Further Developments towards a Minimal Potent Derivative of Human Relaxin-2
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
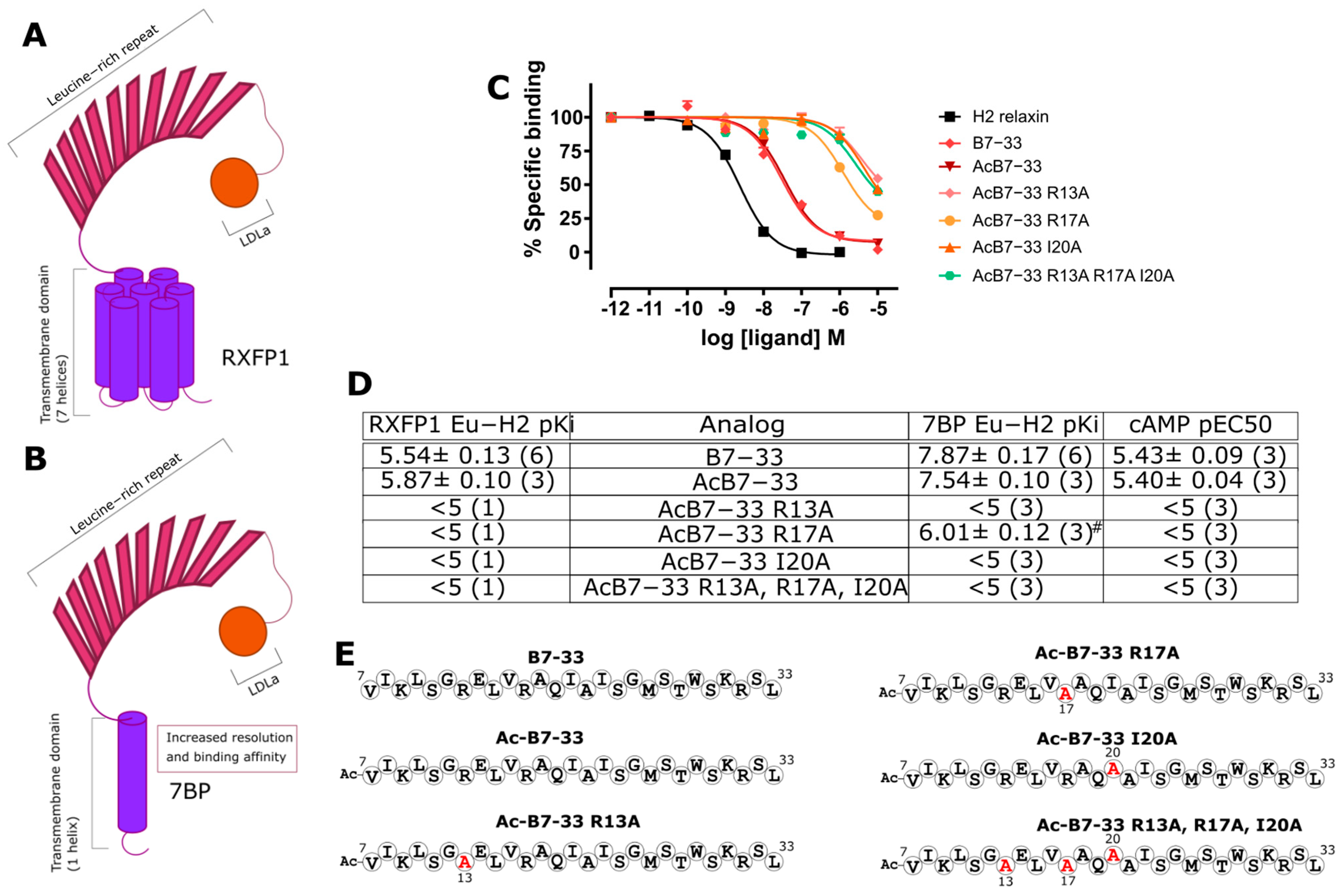
2.1. Identification of Key Residues for Binding to 7BP
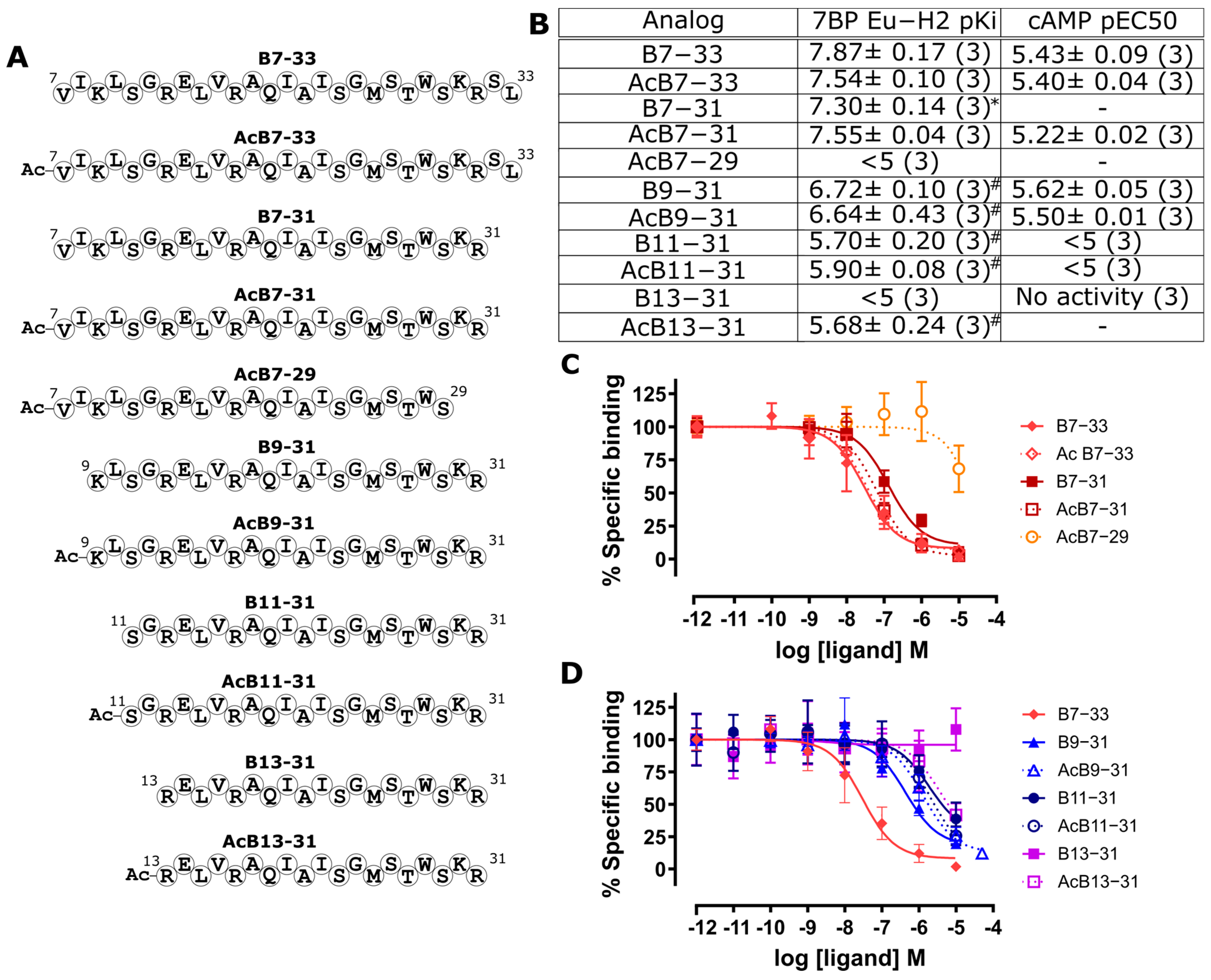
2.2. Identification of a Minimal B7-33-Based Analogue
2.3. Aminoisobuteric Acid Substitutions
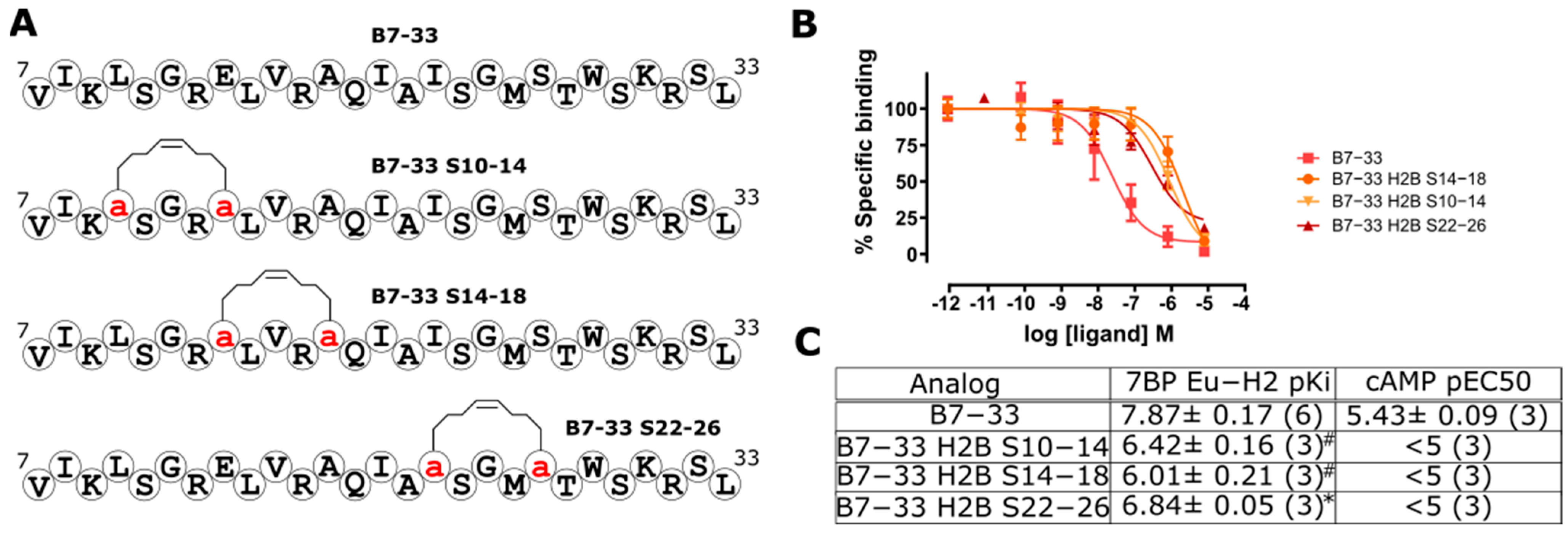
2.4. Hydrocarbon Stapling Effect
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Peptide Synthesis and Purification
3.2. Competitive Binding Assays in HEK-RXFP1 and HEK-7BP Cells
3.3. cAMP Activity Assays in HEK-RXFP1 Cells
3.4. Circular Dichroism Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaszuba, E.; Odeberg, H.; Råstam, L.; Halling, A. Impact of heart failure and other comorbidities on mortality in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A register-based, prospective cohort study. BMC Fam. Pract. 2018, 19, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, N.C.; Rieder, F.; Wynn, T.A. Fibrosis: From mechanisms to medicines. Nature 2020, 587, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, E.S.; Thomas, M.; Stowasser, S.; Tetzlaff, K. Challenges for Clinical Drug Development in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 823085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, C.S.; Royce, S.G.; Hewitson, T.D.; Denton, K.M.; Cooney, T.E.; Bennett, R.G. Anti-fibrotic actions of relaxin. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 962–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo, C.H.; Jelinic, M.; Ng, H.H.; Marshall, S.A.; Novak, J.; Tare, M.; Conrad, K.P.; Parry, L.J. Vascular actions of relaxin: Nitric oxide and beyond. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 1002–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teichman, S.L.; Unemori, E.; Dschietzig, T.; Conrad, K.; Voors, A.A.; Teerlink, J.R.; Felker, G.M.; Metra, M.; Cotter, G. Relaxin, a pleiotropic vasodilator for the treatment of heart failure. Heart Fail. Rev. 2009, 14, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ng, H.H.; Leo, C.H.; Parry, L.J.; Ritchie, R.H. Relaxin as a Therapeutic Target for the Cardiovascular Complications of Diabetes. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bani, D. Recombinant human H2 relaxin (serelaxin) as a cardiovascular drug: Aiming at the right target. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 1239–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, P.C.; Onat, D.; Sabbah, H.N. Acute heart failure as “acute endothelitis”—Interaction of fluid overload and endothelial dysfunction. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2008, 10, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, G.; Felker, G.M.; Adams, K.F.; Milo-Cotter, O.; O’Connor, C.M. The pathophysiology of acute heart failure—Is it all about fluid accumulation? Am. Heart J. 2008, 155, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.; Bathgate, R.A. Challenges in the design of insulin and relaxin/insulin-like peptide mimetics. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 2827–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bathgate, R.A.D.; Halls, M.L.; van der Westhuizen, E.T.; Callander, G.E.; Kocan, M.; Summers, R.J.; Shao, W.; Rosales, C.B.; Gonzalez, C.; Prieto, M.C.; et al. Relaxin family peptides and their receptors. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 405–480. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.A.; Kocan, M.; Yao, S.T.; Royce, S.G.; Nair, V.B.; Siwek, C.; Patil, N.A.; Harrison, I.P.; Rosengren, K.J.; Selemidis, S.; et al. A single-chain derivative of the relaxin hormone is a functionally selective agonist of the G protein-coupled receptor, RXFP1. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 3805–3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler-Jones, C.P. Cell signalling in the cardiovascular system: An overview. Heart 2005, 91, 1366–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinall, R.L.; Mahaffey, C.M.; Davis, R.R.; Luo, Z.; Gandour-Edwards, R.; Ghosh, P.M.; Tepper, C.G.; de Vere White, R.W. Dual blockade of PKA and NF-kappaB inhibits H2 relaxin-mediated castrate-resistant growth of prostate cancer sublines and induces apoptosis. Horm. Cancer 2011, 2, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, N.G.; Mukherjee, S.; Hossain, M.A.; Praveen, P.; Werkmeister, J.A.; Wade, J.D.; Bathgate, R.A.D.; Winkler, D.A.; Thissen, H. Coatings