Abstract
Sphingolipids are exceptionally diverse, comprising hundreds of unique species. The bulk of circulating sphingolipids are synthesized in the liver, thereby plasma sphingolipid profiles represent reliable surrogates of hepatic sphingolipid metabolism and content. As changes in plasma sphingolipid content have been associated to exposure to drugs inducing hepatotoxicity both in vitro and in rodents, in the present study the translatability of the preclinical data was assessed by analyzing the plasma of patients with suspected drug-induced liver injury (DILI) and control subjects. DILI patients, whether intrinsic or idiosyncratic cases, had no alterations in total sphingoid base levels and profile composition compared to controls, whereby cardiovascular disease (CVD) was a confounding factor. Upon exclusion of CVD individuals, elevation of 1-deoxysphingosine (1-deoxySO) in the DILI group emerged. Notably, 1-deoxySO values did not correlate with ALT values. While 1-deoxySO was elevated in all DILI cases, only intrinsic DILI cases concomitantly displayed reduction of select shorter chain sphingoid bases. Significant perturbation of the sphingolipid metabolism observed in this small exploratory clinical study is discussed and put into context, in the consideration that sphingolipids might contribute to the onset and progression of DILI, and that circulating sphingoid bases may function as mechanistic markers to study DILI pathophysiology.
1. Introduction
Profiling plasma lipids, as a reflection of hepatic lipid content [1], has become a powerful translational approach to better understand the role of different lipid species in liver diseases [2], and has been exploited in the study of hepatocellular carcinoma [3,4] and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [5,6]. A major contributor to the heterogeneity of the plasma lipidome, and to the informative potential thereof, are the sphingolipids, which constitute only about 4% of total plasma lipids but comprise hundreds of distinct species [7]. Sphingolipids can be classified in accordance to their complexity. The first level of complexity stems from the sphingoid bases, and their simple derivatives. Sphingoid bases are long-chain saturated (sphingosine, SO) and non-saturated (sphinganine, SA) amino alcohols that represent the basic structural constituents of sphingolipids (Figure 1). The second level of complexity comprises sphingoid bases that are N-acetylated with a second fatty acid (e.g., ceramides). Finally, more complex sphingolipids display an O-linked head group (e.g. sphingomyelins, glycosphingolipids) [8]. Sphingomyelins are the major sphingolipid species found in plasma, constituting ~95% of total plasma sphingolipids [7]. With respect to the sphingoid bases, the profile is more dynamic. C18-sphingosine (C18SO) is the most abundant species, representing ~60% of the total sphingoid base backbones. C18-sphinganine-diene (C18SA-diene), C18SA and C16SO represent 18%, 9% and 10%, respectively [9]. Other sphingoid bases are present to a minor extent [7]. Sphingoid bases are formed by the enzyme serine palmitoyltransferase (SPT) as the first and rate limiting step of the cellular sphingolipid de novo synthesis. The heterogeneity in the sphingoid base profile is related to the intrinsic polyspecificity of SPT [10]. From a biological standpoint, sphingolipids are essential as building elements of cellular membranes, as intra- and extracellular signaling modulators, and as substrates for metabolic pathways. Alterations in the plasma sphingolipid content and profile have been associated with metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease in both animals and patients [11,12,13,14,15,16].
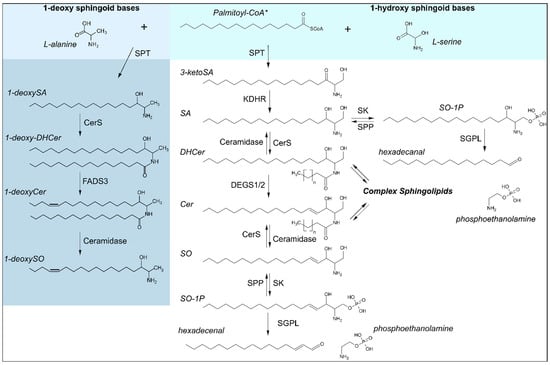
Figure 1.
Sphingoid base biosynthesis. Synthesis of canonical (1-hydroxy) sphingoid bases is catalyzed over the condensation of acyl-CoAs, shown here with the preferred substrate* palmitoyl-CoA (C16:0), with L-serine by serine palmitoyltransferase (SPT) as the rate limiting step in de novo synthesis. 1-deoxy sphingoid bases are likewise synthesized by SPT, using the alternative substrate L-alanine. Enzymes involved are as follows: CerS: ceramide synthases, DEGS1/2: Dihydroceramide desaturases 1/2, FADS3: fatty acid desaturase type 3, KDHR: 3-ketoreductase, SGPL: sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase, SK: sphingosine kinase, SPP: S1P phosphatase, SPT: serine palmitoyltransferase. Substrates and products are abbreviated as follows: Cer: ceramide, DHCer: dihydroceramide, SA: sphinganine, SO: sphingosine, SO-1P: sphingosine-1-phosphate.
Several animal and in vitro studies have observed altered sphingolipid levels and/or metabolism upon treatment with known hepatotoxic drugs. A study in rats has reported changes of plasma ceramides upon treatment with drugs inducing hepatic phospholipidosis, such as the tricyclic antidepressant clomipramine, and the antifungal ketoconazole [17]. Balb/c mice treated with triptolide, a hepatotoxic herbal medicine, revealed significant changes in sphingolipid metabolism at the transcriptional level, which influenced the hepatic and plasmatic sphingolipid profile [18]. Furthermore, the hepatotoxicity of Fumonisin B1 (FB1), which inhibits ceramide synthases, closely correlated with the accumulation of free sphinganine in mice [19,20], leading also to elevations in cytotoxic 1-deoxySA in vitro and in mice [21]. Substantial changes were measured in the cellular sphingolipid profile of human primary hepatocytes exposed to toxic extracellular concentrations of acetaminophen (APAP), a well-characterized hepatotoxic drug [22]. Taken together, these studies suggest that a link between sphingolipid metabolism and drug-induced liver injury (DILI) might exist.
