J. Haematol. 1993, 84, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordigoni, P.; Witz, F.; Von Bueltzingsloewen, A.; Schmitt, C.; Sommelet, D. Prostaglandin E1 (PGE1) induced arthritis following bone marrow transplantation. Br. J. Haematol. 1991, 78, 138–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attal, M.; Huguet, F.; Rubie, H.; Charlet, J.P.; Schlaifer, D.; Huynh, A.; Laurent, G.; Pris, J. Prevention of regimen-related toxicities after bone marrow transplantation by pentoxifylline: A prospective, randomized trial. Blood 1993, 82, 732–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haussmann, U.; Fischer, J.; Eber, S.; Scherer, F.; Seger, R.; Güngör, T. Hepatic veno-occlusive disease in pediatric stem cell transplantation: Impact of pre-emptive antithrombin III replacement and combined antithrombin III/defibrotide therapy. Haematologica 2006, 91, 795–800. [Google Scholar]
- Tay, J.; Tinmouth, A.; Fergusson, D.; Huebsch, L.; Allan, D.S. Systematic Review of Controlled Clinical Trials on the Use of Ursodeoxycholic Acid for the Prevention of Hepatic Veno-occlusive Disease in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2007, 13, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defitelio (Defibrotide Sodium) [Prescribing Information]; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2016.
- Corbacioglu, S.; Cesaro, S.; Faraci, M.; Valteau-Couanet, D.; Gruhn, B.; Rovelli, A.; Boelens, J.J.; Hewitt, A.; Schrum, J.; Schulz, A.S.; et al. Defibrotide for prophylaxis of hepatic veno-occlusive disease in paediatric haemopoietic stem-cell transplantation: An open-label, phase 3, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2012, 379, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, P.G.; Triplett, B.; Ho, V.T.; Chao, N.; Dignan, F.L.; Maglio, M.; Mohty, M. Defibrotide sodium for the treatment of hepatic veno-occlusive disease/sinusoidal obstruction syndrome. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 11, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pescador, R.; Capuzzi, L.; Mantovani, M.; Fulgenzi, A.; Ferrero, M. Defibrotide: Properties and clinical use of an old/new drug. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2013, 59, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissner, G.; Multhoff, G.; Gerbitz, A.; Kirchner, S.; Bauer, S.; Haffner, S.; Sondermann, D.; Andreesen, R.; Holler, E. Fludarabine induces apoptosis, activation, and allogenicity in human endothelial and epithelial cells: Protective effect of defibrotide. Blood 2002, 100, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, P.G.; Riches, M.L.; Kernan, N.A.; Brochstein, J.A.; Mineishi, S.; Termuhlen, A.M.; Arai, S.; Grupp, S.A.; Guinan, E.C.; Martin, P.L.; et al. Phase 3 trial of defibrotide for the treatment of severe veno-occlusive disease and multi-organ failure. Blood 2016, 127, 1656–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbacioglu, S.; Carreras, E.; Mohty, M.; Pagliuca, A.; Boelens, J.J.; Damaj, G.; Iacobelli, M.; Niederwieser, D.; Olavarría, E.; Suarez, F.; et al. Defibrotide for the Treatment of Hepatic Veno-Occlusive Disease: Final Results From the International Compassionate-Use Program. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016, 22, 1874–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, P.; Aggarwal, S.; Topaloglu, O.; Villa, K.F.; Corbacioglu, S. Systematic review of defibrotide studies in the treatment of veno-occlusive disease/sinusoidal obstruction syndrome (VOD/SOS). Bone Marrow Transplant. 2019, 54, 1951–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strouse, C.; Richardson, P.; Prentice, G.; Korman, S.; Hume, R.; Nejadnik, B.; Horowitz, M.M.; Saber, W. Defibrotide for Treatment of Severe Veno-Occlusive Disease in Pediatrics and Adults: An Exploratory Analysis Using Data from the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016, 22, 1306–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schriber, J.; Milk, B.; Shaw, D.; Christiansen, N.; Baer, M.; Slack, J.; Tezcan, H.; Wetzler, M.; Herzig, G. Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) as therapy for hepatotoxicity following bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1999, 24, 1311–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bearman, S.I.; Lee, J.L.; Baroón, A.E.; McDonald, G.B. Treatment of hepatic venocclusive disease with recombinant human tissue plasminogen activator and heparin in 42 marrow transplant patients. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 1997, 89, 1501–1506. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, J.-H.; Min, W.-S.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, J.-H.; Shin, S.-H.; Yahng, S.-A.; Lee, S.-E.; Cho, B.-S.; Eom, K.-S.; Kim, Y.-J.; et al. Experiences of t-PA use in moderate-to-severe hepatic veno-occlusive disease after hematopoietic SCT: Is it still reasonable to use t-PA? Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013, 48, 1562–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkholt, L.; Remberger, M.; Hassan, Z.; Fransson, K.; Omazic, B.; Svahn, B.-M.; Karlsson, H.; Brune, M.; Hassan, M.; Mattsson, J.; et al. A prospective randomized study using N-acetyl-L-cysteine for early liver toxicity after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2008, 41, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.C.-W.; Aung, L. Treatment of hepatic veno-occlusive disease in children with N -acetylcysteine. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2019, 66, e27518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, S.; Yuasa, M.; Uchida, N.; Yamaguchi, K.; Kageyama, K.; Kaji, D.; Taya, Y.; Nishida, A.; Ishiwata, K.; Yamamoto, H.; et al. Possible Therapeutic Potential of Recombinant Human Soluble Thrombomoduline Alpha for the Treatment of SOS/VOD: A Retrospective Study in Toranomon Hospital. Blood 2016, 128, 5747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Su, J.; Tang, Y.; Wu, X.; Ma, X.; Chen, F.; Ruan, C.; Zheng, X.L.; et al. Plasma levels of complement activation fragments C3b and sC5b-9 significantly increased in patients with thrombotic microangiopathy after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Ann. Hematol. 2017, 96, 1849–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heying, R.; Nürnberger, W.; Spiekerkötter, U.; Göbel, U. Hepatic veno-occlusive disease with severe capillary leakage after peripheral stem cell transplantation: Treatment with recombinant plasminogen activator and C1-esterase inhibitor concentrate. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1998, 21, 947–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucalossi, A.; Toraldo, F.; Tozzi, M.; Lenoci, M.; Castagnini, C.; Artuso, R.; Renieri, A.; Marotta, G. Is complement alternative pathway disregulation involved in veno-occlusive disease of the liver? Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2010, 16, 1749–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Changsirikulchai, S.; Myerson, D.; Guthrie, K.A.; McDonald, G.B.; Alpers, C.E.; Hingorani, S.R. Renal thrombotic microangiopathy after hematopoietic cell transplant: Role of GVHD in pathogenesis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. CJASN 2009, 4, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamae, H.; Yamane, T.; Hasegawa, T.; Nakamae, M.; Terada, Y.; Hagihara, K.; Ohta, K.; Hino, M. Risk factor analysis for thrombotic microangiopathy after reduced-intensity or myeloablative allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Am. J. Hematol. 2006, 81, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willems, E.; Baron, F.; Seidel, L.; Frère, P.; Fillet, G.; Beguin, Y. Comparison of thrombotic microangiopathy after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation with high-dose or nonmyeloablative conditioning. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2010, 45, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uderzo, C.; Bonanomi, S.; Busca, A.; Renoldi, M.; Ferrari, P.; Iacobelli, M.; Morreale, G.; Lanino, E.; Annaloro, C.; Della Volpe, A.; et al. Risk Factors and Severe Outcome in Thrombotic Microangiopathy After Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Transplantation 2006, 82, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, V.T.; Cutler, C.; Carter, S.; Martin, P.; Adams, R.; Horowitz, M.; Ferrara, J.; Soiffer, R.; Giralt, S. Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trials Network Toxicity Committee Consensus Summary: Thrombotic Microangiopathy after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2005, 11, 571–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jodele, S.; Davies, S.M.; Lane, A.; Khoury, J.; Dandoy, C.; Goebel, J.; Myers, K.; Grimley, M.; Bleesing, J.; El-Bietar, J.; et al. Diagnostic and risk criteria for HSCT-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: A study in children and young adults. Blood 2014, 124, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoettler, M.; Lehmann, L.; Li, A.; Ma, C.; Duncan, C. Thrombotic Microangiopathy Following Pediatric Autologous Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation: A Report of Significant End-Organ Dysfunction in Eculizumab-Treated Survivors. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019, 25, e163–e168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakellari, I.; Barbouti, A.; I Bamichas, G.; Mallouri, D.; Kaloyannidis, P.; Fragidis, S.K.; Batsis, I.; Apostolou, C.; Karpouza, A.; Yannaki, E.; et al. GVHD-associated chronic kidney disease after allogeneic haematopoietic cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013, 48, 1329–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriilaki, M.; Mainou, M.; Gavriilaki, E.; Haidich, A.; Papagiannopoulos, S.; Sakellari, I.; Anagnostopoulos, A.; Kimiskidis, V. Neurologic complications after allogeneic transplantation: A meta-analysis. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2019, 6, 2037–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakellari, I.; Gavriilaki, E.; Papagiannopoulos, S.; Gavriilaki, M.; Batsis, I.; Mallouri, D.; Vardi, A.; Constantinou, V.; Masmanidou, M.; Yannaki, E.; et al. Neurological adverse events post allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: Major determinants of morbidity and mortality. J. Neurol. 2019, 266, 1960–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavriilaki, E.; Gkaliagkousi, E.; Grigoriadis, S.; Anyfanti, P.; Douma, S.; Anagnostopoulos, A. Hypertension in hematologic malignancies and hematopoietic cell transplantation: An emerging issue with the introduction of novel treatments. Blood Rev. 2019, 35, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoettler, M.; Carreras, E.; Cho, B.; Dandoy, C.; Ho, V.; Jodele, S.; Moissev, I.; Sanchez-Ortega, I.; Srivastava, A.; Atsuta, Y.; et al. Harmonizing Definitions for Diagnostic Criteria and Prognostic Assessment of Transplant Associated Thrombotic Microangiopathy: A Report on Behalf of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT), American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (ASTCT), Asia-Pacific Blood and Marrow Transplantation Group (APBMT) and the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research (CIBMTR). Transplant. Cell Ther. 2023, 29, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriilaki, E.; Anagnostopoulos, A.; Mastellos, D.C. Complement in Thrombotic Microangiopathies: Unraveling Ariadne’s Thread into the Labyrinth of Complement Therapeutics. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavriilaki, E.; Brodsky, R.A. Complementopathies and precision medicine. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 2152–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jodele, S.; Zhang, K.; Zou, F.; Laskin, B.; Dandoy, C.; Myers, K.C.; Lane, A.; Meller, J.; Medvedovic, M.; Chen, J.; et al. The genetic fingerprint of susceptibility for transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Blood 2016, 127, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotz, S.J.; Luebbering, N.; Dixon, B.P.; Gavriilaki, E.; Brodsky, R.A.; Dandoy, C.E.; Jodele, S.; Davies, S.M. In vitro evidence of complement activation in transplantation-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Blood Adv. 2017, 1, 1632–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriilaki, E.; Touloumenidou, T.; Sakellari, I.; Batsis, I.; Mallouri, D.; Psomopoulos, F.; Tsagiopoulou, M.; Koutra, M.; Yannaki, E.; Papalexandri, A.; et al. Pretransplant Genetic Susceptibility: Clinical Relevance in Transplant-Associated Thrombotic Microangiopathy. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 120, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriilaki, E.; Chrysanthopoulou, A.; Sakellari, I.; Batsis, I.; Mallouri, D.; Touloumenidou, T.; Papalexandri, A.; Mitsios, A.; Arampatzioglou, A.; Ritis, K.; et al. Linking Complement Activation, Coagulation, and Neutrophils in Transplant-Associated Thrombotic Microangiopathy. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 119, 1433–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jodele, S.; Medvedovic, M.; Luebbering, N.; Chen, J.; Dandoy, C.E.; Laskin, B.L.; Davies, S.M. Interferon-complement loop in transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 1166–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gloude, N.B.J.; Davies, S.M.; Marsh, R.A.; Jordan, M.B.; Chandra, S.; Jodele, S. Thrombotic Microangiopathy Can Occur Before Transplant in Children with HLH. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2017, 23, 233–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriilaki, E.; Yuan, X.; Ye, Z.; Ambinder, A.J.; Shanbhag, S.P.; Streiff, M.B.; Kickler, T.S.; Moliterno, A.R.; Sperati, C.J.; Brodsky, R.A. Modified Ham test for atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. Blood 2015, 125, 3637–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, A.J.; Breno, M.; Borsa, N.G.; Bu, F.; Frémeaux-Bacchi, V.; Gale, D.P.; Heuvel, L.P.V.D.; Kavanagh, D.; Noris, M.; Pinto, S.; et al. Statistical Validation of Rare Complement Variants Provides Insights into the Molecular Basis of Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome and C3 Glomerulopathy. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 2464–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geerlings, M.; Volokhina, E.; De Jong, E.; Van De Kar, N.; Pauper, M.; Hoyng, C.; Heuvel, L.V.D.; Hollander, A.D. Genotype-phenotype correlations of low-frequency variants in the complement system in renal disease and age-related macular degeneration. Clin. Genet. 2018, 94, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, C.M.; Licht, C.; Muus, P.; Greenbaum, L.A.; Babu, S.; Bedrosian, C.; Bingham, C.; Cohen, D.J.; Delmas, Y.; Douglas, K.; et al. Terminal Complement Inhibitor Eculizumab in Atypical Hemolytic–Uremic Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2169–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathbone, J.; Kaltenthaler, E.; Richards, A.; Tappenden, P.; Bessey, A.; Cantrell, A. A systematic review of eculizumab for atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome (aHUS). BMJ Open 2013, 3, e003573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jodele, S.; Dandoy, C.E.; Danziger-Isakov, L.; Myers, K.C.; El-Bietar, J.; Nelson, A.; Wallace, G.; Teusink-Cross, A.; Davies, S.M. Terminal Complement Blockade after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Is Safe without Meningococcal Vaccination. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016, 22, 1337–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasu, S.; Wu, H.; Satoskar, A.; Puto, M.; Roddy, J.; Blum, W.; Klisovic, R.; Andritsos, L.; Hofmeister, C.; Benson, D.M.; et al. Eculizumab therapy in adults with allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2016, 51, 1241–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Fontbrune, F.S.; Galambrun, C.; Sirvent, A.; Huynh, A.; Faguer, S.; Nguyen, S.; Bay, J.O.; Neven, B.; Moussi, J.; Simon, L.; et al. Use of Eculizumab in Patients with Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplant-Associated Thrombotic Microangiopathy: A Study From the SFGM-TC. Transplantation 2015, 99, 1953–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohl, S.R.; Kuchenbauer, F.; von Harsdorf, S.; Kloevekorn, N.; Schonsteiner, S.S.; Rouhi, A.; Schwarzwälder, P.; Döhner, H.; Bunjes, D.; Bommer, M. Thrombotic Microangiopathy after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Comparison of Eculizumab Therapy and Conventional Therapy. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2017, 23, 2172–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jodele, S.; Dandoy, C.E.; Lane, A.; Laskin, B.L.; Teusink-Cross, A.; Myers, K.C.; Wallace, G.H.; Nelson, A.; Bleesing, J.; Chima, R.S.; et al. Complement blockade for TA-TMA: Lessons learned from large pediatric cohort treated with eculizumab. Blood 2020, 135, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambaldi, A.K.S.; Smith, M.; Zecca, M.; Kwong, Y.L.; Claes, K.; Leung, N.; Whitaker, S. Improved survival following OMS721 treatment of hematopoieic stem cell transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy (HCT-TMA). Eur. Hematol. Assoc. Lib. 2018, 215162, PF724. [Google Scholar]
- Bonifazi, F.; Barbato, F.; Ravaioli, F.; Sessa, M.; DeFrancesco, I.; Arpinati, M.; Cavo, M.; Colecchia, A. Diagnosis and Treatment of VOD/SOS After Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Muñoz, M.E.; Forés, R.; Lario, A.; Bautista, G.; Bueno, J.L.; de Miguel, C.; Navarro, B.; De Laiglesia, A.; Sánchez-Guerrero, A.; Cabrera, J.R.; et al. Use of defibrotide to treat adult patients with transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2019, 54, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeates, L.; Slatter, M.A.; Bonanomi, S.; Lim, F.L.W.I.; Ong, S.Y.; Dalissier, A.; Barberi, W.; Shulz, A.; Duval, M.; Heilmann, C.; et al. Use of defibrotide to treat transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: A retrospective study of the Paediatric Diseases and Inborn Errors Working Parties of the European Society of Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2017, 52, 762–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, E.J.; Wong, K.; Lee, S.J.; Cushing-Haugen, K.L.; Flowers, M.E.; Friedman, D.L.; Leisenring, W.M.; Martin, P.J.; Mueller, B.A.; Baker, K.S. Late cardiovascular complications after hematopoietic cell transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014, 20, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, S.; Francisco, L.; Carter, A.; Sun, C.-L.; Baker, K.S.; Gurney, J.G.; McGlave, P.B.; Nademanee, A.; O’Donnell, M.; Ramsay, N.K.C.; et al. Late mortality after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation and functional status of long-term survivors: Report from the Bone Marrow Transplant Survivor Study. Blood 2007, 110, 3784–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakellari, I.; Gavriilaki, E.; Batsis, I.; Mallouri, D.; Panteliadou, A.-K.; Lazaridou, A.; Vardi, A.; Constantinou, V.; Yannaki, E.; Papalexandri, A.; et al. Favorable impact of extracorporeal photopheresis in acute and chronic graft versus host disease: Prospective single-center study. J. Clin. Apher. 2018, 33, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakellari, I.; Gavriilaki, E.; Kaliou, M.; Mallouri, D.; Batsis, I.; Yannaki, E.; Smias, C.; Sotiropoulos, D.; Tsorlini, E.; Anagnostopoulos, A. Candida is an emerging pathogen beyond the neutropenic period of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Clin. Transplant. 2017, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatzidimitriou, D.; Gavriilaki, E.; Sakellari, I.; Diza, E. Hematopoietic cell transplantation and emerging viral infections. J. Med. Virol. 2010, 82, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gkaliagkousi, E.; Gavriilaki, E.; Vasileiadis, I.; Nikolaidou, B.; Yiannaki, E.; Lazaridis, A.; Triantafyllou, A.; Anyfanti, P.; Markala, D.; Zarifis, I.; et al. Endothelial Microvesicles Circulating in Peripheral and Coronary Circulation Are Associated With Central Blood Pressure in Coronary Artery Disease. Am. J. Hypertens. 2019, 32, 1199–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, S.; Ishii, K.; Inami, N.; Kimura, Y.; Uoshima, N.; Ishida, H.; Yoshihara, T.; Urase, F.; Maeda, Y.; Hayashi, K. Evaluation of angiopoietins and cell-derived microparticles after stem cell transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2008, 14, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pihusch, V.; Rank, A.; Steber, R.; Pihusch, M.; Pihusch, R.; Toth, B.; Hiller, E.; Kolb, H.