Will the Interactions of Some Platinum (II)-Based Drugs with B-Vitamins Reduce Their Therapeutic Effect in Cancer Patients? Comparison of Chemotherapeutic Agents such as Cisplatin, Carboplatin and Oxaliplatin—A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
Motivation of Study
2. Results
3. Experimental Analysis
4. Conclusions
5. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Cancer Research Fund; American Institute for Cancer. Diet, Nutrition, Physical Activity and Breast Cancer; Continuous Update Project, Expert Report 2018; World Cancer Research Fund International: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wiseman, L.R.; Adkins, J.C.; Plosker, G.L.; Goa, K.L. Oxaliplatin: A review of its use in the management of metastatic colorectal cancer. Drugs Aging 1999, 14, 459–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, B.; Vancamo, L.; Trosko, J.E.; Mansour, V.H. Platinum Compounds: A New Class of Potent Antitumour Agents. Nature 1969, 222, 385–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, B.; Van Camp, L.; Krigas, T. Inhibition of cell division in Escherichia coli by electrolysis products from a platinum electrode. Nature 1965, 205, 698–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rixe, O.; Ortuzar, W.; Alvarez, M.; Parker, R.; Reed, E.; Paull, K.; Fojo, T. Oxaliplatin, tetraplatin, cisplatin, and carboplatin: Spectrum of activity in drug-resistant cell lines and in the cell lines of the national cancer institute’s anticancer drug screen panel. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1996, 52, 1855–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, G.Y.; Woodward, N.; Coward, J.I.G. Cisplatin versus carboplatin: Comparative review of therapeutic management in solid malignancies. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2016, 102, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frezza, M.; Hindo, S.; Chen, D.; Davenport, A.; Schmitt, S.; Tomco, D.; Dou, Q.P. Novel metals and metal complexes as platforms for cancer therapy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 1813–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desoize, B.; Madoulet, C. Particular aspects of platinum compounds used at present in cancer treatment. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2002, 42, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuertes, M.A.; Alonso, C.; Pérez, J.M. Biochemical modulation of cisplatin mechanisms of action: Enhancement of antitumor activity and circumvention of drug resistance. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 645–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zyl, B.; Tang, D.; Bowden, N.A. Biomarkers of platinum resistance in ovarian cancer: What can we use to improve treatment. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2018, 25, R303–R318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abotaleb, M.; Kubatka, P.; Caprnda, M.; Varghese, E.; Zolakova, B.; Zubor, P.; Opatrilova, R.; Kruzliak, P.; Stefanicka, P.; Büsselberg, D. Chemotherapeutic agents for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer: An update. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 101, 458–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rugo, H.S.; Olopade, O.I.; DeMichele, A.; Yau, C.; van ’t Veer, L.J.; Buxton, M.B.; Hogarth, M.; Hylton, N.M.; Paoloni, M.; Perlmutter, J.; et al. Adaptive Randomization of Veliparib–Carboplatin Treatment in Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikuła-Pietrasik, J.; Witucka, A.; Pakuła, M.; Uruski, P.; Begier-Krasińska, B.; Niklas, A.; Tykarski, A.; Książek, K. Comprehensive review on how platinum- and taxane-based chemotherapy of ovarian cancer affects biology of normal cells. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 681–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebremedhn, E.G.; Shortland, P.J.; Mahns, D.A. The incidence of acute oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy and its impact on treatment in the first cycle: A systematic review. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaney, S.G.; Campbell, S.L.; Bassett, E.; Wu, Y. Recognition and processing of cisplatin- and oxaliplatin-DNA adducts. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2005, 53, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Francesco, A.M.; Ruggiero, A.; Riccardi, R. Cellular and molecular aspects of drugs of the future: Oxaliplatin. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2002, 59, 1914–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Balibrea, E.; Martínez-Cardús, A.; Ginés, A.; Ruiz de Porras, V.; Moutinho, C.; Layos, L.; Manzano, J.L.; Bugés, C.; Bystrup, S.; Esteller, M.; et al. Tumor-Related Molecular Mechanisms of Oxaliplatin Resistance. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 1767–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.P.; Hamilton, T.C.; Schilder, R.J. Platinum resistance: The role of DNA repair pathways. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 1291–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyerhardt, J.A.; Mayer, R.J. Systemic therapy for colorectal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 476–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seetharam, R.N. Oxaliplatin: Preclinical perspectives on the mechanisms of action, response and resistance. Ecancermedicalscience 2009, 3, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmah, A.; Saha, S.; Bagaria, P.; Kinkar Roy, R. On the complementarity of comprehensive decomposition analysis of stabilization energy (CDASE) Scheme and supermolecular approach. Chem. Phys. 2012, 394, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmah, A.; Roy, R.K. Understanding the preferential binding interaction of aqua-cisplatins with nucleobase guanine over adenine: A density functional reactivity theory based approach. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Lippard, S.J. Cellular processing of platinum anticancer drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Göschl, S.; Schreiber-Brynzak, E.; Pichler, V.; Cseh, K.; Heffeter, P.; Jungwirth, U.; Jakupec, M.A.; Berger, W.; Keppler, B.K. Comparative studies of oxaliplatin-based platinum(iv) complexes in different in vitro and in vivo tumor models. Metallomics 2017, 9, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantri, Y.; Lippard, S.J.; Baik, M.-H. Bifunctional binding of cisplatin to DNA: Why does cisplatin form 1,2-intrastrand cross-links with ag but not with GA? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 5023–5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiegel, K.; Rothlisberger, U.; Carloni, P. Cisplatin Binding to DNA Oligomers from Hybrid Car-Parrinello/Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 2699–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelland, L.R.; Farrell, N.P. Platinum-Based Drugs in Cancer Therapy; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2000; Volume 7, ISBN 1-59259-012-8. [Google Scholar]
- Schewe, G. Platinum-Based Drugs in Cancer Therapy; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2010; ISBN 9781617370915. [Google Scholar]
- Riddell, I.A.; Lippard, S.J. Cisplatin and oxaliplatin: Our current understanding of their actions. Met. Ions Life Sci. 2018, 18, 1–42. [Google Scholar]
- Riddell, I.A.; Lippard, S.J.; Brabec, V.; Kasparkova, J.; Menon, V.; Farrell, N.P.; Taylor, K.M. Metallo-Drugs: Development and Action of Anticancer Agents; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co KG: Berlin, Germany, 2018; Volume 18. [Google Scholar]
