The Genotype-Phenotype Correlation in Human 5α-Reductase Type 2 Deficiency: Classified and Analyzed from a SRD5A2 Structural Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patients and SRD5A2 Gene Analysis
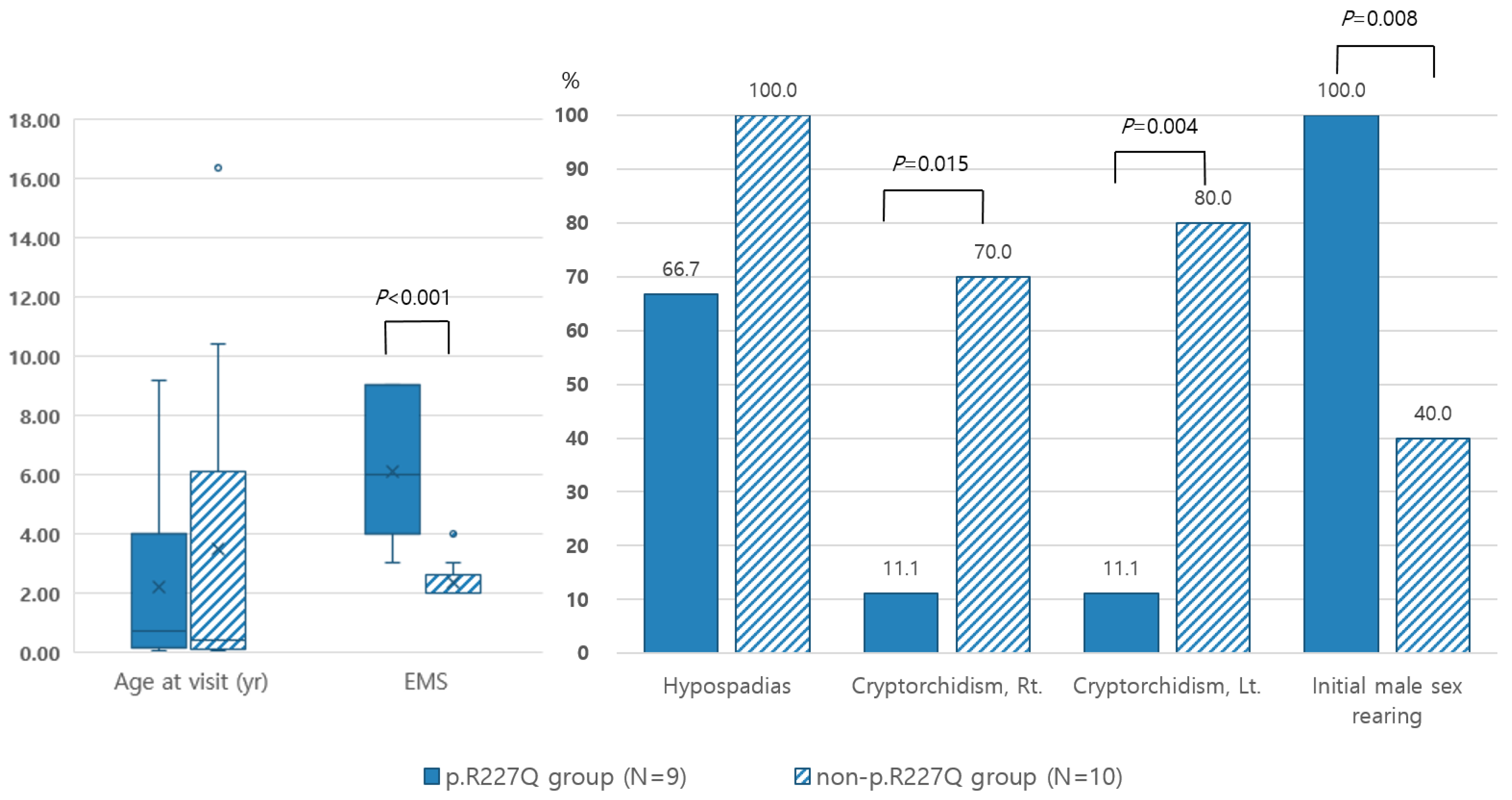
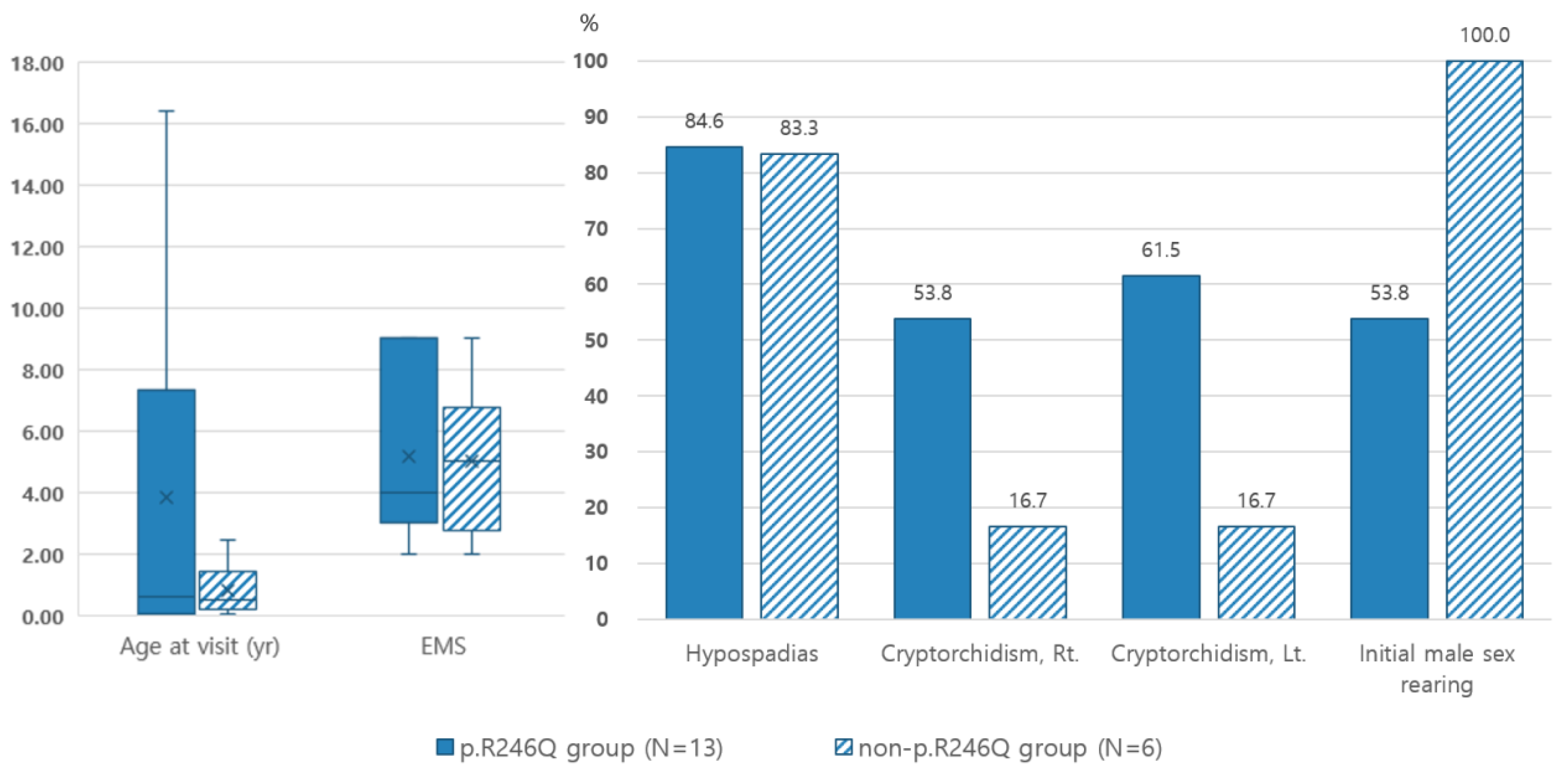
2.2. Phenotype and the Correlation with Genotype
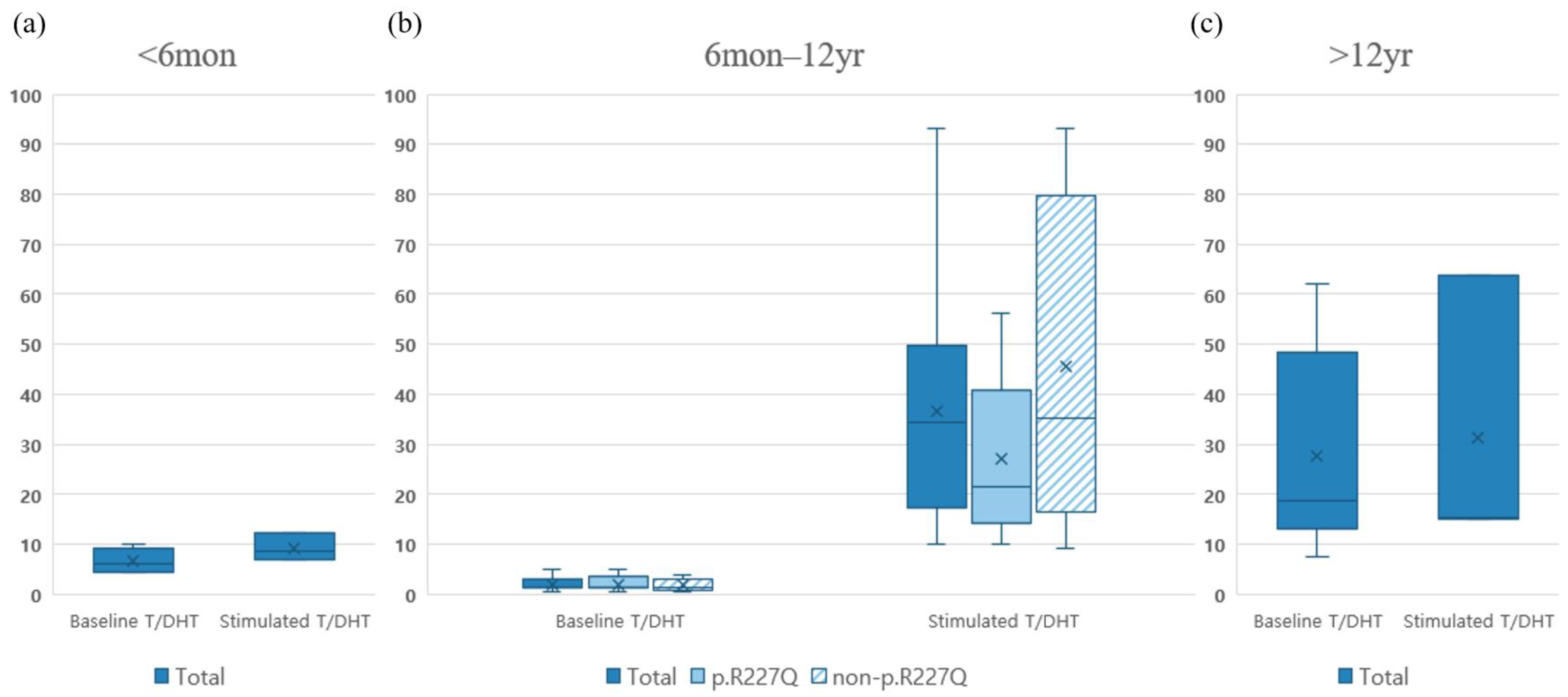
2.3. Biological Investigations and Correlation with Genotype
2.4. Genotype-Phenotype Correlation According to Structural Categories
- Catalytic site mutations:
- 2.
- NADPH-binding residue mutations:
- 3.
- Structure-destabilizing mutations:
- 4.
- Helix-breaking mutations:
- 5.
- Small to bulky residues:
2.5. Crystal Structure of the Human SRD5A2 Gene and Changes in Structure Relative to Variants
3. Discussion
Limitations and Future Prospects
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. Evaluation of Clinical Manifestation
4.3. Molecular Genetic Testing
4.4. 3D Protein Structure of SRD5A2 with NADPH and Computational Mutagenesis