DILI is an adverse event that is often reversible; however, some patients can develop chronic liver injury and, in some cases, acute liver failure occurs. DILI is indeed the most frequent cause of acute liver failure in the U.S.A. and Europe [23,24]. Except for APAP-induced liver injury, which is the result of the intrahepatic accumulation of its reactive metabolite N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI), being dose-dependent and having an onset typically shortly after exposure (intrinsic DILI) [25], DILI is largely an idiosyncratic event that poses a true diagnostic challenge because it is dose-independent and may manifest only after a relatively long latency period after exposure to causative agents. Literature suggests that the frequency of idiosyncratic DILI varies strongly across drugs and drug classes, occurring in a European population-based study in 5 to 750 individuals out of every 100.000 exposed [26], underscoring genetic predisposition as a key risk factor. A large body of evidence suggests that idiosyncratic DILI is often immune-related, arguably triggered by a faulty adaptive immune response involving certain human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system variants. HLA polymorphisms associated to DILI have been reported for a number of drugs, including amoxicillin in combination with clavulanic acid [27,28], flucloxacillin [29], penicillin [30], terbinafine [31] and sulfomethazole/trimethoprim [32].
As studies in humans on the perturbations of sphingolipid metabolism caused by DILI are missing, we performed a simplified sphingoid base analysis of the plasma of patients with suspected DILI, comparing the findings with plasma profiles obtained from healthy volunteers. We found that the sphingolipid content and profile of the plasma of the DILI patients overlapped with that of healthy volunteers, and that the only significant change was in the level of 1-deoxysphingolipids. We then interrogated the circulating sphingolipidome of the DILI patients to explore the informative potential of circulating sphingolipids with respect to type, severity, and perpetrator drug.
2. Results
2.1. Clinical Outcome
Twenty-eight patients were referred to our center with the suspicion of DILI and included in the Swiss Drug-Induced Liver Injury Cohort Study. Based on the pattern of serum enzyme elevations at disease onset (R ratio: [(ALT/ULN) ÷ (ALP/ULN)]), 20 cases were characterized as suffering a hepatocellular injury (R > 5.0), six cases were defined as cholestatic (R < 2.0) and two cases as a mixed type of injury (R = 2.0–5.0). Six patients met the criteria of “nR Hy’s law” ([(ALT/ULN) ÷ (ALP/ULN)] > 5 and total bilirubin (TBL) > 2.5 mg/dL) [33], hence considered at a higher risk of progressing to acute liver failure, with one of these patients progressing to acute liver failure and receiving a liver transplant. One non-nR Hy’s Law case was fatal (advanced age and several comorbidities). In all patients, liver function parameters that were found elevated at the time of the diagnosis decreased after the discontinuation of the suspected DILI-causing medications (dechallenge), whereby in five cases the discontinuation date of the suspected medication was not known. In 11 cases, the liver enzymes did not normalize completely by the end of the follow-up, in 12 cases a restitutio ad integrum could be demonstrated. A rechallenge, i.e., re-administration of the suspected drugs, did not take place in any of the cases. After the suspected causative drugs were discontinued, a median of 3 days was necessary for the functional parameters to regress (between 0 and 48 days). For the 12 restitutio ad integrum cases, liver function normalized after an average of 36 days from the discontinuation of the suspected drugs (between 5 and 251 days).
Across all cases, the two main classes of perpetrator drugs were analgesics, mainly APAP, and antibiotics, primarily amoxicillin in combination with clavulanic acid. APAP was being taken by a total of 14 patients. Seven patients were within normal dose ranges (up to 4 g/24 h), where other substances being taken aside from APAP were identified as the suspected perpetrator drugs, resulting in 21 idiosyncratic DILI cases and seven high-dose APAP (intrinsic) DILI cases. In the latter patients, APAP could be assumed the sole perpetrator drug in four cases of intentional overdose, whereas for all seven cases, high doses of at least or more than a single ingestion of 24 g within 24 h were recorded, or high serum levels were detected (>380 µmol/L) in one case where the dose was unknown. The causal relationship between the suspected drugs and liver damage was evaluated using the Roussel Uclaf Causality Assessment Method (RUCAM) [34] in all cases of idiosyncratic DILI cases (not caused by high-dose APAP). Of 21 idiosyncratic DILI cases, the causality between drugs and liver damage was classified as “highly probable” (score > 9) in eight cases, in 12 cases as “probable” (score of 6–8) and in the remaining six cases as “possible” (score of 3–5). Referring to the treatment history of the 28 patients, 34 potentially hepatotoxic substances were identified.
2.2. Plasma Sphingolipid Levels in Healthy Volunteers and Patients Diagnosed with DILI
Thirteen sphingoid bases were measured in the plasma of the patients with DILI and the control subjects. Suspected intrinsic (APAP overdose) and idiosyncratic cases were grouped together in initial analyses due to the available case numbers and clinical descriptions. The calculated concentrations of the different sphingoid bases agreed well with previous analytical studies [35,36,37,38]. Firstly, we assessed the effect of the co-variants gender and age on plasma sphingolipid profile across both groups and found that neither seem to affect the plasma sphingolipid profile (Figure 2A,C). As alterations in the sphingolipid content and profile have been associated with cardiovascular disease (CVD) in both animal and human studies [11,12,13,14], the effect of underlying CVD on sphingolipid content and profile was also investigated. It can be seen that the total level of sphingolipids (Figure 2D) and the level of most of the sphingoid bases (Figure 2B) were comparable between the CVD and the non-CVD group. However, the level of circulating 1-deoxysphingosine (1-deoxySO) was significantly higher in the CVD group than in the non-CVD group (0.17 ± 0.02 vs. 0.10 ± 0.01 μmol/L) (Figure 2B,E) when comparing all cases and controls.
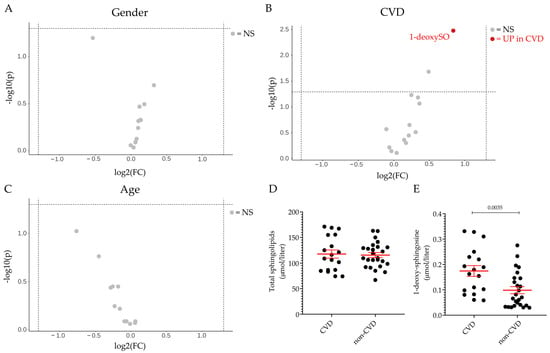
Figure 2.
