A Novel Look at Dosage-Sensitive Sex Locus Xp21.2 in a Case of 46,XY Partial Gonadal Dysgenesis without NR0B1 Duplication
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Detailed Case Description
2.1. Patient
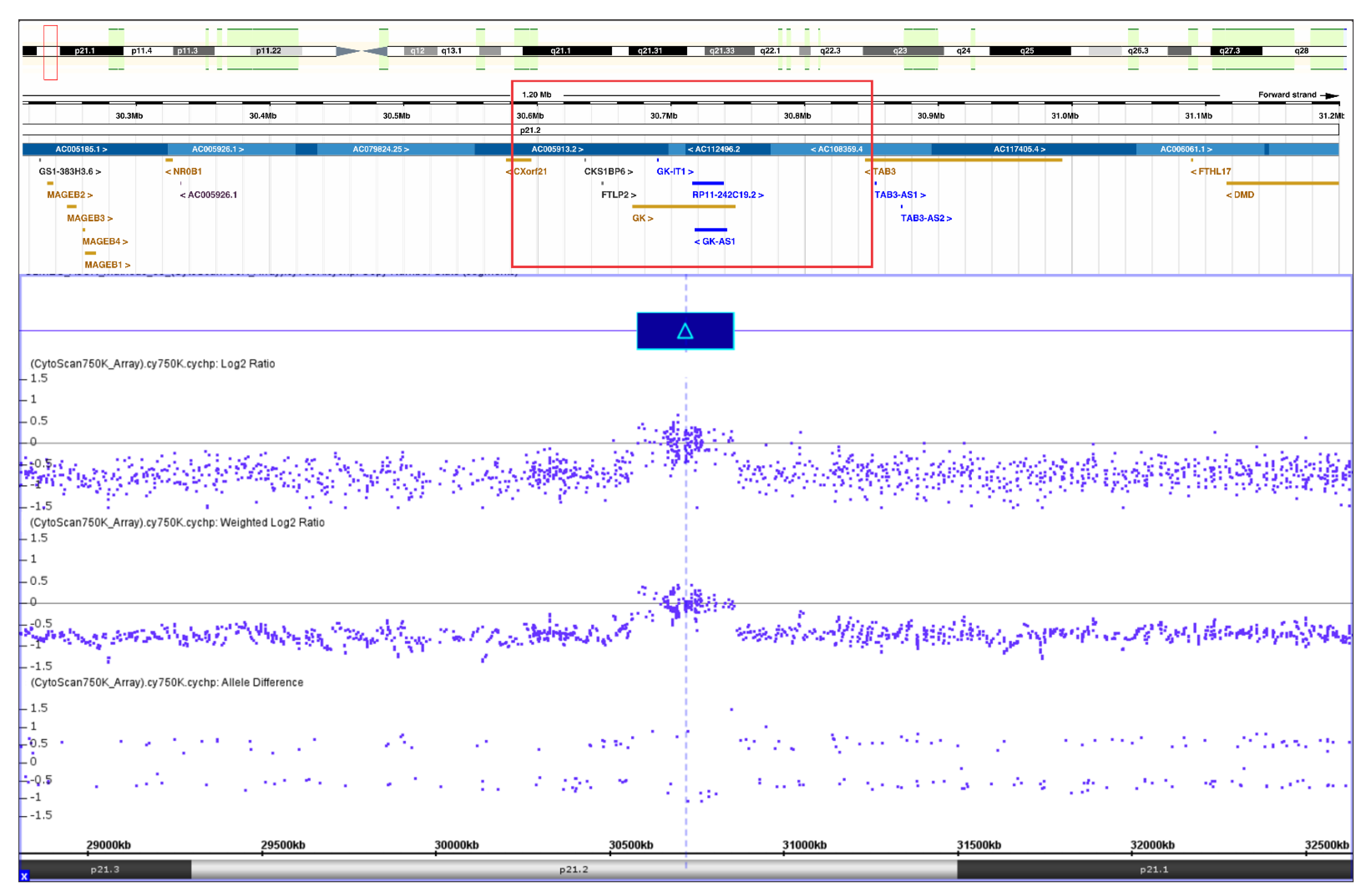
2.2. Genetic Studies
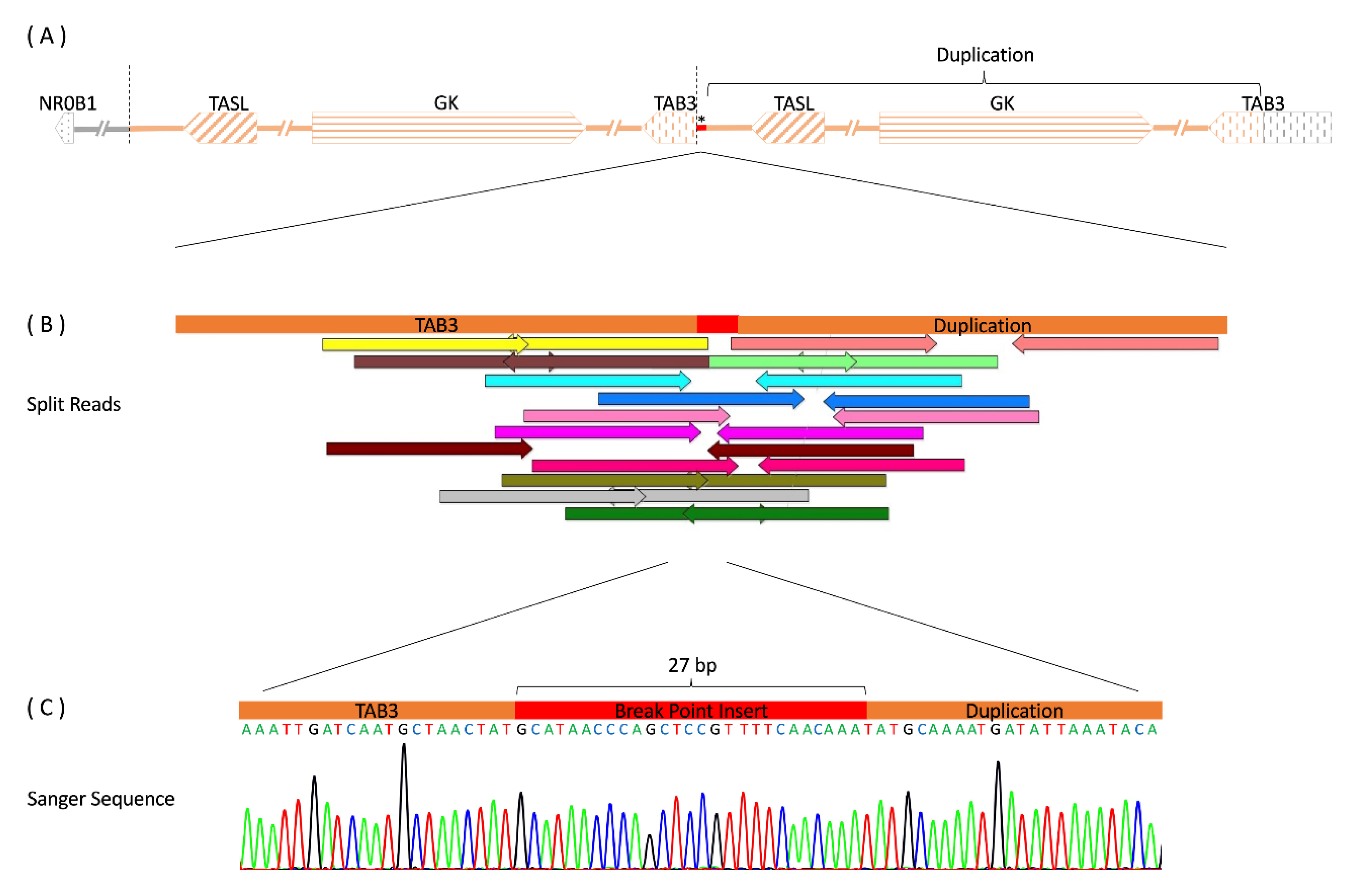
2.3. Results
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gomes, N.L.; Lerário, A.M.; Machado, A.Z.; Moraes, D.R.; Silva, T.E.D.; Arnhold, I.J.P.; Batista, R.L.; Faria Júnior, J.A.D.; Costa, E.F.; Nishi, M.Y.; et al. Long-term outcomes and molecular analysis of a large cohort of patients with 46,XY disorder of sex development due to partial gonadal dysgenesis. Clin. Endocrinol. 2018, 89, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, J.G.R.; Fabbri-Scallet, H.; Dos Santos, A.P.; Cools, M.; Werner, R.; Hiort, O.; de Mello, M.P.; Guerra-Júnior, G.; Maciel-Guerra, A.T. Clinical Findings and Follow-Up of 46,XY and 45,X/46,XY Testicular Dysgenesis. Sex. Dev. 2019, 13, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardoni, B.; Zanaria, E.; Guioli, S.; Floridia, G.; Worley, K.C.; Tonini, G.; Ferrante, E.; Chiumello, G.; McCabe, E.R.; Fraccaro, M.; et al. A dosage sensitive locus at chromosome Xp21 is involved in male to female sex reversal. Nat. Genet. 1994, 7, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukumaran, A.; Desmangles, J.C.; Gartner, L.A.; Buchlis, J. Duplication of dosage sensitive sex reversal area in a 46, XY patient with normal sex determining region of Y causing complete sex reversal. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 26, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kon, M.; Fukami, M. Submicroscopic copy-number variations associated with 46,XY disorders of sex development. Mol. Cell Pediatr. 