Exploring Tumor–Immune Interactions in Co-Culture Models of T Cells and Tumor Organoids Derived from Patients
Abstract
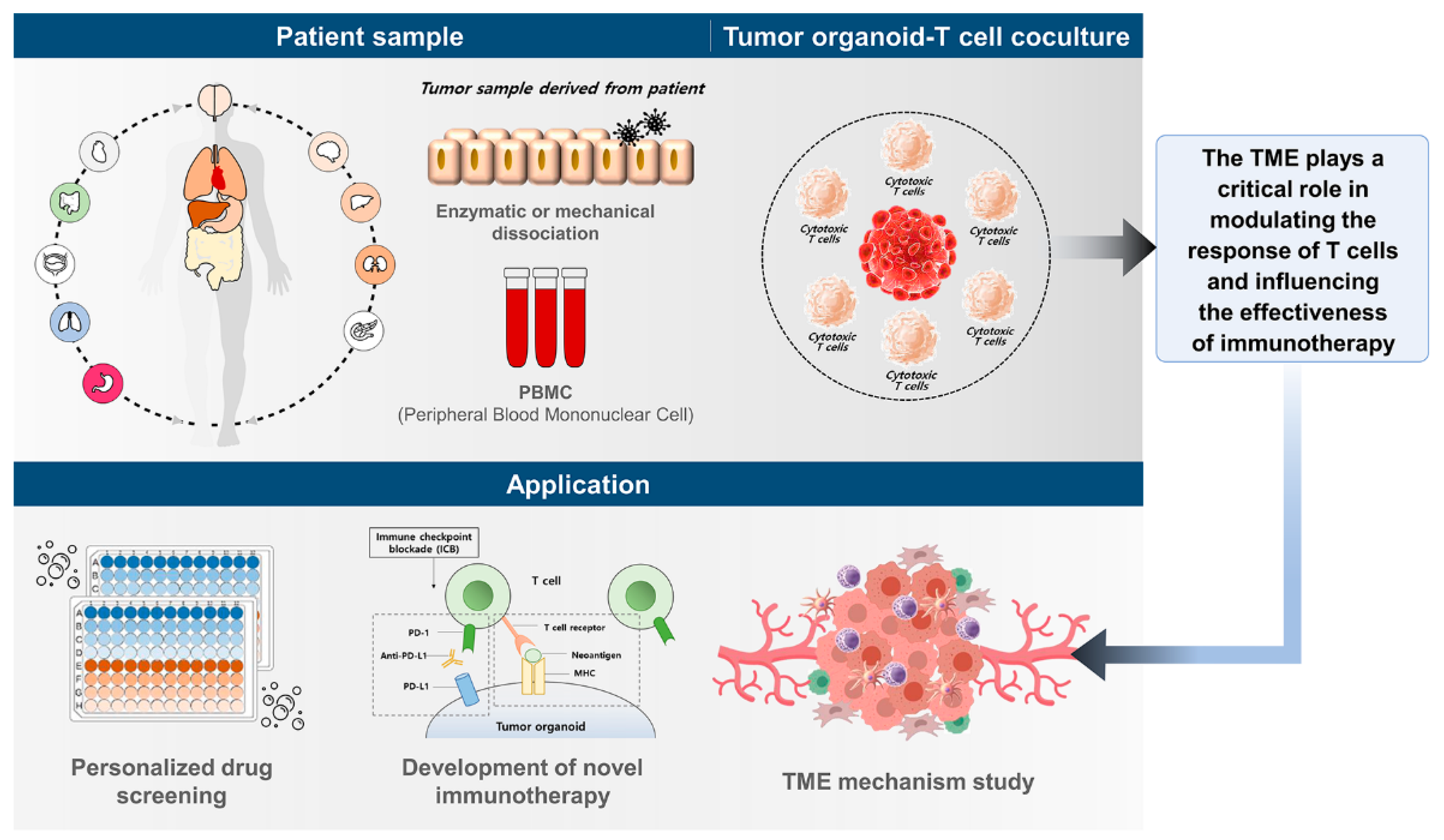
:1. Introduction
2. Overview of Co-Culture Models in Cancer Research
3. Co-Culture Models of T Cells and Tumor Organoids
4. Clinical Relevance of Co-Culture Models of T Cells and Tumor Organoids
5. Challenges and Limitations of Co-Culture Models of T Cells and Tumor Organoids
6. Future Directions for Co-Culture Models of T Cells and Tumor Organoids
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giraldo, N.A.; Taube, J.M. PD-L1 and Other Immunological Diagnosis Tools; Zitvogel, L., Kroemer, G., Eds.; Springer: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2018; pp. 371–385. [Google Scholar]
- Giraldo, N.A.; Sanchez-Salas, R.; Peske, J.D.; Vano, Y.; Becht, E.; Petitprez, F.; Validire, P.; Ingels, A.; Cathelineau, X.; Fridman, W.H.; et al. The clinical role of the TME in solid cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toor, S.M.; Nair, V.S.; Decock, J.; Elkord, E. Immune checkpoints in the tumor microenvironment. Seminars in cancer biology. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 65, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammers, H.J.; Plimack, E.R.; Infante, J.R.; Rini, B.I.; McDermott, D.F.; Lewis, L.D.; Voss, M.H.; Sharma, P.; Pal, S.K.; Razak, A.R.A.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Nivolumab in Combination with Ipilimumab in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: The CheckMate 016 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3851–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardoll, D. The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Xu, H.; Xu, X.; Guo, T.; Ge, W. High tumor mutation burden predicts better efficacy of immunotherapy: A pooled analysis of 103078 cancer patients. Oncoimmunology 2019, 8, e1629258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, S.; Shin, S.; Dy, G. Advances in Cancer Immunotherapy in Solid Tumors. Cancers 2016, 8, 106–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garon, E.B.; Rizvi, N.A.; Hui, R.; Leighl, N.; Balmanoukian, A.S.; Eder, J.P.; Patnaik, A.; Aggarwal, C.; Gubens, M.; Horn, L.; et al. Pembrolizumab for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2018–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, P.A.; Bang, Y.J.; Piha-Paul, S.A.; Razak, A.R.A.; Bennouna, J.; Soria, J.C.; Rugo, H.S.; Cohen, R.B.; O’Neil, B.H.; Mehnert, J.M.; et al. T-Cell-Inflamed Gene-Expression Profile, Programmed Death Ligand 1 Expression, and Tumor Mutational Burden Predict Efficacy in Patients Treated with Pembrolizumab Across 20 Cancers: KEYNOTE-028. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagchi, S.; Yuan, R.; Engleman, E.G. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for the Treatment of Cancer: Clinical Impact and Mechanisms of Response and Resistance. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2021, 16, 223–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, B.; Henriques, A.C.; Silva, P.M.A.; Bousbaa, H. Three-Dimensional Spheroids as In Vitro Preclinical Models for Cancer Research. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1186–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jubelin, C.; Muñoz-Garcia, J.; Griscom, L.; Cochonneau, D.; Ollivier, E.; Heymann, M.F.; Vallette, F.M.; Oliver, L.; Heymann, D. Three-dimensional in vitro culture models in oncology research. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 155–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Guo, F.; Jin, Y.; Ma, Y. Applications of human organoids in the personalized treatment for digestive diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 336–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Chen, X.; Dowbaj, A.M.; Sljukic, A.; Bratlie, K.; Lin, L.; Fong, E.L.S.; Balachander, G.M.; Chen, Z.; Soragni, A.; et al. Organoids. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2022, 2, 94–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.P.; Lan, H.R.; Fang, X.L.; Yang, X.Y.; Jin, K.T. Organoid Models for Precision Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 5, 770465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veninga, V.; Voest, E.E. Tumor organoids: Opportunities and challenges to guide precision medicine. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 1190–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahcecioglu, G.; Basara, G.; Ellis, B.W.; Ren, X.; Zorlutun, P. Breast cancer models: Engineering the tumor microenvironment. Acta Biomater. 2020, 106, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Kuang, G.; Fan, Q.; Ye, F. Construction and application of liver cancer models in vitro. Eng. Regen. 2022, 3, 310–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, W.; Cai, C.; Zhang, H.; Shen, H.; Han, Y. Patient-derived xenograft models in cancer therapy: Technologies and applications. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, C.M.; Dijkstra, K.K.; Fanchi, L.F.; Kelderman, S.; Kaing, S.; van Rooij, N.; van den Brink, S.; Schumacher, T.N.; Voest, E.E. Tumor organoid-T-cell coculture systems. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 15–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, K.K.; Monkhorst, K.; Schipper, L.J.; Hartemink, K.J.; Smit, E.F.; Kaing, S.; de Groot, R.; Wolkers, M.C.; Clevers, H.; Cuppen, E.; et al. Challenges in Establishing Pure Lung Cancer Organoids Limit Their Utility for Personalized Medicine. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, J.T.; Li, X.; Zhu, J.; Giangarra, V.; Grzeskowiak, C.L.; Ju, J.; Liu, I.H.; Chiou, S.H.; Salahudeen, A.A.; Smith, A.R.; et al. Organoid Modeling of the Tumor Immune Microenvironment. Cell 2018, 175, 1972–1988.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Choi, H.; Koh, S.K.; Park, D.; Yu, J.; Kang, H.; Kim, Y.; Cho, D.; Jeon, N.L. High-Throughput 3D In Vitro Tumor Vasculature Model for Real-Time Monitoring of Immune Cell Infiltration and Cytotoxicity. Front. Immunol. 2021, 24, 733317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belloni, D.; Heltai, S.; Ponzoni, M.; Villa, A.; Vergani, B.; Pecciarini, L.; Marcatti, M.; Girlanda, S.; Tonon, G.; Ciceri, F.; et al. Modeling multiple myeloma-bone marrow interactions and response to drugs in a 3D surrogate microenvironment. Haematologica 2018, 103, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magré, L.; Verstegen, M.M.A.; Buschow, S.; van der Laan, L.J.W.; Peppelenbosch, M.; Desai, J. Emerging organoid-immune co-culture models for cancer research: From oncoimmunology to personalized immunotherapies. J. Immunother. Cancer 2023, 11, e006290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuki, K.; Cheng, N.; Nakano, M.; Kuo, C.J. Organoid Models of Tumor Immunology. Trends Immunol. 2020, 41, 652–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weeber, F.; Ooft, S.N.; Dijkstra, K.K.; Voest, E.E. Tumor Organoids as a Pre-clinical Cancer Model for Drug Discovery. Cell Chem. Biol. 2017, 24, 1092–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, E.A.; Aldrak, N.A.; Albrahim, S.H.; Alzahrani, D.A.; Alfassam, H.A.; Alkoblan, S.M.; Almalik, A.M.; Chen, K.