Gender, age and CVD effect on plasma sphingolipid profile. Volcano plot of the 13 sphingoid base species identified by LC–MS/MS according to gender (A), pre-existing cardiovascular disease (CVD) in individuals irrespective of DILI diagnosis (B), and age (≤50 vs. >50) (C). The fold-change of concentration is reported on the x-axis, the significance (p-value) on the y-axis. The vertical and horizontal dotted lines show the cut-off of fold-change = ±1.5, and of p-value = 0.05, respectively. Plasma level of total sphingolipids (D) and 1-deoxy-sphingosine (1-deoxySO) (E) in individuals with pre-existing cardiovascular disease (CVD group) and in those without CVD (non-CVD group). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. The comparison of the means was performed by unpaired Student t-test. In scatter plot representation, each dot represents one individual sample. NS: not significant, UP: significantly increased.
Next, we compared the plasma sphingolipid profile of DILI and control groups. It can be seen that the level of total sphingolipids (Figure 3A) and of the individual sphingoid bases (Figure 3B) was comparable between the two groups. However, when the analysis was performed upon exclusion of the individuals with underlying CVD in both groups, it was found that the plasma level of 1-deoxysphingosine (1-deoxySO) was significantly elevated in the DILI group in comparison to the control group (0.13 ± 0.02 vs. 0.06 ± 0.02 μmol/L, p = 0.0045) (Figure 3C,D). Figure 3E shows that the level of 1-deoxySO in the plasma of patients with DILI did not correlate with the ALT values measured at the time of the diagnosis, suggesting that the higher level of circulating 1-deoxySO did not reflect the extent of the liver damage, as defined by the ALT value.
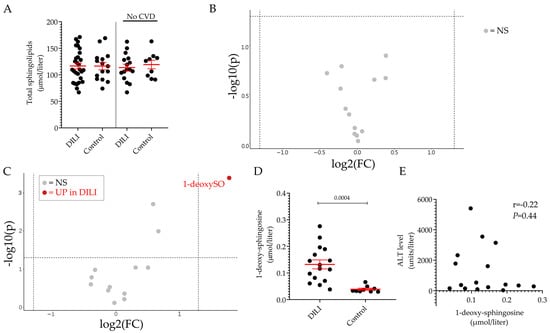
Figure 3.
Plasmatic sphingolipid profile of individuals DILI patients and healthy volunteers. Total sphingolipid levels in DILI and control groups. Results are expressed as the mean ± SEM, where each dot represents one individual sample. Comparison of the means was performed by unpaired t-test (A). Volcano plot of the 13 sphingoid base species identified by LC–MS/MS between DILI and control groups (B) and between the non-CVD respective subgroups (C). The fold-change of concentration is reported on the x-axis, the significance (p-value) on the y-axis. The vertical and horizontal dotted lines show the cut-off of fold-change = ±1.5, and of p-value = 0.05, respectively. Plasma level of 1-deoxy-sphingosine (1-deoxySO) in non-CVD DILI and control groups (D). Pearson’s correlation analysis between ALT values and 1-deoxysphingosine in the non-CVD DILI group (E). NS: not significant, UP: significantly increased.
2.3. Sphingolipid Profile in DILI Subgroups
Among the thirteen sphingoid bases measured in plasma, the level of 1-deoxySO was the only significant difference between individuals with ongoing DILI and healthy volunteers. This difference could be detected only when comparing cases and controls without underlying CVD. Further analyses on the non-CVD groups were carried out based on the type or severity of DILI. Based on the R ratio, 11 hepatocellular and five cholestatic/mixed DILI were observed. In Figure 3A, the plasma level of 1-deoxySO was comparable between the two groups. Then, DILI cases were regrouped according to Hy’s law and non-Hy’s law cases, using the revised nR Hy’s law where DILI cases (i) displaying an R ratio > 5 ([(ALT or AST (whichever is highest) /ULN) ÷ ALP/ULN)] > 5) and (ii) serum TBL of greater than 2.5 mg/dL were considered severe (fulfilling nR Hy’s law criteria) [33,39]. Similar to the type of injury analysis, the plasma level of 1-deoxySO was comparable between the two groups (Figure 4B). Five out of 16 DILI cases without underlying CVD were caused by APAP intoxication. The level of 1-deoxySO in the APAP group was significantly higher than that in the control group (Figure 5A). Yet, most of the other sphingoid bases were underrepresented in the APAP group (Figure 5C) as reflected by the significantly lower level of total sphingolipids (Figure 5B). In particular, in Figure 4, it can be seen that the circulating level of the atypical sphingoid bases C16 and C17 were significantly reduced in the plasma of individuals who experienced APAP intoxication.
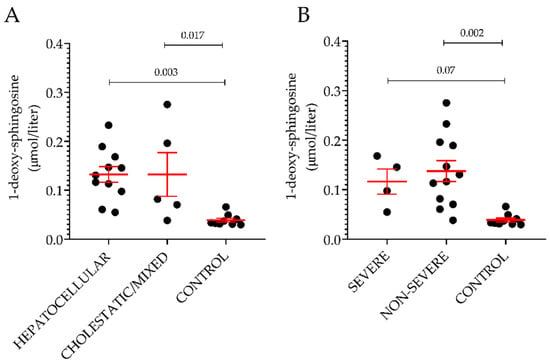
Figure 4.
Plasma level of 1-deoxysphingosine according to type and severity of the injury. Classification was done based on the R ratio (A) or on the nR Hy’s law (B). Results are expressed as the mean ± SEM, where each dot represents one individual sample. Comparison of the means was performed by unpaired t-test.
