Meta-Analysis and Multivariate GWAS Analyses in 80,950 Individuals of African Ancestry Identify Novel Variants Associated with Blood Pressure Traits
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
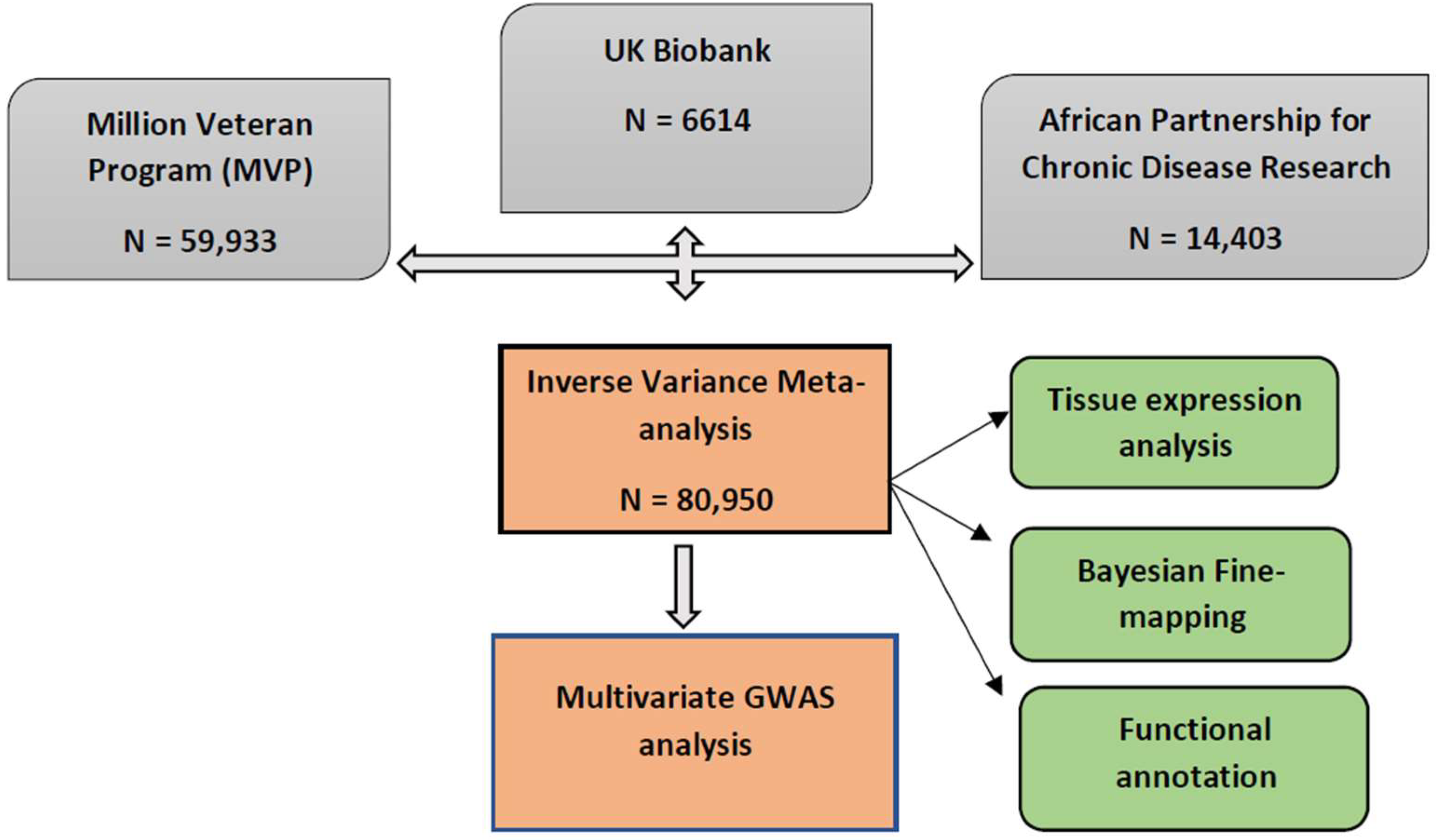
2.1. Results Overview
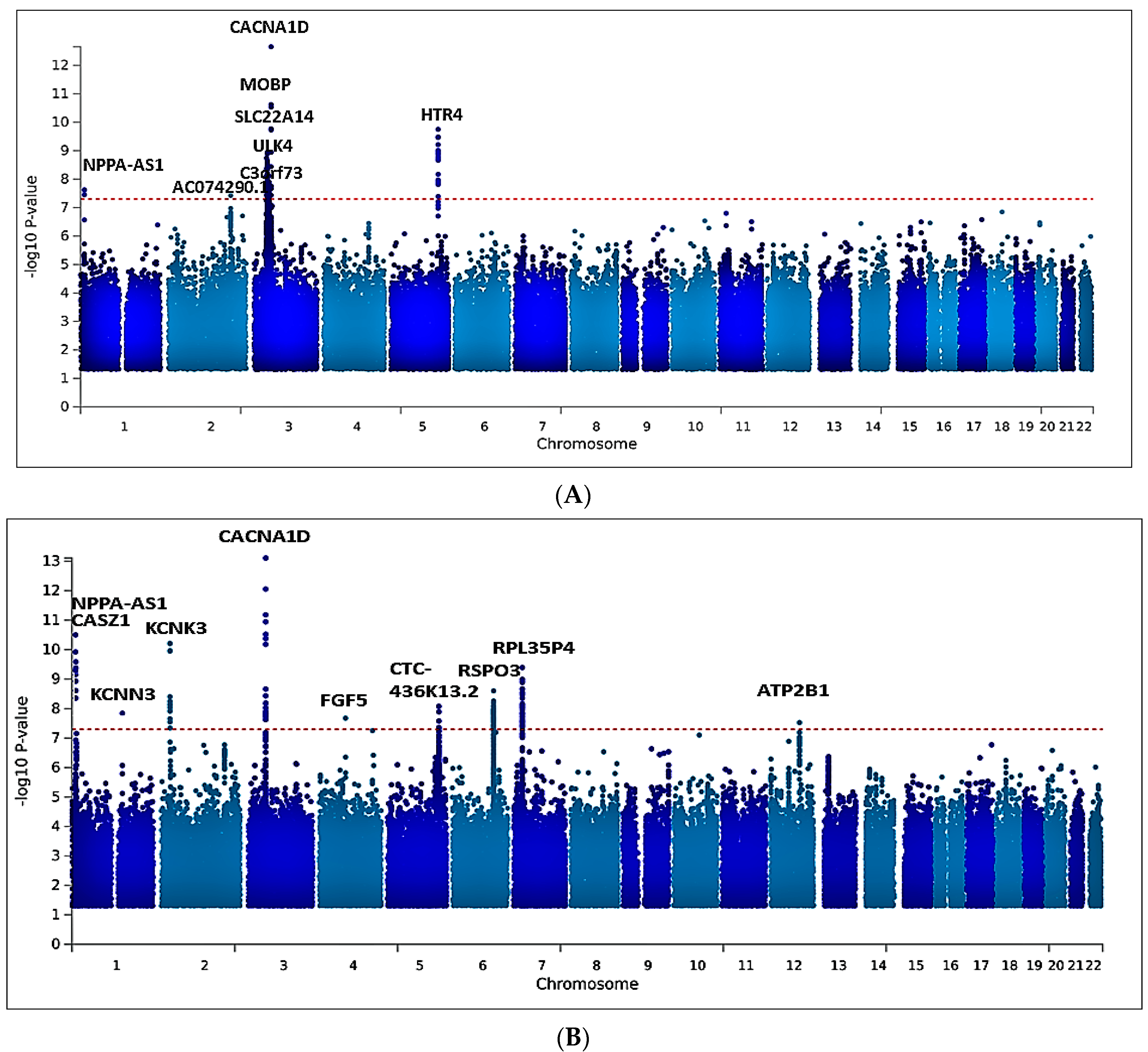
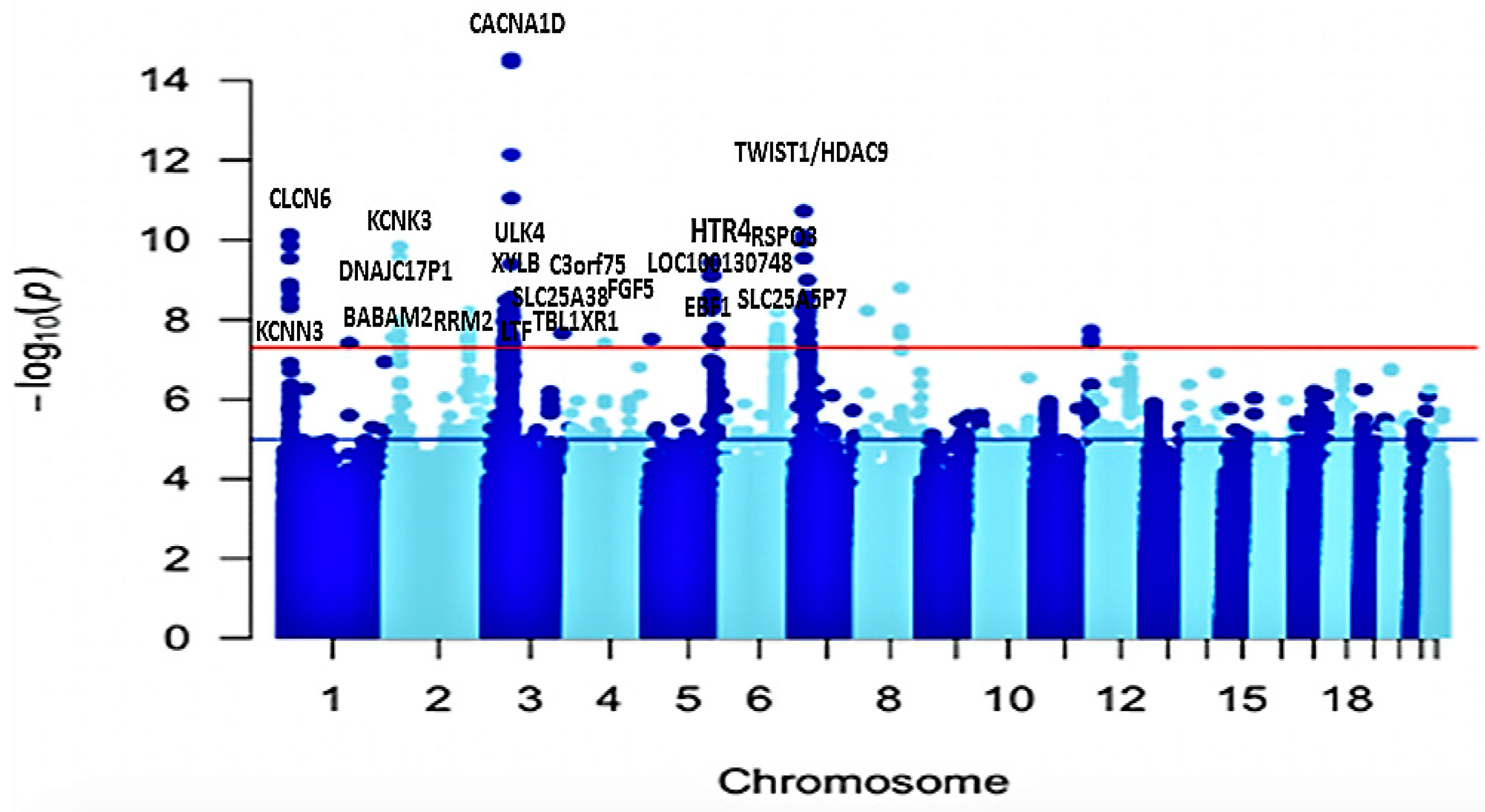
2.2. Univariate GWAS Meta-Analysis
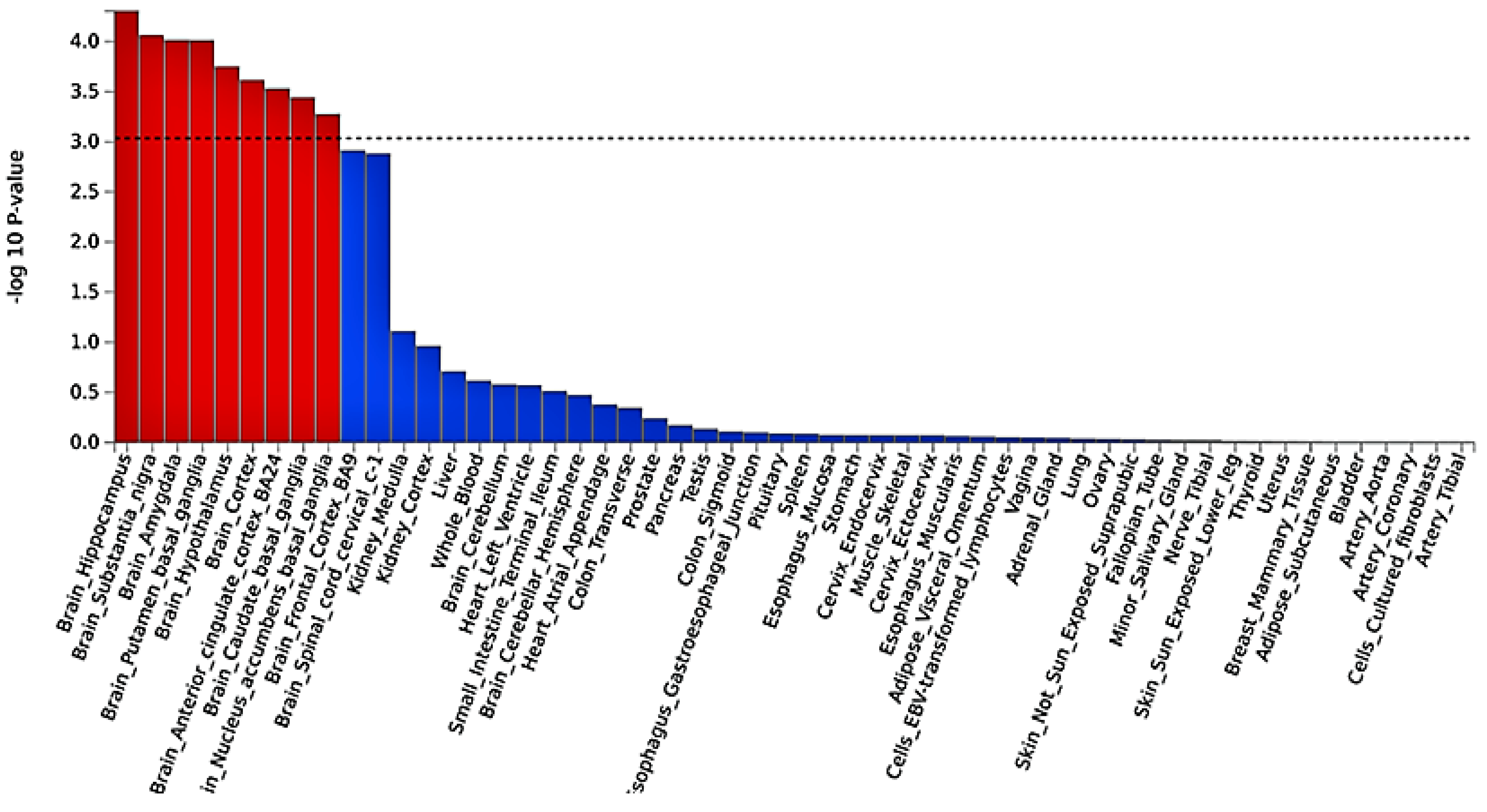
2.3. Functional Mapping and Annotation Analyses from FUMA of the Meta-Analysis
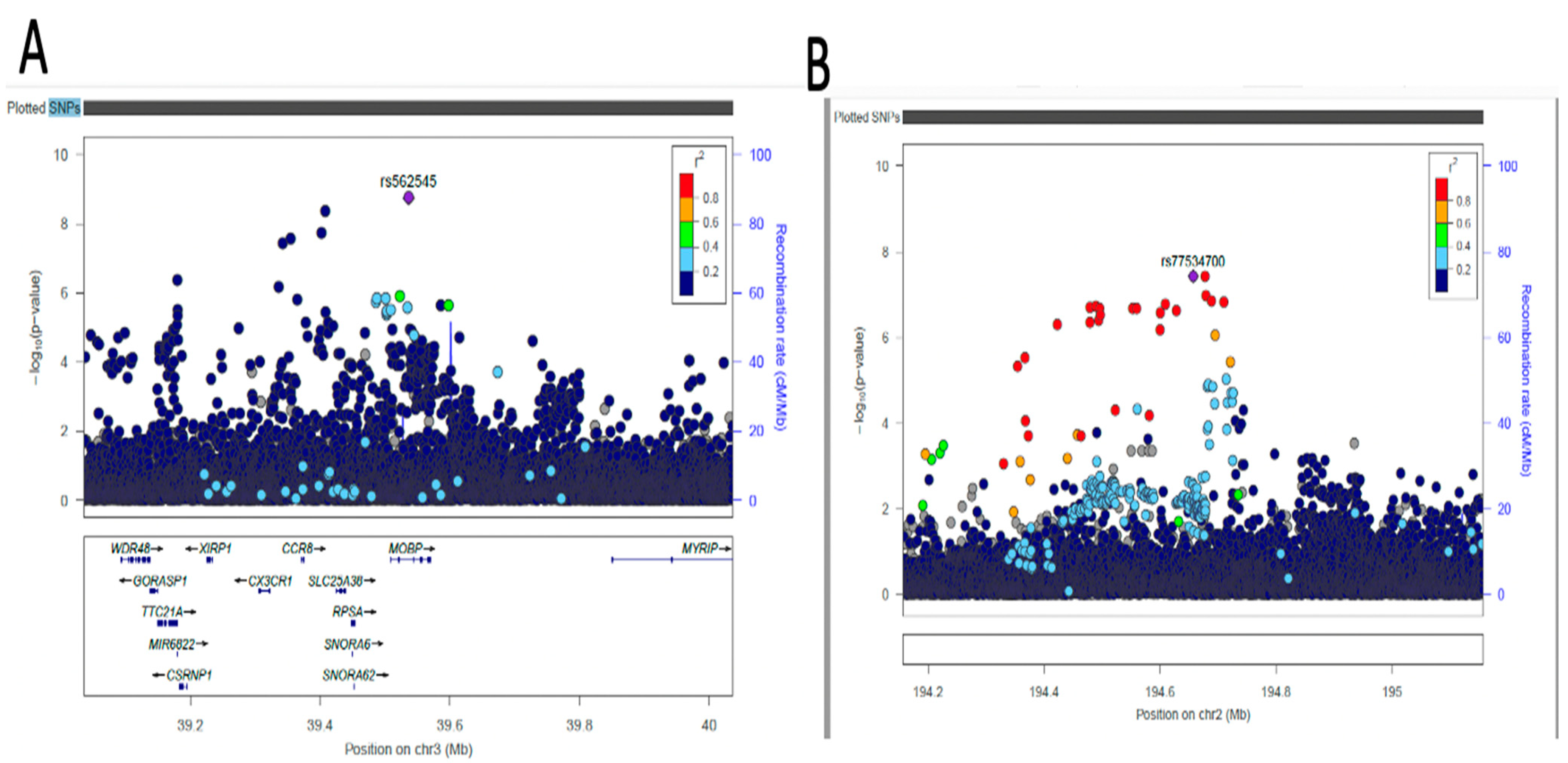
2.4. Fine-Mapping of Putatively Causal Variants
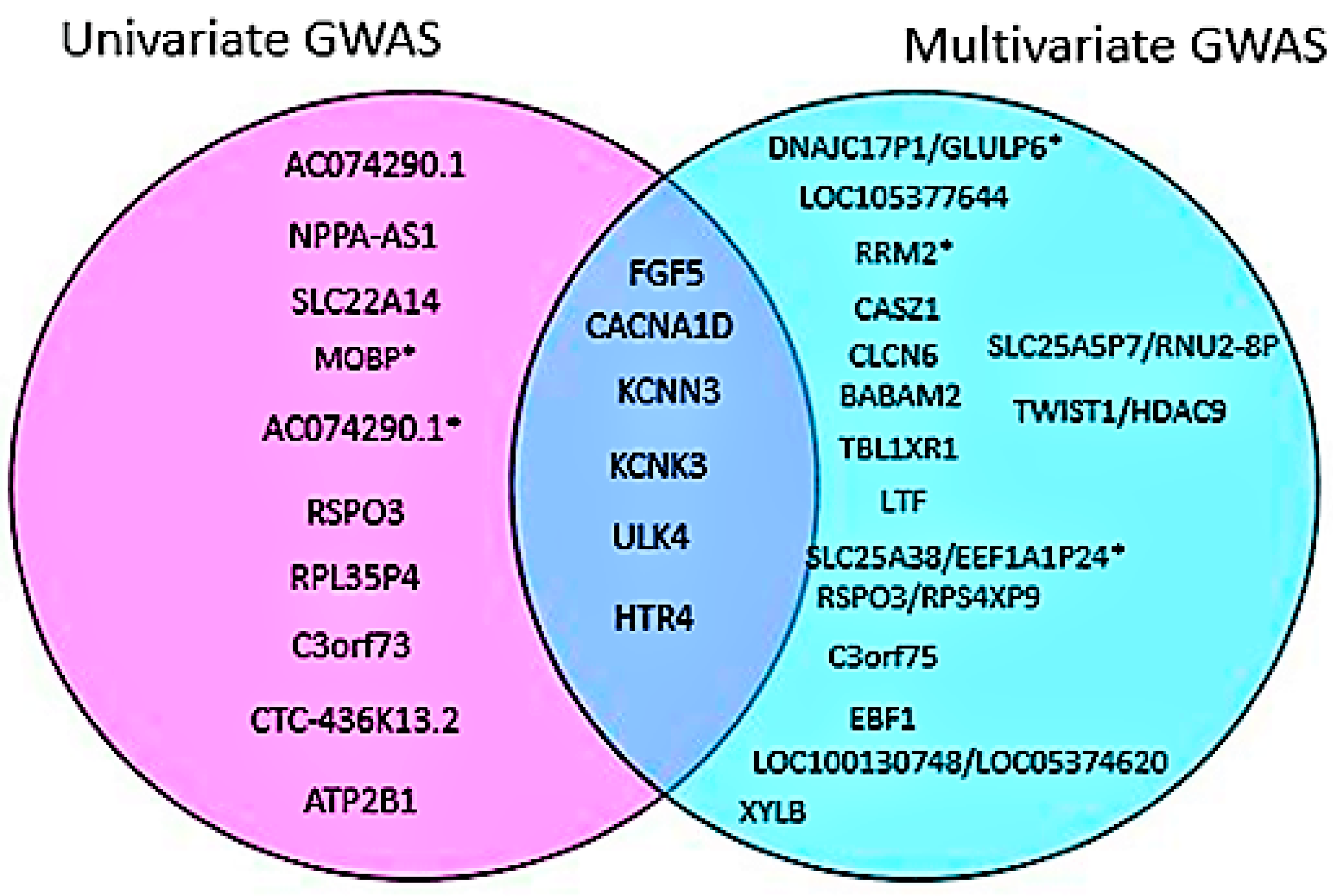
2.5. Multivariate GWAS Analysis of Blood Pressure Traits Identifies Additional Novel Loci
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.2. Meta-Analysis of BP Summary Statistics in African-Ancestry Individuals
4.3. Tissue Expression Enrichment Pathway Analysis
4.4. Functional Mapping and Annotation Analysis
4.5. Locus Definition
4.6. Fine-Mapping Analysis of Sentinel Variants
4.7. Multivariate GWAS Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muñoz, M.; Pong-Wong, R.; Canela-Xandri, O.; Rawlik, K.; Haley, C.S.; Tenesa, A. Evaluating the contribution of genetics and familial shared environment to common disease using the UK Biobank. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 980–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feinleib, M.; Garrison, R.J.; Fabsitz, R.; Christian, J.C.; Hrubec, Z.; Borhani, N.O.; Kannel, W.B.; Rosenman, R.; Schwartz, J.T.; Wagner, J.O. The Nhlbi Twin Study of Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors: Methodology and Summary of Results. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1977, 106, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulter, N.R.; Prabhakaran, D.; Caulfield, M. Hypertension. Lancet 2015, 386, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, D.; Larson, M.G.; Benjamin, E.J.; Newton-Cheh, C.; Wang, T.J.; Hwang, S.-J.; Vasan, R.S.; Mitchell, G.F. Framingham Heart Study 100K Project: Genome-wide associations for blood pressure and arterial stiffness. BMC Med. Genet. 