Novel Synthetic Derivative of Renieramycin T Right-Half Analog Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Cancer Stem Cells via Targeting the Akt Signal in Lung Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
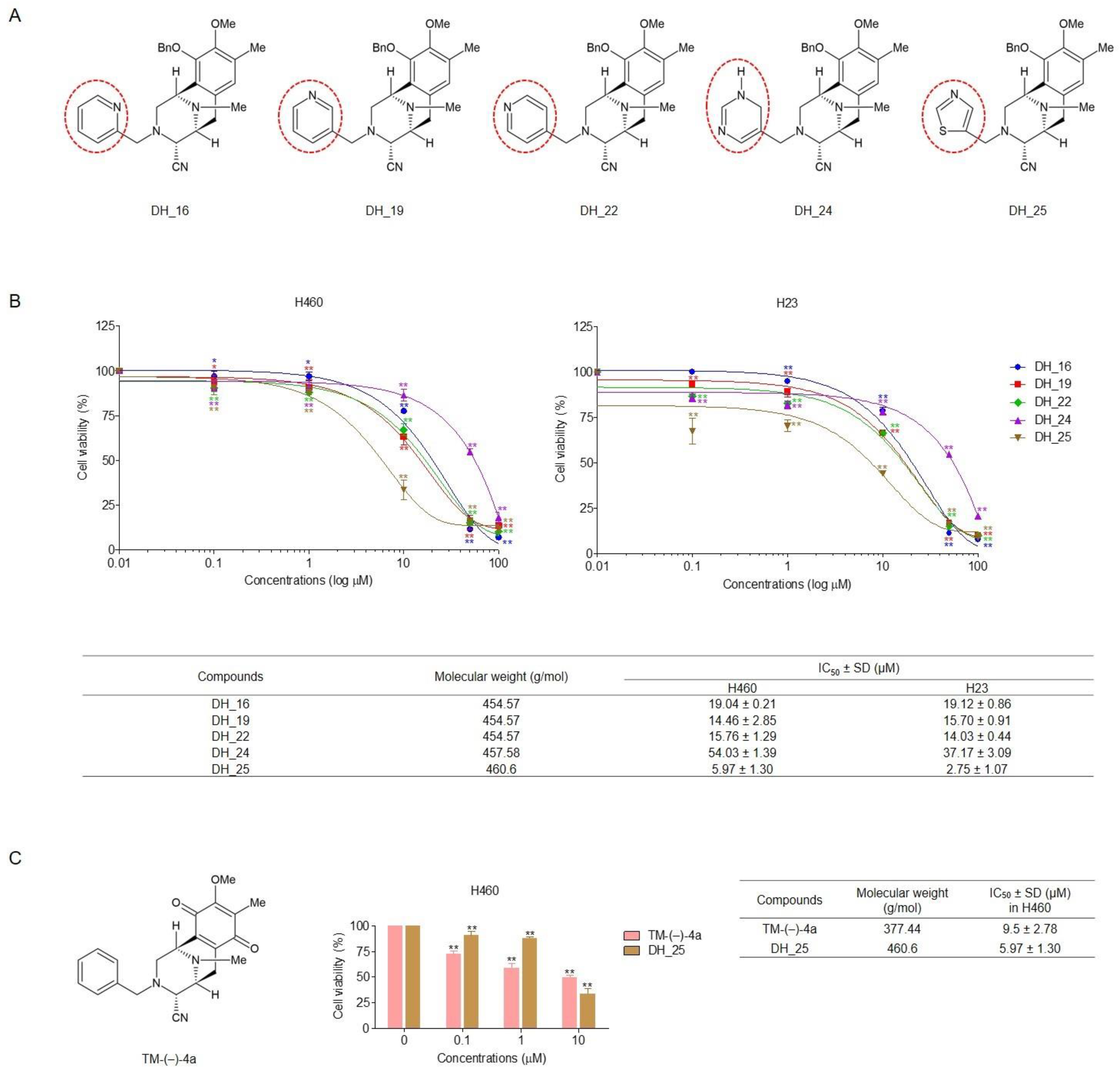
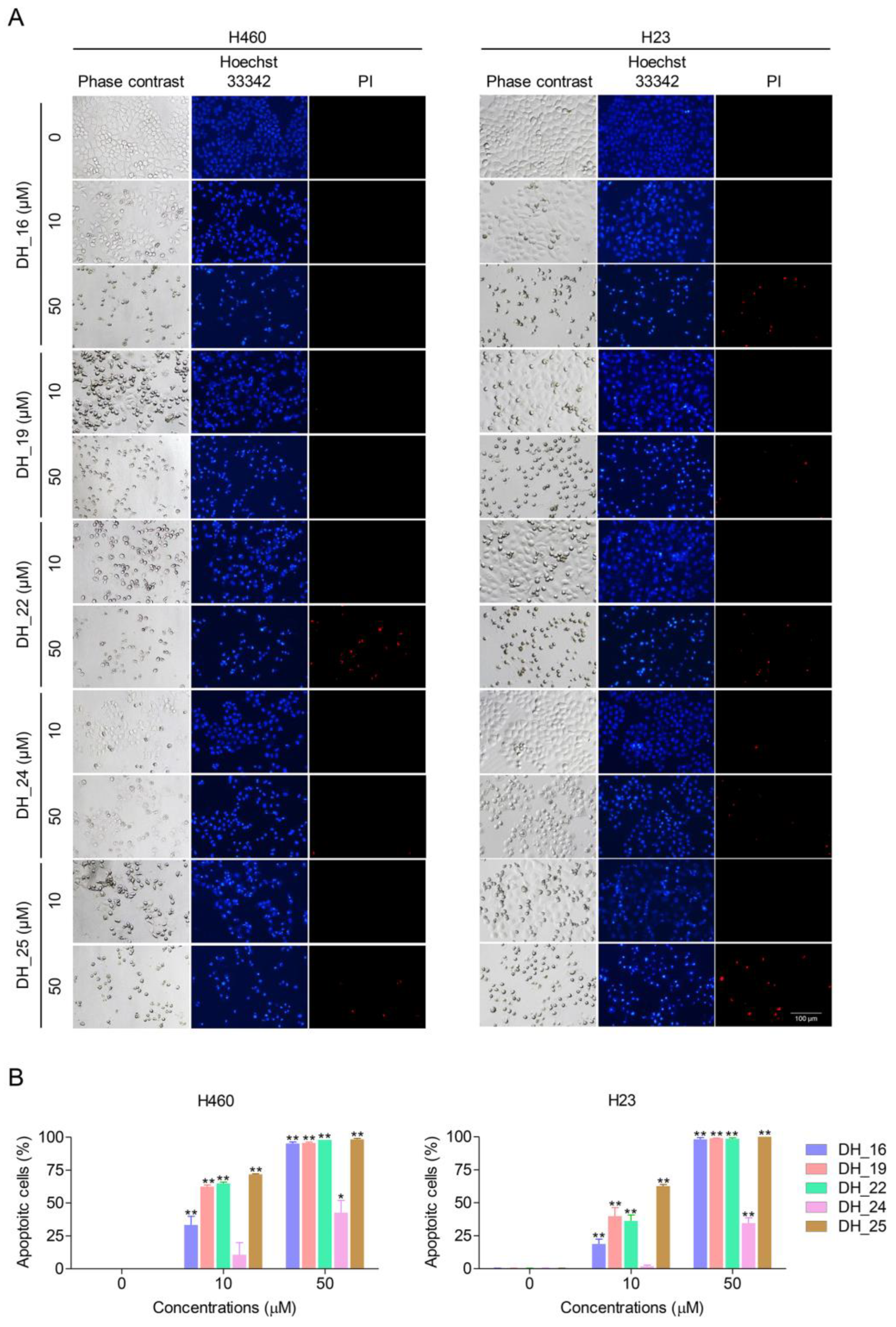
2.1. Derivatives of RT Right-Half Analog of RT Induce Cytotoxicity, Apoptosis, and Morphological Changes in NSCLC Cells
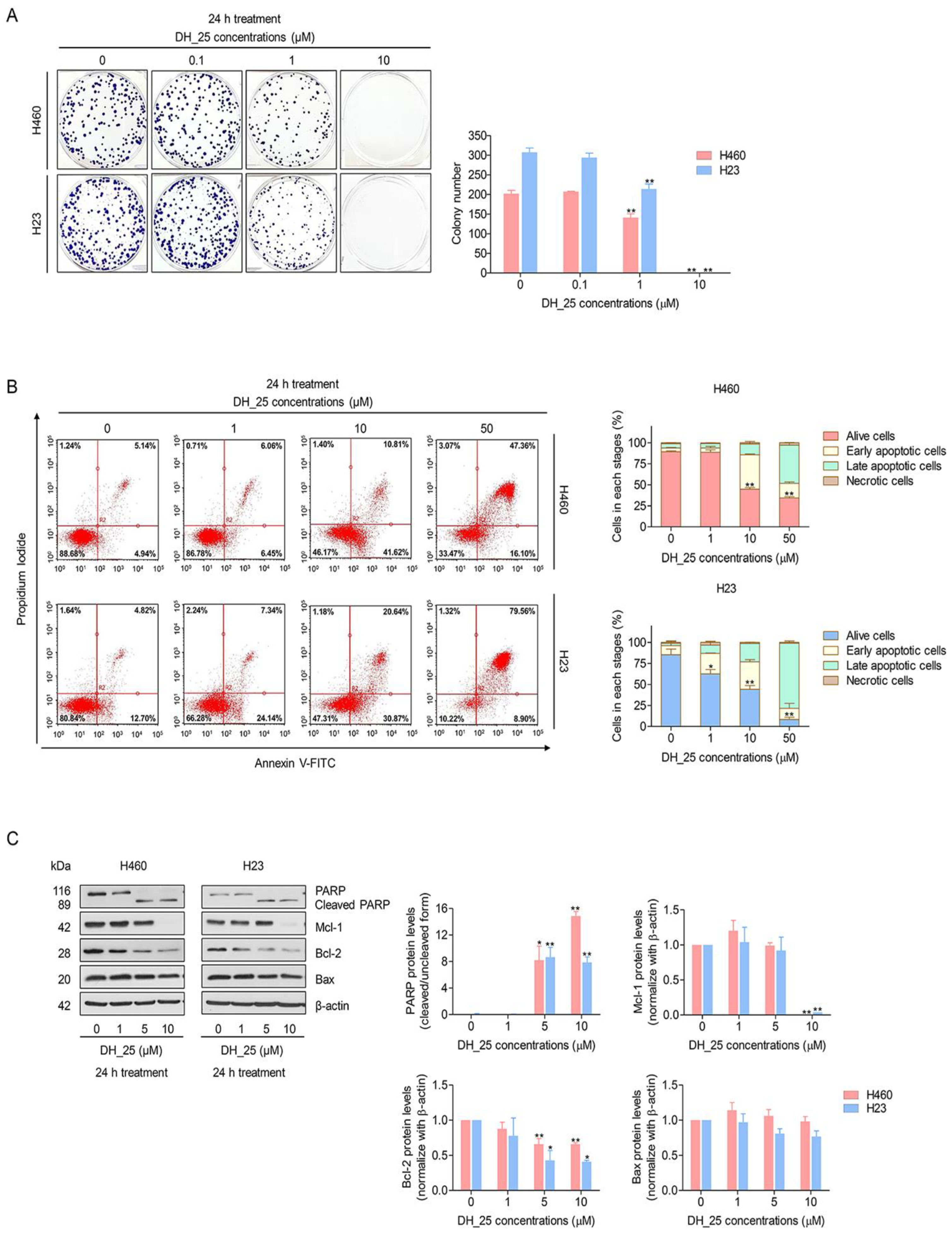
2.2. DH_25 Inhibits Colony-Forming Activity and Induces Apoptosis in NSCLC Cells
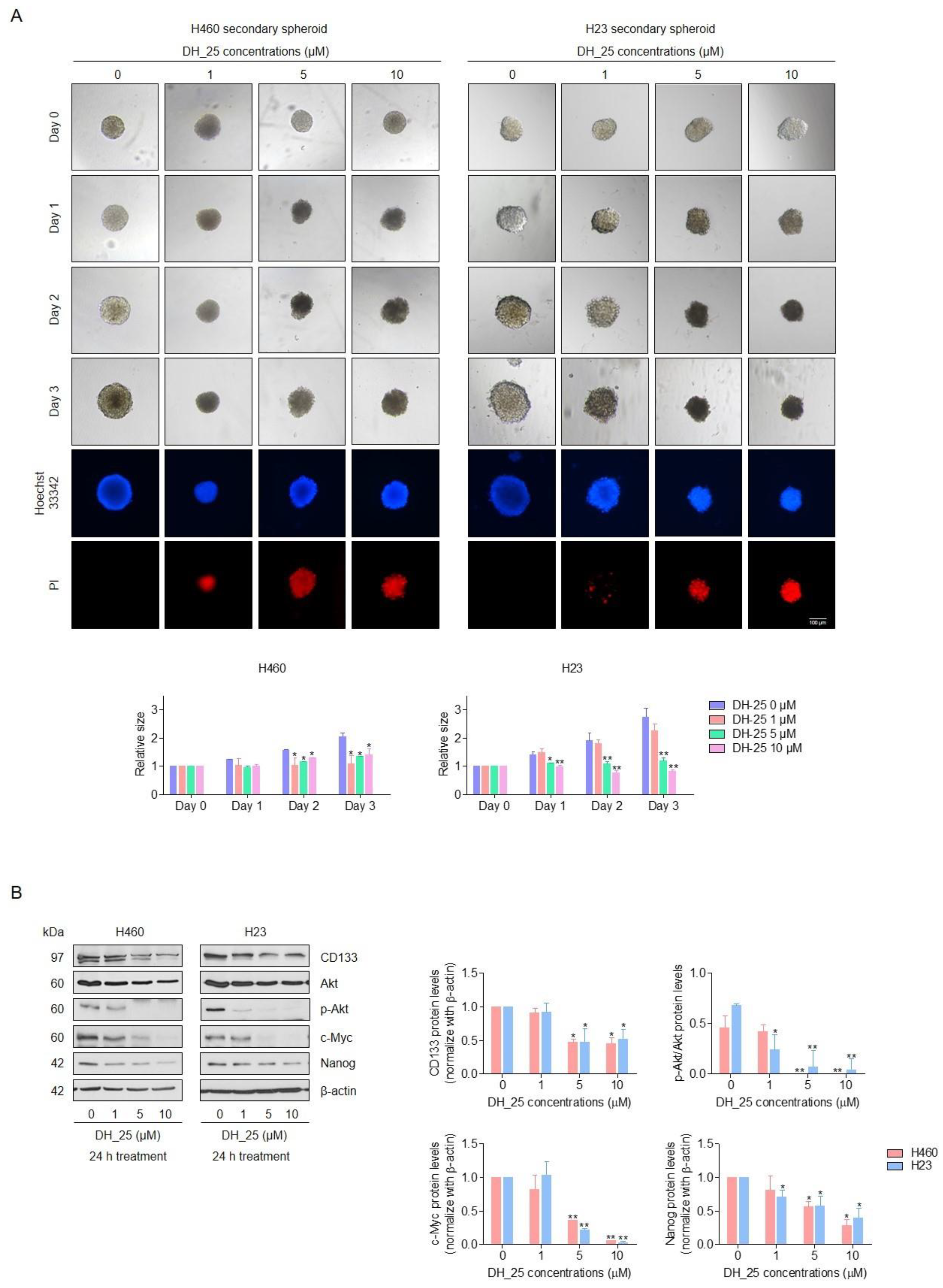
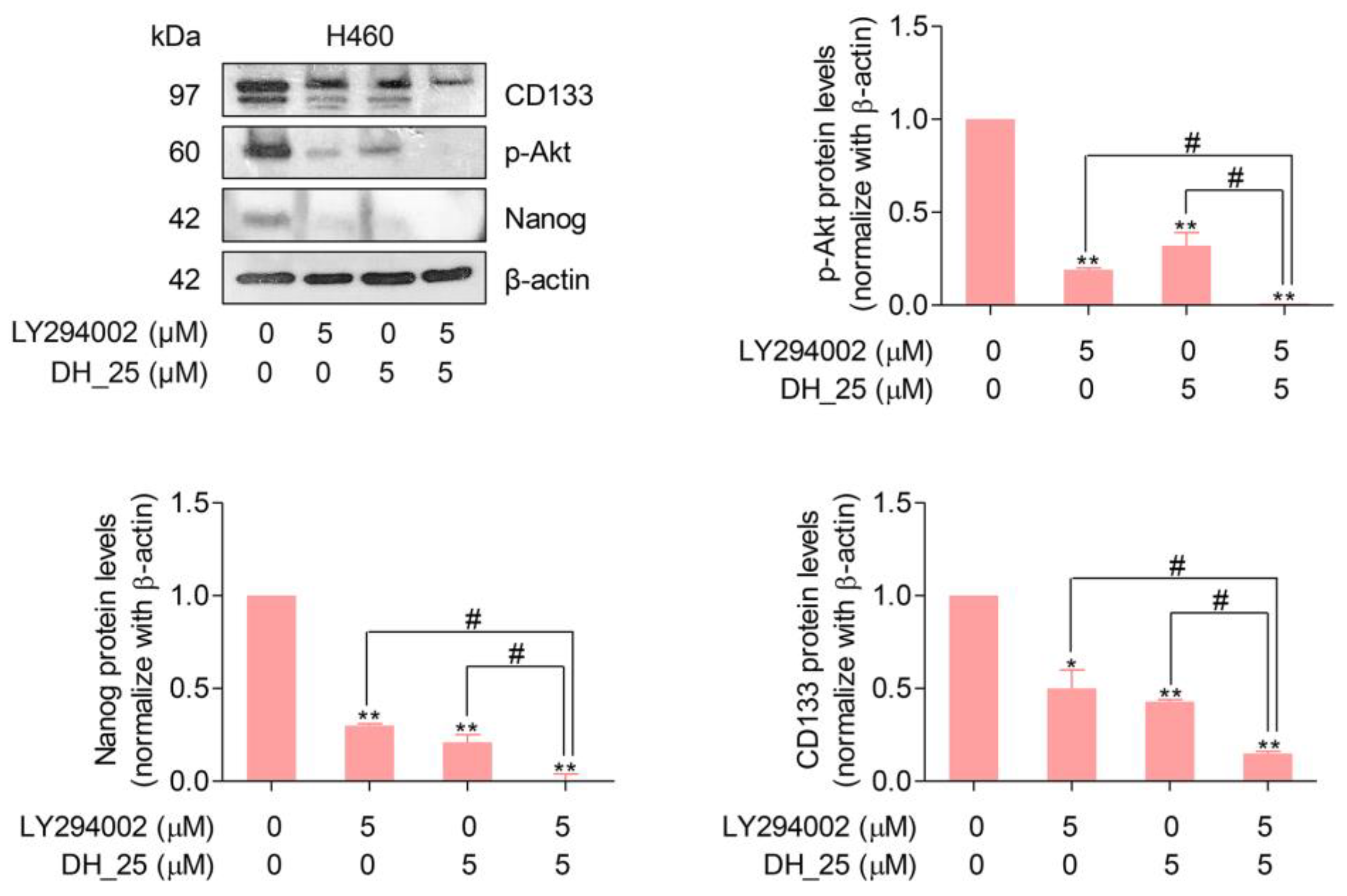
2.3. DH_25 Suppresses CSC Spheroid Formation and CSC Signals in NSCLC Cells
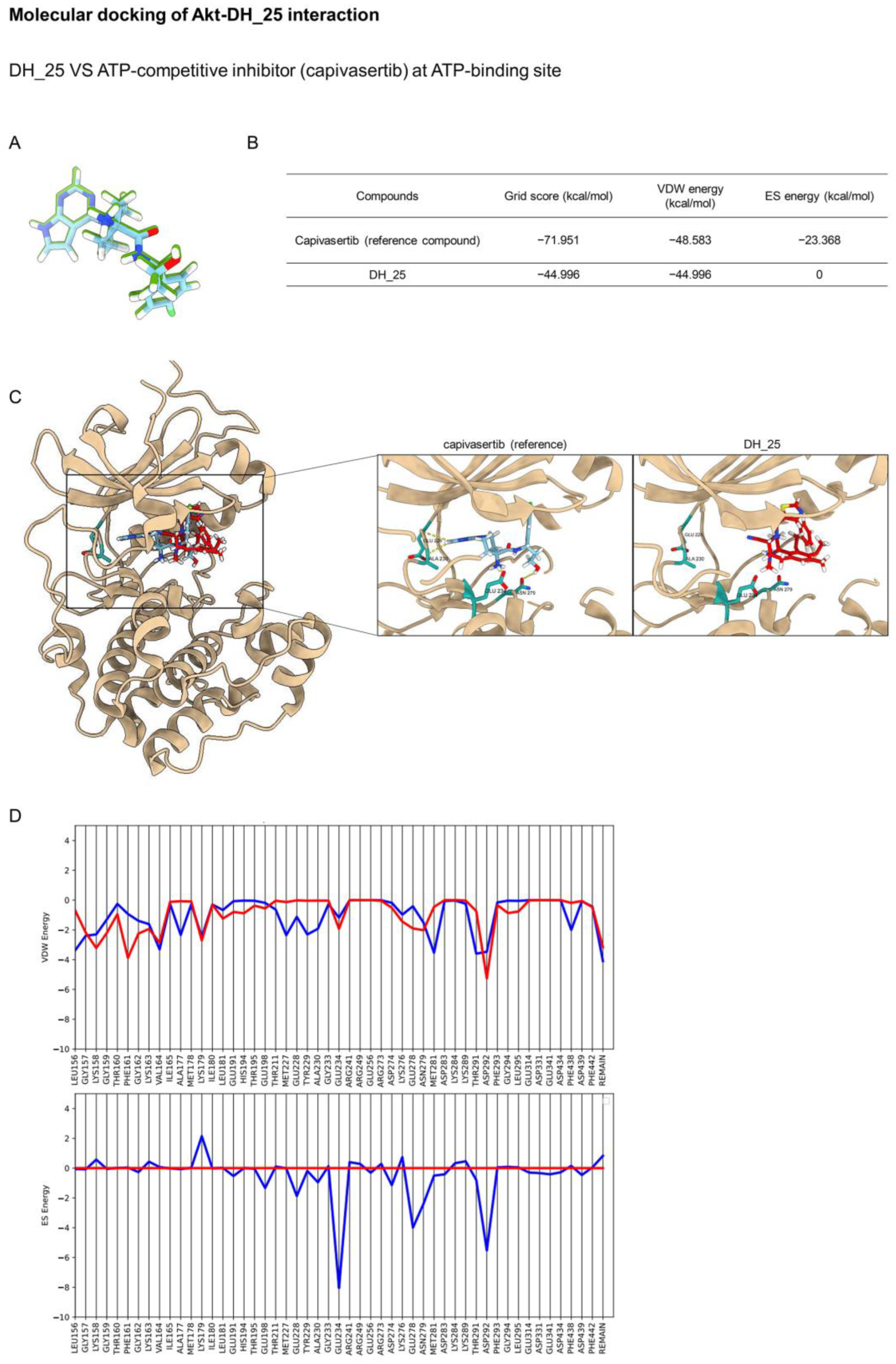
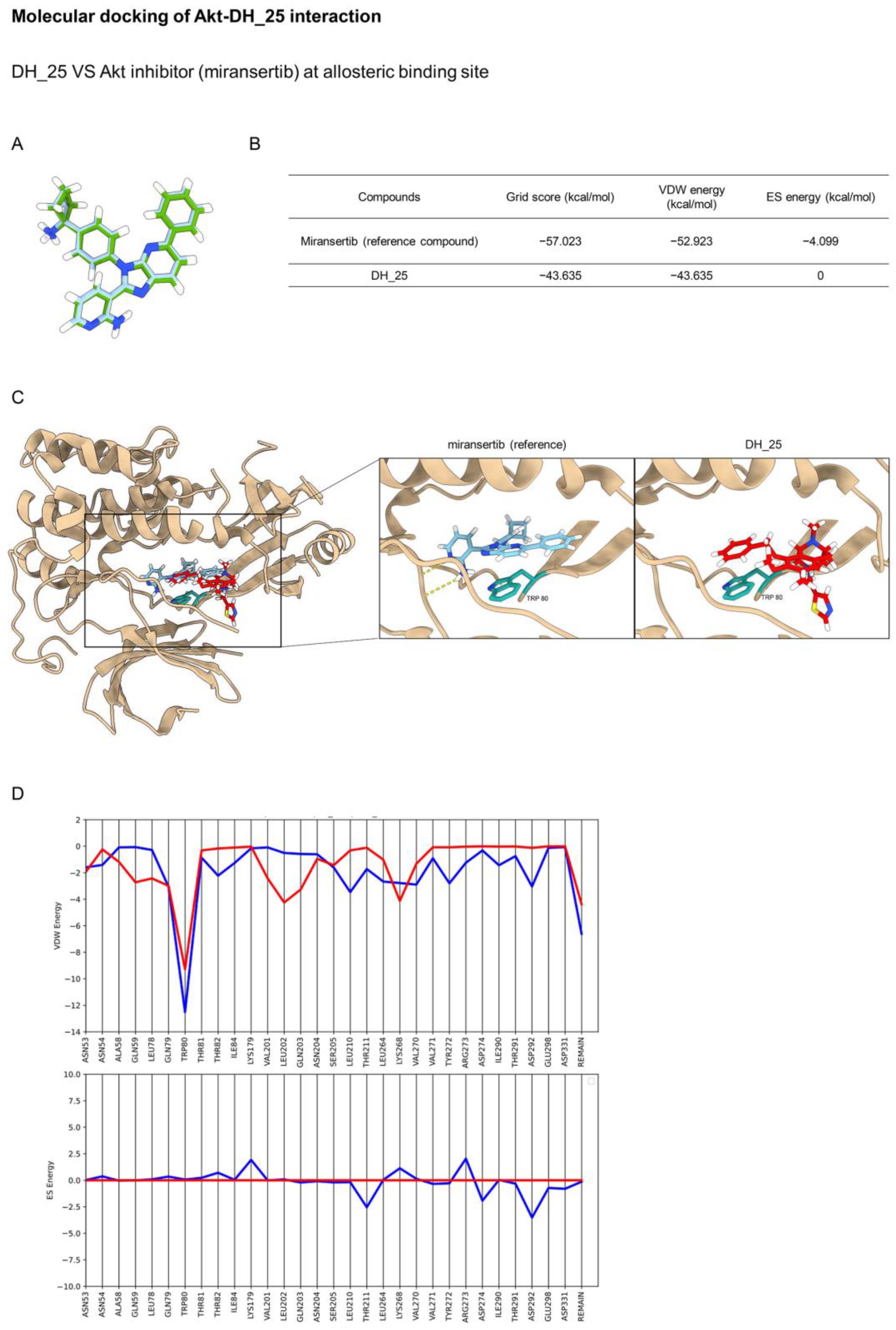
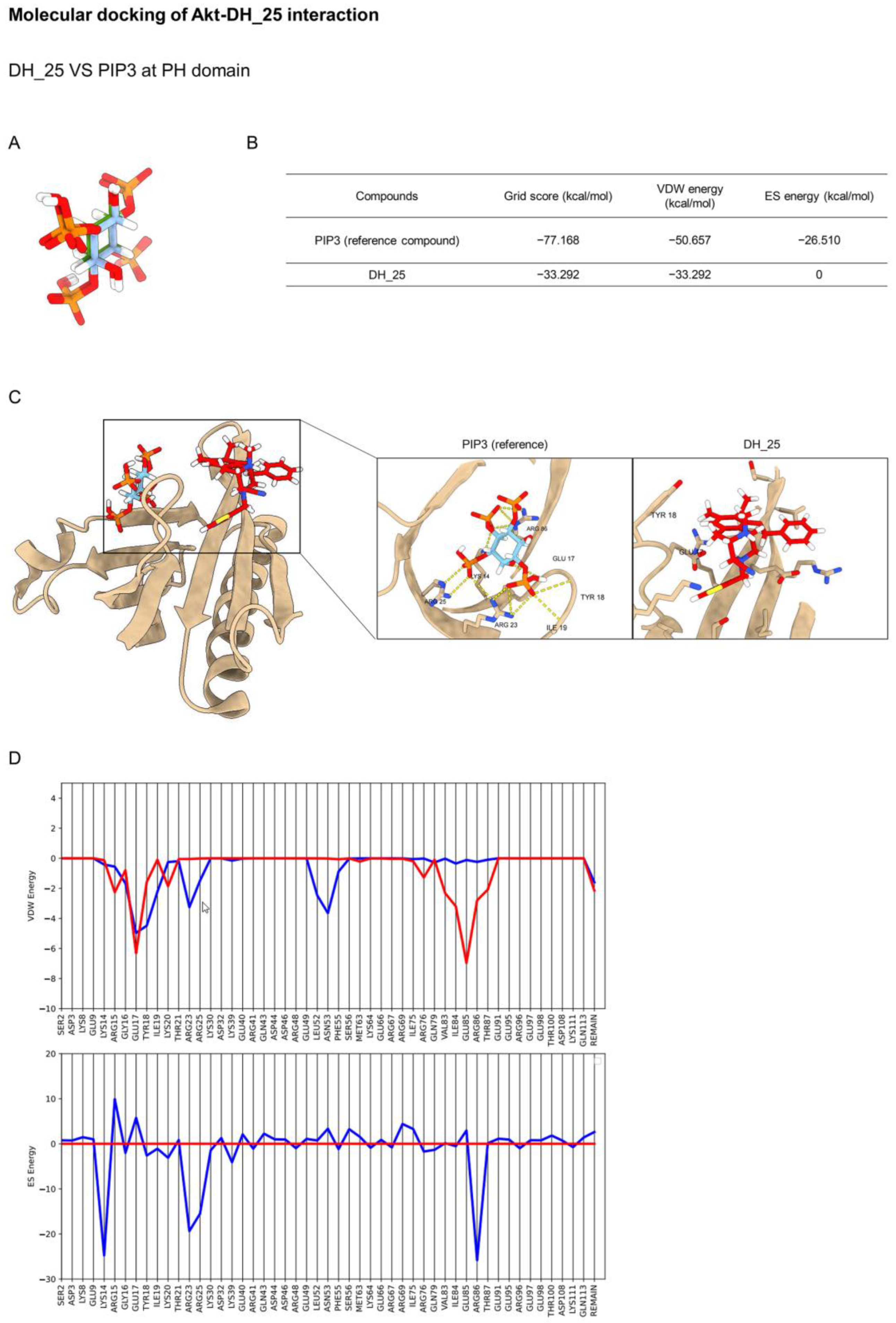
2.4. DH_25 Directly Interacts with Akt, the Upstream Regulatory Signal of CSC
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Antibodies
4.2. Cell Lines and Culture
4.3. Derivatives of RT Right-Half Analog Synthesis
4.4. Preparation of Compound Stock Solutions
4.5. Cell Viability Assay
4.6. Nuclear Staining Assay
4.7. Colony Formation Assay
4.8. Annexin V-FITC/PI Staining Apoptotic Assay
4.9. Western Blot Analysis
4.10. Three-Dimensional (3D) Spheroid Formation Assay
4.11. Molecular Docking Analysis
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 144, 1941–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre, L.A.; Siegel, R.L.; Jemal, A. Lung Cancer Statistics. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 893, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanathamsan, O.; Hayakawa, Y.; Pongrakhananon, V. Molecular mechanisms of natural compounds in cell death induction and sensitization to chemotherapeutic drugs in lung cancer. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 2531–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanathamsan, O.; Treesuwan, S.; Sritularak, B.; Pongrakhananon, V. Cypripedin, a phenanthrenequinone from Dendrobium densiflorum, sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer H460 cells to cisplatin-mediated apoptosis. J. Nat. Med. 2018, 72, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariati, M.; Meric-Bernstam, F. Targeting AKT for cancer therapy. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2019, 28, 977–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsurutani, J.; Fukuoka, J.; Tsurutani, H.; Shih, J.H.; Hewitt, S.M.; Travis, W.D.; Jen, J.; Dennis, P.A. Evaluation of two phosphorylation sites improves the prognostic significance of Akt activation in non-small-cell lung cancer tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janku, F.; Yap, T.A.; Meric-Bernstam, F. Targeting the PI3K pathway in cancer: Are we making headway? Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, P.; Xu, X.Y. PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in cancer stem cells: From basic research to clinical application. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 1602–1609. [Google Scholar]