4.5. Statistics Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilson, J.D.; Griffin, J.E.; Russell, D.W. Steroid 5 alpha-reductase 2 deficiency. Endocr. Rev. 1993, 14, 577–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imperato-McGinley, J.; Guerrero, L.; Gautier, T.; Peterson, R.E. Steroid 5alpha-reductase deficiency in man: An inherited form of male pseudohermaphroditism. Science 1974, 186, 1213–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, S.; Berman, D.M.; Jenkins, E.P.; Russell, D.W. Deletion of steroid 5 alpha-reductase 2 gene in male pseudohermaphroditism. Nature 1991, 354, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labrie, F.; Sugimoto, Y.; Luu-The, V.; Simard, J.; Lachance, Y.; Bachvarov, D.; Leblanc, G.; Durocher, F.; Paquet, N. Structure of human type II 5 alpha-reductase gene. Endocrinology 1992, 131, 1571–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheon, C.K. Practical approach to steroid 5alpha-reductase type 2 deficiency. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2011, 170, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yang, J.; Zhang, H.; Ning, G.; Li, X.; Sun, S. A novel SRD5A2 mutation with loss of function identified in Chinese patients with hypospadias. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2011, 76, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Lin, R.; Zhang, W.; Liu, G.; Sheng, H.; Li, X.; Zhou, Z.; Mao, X.; Liu, L. Phenotype and molecular characteristics in 45 Chinese children with 5α-reductase type 2 deficiency from South China. Clin. Endocrinol. 2015, 83, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Song, Y.; Polak, M.; Li, L.; Ren, X.; Zhang, B.; Wu, D.; Gong, C. Clinical characteristics and genotype-phenotype correlations of 130 Chinese children in a high-homogeneity single-center cohort with 5α-reductase 2 deficiency. Mol. Genet. Genomic. Med. 2020, 8, e1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Human Gene Mutation Database. Available online: https://www.hgmd.cf.ac.uk/ (accessed on 30 November 2022).
