Abstract
Plant roots, due to a high content of natural antioxidants for many years, have been used in herbal medicine. It has been documented that the extract of Baikal skullcap (Scutellaria baicalensis) has hepatoprotective, calming, antiallergic, and anti-inflammatory properties. Flavonoid compounds found in the extract, including baicalein, have strong antiradical activity, which improves overall health and increases feelings of well-being. Plant-derived bioactive compounds with antioxidant activity have for a long time been used as an alternative source of medicines to treat oxidative stress-related diseases. In this review, we summarized the latest reports on one of the most important aglycones with respect to the pharmacological activity and high content in Baikal skullcap, which is 5,6,7-trihydroxyflavone (baicalein).
1. Introduction
Natural flavones with free hydroxyl groups attached to the aromatic A-ring belong to a group of plant polyphenols that are commonly found in nature []. They are found in fruits, vegetables, and herbs; therefore, they are a part of our daily diet. After consumption, the compounds are oxidized in the human organism by the cytochrome P450 pathway and by liver microsomal enzymes, which leads to changes in their structures and pharmacological properties []. According to the most recent research, these compounds demonstrate a wide spectrum of biological activities, such as antihypertensive [], proapoptotic [], inducing hypertrophy of skeletal muscles [], antiallergic [], anti-inflammatory, antioxidative, antimicrobial [], and anti-tumorigenic ones []. The substances that are the most promising for potential therapeutic use are subjected to clinical trials [,]. Scutellaria baicalensis belongs to one of the most important plants in Chinese medicine and has been used for centuries. Compounds such as baicalein, baicalin, wogonin, and oroxylin A (Figure 1) are the main components isolated from the roots of S. baicalensis, and their wide application in the treatment of various diseases has been reported [,,]. Moreover, fruits, root barks, and leaves of S. baicalensis are abundant in baicalein, with the amount ranging from 12, 54 to 37, 43 mg g−1 [,]. In the recent study on the chemical composition of dandelion (Taraxacum mongolicum), the plant well known for its therapeutic properties, baicalein was found as one of the ingredients, along with newly identified antioxidants, e.g., hesperetin-5-O-β-rhamnoglucoside []. However, the content of baicalein in dandelion is much lower than in Baikal skullcap root. Additionally, baicalein was obtained by enzymatic conversion of pinocembrin using recombinant flavone synthase I from Daucus carota (DcFNS I) [].
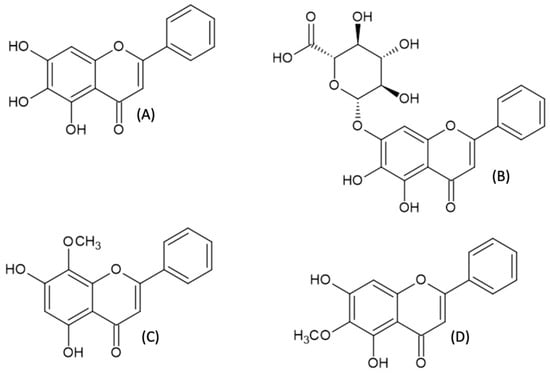
Figure 1.
Structures of selected compounds extracted from Scutellaria baicalensis; baicalein (A), baicalin (B), wogonin (C), and oraoxilin A (D).
Baicalein has been found to exhibit multiple pharmacological properties, including neuroprotective, hepatoprotective, antiviral, and anti-asthmatic ones [,,,,]. According to the newest research results, baicalein can reduce myocardial injury by suppressing harmful changes caused by lipid peroxidation in cardiomyocytes [,]. Currently, the metabolism of baicalein in humans is under investigation. An initial study has shown that baicalein administered orally is metabolized in almost 95%, and only slightly more than 5% of the compound remains unchanged in the circulatory system. The most abundant metabolites of baicalein were determined to be baicalein-7-O-sulfate and baicalein-6-O-glucuronide-7-O-glucuronide [].
However, little information is available so far on possible unwanted side effects of baicalein in humans and effective ways of its delivery. We also do not know what safe therapeutic doses of baicalein are.
To support further development of the research in this field, the objective of our work was to summarize the results of current studies on 5,6,7-trihydroxyflavone (baicalein), including its presence in diet, pro-health properties, and interactions with some drugs.
2. Biological Activity
2.1. Anticancer Activity of Baicalein and Its Derivatives
With the multiple therapeutic benefits of baicalein, its anticancer properties against a broad panel of human cancer cell lines both in vitro and in vivo were documented []. It acts through the induction of apoptosis [], induction of cell-cycle arrest [], inhibition of proliferation via different signaling pathways such as miR-7/FAK/AKT [], Akt/mTOR and Nrf2/Keap 1 [], downregulation of Notch 1/hairy and enhancer of split (Hes) [], modulation of the activity of Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway [], and regulation of the Src/inhibitor of differentiation 1 (Id1) pathway []. It was also demonstrated that baicalein was able to inhibit the phosphorylation of extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) [,]. Moreover, baicalein inhibited cancer-cell migration through the suppression of Wnt/β-catenin and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways []. In line with this, numerous studies showed that baicalein-induced autophagy through the modulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), signaling and downregulation of vacuolar protein sorting 34 (Vps34), autophagy-related (Atg)5, Atg7, and beclin 1 [].
Antitumor properties of baicalein were proven for various malignancies (Table 1), including cholangiocarcinoma (HUH28, TFK1, HUCCT1, QBC939, and MZ-Cha-1) [], gastric cancer (SGC-7901, SGC-7901/DDP, MGC-803, and HGC-27) [], colorectal cancer (HT-29, HCT-116, SW480, and SW620) [], multiple myeloma (RPMI 8226) [], hepatocellular carcinoma (BEL-7402 and BEL-7402/5-FU) [], breast cancer (MCF-7) [], osteosarcoma (143 B, MG63, and U2OS) [], glioma (U251MG) [], nasopharyngeal cancer (CNE1 and CNE2) [], and cervical cancer (C33A) []. According to the Bonham et al. study [], oral administration of 20 mg kg−1 of baicalein inhibits the growth of prostate cancer xenografts in nude mice by approximately 55%.
Although rapid progress in current cancer treatments has been made over the last years, there are still ongoing studies aiming to find therapeutic agents and their derivatives that would be more potent than the parent compounds.
Previous studies proved the anticancer activity of baicalein derivatives []. Baicalein was modified by derivatization of the C6-OH group and by introducing a nitrogen-containing hydrophilic heterocyclic ring to C7-OH via the length of the 3- or 4-carbon chain []. The most potent compound with a pyrrolidine ring showed the highest antiproliferative activity against HepG2, A549, and BCG-823 cancer cells, with IC50 values of 2.0 μM, 0.8 μM, and 3.2 μM, respectively. Other studies [] also demonstrated that 7-OBn-6-O substituted baicalein with the piperazine acetamide group at the 6-position has a significant anticancer effect and inhibits the growth of human lung cancer A549 (IC50 4.73 μM). Additionally, numerous studies demonstrated valuable pharmacological properties of the methylated metabolite of baicalein—Oroxilin A, which inhibited the activity of the CYP1B1 mediator, which is responsible for the progression of human breast cancer (IC50 0.0146 and 2.27 μM for oroxilin A and baicalein, respectively) [,,].
2.2. Synergistic Effect of Baicalein with Anticancer Agents
Over the past years, naturally occurring compounds with antineoplastic properties took a lot of attention in cancer treatment due to their efficiency and minimal toxicity []. Combination or synergistic chemopreventive therapies have been highlighted in order to achieve selectivity of action and the least side effects.
