Association between Loss of Immune Checkpoint Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 and Active ANCA-Associated Renal Vasculitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
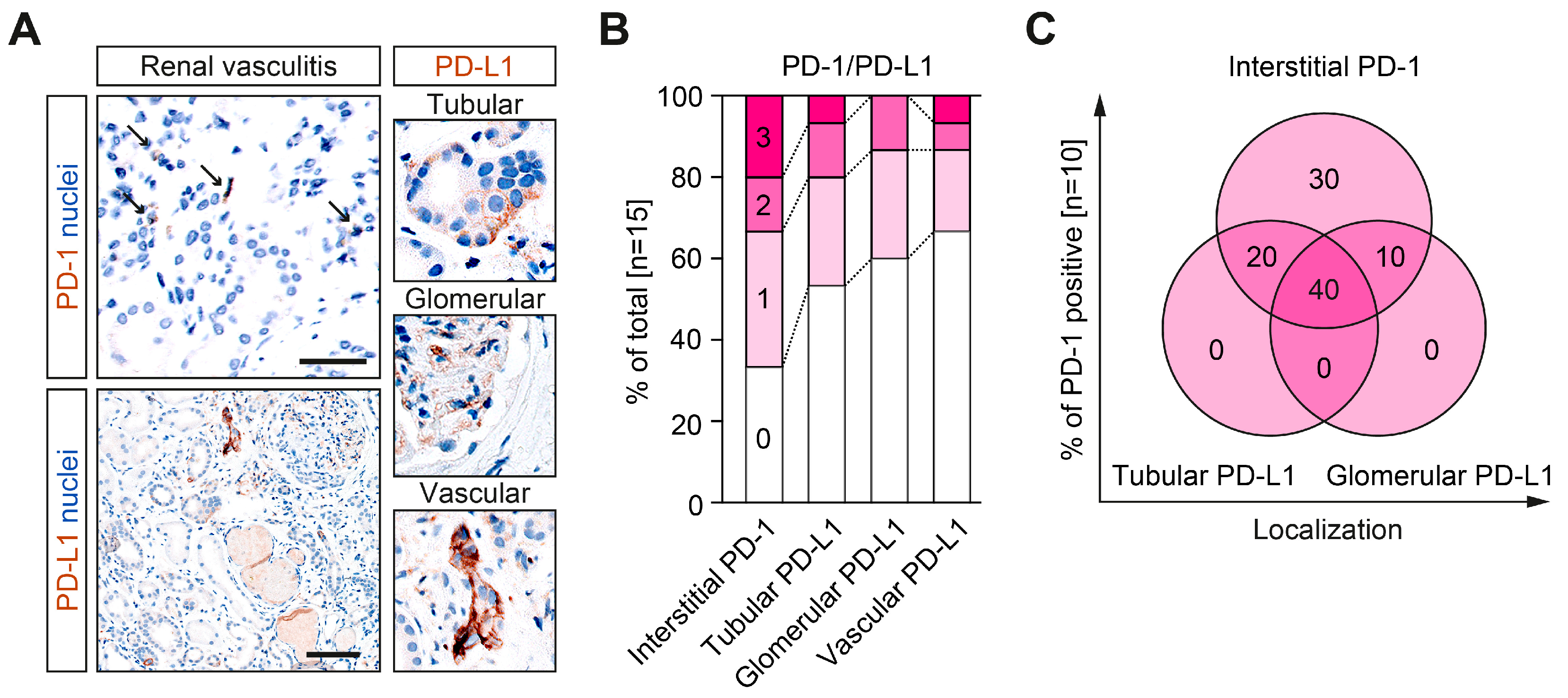
2.1. Immune Checkpoints PD-1 and PD-L1 Are Present in Different Renal Compartments in ANCA-Associated Renal Vasculitis
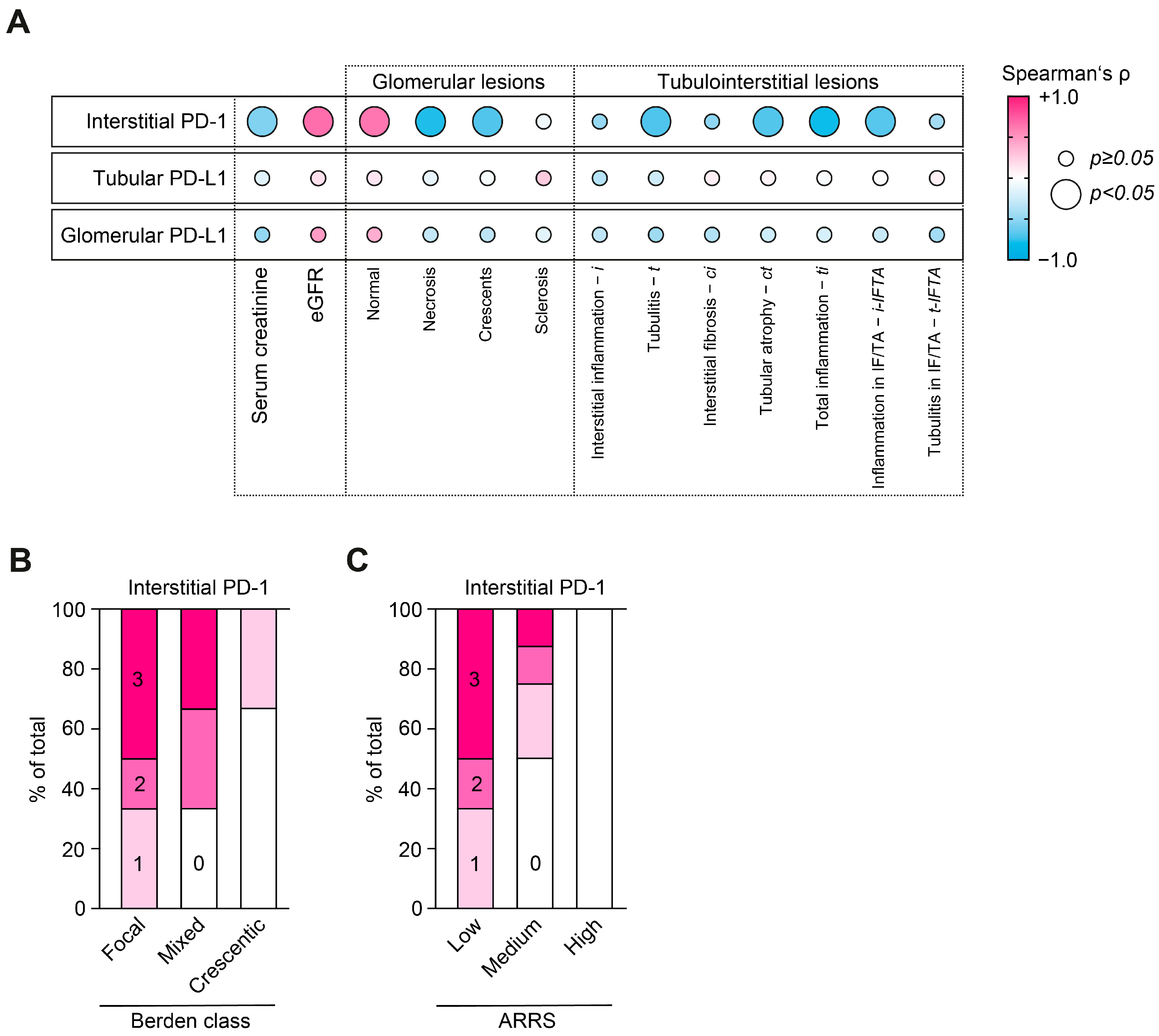
2.2. Loss of Interstitial PD-1 Correlates with Active ANCA-Associated Renal Vasculitis
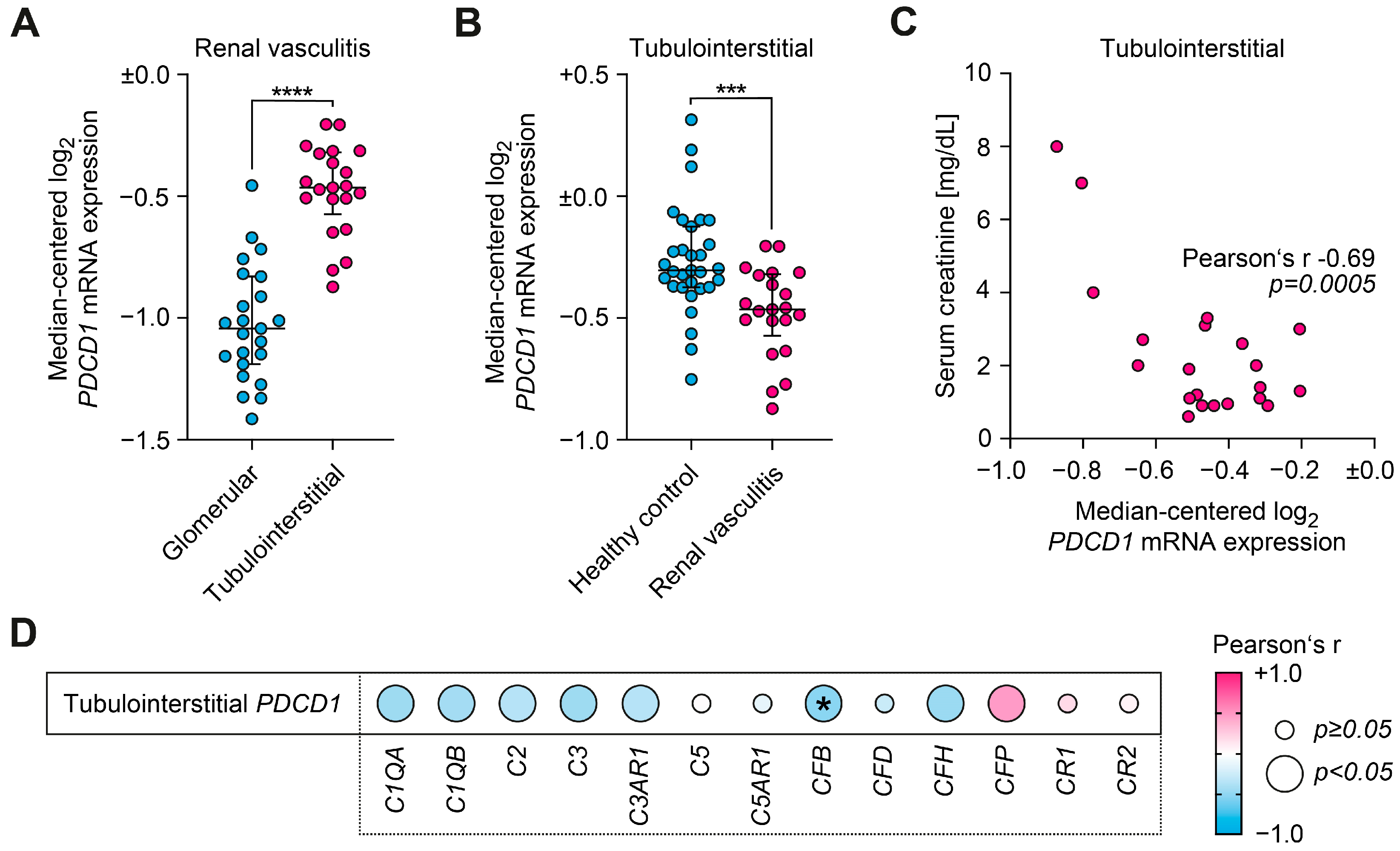
2.3. PD-1 Associates with Decreased Local Synthesis of Complement Factor B
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population and Approval
4.2. Renal Histopathology
4.3. Immunostaining
4.4. Analyses of Publicly Available Array Datasets
4.5. Statistical Methods
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gamerith, G.; Mildner, F.; Merkel, P.A.; Harris, K.; Cooney, L.; Lim, N.; Spiera, R.; Seo, P.; Langford, C.A.; Hoffman, G.S.; et al. Association of baseline soluble immune checkpoints with the risk of relapse in PR3-ANCA vasculitis following induction of remission. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 82, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakroush, S.; Kopp, S.B.; Tampe, D.; Gersmann, A.-K.; Korsten, P.; Zeisberg, M.; Tampe, B. Variable Expression of Programmed Cell Death Protein 1-Ligand 1 in Kidneys Independent of Immune Checkpoint Inhibition. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 624547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqeel, F.; Monroy-Trujillo, J.; Geetha, D. Immune checkpoint inhibitors as potential triggers for ANCA vasculitis. RMD Open 2022, 8, e002500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennette, J.C.; Falk, R.J.; Andrassy, K.; Bacon, P.A.; Churg, J.; Gross, W.L.; Hagen, E.C.; Hoffman, G.S.; Hunder, G.G.; Kallenberg, C.G.M.; et al. Nomenclature of systemic vasculitides. Proposal of an international consensus conference. Arthritis Rheum. 