- Dasari, S.; Tchounwou, P.B. Cisplatin in cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 740, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa, G.F.; Wlodarczyk, S.R.; Monteiro, G. Carboplatin: Molecular mechanisms of action associated with chemoresistance. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 50, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcindor, T.; Beauger, N. Oxaliplatin: A review in the era of molecularly targeted therapy. Curr. Oncol. 2011, 18, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woynarowski, J.M.; Faivre, S.; Herzig, M.C.S.; Arnett, B.; Chapman, W.G.; Trevino, A.V.; Raymond, E.; Chaney, S.G.; Vaisman, A.; Varchenko, M.; et al. Oxaliplatin-induced damage of cellular DNA. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 58, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasetto, L.M.; D’Andrea, M.R.; Rossi, E.; Monfardini, S. Oxaliplatin-related neurotoxicity: How and why? Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2006, 59, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hah, S.S.; Stivers, K.M.; De Vere White, R.W.; Henderson, P.T. Kinetics of carboplatin-DNA binding in genomic DNA and bladder cancer cells as determined by accelerator mass spectrometry. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2006, 19, 622–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brabec, V.; Kasparkova, J. Modifications of DNA by platinum complexes. Drug Resist. Updat. 2005, 8, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuertes, M.A.; Castilla, J.; Alonso, C.; Pérez, J.M. Novel concepts in the development of platinum antitumor drugs. Curr. Med. Chem. Anticancer. Agents 2002, 2, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, J.; Robin Ganellin, C. Analogue-Based Drug Discovery; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; ISBN 3527312579. [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkinson, E.; Neville-Webbe, H.L.; Coleman, R.E. Magnesium depletion in patients receiving cisplatin-based chemotherapy. Clin. Oncol. R. Coll. Radiol. 2006, 18, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, C.A.; Blair, B.G.; Safaei, R.; Howell, S.B. The role of the mammalian copper transporter 1 in the cellular accumulation of platinum-based drugs. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 75, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, S.; Lee, J.; Thiele, D.J.; Herskowitz, I. Uptake of the anticancer drug cisplatin mediated by the copper transporter Ctr1 in yeast and mammals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 14298–14302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, S.B.; Safaei, R.; Larson, C.A.; Sailor, M.J. Copper transporters and the cellular pharmacology of the platinum-containing cancer drugs. Mol. Pharmacol. 2010, 77, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzer, A.K.; Manorek, G.H.; Howell, S.B. Contribution of the major copper influx transporter CTR1 to the cellular accumulation of cisplatin, carboplatin, and oxaliplatin. Mol. Pharmacol. 2006, 70, 1390–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, T.C.; Suntharalingam, K.; Lippard, S.J. The next generation of platinum drugs: Targeted Pt (II) agents, nanoparticle delivery, and Pt (IV) prodrugs. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 3436–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.H.; Khwaounjoo, P.; Hill, A.G.; Miskelly, G.M.; McKeage, M.J. Predicting effects on oxaliplatin clearance: In vitro, kinetic and clinical studies of calcium- and magnesium-mediated oxaliplatin degradation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baik, M.-H.; Friesner, R.A.; Lippard, S.J. Theoretical Study of Cisplatin Binding to Purine Bases: Why Does Cisplatin Prefer Guanine over Adenine? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 14082–14092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szefler, B.; Czeleń, P. Docking of cisplatin on fullerene derivatives and some cube rhombellane functionalized homeomorphs. Symmetry 2019, 11, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szefler, B.; Czeleń, P.; Szczepanik, A.; Cysewski, P. Does the affinity of cisplatin to B-vitamins impair the therapeutic effect in the case of patients with lung cancer-consuming carrot or beet juice? Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 1775–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szefler, B.; Czeleń, P.; Krawczyk, P. The Affinity of Carboplatin to B-Vitamins and Nucleobases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szefler, B.; Czeleń, P.; Kruszewski, S.; Siomek-Górecka, A.; Krawczyk, P. The assessment of physicochemical properties of Cisplatin complexes with purines and vitamins B group. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2022, 113, 108144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szefler, B.; Czeleń, P.; Wojtkowiak, K.; Jezierska, A. Affinities to Oxaliplatin: Vitamins from B Group vs. Nucleobases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, N.P. Preclinical perspectives on the use of platinum compounds in cancer chemotherapy. Semin. Oncol. 