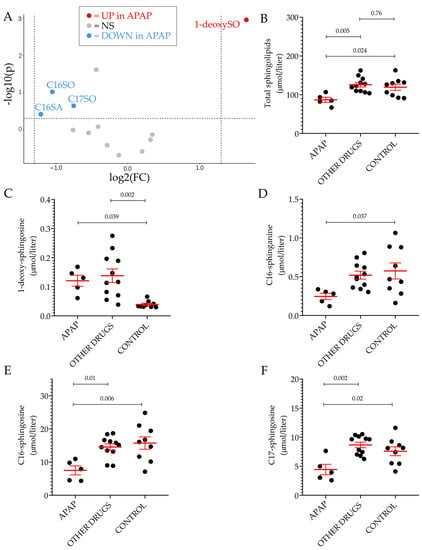
Figure 5.
Plasmatic sphingolipid profile of patients with acetaminophen intoxication. Volcano plot of the 13 sphingoid base species identified by LC–MS/MS between individuals who experience APAP intoxication and the control group, excluding patients and controls with underlying CVD (A). The fold-change of concentration is reported on the x-axis, the significance (p-value) on the y-axis. The vertical and horizontal dotted lines show the cut-off of fold-change = ±1.5, and of p-value = 0.05, respectively. Scatter dot plot of total sphingolipid (B), 1-deoxysphingosine (C), C16-sphinganine (D), C16-sphingosine (E) and C17-sphingosine (F) levels in the indicated groups. In all scatter dot plots, results are expressed as the mean ± SEM, where each dot represents one individual sample. Comparisons of the means was performed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. NS: not significant, UP: significantly increased. DOWN: significantly decreased.
3. Discussion
The level of sphingolipids largely depends on the expression and activity of the serine palmitoyltransferase (SPT), which catalyzes the formation of the sphingoid base from acyl-CoA species, preferentially palmitoyl-CoA, and serine, and is considered the rate-limiting step in sphingolipid de novo synthesis [40]. SPT is an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) protein ubiquitously expressed in the body, and its expression level and activity have been shown to increase in response to several stress stimuli [40]. With respect to the liver, it has been shown that the expression and activity of SPT was significantly induced in rats treated with hexachlorobenzene, a chlorinated hydrocarbon associated with porphyria [41]. We have previously shown that the level of hepatic and circulating sphingolipids are increased in a diet-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) mouse model [14], but not in the plasma of patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), suggesting that sphingolipid metabolism adaptation to liver injury might differ between humans and rodents [14]. In line with these results, the level of total sphingolipids is not increased in the plasma of patients diagnosed with DILI in comparison to that measured in the plasma of healthy volunteers.
1-deoxysphingolipids (mostly 1-deoxySO) are atypical sphingolipids formed when SPT metabolizes alanine instead of serine. 1-deoxysphingolipid levels have been found to be elevated in patients carrying SPT mutations, causing hereditary sensory autonomic neuropathy type 1 [42,43], and, while no studies specifically confirm elevations in patients with CVD, in metabolic disorders such as nondiabetic metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes [12,13,14,44]. 1-deoxysphingolipids are toxic metabolites that seem to target mitochondria, causing mitochondrial dysfunction and ER stress [45,46]. It is conceivable that the elevated 1-deoxysphingolipids content measured in the plasma of the individuals that experienced DILI might contribute to extensive mitochondrial damage and ER stress in hepatocytes. Being highly enriched in mitochondria to meet the high ATP demand to sustain the exceptional anabolic and catabolic activity that the liver must ensure to the body, hepatocytes must cope with a relatively high level of reactive oxygen species (ROS) that are normally generated during mitochondrial respiration [47]. An insult at the expense of the mitochondria can rapidly elevate intrahepatic ROS level to toxic concentrations that exacerbate the initial mitochondrial damage, endangering the whole cell. ER stress appears to be exceptionally high in DILI [48]. Moreover, the level of oxidation protein products, a typical sign of ER stress, has been shown to correlate well with the severity of the hepatic damage [49].
The sphingoid base profile does not appear to be informative with regard to the type and the severity of the injury. Conversely, when the DILI cases were grouped into APAP-induced (intrinsic) DILI and other (idiosyncratic) DILI, a pattern emerged. C16-sphinganine (C16SA), C16-sphingosine (C16SO) and C17-sphinganine (C17SO) were all consistently reduced in the plasma of individuals with intrinsic DILI but not in the idiosyncratic DILI group. C16SA and C17SA are atypical sphingoid bases, formed by reaction of SPT with acyl-CoAs with different carbon numbers than palmitoyl-CoA. Mammalian SPT is ubiquitously present as a tetramer formed by two dimers of the subunits SPTLC1 and SPTLC2. In some tissues, SPTLC1 predominantly dimerizes with a third subunit, SPTLC3, which has the highest affinity for the acyl-CoAs other than palmitoyl-CoA [50,51]. It has been shown that the expression levels of SPTLC1 and SPTLC2 are induced by acute ER stress in primary hepatocytes and HepG2 cells. Moreover, Sptlc2 was upregulated by tunicamycin, an ER stress inducer, in the livers of C57BL/6J wild-type mice [52]. In another study, it has been shown that SPT activity in the liver of Syrian hamsters and in HepG2 cells was elevated during inflammation [53]. Although the liver also expresses SPTLC3, data on the role of ER stress and inflammation on hepatic SPTLC3 expression are lacking [54]. It is conceivable that an increase in the SPTLC2:SPTLC3 induced by acute ER stress and/or inflammation would favor the synthesis of canonical (C18-, C19-sphingolipids) over atypical sphingolipids (C16-, C17-sphingolipids). ER stress is not specific to APAP-induced liver injury, although well known for this drug and likely secondary to extensive mitochondrial stress, and has been observed with several other DILI-causing drugs [55,56]. However, ALT values for the APAP-DILI patients included in this study were strongly elevated (all cases presented with ALT > 2300 U/liter), which may indicate advanced inflammatory processes and ER stress in comparison with the idiosyncratic DILI cases, and result in the observed alterations in sphingoid base profiles in these patients. As ALT levels do not correlate with severe clinical outcomes in acute or chronic liver diseases, the potential of select sphingoid bases functioning not only as biomarkers offering mechanistic insights into liver injury, but also serving alongside standard measures as independent conditional variables in the assessment of DILI, will warrant further studies in both intrinsic and idiosyncratic DILI cases.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Selection