-J. Endothelial Cell–Derived Microparticles in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Recipients. Transplantation 2006, 81, 1405–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, X.; Hong, M.; Luo, T.; Zhao, M.; Shen, H.; Fang, J.; Li, X.; Zang, S.; Chen, P.; et al. Endothelial microparticles delivering microRNA-155 into T lymphocytes are involved in the initiation of acute graft-versus-host disease following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 23360–23375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, V.T.; Revta, C.; Richardson, P.G. Hepatic veno-occlusive disease after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: Update on defibrotide and other current investigational therapies. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2008, 41, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Modified Seattle | Baltimore | EBMT–Classical | EBMT–Late Onset | EBMT–Pediatric |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| At least 2 of the following before day 20 post-HSCT | Bilirubin ≥ 2 mg/dL before day 21 post-HSCT AND at least 2 of the following: | Bilirubin ≥ 2 mg/dL before day 21 post-HSCT AND at least 2 of the following: | Classical SOS beyond day 21 OR Histologically proven SOS OR At least 2 of the following: | Presence of at least 2 of the following with no limitation for time of onset: |
| Bilirubin ≥ 2 mg/dL | Bilirubin ≥ 2 mg/dL | Rising bilirubin on at least 3 consecutive days OR Bilirubin ≥ 2 mg/dL within 72 h | ||
| Hepatomegaly, RUQ pain | Hepatomegaly | Painful hepatomegaly | Painful hepatomegaly | Hepatomegaly |
| Ascites with or w/o unexplained weight gain >2% from baseline | Ascites | Ascites | Ascites AND Hemodynamical and/or ultrasound evidence of SOS | Ascites Unexplained consumptive and transfusion-refractory thrombocytopenia |
| Weight gain > 5% from baseline | Weight gain > 5% from baseline | Weight gain > 5% from baseline | Unexplained weight gain on 3 consecutive days (despite diuretics) OR Weight gain > 5% from baseline |
| Mild | Moderate | Severe | Very Severe-MOD/MOF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time since first clinical symptoms of SOS/VOD | <7 Days | 5–7 Days | ≤4 Days | Any time |
| Bilirubin (mg/dL) | ≥2 and <3 | ≥3 and <5 | ≥5 and <8 | ≥8 |
| Bilirubin kinetics | Doubling within 48 h | |||
| Transaminases | ≤2 × normal | > 2 and ≤5 × normal | >5 and ≤8 × normal | >8 × normal |
| Weight increase | <5% | ≥5% and <10% | ≥5% and <10% | ≥10% |
| Renal function | <1.2 × baseline at transplant | ≥1.2 and <1.5 × baseline at transplant | ≥1.5 and <2 × baseline at transplant | ≥2 × baseline transplant or other signs of MOD/MOF |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mavrikou, I.; Chatzidimitriou, D.; Skoura, L.; Nikolousis, E.; Sakellari, I.; Gavriilaki, E. Molecular Advances in Sinusoidal Obstruction Syndrome/Veno-Occlusive Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5620. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065620
Mavrikou I, Chatzidimitriou D, Skoura L, Nikolousis E, Sakellari I, Gavriilaki E. Molecular Advances in Sinusoidal Obstruction Syndrome/Veno-Occlusive Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(6):5620. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065620
Chicago/Turabian StyleMavrikou, Ioulia, Dimitrios Chatzidimitriou, Lemonia Skoura, Emmanouil Nikolousis, Ioanna Sakellari, and Eleni Gavriilaki. 2023. "Molecular Advances in Sinusoidal Obstruction Syndrome/Veno-Occlusive Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 6: 5620. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065620
APA StyleMavrikou, I., Chatzidimitriou, D., Skoura, L., Nikolousis, E., Sakellari, I., & Gavriilaki, E. (2023). Molecular Advances in Sinusoidal Obstruction Syndrome/Veno-Occlusive Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(6), 5620. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065620