- Avendaño, A.; Paradisi, I.; Cammarata-Scalisi, F.; Callea, M. 5-α-Reductase type 2 deficiency: Is there a genotype-phenotype correlation? A review. Hormones 2018, 17, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, B.; Song, Y.; Su, Z.; Luo, F.-H.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, R.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; et al. New insights into 5α-reductase type 2 deficiency based on a multi-centre study: Regional distribution and genotype-phenotype profiling of SRD5A2 in 190 Chinese patients. J. Med. Genet. 2019, 56, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, R.L.; Mendonca, B.B. Integrative and Analytical Review of the 5-Alpha-Reductase Type 2 Deficiency Worldwide. Appl. Clin. Genet. 2020, 13, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Yin, X.; Li, P. Clinical, Hormonal, and Genetic Characteristics of 5α-Reductase Type 2 Deficiency in 103 Chinese Patients. Endocr. Pract. 2022, 28, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maimoun, L.; Philibert, P.; Cammas, B.; Audran, F.; Bouchard, P.; Fenichel, P.; Cartigny, M.; Pienkowski, C.; Polak, M.; Skordis, N.; et al. Phenotypical, biological, and molecular heterogeneity of 5α-reductase deficiency: An extensive international experience of 55 patients. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abacı, A.; Çatlı, G.; Kırbıyık, Ö.; Şahin, N.M.; Abalı, Z.Y.; Ünal, E.; Şıklar, Z.; Mengen, E.; Özen, S.A.M.İ.M.; Güran, T.Ü.L.A.Y.; et al. Genotype-phenotype correlation, gonadal malignancy risk, gender preference, and testosterone/dihydrotestosterone ratio in steroid 5-alpha-reductase type 2 deficiency: A multicenter study from Turkey. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2019, 42, 453–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alswailem, M.M.; Alzahrani, O.S.; Alghofaili, L.; Qasem, E.; Almohanaa, M.; Alsagheir, A.; Bin Abbas, B.; Attia, N.A.; Al Shaikh, A.; Alzahrani, A.S. Molecular genetics and phenotype/genotype correlation of 5-α reductase deficiency in a highly consanguineous population. Endocrine 2019, 63, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andonova, S.; Robeva, R.; Vazharova, R.; Ledig, S.; Grozdanova, L.; Stefanova, E.; Bradinova, I.; Todorov, T.; Hadjidekov, G.; Sirakov, M.; et al. New Territory for an Old Disease: 5-Alpha-Reductase Type 2 Deficiency in Bulgaria. Sex Dev. 2017, 11, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinnecker, G.H.; Hiort, O.; Dibbelt, L.; Albers, N.; Dörr, H.G.; Hauß, H.; Heinrich, U.; Hemminghaus, M.; Hoepffner, W.; Holder, M.; et al. Phenotypic classification of male pseudohermaphroditism due to steroid 5 alpha-reductase 2 deficiency. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1996, 63, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Liu, W.; Han, B.; Fan, M.; Zhao, S. Phenotypic and molecular characteristics in eleven C hinese patients with 5α-reductase T ype 2 deficiency. Clinical 2014, 81, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Wang, L.; Supekar, S.; Shen, T.; Liu, H.; Ye, F.; Huang, J.; Fan, H.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, C. Structure of human steroid 5α-reductase 2 with the anti-androgen drug finasteride. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zhuang, Q.; Sun, B.; Lv, W.; Wang, S.; Xiao, Q.; Pang, B.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, F.; Chi, P.; et al. Crystal structure of steroid reductase SRD5A reveals conserved steroid reduction mechanism. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonca, B.B.; Batista, R.L.; Domenice, S.; Costa, E.M.; Arnhold, I.J.; Russell, D.W.; Wilson, J.D. Steroid 5α-reductase 2 deficiency. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 163, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.M.; Cheon, C.-K.; Kim, G.-H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, K.S.; Yoo, H.