2015, 2, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nishi, M.Y.; Faria Júnior, J.A.D.; Krepischi, A.C.V.; de Moraes, D.R.; da Costa, S.S.; Silva, E.S.D.N.; Costa, E.M.F.; Mendonca, B.B.; Domenice, S. A Small Supernumerary Xp Marker Chromosome Including Genes NR0B1 and MAGEB Causing Partial Gonadal Dysgenesis and Gonadoblastoma. Sex. Dev. 2022, 16, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.F.; Khwaja, O.; Hughes, I.A. The role of a clinical score in the assessment of ambiguous genitalia. BJU Int. 2000, 85, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, A.P.; Muscatelli, F.; Monaco, A.P. Isolation of the human Xp21 glycerol kinase gene by positional cloning. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1993, 2, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, V.M.; Harley, I.T.W.; Kurien, B.T.; Koelsch, K.A.; Scofield, R.H. Lysosomal pH Is Regulated in a Sex Dependent Manner in Immune Cells Expressing CXorf21. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, G.; Klika, A.; Callahan, M.; Faga, B.; Danzig, J.; Jiang, Z.; Li, X.; Stark, G.R.; Harrington, J.; Sherf, B. Identification of a human NF-kappaB-activating protein, TAB3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 2028–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Burris, T.P.; Zhang, Y.H.; Huang, B.L.; Mason, J.; Copeland, K.C.; Kupfer, S.R.; Pagon, R.A.; McCabe, E.R. Genomic sequence of the DAX1 gene: An orphan nuclear receptor responsible for X-linked adrenal hypoplasia congenita and hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1996, 81, 2481–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niakan, K.K.; McCabe, E.R. DAX1 origin, function, and novel role. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2005, 86, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, E.R. DAX1: Increasing complexity in the roles of this novel nuclear receptor. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2007, 265–266, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suntharalingham, J.P.; Buonocore, F.; Duncan, A.J.; Achermann, J.C. DAX-1 (NR0B1) and steroidogenic factor-1 (SF-1, NR5A1) in human disease. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 29, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, T.; Matsuo, N. Sex determining gene on the X chromosome short arm: Dosage sensitive sex reversal. Acta Paediatr. Jpn. 1996, 38, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbaro, M.; Cook, J.; Lagerstedt-Robinson, K.; Wedell, A. Multigeneration Inheritance through Fertile XX Carriers of an NR0B1 (DAX1) Locus Duplication in a Kindred of Females with Isolated XY Gonadal Dysgenesis. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 2012, 504904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekido, R.; Lovell-Badge, R. Sex determination involves synergistic action of SRY and SF1 on a specific Sox9 enhancer. Nature 2008, 453, 930–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludbrook, L.M.; Bernard, P.; Bagheri-Fam, S.; Ryan, J.; Sekido, R.; Wilhelm, D.; Lovell-Badge, R.; Harley, V.R. Excess DAX1 leads to XY ovotesticular disorder of sex development (DSD) in mice by inhibiting steroidogenic factor-1 (SF1) activation of the testis enhancer of SRY-box-9 (Sox9). Endocrinology 2012, 153, 1948–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonen, N.; Futtner, C.R.; Wood, S.; Garcia-Moreno, S.A.; Salamone, I.M.; Samson, S.C.; Sekido, R.; Poulat, F.; Maatouk, D.M.; Lovell-Badge, R. Sex reversal following deletion of a single distal enhancer of Sox9. Science 2018, 360, 1469–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.; Ohnesorg, T.; Notini, A.; Roeszler, K.; Hewitt, J.; Daggag, H.; Smith, C.; Turbitt, E.; Gustin, S.; van den Bergen, J.; et al. Copy number variation in patients with disorders of sex development due to 46,XY gonadal dysgenesis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinel, J.A.; Yumiceba, V.; Künstner, A.; Schultz, K.; Kruse, N.; Kaiser, F.J.; Holterhus, P.M.; Claviez, A.; Hiort, O.; Busch, H.; et al. Disruption of the topologically associated domain at Xp21.2 is related to 46,XY gonadal dysgenesis. J. Med. Genet. 