2007, 8 (Suppl. 1). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, C.L.; Bayraktutan, U. Risk factors for ischaemic stroke. Int. J. Stroke Off. J. Int. Stroke Soc. 2008, 3, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Stroke Organisation (ESO). Executive Committee; ESO Writing Committee Guidelines for management of ischaemic stroke and transient ischaemic attack 2008. Cerebrovasc. Dis. Basel Switz. 2008, 25, 457–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC) Worldwide trends in hypertension prevalence and progress in treatment and control from 1990 to 2019: A pooled analysis of 1201 population-representative studies with 104 million participants. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2021, 398, 957–980. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carson, A.P.; Howard, G.; Burke, G.L.; Shea, S.; Levitan, E.B.; Muntner, P. Ethnic differences in hypertension incidence among middle-aged and older adults: The multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. Hypertens. Dallas Tex 1979 2011, 57, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berenson, G.S.; Wattigney, W.A.; Webber, L.S. Epidemiology of hypertension from childhood to young adulthood in black, white, and Hispanic population samples. Public Health Rep. Wash. DC 1974 1996, 111 (Suppl. 2), 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Writing Group Members; Mozaffarian, D.; Benjamin, E.J.; Go, A.S.; Arnett, D.K.; Blaha, M.J.; Cushman, M.; Das, S.R.; de Ferranti, S.; Després, J.-P.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2016 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2016, 133, e38–e360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chor, D.; Pinho Ribeiro, A.L.; Sá Carvalho, M.; Duncan, B.B.; Andrade Lotufo, P.; Araújo Nobre, A.; de Aquino, E.M.L.L.; Schmidt, M.I.; Griep, R.H.; Molina, M.D.C.B.; et al. Prevalence, Awareness, Treatment and Influence of Socioeconomic Variables on Control of High Blood Pressure: Results of the ELSA-Brasil Study. PloS One 2015, 10, e0127382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, D.; Ehret, G.B.; Rice, K.; Verwoert, G.C.; Launer, L.J.; Dehghan, A.; Glazer, N.L.; Morrison, A.C.; Johnson, A.D.; Aspelund, T.; et al. Genome-wide association study of blood pressure and hypertension. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton-Cheh, C.; Johnson, T.; Gateva, V.; Tobin, M.D.; Bochud, M.; Coin, L.; Najjar, S.S.; Zhao, J.H.; Heath, S.C.; Eyheramendy, S.; et al. Eight blood pressure loci identified by genome-wide association study of 34,433 people of European ancestry. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Brandenburg, J.T.; Choudhury, A.; Gómez-Olivé, F.X.; Ramsay, M. Systematic Review of Genomic Associations with Blood Pressure and Hypertension in Populations with African-Ancestry. Front Genet. 2021, 12, 699445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelou, E.; Warren, H.R.; Mosen-Ansorena, D.; Mifsud, B.; Pazoki, R.; Gao, H.; Ntritsos, G.; Dimou, N.; Cabrera, C.P.; Karaman, I.; et al. Genetic analysis of over 1 million people identifies 535 new loci associated with blood pressure traits. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1412–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehret, G.B.; Munroe, P.B.; Rice, K.M.; Bochud, M.; Johnson, A.D.; Chasman, D.I.; Smith, A.V.; Tobin, M.D.; Verwoert, G.C.; Hwang, S.-J.; et al. Genetic variants in novel pathways influence blood pressure and cardiovascular disease risk. Nature 2011, 478, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, N.; Takeuchi, F.; Tabara, Y.; Kelly, T.N.; Go, M.J.; Sim, X.; Tay, W.T.; Chen, C.-H.; Zhang, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies identifies common variants associated with blood pressure variation in east Asians. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, H.R.; Evangelou, E.; Cabrera, C.P.; Gao, H.; Ren, M.; Mifsud, B.; Ntalla, I.; Surendran, P.; Liu, C.; Cook, J.P.; et al. Genome-wide association analysis identifies novel blood pressure loci and offers biological insights into cardiovascular risk. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemo, A.; Gerry, N.; Chen, G.; Herbert, A.; Doumatey, A.; Huang, H.; Zhou, J.; Lashley, K.; Chen, Y.; Christman, M.; et al. A genome-wide association study of hypertension and blood pressure in African Americans. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, T.J.; Ehret, G.B.; Nandakumar, P.; Ranatunga, D.; Schaefer, C.; Kwok, P.Y.; Iribarren, C.; Chakravarti, A.; Risch, N. Genome-wide association analyses using electronic health records identify new loci influencing blood pressure variation. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, A.; Hellwege, J.N.; Keaton, J.M.; Park, J.; Qiu, C.; Warren, H.R.; Torstenson, E.S.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Sun, Y.V.; Wilson, O.D.; et al. Trans-ethnic association study of blood pressure determinants in over 750,000 individuals. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Le, T.H.; Edwards, D.R.V.; Tayo, B.O.; Gaulton, K.J.; Smith, J.A.; Lu, Y.; Jensen, R.A.; Chen, G.; Yanek, L.R.; et al. Single-trait and multi-trait genome-wide association analyses identify novel loci for blood pressure in African-ancestry populations. PLOS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, E.R.; Young, J.H.; Li, Y.; Dreisbach, A.W.; Keating, B.J.; Musani, S.K.; Liu, K.; Morrison, A.C.; Ganesh, S.; Kutlar, A.; et al. Association of genetic variation with systolic and diastolic blood pressure among African Americans: The Candidate Gene Association Resource study. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 2273–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschini, N.; Fox, E.; Zhang, Z.; Edwards, T.; Nalls, M.A.; Sung, Y.; Tayo, B.; Sun, Y.; Gottesman, O.; Adeyemo, A.; et al. Genome-wide Association Analysis of Blood-Pressure Traits in African-Ancestry Individuals Reveals Common Associated Genes in African and Non-African Populations. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 93, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendry, L.M.; Sahibdeen, V.; Choudhury, A.; Norris, S.A.; Ramsay, M.; Lombard, Z. Insights into the genetics of blood pressure in black South African individuals: The Birth to Twenty cohort. BMC Med. Genom. 