1994, 37, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennette, J.C.; Falk, R.J.; Bacon, P.A.; Basu, N.; Cid, M.C.; Ferrario, F.; Flores-Suarez, L.F.; Gross, W.L.; Guillevin, L.; Hagen, E.C.; et al. 2012 Revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 65, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersson, E.E.; Sundelin, B.; Heigl, Z. Incidence and outcome of pauci-immune necrotizing and crescentic glomerulonephritis in adults. Clin. Nephrol. 1995, 43, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hruskova, Z.; Stel, V.S.; Jayne, D.; Aasarød, K.; De Meester, J.; Ekstrand, A.; Eller, K.; Heaf, J.G.; Hoitsma, A.; Jimenéz, C.M.; et al. Characteristics and Outcomes of Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (Wegener) and Microscopic Polyangiitis Requiring Renal Replacement Therapy: Results from the European Renal Association–European Dialysis and Transplant Association Registry. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 66, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennette, J.C.; Wilkman, A.S.; Falk, R.J. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-associated glomerulonephritis and vasculitis. Am. J. Pathol. 1989, 135, 921–930. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, H.; Schreiber, A.; Heeringa, P.; Falk, R.J.; Jennette, J.C. Alternative Complement Pathway in the Pathogenesis of Disease Mediated by Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Autoantibodies. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 170, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tampe, D.; Kopp, S.B.; Baier, E.; Hakroush, S.; Tampe, B. Compartmentalization of Intrarenal Programmed Cell Death Protein 1-Ligand 1 and Its Receptor in Kidney Injury Related to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Nephrotoxicity. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 902256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Watanabe, R.; Berry, G.J.; Vaglio, A.; Liao, Y.J.; Warrington, K.J.; Goronzy, J.J.; Weyand, C.M. Immunoinhibitory checkpoint deficiency in medium and large vessel vasculitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E970–E979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L. Co-inhibitory molecules of the B7–CD28 family in the control of T-cell immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, H.; Honjo, T. PD-1: An inhibitory immunoreceptor involved in peripheral tolerance. Trends Immunol. 2001, 22, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwai, Y.; Ishida, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Okazaki, T.; Honjo, T.; Minato, N. Involvement of PD-L1 on tumor cells in the escape from host immune system and tumor immunotherapy by PD-L1 blockade. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 12293–12297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, O.; Robert, C.; Daud, A.; Hodi, F.S.; Hwu, W.J.; Kefford, R.; Wolchok, J.D.; Hersey, P.; Joseph, R.W.; Weber, J.S.; et al. Safety and tumor responses with lambrolizumab (anti-PD-1) in melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garon, E.B.; Rizvi, N.A.; Hui, R.; Leighl, N.; Balmanoukian, A.S.; Eder, J.P.; Patnaik, A.; Aggarwal, C.; Gubens, M.; Horn, L.; et al. Pembrolizumab for the Treatment of Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2018–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmer, J.R.; Tykodi, S.S.; Chow, L.Q.M.; Hwu, W.-J.; Topalian, S.L.; Hwu, P.; Drake, C.G.; Camacho, L.H.; Kauh, J.; Odunsi, K.; et al. Safety and Activity of Anti-PD-L1 Antibody in Patients with Advanced Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2455–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, H.; Nose, M.; Hiai, H.; Minato, N.; Honjo, T. Development of Lupus-like Autoimmune Diseases by Disruption of the PD-1 Gene Encoding an ITIM Motif-Carrying Immunoreceptor. Immunity 1999, 11, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keir, M.E.; Liang, S.C.; Guleria, I.; Latchman, Y.E.; Qipo, A.; Albacker, L.A.; Koulmanda, M.; Freeman, G.J.; Sayegh, M.H.; Sharpe, A.H. Tissue expression of PD-L1 mediates peripheral T cell tolerance. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latchman, Y.E.; Liang, S.C.; Wu, Y.; Chernova, T.; Sobel, R.A.; Klemm, M.; Kuchroo, V.K.; Freeman, G.J.; Sharpe, A.H. PD-L1-deficient mice show that PD-L1 on T cells, antigen-presenting cells, and host tissues negatively regulates T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10691–10696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, L.M.; Salinas, V.H.; Brown, K.E.; Vanguri, V.K.; Freeman, G.J.; Kuchroo, V.K.; Sharpe, A.H. PD-L1 regulates the development, maintenance, and function of induced regulatory T cells. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 3015–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAlees, J.W.; Lajoie, S.; Dienger, K.; Sproles, A.A.; Richgels, P.K.; Yang, Y.; Khodoun, M.; Azuma, M.; Yagita, H.; Fulkerson, P.C.; et al. Differential control of CD4(+) T-cell subsets by the PD-1/PD-L1 axis in a mouse model of allergic asthma. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 45, 1019–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiura, D.; Okazaki, I.-M.; Maeda, T.K.; Maruhashi, T.; Shimizu, K.; Arakaki, R.; Takemoto, T.; Ishimaru, N.; Okazaki, T. PD-1 agonism by anti-CD80 inhibits T cell activation and alleviates autoimmunity. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakroush, S.; Tampe, D.; Korsten, P.; Ströbel, P.; Tampe, B. Complement Components C3 and C4 Indicate Vasculitis Manifestations to Distinct Renal Compartments in ANCA-Associated Glomerulonephritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berden, A.E.; Ferrario, F.; Hagen, E.C.; Jayne, D.R.; Jennette, J.C.; Joh, K.; Neumann, I.; Noël, L.-H.; Pusey, C.D.; Waldherr, R.; et al. Histopathologic Classification of ANCA-Associated Glomerulonephritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 1628–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brix, S.R.; Noriega, M.; Tennstedt, P.; Vettorazzi, E.; Busch, M.; Nitschke, M.; Jabs, W.J.; Özcan, F.; Wendt, R.; Hausberg, M.; et al. Development and validation of a renal risk score in ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 2018, 94, 1177–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roufosse, C.; Simmonds, N.; Groningen, M.C.