The Adsorption Efficiency of Regenerable Chitosan-TiO2 Composite Films in Removing 2,4-Dinitrophenol from Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
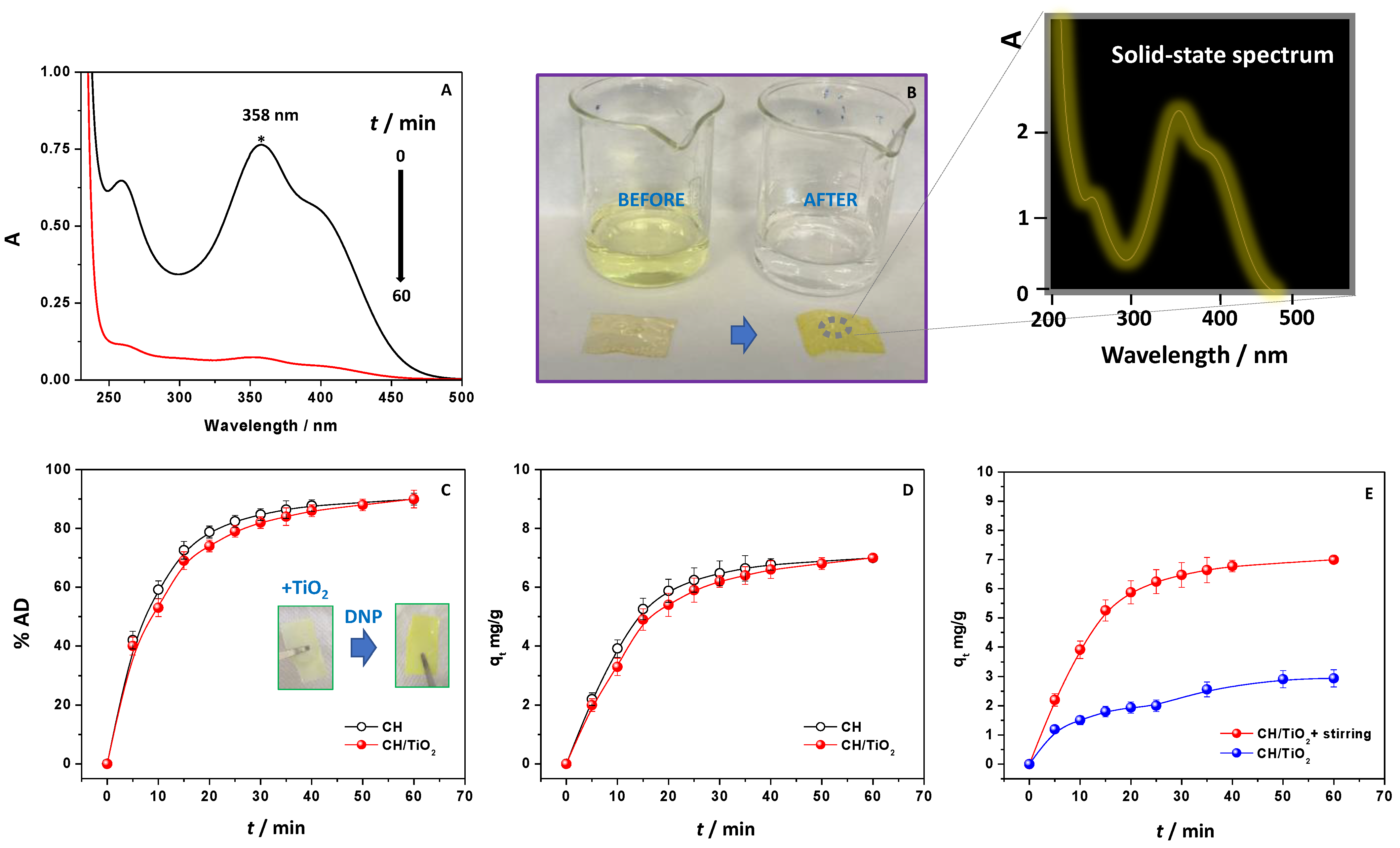
