Metabolic, Apoptotic and Fibro-Inflammatory Profiles of the Heart Exposed to Environmental Electromagnetic Fields
Abstract
1. Introduction
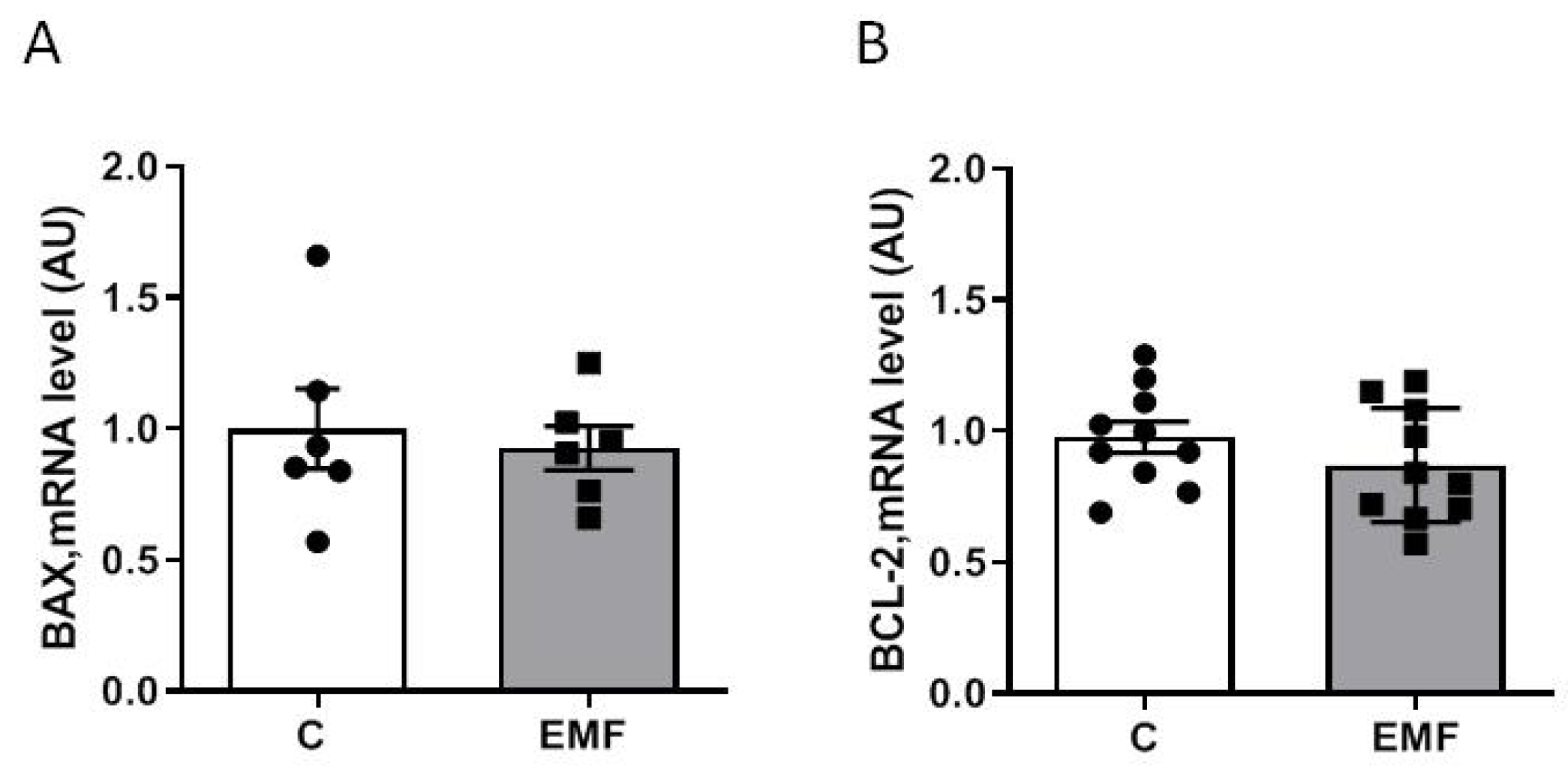
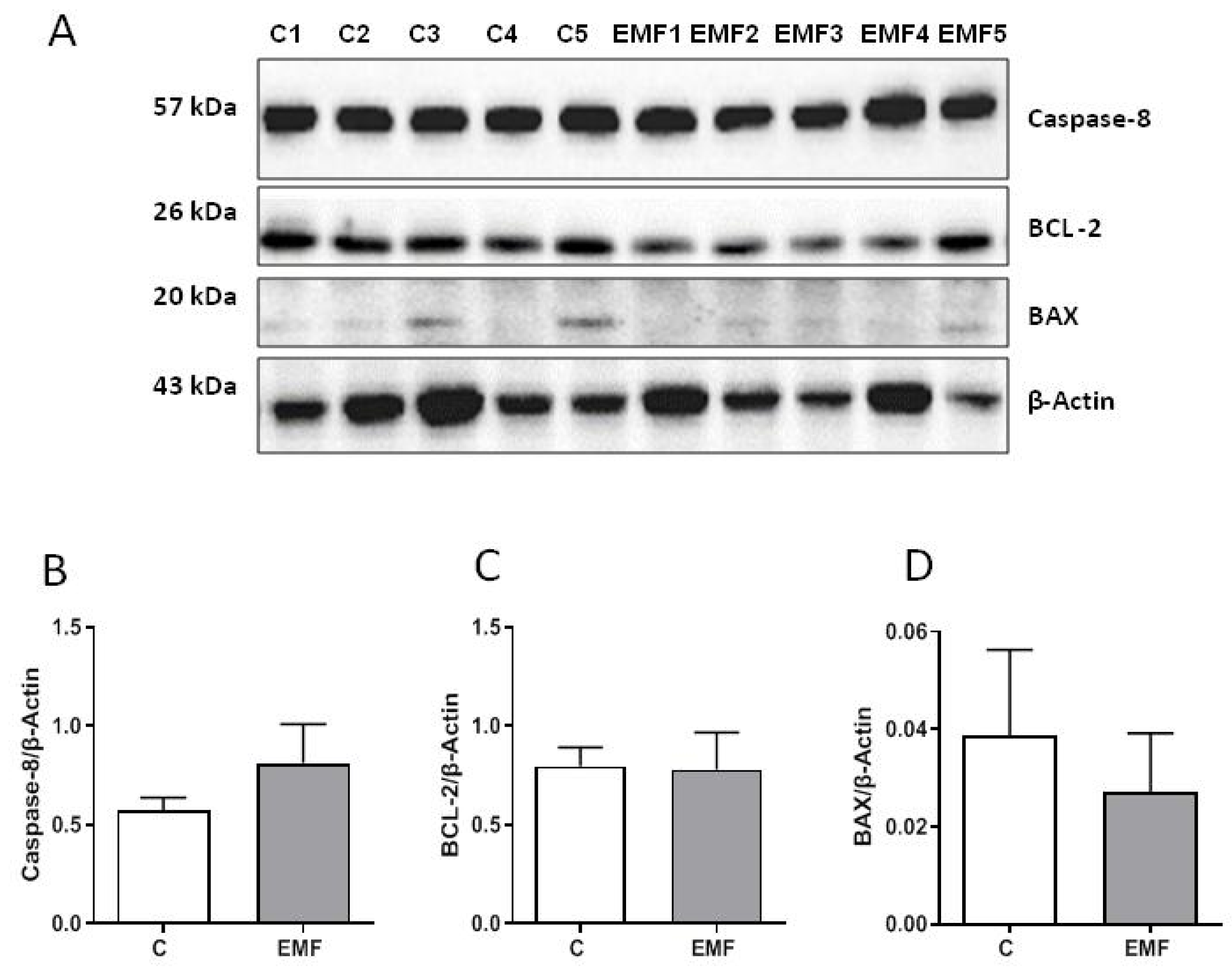
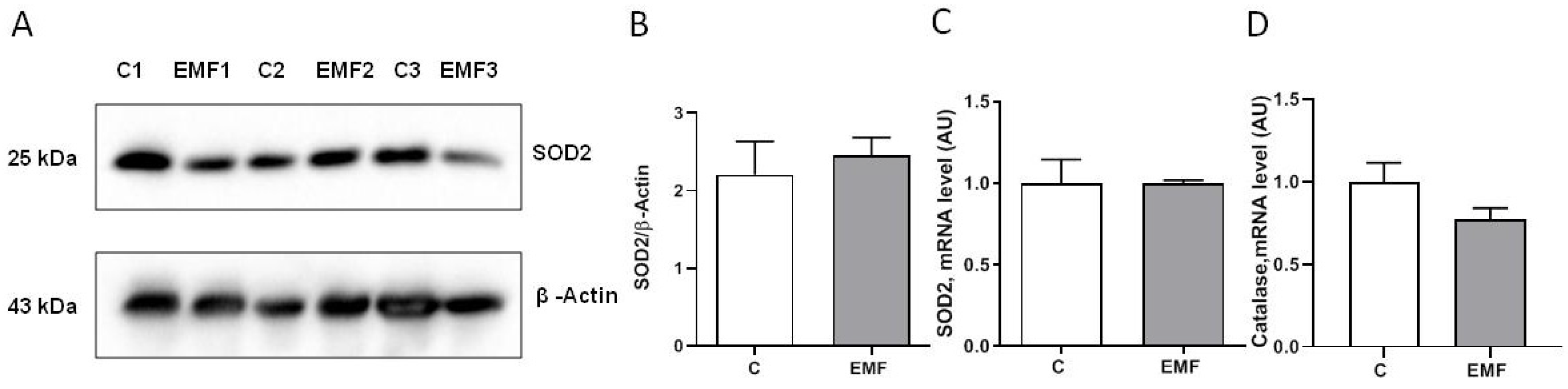
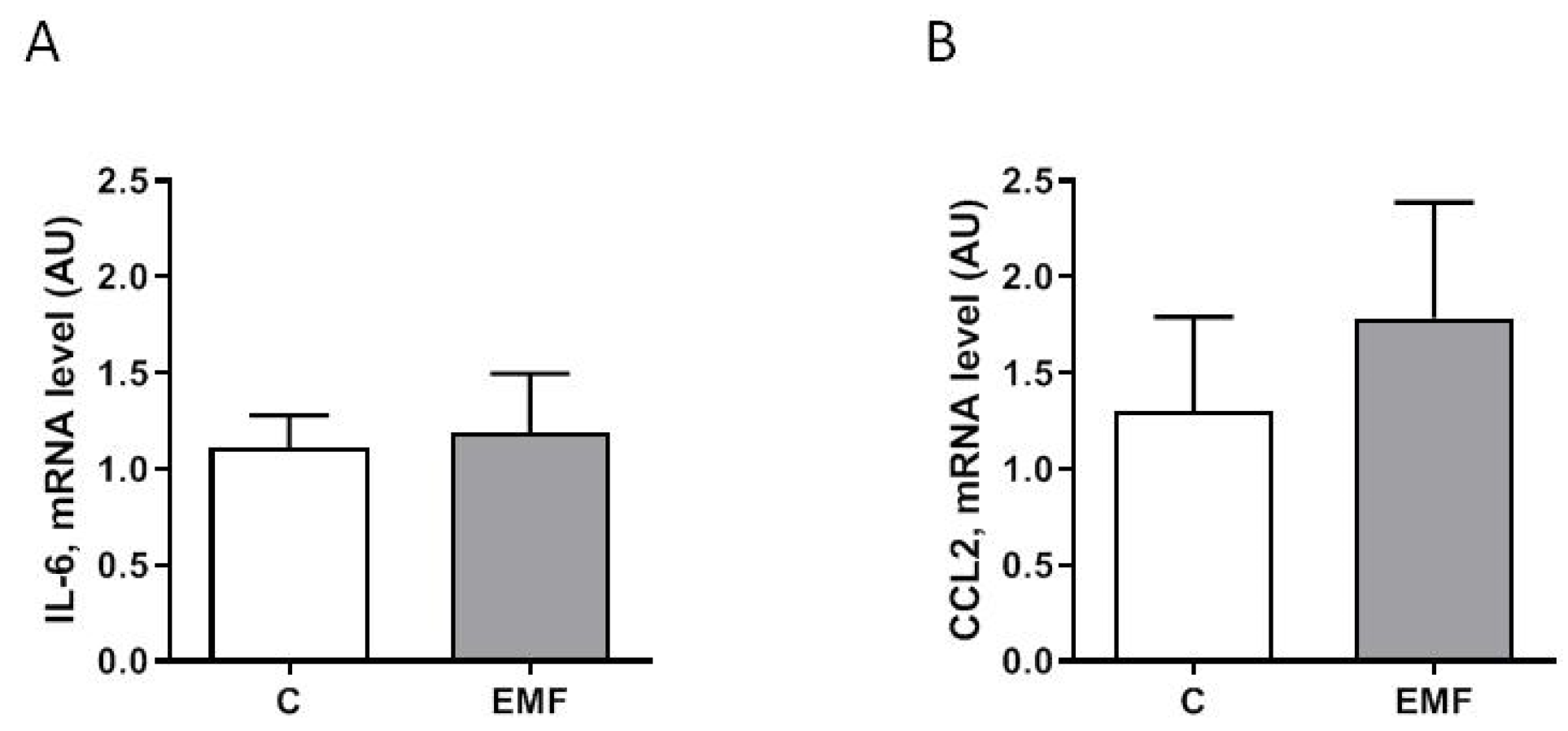
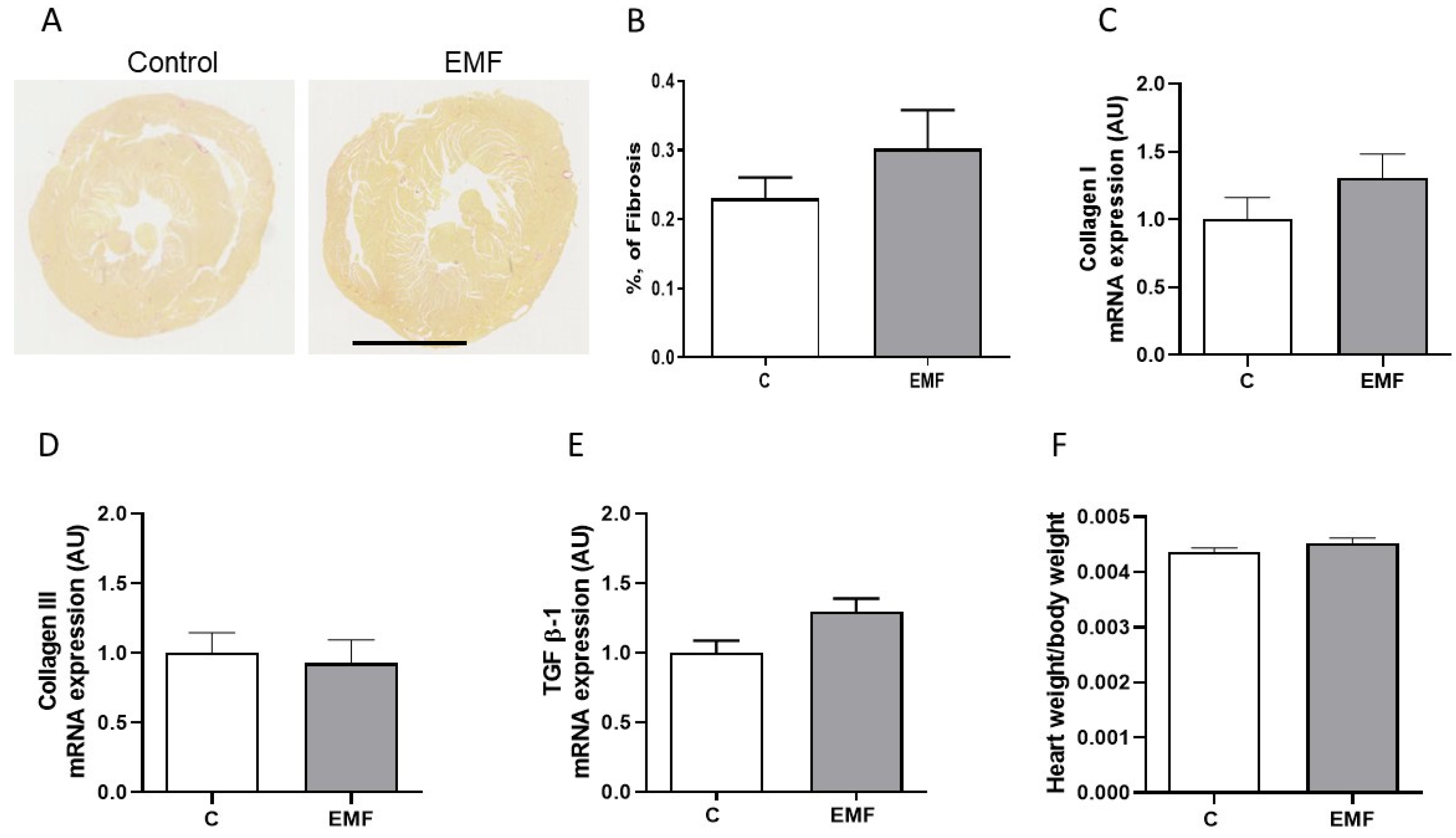
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
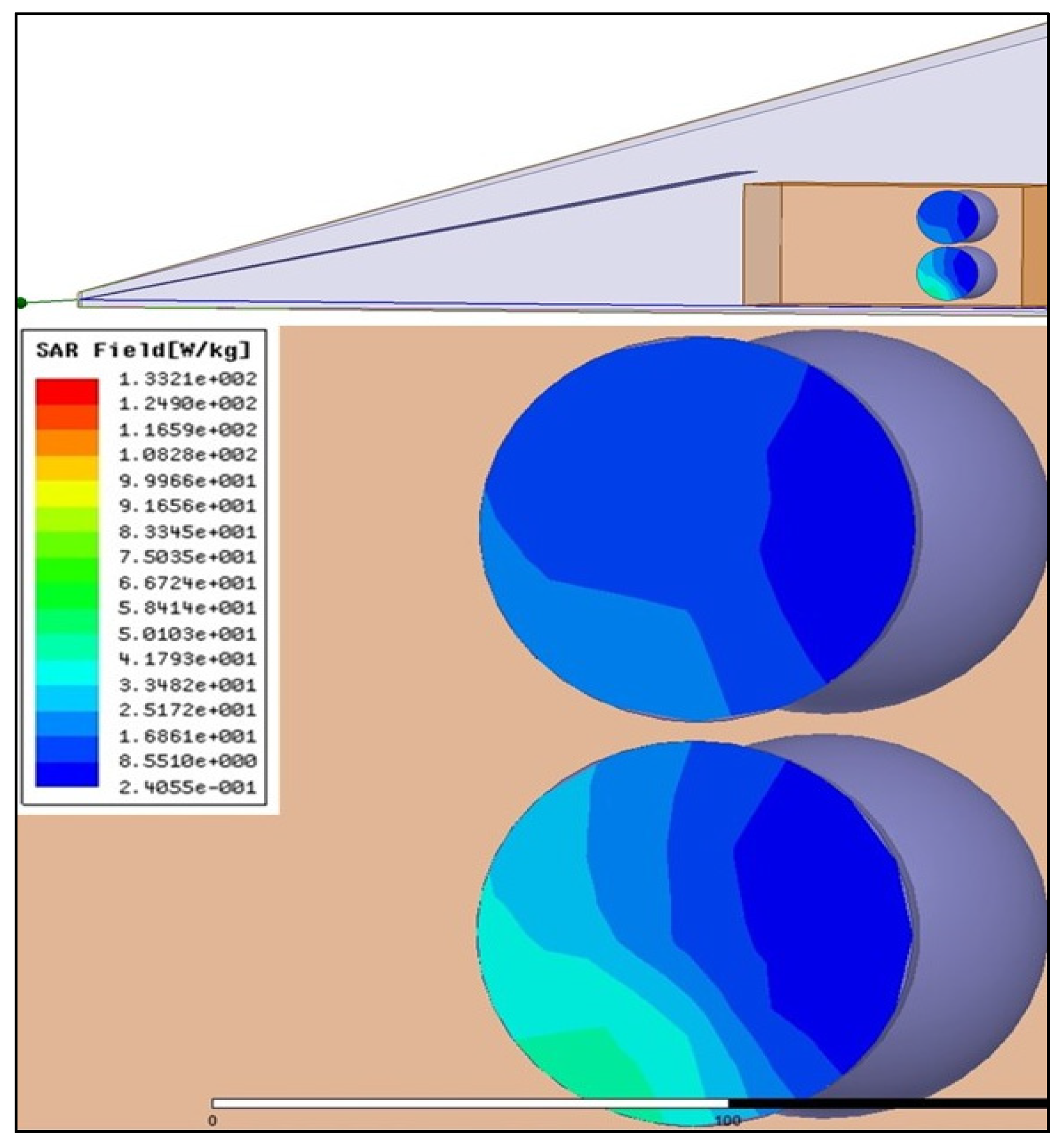
4.2. Radiofrequency Equipements
4.3. Western Blot
4.4. Collagen Content Detection
4.5. Quantitative RT–PCR Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cifra, M.; Cifra, M.; Apollonio, F.; Liberti, M.; García-Sánchez, T.; Mir, L.M. Possible molecular and cellular mechanisms at the basis of atmospheric electromagnetic field bioeffects. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2021, 65, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuermann, D.; Mevissen, M. Manmade Electromagnetic Fields and Oxidative Stress—Biological Effects and Consequences for Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaszuba-Zwoińska, J.; Gremba, J.; Gałdzińska-Calik, B.; Wójcik-Piotrowicz, K.; Thor, P.J. Electromagnetic field induced biological effects in humans. Przegląd Lek. 2015, 72, 636–641. [Google Scholar]
- Kıvrak, E.G.; Yurt, K.K.; Kaplan, A.A.; Alkan, I.; Altun, G. Effects of electromagnetic fields exposure on the antioxidant defense system. J. Microsc. Ultrastruct. 2017, 5, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usman, J.D.; Isyaku, U.M.; Magaji, R.A.; Fasanmade, A.A. Assessment of electromagnetic fields, vibration and sound exposure effects from multiple transceiver mobile phones on oxidative stress levels in serum, brain and heart tissue. Sci. Afr. 2020, 7, e00271. [Google Scholar]