- Valent, P.; Bonnet, D.; De Maria, R.; Lapidot, T.; Copland, M.; Melo, J.V.; Chomienne, C.; Ishikawa, F.; Schuringa, J.J.; Stassi, G.; et al. Cancer stem cell definitions and terminology: The devil is in the details. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragu, D.L.; Necula, L.G.; Bleotu, C.; Diaconu, C.C.; Chivu-Economescu, M. Therapies targeting cancer stem cells: Current trends and future challenges. World J. Stem Cells 2015, 7, 1185–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radpour, R. Tracing and targeting cancer stem cells: New venture for personalized molecular cancer therapy. World J. Stem Cells 2017, 9, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.G.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Heo, C.K.; Kim, R.K.; Cho, E.W. Targeting therapy-resistant lung cancer stem cells via disruption of the AKT/TSPYL5/PTEN positive-feedback loop. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunayama, J.; Matsuda, K.; Sato, A.; Tachibana, K.; Suzuki, K.; Narita, Y.; Shibui, S.; Sakurada, K.; Kayama, T.; Tomiyama, A.; et al. Crosstalk between the PI3K/mTOR and MEK/ERK pathways involved in the maintenance of self-renewal and tumorigenicity of glioblastoma stem-like cells. Stem Cells 2010, 28, 1930–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, M.J.; Rho, J.K.; Kim, Y.M.; Jung, J.E.; Jin, Y.B.; Ko, Y.G.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, J.C.; Park, M.J. Upregulation of CXCR4 is functionally crucial for maintenance of stemness in drug-resistant non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncogene 2013, 32, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.L.; Wang, P.; Lu, M.Z.; Zhang, S.D.; Zheng, L. c-Myc maintains the self-renewal and chemoresistance properties of colon cancer stem cells. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 4487–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petsri, K.; Chamni, S.; Suwanborirux, K.; Chanvorachote, P. Renieramycin T Induces Lung Cancer Cell Apoptosis by Targeting Mcl-1 Degradation: A New Insight in the Mechanism of Action. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantarawong, W.; Chamni, S.; Suwanborirux, K.; Saito, N.; Chanvorachote, P. 5-O-Acetyl-Renieramycin T from Blue Sponge Xestospongia sp. Induces Lung Cancer Stem Cell Apoptosis. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suksamai, D.; Racha, S.; Sriratanasak, N.; Chaotham, C.; Aphicho, K.; Lin, A.C.K.; Chansriniyom, C.; Suwanborirux, K.; Chamni, S.; Chanvorachote, P. 5-O-(N-Boc-l-Alanine)-Renieramycin T Induces Cancer Stem Cell Apoptosis via Targeting Akt Signaling. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, K.; Kubo, K.; Yokoya, M.; Saito, N. Preparation of renieramycin left-half model compounds. Tetrahedron 2014, 70, 6529–6545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, T.; Yokoya, M.; Sirimangkalakitti, N.; Saito, N. Asymmetric Synthesis and Cytotoxicity Evaluation of Right-Half Models of Antitumor Renieramycin Marine Natural Products. Mar. Drugs 2018, 17, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petsri, K.; Yokoya, M.; Tungsukruthai, S.; Rungrotmongkol, T.; Nutho, B.; Vinayanuwattikun, C.; Saito, N.; Takehiro, M.; Sato, R.; Chanvorachote, P. Structure-Activity Relationships and Molecular Docking Analysis of Mcl-1 Targeting Renieramycin T Analogues in Patient-derived Lung Cancer Cells. Cancers 2020, 12, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Blenis, J.; Yuan, J. Activation of PI3K/Akt and MAPK pathways regulates Myc-mediated transcription by phosphorylating and promoting the degradation of Mad1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 6584–6589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toson, B.; Fortes, I.S.; Roesler, R.; Andrade, S.F. Targeting Akt/PKB in pediatric tumors: A review from preclinical to clinical trials. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 183, 106403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savill, K.; Lee, B.; Oeh, J.; Lin, J.; Lin, E.; Chung, W.-J.; Young, A.; Chen, W.; Miś, M.; Mesh, K.; et al. Distinct resistance mechanisms arise to allosteric vs. ATP-competitive AKT inhibitors. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Fan, D.; Zhou, G.; Li, X.; Deng, H. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor(LY294002) induces apoptosis of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 29, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frincke, J.M.; Faulkner, D.J. Antimicrobial metabolites of the sponge Reniera sp. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1982, 104, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amnuoypol, S.; Suwanborirux, K.; Pummangura, S.; Kubo, A.; Tanaka, C.; Saito, N. Chemistry of renieramycins. Part 5. Structure elucidation of renieramycin-type derivatives O, Q, R, and S from thai marine sponge Xestospongia species pretreated with potassium cyanide. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, N.; Hiramatsu, A.; Hirade, H.; Kubota, M.; Toyoshima, R.; Fujino, A.; Sirimangkalakitti, N.; Suwanborirux, K.; Concepcion, G. Chemistry of Renieramycins. 16. Structure of 7-Desmethylrenieramycin O (= 14α-Hydroxyrenieramycin S) from Blue Sponge, Xestospongia sp. Heterocycles 2017, 95, 748–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parameswaran, P.s. Renieramycins H and I, two novel alkaloids from the sponge Haliclona cribricutis Dendy. Indian J. Chem.–Sect. B Org. Med. Chem. 1998, 37, 1258–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oku, N.; Matsunaga, S.; van Soest, R.; Fusetani, N. Renieramycin J, a highly cytotoxic tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloid, from a marine sponge Neopetrosia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 1136–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongwiangchan, N.; Sriratanasak, N.; Wichadakul, D.; Aksorn, N.; Chamni, S.; Chanvorachote, P. Hydroquinone 5-O-Cinnamoyl Ester of Renieramycin M Suppresses Lung Cancer Stem Cells by Targeting Akt and Destabilizes c-Myc. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamni, S.; Sirimangkalakitti, N.; Chanvorachote, P.; Suwanborirux, K.; Saito, N. Chemistry of Renieramycins. Part 19: Semi-Syntheses of 22-O-Amino Ester and Hydroquinone 5-O-Amino Ester Derivatives of Renieramycin M and Their Cytotoxicity against Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cell Lines. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirimangkalakitti, N.; Chamni, S.; Suwanborirux, K.; Chanvorachote, P. Renieramycin M Attenuates Cancer Stem Cell-like Phenotypes in H460 Lung Cancer Cells. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tun, J.O.; Salvador-Reyes, L.A.; Velarde, M.C.; Saito, N.; Suwanborirux, K.; Concepcion, G.P. Synergistic Cytotoxicity of Renieramycin M and Doxorubicin in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daikuhara, N.; Tada, Y.; Yamaki, S.; Charupant, K.; Amnuoypol, S.; Suwanborirux, K.; Saito, N. Chemistry of renieramycins. Part 7: Renieramycins T and U, novel renieramycin–ecteinascidin hybrid marine natural products from Thai sponge Xestospongia sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009, 50, 4276–4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoya, M.; Toyoshima, R.; Suzuki, T.; Le, V.H.; Williams, R.M.; Saito, N. Stereoselective Total Synthesis of (−)-Renieramycin. T. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 4039–4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamni, S.; Sirimangkalakitti, N.; Chanvorachote, P.; Saito, N.; Suwanborirux, K. Chemistry of Renieramycins. 17. A New Generation of Renieramycins: Hydroquinone 5-O-Monoester Analogues of Renieramycin M as Potential Cytotoxic Agents against Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, R. On exploring structure-activity relationships. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 993, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrou, A.; Fesatidou, M.; Geronikaki, A. Thiazole Ring-A Biologically Active Scaffold. Molecules 2021, 26, 3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.S. Apoptosis in cancer: From pathogenesis to treatment. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 30, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varun, B.R.; Jayanthi, P.; Ramani, P. Cancer stem cells: A comprehensive review on identification and therapeutic implications. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Pathol. 2020, 24, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayob, A.Z.; Ramasamy, T.S. Cancer stem cells as key drivers of tumour progression. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018, 25, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Cui, W. Proliferation, survival and metabolism: The role of PI3K/AKT/ mTOR signalling in pluripotency and cell fate determination. Development 2016, 143, 3050–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.; Yu, X.; Liu, S. Pluripotency transcription factors and cancer stem cells: Small genes make a big difference. Chin. J. Cancer 2013, 32, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodes, N.; Heerding, D.A.; Duckett, D.R.; Eberwein, D.J.; Knick, V.B.; Lansing, T.J.; McConnell, R.T.; Gilmer, T.M.; Zhang, S.Y.; Robell, K.; et al. Characterization of an Akt kinase inhibitor with potent pharmacodynamic and antitumor activity. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 2366–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumarola, C.; Bonelli, M.A.; Petronini, P.G.; Alfieri, R.R. Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in non small cell lung cancer. Biochem. Pharm. 2014, 90, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.; Lin, J.; Wu, W.I.; Ballard, J.; Lee, B.B.; Gloor, S.L.; Vigers, G.P.; Morales, T.H.; Friedman, L.S.; Skelton, N.; et al. An ATP-site on-off switch that restricts phosphatase accessibility of Akt. Sci. Signal. 2012, 5, ra37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.C.; Madison, V. AKT crystal structure and AKT-specific inhibitors. Oncogene 2005, 24, 7493–7501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaro, G.; Kostaras, E.; Vivanco, I. Inhibitors in AKTion: ATP-competitive vs allosteric. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2020, 48, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iksen; Pothongsrisit, S.; Pongrakhananon, V. Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway in Lung Cancer: An Update Regarding Potential Drugs and Natural Products. Molecules 2021, 26, 4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innets, B.; Thongsom, S.; Petsri, K.; Racha, S.; Yokoya, M.; Moriue, S.; Chaotham, C.; Chanvorachote, P. Akt/mTOR Targeting Activity of Resveratrol Derivatives in Non-Small Lung Cancer. Molecules 2022, 27, 8268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takebe, N.; Miele, L.; Harris, P.J.; Jeong, W.; Bando, H.; Kahn, M.; Yang, S.X.; Ivy, S.P. Targeting Notch, Hedgehog, and Wnt pathways in cancer stem cells: Clinical update. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 12, 445–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Vashishta, M.; Kong, L.; Wu, X.; Lu, J.J.; Guha, C.; Dwarakanath, B.S. The Role of Notch, Hedgehog, and Wnt Signaling Pathways in the Resistance of Tumors to Anticancer Therapies. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 650772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galluzzo, P.; Bocchetta, M. Notch signaling in lung cancer. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2011, 11, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capaccione, K.M.; Pine, S.R. The Notch signaling pathway as a mediator of tumor survival. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 1420–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henley, D.B.; Sundell, K.L.; Sethuraman, G.; Dowsett, S.A.; May, P.C. Safety profile of semagacestat, a gamma-secretase inhibitor: IDENTITY trial findings. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2014, 30, 2021–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, N.; Kurzrock, R. Targeting the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in cancer: Update on effectors and inhibitors. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018, 62, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xiao, Q.; Xiao, J.; Niu, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Shu, G.; Yin, G. Wnt/β-catenin signalling: Function, biological mechanisms, and therapeutic opportunities. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2022, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrobono, S.; Stecca, B. Targeting the Oncoprotein Smoothened by Small Molecules: Focus on Novel Acylguanidine Derivatives as Potent Smoothened Inhibitors. Cells 2018, 7, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, C.M. Vismodegib. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 3218–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoda, A.M.; Simovic, D.; Karin, V.; Kardum, V.; Vranic, S.; Serman, L. The role of the Hedgehog signaling pathway in cancer: A comprehensive review. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2018, 18, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taipale, J.; Beachy, P.A. The Hedgehog and Wnt signalling pathways in cancer. Nature 2001, 411, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzegar Behrooz, A.; Syahir, A.; Ahmad, S. CD133: Beyond a cancer stem cell biomarker. J. Drug Target. 2019, 27, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahmad, H.F.; Mouhieddine, T.H.; Chalhoub, R.M.; Assi, S.; Araji, T.; Chamaa, F.; Itani, M.M.; Nokkari, A.; Kobeissy, F.; Daoud, G.; et al. The Akt/mTOR pathway in cancer stem/progenitor cells is a potential therapeutic target for glioblastoma and neuroblastoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 33549–33561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addie, M.; Ballard, P.; Buttar, D.; Crafter, C.; Currie, G.; Davies, B.R.; Debreczeni, J.; Dry, H.; Dudley, P.; Greenwood, R.; et al. Discovery of 4-amino-N-[(1S)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-hydroxypropyl]-1-(7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)piperidine-4-carboxamide (AZD5363), an orally bioavailable, potent inhibitor of Akt kinases. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 2059–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapierre, J.M.; Eathiraj, S.; Vensel, D.; Liu, Y.; Bull, C.O.; Cornell-Kennon, S.; Iimura, S.; Kelleher, E.W.; Kizer, D.E.; Koerner, S.; et al. Discovery of 3-(3-(4-(1-Aminocyclobutyl)phenyl)-5-phenyl-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-2-yl)pyridin-2-amine (ARQ 092): An Orally Bioavailable, Selective, and Potent Allosteric AKT Inhibitor. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 6455–6469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milburn, C.C.; Deak, M.; Kelly, S.M.; Price, N.C.; Alessi, D.R.; Van Aalten, D.M. Binding of phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate to the pleckstrin homology domain of protein kinase B induces a conformational change. Biochem. J. 2003, 375, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, E.F.X.; Sircar, R.; Miller, P.S.; Hedger, G.; Luchetti, G.; Nachtergaele, S.; Tully, M.D.; Mydock-McGrane, L.; Covey, D.F.; Rambo, R.P.; et al. Structural basis of Smoothened regulation by its extracellular domains. Nature 2016, 535, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, Y.; Duarte, J.M.; Lowe, R.; Segura, J.; Bi, C.; Bhikadiya, C.; Chen, L.; Rose, A.S.; Bittrich, S.; Burley, S.K.; et al. RCSB Protein Data Bank: Architectural Advances Towards Integrated Searching and Efficient Access to Macromolecular Structure Data from the PDB Archive. J. Mol. Biol. 2021, 433, 166704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, B.; Sali, A. Comparative Protein Structure Modeling Using MODELLER. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2016, 54, 5.6.1–5.6.37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.; Trucks, G.; Schlegel, H.; Scuseria, G.; Robb, M.; Cheeseman, J.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.; et al. Gaussian 09, Revision A02; Gaussian Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, W.J.; Balius, T.E.; Mukherjee, S.; Brozell, S.R.; Moustakas, D.T.; Lang, P.T.; Case, D.A.; Kuntz, I.D.; Rizzo, R.C. DOCK 6: Impact of new features and current docking performance. J. Comput. Chem. 2015, 36, 1132–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Meng, E.C.; Couch, G.S.; Croll, T.I.; Morris, J.H.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF ChimeraX: Structure visualization for researchers, educators, and developers. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petsri, K.; Yokoya, M.; Racha, S.; Thongsom, S.; Thepthanee, C.; Innets, B.; Ei, Z.Z.; Hotta, D.; Zou, H.; Chanvorachote, P. Novel Synthetic Derivative of Renieramycin T Right-Half Analog Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Cancer Stem Cells via Targeting the Akt Signal in Lung Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5345. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065345
Petsri K, Yokoya M, Racha S, Thongsom S, Thepthanee C, Innets B, Ei ZZ, Hotta D, Zou H, Chanvorachote P. Novel Synthetic Derivative of Renieramycin T Right-Half Analog Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Cancer Stem Cells via Targeting the Akt Signal in Lung Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(6):5345. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065345
Chicago/Turabian StylePetsri, Korrakod, Masashi Yokoya, Satapat Racha, Sunisa Thongsom, Chorpaka Thepthanee, Bhurichaya Innets, Zin Zin Ei, Daiki Hotta, Hongbin Zou, and Pithi Chanvorachote. 2023. "Novel Synthetic Derivative of Renieramycin T Right-Half Analog Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Cancer Stem Cells via Targeting the Akt Signal in Lung Cancer Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 6: 5345. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065345
APA StylePetsri, K., Yokoya, M., Racha, S., Thongsom, S., Thepthanee, C., Innets, B., Ei, Z. Z., Hotta, D., Zou, H., & Chanvorachote, P. (2023). Novel Synthetic Derivative of Renieramycin T Right-Half Analog Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Cancer Stem Cells via Targeting the Akt Signal in Lung Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(6), 5345. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065345