Very successful was the combination of baicalein (0.2 μM) and resveratrol (0.1 μM), which proved efficacious with enhanced synergistic antioxidant effect on human skin fibroblasts (HSF) []. Moreover, a combined treatment with an ERK inhibitor (U0126) and baicalein against colorectal carcinoma (CRC) led to the synergistic reduction of MMP-2/9 expression, which is responsible for the anti-metastatic effect in CRC cells []. Other studies provided evidence that baicalein, in combination with 10hydroxycamptothecin (HCPT), exerts a significant anticancer effect by triggering DNA damage through targeting topoisomerase 1 (Topo 1) to up-regulate p53 protein, which is a tumor suppressor []. There are many reports on the successful treatment of human pancreatic cancer using baicalein combined with gemcitabine or docetaxel []. This combination caused a strong suppression of migration of the pancreatic cancer cells and induced their apoptosis via the caspase-3/PARP signaling pathway. Moreover, in another in vivo study, gemcitabine and baicalein were prepared as prodrug-based targeted nanostructure lipid carriers (BCL NLCs). The obtained nanomedicines showed significant tumor growth inhibitory activity in the murine pancreatic cancer model []. Similarly, baicalein has been found to enhance the anticancer action of docetaxel in thyroid cancer [], doxorubicin in breast cancer [], taxol in ovarian cancer [], paclitaxel in lung cancer [], and silymarin in human hepatoma [].
The antiviral potential of baicalein was observed for many viruses, including dengue virus [], SARS-CoV-2 [], influenza [], and Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) [].
Recently, the group of Zhang [] demonstrated that baicalein triazole derivatives prevented respiratory tract infection in RSV-induced human lung cells. The compounds with substituents in the ortho-position, containing fluoro, trifluoromethyl, nitril, and bromo groups, enhanced RIG-I and IFN-β1 gene expression, which play significant roles in combating viral infections. Moreover, all the compounds inhibited the secretory activity of interleukins and reduced nitric oxide and malondialdehyde production, showing antioxidant activity. In addition, the effect of baicalein on the inhibition of proinflammatory cytokines production was described against infectious bursal disease virus in embryonic eggs [].
According to Luo et al. [], replication of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) was inhibited by baicalein treatment due to suppression of ICP27, ICP8, and GB proteins in HaCat cells in all stages of infection. Therefore, dual mechanisms were involved in its antivirus action, impediment of NF-κB activation via inhibiting IKK-B and IκB-α phosphorylation and inactivation of free viral particles in a dose-dependent manner (EC50 3.64 mol L−1).
Baicalein may potentially be developed as a novel antiviral and anticancer drug, which can be administered alone or combined with commonly used chemotherapeutics, thus improving the treatment of cancer in the future.

Table 1.
In vitro studies demonstrating half maximal inhibitory concentration values of baicalein against several types of malignancies.
Table 1.
In vitro studies demonstrating half maximal inhibitory concentration values of baicalein against several types of malignancies.
| Cell Lines | Type of Cancer | Assay | Time | Dose, IC50 [μM] | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QBC939 | Cholangiocarcinoma | CCK-8 | 72 h | 32.73 | [] |
| MGC-803 | Gastric cancer | MTT | 48 h | 85.70 | [] |
| HT-29 | Colorectal cancer | MTS | 72 h | 40 | [] |
| RPMI 8226 | Myeloma | MTT | 24 h | 168.5 | [] |
| BEL-7402 | Hepatocellular carcinoma | MTT | 48 h | 54.96 | [] |
| MCF-7 | Breast cancer | MTT | 72 h | CC50 = 56.46 μM | [] |
| U2OS | Osteosarcoma | MTT | 48 h | 53 | [] |
| CNE1 | Nasopharyngeal cancer | MTT | 144 h | 20.95 | [] |
| C33A | Cervical cancer | MTT | 96 h | 200 | [] |
2.3. Antimicrobial Activity and Biofilm Formation
Various biological effects of baicalein have been reported, including antimicrobial and antifungal ones [,,]. According to the study by Jang [], baicalein exhibited antimicrobial activity against cariogenic bacteria and periodontal pathogenic bacteria (MICs 80–320 μg mL−1; MBCs 160–640 μg mL−1), but the effect was lower compared to ampicillin (MICs 0.25–0.5 μg mL−1; MBCs 32–64 μg mL−1). Additionally, baicalein showed antibacterial action towards Staphylococcus aureus with minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 256 μg mL−1 []. Moreover, baicalein at a dose of 16 μg mL−1 synergistically restored the antibacterial actions of ciprofloxacin against Gram-positive bacteria []. In addition, the bacteriostatic effect of baicalein was also shown in combination with baicalein-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex into polyvinyl alcohol nanofibers (PVA-Ba-IC-NF) against Gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli []. The latest studies confirmed the antibacterial activity of baicalein against Staphylococcus epidermidis with a MIC value of 34 μg mL−1 (corresponds to 126 μmol L−1) []. What is more, in the same report antimicrobial action of baicalein adsorbed on the hydroxyapatite layer is described. Bacterial growth was significantly reduced (by one order of magnitude) on the baicalein-HAp particles compared to pure hydroxyapatite.
Another feature of baicalein is its antifungal activity. The group of Serpa [] demonstrated inhibitory effect of baicalein against several Candida strains (C. albicans, C. tropicalis, C. parapsilosis) with MIC50 values ranging from 13 to 104 μg mL−1. Moreover, all tested species exposed to baicalein showed a high loss of viability through ROS accumulation. For Candida krusei isolates, baicalein exhibited in vitro antifungal activity with a MIC value of 2.7 μg mL−1 []. Antifungal activity has also been tested on Aspergillus fumigatus, where baicalein at the concentration of 0.25 mM inhibited the growth of the fungus by 90% []. Additionally, baicalein, at the same amount, remarkably decreased the number of conidia adhering to the surface of human corneal epithelial cells (HCECs). Furthermore, in the microbroth dilution method, the antifungal action of baicalein was observed against human pathogenic fungi Trichophyton rubrum and Trichophyton mentagrophytes []. Pronounced growth inhibition was detected at MICs doses of 0.12 mM and 0.06 mM for T. rubrum and T. mentagrophytes, respectively.
Further studies were conducted to evaluate synergism between baicalein and other antifungal compounds. A combination of baicalein and berberine hydrochloride showed a strong inhibitory effect on the growth of Candida albicans, with a fractional inhibitory concentration index (FICI) of 0.5. Moreover, the combinations of baicalein-quercetin and baicalein-fluctonazole also demonstrated synergistic interactions against C. albicans with FICI values of 0.37 and 0.32, respectively [].
Biofilm formation is a common strategy of bacteria in response to environmental stress []. The development of a biofilm intensifies the capacity of bacteria to evade antibiotics by blocking their penetration through the bacterial biofilm layers. This may be very dangerous for patients.
It was confirmed that baicalein, in combination with linezolid, had the potential to decrease biofilm formation by over 50% []. An in vivo study [] showed that baicalein reduced cell attachment and was able to eradicate 7-day biofilms of Staphylococcus aureus in a dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, treatment with baicalein and vancomycin remarkably reduced the number of bacteria on the carrier. Other studies have been carried out to investigate the efficacy of baicalein-coated gold nanoparticles (BCL-AuNPs) against biofilm formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa []. It was indicated that BCL-AuNPs significantly attenuated bacterial biofilm formation (by approximately 60%). Recent reports revealed a good anti-biofilm potential of baicalein against avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) []. In the range from 12.5 to 50 μg mL−1, baicalein significantly reduced the biofilm formation and adhesion capacity, and this activity was associated with curli fimbria genes—csgA and csgB.