Between 2012 and 2015, patients presenting with possible drug-induced liver injury (DILI), as recorded by the pharmacovigilance service of the department of Clinical Pharmacology and Toxicology at the University Hospital Zurich, associated outpatient clinics, and GZO Spital Wetzikon, were enrolled into the Swiss Drug-Induced Liver Injury Cohort Study, giving informed consent for participation in the observational study. The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Swiss Cantonal Ethics Committee of Zürich (Kantonale Ethikkomission Zürich, SDILIC study ID KEK-ZH-Nr. 2012-0166). Cases were reviewed and potential causative agents determined by an adjudication committee consisting of a team of independent clinical experts, including at least one experienced pharmacologist. Differential diagnosis of DILI was made after careful assessment of patient and medication records, using the Roussel Uclaf Causality Assessment Method (RUCAM) for idiosyncratic DILI cases to assess causality, and APAP doses, serum APAP levels, and liver enzyme time course data to assess cases where intrinsic DILI was suspected. Blood samples were collected from patients on the day of trial inclusion/diagnosis of DILI and regularly during the course of clinical care. Sphingoid bases and liver laboratory parameters reported here were quantified in initial samplings obtained upon diagnosis of DILI and inclusion into the study. For sphingoid base quantification, blood was collected in EDTA tubes (BD Vacutainer system, BD Plymouth, Plymouth, UK), centrifuged at 2600gav for 10 minutes, aliquoted, and immediately placed at −80 °C. Patient characteristics are provided in Table 1. Control patients without elevated liver enzymes or pre-existing diagnosed liver diseases were recruited within the same study, with blood samples being taken on the day of inclusion to the study. Inclusion and exclusion criteria for DILI and non-DILI control patients are shown in Table S2. Suspected perpetrator drugs for DILI patients are shown in Table S3. To supplement the 6 non-DILI control samples, 9 anonymized randomly selected biobanked samples collected from consenting normal healthy volunteers without pre-existing diagnosed CVD, liver disease, or diabetes, were included in the reported analyses as controls, for a total of n = 15 controls. Select demographic, clinical, and normalized sphingolipid data for all subjects are reported in Table S1.

Table 1.
Demographics and patient characteristics.
4.2. Classification According to Type, Severity and Mechanism of Injury
The liver injury was categorized as hepatocellular, cholestatic or mixed based on the R ratio [(ALT/ULN) ÷ ALP/ULN)]. DILI cases with an R factor >5 were defined as hepatocellular injury, whereas those cases with an R factor <2 were considered of cholestatic nature. An R factor between two and five defined a mixed injury [57]. nR Hy’s law was used to identify severe cases of injury [33]. For classification of DILI cases into intrinsic versus idiosyncratic, a conservative classification was performed in which only cases where APAP intoxication was recorded were classified as intrinsic, and only cases where perpetrator drugs with existing indications of adverse liver events, as recorded in the LiverTox® database and other literature as cited throughout, were classified as “other”/idiosyncratic DILI [58].
4.3. Sphingolipid Analysis
Sample preparation was done as described previously [44]. Briefly, 100 ul plasma was extracted in 0.5 ml MetOH spiked with 200 pmol d7-Sphingosine and d7-sphinganiene (Avanti Polar Lipids Inc, Alabaster, AL, United States). After extraction, the lipids were hydrolyzed in 1N HCl (16 h, 65°C) to release the N-acyl chain and head groups. The resulting long chain bases were re-extracted in chloroform/water and dried as described previously [44]. For the analysis, the sphingoid bases were dissolved in 75 µL of sample buffer (56% MetOH, 34% EtOH, 10% H2O) and derivatized with 5 µL ο-phthalaldehyde (OPA) working solution (990 µL boric acid [3%] + 10 µL OPA [50 mg/mL in EtOH] + 0.5 µL 2-mercaptoethanol). The long chain bases were separated on a C18 column (Uptispere 120 Å, 5 µm, 125 × 2 mm, Interchim, Montluçon, France) coupled to a Transcend UPLC pump (Thermo Scientific, Reinach, BL, Switzerland). A binary solvent system was applied at a flow rate of 0.3 ml/min, with solvent A (1:1 MetOH/ammonium acetate (5 mM) in water) and solvent B (100% methanol). The column was equilibrated with a 1:1 mixture of mobile phase A and B followed by injection of 25 µL of the sample. Sphingoid bases were eluted by a linear gradient from A to B (25 min) followed by a regeneration phase with 100% B (7 min). Analysis was done on a Q-Exactive Orbitrap mass spectrometer (Thermo, Reinach, BL, Switzerland) in full scan mode using atmospheric pressure chemical ionization. The following MS settings were used: scan range of m/z 120-1200, mass resolution of 140000, automatic gain control target of 3.00E+06 and max injection time of 512 msec. Peaks were quantified using the Quan Browser Software (Thermo Scientific, Reinach, BL, Switzerland).
4.4. Statistical Analysis
Mann–Whitney U-Test and One-Way ANOVA for comparison of sphingolipid levels, and Pearson’s correlation analyses between ALT and sphingolipid levels were performed with GraphPad Prism (version 9.0 for Windows, GraphPad Software). Volcano plots were plotted using MetaboAnalyst (version 5.0).
5. Conclusions
Despite all the limitations that are intrinsic of an observational study on a small number of patients and controls, including confounding factors and the impossibility to demonstrate causality, our data indicate the clinical relevance of drug-induced perturbations of the sphingolipid metabolism observed in vitro and in animals. While total sphingoid base levels were not altered across patient and control groups, 1-deoxySO was elevated in DILI patients, after removal of underlying CVD as a confounding factor. In addition, shorter chain sphingoid bases C16SO, C16SA, and C17SO were specifically and exclusively reduced in patients with intrinsic DILI (caused by APAP overdose). The role of these species and significance of alterations in the levels thereof in the onset, progression, and clinical outcome of DILI cannot be determined from this small study. Nonetheless, our results warrant further larger scale clinical investigations, perhaps on more informative global lipidomics analyses into (i) how alteration of lipid metabolism can provide new mechanistic insights into hepatotoxicity and their role in it, and (ii) whether specific lipid species can be used as biomarkers in the delineation of the type of DILI or assessment of severity of injury in the frame of both drug development and pharmacovigilance.
