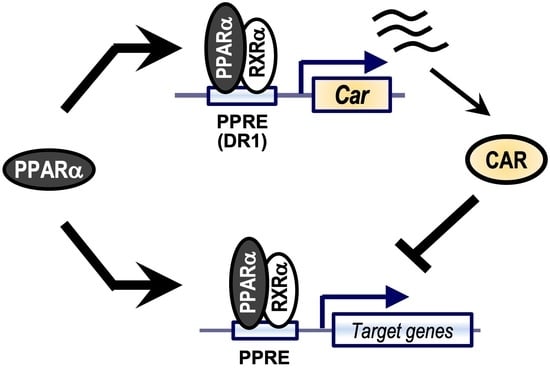
PPARα Induces the Expression of CAR That Works as a Negative Regulator of PPARα Functions in Mouse Livers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
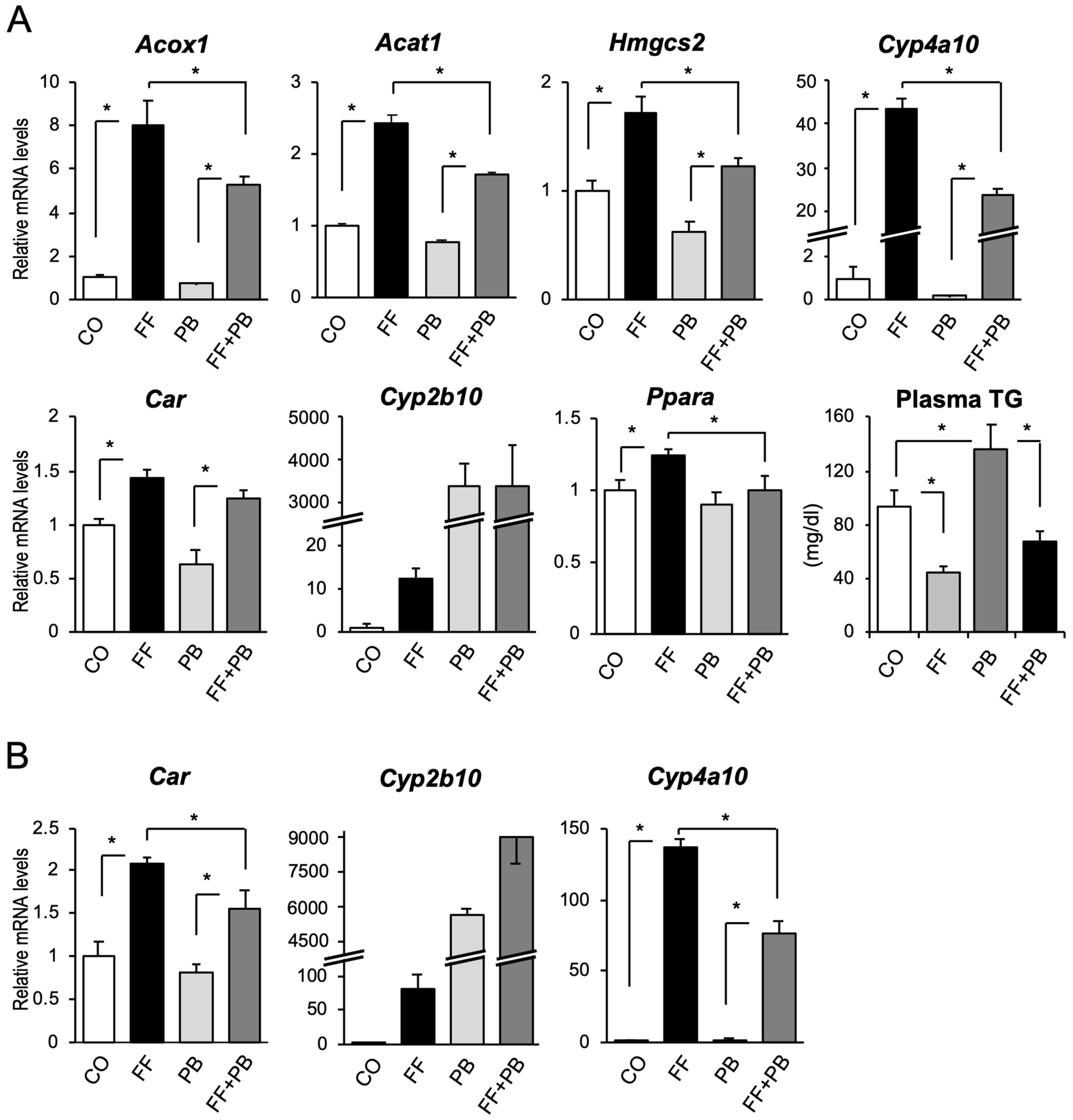
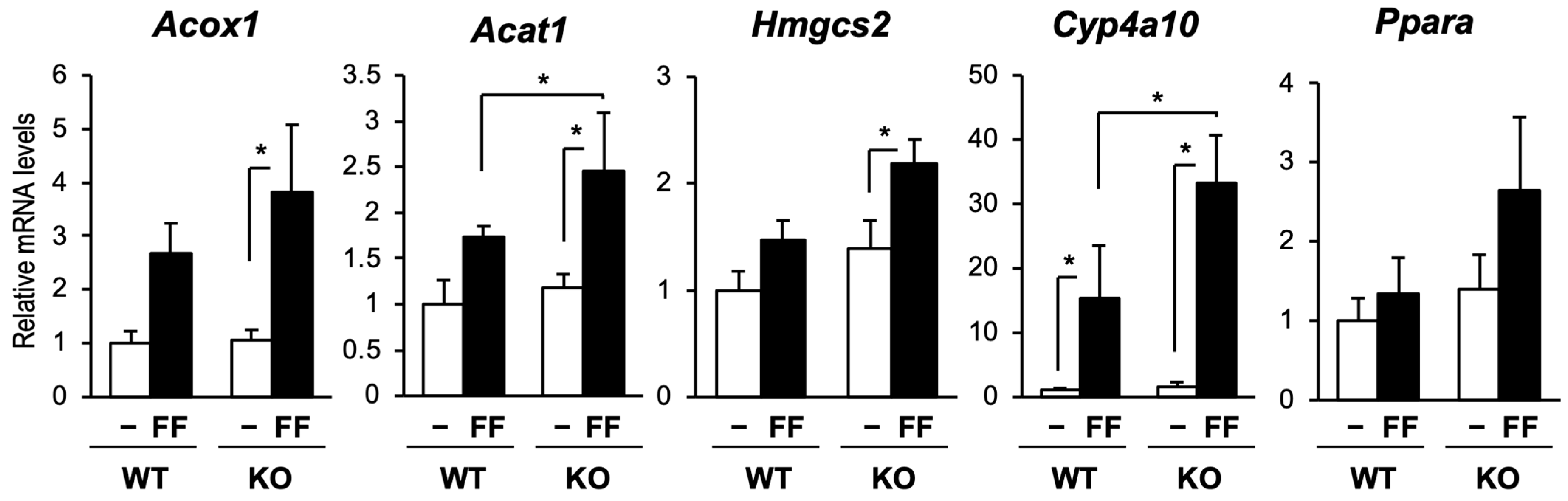
2.1. CAR Inactivates PPARα and PPARα Activates CAR in the Mouse Liver
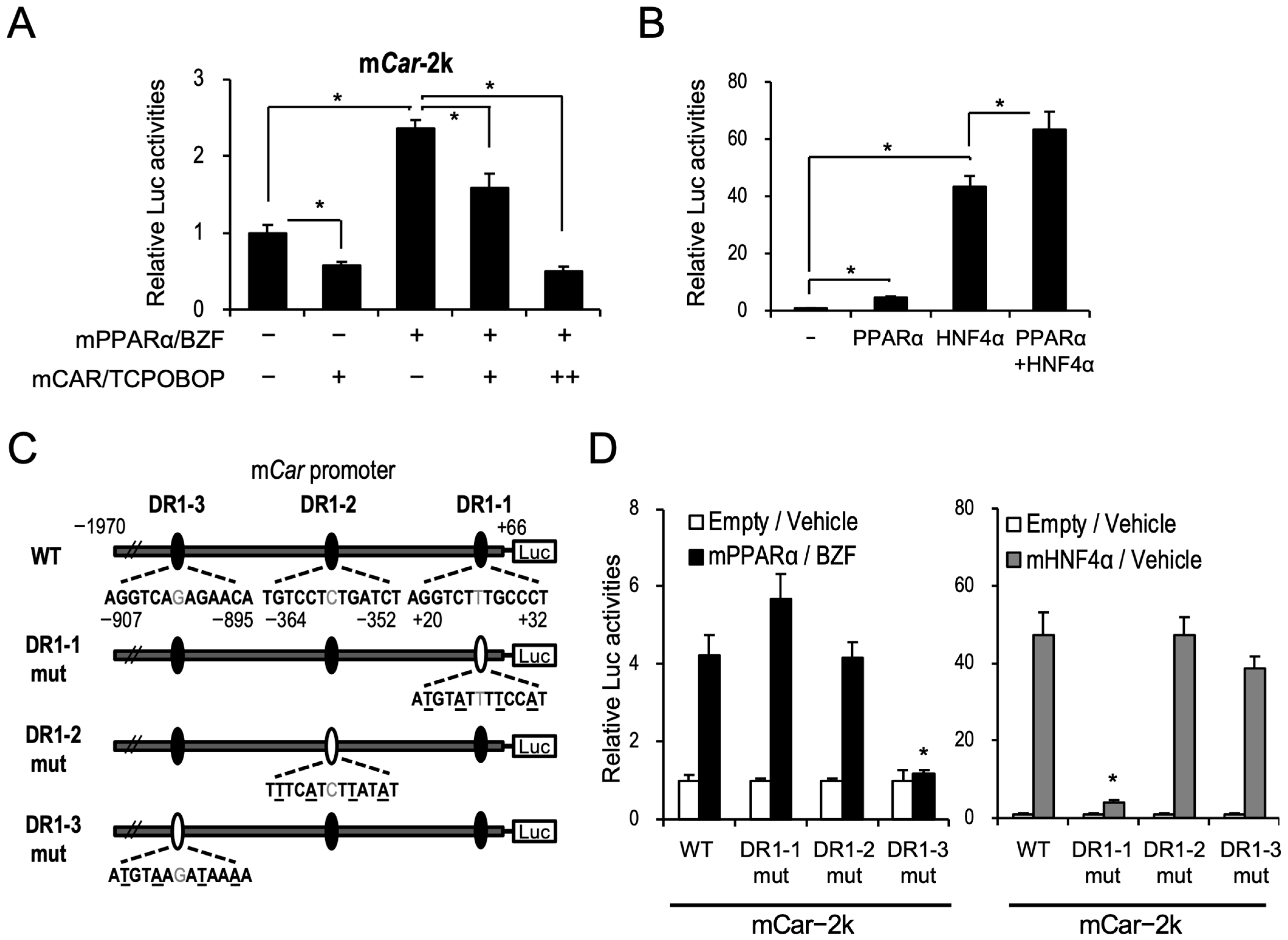
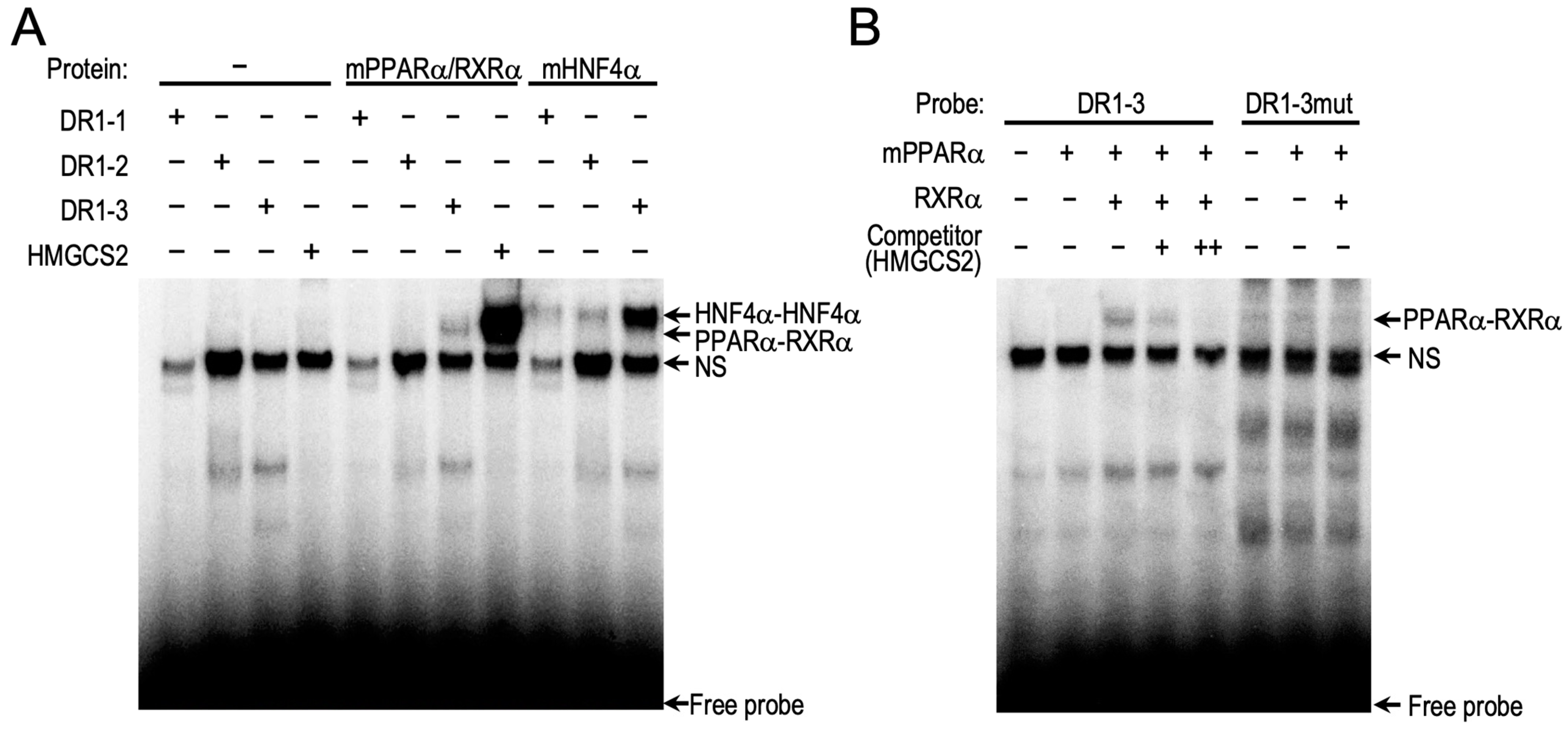
2.2. PPARα Induces CAR Expression through Binding to the Novel DR1 Motif in Car Promoter
2.3. PPARα Activation Was Enhanced in the Liver of CAR-Knockout Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Animal Experiment
4.3. Plasmid Preparation
4.4. Cell Culture
4.5. RT-qPCR
4.6. Reporter Assays
4.7. Electrophoresis Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA)
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pawlak, M.; Lefebvre, P.; Staels, B. Molecular mechanism of PPARα action and its impact on lipid metabolism, inflammation and fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 720–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, J.; Moller, D.E. The Mechanisms of Action of PPARs. Annu. Rev. Med. 2002, 53, 409–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memon, R.A.; Tecott, L.H.; Nonogaki, K.; Beigneux, A.; Moser, A.H.; Grunfeld, C.; Feingold, K.R. Up-regulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPAR-alpha) and PPAR-gamma messenger ribonucleic acid expression in the liver in murine obesity: Troglitazone induces expression of PPAR-gamma-responsive adipose tissue-specific genes in the liver of obese diabetic mice. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 4021–4031. [Google Scholar]