2022; Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Francese-Santos, A.P.; Meinel, J.A.; Piveta, C.S.C.; Andrade, J.G.R.; Barros, B.A.; Fabbri-Scallet, H.; Gil-da-Silva-Lopes, V.L.; Guerra-Junior, G.; Künstner, A.; Busch, H.; et al. A Novel Look at Dosage-Sensitive Sex Locus Xp21.2 in a Case of 46,XY Partial Gonadal Dysgenesis without NR0B1 Duplication. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010494
Francese-Santos AP, Meinel JA, Piveta CSC, Andrade JGR, Barros BA, Fabbri-Scallet H, Gil-da-Silva-Lopes VL, Guerra-Junior G, Künstner A, Busch H, et al. A Novel Look at Dosage-Sensitive Sex Locus Xp21.2 in a Case of 46,XY Partial Gonadal Dysgenesis without NR0B1 Duplication. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(1):494. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010494
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrancese-Santos, Ana Paula, Jakob A. Meinel, Cristiane S. C. Piveta, Juliana G. R. Andrade, Beatriz A. Barros, Helena Fabbri-Scallet, Vera Lúcia Gil-da-Silva-Lopes, Gil Guerra-Junior, Axel Künstner, Hauke Busch, and et al. 2023. "A Novel Look at Dosage-Sensitive Sex Locus Xp21.2 in a Case of 46,XY Partial Gonadal Dysgenesis without NR0B1 Duplication" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 1: 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010494
APA StyleFrancese-Santos, A. P., Meinel, J. A., Piveta, C. S. C., Andrade, J. G. R., Barros, B. A., Fabbri-Scallet, H., Gil-da-Silva-Lopes, V. L., Guerra-Junior, G., Künstner, A., Busch, H., Hiort, O., de Mello, M. P., Werner, R., & Maciel-Guerra, A. T. (2023). A Novel Look at Dosage-Sensitive Sex Locus Xp21.2 in a Case of 46,XY Partial Gonadal Dysgenesis without NR0B1 Duplication. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(1), 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010494