-W. Clinical Characterization and Analysis of the SRD5A2 Gene in Six Korean Patients with 5α-Reductase Type 2 Deficiency. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2010, 73, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahakitrungruang, T.; Wacharasindhu, S.; Yeetong, P.; Snabboon, T.; Suphapeetiporn, K.; Shotelersuk, V. Identification of mutations in the SRD5A2 gene in Thai patients with male pseudohermaphroditism. Fertil. Steril. 2008, 90, 2015.e11–2015.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigley, W.C.; Prihoda, J.S.; Mowszowicz, I.; Mendonca, B.B.; New, M.I.; Wilson, J.D.; Russell, D.W. Natural Mutagenesis Study of the Human Steroid 5.alpha.-Reductase 2 Isoenzyme. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 1265–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Thigpen, A.; Davis, D.L.; Milatovich, A.; Mendonça, B.B.; Imperato-McGinley, J.; E Griffin, J.; Francke, U.; Wilson, J.D.; Russell, D.W. Molecular genetics of steroid 5 alpha-reductase 2 deficiency. J. Clin. Investig. 1992, 90, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maimoun, L.; Philibert, P.; Bouchard, P.; Öcal, G.; Leheup, B.; Fenichel, P.; Servant, N.; Paris, F.; Sultan, C. Primary amenorrhea in four adolescents revealed 5α-reductase deficiency confirmed by molecular analysis. Fertil. Steril. 2011, 95, 804.e1–804.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilchis, F.; Valdez, E.; Ramos, L.; García, R.; Gómez, R.; Chávez, B. Novel compound heterozygous mutations in the SRD5A2 gene from 46,XY infants with ambiguous external genitalia. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 53, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qiao, J.; Cheng, T.; Wang, H.; Han, B.; Zhu, H.; Yao, H.-J.; Zhao, S.-X.; Zhu, W.-J.; Zhai, H.-L.; et al. Identification of three novel SRD5A2 mutations in Chinese patients with 5α-reductase 2 deficiency. Asian J. Androl. 2019, 21, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.; Cheng, T.; Zhu, H.; Yu, J.; Zhu, W.-J.; Song, H.-D.; Yao, H.; Qiao, J. Genetic Analysis of 25 Patients with 5α-Reductase Deficiency in Chinese Population. Biomed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 1789514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- María Guadalupe, O.-L.; Katy, S.-P.; Charmina, A.-A.; Vihko, P.; Marta, M. Molecular Characterization of Two Known SRD5A2 Gene Variants in Mexican Patients with Disorder of Sexual Development. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 794476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makridakis, N.M.; di Salle, E.; Reichardt, J.K. Biochemical and pharmacogenetic dissection of human steroid 5 alpha-reductase type II. Pharmacogenetics 2000, 10, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilchis, F.; Ramos, L.; Mendez, J.P.; Benavides, S.; Canto, P.; Chavez, B. Molecular Analysis of the SRD5A2 in 46,XY Subjects With Incomplete Virilization: The P212R Substitution of the Steroid 5 -Reductase 2 May Constitute an Ancestral Founder Mutation in Mexican Patients. J. Androl. 2010, 31, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thigpen, A.E.; Davis, D.L.; Gautier, T.; Imperato-McGinley, J.; Russell, D.W. Brief report: The molecular basis of steroid 5 alpha-reductase deficiency in a large Dominican kindred. N. Engl. J. Med. 1992, 327, 1216–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leshin, M.; Griffin, J.E.; Wilson, J.D. Hereditary male pseudohermaphroditism associated with an unstable form of 5 alpha-reductase. J. Clin. Investig. 1978, 62, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Cancio, M.; Nistal, M.; Gracia, R.; Molina, M.A.; Tovar, J.A.; Esteban, C.; Carrascosa, A.; Audí, L. Compound heterozygous mutations in the SRD5A2 gene exon 4 in a male pseudohermaphrodite patient of Chinese origin. J. Androl. 