- Roser, K.; Schoeni, A.; Röösli, M. Mobile phone use, behavioural problems and concentration capacity in adolescents: A prospective study. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2016, 219, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boscolo, P.; Di Gioacchino, M.; Di Giampaolo, L.; Antonucci, A.; Di Luzio, S. Combined effects of electromagnetic fields on immune and nervous responses. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2007, 20, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, R.; Ardoino, L.; Villani, P.; Marino, C. In Vivo Studies on Radiofrequency (100 kHz–300 GHz) Electromagnetic Field Exposure and Cancer: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mevissen, M.; Ward, J.M.; Kopp-Schneider, A.; McNamee, J.P.; Wood, A.W.; Rivero, T.M.; Thayer, K.; Straif, K. Effects of radiofrequency electromagnetic fields (RF EMF) on cancer in laboratory animal studies: A protocol for a systematic review. Environ. Int. 2022, 161, 107106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altun, G.; Deniz, Ø.G.; Yurt, K.K.; Davis, D.; Kaplan, S. Effects of mobile phone exposure on metabolomics in the male and female reproductive systems. Environ. Res. 2018, 167, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghari, A.; Khaki, A.A.; Rajabzadeh, A.; Khaki, A. A review on Electromagnetic fields (EMFs) and the reproductive system. Electron. Phys. 2016, 8, 2655–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosado, M.M.; Simkó, M.; Mattsson, M.-O.; Pioli, C. Immune-Modulating Perspectives for Low Frequency Electromagnetic Fields in Innate Immunity. Front. Public Health 2018, 6, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazemi, E.; Mortazavi, S.M.J.; Ali-Ghanbari, A.; Sharifzadeh, S.; Ranjbaranm, R.; Mostafavi-Pour, Z.; Zal, F.; Haghani, M. Effect of 900 MHz electromagnetic radiation on the induction of ROS in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J. Biomed. Phys. Eng. 2015, 5, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Johansson, O. Disturbance of the immune system by electromagnetic fields-A potentially underlying cause for cellular damage and tissue repair reduction which could lead to disease and impairment. Pathophysiology 2009, 16, 157–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, Y.; Kim, J.S.; Jeong, Y.J.; Jeong, Y.K.; Kwon, J.H.; Choi, H.-D.; Pack, J.