Supplementary Materials
The supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijms24033013/s1. References [59,60] are cited in supplementary materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.G. and G.A.K.-U.; methodology, I.A. and T.H.; formal analysis, Z.G., S.L.S., I.A., J.I.G., G.P.A. and M.V.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.G., S.L.S. and M.V.; writing—review and editing, I.A., T.H., J.I.G., G.P.A. and G.A.K.-U.; funding acquisition, T.H., G.P.A., G.A.K.-U. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Swiss National Science Foundation to G.A.-K.U. (#310030_175639) and to T.H. (#31003A_179371), by the EU IMI (Innovative Medicines Initiative Joint Undertaking) SAFE-T (Safer and Faster Evidence-Based Translation) Consortium (#115003, www.imi.europa.eu), and the IMI 2 TransBioLine (Translational Safety Biomarker Pipeline) Consortium (#821283), and by COST (European Cooperation in Science & Technology) Action CA17112 – Prospective European Drug-Induced Liver Injury Network (Pro-Euro-DILI-Net). The Innovative Medicines Initiative Joint Undertakings receive/received support from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program and EFPIA. This communication reflects the author’s view and neither IMI nor the European Union or EFPIA are responsible for any use that may be made of the information contained therein.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Swiss Cantonal Ethics Committee of Zürich (Kantonale Ethikkomission Zürich, SDILIC study ID KEK-ZH-Nr. 2012-0166).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Additional patient data are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
Gerd A. Kullak-Ublick is employed by Novartis Pharma. The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kotronen, A.; Seppanen-Laakso, T.; Westerbacka, J.; Kiviluoto, T.; Arola, J.; Ruskeepaa, A.L.; Yki-Jarvinen, H.; Oresic, M. Comparison of lipid and fatty acid composition of the liver, subcutaneous and intra-abdominal adipose tissue, and serum. Obesity 2010, 18, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojima, H.; Freeman, C.M.; Gulbins, E.; Lentsch, A.B. Sphingolipids in liver injury, repair and regeneration. Biol. Chem. 2015, 396, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, A.D.; Maurhofer, O.; Beyoglu, D.; Lanz, C.; Krausz, K.W.; Pabst, T.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Dufour, J.F.; Idle, J.R. Aberrant lipid metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma revealed by plasma metabolomics and lipid profiling. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 6590–6600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yin, P.; Zhao, X.; Xing, W.; Hu, C.; Zhou, L.; Xu, G. Serum lipid profiling of patients with chronic hepatitis B, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma by ultra fast LC/IT-TOF MS. Electrophoresis 2013, 34, 2848–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puri, P.; Wiest, M.M.; Cheung, O.; Mirshahi, F.; Sargeant, C.; Min, H.K.; Contos, M.J.; Sterling, R.K.; Fuchs, M.; Zhou, H.; et al. The plasma lipidomic signature of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1827–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sztolsztener, K.; Konstantynowicz-Nowicka, K.; Harasim-Symbor, E.; Chabowski, A. Time-Dependent Changes in Hepatic Sphingolipid Accumulation and PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway in a Rat Model of NAFLD. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quehenberger, O.; Armando, A.M.; Brown, A.H.; Milne, S.B.; Myers, D.S.; Merrill, A.H.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Jones, K.N.; Kelly, S.; Shaner, R.L.; et al. Lipidomics reveals a remarkable diversity of lipids in human plasma. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 3299–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahy, E.; Subramaniam, S.; Brown, H.A.; Glass, C.K.; Merrill, A.H., Jr.; Murphy, R.C.; Raetz, C.R.; Russell, D.W.; Seyama, Y.; Shaw, W.; et al. A comprehensive classification system for lipids. J. Lipid Res. 2005, 46, 839–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruett, S.T.; Bushnev, A.; Hagedorn, K.; Adiga, M.; Haynes, C.A.; Sullards, M.C.; Liotta, D.C.; Merrill, A.H., Jr. Biodiversity of sphingoid bases (“sphingosines”) and related amino alcohols. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1621–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lone, M.A.; Hulsmeier, A.J.; Saied, E.M.; Karsai, G.; Arenz, C.; von Eckardstein, A.; Hornemann, T. Subunit composition of the mammalian serine-palmitoyltransferase defines the spectrum of straight and methyl-branched long-chain bases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 15591–15598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poss, A.M.; Maschek, J.A.; Cox, J.E.; Hauner, B.J.; Hopkins, P.N.; Hunt, S.C.; Holland, W.L.; Summers, S.A.; Playdon, M.C. Machine learning reveals serum sphingolipids as cholesterol-independent biomarkers of coronary artery disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 1363–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Othman, A.; Rutti, M.F.; Ernst, D.; Saely, C.H.; Rein, P.; Drexel, H.; Porretta-Serapiglia, C.; Lauria, G.; Bianchi, R.; von Eckardstein, A.; et al. Plasma deoxysphingolipids: A novel class of biomarkers for the metabolic syndrome? Diabetologia 2012, 55, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chew, W.S.; Torta, F.; Ji, S.; Choi, H.; Begum, H.; Sim, X.; Khoo, C.M.; Khoo, E.Y.H.; Ong, W.Y.; Van Dam, R.M.; et al. Large-scale lipidomics identifies associations between plasma sphingolipids and T2DM incidence. JCI Insight 2019, 5, e126925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gai, Z.; Gui, T.; Alecu, I.; Lone, M.A.; Hornemann, T.; Chen, Q.; Visentin, M.; Hiller, C.; Hausler, S.; Kullak-Ublick, G.A. Farnesoid X receptor activation induces the degradation of hepatotoxic 1-deoxysphingolipids in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Liver 2020, 40, 844–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkowitz, L.; Salazar, C.; Ryff, C.D.; Coe, C.L.; Rigotti, A. Serum sphingolipid profiling as a novel biomarker for metabolic syndrome characterization. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 1092331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balram, A.; Thapa, S.; Chatterjee, S. Glycosphingolipids in Diabetes, Oxidative Stress, and Cardiovascular Disease: Prevention in Experimental Animal Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Maekawa, K.; Ishikawa, M.; Senoo, Y.; Urata, M.; Murayama, M.; Nakatsu, N.; Yamada, H.; Saito, Y. Glucosylceramide and lysophosphatidylcholines as potential blood biomarkers for drug-induced hepatic phospholipidosis. Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2014, 141, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, L.; Qu, F.; Jia, Z.; Wang, C.; Wu, C.; Zhang, J. Integrated targeted sphingolipidomics and transcriptomics reveal abnormal sphingolipid metabolism as a novel mechanism of the hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity of triptolide. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 170, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsunoda, M.; Sharma, R.P.; Riley, R.T. Early fumonisin B1 toxicity in relation to disrupted sphingolipid metabolism in male BALB/c mice. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 1998, 12, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, R.T.; Enongene, E.; Voss, K.A.; Norred, W.P.; Meredith, F.I.; Sharma, R.P.; Spitsbergen, J.; Williams, D.E.; Carlson, D.B.; Merrill, A.H., Jr. Sphingolipid perturbations as mechanisms for fumonisin carcinogenesis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109 (Suppl. S2), 301–308. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zitomer, N.C.; Mitchell, T.; Voss, K.A.; Bondy, G.S.; Pruett, S.T.; Garnier-Amblard, E.C.; Liebeskind, L.S.; Park, H.; Wang, E.; Sullards, M.C.; et al. Ceramide synthase inhibition by fumonisin B1 causes accumulation of 1-deoxysphinganine: A novel category of bioactive 1-deoxysphingoid bases and 1-deoxydihydroceramides biosynthesized by mammalian cell lines and animals. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 4786–4795. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Wang, H.; Jones, J.W. Sphingolipid metabolism as a marker of hepatotoxicity in drug-induced liver injury. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2020, 151, 106484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kullak-Ublick, G.A.; Andrade, R.J.; Merz, M.; End, P.; Benesic, A.; Gerbes, A.L.; Aithal, G.P. Drug-induced liver injury: Recent advances in diagnosis and risk assessment. Gut 2017, 66, 1154–1164. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, R.J.; Chalasani, N.; Bjornsson, E.S.; Suzuki, A.; Kullak-Ublick, G.A.; Watkins, P.B.; Devarbhavi, H.; Merz, M.; Lucena, M.I.; Kaplowitz, N.; et al. Drug-induced liver injury. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2019, 5, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, A.; Jaeschke, H. Acetaminophen Hepatotoxicity. Semin. Liver Dis. 2019, 39, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjornsson, E.S.; Bergmann, O.M.; Bjornsson, H.K.; Kvaran, R.B.; Olafsson, S. Incidence, presentation, and outcomes in patients with drug-induced liver injury in the general population of Iceland. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 1419–1425.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucena, M.I.; Molokhia, M.; Shen, Y.; Urban, T.J.; Aithal, G.P.; Andrade, R.J.; Day, C.P.; Ruiz-Cabello, F.; Donaldson, P.T.; Stephens, C.; et al. Susceptibility to amoxicillin-clavulanate-induced liver injury is influenced by multiple HLA class I and II alleles. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hautekeete, M.L.; Horsmans, Y.; Van Waeyenberge, C.; Demanet, C.; Henrion, J.; Verbist, L.; Brenard, R.; Sempoux, C.; Michielsen, P.P.; Yap, P.S.; et al. HLA association of amoxicillin-clavulanate--induced hepatitis. Gastroenterology 1999, 117, 1181–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daly, A.K.; Donaldson, P.T.; Bhatnagar, P.; Shen, Y.; Pe’er, I.; Floratos, A.; Daly, M.J.; Goldstein, D.B.; John, S.; Nelson, M.R.; et al. HLA-B*5701 genotype is a major determinant of drug-induced liver injury due to flucloxacillin. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 816–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krebs, K.; Bovijn, J.; Zheng, N.; Lepamets, M.; Censin, J.C.; Jurgenson, T.; Sarg, D.; Abner, E.; Laisk, T.; Luo, Y.; et al. Genome-wide Study Identifies Association between HLA-B(*)55:01 and Self-Reported Penicillin Allergy. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 107, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoletti, P.; Aithal, G.P.; Bjornsson, E.S.; Andrade, R.J.; Sawle, A.; Arrese, M.; Barnhart, H.X.; Bondon-Guitton, E.; Hayashi, P.H.; Bessone, F.; et al. Association of Liver Injury From Specific Drugs, or Groups of Drugs, With Polymorphisms in HLA and Other Genes in a Genome-Wide Association Study. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1078–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.J.; Phillips, E.J.; Dellinger, A.; Nicoletti, P.; Schutte, R.; Li, D.; Ostrov, D.A.; Fontana, R.J.; Watkins, P.B.; Stolz, A.; et al. Human Leukocyte Antigen B*14:01 and B*35:01 Are Associated With Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole Induced Liver Injury. Hepatology 2021, 73, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, P.H.; Rockey, D.C.; Fontana, R.J.; Tillmann, H.L.; Kaplowitz, N.; Barnhart, H.X.; Gu, J.; Chalasani, N.P.; Reddy, K.R.; Sherker, A.H.; et al. Death and liver transplantation within 2 years of onset of drug-induced liver injury. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1275–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel Uclaf Causality Assessment Method (RUCAM) in Drug Induced Liver Injury. In LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury; National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2012.