-V.; Haas, M.; Henriksen, K.J.; Horsfield, C.; Loupy, A.; Mengel, M.; Perkowska-Ptasińska, A.; Rabant, M.; et al. A 2018 Reference Guide to the Banff Classification of Renal Allograft Pathology. Transplantation 2018, 102, 1795–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, W.; Nair, V.; Smith, S.; Zhu, L.; Shedden, K.; Song, P.X.K.; Mariani, L.H.; Eichinger, F.H.; Berthier, C.C.; Randolph, A.; et al. Tissue transcriptome-driven identification of epidermal growth factor as a chronic kidney disease biomarker. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 316ra193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hakroush, S.; Tampe, B. Association between Loss of Immune Checkpoint Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 and Active ANCA-Associated Renal Vasculitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2975. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032975
Hakroush S, Tampe B. Association between Loss of Immune Checkpoint Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 and Active ANCA-Associated Renal Vasculitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(3):2975. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032975
Chicago/Turabian StyleHakroush, Samy, and Björn Tampe. 2023. "Association between Loss of Immune Checkpoint Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 and Active ANCA-Associated Renal Vasculitis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 3: 2975. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032975
APA StyleHakroush, S., & Tampe, B. (2023). Association between Loss of Immune Checkpoint Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 and Active ANCA-Associated Renal Vasculitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(3), 2975. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032975