These results suggest that baicalein, in association with various antibiotics, is an effective way to overcome the mechanisms of bacterial resistance and may be used in antifungal therapy.
2.4. Antioxidant Activity
Among other significant biological activities of baicalein, it is worth noting that it has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties [,]. Oxidative stress plays a major role in the pathogenesis of chronic diseases such as respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and neurotic disorders. These activities of baicalein are mainly due to its ability to scavenge reactive oxygen species (ROS) via various mechanisms, in particular by attenuation of the activity of NF-κB [] and suppression of the expression of various inflammatory cytokines and enzymes (e.g., COX, TNF, IL, NO) [].
Ma and co-workers [] reported that baicalein successfully inhibited H2O2-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis in human vitiligo melanocytes (PIG3V) by abolishing Nrf2 knockdown. On top of that, baicalein promoted the expression of Nrf2 nucleus translocation and its target gene, oxygenase-1 (HO-1). The same conclusions were drawn by Lee [] in an in vivo study on Chinese hamster lung fibroblasts (V79-4). Because of its chemopreventive activity, baicalein improves antioxidant status in lung carcinogenesis by reducing DNA damage in lung tissue and restoring the elevated glycoprotein level to normality []. The ability of baicalein to indirectly inhibit •OH radical production was observed in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells through the Fe2+-chelation pathway [].
2.5. Antidiabetic Activity of Baicalein
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disease characterized by insufficiency in insulin secretion from pancreatic β-cells, which leads to the accumulation of glucose in plasma and eventually to hyperglycemia []. Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is an autoimmune disorder resulting from the destruction of the insulin-making cells in the pancreas, while type 2 diabetes (T2D) is due to insulin resistance, which is the case when cells do not respond properly to insulin []. A decrease in insulin action is accompanied by the upregulation of insulin secretion and vice versa. Dysregulation of these metabolic pathways is a main factor leading to both T1D and T2D []. In consequence, an agent capable of improving the function of the pancreatic β-cells would be potent for the treatment of diabetes.
A diet containing baicalein (250 and 500 mg/kg/day) administered to mice with non-genetic type 2 diabetes fed with a high-fat diet (HFD) led to a significant amelioration of glucose tolerance, hyperglycemia, and blood insulin levels compared to the control group []. These effects of baicalein are associated with the improvement of islet β-cell survival and mass. In another animal model study, oral administration of baicalein (400 mg/kg/day) to HFD-fed mice improved the severity of obesity, insulin resistance, inflammation, hyperglycemia, and hyperlipidemia in diabetic mice []. Supplementation with baicalein revealed that inhibition of inflammation and insulin resistance works through activation of AMPK. Additionally, baicalein (90 mg mL−1) pretreatment to primary culture of hepatocytes from the liver of wild-type mice and AMPKa2-stimulated mice in glucose solution (25 mM) showed noteworthy inhibition of MAPKs signaling pathway by downregulation of ERK and p38 phosphorylation in a wild-type hepatocyte culture. However, it was no such effect in AMPKa2-stimulated hepatocytes [].
In another study carried out by the group of Fu et al. [], the treatment of insulin-secreting pancreatic INS382/13 cells and human islets cultured under hyperlipidemic conditions with baicalein at a dose of 5 mM significantly elevated glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) and promoted the viability of the insulin-secreting cells and the islets.
These findings demonstrate that baicalein may serve as a natural antidiabetic agent that directly modulates pancreatic β-cell function and significantly improves metabolic syndrome disorders by blocking the AMPKa2-mediated MAPKs signaling pathway.
2.6. Baicalein’s Activity in Respiratory Diseases
Pulmonary fibrosis is a severe lung condition in which collagen is excessively accumulating in the extracellular matrix, leading to respiratory failure []. Although the mechanism by which baicalein suppresses the increase in collagen in fibroblasts remains unknown, recent studies suggest that baicalein attenuates mRNA molecules and downregulates connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) in correlation with transforming growth factor β1 (TGF β1) [].
Long-term supplementation of baicalein (50 and 100 mg/kg/day) to bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrotic rats notably decreased the severity of pulmonary fibrosis in the baicalein-treated rats []. Baicalein demonstrated the antifibrotic effect by lowering levels of miR-21 and downregulating expression of TGF-β1, as well as by reduction of hydroxyproline and alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) levels in the lung tissue.
The human mast cells (HMCs) are multifunctional tissue-dwelling cells associated with the allergic response. They are capable of regulating inflammation and are involved in host defense and innate immunity []. The HMCs display different pharmacological properties depending on their locations within tissues. They express high-affinity receptors for antibodies [], have the ability to secret inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-6 and IL-8) [], and mediate in antigen-induced inflammation of the respiratory endothelium [].
In an in vivo assay performed by Hsieh and co-workers [], baicalein at a dose of 30 μM inhibited the production of cytokines IL-6, IL-8, and MCP-1 from IL-1β and TNF-α-activated culture of human must cells (HMCs). The inhibitory effects are associated with the suppression of NF-κB activation and IκBα phosphorylation and degradation (Table 2).
Consequently, these findings indicate the usefulness of baicalein in the treatment of allergic and asthmatic disorders in humans by regulation of the NF-κB pathway. What is more, baicalein demonstrated a protective effect against acute lung injury (ALI) through direct and selective binding to myeloid differentiation factor 2 (MD2) [].
2.7. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Baicalein in Food Allergy
Bowel diseases are a group of disorders caused by chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. It happens through interference or dysfunction of regulatory T cells (Treg), which play a pivotal role in immune homeostasis [].
In a mouse model study, administration of baicalein at a dose of 20 mg kg−1 to mice with ovalbumin-induced food allergy alleviated the symptoms of food allergy and reduced the level of serum IgE and effector T cells by induction of CD4+Foxp3+T cell differentiation []. Food allergic immune response was attenuated by differentiation of Treg cells through the aryl hydrocarbon receptor and by enhancement of intestinal barrier function. In addition, supplementation with baicalein may contribute to the prevention of food allergic disorders and inflammatory bowel diseases.
Additionally, baicalein (10 mg kg−1 or 25 mg kg−1) was administrated to mice with experimental colitis in combination with curcumin []. Co-administration of baicalein and curcumin ameliorated pathological symptoms of colonic inflammation, such as the severity of rectal bleeding and diarrhea, by blocking the expression of downstream enzymes, COX-2, iNOS, and cyclin D1, which are associated with the induction of colitis. The synergistic effect was much stronger than those achieved with each of the compounds alone.
Thus, further research on baicalein potency might be essential to understand its mechanism of action and could be helpful in preventing inflammatory bowel diseases caused by food allergies.
2.8. Baicalein’s Activity in Cardiovascular Diseases
Cardiac fibrosis occurring after myocardial infarction is frequently the cause of morbidity and mortality []. Activation of 12-lipoxygenase (12-LOX) has been shown to promote neuronal death, along with overexpression of MMP-9 (Figure 2) []. Additionally, brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) is considered a key marker in heart failure [].
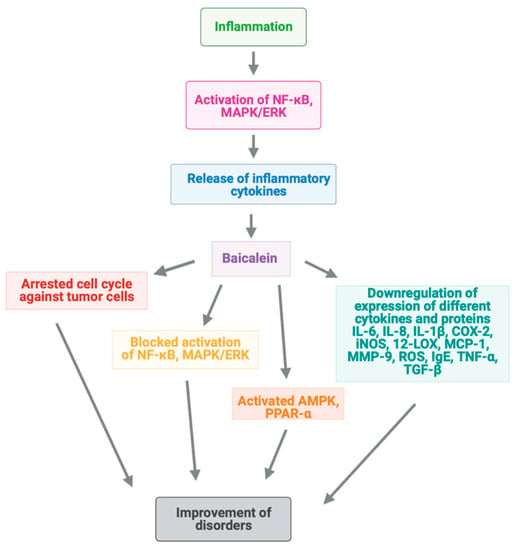
Figure 2.