2004, 31, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabalin, I.; Dauter, Z.; Jaskolski, M.; Minor, W.; Wlodawer, A. Crystallography and chemistry should always go together: A cautionary tale of protein complexes with cisplatin and carboplatin. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2015, 71, 1965–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S. Platinum–DNA interactions and subsequent cellular processes controlling sensitivity to anticancer platinum complexes. Chem. Biodivers. 2010, 7, 543–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stipanuk, M.H.; Caudill, M. Biochemical, Physiological, and Molecular Aspects of Human Nutrition; Saunders: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2013; ISBN 9781455746293. [Google Scholar]
- Stargrove, M.B.; Treasure, J.; McKee, D.L. Herb, Nutrient, and Drug Interactions: Clinical Implications and Therapeutic Strategies; Mosby Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; ISBN 9780323029643. [Google Scholar]
- Polskie Towarzystwo Farmaceutyczne. Farmakopea Polska X; Urząd Rejestracji Produktów Leczniczych, Wyrobów Medycznych i Produktów Biobójczych: Warszawa, Poland, 2014; ISBN 978-83-63724-47-4. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosal, A.; Said, H.M. Mechanism and regulation of vitamin B2 (riboflavin) uptake by mouse and human pancreatic β-cells/islets: Physiological and molecular aspects. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2012, 303, G1052–G1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, D. B Vitamins and the Brain: Mechanisms, Dose and Efficacy—A Review. Nutrients 2016, 8, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielińska-Dawidziak, M.; Grajek, K.; Olejnik, A.; Czaczyk, K.; Grajek, W. Transport of high concentration of thiamin, riboflavin and pyridoxine across intestinal epithelial cells Caco-2. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2008, 54, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, E.; Patterson, R.E.; Kristal, A.R.; Thornquist, M.; King, I.; Shattuck, A.L.; Evans, I.; Satia-Abouta, J.; Littman, A.J.; Potter, J.D. VITamins and Lifestyle Cohort Study: Study Design and Characteristics of Supplement Users. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2004, 159, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, C.; Wirleitner, B.; Schroecksnadel, K.; Schennach, H.; Fuchs, D. Beer down-regulates activated peripheral blood mononuclear cells in vitro. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2006, 6, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