- Sengupta, S.; Peterson, T.R.; Laplante, M.; Oh, S.; Sabatini, D.M. mTORC1 controls fasting-induced ketogenesis and its modulation by ageing. Nature 2010, 468, 1100–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shizu, R.; Otsuka, Y.; Ezaki, K.; Ishii, C.; Arakawa, S.; Amaike, Y.; Abe, T.; Hosaka, T.; Sasaki, T.; Kanno, Y.; et al. Antiepileptic Drug-Activated Constitutive Androstane Receptor Inhibits Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor alpha and Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor gamma Coactivator 1alpha-Dependent Gene Expression to Increase Blood Triglyceride Levels. Mol. Pharmacol. 2020, 98, 634–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timsit, Y.E.; Negishi, M. CAR and PXR: The xenobiotic-sensing receptors. Steroids 2007, 72, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-M.; Ong, S.S.; Chai, S.C.; Chen, T. Role of CAR and PXR in xenobiotic sensing and metabolism. Expert. Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2012, 8, 803–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Lichti, K.; Kim, I.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Staudinger, J.L. Regulation of constitutive androstane receptor and its target genes by fasting, cAMP, hepatocyte nuclear factor alpha, and the coactivator peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1alpha. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 26540–26551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Qatanani, M.; Moore, D.D. Constitutive androstane receptor mediates the induction of drug metabolism in mouse models of type 1 diabetes. Hepatology 2009, 50, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Mizuno, Y.; Fukuchi, Y.; Furihata, T.; Chiba, K. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha) agonists induce constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) and cytochrome P450 2B in rat primary hepatocytes. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2010, 25, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aibara, D.; Takahashi, S.; Yagai, T.; Kim, D.; Brocker, C.N.; Levi, M.; Matsusue, K.; Gonzalez, F.J. Gene repression through epigenetic modulation by PPARA enhances hepatocellular proliferation. iScience 2022, 25, 104196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daujat-Chavanieu, M.; Gerbal-Chaloin, S. Regulation of CAR and PXR Expression in Health and Disease. Cells 2020, 9, 2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirona, R.G.; Lee, W.; Leake, B.F.; Lan, L.-B.; Cline, C.B.; Lamba, V.; Parviz, F.; Duncan, S.A.; Inoue, Y.; Gonzalez, F.J.; et al. The orphan nuclear receptor HNF4α determines PXR- and CAR-mediated xenobiotic induction of CYP3A4. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.; Aleksunes, L.M.; Wood, C.; Vallanat, B.; George, M.H.; Klaassen, C.D.; Corton, J.C. Characterization of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha--independent effects of PPARalpha activators in the rodent liver: Di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate also activates the constitutive-activated receptor. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 113, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R.M.; Barish, G.D.; Wang, Y.X. PPARs and the complex journey to obesity. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferre, P. The biology of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: Relationship with lipid metabolism and insulin sensitivity. Diabetes 2004, 53 (Suppl. S1), S43–S50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Saha, P.K.; Huang, W.; Chen, W.; Abu-Elheiga, L.A.; Wakil, S.J.; Stevens, R.D.; Ilkayeva, O.; Newgard, C.B.; Chan, L.; et al. Activation of nuclear receptor CAR ameliorates diabetes and fatty liver disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 18831–18836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; He, J.; Zhai, Y.; Wada, T.; Xie, W. The constitutive androstane receptor is an anti-obesity nuclear receptor that improves insulin sensitivity. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 25984–25992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal-Mizrachi, C.; Weng, S.; Feng, C.; Finck, B.N.; Knutsen, R.H.; Leone, T.C.; Coleman, T.; Mecham, R.P.; Kelly, D.P.; Semenkovich, C.F. Dexamethasone induction of hypertension and diabetes is PPAR-alpha dependent in LDL receptor-null mice. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerre-Millo, M.; Rouault, C.; Poulain, P.; Andre, J.; Poitout, V.; Peters, J.M.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Fruchart, J.C.; Reach, G.; Staels, B. PPAR-alpha-null mice are protected from high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance. Diabetes 2001, 50, 2809–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-C.; Hardie, D.G. AMPK: Sensing Glucose as well as Cellular Energy Status. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardie, D.G.; Ross, F.A.; Hawley, S.A. AMPK: A nutrient and energy sensor that maintains energy homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blattler, S.M.; Rencurel, F.; Kaufmann, M.R.; Meyer, U.A. In the regulation of cytochrome P450 genes, phenobarbital targets LKB1 for necessary activation of AMP-activated protein kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shindo, S.; Numazawa, S.; Yoshida, T. A physiological role of AMP-activated protein kinase in phenobarbital-mediated constitutive androstane receptor activation and CYP2B induction. Biochem. J. 2007, 401, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.C.; Puigserver, P.; Chen, G.; Donovan, J.; Wu, Z.; Rhee, J.; Adelmant, G.; Stafford, J.; Kahn, C.R.; Granner, D.K.; et al. Control of hepatic gluconeogenesis through the transcriptional coactivator PGC-1. Nature 2001, 413, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Handschin, C.; Spiegelman, B.M. Metabolic control through the PGC-1 family of transcription coactivators. Cell Metab. 2005, 1, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Yan, J.; Xu, M.; Ren, S.; Xie, W. CAR Suppresses Hepatic Gluconeogenesis by Facilitating the Ubiquitination and Degradation of PGC1alpha. Mol. Endocrinol. 2015, 29, 1558–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shizu, R.; Ezaki, K.; Sato, T.; Sugawara, A.; Hosaka, T.; Sasaki, T.; Yoshinari, K. PXR Suppresses PPARalpha-Dependent HMGCS2 Gene Transcription by Inhibiting the Interaction between PPARalpha and PGC1alpha. Cells 2021, 10, 2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buler, M.; Aatsinki, S.M.; Skoumal, R.; Hakkola, J. Energy sensing factors PGC-1alpha and SIRT1 modulate PXR expression and function. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 82, 2008–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, S.; Yoshinari, K.; Sugawara, M.; Yamazoe, Y. Activated sterol regulatory element-binding protein-2 suppresses hepatocyte nuclear factor-4-mediated Cyp3a11 expression in mouse liver. Mol. Pharmacol. 2011, 79, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shizu, R.; Otsuka, Y.; Ishii, C.; Ezaki, K.; Yoshinari, K. PPARα Induces the Expression of CAR That Works as a Negative Regulator of PPARα Functions in Mouse Livers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3953. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043953
Shizu R, Otsuka Y, Ishii C, Ezaki K, Yoshinari K. PPARα Induces the Expression of CAR That Works as a Negative Regulator of PPARα Functions in Mouse Livers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(4):3953. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043953
Chicago/Turabian StyleShizu, Ryota, Yuta Otsuka, Chizuru Ishii, Kanako Ezaki, and Kouichi Yoshinari. 2023. "PPARα Induces the Expression of CAR That Works as a Negative Regulator of PPARα Functions in Mouse Livers" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 4: 3953. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043953
APA StyleShizu, R., Otsuka, Y., Ishii, C., Ezaki, K., & Yoshinari, K. (2023). PPARα Induces the Expression of CAR That Works as a Negative Regulator of PPARα Functions in Mouse Livers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(4), 3953. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043953