Mechanisms of baicalein action for amendment of inflammation via different signaling pathways.
Oral administration of baicalein (200 mg kg−1 per day) for a 12-day period to spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs) attenuated myocardial fibrosis by diminution the collagen content in the left ventricle and reduced both systolic blood pressure and plasma BNP level. These happened by suppression of the expression or activity of 12-LOX, pERK, and MMP-9 in cardiac tissue []. Therefore, baicalein could be an adequate agent for the treatment of hypertension-related cardiac fibrosis.
Macrophage cholesterol accumulation and foam cell formation are the crucial steps leading to the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis []. Under oxidative stress, reactive oxygen species (ROS) produced by vascular cells oxidize LDL to form oxidized low-density lipoproteins (oxLDL). These particles are taken up by activated macrophages through their scavenger receptors. This leads to the cellular accumulation of cholesterol and oxysterols [].
Most recent studies showed that baicalein suppressed oxLDL-induced cholesterol accumulation by reducing oxLDL uptake through competitive inhibition of the CD36 binding to the epitope structure of oxLDL []. Furthermore, this junction (baicalein to CD36 receptor) enhanced the cholesterol efflux through the CD36-Src-JNK-ABCA1 signaling pathway.
Pretreatment of the cultured high glucose-stimulated human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) with baicalein at a dose of 10 mM suppressed vascular inflammation due to inhibition of NF-kB activation, attenuation of expression of cell adhesion molecules (CAMs), decreasing cell-cell adhesion/migration and diminishing disruption of endothelial barrier function [].
Another in vivo study demonstrated that post-treatment with baicalein (20 mg kg−1) in LPS-induced septic rats effectively ameliorated cardiovascular dysfunction by improving blood pressure and survival rate through the inhibition of NF-kB activation and reduction of elevated levels of plasma necrosis factor α (TNF-α), iNOS protein, NO and superoxide anions []. Moreover, further studies on LPS-induced septic rats showed that supplementation with baicalein (10 mg kg−1) improved cardiac contractile function by reducing the oxidative stress and apoptosis through induction of cardiac HO-1 production and reduction of increased levels of iNOS and MCP-1 protein []. Other works also revealed that baicalein plays a protective role in myocardial damage [].
2.9. Baicalein in Diet
Insufficiency of nutrients may have a negative impact on human and animal health and lead to the derangement of homeostasis. Naturally derived supplements are desirable in a diet due to their numerous physiological benefits [].
Supplementation of baicalein (0.1% and 0.3% of initial body weight per day) to koi carp fish (Cyprus carpio) significantly increased their weight gain rate, specific growth rate, and spleen index and simultaneously decreased their liver-to-body weight ratio leading to improvement of the growth performance [].
Additionally, a long-term diet supplemented with baicalein (100 and 200 mg kg−1) to broiler chickens demonstrated a noteworthy increase in the body weight and feed conversion ratio of the birds compared to the basal diet []. Furthermore, triglycerides and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol were significantly decreased after the intake of baicalein compared to the chickens fed with the control diet. Other studies have been established on the same chicken model, but the animals were fed with baicalein during the early post-hatch stage []. These data indicated that breast muscles, as well as subcutaneous and abdominal fat weights, were reduced in chicks fed with 500 mg kg−1 of baicalein.
These observations provide evidence for the opposite double-effect of baicalein supplementation, depending on the period of maturation.
2.10. Antidepressant Action of Baicalein
Depression is a common mental disorder in which monoamines are the major neurotransmitters []. Nearly all compounds that are able to inhibit monoamine reuptake have been proven to be clinically effective antidepressants [].
In the animal model study, treatment of mice with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (5 mg kg−1) induced depression-like behavior, then administration of baicalein (3 mg kg−1) notably diminished the duration of their immobility in behavioral tests, indicating that baicalein can normalize depression-like symptoms []. Moreover, upon treatment with baicalein the production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which is a critical regulator in neuronal survival, decreased significantly. Similar conclusions were drawn by Xiong and co-workers [].
Earlier reports suggest that baicalein demonstrates antidepressant action through the inhibition of MAO A, the enzyme which plays a crucial role in CNS regulation []. The most current studies indicate that baicalein (20 mg kg−1) promotes neuronal maturation and rescues neurons from apoptosis via inhibiting activation of the GSK3β/NF-κB/NLRP3 signal pathway in chronic unpredictable mild stress mice (CUMS) [].
Other studies have been conducted to assess the therapeutic potential of baicalein for the treatment of brain injury caused mostly by an ischemic stroke.
The team of Yang [] proved that baicalein enhanced neurobehavioral function recovery after ischemia-reperfusion brain injury. The effects of treatment with baicalein, such as suppression of neuronal swelling and restoration of a dense arrangement of neurons, appear to be due to the regulation of microglia/macrophages M1/M2 transformation. On that basis, the latest reports demonstrate that baicalein attenuates ferroptosis activity through GPX4/ACSL4/ACSL3 axis [].
These data suggest that baicalein is likely to protect neurons by reducing neuroinflammation, apoptosis, and oxidative stress, and therefore it is an effective agent for neurological dysfunctions.

Table 2.
Summary of the protective effects of baicalein in various experimental models.
Table 2.
Summary of the protective effects of baicalein in various experimental models.