-K.; Kim, N.; Lee, Y.-S.; Lee, H.-J. Long-term RF exposure on behavior and cerebral glucose metabolism in 5xFAD mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2018, 666, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deniz, O.G.; Kaplan, S.; Selçuk, M.B.; Terzi, M.; Altun, G.; Yurt, K.K.; Aslan, K.; Davis, D. Effects of short and long term electromagnetic fields exposure on the human hippocampus. J. Microsc. Ultrastruct. 2017, 5, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmas, O. Effects of electromagnetic field exposure on the heart: A systematic review. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2016, 32, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodewein, L.; Dechent, D.; Graefrath, D.; Kraus, T.; Krause, T.; Driessen, S. Systematic review of the physiological and health-related effects of radiofrequency electromagnetic field exposure from wireless communication devices on children and adolescents in experimental and epidemiological human studies. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0268641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiray, A.; Tayefi, H.; Kiray, M.; Bagriyanik, H.A.; Pekcetin, C.; Ergur, B.U.; Ozogul, C. The effects of exposure to electromagnetic field on rat myocardium. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2013, 29, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozok, S.; Karaagac, E.; Sener, D.; Akakin, D.; Tumkaya, L. The effects of long-term prenatal exposure to 900, 1800, and 2100 MHz electromagnetic field radiation on myocardial tissue of rats. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2023, 39, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, X.; Ding, L.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; He, M.; Hou, H.; Ruan, G.; Lai, J.; et al. Examination of the Effect of a 50-Hz Electromagnetic Field at 500 μT on Parameters Related With the Cardiovascular System in Rats. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Wan, B.