-S.; Abou-Khalil, R.; Shah, K.; et al. Immunotherapy in hematological malignancies: Recent advances and open questions. Immunotherapy 2021, 13, 1215–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Corte, C.M.; Barra, G.; Ciaramella, V.; Di Liello, R.; Vicidomini, G.; Zappavigna, S.; Luce, A.; Abate, M.; Fiorelli, A.; Caraglia, M.; et al. Antitumor activity of dual blockade of PD-L1 and MEK in NSCLC patients derived three-dimensional spheroid cultures. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, P.; Zhou, S.; Lv, T.; Xia, F.; Shen, L.; Wan, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Cai, S.; Peng, J.; et al. Newly developed 3D in vitro models to study tumor–immune interaction. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guido, G.; Manuela, G.; Christian, R.; Alessandra, S. From Chemotherapy to Combined Targeted Therapeutics: In Vitro and in Vivo Models to Decipher Intra-tumor Heterogeneity. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vis, M.A.M.; Ito, K.; Hofmann, S. Impact of Culture Medium on Cellular Interactions in in vitro Co-culture Systems. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 4, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunti, S.; Hoke, A.T.K.; Vu, K.P.; London, N.R., Jr. Organoid and Spheroid Tumor Models: Techniques and Applications. Cancers 2021, 13, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elena, F.; Lisa, V.; Vincenzo, C. Modeling Cell Communication in Cancer With organoids: Making the Complex Simple. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 18, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, B.; Junkin, M.; Saheb, K.S.; Romero-Calvo, I.; Kirby, K.; Matthews, J.; Weber, C.R.; Andrey, R.; White, K.P.; Tay, S. Automated microfluidic platform for dynamic and combinatorial drug screening of tumor organoids. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edmondson, R.; Broglie, J.J.; Adcock, A.F.; Yang, L. Three-dimensional cell culture systems and their applications in drug discovery and cell-based biosensors. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2014, 12, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Árnadóttir, S.S.; Jeppesen, M.; Lamy, P.; Bramsen, J.B.; Nordentoft, I.; Knudsen, M.; Vang, S.; Madsen, M.R.; Thastrup, O.; Thastrup, J.; et al. Characterization of genetic intratumor heterogeneity in colorectal cancer and matching patient-derived spheroid cultures. Mol. Oncol. 2018, 12, 132–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Kang, E.; Wilson, M.; Basso, T.; Chen, E.; Yu, Y.; Li, Y.-R. 3D Tumor Spheroid and Organoid to Model Tumor Microenvironment for Cancer Immunotherapy. Organoids 2022, 1, 149–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnereau, J.; Courau, T.; Asesio, N.; Salfati, D.; Bouhidel, F.; Corte, H.; Hamoudi, S.; Hammoudi, N.; Lavolé, J.; Vivier-Chicoteau, J.; et al. Autologous T cell responses to primary human colorectal cancer spheroids are enhanced by ectonucleotidase inhibition. Gut 2023, 72, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinman, H.K.; Martin, G.R. Matrigel: Basement membrane matrix with biological activity. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2005, 15, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, M.; Paramesh, V.; Kaviya, S.R.; Anuradha, E.; Solomon, F.D. 3D cell culture systems: Advantages and applications. J. Cell. Physiol. 2015, 230, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, T.R.; Fonseca, N.A.; Gonçalves, N.; Moreira, J.N. Current challenges and emerging opportunities of CAR-T cell therapies. J. Control Release 2020, 319, 246–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipson, B.; Milone, M.C. Chapter 4—T Cell Engineering and the Rise of CAR-T Cell Therapies. In Second Generation Cell and Gene-Based Therapies; Vertès, A.A., Smith, D.M., Qureshi, N., Dowden, N.