| Experimental Model | Mechanism of Action | Effect | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mouse | Promoted pancreatic β-cell insulin secretory function | Antidiabetic | [] |
| Rat pulmonary fibrosis model | Repressed miR-21 expression | Antifibrotic | [] |
| Cell culture of HMC-1 cells | Inhibited IL-6, IL-8, and MCP-1 production | Anti-inflammatory | [] |
| Mouse | Decreased level of serum IgE, mMCP-1, Th-1, and Th-17 | Antiallergic | [] |
| Sodium-induced mouse colitis | Attenuated activity and phosphorylation of IKKβ | Anticancer | [] |
| Culture of THP-1 macrophages | Inhibited intracellular cholesterol accumulation | Anti-atherosclerosis | [] |
| LPS-induced rats septic shock | Ameliorated increase in hepatic TNF-a, and inhibited iNOS protein expression | Protective effect against endotoxemia | [] |
3. Conclusions
Baicalein is one of the most potent antioxidants contained in Baikal skullcap, with significant anti-inflammatory activity. More and more research teams all over the world also confirm its high anticancer potential. Moreover, it was demonstrated that baicalein is beneficial in the treatment of metabolic diseases, e.g., diabetes, cardiovascular diseases (such as hypertension), and respiratory diseases, including allergic and asthmatic ones. There is some evidence that baicalein may help in the treatment of nervous system disorders, including neurological diseases, by preventing destructive changes to neurons caused by, for example, oxidative stress. Baicalein may also be used as a therapeutic agent to inhibit the development of pathogenic microorganisms, such as coagulase-positive Staphylococcus aureus, Enterobacteriaceae, and yeasts of the genus Candida, which are often responsible for nosocomial infections and development of many diseases. The data presented above spur further research on finding optimal ways of baicalein delivery and the methods of its medical use for people. Along with a dynamic increase in the number of patients, especially oncology ones, and the emergence of new human diseases, and because of the acquired drug resistance to therapies used so far, there is a growing need for new initiatives aiming to develop more precise methods of targeted therapies. Ingesting natural antioxidants with food is one of the safer health promotion strategies. Determination of safe therapeutic doses of natural low-molecular-weight polyphenols, including baicalein, may be effective in the treatment of oxidative-stress-related disorders, which play an important role in the pathogenesis of many diseases, including cancers, cardiovascular diseases, and neurodegenerative disorders. Therefore, the next steps of the research should focus on providing evidence that baicalein has no side effects and on the determination of effective physiological concentrations of baicalein based on detailed preclinical studies, followed by clinical trials in people.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.C. and M.S.-G.; writing—original draft preparation, M.C. and M.S.-G.; writing—review and editing, M.C. and M.S.-G.; supervision, M.S.-G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Monika Stompor-Gorący acknowledges support from the National Centre NCN Poland, Grant SONATA 16 number 2020/39/D/NZ9/02023), and also would like to thank the Polish Ministry of Science and Higher Education (currently Polish Ministry of Education and Science) for the financial support under the MNiSW scholarship for outstanding young researchers (STYP/15/0763/E-546/2020). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Stompor, M. A review on sources and pharmacological aspects of sakuranetin. Nutrients 2020, 12, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haruna, N.; Norie, M.; Kensaku, K.; Masaki, T.; Shigeo, T.; Jun, K.; Young-Ran, L.; Donghak, K.; Hiroshi, Y.; Masayuki, K.; et al. Oxidation of flavone, 5-hydroxyflavone, and 5,7-dihydroxyflavone to mono-, di-, and tri-hydroxyflavones by human cytochrome P450 enzymes. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2019, 32, 1268–1280. [Google Scholar]
- Wan Yin, T.; Chu Shan, T.; Chong Seng, Y.; Hui Wei, L.; Xu, W.; Xu, W.; Fei, Y.M. Evaluation of vasodilatory effect and antihypertensive effect of chrysin through in vitro and sub-chronic in vivo study. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 157, 114020. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, G.H.; Lee, J.H.; Han, S.H.; Woo, J.S.; Choi, E.Y.; Jeon, S.J.; Han, E.J.; Jung, S.H.; Park, Y.S.; Park, B.K.; et al. Chrysin induces apoptosis via the MAPK pathway and regulates ERK/mTOR-mediated autophagy in MC-3 cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shintaro, O.; Naoki, Y.; Daisuke, M.; Tomoya, K.; Yasuyuki, K.; Takehiro, K.; Takanori, F.; Hirotaka, O.H.; Naoki, H.; Yoshihisa, N.; et al. 5-Hydroxy-7-methoxyflavone derivatives from Kaempferia parviflora induce skeletal muscle hypertrophy. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 312–321. [Google Scholar]
- Escribano-Ferrer, E.; Queralt Regué, J.; Garcia-Sala, X.; Boix Montanés, A.; Lamuela-Raventos, R.M. In vivo anti-inflammatory and antiallergic activity of pure narninegnin, naringenin chalcone, and quercetin in mice. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stompor, M.; Żarowska, B. Antimicrobial activity of xanthohumol and its selected structural analogues. Molecules 2016, 21, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stompor, M.; Uram, Ł.; Podgórski, R. In vitro effect of 8-prenylnaringenin and naringenin on fibroblasts and glioblastoma cells-cellular accumulation and cytotoxicity. Molecules 2017, 22, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeini, F.; Namkhah, Z.; Tutunchi, H.; Rezayat, S.M.; Mansouri, S.; Yaseri, M.; Hosseinzadeh-Attar, M.J. Effects of naringenin supplementation on cardiovascular risk factors in overweight/obese patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A pilot double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 34, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazyar, H.; Moradi, L.; Zaman, F.; Zare Javid, A. The effects of rutin flavonoid supplement on glycemic status, lipid profile, atherogenic index of plasma, brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), some serum inflammatory, and oxidative stress factors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Phytother. Res. 2023, 37, 271–284. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, L.; Wang, W.; Luo, Y.; Ning, Q.; Xia, Z.; Chen, J.; Jia, X. Polysaccharide from Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi ameliorates colitis via suppressing NF-κB signaling and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 132, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Chen, X.; Yuan, D.; Tang, M.; Xu, K. Baicalin alleviates deoxynivalenol-induced intestinal inflammation and oxidative stress damage by inhibiting NF-κB and increasing mTOR signaling pathways in piglets. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 140, 111326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, N.; Mishra, A.; Li, H.; Liu, H.; Wu, Z. Wogonin preventive impact on hippocampal neurodegeneration, inflammation and cognitive defects in temporal lobe epilepsy. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 2149–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.C.; Wei, M.C.; Huang, T.C.; Lee, S.Z.; Lin, S.S. Comparison of modified ultrasound-assisted and traditional extraction methods for the extraction of baicalin and baicalein from Radix Scutellariae. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 45, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Zhang, H.; Ding, L.; Xiao, T.; Zhang, H.; Song, D. Dynamic microwave-assisted extraction of flavonoids from Radix Scutellariae. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2007, 23, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, I.C.; Lin, J.H.; Lee, W.S.; Liu, C.H.; Lin, T.Y.; Yang, K.T. Baicalein and luteolin inhibit ischemia/reperfusion-induced ferroptosis in rat cardiomyocytes. Int. J. Cardiol. 2023, 375, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qi, Z.; Fan, X.; Zhang, H.; Pei, J.; Zhao, L. Biochemical characterization of a flavone synthase I from Daucus carota and its application for bioconversion of flavanones to flavones. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2023, 195, 933–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonawane, S.K.; Balmik, A.A.; Boral, D.; Ramasamy, S.; Chinnathambi, S. Baicalein suppresses Repeat Tau fibrillization by sequestering oligomers. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2019, 675, 108119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhuang, X.; Lu, J. Neuroprotective effects of baicalein in animal models of Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review of experimental studies. Phytomedicine 2018, 1, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Yang, D.; Zhang, L.; Yang, S.; Du, G. The comprehensive study on the therapeutic effects of baicalein for the treatment of COVID-19 in vivo and in vitro. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 183, 114302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Lei, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, B.; Yang, S.; Tuo, X. Inhibition mechanism of baicalein against alcohol dehydrogenase in vitro via biological techniques, spectroscopy and computer simulation. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 360, 119534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Mehrabi Nasab, E.; Athari, S.S. Study effect of baicalein encapsulated/loaded chitosan-nanoparticle on allergic asthma pathology in mouse model. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 4311–4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Li, W.; Fang, C.; Zheng, X.; Liu, C.; Huang, Q. Extraction and identification of new flavonoid compounds in dandelion Taraxacum mongolicum Hand. Mazz. with evaluation of antioxidant activities. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farzipour, S.; Jalali, F.; Alvandi, M.; Shaghaghi, Z. Ferroptosis inhibitors as new therapeutic insights into radiation-induces heart disease. Cardiovasc. Hematol. Agents Med. Chem. 2023, 21, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Sun, Y.; Guo, W.; Wang, J.; Gao, J.; Peng, W.; Gu, J. Identification and high-throughput quantification of baicalein and its metabolites in plasma and urine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 301, 115853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cathcart, M.C.; Useckaite, Z.; Drakeford, C. Anti-cancer effects of baicalein in non-small cell lung cancer in-vitro and in-vivo. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Li, J.; Bie, B.; Sun, J.; Mu, Y.; Shi, M.; Guo, Y. MiR-3663-3p participates in the anti-hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation activity of baicalein by targeting SH3GL1 and negatively regulating EGFR/ERK/NF-κB signaling. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2021, 420, 115522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.Z.; Leung, H.W.; Lai, M.Y.; Wu, C. Baicalein induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human lung squamous carcinoma CH27 cells. Anticancer Res. 2005, 25, 959–964. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, D.; Xing, J.; Duan, Y.; Wang, S.; Yao, G.; Zhang, S.; Jin, J.; Lin, Z.; Chen, L.; Piao, Y. The molecular mechanism of baicalein repressing progression of gastric cancer mediating miR-7/FAK/AKT signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 2022, 100, 154046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Hu, J.; Shi, B.; Tie, J. Baicalein enhanced cisplatin sensitivity of gastric cancer cells by inducing cell apoptosis and autophagy via Akt/mTOR and Nrf2/Keap 1 pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 531, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, H.; Hui, Y.; Xiaoping, T.; Wei, T.; Jiyi, X.; Xiaolan, Y. Baicalein suppresses the proliferation of human cervical cancer cells via Notch 1/Hes signaling pathway. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2019, 15, 1216–1220. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; You, H.; Li, D. Baicalein exerts anticancer effect in nasopharyngeal carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Oncol. Res. Featur. Preclin. Clin. Cancer Ther. 2019, 27, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Liu, B.; Sun, J.; Lu, L.; Liu, L.; Qiu, J.; Li, Q.; Yan, C.; Jiang, S.; Mohammadtursun, N.; et al. Baicalein inhibits orthotopic human non-small cell lung cancer xenografts via Src/Id1 pathway. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 9806062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.C.; Yan, W.; Dai, Z.; Gao, X.; Ma, Y.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, S. Baicalein suppresses metastasis of breast cancer cells by inhibiting EMT via downregulation of SATB1 and Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2016, 10, 1419–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, Y.; Xu, J.; Yan, B. The anti-metastatic effect of baicalein on colorectal cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 2317–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Lu, M.; Jiang, X.X.; Pan, M.X.; Mao, J.W.; Chen, M. Correction to: Inhibiting reactive oxygen species-dependent autophagy enhanced baicalein-induced apoptosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Nat. Med. 2021, 75, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Shang, J.; Chen, D.L.; Li, S.Y.; Fan, R.; Li, R.H.; Li, H.Q.; Zhang, S.Y.; Shen, D.Y. Baicalein mediates anticancer effect on cholangiocarcinoma through co-targeting the AKT/NF-κB and STAT3 signaling pathway. Process Biochem. 2021, 102, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.; Nguyen, V.H.; A’lincourt Salazar, M.; Wong, P.; Diamond, D.J.; Yim, J.H.; Melstrom, L.G. Inhibition of autophagy amplifies baicalein-induced apoptosis in human colorectal cancer. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2020, 19, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.Y.; Liu, L.P.; Qin, J.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, D.; Mo, S.L. Baicalein decreases side population proportion via inhibition of ABCG2 in multiple myeloma cell line RPMI 8226 in vitro. Fitoterapia 2014, 94, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Duan, B.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, R.; Sun, J.; Bie, B.; Li, Z. Baicalein sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to 5-FU and Epirubicin by activating apoptosis and ameliorating P-glycoprotein activity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 98, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.T.; Liu, C.H.; Wong, S.H.; Pan, Y.C.; Lin, L.T. Small molecules baicalein and cinnamaldehyde are potentiators of measles virus-induced breast cancer oncolysis. Phytomedicine 2021, 89, 153611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Peng, L.; Shi, C.J.; Li, J.; Pang, F.; Fu, W.; Pan, X.; Zhang, J. Baicalein mediates the anti-tumor activity in Osteosarcoma through lncRNA-NEF driven Wnt/β-catenin signaling regulatory axis. J. Orthop. Transl. 2022, 33, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Ding, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Li, L. Baicalein induces autophagy and apoptosis through AMPK pathway in human glioma cells. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2019, 47, 1405–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Mao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, J. Baicalein induces cervical cancer apoptosis through the NF-κB signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 5088–5094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonham, M.; Posakony, J.; Coleman, I.; Montgomery, B.; Simon, J.; Nelson, P.S. Characterization of chemical constituents in Scutellaria baicalensis with antiandrogenic and growth-inhibitory activities toward prostate carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 3905–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Liu, W.Y.; Feng, F.; Wu, C.Y.; Xie, N. Synthesis and in vitro cytotoxicity evaluation of baicalein amino acid derivatives. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2013, 11, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Wang, J.; Zhao, L.; Lu, N.; You, Q.; Guo, Q.; Li, Z. Synthesis and biological evaluation of baicalein derivatives as potent antitumor agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 1334–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhou, J.; Lin, Q.; Gong, G.; Sun, H.; Liu, W.; Qu, W. Anti-angiogenic and anticancer effects of baicalein derivatives based on transgenic zebrafish model. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 4481–4492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, D.; Song, Z.; Yi, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, G.; Cong, D.; Li, N.; et al. Oroxylin A, a methylated metabolite of baicalein, exhibits a stronger inhibitory effect than baicalein on the CYP1B1-mediated carcinogenic estradiol metabolite formation. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, T.; He, Z.; Dai, Y.; Yao, J.; Guo, Q.; Wei, L. Oroxylin A suppresses the development and growth of colorectal cancer through reprogram of HIF1α-modulated fatty acid metabolism. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, M.; Shen, M.; Li, Y.; Tan, S.; Shao, J.; Zhang, F.; Chen, A.; Wang, S.; Zheng, S. Oroxylin A regulates the turnover of lipid droplet via downregulating adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL) in hepatic stellate cells. Life Sci. 2019, 238, 116934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhtari, R.B.; Homayouni, T.S.; Baluch, N.; Morgatskaya, E.; Kumar, S.; Das, B.; Yeger, H. Combination therapy in combating cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 38022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Sharma, A.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Ding, X. Orthogonal array composite design to study and optimize antioxidant combinations in the prevention of UVB-induced HSF damage. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2018, 178, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Ji, F.; Sun, W.; Wang, J.; Guo, J.; Guo, L.; Bao, Y. Combination of baicalein and 10-hydroxy camptothecin exerts remarkable synergetic anti-cancer effects. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 1778–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Feng, J.; Sun, M.; Yuan, W.; Xiao, R.; Xiong, J.; Shao, L. Synergistic effects of baicalein with gemcitabine or docetaxel on the proliferation, migration and apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 51, 1878–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Su, J.; Li, Z.; Zhan, Y.; Ye, D. Hyaluronic acid-coated, prodrug-based nanostructured lipid carriers for enhanced pancreatic cancer therapy. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2016, 43, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Han, S.E.; Nam-Goong, I.S.; Kim, Y.I.; Kim, E.S. Combined effects of baicalein and docetaxel on apoptosis in 8505c anaplastic thyroid cancer cells via downregulation of the ERK and Akt/mTOR pathways. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 33, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, J.; Pu, G.; Zhang, F.