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lai, J.; Ruan, G.; He, M.; Chen, C.; Wang, D.W. The effects of a 50-Hz magnetic field on the cardiovascular system in rats. J. Radiat. Res. 2016, 57, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangge, H.; Becker, K.; Fuchs, D.; Gostner, J.M. Antioxidants, inflammation and cardiovascular disease. World J. Cardiol. 2014, 6, 462–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois-Deruy, E.; Peugnet, V.; Turkieh, A.; Pinet, F. Oxidative Stress in Cardiovascular Diseases. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Oria, R.; Schipani, R.; Leonardini, A.; Natalicchio, A.; Perrini, S.; Cignarelli, A.; Laviola, L.; Giorgino, F. The Role of Oxidative Stress in Cardiac Disease: From Physiological Response to Injury Factor. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 2020, 5732956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi-Rad, M.; Anil Kumar, N.V.; Zucca, P.; Varoni, E.M.; Dini, L.; Panzarini, E.; Rajkovic, J.; Tsouh Fokou, P.V.; Azzini, E.; Peluso, I.; et al. Lifestyle, Oxidative Stress, and Antioxidants: Back and Forth in the Pathophysiology of Chronic Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halade, G.V.; Lee, D.H. Inflammation and resolution signaling in cardiac repair and heart failure. EBioMedicine 2022, 79, 103992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfaddagh, A.; Martin, S.S.; Leucker, T.M.; Michos, E.D.; Blaha, M.J.; Lowenstein, C.J.; Jones, S.R.; Toth, P.P. Inflammation and cardiovascular disease: From mechanisms to therapeutics. Am. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2020, 4, 100130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaban, R.S. Maintenance of the metabolic homeostasis of the heart: Developing a systems analysis approach. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1080, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaban, R.S. Perspectives on: SGP symposium on mitochondrial physiology and medicine: Metabolic homeostasis of the heart. J. Gen. Physiol. 2012, 139, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopaschuk, G.D.; Karwi, Q.G.; Tian, R.; Wende, A.R.; Abel, E.D. Cardiac Energy Metabolism in Heart Failure. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 1487–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tomar, N.; Kandel, S.M.; Audi, S.H.; Cowley, A.W., Jr.; Dash, R.K. Substrate- and Calcium-Dependent Differential Regulation of Mitochondrial Oxidative Phosphorylation and Energy Production in the Heart and Kidney. Cells 2022, 11, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, D.G.; Ferguson, S.J. Bioenergetics, 4th ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2013; 419p. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, R.Z.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Z.B. Mitochondrial electron transport chain, ROS generation and uncoupling (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 44, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernansanz-Agustín, P.; Enríquez, J.A. Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species by Mitochondria. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzino, G.; Irrera, N.; Cucinotta, M.; Pallio, G.; Mannino, F.; Arcoraci, V.; Squadrito, F.; Altavilla, D.; Bitto, A. Oxidative Stress: Harms and Benefits for Human Health. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2017, 2017, 8416763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Branicky, R.; Noë, A.; Hekimi, S. Superoxide dismutases: Dual roles in controlling ROS damage and regulating ROS signaling. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 1915–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Abreu, I.A.; Cabelli, D.E.; Maroney, M.J.; Miller, A.F.; Teixeira, M.; Valentine, J.S. Superoxide dismutases and superoxide reductases. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 3854–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridovich, I. Superoxide anion radical (O2−.), superoxide dismutases, and related matters. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 18515–18517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, J.S.; Bhatti, G.K.; Reddy, P.H. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in metabolic disorders—A step towards mitochondria based therapeutic strategies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 1066–1077. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Zuo, H.; Li, Y. Effects of Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Radiation on Neurotransmitters in the Brain. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 691880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.K.; Kim, H.G.; Kim, K.B.; Kim, H.R. Possible Effects of Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Field Exposure on Central Nerve System. Biomol. Ther. 2019, 27, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.-P.; Li, J.-H.; Zhang, J.; Xu, S.-L.; Kuang, F.; Lang, H.-Y.; Wang, Y.-F.; An, G.-Z.; Li, J.; Guo, G.-Z. Long-term electromagnetic pulse exposure induces Abeta deposition and cognitive dysfunction through oxidative stress and overexpression of APP and BACE1. Brain Res. 2016, 1642, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azab, A.E.; Ebrahim, S.A. Exposure to electromagnetic fields induces oxidative stress and pathophysiological changes in the cardiovascular system. J. Appl. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2017, 4, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, K.; Das, J.; Pal, P.B.; Sil, P.C. Oxidative stress: The mitochondria-dependent and mitochondria-independent pathways of apoptosis. Arch. Toxicol. 2013, 87, 1157–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attah, T.A.; Ayantunji, B.; Adamu, A.; Omede, A.; Leleji, J.; Hussiani, S.; Enemali, J.P.; Suleiman, Z.I.; Dumbiri, C.; Bwala, I.; et al. Biological Effects of High Radiofrequency Radiation on Wistar Rats: A Literature Review. J. Public Health Int. 2022, 5, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragy, M.M. Effect of exposure and withdrawal of 900-MHz-electromagnetic waves on brain, kidney and liver oxidative stress and some biochemical parameters in male rats. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2015, 34, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romeo, S.; Zeni, O.; Scarfì, M.R.; Poeta, L.; Lioi, M.B.; Sannino, A. Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Field Exposure and Apoptosis: A Scoping Review of In Vitro Studies on Mammalian Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghlidospour, M.; Ghanbari, A.; Mortazavi, S.M.J.; Azari, H. Effects of radiofrequency exposure emitted from a GSM mobile phone on proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis of neural stem cells. Anat. Cell Biol. 2017, 50, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joubert, V.; Leveque, P.; Cueille, M.; Bourthoumieu, S.; Yardin, C. No apoptosis is induced in rat cortical neurons exposed to GSM phone fields. Bioelectromagnetics 2007, 28, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.S. Apoptosis in cancer: From pathogenesis to treatment. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 30, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savchenko, L.; Martinelli, I.; Marsal, D.; Zhdan, V.; Tao, J.; Kunduzova, O. Myocardial capacity of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation in response to prolonged electromagnetic stress. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1205893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, A.; Ustunova, S.; Bulut, H.; Meral, I. Pre and postnatal exposure to 900 MHz electromagnetic fields induce inflammation and oxidative stress, and alter renin-angiotensin system components differently in male and female offsprings. Life Sci. 2023, 321, 121627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinelli, I.; Cinato, M.; Keita, S.; Marsal, D.; Antoszewski, V.; Tao, J.; Kunduzova, O. Cardiac Cell Exposure to Electromagnetic Fields: Focus on Oxdative Stress and Apoptosis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | Forward Sequence (5′-3′) | Reverse Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| BAX | GGCGAATTGGAGATGAACTG | CCCCAGTTGAAGTTGCCAT |
| BCL2 | GATGACTGAGTACCTGAACCG | CAGAGACAGCCAGGAGAAATC |
| Catalase | CGAAGGTGAAGCAGGACATG | CTCCAGTAGCCAAAGATCAAGG |