2018, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Kelly, T.N.; Zhao, Q.; Li, H.; Huang, J.; Wang, L.; Jaquish, C.E.; Sung, Y.J.; Shimmin, L.C.; Lu, F.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies 8 novel loci associated with blood pressure responses to interventions in Han Chinese. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2013, 6, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatumo, S.; Carstensen, T.; Nashiru, O.; Gurdasani, D.; Sandhu, M.; Kaleebu, P. Complimentary Methods for Multivariate Genome-Wide Association Study Identify New Susceptibility Genes for Blood Cell Traits. Front. Genet. 2019, 10. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fgene.2019.00334 (accessed on 2 June 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nudel, R.; Wang, Y.; Appadurai, V.; Schork, A.J.; Buil, A.; Agerbo, E.; Bybjerg-Grauholm, J.; Børglum, A.D.; Daly, M.J.; Mors, O.; et al. A large-scale genomic investigation of susceptibility to infection and its association with mental disorders in the Danish population. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okbay, A.; Wu, Y.; Wang, N.; Jayashankar, H.; Bennett, M.; Nehzati, S.M.; Sidorenko, J.; Kweon, H.; Goldman, G.; Gjorgjieva, T.; et al. Polygenic prediction of educational attainment within and between families from genome-wide association analyses in 3 million individuals. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagerberg, L.; Hallström, B.M.; Oksvold, P.; Kampf, C.; Djureinovic, D.; Odeberg, J.; Habuka, M.; Tahmasebpoor, S.; Danielsson, A.; Edlund, K.; et al. Analysis of the human tissue-specific expression by genome-wide integration of transcriptomics and antibody-based proteomics. Mol. Cell. Proteom. MCP 2014, 13, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wang, T.; Li, N.; Zhang, W.; Hu, Y. The High Expression of RRM2 Can Predict the Malignant Transformation of Endometriosis. Adv. Ther. 