- Bertea, M.; Rutti, M.F.; Othman, A.; Marti-Jaun, J.; Hersberger, M.; von Eckardstein, A.; Hornemann, T. Deoxysphingoid bases as plasma markers in diabetes mellitus. Lipids Health Dis. 2010, 9, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knapp, M.; Baranowski, M.; Lisowska, A.; Musial, W. Decreased free sphingoid base concentration in the plasma of patients with chronic systolic heart failure. Adv. Med. Sci. 2012, 57, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mwinyi, J.; Bostrom, A.; Fehrer, I.; Othman, A.; Waeber, G.; Marti-Soler, H.; Vollenweider, P.; Marques-Vidal, P.; Schioth, H.B.; von Eckardstein, A.; et al. Plasma 1-deoxysphingolipids are early predictors of incident type 2 diabetes mellitus. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175776. [Google Scholar]
- Morano, C.; Zulueta, A.; Caretti, A.; Roda, G.; Paroni, R.; Dei Cas, M. An Update on Sphingolipidomics: Is Something Still Missing? Some Considerations on the Analysis of Complex Sphingolipids and Free-Sphingoid Bases in Plasma and Red Blood Cells. Metabolites 2022, 12, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, H.J. Drug-Induced Liver Disease. In Hepatotoxicity, The Adverse Effects of Drugs and Other Chemicals on the Liver, 2nd ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1978; pp. 428–433. [Google Scholar]
- Hanada, K. Serine palmitoyltransferase, a key enzyme of sphingolipid metabolism. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta 2003, 1632, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billi de Catabbi, S.C.; Setton-Advruj, C.P.; Sterin-Speziale, N.; San Martin de Viale, L.C.; Cochon, A.C. Hexachlorobenzene-induced alterations on neutral and acidic sphingomyelinases and serine palmitoyltransferase activities. A time course study in two strains of rats. Toxicology 2000, 149, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejaoui, K.; Wu, C.; Scheffler, M.D.; Haan, G.; Ashby, P.; Wu, L.; de Jong, P.; Brown, R.H., Jr. SPTLC1 is mutated in hereditary sensory neuropathy, type 1. Nat. Genet. 2001, 27, 261–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawkins, J.L.; Hulme, D.J.; Brahmbhatt, S.B.; Auer-Grumbach, M.; Nicholson, G.A. Mutations in SPTLC1, encoding serine palmitoyltransferase, long chain base subunit-1, cause hereditary sensory neuropathy type I. Nat. Genet. 2001, 27, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, A.; Saely, C.H.; Muendlein, A.; Vonbank, A.; Drexel, H.; von Eckardstein, A.; Hornemann, T. Plasma 1-deoxysphingolipids are predictive biomarkers for type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2015, 3, e000073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alecu, I.; Tedeschi, A.; Behler, N.; Wunderling, K.; Lamberz, C.; Lauterbach, M.A.; Gaebler, A.; Ernst, D.; Van Veldhoven, P.P.; Al-Amoudi, A.; et al. Localization of 1-deoxysphingolipids to mitochondria induces mitochondrial dysfunction. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettigole, S.E.; Glimcher, L.H. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 33, 107–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, M.P. How mitochondria produce reactive oxygen species. Biochem. J. 2009, 417, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver; Clinical Practice Guideline Panel: Chair; Panel Members; EASL Governing Board Representative. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Drug-induced liver injury. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 1222–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.L.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, Y.L.; Zhang, L.J.; Xie, Z.Y.; Huang, K.Z.; Ouyang, X.X.; Wu, X.X.; Xu, X.W.; Li, L.J. Using advanced oxidation protein products and ischaemia-modified albumin to monitor oxidative stress levels in patients with drug-induced liver injury. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornemann, T.; Penno, A.; Rutti, M.F.; Ernst, D.; Kivrak-Pfiffner, F.; Rohrer, L.; von Eckardstein, A. The SPTLC3 subunit of serine palmitoyltransferase generates short chain sphingoid bases. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 26322–26330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lone, M.A.; Bourquin, F.; Hornemann, T. Serine Palmitoyltransferase Subunit 3 and Metabolic Diseases. In Sphingolipid Metabolism and Metabolic Disease; Jiang, X.-C., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; Volume 1372, pp. 47–56. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, G.T.; Devi, S.; Sharma, A.; Cho, K.H.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, B.R.; Kwon, S.H.; Park, T.S. Upregulation of the serine palmitoyltransferase subunit SPTLC2 by endoplasmic reticulum stress inhibits the hepatic insulin response. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, R.A.; Holleran, W.M.; Moser, A.H.; Seki, T.; Uchida, Y.; Fuller, J.; Shigenaga, J.K.; Grunfeld, C.; Feingold, K.R. Endotoxin and cytokines increase hepatic sphingolipid biosynthesis and produce lipoproteins enriched in ceramides and sphingomyelin. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1998, 18, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornemann, T.; Richard, S.; Rutti, M.F.; Wei, Y.; von Eckardstein, A. Cloning and initial characterization of a new subunit for mammalian serine-palmitoyltransferase. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 37275–37281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foufelle, F.; Fromenty, B. Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in drug-induced toxicity. Pharm. Res. Perspect. 2016, 4, e00211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Melchior, W.B., Jr.; Guo, L. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in drug- and environmental toxicant-induced liver toxicity. J. Environ. Sci. Health. Part C Environ. Carcinog. Ecotoxicol. Rev. 2014, 32, 83–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalasani, N.P.; Hayashi, P.H.; Bonkovsky, H.L.; Navarro, V.J.; Lee, W.M.; Fontana, R.J.; on behalf of the Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology. ACG Clinical Guideline: The diagnosis and management of idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 109, 950–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NIH. LiverTox. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547852/ (accessed on 3 October 2022).
- Church, R.J.; Kullak-Ublick, G.A.; Aubrecht, J.; Bonkovsky, H.L.; Chalasani, N.; Fontana, R.J.; Goepfert, J.C.; Hackman, F.; King, N.M.P.; Kirby, S.; et al. Candidate biomarkers for the diagnosis and prognosis of drug-induced liver injury: An international collaborative effort. Hepatology 2019, 69, 760–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aithal, G.P.; Watkins, P.B.; Andrade, R.J.; Larrey, D.; Molokhia, M.; Takikawa, H.; Hunt, C.M.; Wilke, R.A.; Avigan, M.; Kaplowitz, N.; et al. Case definition and phenotype standardization in drug-induced liver injury. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 89, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).