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnalzger, T.E.; De Groot, M.H.; Zhang, C.; Mosa, M.H.; Michels, B.E.; Röder, J.; Darvishi, T.; Wels, W.S.; Farin, H.F. 3D model for CAR-mediated cytotoxicity using patient-derived colorectal cancer organoids. EMBO J. 2019, 38, e100928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekkers, J.F.; Alieva, M.; Cleven, A.; Keramati, F.; Wezenaar, A.K.L.; van Vliet, E.J.; Puschhof, J.; Brazda, P.; Johanna, I.; Meringa, A.D.; et al. Uncovering the mode of action of engineered T cells in patient cancer organoids. Nat. Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Guo, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, H.; Cui, J.; Wu, W.; He, J.; et al. Single-Cell Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals BCMA CAR-T Cell Dynamics in a Patient with Refractory Primary Plasma Cell Leukemia. Mol. Ther. 2021, 29, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murad, J.P.; Tilakawardane, D.; Park, A.K.; Lopez, L.S.; Young, C.A.; Gibson, J.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Lee, H.J.; Kennewick, K.T.; Gittins, B.J.; et al. Pre-conditioning modifies the TME to enhance solid tumor CAR T cell efficacy and endogenous protective immunity. Mol. Ther. 2021, 29, 2335–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatehullah, A.; Tan, S.H.; Barker, N. Organoids as an in vitro model of human development and disease. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 18, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhans, S.A. Three-dimensional in vitro cell culture models in drug discovery and drug repositioning. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 23, 6–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Ephraim, Y.E.; Kretzschmar, K.; Clevers, H. Organoids in immunological research. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Huang, J.; Ayansola, H.; Masatoshi, H.; Zhang, B. Intestinal Stem Cells and Immune Cell Relationships:Potential Therapeutic Targets for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 623691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, K.K.; Cattaneo, C.M.; Weeber, F.; Chalabi, M.; Van De Haar, J.; Fanchi, L.F.; Slagter, M.; Van Der Velden, D.L.; Kaing, S.; Kelderman, S.; et al. Generation of Tumor-Reactive T Cells by Co-culture of Peripheral Blood Lymphocytes and Tumor Organoids. Cell 2018, 174, 1586–1598.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Lieshout, R.; van Tienderen, G.S.; de Ruiter, V.; van Royen, M.E.; Boor, P.P.C.; Magré, L.; Desai, J.; Köten, K.; Kan, Y.Y.; et al. Modelling immune cytotoxicity for cholangiocarcinoma with tumour-derived organoids and effector T cells. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 127, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Xie, S.; Gray, G.K.; Dezfulian, M.H.; Li, W.; Huang, L.; Akshinthala, D.; Ferrer, E.; Conahan, C.; Perea Del Pino, S.; et al. Empirical identification and validation of tumor-targeting T cell receptors from circulation using autologous pancreatic tumor organoids. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e003213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.C.H.; Guerra, G.R.; Millen, R.M.; Roth, S.; Xu, H.; Neeson, P.J.; Darcy, P.K.; Kershaw, M.H.; Sampurno, S.; Malaterre, J.; et al. Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte Function Predicts Response to Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy in Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2018, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, G.; Belli, V.; Napolitano, S.; Ciaramella, V.; Ciardiello, D.; Belli, A.; Izzo, F.; Avallone, A.; Selvaggi, F.; Menegon Tasselli, F.; et al. Establishment of patient-derived tumor organoids to functionally inform treatment decisions in metastatic colorectal cancer. ESMO Open 2023, 8, 10119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subtil, B.; Iyer, K.K.; Poel, D.; Bakkerus, L.; Gorris, M.A.J.; Escalona, J.C.; van den Dries, K.; Cambi, A.; Verheul, H.M.W.; de Vries, I.J.M.; et al. Dendritic cell phenotype and function in a 3D co-culture model of patient-derived metastatic colorectal cancer organoids. Front. Immunol. 2023, 25, 1105244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, L.; Alfonsi, R.; Francescangeli, F.; Signore, M.; De Angelis, M.L.; Addario, A.; Costantini, M.; Flex, E.; Ciolfi, A.; Pizzi, S.; et al. Organoids as a new model for improving regenerative medicine and cancer personalized therapy in renal diseases. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, W.; Jankovic, V.; Golubov, J.; Poon, P.; Oswald, E.M.; Gurer, C.; Wei, J.; Ramos, I.; Wu, Q.; et al. Combination cancer immunotherapy targeting PD-1 and GITR can rescue CD8+ T cell dysfunction and maintain memory phenotype. Sci. Immunol. 2018, 3, eaat7061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Sui, X.; Song, F.; Li, Y.; Li, K.; Chen, Z.; Yang, F.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Lung cancer organoids analyzed on microwell arrays predict drug responses of patients within a week. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balážová, K.; Clevers, H.; Dost, A.F.M. The role of macrophages in non-small cell lung cancer and advancements in 3D co-cultures. elife 2023, 21, e82998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Mun, H.; Sung, C.O.; Cho, E.J.; Jeon, H.J.; Chun, S.M.; Jung, D.J.; Shin, T.H.; Jeong, G.S.; Kim, D.K.; et al. Patient-derived lung cancer organoids as in vitro cancer models for therapeutic screening. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullenders, J.; de Jongh, E.; Brousali, A.; Roosen, M.; Blom, J.P.A.; Begthel, H.; Korving, J.; Jonges, T.; Kranenburg, O.; Meijer, R.; et al. Mouse and human urothelial cancer organoids: A tool for bladder cancer research. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 4567–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Hu, W.; Matulay, J.T.; Silva, M.V.; Owczarek, T.B.; Kim, K.; Chua, C.W.; Barlow, L.J.; Kandoth, C.; Williams, A.B.; et al. Tumor Evolution and Drug Response in Patient-Derived Organoid Models of Bladder Cancer. Cell 2018, 173, 515–528.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Bi, Y.; Zhang, N.; Wang, H.; Xing, T.; Bai, S.; Shen, Z.; Naz, F.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Immune escape mechanisms and immunotherapy of urothelial bladder cancer. J. Clin. Transl. Res. 2021, 7, 485–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Choi, S.; Kang, B.; Kong, J.; Kim, Y.; Yoon, W.H.; Lee, H.R.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.M.; Lee, H.; et al. Creation of bladder assembloids mimicking tissue regeneration and cancer. Nature 2020, 588, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiriac, H.; Bucobo, J.C.; Tzimas, D.; Grewel, S.; Lacomb, J.F.; Rowehl, L.M.; Nagula, S.; Wu, M.; Kim, J.; Sasson, A.; et al. Successful creation of pancreatic cancer organoids by means of EUS-guided fine-needle biopsy sampling for personalized cancer treatment. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2018, 87, 1474–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacomb, J.F.; Plenker, D.; Tiriac, H.; Bucobo, J.C.; D'souza, L.S.; Khokhar, A.S.; Patel, H.; Channer, B.; Joseph, D.; Wu, M.; et al. Single-Pass vs 2-Pass Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Biopsy Sample Collection for Creation of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Organoids. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 1, 845–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boj, S.F.; Hwang, C.I.; Baker, L.A.; Chio, I.I.; Engle, D.D.; Corbo, V.; Jager, M.; Ponz-Sarvise, M.; Tiriac, H.; Spector, M.S.; et al. Organoid models of human and mouse ductal pancreatic cancer. Cell 2015, 160, 324–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holokai, L.; Chakrabarti, J.; Lundy, J.; Croagh, D.; Adhikary, P.; Richards, S.S.; Woodson, C.; Steele, N.; Kuester, R.; Scott, A.; et al. Murine- and Human-Derived Autologous Organoid/Immune Cell Co-Cultures as Pre-Clinical Models of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Calvisi, D.F.; Chen, X. Organoids for the Study of Liver Cancer. Semin. Liver Dis. 2021, 41, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Van der Jeught, K.; Li, Y.; Sharma, S.; Yu, T.; Moulana, I.; Liu, S.; Wan, J.; Territo, P.R.; Opyrchal, M.; et al. Cell-Engaging Tumor Organoid Platform for Pancreatic Cancer Immunotherapy. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2300548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Lu, D.; Chen, R.; Lin, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Cai, S.; Cui, P.; Song, G.; Rao, D.; et al. Proteogenomic characterization identifies clinically relevant subgroups of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 70–87e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzucchelli, S.; Piccotti, F.; Allevi, R.; Truffi, M.; Sorrentino, L.; Russo, L.; Agozzino, M.; Signati, L.; Bonizzi, A.; Villani, L.; et al. Establishment and Morphological Characterization of Patient-Derived Organoids from Breast Cancer. Biol. Proced. Online 2019, 15, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; He, Q.; Xu, G. Screening of Prognostic Factors in Early-Onset Breast Cancer. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 19, 1533033819893670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, C. Application of Organoid Models in Prostate Cancer Research. Front. Oncol. 2021, 27, 736431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Votanopoulos, K.I.; Forsythe, S.; Sivakumar, H.; Mazzocchi, A.; Aleman, J.; Miller, L.; Levine, E.; Triozzi, P.; Skardal, A. Model of Patient-Specific Immune-Enhanced Organoids for Immunotherapy Screening: Feasibility Study. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 27, 1956–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalabi, M.; Fanchi, L.F.; Dijkstra, K.K.; Van den Berg, J.G.; Aalbers, A.G.; Sikorska, K.; Lopez-Yurda, M.; Grootscholten, C.; Beets, G.L.; Snaebjornsson, P.; et al. Neoadjuvant immunotherapy leads to pathological responses in MMR-proficient and MMR-deficient early-stage colon cancers. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teijeira, A.; Migueliz, I.; Garasa, S.; Karanikas, V.; Luri, C.; Cirella, A.; Olivera, I.; Cañamero, M.; Alvarez, M.; Ochoa, M.C.; et al. Three-dimensional colon cancer organoids model the response to CEA-CD3 T-cell engagers. Theranostics 2022, 12, 1373–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Q.; Zhang, X.; Chen, C.; Tang, J.; Yu, J.; Li, W.; Han, K.; Jiang, W.; Liao, L.; Kong, L.; et al. Inflammation promotes resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors in high microsatellite instability colorectal cancer. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Zhang, T.; Zheng, L.; Liu, H.; Song, W.; Liu, D.; Li, Z.; Pan, C.X. Combination strategies to maximize the benefits of cancer immunotherapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Meng, L.H. Emerging roles of class I PI3K inhibitors in modulating tumor microenvironment and immunity. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 1395–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.M.; Webster, S.J.; Flower, D.; Woll, P.J. Interleukin-8/CXCL8 is a growth factor for human lung cancer cells. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 91, 1970–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maru, Y.; Tanaka, N.; Itami, M.; Hippo, Y. Efficient use of patient-derived organoids as a preclinical model for gynecologic tumors. Gynecol. Oncol. 2019, 154, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Jiao, D.; Liu, A.; Wu, K. Tumor organoids: Applications in cancer modeling and potentials in precision medicine. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 58–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.C.; Park, J.W.; Seo, H.Y.; Kim, M.; Park, J.H.; Kim, G.H.; Lee, J.O.; Shin, Y.K.; Bae, J.M.; Koo, B.K.; et al. Multifocal Organoid Capturing of Colon Cancer Reveals Pervasive Intratumoral Heterogenous Drug Responses. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, e2103360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura Rosa, P.; Gopalakrishnan, N.; Ibrahim, H.; Haug, M.; Halaas, Ø. The intercell dynamics of T cells and dendritic cells in a lymph node-on-a-chip flow device. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 3728–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aung, A.; Kumar, V.; Theprungsirikul, J.; Davey, S.K.; Varghese, S. An Engineered Tumor-on-a-Chip Device with Breast Cancer-Immune Cell Interactions for Assessing T-cell Recruitment. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artegiani, B.; Clevers, H. Use and application of 3D-organoid technology. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 27, R99–R107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broutier, L.; Mastrogiovanni, G.; Verstegen, M.M.; Francies, H.E.; Gavarró, L.M.; Bradshaw, C.R.; Allen, G.E.; Arnes-Benito, R.; Sidorova, O.; Gaspersz, M.P.; et al. Human primary liver cancer-derived organoid cultures for disease modeling and drug screening. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1424–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs, N.; de Ligt, J.; Kopper, O.; Gogola, E.; Bounova, G.; Weeber, F.; Balgobind, A.V.; Wind, K.; Gracanin, A.; Begthel, H.; et al. A Living Biobank of Breast Cancer Organoids Captures Disease Heterogeneity. Cell 2018, 11, 373–386.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Vela, I.; Sboner, A.; Iaquinta, P.J.; Karthaus, W.R.; Gopalan, A.; Dowling, C.; Wanjala, J.N.; Undvall, E.A.; Arora, V.K.; et al. Organoid cultures derived from patients with advanced prostate cancer. Cell 2014, 159, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Wetering, M.; Francies, H.E.; Francis, J.M.; Bounova, G.; Iorio, F.; Pronk, A.; van Houdt, W.; van Gorp, J.; Taylor-Weiner, A.; Kester, L.; et al. Prospective derivation of a living organoid biobank of colorectal cancer patients. Cell 2015, 161, 933–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weeber, F.; van de Wetering, M.; Hoogstraat, M.; Dijkstra, K.K.; Krijgsman, O.; Kuilman, T.; Gadellaa-van Hooijdonk, C.G.; van der Velden, D.L.; Peeper, D.S.; Cuppen, E.P.; et al. Preserved genetic diversity in organoids cultured from biopsies of human colorectal cancer metastases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 13308–13311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, M.; Shimokawa, M.; Date, S.; Takano, A.; Matano, M.; Nanki, K.; Ohta, Y.; Toshimitsu, K.; Nakazato, Y.; Kawasaki, K.; et al. A Colorectal Tumor Organoid Library Demonstrates Progressive Loss of Niche Factor Requirements during Tumorigenesis. Cell Stem Cell 2016, 18, 827–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Holtzinger, A.; Jagan, I.; BeGora, M.; Lohse, I.; Ngai, N.; Nostro, C.; Wang, R.; Muthuswamy, L.B.; Crawford, H.C.; et al. Ductal pancreatic cancer modeling and drug screening using human pluripotent stem cell- and patient-derived tumor organoids. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1364–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seino, T.; Kawasaki, S.; Shimokawa, M.; Tamagawa, H.; Toshimitsu, K.; Fujii, M.; Ohta, Y.; Matano, M.; Nanki, K.; Kawasaki, K.; et al. Human Pancreatic Tumor Organoids Reveal Loss of Stem Cell Niche Factor Dependence during Disease Progression. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 22, 454–467.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubert, C.G.; Rivera, M.; Spangler, L.C.; Wu, Q.; Mack, S.C.; Prager, B.C.; Couce, M.; McLendon, R.E.; Sloan, A.E.; Rich, J.N. A Three-Dimensional Organoid Culture System Derived from Human Glioblastomas Recapitulates the Hypoxic Gradients and Cancer Stem Cell Heterogeneity of Tumors Found In Vivo. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2465–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Park, S.; Han, K.Y.; Lee, N.; Kim, H.; Jung, H.A.; Sun, J.M.; Ahn, J.S.; Ahn, M.J.; Lee, S.H.; et al. Clonal expansion of resident memory T cells in peripheral blood of patients with non-small cell lung cancer during immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment. J. Immunother. Cancer 2023, 11, e005509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Tissue Origin | Organoid Success Rate | Co-Culture-Immune Cell | Co-Culture Method | Drug Test | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colorectal cancer | 80% | Dendritic cells CD8+ T cell, macrophage | Domes Matrigel | Immunotherapy | [20,56,57] |
| Renal cell carcinoma | 67% | CD8+ T cell | Submerged Matrigel, ALI system, a 3D spheroid co-culture system | Immunotherapy | [58,59] |
| Lung cancer | 79% | CD4+ T cell, CD8+ T cell, macrophages | Submerged Matrigel domes, ALI system | Immunotherapy, CART cell therapy | [21,60,61,62] |
| Bladder cancer | 50% | CD8+ T cell | Domes Matrigel | Immunotherapy | [63,64,65,66] |
| Pancreatic cancer | 75–83% | CD8+ T cell, Dendritic cell | Domes Matrigel | Immunotherapy | [67,68,69,70] |
| Liver cancer and CCA 1 | HCC organoids: 26%, CCA organoids: 36% | CD8+ T cell, TILs, PBMCs | Domes Matrigel | None | [71,72,73] |
| Breast cancer | 87.5% | None | None | None | [74,75] |
| Prostate cancer | 20% | None | None | None | [76] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, S.-R.; Kang, M. Exploring Tumor–Immune Interactions in Co-Culture Models of T Cells and Tumor Organoids Derived from Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14609. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241914609
Jeong S-R, Kang M. Exploring Tumor–Immune Interactions in Co-Culture Models of T Cells and Tumor Organoids Derived from Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(19):14609. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241914609
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, So-Ra, and Minyong Kang. 2023. "Exploring Tumor–Immune Interactions in Co-Culture Models of T Cells and Tumor Organoids Derived from Patients" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 19: 14609. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241914609
APA StyleJeong, S.-R., & Kang, M. (2023). Exploring Tumor–Immune Interactions in Co-Culture Models of T Cells and Tumor Organoids Derived from Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(19), 14609. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241914609