2021, 38, 5178–5190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherva, R.; Tripodis, Y.; Bennett, D.A.; Chibnik, L.B.; Crane, P.K.; de Jager, P.L.; Farrer, L.A.; Saykin, A.J.; Shulman, J.M.; Naj, A.; et al. Genome-wide association study of the rate of cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. J. Alzheimers Assoc. 2014, 10, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Need, A.C.; Attix, D.K.; McEvoy, J.M.; Cirulli, E.T.; Linney, K.L.; Hunt, P.; Ge, D.; Heinzen, E.L.; Maia, J.M.; Shianna, K.V.; et al. A genome-wide study of common SNPs and CNVs in cognitive performance in the CANTAB. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 4650–4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Jose, P.A.; Zeng, C. Gastrointestinal–Renal Axis: Role in the Regulation of Blood Pressure. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e005536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, K.S.; Dhikav, V. Hippocampus in health and disease: An overview. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2012, 15, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Rolls, E.T.; Cheng, W.; Feng, J. Hypertension is associated with reduced hippocampal connectivity and impaired memory. EBioMedicine 2020, 61, 103082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mägi, R.; Morris, A. GWAMA: Software for genome-wide association meta-analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Leeuw, C.A.; Mooij, J.M.; Heskes, T.; Posthuma, D. MAGMA: Generalized Gene-Set Analysis of GWAS Data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11, e1004219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, K.; Taskesen, E.; Van Bochoven, A.; Posthuma, D. Functional mapping and annotation of genetic associations with FUMA. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westra, H.J.; Peters, M.J.; Esko, T.; Yaghootkar, H.; Schurmann, C.; Kettunen, J.; Christiansen, M.W.; Fairfax, B.P.; Schramm, K.; Powell, J.E.; et al. Systematic identification of trans eQTLs as putative drivers of known disease associations. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1238–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, M.; Hakonarson, H. ANNOVAR: Functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kircher, M.; Witten, D.M.; Jain, P.; O’roak, B.J.; Cooper, G.M.; Shendure, J. A general framework for estimating the relative pathogenicity of human genetic variants. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 1000 Genomes Project Consortium. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature 2015, 526, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, A.; Watson, H.; Wallace, C. Improving the coverage of credible sets in Bayesian genetic fine-mapping. PLOS Comput. Biol. 2020, 16, e1007829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhu, X. Cross-Phenotype Association Analysis Using Summary Statistics from GWAS. Methods Mol. Biol. Clifton NJ 2017, 1666, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cohort | Continent | Country | Sample Size (N) | Phenotype | Imputation Panel and Genome Build |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APCDR-UGR (27) | Africa | Uganda | 6407 | DBP SBP | Africa genome panel, hg19 |
| APCDR-DCC (27) | Africa | South Africa | 1600 | DBP SBP | Africa genome panel, hg19 |
| APCDR-DDS (27) | Africa | South Africa | 1165 | DBP SBP | Africa genome panel, hg19 |
| APCDR-AADM (27) | Africa | Nigeria Ghana Kenya | 5231 | DBP SBP | Africa genome panel, hg19 |
| MVP–AFR | America | USA | 59,933 | DBP SBP | 1000 Genome, hg19 |
| UKB–AFR (28) | Europe | UK | 6614 | DBP SBP | 1000 Genome, hg19 |
| Nearest Gene | Lead SNPs | Chr | BP | Effect Allele | Other Allele | Trait | Beta | SE | MAF | p-Value | Functional Consequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AC074290.1 | rs77534700 | 2 | 194657479 | A | G | DBP | −0.0967 | 0.0176 | 0.0836 | 3.749x10−8 | Intergenic variant |
| MOBP | rs562545 | 3 | 39536524 | A | G | DBP | 0.0593 | 0.0099 | 0.8973 | 1.823x10−9 | Intron variant |