2.1. An Overview
2.2. Effect of Stirring on the Adsorption Process
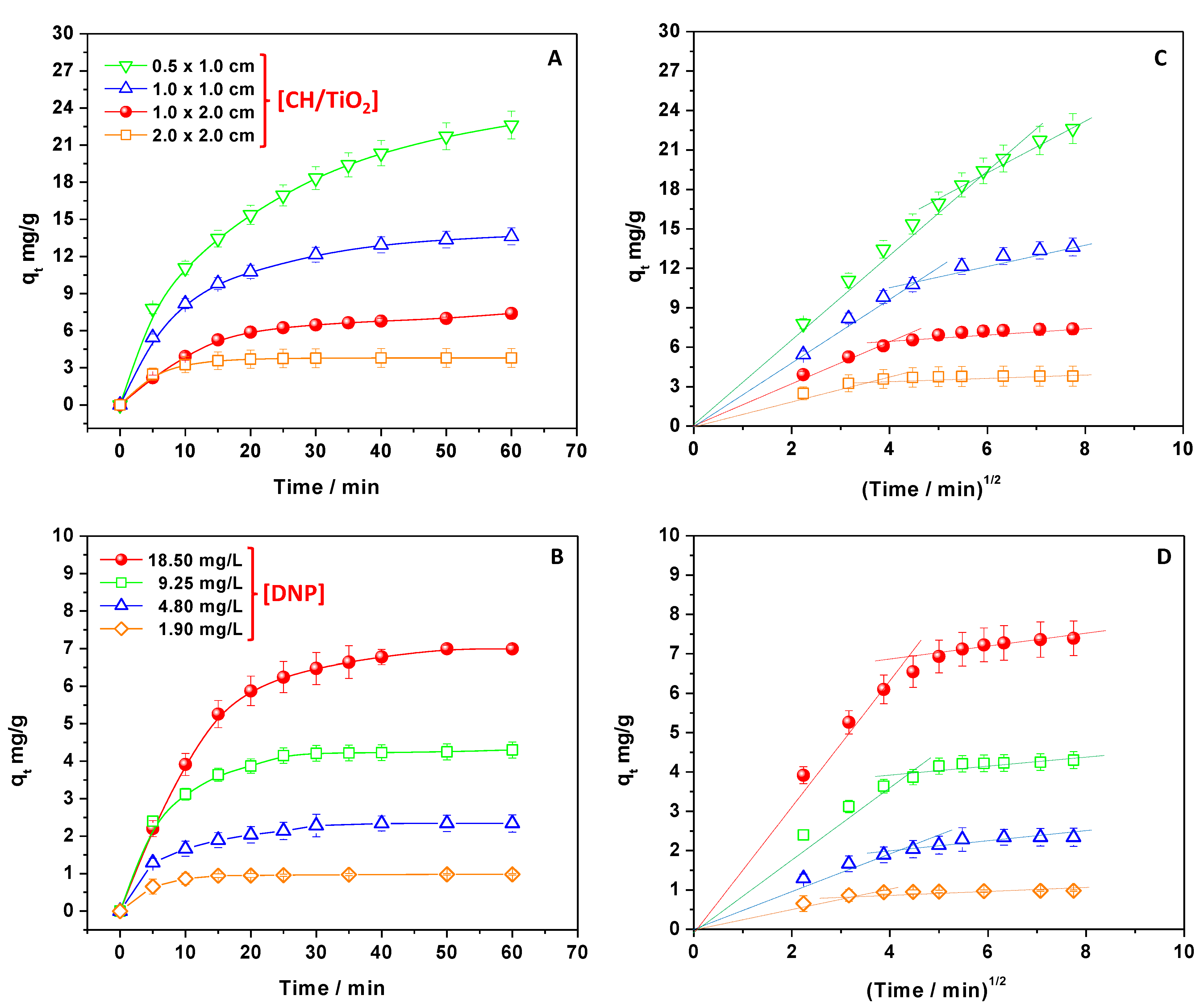
2.3. Effect of DNP Concentration and CH/TiO2 Amount on the Adsorption Process