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y. Co-delivery of baicalein and doxorubicin by hyaluronic acid decorated nanostructured lipid carriers for breast cancer therapy. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 1364–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Xue, M.; Xiao, S.S.; Wan, Y.J.; Xu, D.B. A Combination therapy with baicalein and taxol promotes mitochondria-mediated cell apoptosis: Involving in akt/β-catenin signaling pathway. DNA Cell Biol. 2016, 35, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, F.; Wang, W.; Xi, M.; Duan, X.; Wang, Y. Delivery of baicalein and paclitaxel using self-assembled nanoparticles: Synergistic antitumor effect in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Huang, T.S.; Wong, C.H.; Hong, C.L.; Tsai, Y.H.; Liang, C.C.; Lu, F.J.; Chang, W.H. Synergistic anti-cancer effect of baicalein and silymarin on human hepatoma HepG2 Cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, Z.X.; OuYong, B.M.; Hassandarvish, P.; Poh, C.L.; Ramanathan, B. Antiviral activity of silymarin and baicalein against dengue virus. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, S.; Kim, S.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, M.S.; Shin, D.H. Flavonoids with inhibitory activity against SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 1539–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Q.F.; Wang, H.; Han, X.B.; Lin, Y.; Yang, Y.H.; Gu, L.G.; Zhao, J.Q.; Wang, L.; Huang, L.; Li, Y.B.; et al. Baicalin inhibits TLR7/MYD88 signaling pathway activation to suppress lung inflammation in mice infected with influenza A virus. Biomed. Rep. 2014, 2, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Long, C.; Sun, X. Baicalein inhibits growth of Epstein-Barr virus-positive nasopharyngeal carcinoma by repressing the activity of EBNA1 Q-promoter. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 102, 1003–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Li, N.; Niu, F. Baicalein triazole prevents respiratory tract infection by RSV through suppression of oxidative damage. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 131, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, D.; Jia, Y.; He, L.; Li, J.; Yu, C.; Liao, C.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, C. Anti-inflammatory effects and antiviral activities of baicalein and chlorogenic acid against infectious bursal disease virus in embryonic eggs. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 100987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Kuang, X.; Zhou, Q.; Yan, C.; Li, W.; Gong, H.; He, R. Inhibitory effects of baicalein against herpes simplex virus type 1. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10, 2323–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Dai, B.; Wang, Y.; Huang, S.; Xu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Gao, P.; Zhu, Z.; Jiang, Y. In vitro activity of baicalein against Candida albicans biofilms. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2008, 32, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jiao, H.; Meng, J.; Qiao, M.; Du, H.; He, M.; Wu, Y. Baicalin inhibits biofilm formation and the quorum-sensing system by regulating the MsrA drug efflux pump in Staphylococcus saprophyticus. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xie, S.; Gao, J.; He, L.; Luo, W.; Tang, Y.; Weir, M.D.; Oates, T.W.; Xu, H.H.K.; Yang, D. Flavonoid baicalein suppresses oral biofilms and protects enamel hardness to combat dental caries. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, E.J.; Cha, S.M.; Choi, S.M.; Cha, J.D. Combination effects of baicalein with antibiotics against oral pathogens. Arch. Oral Biol. 2014, 59, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, T.; Wang, K.; Hou, C.; Cai, S.; Huang, Y. Baicalein inhibits Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation and the quorum sensing system in vitro. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, B.C.L.; Ip, M.; Lau, C.B.S.; Lui, S.L.; Jolivalt, C.; Ganem-Elbaz, C.; Leung, P.C. Synergistic effects of baicalein with ciprofloxacin against NorA over-expressed methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and inhibition of MRSA pyruvate kinase. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 137, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wang, X.; Han, L.; Li, S.; Zhou, W. Antioxidant and antimicrobial polyvinyl alcohol electrospun nanofibers containing baicalein-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 614, 126135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palierse, E.; Hélary, C.; Krafft, J.M.; Génois, I.; Masse, S.; Laurent, G.; Jolivalt, C. Baicalein-modified hydroxyapatite nanoparticles and coatings with antibacterial and antioxidant properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 118, 111537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serpa, R.; Franca, E.J.G.; Furlaneto-Maia, L.; Andrade, C.G.T.J.; Diniz, A.; Furlaneto, M.C. In vitro antifungal activity of the flavonoid baicalein against Candida species. J. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 61, 1704–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.A.; Zhang, R.; Piao, M.J.; Chae, S.; Kim, H.S.; Park, J.H.; Hyun, J.W. Baicalein inhibits oxidative stress-induced cellular damage via antioxidant effects. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2011, 28, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Peng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, J.; Zhao, G. Baicalein protects against Aspergillus fumigatus keratitis by reducing fungal load and inhibiting TSLP-induced inflammatory response. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2021, 62, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, X.; Nishiyama, Y.; Tie, D.; Hein, K.Z.; Yamamoto, O.; Morita, E. Antifungal activity and mechanism of action of Ou-gon (Scutellaria root extract) components against pathogenic fungi. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janeczko, M.; Gmur, D.; Kochanowicz, E.; Górka, K.; Skrzypek, T. Inhibitory effect of a combination of baicalein and quercetin flavonoids against Candida albicans strains isolated from the female reproductive system. Fungal Biol. 2022, 126, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvasnickova, E.; Matatkova, O.; Cejkova, A.; Masak, J. Evaluation of baicalein, chitosan and usnic acid effect on Candida parapsilosis and Candida krusei biofilm using a Cellavista device. J. Microbiol. Methods 2015, 118, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Luo, J.; Bi, G.; Du, Z.; Kong, J.; Chen, Y. Antibacterial synergy between linezolid and baicalein against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus biofilm in vivo. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 147, 104411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajkumari, J.; Busi, S.; Vasu, A.C.; Reddy, P. Facile green synthesis of baicalein fabricated gold nanoparticles and their antibiofilm activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 107, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.Y.; Yuan, M.; Wu, Z.M.; Song, K.; Zhang, C.L.; An, Q.; Via, F.; You, J.L.; Yi, P.F.; Fu, B.D.; et al. Anti-bacterial activity of baicalin against APEC through inhibition of quorum sensing and inflammatory responses. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Wang, F.; Cao, X.; Pan, H.; Liu, X.; Hu, X.; Sun, Y. Baicalin protects PC-12 cells from oxidative stress induced by hydrogen peroxide via anti-apoptotic effects. Brain Inj. 2014, 28, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Du, G.; Qin, X.; Gao, L. Baicalein attenuates the neuroinflammation in LPS-activated BV-2 microglial cells through suppression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, COX2/NF-κB expressions and regulation of metabolic abnormality. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 79, 106092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, B.; Yu, Z.; Yuan, P.; Sun, T.; Gong, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, S.; Liu, K.; et al. Baicalein alleviates erectile dysfunction associated with streptozotocin-induced type I diabetes by ameliorating endothelial nitric oxide synthase dysfunction, inhibiting oxidative stress and fibrosis. J. Sex. Med. 2020, 17, 1434–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, S.; Zhu, L.; Guo, S.; Yi, X.; Cui, T.; Jian, Z. Baicalein protects human vitiligo melanocytes from oxidative stress through activation of NF-E2-related factor2 (Nrf2) signaling pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 129, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.K.; Kang, K.A.; Zhang, R.; Kim, B.J.; Kang, S.S.; Hyun, J.W. Mitochondria protection of baicalein against oxidative damage via induction of manganese superoxide dismutase. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2011, 31, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveenkumar, C.; Raghunandhakumar, S.; Asokkumar, S.; Binuclara, J.; Devaki, T. Baicalein improves antioxidant status and membrane-bound enzymes during oxidative stress in benzo(a)pyrene-induced lung carcinogenesis in mice. Biomed. Prev. Nutr. 2012, 2, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Li, X.; Xie, H.; Wang, X.; Xie, Y.; Chen, C.; Chen, D. Protective mechanism of the antioxidant baicalein toward hydroxyl radical-treated bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Molecules 2018, 23, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golbidi, S.; Alireza Ebadi, S.; Laher, I. Antioxidants in the treatment of diabetes. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2011, 7, 106–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndisang, J.F.; Vannacci, A.; Rastogi, S. Insulin Resistance, Type 1 and type 2 diabetes, and related complications. J. Diabetes Res. 2017, 2017, 1478294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stumvoll, M.; Goldstein, B.J.; van Haeften, T.W. Type 2 diabetes: Principles of pathogenesis and therapy. Lancet 2005, 365, 1333–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Luo, J.; Jia, Z.; Zhen, W.; Zhou, K.; Gilbert, E.; Liu, D. Baicalein protects against type 2 diabetes via promoting islet β-cell function in obese diabetic mice. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 2014, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, P.; Wang, X.A.; Salim, M.; Zhu, L.H.; Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Li, H.L. Baicalein, a natural product, selectively activating AMPKα2 and ameliorates metabolic disorder in diet-induced mice. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 362, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winder, W.W.; Hardie, D.G. AMP-activated protein kinase, a metabolic master switch: Possible roles in Type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 1999, 277, E1–E10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Cui, X.; Chen, X.; Jiang, X. Baicalein alleviated TGF β1-induced type I collagen production in lung fibroblasts via downregulation of connective tissue growth factor. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 131, 110744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.C.; Kan, L.D. Traditional Chinese medicine for pulmonary fibrosis therapy: Progress and future prospects. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 198, 45–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, Z.; Jiang, X. Baicalein attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats through inhibition of miR-21. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 26, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnaswamy, G.; Ajitawi, O.; Chi, D.S. The human mast cell: An overview. Methods Mol. Biol. 2006, 315, 13–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tsujimura, Y.; Obata, K.; Mukai, K.; Shindou, H.; Yoshida, M.; Nishikado, H.; Karasuyama, H. Basophils play a pivotal role in immunoglobulin-G-mediated but not immunoglobulin-E-mediated systemic anaphylaxis. Immunity 2008, 28, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibilano, R.; Frossi, B.; Pucillo, C.E. Mast cell activation: A complex interplay of positive and negative signaling pathways. Eur. J. Immunol. 2014, 44, 2558–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collington, S.J.; Williams, T.J.; Weller, C.L. Mechanisms underlying the localisation of mast cells in tissues. Trends Immunol. 2011, 32, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.J.; Hall, K.; Ha, T.; Li, C.; Krishnaswamy, G.; Chi, D.S. Baicalein inhibits IL-1β- and TNF-α-induced inflammatory cytokine production from human mast cells via regulation of the NF-κB pathway. Clin. Mol. Allergy 2007, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, H.; Sun, C.; Zhang, B.; Liang, G. Inhibition of myeloid differentiation factor 2 by baicalein protects against acute lung injury. Phytomedicine 2019, 63, 152997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuerer, M.; Hill, J.A.; Mathis, D.; Benoist, C. Foxp3+ regulatory T cells: Differentiation, specification, subphenotypes. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, M.J.; Shin, H.S.; See, H.J.; Jung, S.Y.; Kwon, D.A.; Shon, D.H. Baicalein induces CD4+Foxp3+ T cells and enhances intestinal barrier function in a mouse model of food allergy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Surh, Y.; Do, S.; Shin, E.; Shim, K.; Lee, C.; Na, H. Baicalein inhibits dextran sulfate sodium-induced mouse colitis. J. Cancer Prev. 2019, 24, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Chen, Y.; Tillman, K.A.; Cui, Y.; Williams, R.W.; Bhattacharya, S.K.; Sun, Y. Characterizing modifier genes of cardiac fibrosis phenotype in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Int. J. Cardiol. 2021, 330, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayama, Y.; Minamino, T.; Toko, H.; Sakamoto, M.; Shimizu, I.; Takahashi, H.; Komuro, I. Cardiac 12/15 lipoxygenase–induced inflammation is involved in heart failure. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 1565–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Wang, J.A. Brain natriuretic peptide and optimal management of heart failure. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B. 2005, 6, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, E.K.C.; Yu, S.; Sanderson, J.E.; Chen, K.B.; Huang, Y.; Yu, C.M. A novel anti-fibrotic agent, baicalein, for the treatment of myocardial fibrosis in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 658, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, P. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature 2002, 420, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, K.K.; Gershenzon, E.; Grinstein, S. Cholesterol accumulation by macrophages impairs phagosome maturation. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 35745–35755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Xiong, T.; Wang, T.; Wang, M.; Wang, C.; Yang, F.; Wang, X.; Tan, Z.; Sun, W. Baicalein targets CD36 to prevent foam cell formation by suppressing the excessive uptake of oxLDL and accelerating ABCA1-mediated cholesterol efflux in oxLDL-induced THP-1 macrophages. J. Funct. Food. 2022, 97, 105253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, S.K.; Bae, J.S. Baicalin, baicalein and wogonin inhibits high glucose-induced vascular inflammation in vitro and in vivo. BMB Rep. 2015, 48, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.Y.; Lee, Y.M.; Wu, Y.S.; Chang, T.W.; Jin, J.S.; Yen, M.H. Protective effect of baicalein against endotoxic shock in rats in vivo and in vitro. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 73, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.M.; Cheng, P.Y.; Chim, L.S.; Kung, C.W.; Ka, S.M.; Chung, M.T.; Sheu, J.R. Baicalein, an active component of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi, improves cardiac contractile function in endotoxaemic rats via induction of heme oxygenase-1 and suppression of inflammatory responses. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 135, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’amico, R.; Fusco, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Paola, R.D. Effects of a new compound containing palmitoylethanolamide and baicalein in myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury in vivo. Phytomedicine 2018, 54, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, S.R.; Davoodi, H. Herbal plants and their derivatives as growth and health promoters in animal nutrition. Vet. Res. Commun. 2011, 35, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Han, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Bao, S.; Cao, Y. Dietary baicalein improves growth performance, antioxidant activity, and intestinal flora of koi carp (Cyprinus carpio). Aquac. Rep. 2022, 27, 101421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Mao, S.; Zhou, M. Effect of the flavonoid baicalein as a feed additive on the growth performance, immunity, and antioxidant capacity of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 2790–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Halter, B.; Boyer, C.; Cline, M.A.; Liu, D.; Gilbert, E.R. Dietary supplementation of baicalein affects gene expression in broiler adipose tissue during the first week post-hatch. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 697384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasler, G. Pathophysiology of depression: Do we have any solid evidence of interest to clinicians? World Psychiatry 2010, 9, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmaker, R.H.; Agam, G. Major depressive disorder. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.T.; Lin, Y.N.; Tsai, M.C.; Wu, Y.C.; Lee, M.C. Baicalein exerts therapeutic effects against endotoxin-induced depression-like behavior in mice by decreasing inflammatory cytokines and increasing brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Jiang, B.; Wu, P.F.; Tian, J.; Shi, L.L.; Gu, J.; Chen, J.G. Antidepressant effects of a plant-derived flavonoid baicalein involving extracellular signal-regulated kinases cascade. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 34, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Ma, S.; Qu, R.; Kang, D.; Liu, Y. Antidepressant effect of baicalin extracted from the root of Scutellaria baicalensis. in mice and rats. Pharm. Biol. 2006, 44, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, M.; Wu, X.; Zhang, S.; Hua, D.; Li, S.; Yu, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z. Application of TPGS as an efflux inhibitor and a plasticizer in baicalein solid dispersion. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 168, 106071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Du, G. Baicalein administered in the subacute phase ameliorates ischemia-reperfusion-induced brain injury by reducing neuroinflammation and neuronal damage. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 117, 109102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhaoli, Z.; Yu, S.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, W.; Wu, H. Baicalein ameliorates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting ferroptosis via regulating GPX4/ACSL4/ACSL3 axis. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 366, 110137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).