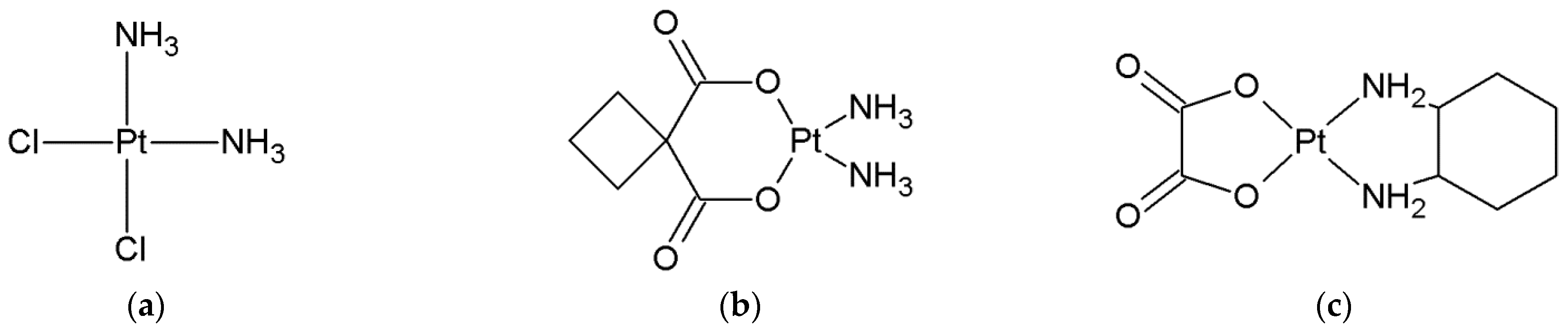
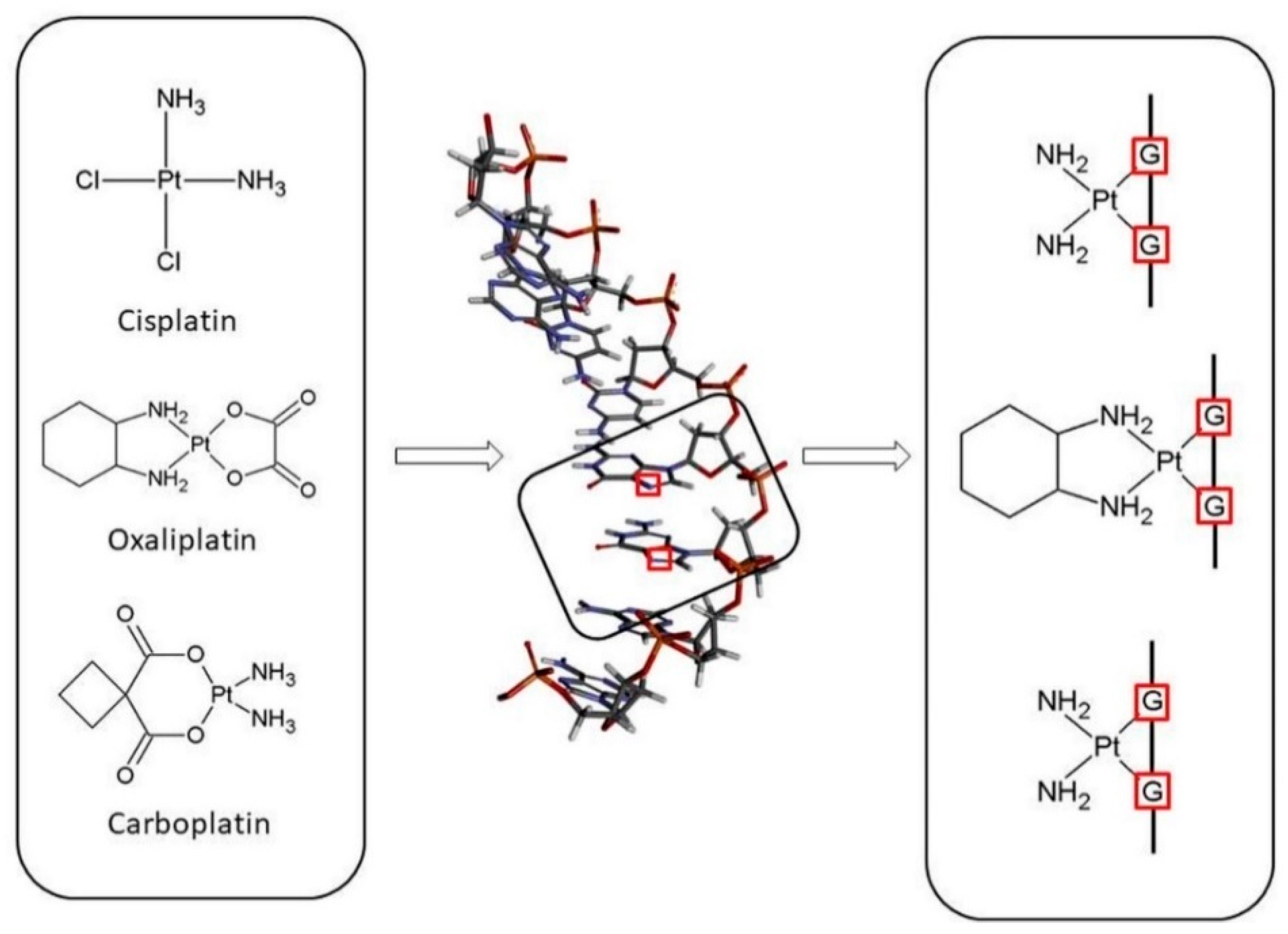

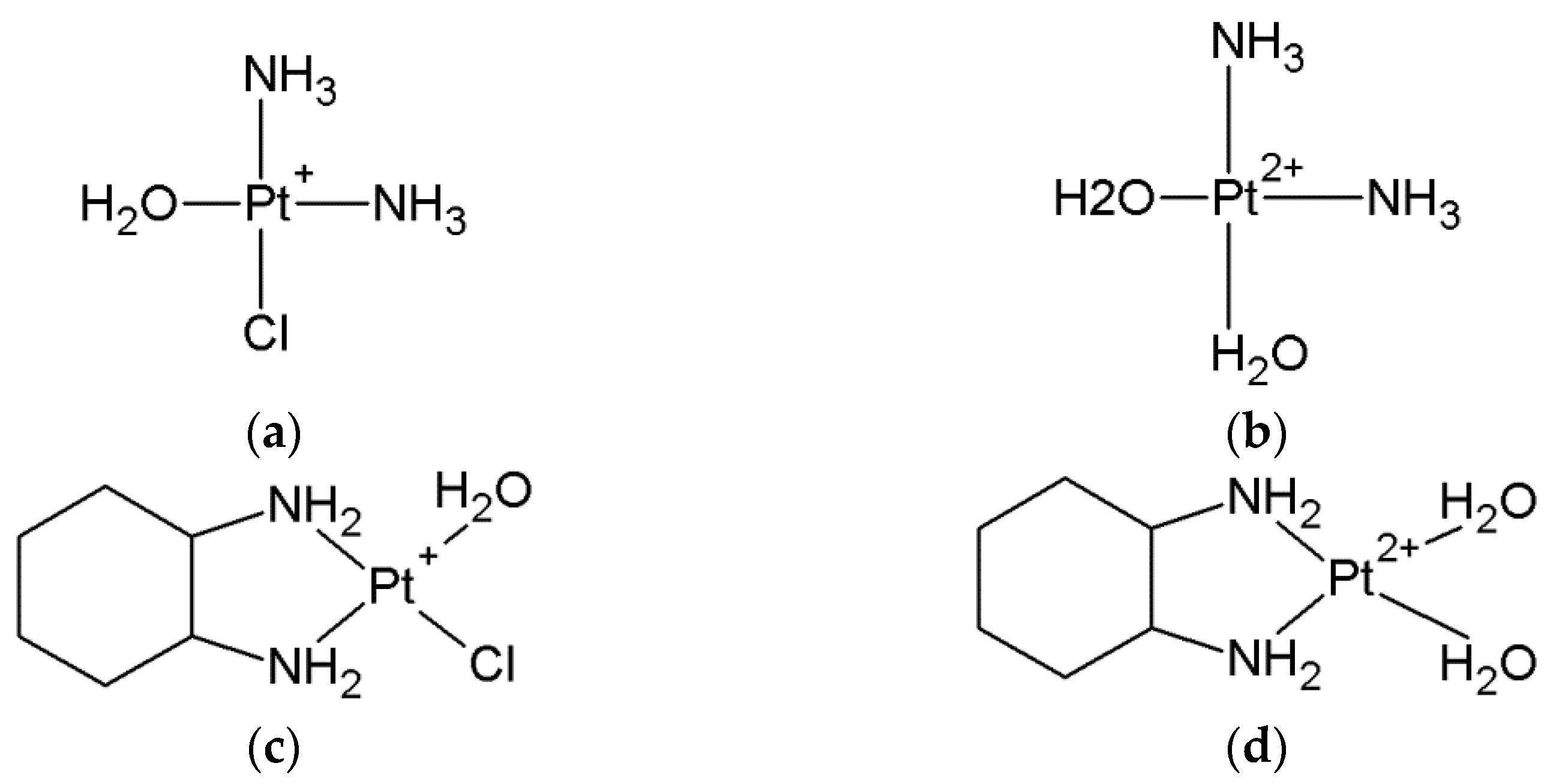

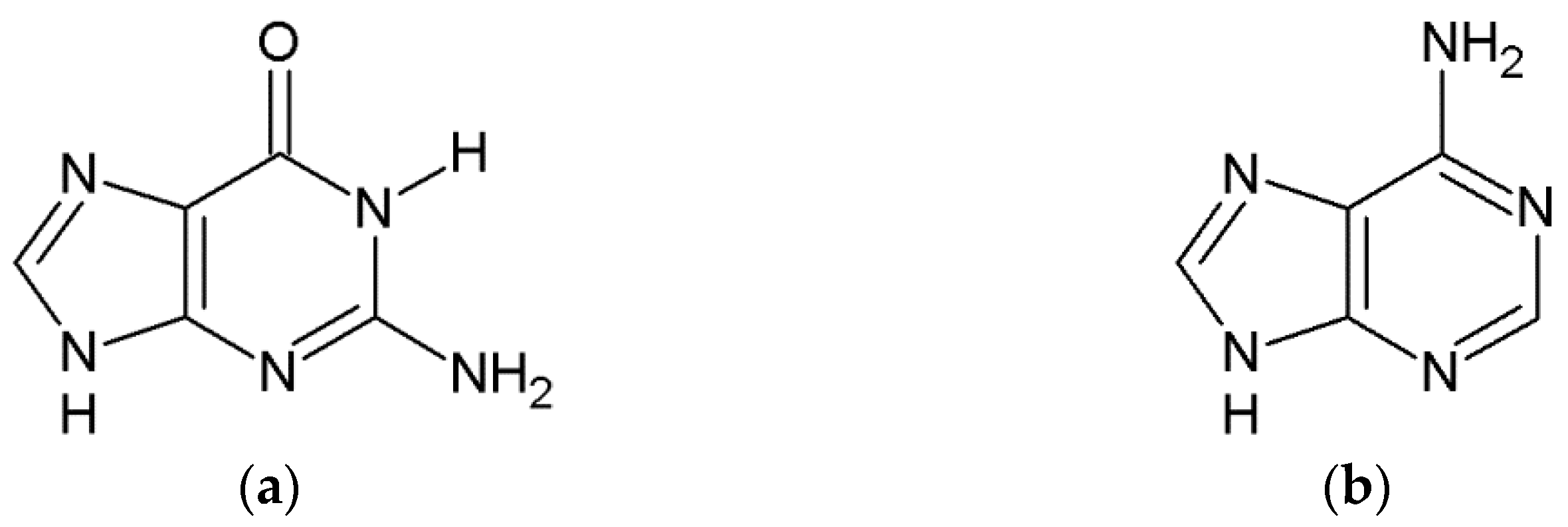
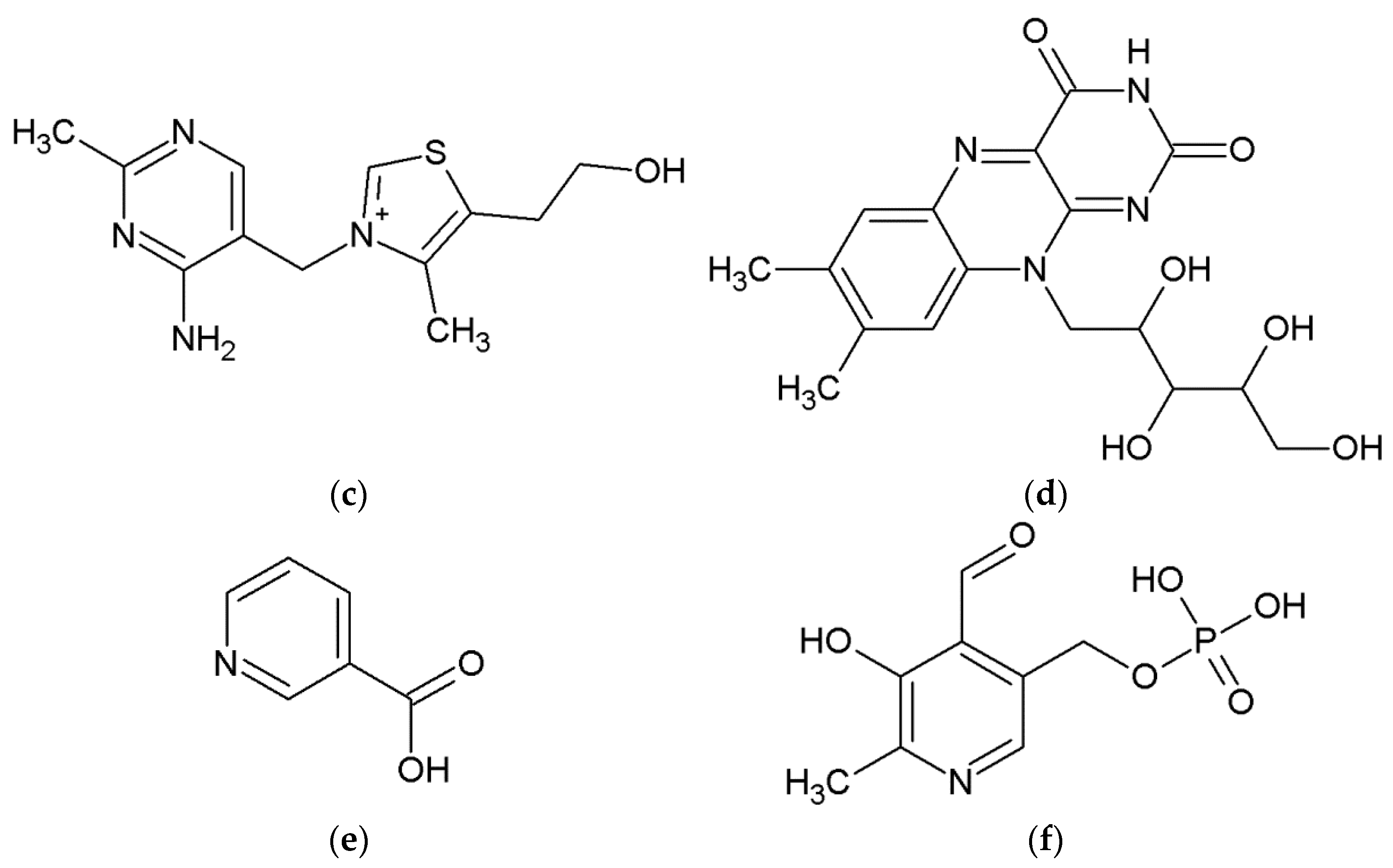
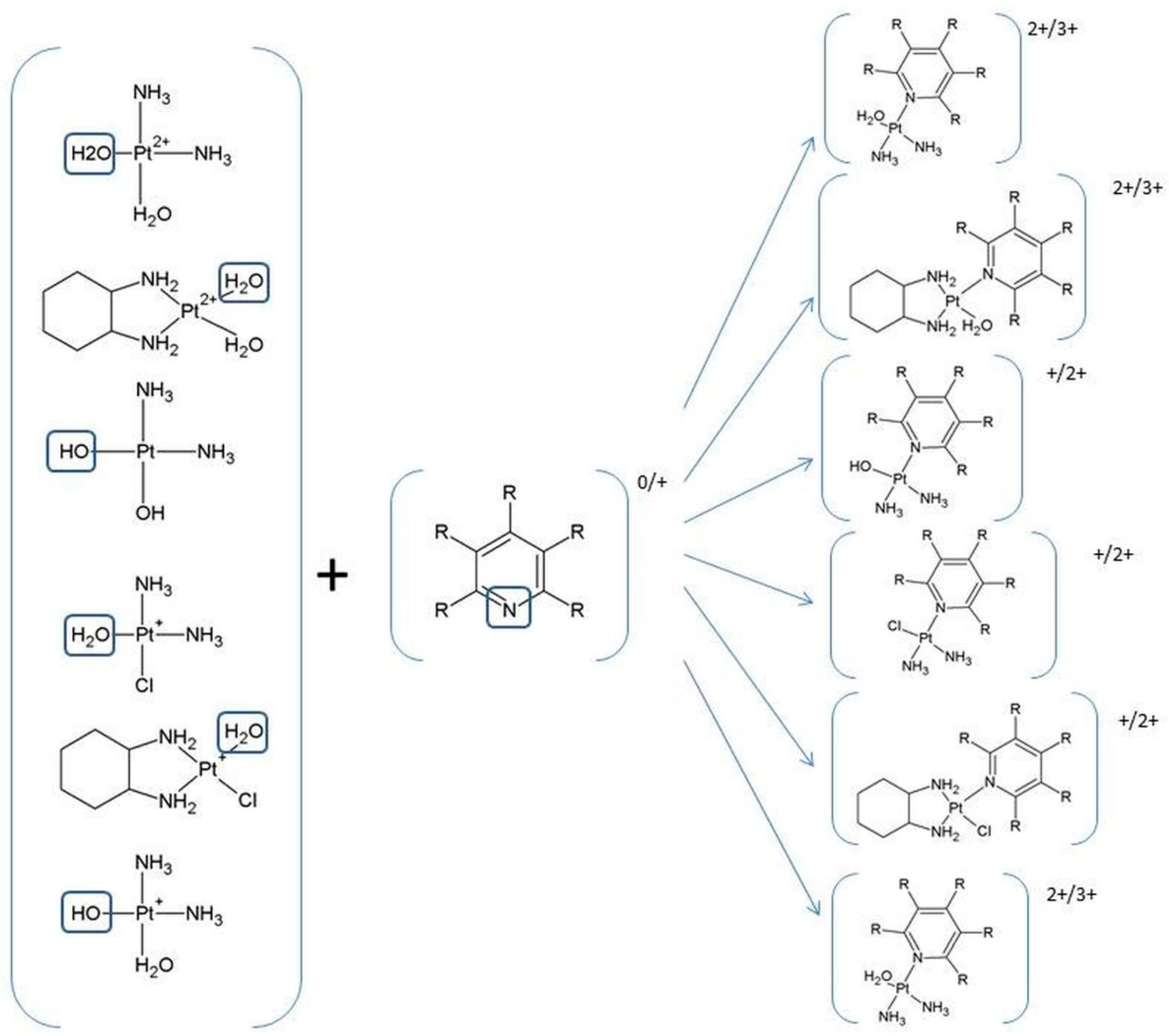
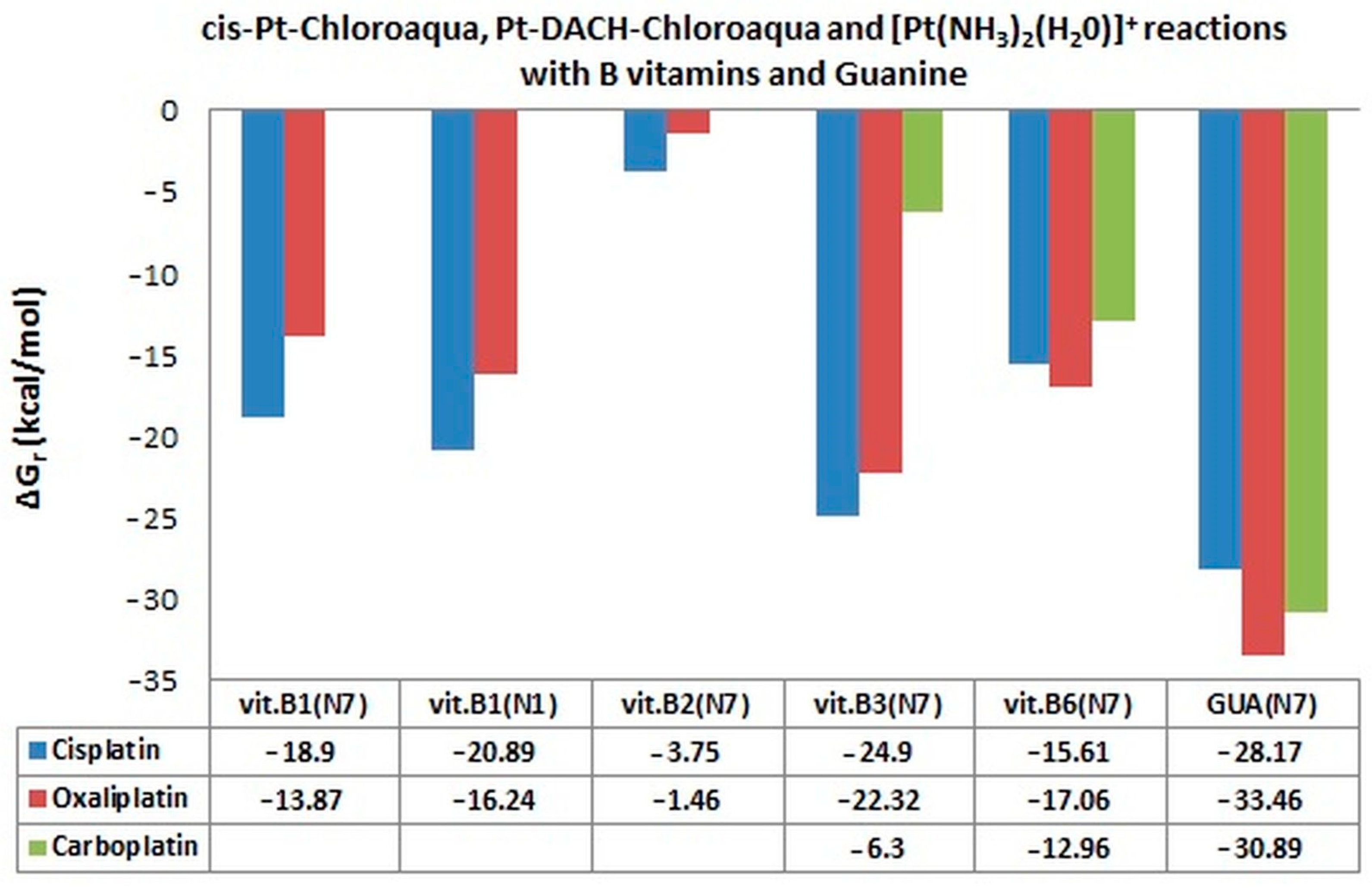
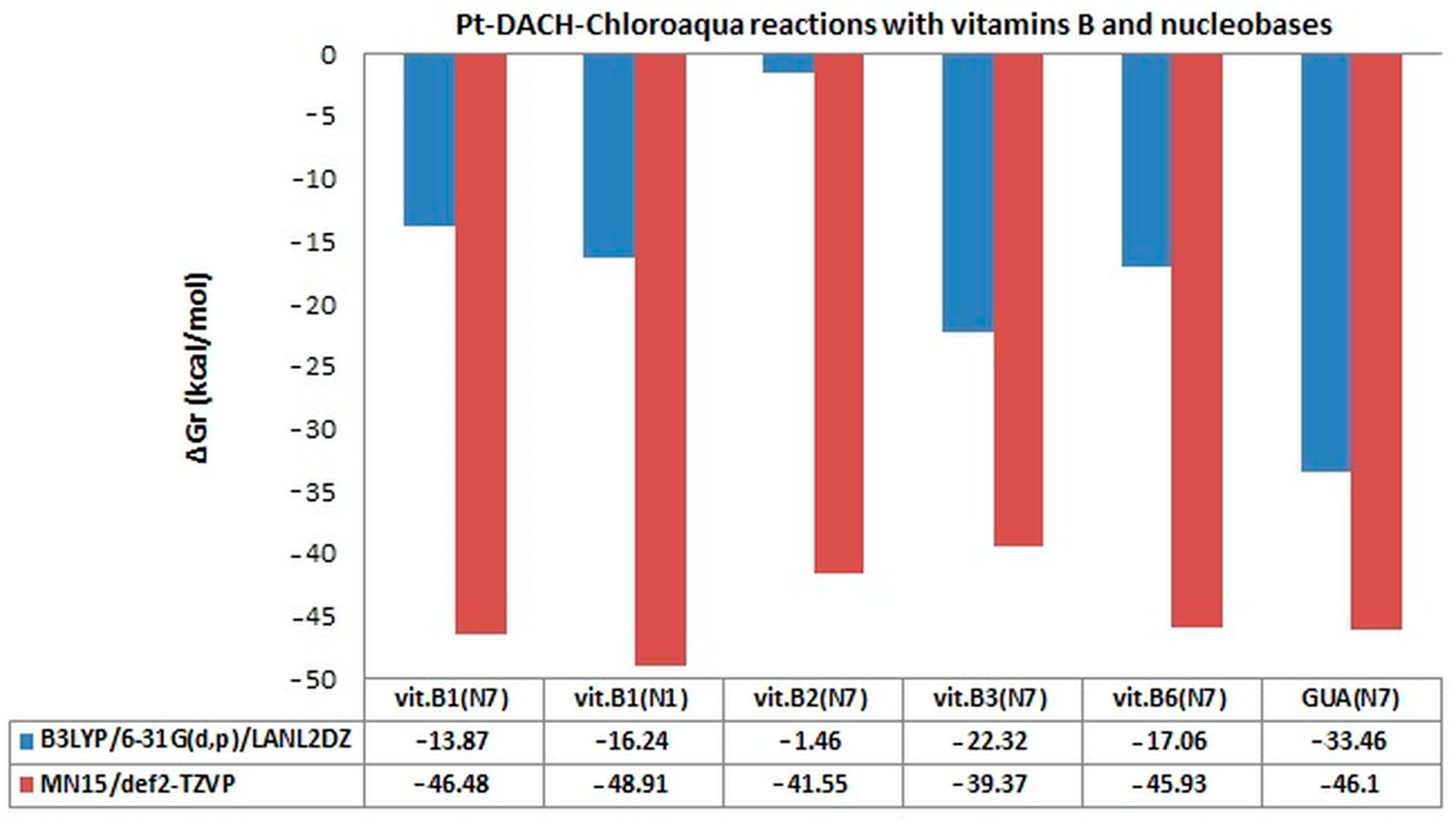
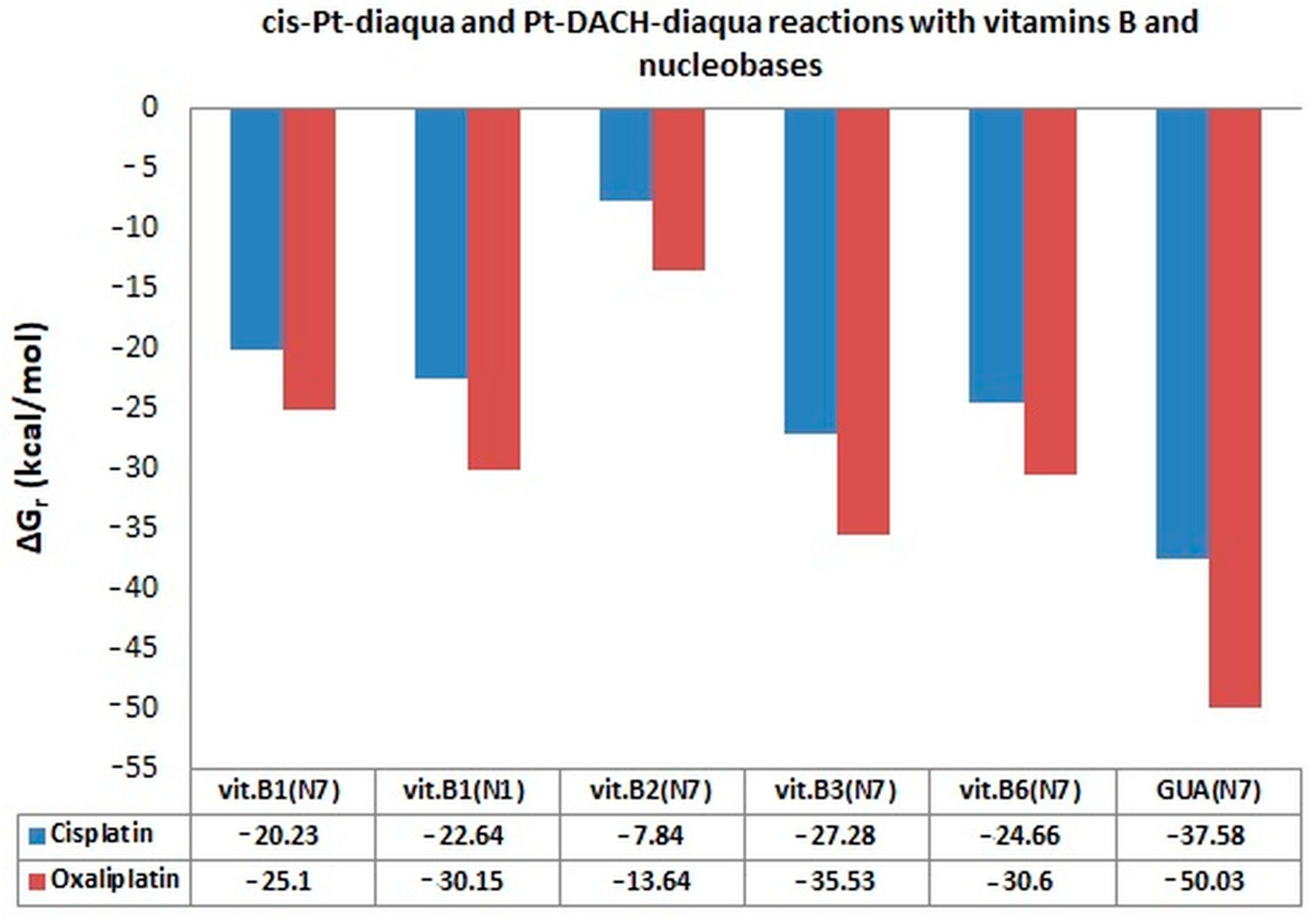
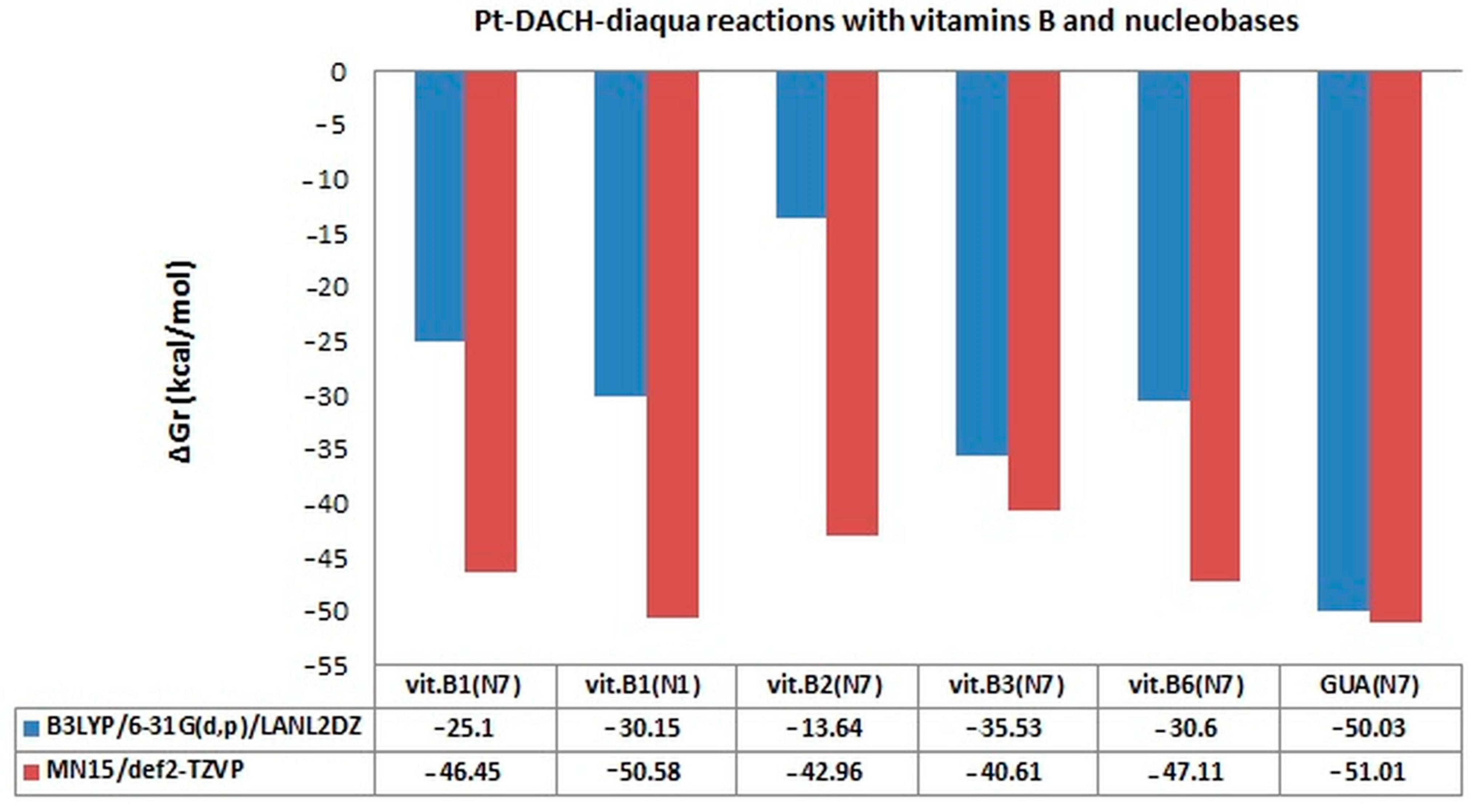


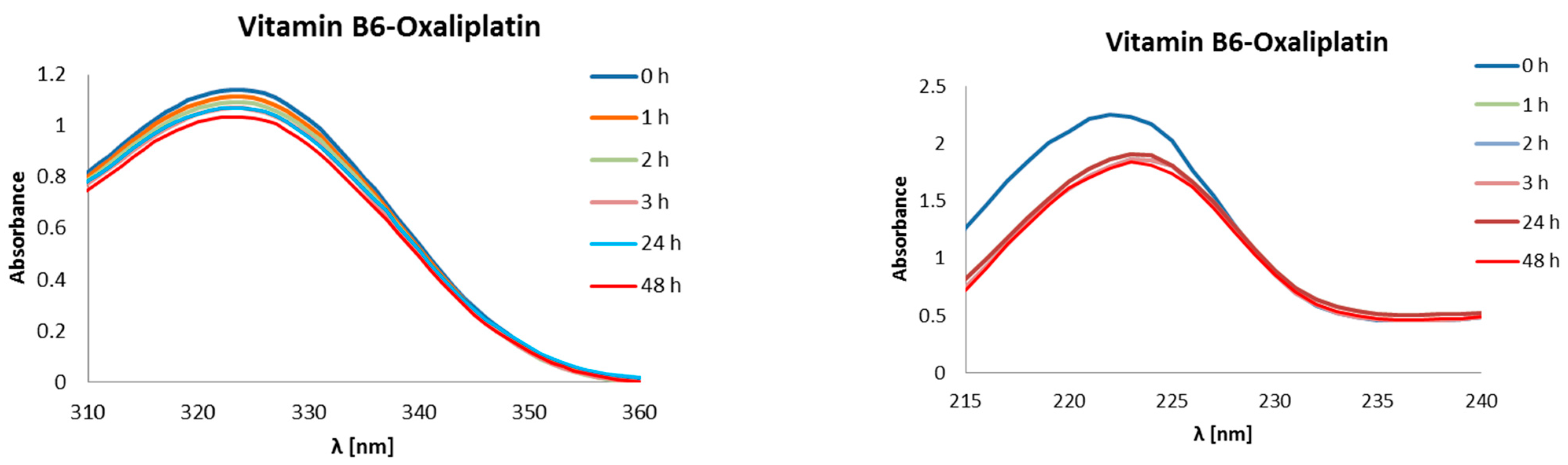
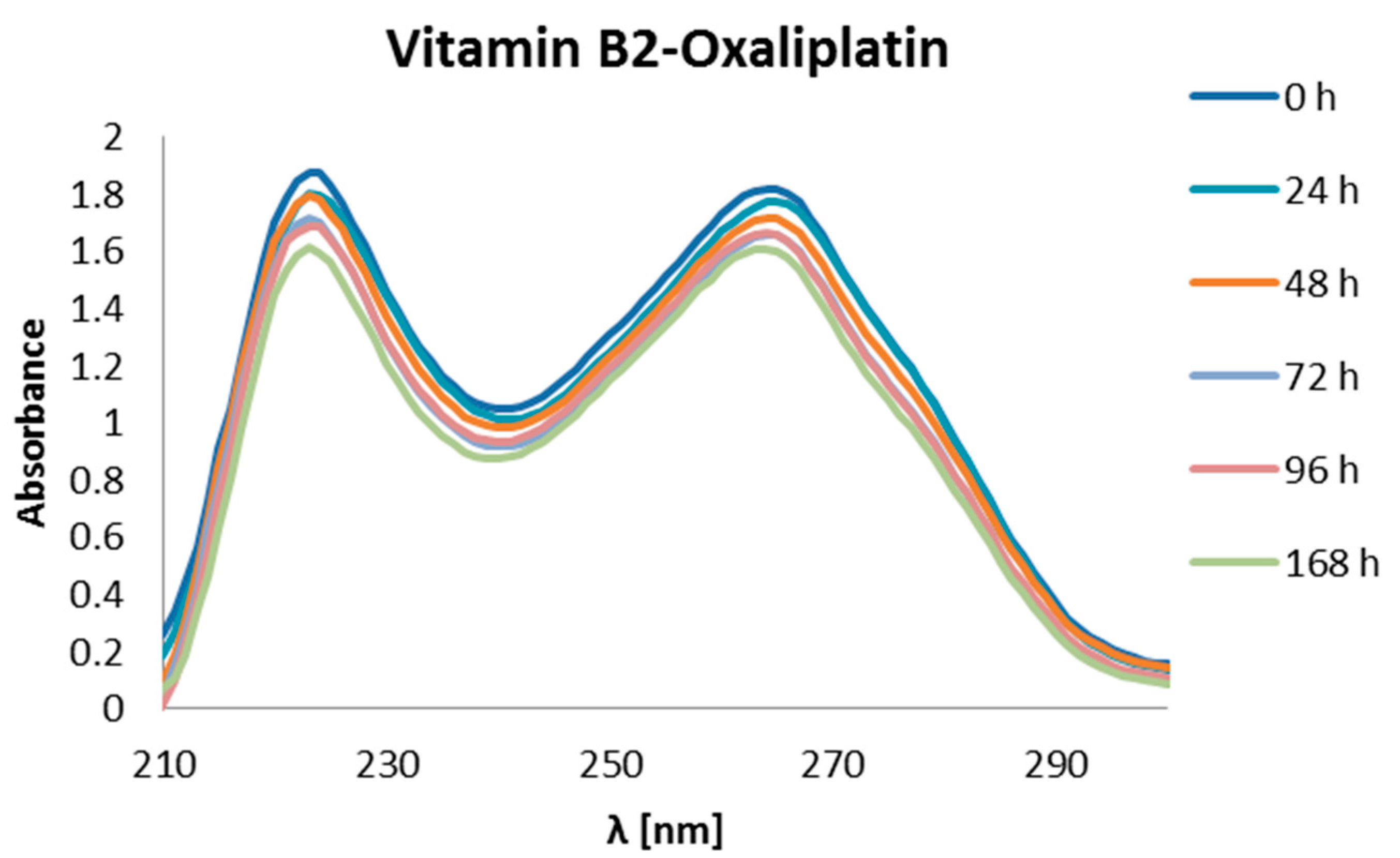
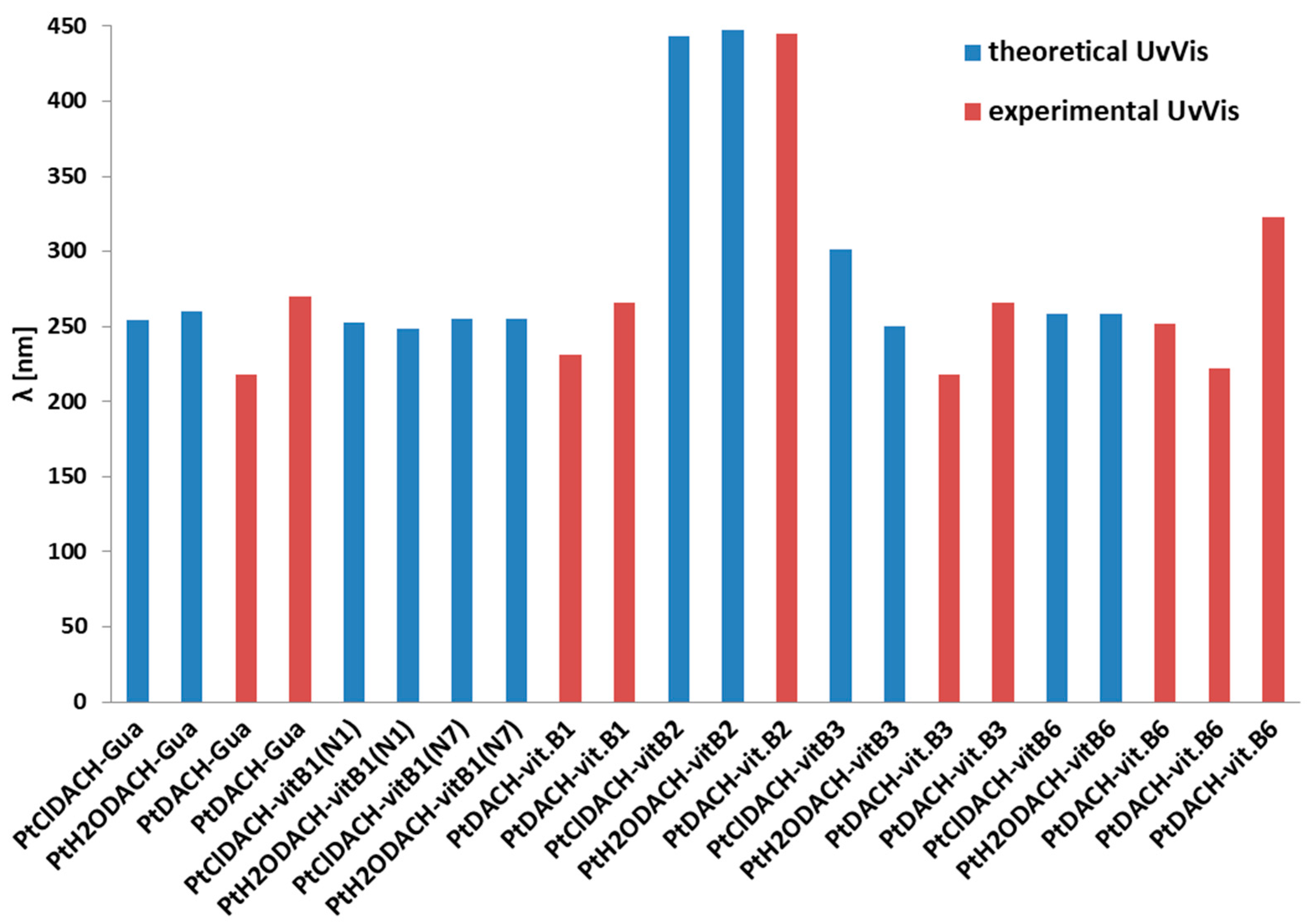
| ΔGr (kcal/mol) | Reaction | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cisplatin | Oxaliplatin | Carboplatin | |
| −18.90 | −13.87 | 149.53 | cis[Pt*/**/***]+/+/2+ + [B1(N7)]+ → cis[Pt/**/***-B1(N7)]2+/2+/3+ |
| −20.89 | −16.24 | 144.60 | cis[Pt*/**/***]+/+/2+ + [B1(N1)]+ → cis[Pt/**/***-B1(N1)]2+/2+/3+ |
| −3.75 | −1.46 | 233.04 | cis[Pt*/**/***]+/+/2+ + B2(N7) → cis[Pt/**/***-B2(N7)]+/+/2+ |
| −24.90 | −22.32 | −6.3 | cis[Pt*/**/***]+/+/2+ + B3(N7) → cis[Pt/**/***-B3(N7)]+/+/2+ |
| −15.61 | −17.06 | −12.96 | cis[Pt*/**/***]+/+/2+ + B6(N7) → cis[Pt/**/***-B6(N7)]+/+/2+ |
| −28.17 | −33.46 | −30.89 | cis[Pt*/**/***]+/+/2+ + GUA(N7)→cis[Pt/**/***-GUA(N7)]+/+/2+ |
| Number of Reaction | ΔGr | Reaction |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | −46.48 | [Pt*]+ + [B1(N7)]+ → [Pt*-B1(N7)]2+ |
| 2 | −48.91 | [Pt*]+ + [B1(N1)]+ → [Pt*-B1(N1)]2+ |
| 3 | −41.55 | [Pt*]+ + B2 → [Pt*-B2]+ |
| 4 | −39.37 | [Pt*]+ + B3 → [Pt*-B3]+ |
| 5 | −45.93 | [Pt*]+ + B6 → [Pt*-B6]+ |
| 6 | −46.10 | [Pt*]+ + GUA → [Pt*-GUA]+ |
| ΔGr (kcal/mol) | Reaction | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cisplatin | Oxaliplatin | Carboplatin | |
| −20.23 | −25.10 | 149.53 | cis[Pt*/**/***]2+/2+/+ + [B1(N7)]+ → cis[Pt/**-B1(N7)]3+/3+/2+ |
| −22.64 | −30.15 | 144.60 | cis[Pt*/**/***]2+/2+/+ + [B1(N1)]+ → cis[Pt/**-B1(N1)]3+/3+/2+ |
| −7.84 | −13.64 | 233.04 | cis[Pt*/**/***]2+/2+/+ + B2(N7) → cis[Pt/**-B2(N7)]2+/2+/+ |
| −27.28 | −35.53 | −6.3 | cis[Pt*/**/***]2+/2+/+ + B3(N7) → cis[Pt/**-B3(N7)]2+/2+/+ |
| −24.66 | −30.60 | −12.96 | cis[Pt*/**/***]2+/2+/+ + B6(N7) → cis[Pt/**-B6(N7)]2+/2+/+ |
| −37.58 | −50.03 | −30.89 | cis[Pt*/**/***]2+/2+/+ + GUA(N7)→cis[Pt/**-GUA(N7)]2+/2+/+ |