| CCL2 | GTCCCTGTCATGCTTCTGG | GCTCTCCAGCCTACTCATTG |
| Collagen type I | TGTGTGCGATGACGTGCAAT | GGGTCCCTCGACTCCTACA |
| Collagen type III | AAGGCGAATTCAAGGCTGAA | TGTGTTTAGTACAGCCATCCTCTAGAA |
| HPRT | TGAAAGACTTGCTCGAGATGTCAT | TCCAGCAGGTCAGCAAAGAA |
| IL-6 | CAAAGCCAGAGTCCTTCAGAG | GTCCTTAGCCACTCCTTCTG |
| SOD2 | GGACAAACCTGAGCCCTAAG | CAAAAGACCCAAAGTCACGC |
| TGF β-1 | GAGCCCGAAGCGGACTACTA | CACTGCTTCCCGAATGTCTGA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Savchenko, L.; Martinelli, I.; Marsal, D.; Batkivska, O.; Zhdan, V.; Kaidashev, I.; Pizzinat, N.; Boal, F.; Tronchere, H.; Tao, J.; et al. Metabolic, Apoptotic and Fibro-Inflammatory Profiles of the Heart Exposed to Environmental Electromagnetic Fields. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11709. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411709
Savchenko L, Martinelli I, Marsal D, Batkivska O, Zhdan V, Kaidashev I, Pizzinat N, Boal F, Tronchere H, Tao J, et al. Metabolic, Apoptotic and Fibro-Inflammatory Profiles of the Heart Exposed to Environmental Electromagnetic Fields. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(14):11709. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411709
Chicago/Turabian StyleSavchenko, Lesia, Ilenia Martinelli, Dimitri Marsal, Oksana Batkivska, Vyacheslav Zhdan, Igor Kaidashev, Nathalie Pizzinat, Frederic Boal, Helene Tronchere, Junwu Tao, and et al. 2023. "Metabolic, Apoptotic and Fibro-Inflammatory Profiles of the Heart Exposed to Environmental Electromagnetic Fields" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 14: 11709. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411709
APA StyleSavchenko, L., Martinelli, I., Marsal, D., Batkivska, O., Zhdan, V., Kaidashev, I., Pizzinat, N., Boal, F., Tronchere, H., Tao, J., & Kunduzova, O. (2023). Metabolic, Apoptotic and Fibro-Inflammatory Profiles of the Heart Exposed to Environmental Electromagnetic Fields. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(14), 11709. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411709