Releasing the Relaxin Peptide Analogue B7-33 Reduce Fibrotic Encapsulation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 45511–45519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devarakonda, T.; Mauro, A.G.; Guzman, G.; Hovsepian, S.; Cain, C.; Das, A.; Praveen, P.; Hossain, M.A.; Salloum, F.N. B7-33, a Functionally Selective Relaxin Receptor 1 Agonist, Attenuates Myocardial Infarction-Related Adverse Cardiac Remodeling in Mice. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e015748. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, S.A.; O’Sullivan, K.; Ng, H.H.; Bathgate, R.A.; Parry, L.J.; Hossain, M.A.; Leo, C.H. B7-33 replicates the vasoprotective functions of human relaxin-2 (serelaxin). Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 807, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, F.; Gaspari, T.A.; Kemp-Harper, B.K.; Low, E.; Aw, A.; Ferens, D.; Spizzo, I.; Jefferis, A.-M.; Praveen, P.; Widdop, R.E.; et al. The single-chain relaxin mimetic, B7-33, maintains the cardioprotective effects of relaxin and more rapidly reduces left ventricular fibrosis compared to perindopril in an experimental model of cardiomyopathy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 160, 114370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallart, S.; Ingenito, R.; Bianchi, E.; Bresciani, A.; Esposito, S.; Gallo, M.; Magotti, P.; Monteagudo, E.; Orsatti, L.; Roversi, D.; et al. Identification of Potent and Long-Acting Single-Chain Peptide Mimetics of Human Relaxin-2 for Cardiovascular Diseases. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 2139–2150. [Google Scholar]
- Illiano, S.; Poirier, B.; Minoletti, C.; Pasquier, O.; Riva, L.; Chenede, X.; Menguy, I.; Guillotel, M.; Prigent, P.; Le Claire, S.; et al. Characterization of a new potent and long-lasting single chain peptide agonist of RXFP1 in cells and in vivo translational models. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheau, Y.H.; Nakabayashi, K.; Nishi, S.; Kumagai, J.; Kudo, M.; Sherwood, O.D.; Hsueh, A.J.W. Activation of orphan receptors by the hormone relaxin. Science 2002, 295, 671–674. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, D.J.; Rosengren, K.J.; Bathgate, R.A.D. The different ligand-binding modes of relaxin family peptide receptors RXFP1 and RXFP2. Mol. Endocrinol. 2012, 26, 1896–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Praveen, P.; Wang, C.; Handley, T.N.G.; Wu, H.; Samuel, C.S.; Bathgate, R.A.D.; Hossain, M.A. A Lipidated Single-B-Chain Derivative of Relaxin Exhibits Improved In Vitro Serum Stability without Altering Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, N.A.; Rosengren, K.J.; Separovic, F.; Wade, J.D.; Bathgate, R.A.D.; Hossain, M.A. Relaxin family peptides: Structure-activity relationship studies. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 950–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullesbach, E.E.; Schwabe, C. On the receptor binding site of relaxins. Int. J. Pept. Protein Res. 1988, 32, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Filippis, V.; De Antoni, F.; Frigo, M.; de Laureto, P.P.; Fontana, A. Enhanced protein thermostability by Ala-->Aib replacement. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 1686–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisma, M.; Formaggio, F.; Moretto, A.; Toniolo, C. Peptide helices based on α-amino acids. Pept. Sci. 2006, 84, 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Hojo, K.; Hossain, M.A.; Tailhades, J.; Shabanpoor, F.; Wong, L.L.L.; Ong-Pålsson, E.E.K.; Kastman, H.E.; Ma, S.; Gundlach, A.L.; Rosengren, K.J.; et al. Development of a Single-Chain Peptide Agonist of the Relaxin-3 Receptor Using Hydrocarbon Stapling. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 7445–7456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Ercole, A.; Nistri, S.; Pacini, L.; Carotenuto, A.; Santoro, F.; Papini, A.M.; Bathgate, R.A.D.; Bani, D.; Rovero, P. Synthetic short-chain peptide analogues of H1 relaxin lack affinity for the RXFP1 receptor and relaxin-like bioactivity. Clues to a better understanding of relaxin agonist design. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 942178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.; Rosengren, K.J.; Zhang, S.; Bathgate, R.A.D.; Tregear, G.W.; van Lierop, B.J.; Robinson, A.J.; Wade, J.D. Solid phase synthesis and structural analysis of novel A-chain dicarba analogs of human relaxin-3 (INSL7) that exhibit full biological activity. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 1547–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, D.J.; Layfield, S.; Yan, Y.; Sudo, S.; Hsueh, A.J.; Tregear, G.W.; Bathgate, R.A. Characterization of novel splice variants of LGR7 and LGR8 reveals that receptor signaling is mediated by their unique low density lipoprotein class A modules. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 34942–34954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenfield, N.J. Using circular dichroism spectra to estimate protein secondary structure. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2876–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, N.E.; Hoang, H.N.; Abbenante, G.; Fairlie, D.P. Single Turn Peptide Alpha Helices with Exceptional Stability in Water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 2974–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Handley, T.N.G.; Praveen, P.; Tailhades, J.; Wu, H.; Bathgate, R.A.D.; Hossain, M.A. Further Developments towards a Minimal Potent Derivative of Human Relaxin-2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12670. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612670
Handley TNG, Praveen P, Tailhades J, Wu H, Bathgate RAD, Hossain MA. Further Developments towards a Minimal Potent Derivative of Human Relaxin-2. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(16):12670. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612670
Chicago/Turabian StyleHandley, Thomas N. G., Praveen Praveen, Julien Tailhades, Hongkang Wu, Ross A. D. Bathgate, and Mohammed Akhter Hossain. 2023. "Further Developments towards a Minimal Potent Derivative of Human Relaxin-2" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 16: 12670. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612670
APA StyleHandley, T. N. G., Praveen, P., Tailhades, J., Wu, H., Bathgate, R. A. D., & Hossain, M. A. (2023). Further Developments towards a Minimal Potent Derivative of Human Relaxin-2. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(16), 12670. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612670