2004, 25, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akcay, T.; Fernandez-Cancio, M.; Turan, S.; Güran, T.; Audi, L.; Bereket, A. AR and SRD5A2 gene mutations in a series of 51 Turkish 46,XY DSD children with a clinical diagnosis of androgen insensitivity. Andrology 2014, 2, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, G.; Ogata, T.; Ishii, T.; Kosaki, K. Micropenis and the 5α-reductase-2 (SRD5A2) gene: Mutation and V89L polymorphism analysis in 81 Japanese patients. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 3431–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertelloni, S.; Baldinotti, F.; Russo, G.; Ghirri, P.; Dati, E.; Michelucci, A.; Moscuzza, F.; Meroni, S.; Colombo, I.; Sessa, M.R.; et al. 5α-Reductase-2 Deficiency: Clinical Findings, Endocrine Pitfalls, and Genetic Features in a Large Italian Cohort. Sex Dev. 2016, 10, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, A.; Baldazzi, L.; Balsamo, A.; Barp, L.; Pirazzoli, P.; Gennari, M.; Radetti, G.; Cacciari, E.; Cicognani, A. SRD5A2 gene analysis in an Italian population of under-masculinized 46,XY subjects. Clin. Endocrinol. 2005, 63, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, M.; Zhou, Q.; Mao, J.; Lu, S.; Wu, X. Five novel mutations of SRD5A2 found in eight Chinese patients with 46,XY disorders of sex development. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2011, 17, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, D.W.; Berman, D.M.; Bryant, J.T.; Cala, K.M.; Davis, D.L.; Landrum, C.P.; Prihoda, J.S.; Silver, R.I.; Thigpen, A.E.; Wigley, W.C. The molecular genetics of steroid 5 alpha-reductases. Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 1994, 49, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Canto, P.; Vilchis, F.; Chávez, B.; Mutchinick, O.; Imperato-McGinley, J.; Pérez-Palacios, G.; Ulloa-Aguirre, A.; Méndez, J.P. Mutations of the 5α-reductase Type 2 gene in eight Mexican patients from six different pedigrees with 5α-reductase-2 deficiency. Clin. Endocrinol. 1997, 46, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.F.; Khwaja, O.; Hughes, I.A. The role of a clinical score in the assessment of ambiguous genitalia. BJU Int. 2000, 85, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Chung, J.M.; Kang, D.I.; Ryu, D.S.; Cho, W.Y.; Lee, S.D. The Change of Stretched Penile Length and Anthropometric Data in Korean Children Aged 0–14 Years: Comparative Study of Last 25 Years. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2016, 31, 1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cock, P.J.A.; Fields, C.J.; Goto, N.; Heuer, M.L.; Rice, P.M. The Sanger FASTQ file format for sequences with quality scores, and the Solexa/Illumina FASTQ variants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 1767–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Aligning sequence reads, clone sequences and assembly contigs with BWA-MEM. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1303.3997v2. [Google Scholar]
- Lander, E.S.; Linton, L.M.; Birren, B.; Nusbaum, C. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 2001, 409, 860–921. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kircher, M.; Witten, D.M.; Jain, P.; O’Roak, B.J.; Cooper, G.M.; Shendure, J. A general framework for estimating the relative pathogenicity of human genetic variants. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinVar. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/clinvar (accessed on 31 July 2022).
- NHLBI Grand Opportunity Exome Sequencing Project. Available online: http://esp.gs.washington.edu/ (accessed on 31 July 2022).
- 1000 Genomes Project. Available online: ftp://hgdownload.cse.ucsc.edu/ (accessed on 31 July 2022).
- Genome Aggregation Database. Available online: www.gnomad-sg.org (accessed on 31 July 2022).
- Korean Reference Genome database. Available online: koref.koreanreference.org (accessed on 30 November 2022).