| Number of Reaction | ΔGr | Reaction |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | −46.45 | [Pt**]2+ + [B1(N7)]+ → [Pt**-B1(N7)]3+ |
| 2 | −50.58 | [Pt**]2+ + [B1(N1)]+ → [Pt**-B1(N1)]3+ |
| 3 | −42.96 | [Pt**]2+ + B2 → [Pt**-B2]2+ |
| 4 | −40.61 | [Pt**]2+ + B3 → [Pt**-B3]2+ |
| 5 | −47.11 | [Pt**]2+ + B6 → [Pt**-B6]2+ |
| 6 | −51.01 | [Pt**]2+ + GUA → [Pt**-GUA]2+ |
| BCP | PtClDACH-Gua | BCP | PtH2ODACH-Gua | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ρBCP(e×a0−3) | ∇2ρBCP(e×a0−5) | V (r) | ρBCP(e×a0−3) | ∇2ρBCP(e×a0−5) | V (r) | ||
| Cl-Pt | 1.02 × 10−1 | 1.97 × 10−1 | -1.27 × 10−1 | H2O-Pt | 9.54 × 10−2 | 4.69 × 10−1 | −1.65 × 10−1 |
| N-Pt | 1.25 × 10−1 | 4.53 × 10−1 | −2.06 × 10−1 | N-Pt | 1.28 × 10−1 | 4.31 × 10−1 | −2.07 × 10−1 |
| H2N-Pt | 1.25 × 10−1 | 4.12 × 10−1 | −1.96 × 10−1 | H2N-Pt | 1.39 × 10−1 | 3.77 × 10−1 | −2.12 × 10−1 |
| H2N-Pt | 1.26 × 10−1 | 4.15 × 10−1 | -1.99 × 10−1 | H2N-Pt | 1.27 × 10−1 | 4.04 × 10−1 | −1.99 × 10−1 |
| O…HN | 1.84 × 10−2 | 7.27 × 10−2 | −1.23 × 10−2 | O…HN | 1.90 × 10−2 | 7.36 × 10−2 | −1.27 × 10−2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szefler, B.; Czeleń, P. Will the Interactions of Some Platinum (II)-Based Drugs with B-Vitamins Reduce Their Therapeutic Effect in Cancer Patients? Comparison of Chemotherapeutic Agents such as Cisplatin, Carboplatin and Oxaliplatin—A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021548
Szefler B, Czeleń P. Will the Interactions of Some Platinum (II)-Based Drugs with B-Vitamins Reduce Their Therapeutic Effect in Cancer Patients? Comparison of Chemotherapeutic Agents such as Cisplatin, Carboplatin and Oxaliplatin—A Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(2):1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021548
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzefler, Beata, and Przemysław Czeleń. 2023. "Will the Interactions of Some Platinum (II)-Based Drugs with B-Vitamins Reduce Their Therapeutic Effect in Cancer Patients? Comparison of Chemotherapeutic Agents such as Cisplatin, Carboplatin and Oxaliplatin—A Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 2: 1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021548
APA StyleSzefler, B., & Czeleń, P. (2023). Will the Interactions of Some Platinum (II)-Based Drugs with B-Vitamins Reduce Their Therapeutic Effect in Cancer Patients? Comparison of Chemotherapeutic Agents such as Cisplatin, Carboplatin and Oxaliplatin—A Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(2), 1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021548