| Nearest Gene | Lead SNPs | Chr | BP | Effect Allele | Other Allele | HET_p Value | Functional Consequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNAJC17P1/GLULP6 GLULP6GLULP6 GLULP6 | rs138493856 | 2 | 194678067 | A | G | 6.1322 × 10−9 | Intergenic variant |
| RRM2 | rs139235642 | 2 | 10278626 | T | C | 2.7981 × 10−8 | Intron variant NMD transcript variant |
| LOC105377644 | rs72619992 | 3 | 39407952 | A | C | 1.1339 × 10−8 | Intron variant |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Udosen, B.; Soremekun, O.; Kamiza, A.; Machipisa, T.; Cheickna, C.; Omotuyi, O.; Soliman, M.; Wélé, M.; Nashiru, O.; Chikowore, T.; et al. Meta-Analysis and Multivariate GWAS Analyses in 80,950 Individuals of African Ancestry Identify Novel Variants Associated with Blood Pressure Traits. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032164
Udosen B, Soremekun O, Kamiza A, Machipisa T, Cheickna C, Omotuyi O, Soliman M, Wélé M, Nashiru O, Chikowore T, et al. Meta-Analysis and Multivariate GWAS Analyses in 80,950 Individuals of African Ancestry Identify Novel Variants Associated with Blood Pressure Traits. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(3):2164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032164
Chicago/Turabian StyleUdosen, Brenda, Opeyemi Soremekun, Abram Kamiza, Tafadzwa Machipisa, Cisse Cheickna, Olaposi Omotuyi, Mahmoud Soliman, Mamadou Wélé, Oyekanmi Nashiru, Tinashe Chikowore, and et al. 2023. "Meta-Analysis and Multivariate GWAS Analyses in 80,950 Individuals of African Ancestry Identify Novel Variants Associated with Blood Pressure Traits" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 3: 2164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032164
APA StyleUdosen, B., Soremekun, O., Kamiza, A., Machipisa, T., Cheickna, C., Omotuyi, O., Soliman, M., Wélé, M., Nashiru, O., Chikowore, T., & Fatumo, S. (2023). Meta-Analysis and Multivariate GWAS Analyses in 80,950 Individuals of African Ancestry Identify Novel Variants Associated with Blood Pressure Traits. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(3), 2164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032164