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Patient No. | SRD5A2 Mutation | Exon | Sex of Rearing | Age at First Visit | Phenotypes at First Visit | EMS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C/P | Hypospadias | Rt. Testis | Lt. Testis | P-S Disposition | ||||||
| 1 | R227Q/R227Q | 4/4 | M | 2.4Y | MP | Midshaft | Scrotum | Scrotum | Y | 4 |
| 2 | R227Q/T53R | 4/1 | M | 1.1Y | MP | Perineal | Scrotum | Scrotum | Y | 3 |
| 3 | R227Q/A65P | 4/1 | M | 4M | MP | Penoscrotal | Scrotum | Scrotum | N | 6 |
| 4 | R227Q/Q6* | 4/1 | M | 21D | MP | Penoscrotal | Scrotum | Scrotum | N | 6 |
| 5 | M | 9M | MP | None | Scrotum | Scrotum | N | 9 | ||
| 6 | R227Q/R246Q | 4/5 | M | 5.5Y | MP | None | Scrotum | Scrotum | N | 9 |
| 7 | M | 9.1Y | MP | None | Scrotum | Scrotum | N | 9 | ||
| 8 | M | 10D | MP | Perineal | Inguinal | Inguinal | Y | 5 | ||
| 9 | M | 5M | MP | Proximal | Scrotum | Scrotum | Y | 3 | ||
| 10 | R246Q/R246Q | 5/5 | M | 10D | CM | Perineal | Scrotum | Scrotum | Y | 3 |
| 11 | M | 8M | CM | Proximal | Scrotum | Scrotum | Y | 3 | ||
| 12 | M | 7D | CM | Scrotal | Inguinal | Inguinal | Y | 2 | ||
| 13 | F | 4.6Y | CM | Perineal | Inguinal | Inguinal | Y | 2 | ||
| 14 | R246Q/R246W | 5/5 | F->M | 16.4Y | MP | Perineal | Inguinal | Inguinal | Y | 2 |
| 15 | R246Q/G203S | 5/4 | F->M | 2M | CM | Perineal | Inguinal | Inguinal | Y | 2 |
| 16 | F | 2M | C | Perineal | Scrotum | Inguinal | Y | 2.5 | ||
| 17 | R246Q/F219Sfs*60 | 5/4 | F | 2.5Y | C | Perineal | Inguinal | Inguinal | Y | 2 |
| 18 | R246Q/Q6* | 5/1 | F | 10.4Y | C | Perineal | Inguinal | Inguinal | Y | 2 |
| 19 | Q6*/Q6* | 1/1 | M | 3M | C | Scrotal | Abd | Abd | Y | 2 |
| Structural Category [21] | Mutations in SRD5A2 | Location [20] | Enzymatic Activity | Mechanism | EMS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Catalytic site mutations | p.Q56R | TM2 | No [25,26] † (L55Q) | 3.0 [27] ‡ 2.5 [26] † (L55Q) | |
| p.E57Q | TM2 | Reduced [28] | 3.0 [28] † (G85D) | ||
| p.E57D | TM2 | 2.0 [8] † (R227Q) | |||
| p.Y91D | TM3 | No [25] | Shortening protein half-life [25] | 2.0 [26] † (D164V) | |
| NADPH binding residue mutations | p.N160D | TM5 | 4.8 ± 3.0 [10] ‡ | ||
| p.D164V | TM5 | No [25] | |||
| p.R171S | TM5 | Reduced [25,26] † (G34R) | NADPH-binding abnormality [25] Shortening protein half-life [25] Change optimum pH [25] | 5.0 [29] † (G196V) 5.0 [30] † (G196V) | |
| p.N193S | TM6 | Reduced [25] | NADPH-binding abnormality [25] Shortening protein half-life [25] Change optimum pH [25] | 2.0 [27] ‡ 2.0 [13] † 7.0 [8] † (R227Q) | |
| p.E197D | TM6 | No [25,31] | Shortening protein half-life [25] | ||
| p.R227Q | TM7 | Reduced [32] | NADPH-binding abnormality [32] Testosterone-binding abnormality [32] | 8.0 ± 1.8 [10] ‡ 6.0 [13] ‡ 7.0 [8] ‡ 7.8 [8] † (G203S) 7.0 [8] † (R246Q) 7.0 [8] † (N193S) 4.0 [8] † (G34R) 6.0 [13] † 6.0 [8] † | |
| p.H231R | TM7 | Reduced [25] | Testosterone-binding abnormality [25] Change optimum pH [25] | 2.0 ± 1.2 [10] ‡ | |
| p.Y235F | TM7 | 4.0 ± 3.5 [10] ‡ | |||
| Structure destabilizing mutations | p.Q126R | TM4 | No [25,26] | Shortening protein half-life [25] | 4.2 ± 1.5 [10] ‡ |
| p.P181L | TM5-TM6 | Reduced [25] | NADPH-binding abnormality [25] Shortening protein half-life [25] Change optimum pH [25] | 2.0 [16] ‡ 4.0 ± 2.8 [10] ‡ 6.0 [13] † | |
| p.G183S | TM5-TM6 | Reduced [25] | Decrease of testosterone affinity NADPH-binding abnormality [25] | 4.2 ± 2.5 [10] ‡ 8.0 [13] † | |
| p.A207D | TM6 | No [25] Reduced [26] † (R246Q) | Shortening protein half-life [25] | ||
| p.P212R | TM6 | No [6,19,25,29,31,33] | Shortening protein half-life [25] | ||
| p.R246Q | TM7 | Reduced [25,26] | NADPH-binding abnormality [25] Shortening protein half-life [25] Change optimum pH [25] | 2.0 [15] ‡ 3.7 ± 1.7 [10] ‡ 3.0 [8] ‡ 2.5 [30] ‡ 5.0 [8] † (G203S) 5.0 [13] † | |
| p.R246W | TM7 | No [26] Reduced [25,34,35] | NADPH-binding abnormality [25,34] Shortening protein half-life [25] Change optimum pH [25] | 2.7 ± 1.2 [10] ‡ 2.0 [13] † | |
| Helix breaking mutations | p.L55Q | TM2 | No [25,26] † (Q56R) | Shortening protein half-life [25] | 3.0 ± 3.0 [10] ‡ 2.0 [27] ‡ |
| p.H162P | TM5 | Reduced [29] | 2.0 [30] † (Q6*) | ||
| p.L224P | TM7 | No [25,26] | Shortening protein half-life [25] | ||
| p.H230P | TM7 | No [25] | Shortening protein half-life [25] | ||
| Small to bulky residues | p.G34R | TM1-TM2 | No [26] ‡ † (G115D) Reduced [25,26] † (R171S) | NADPH-binding abnormality [26] ‡ Testosterone-binding abnormality [25,26] † (G115D) Change optimum pH [25,26] | 3.3 ± 2.1 [10] ‡ 4.0 [8] † (R227Q) |
| p.P59R | MT2 | No [25] | Shortening protein half-life [25] | ||
| p.G115D | TM4 | No [25,26] † (G34R) | Testosterone-binding abnormality [26] † (G34R) (mild) Shortening protein half-life [25] | 2.6 ± 0.6 [10] ‡ | |
| p.G196S | TM6 | Reduced [25,26] | NADPH-binding abnormality [25,26] Shortening protein half-life [25] | 3.3 ± 1.0 [10] ‡ 5.8 [13] † | |
| p.G203S | TM6 | Reduced [6] | 2.5 [8] ‡ 2.0 [29] ‡ 6.0 [13] † 5.0 [8] † (R246Q) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seo, J.; Shin, S.; Kim, S.-w.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, M.; Song, K.; Suh, J.; Lee, S.-T.; Lee, Y.S.; Chae, H.W.; et al. The Genotype-Phenotype Correlation in Human 5α-Reductase Type 2 Deficiency: Classified and Analyzed from a SRD5A2 Structural Perspective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3297. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043297
Seo J, Shin S, Kim S-w, Kim SJ, Lee M, Song K, Suh J, Lee S-T, Lee YS, Chae HW, et al. The Genotype-Phenotype Correlation in Human 5α-Reductase Type 2 Deficiency: Classified and Analyzed from a SRD5A2 Structural Perspective. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(4):3297. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043297
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeo, Jieun, Saeam Shin, Sang-woon Kim, Su Jin Kim, Myeongseob Lee, Kyungchul Song, Junghwan Suh, Seung-Tae Lee, Yong Seung Lee, Hyun Wook Chae, and et al. 2023. "The Genotype-Phenotype Correlation in Human 5α-Reductase Type 2 Deficiency: Classified and Analyzed from a SRD5A2 Structural Perspective" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 4: 3297. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043297
APA StyleSeo, J., Shin, S., Kim, S.-w., Kim, S. J., Lee, M., Song, K., Suh, J., Lee, S.-T., Lee, Y. S., Chae, H. W., Kim, H.-S., Choi, J. R., Han, S., & Kwon, A. (2023). The Genotype-Phenotype Correlation in Human 5α-Reductase Type 2 Deficiency: Classified and Analyzed from a SRD5A2 Structural Perspective. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(4), 3297. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043297