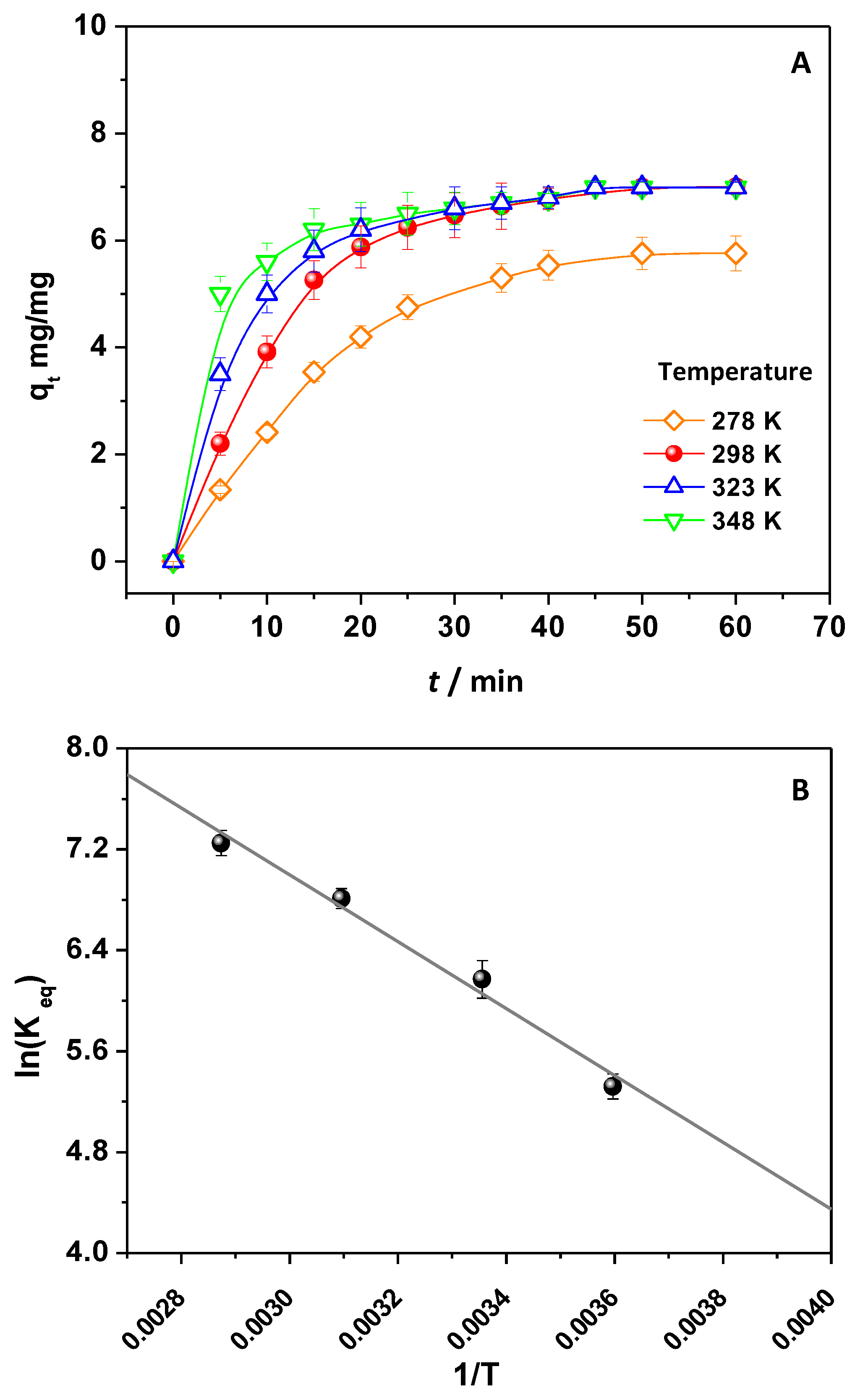
2.4. Kinetic Analysis
2.5. Thermodynamic Analysis
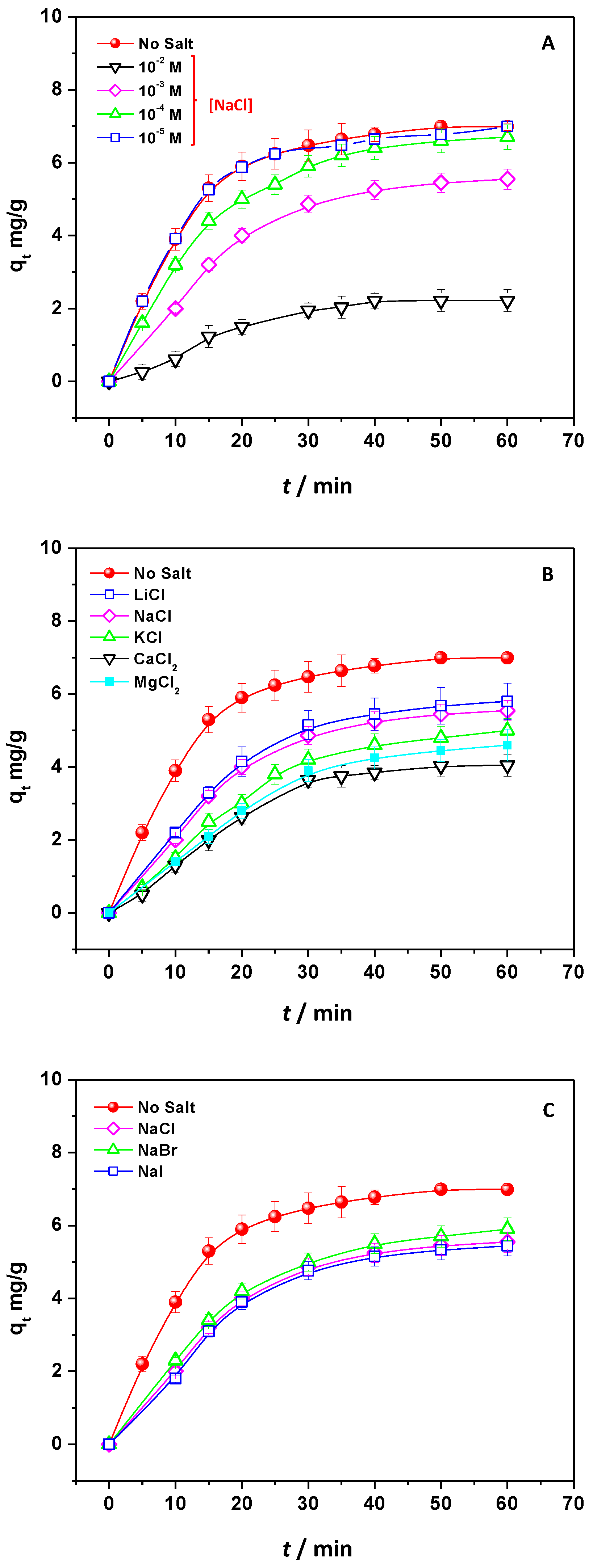
2.6. Effect of pH and Ionic Strength
2.7. Swelling Ratio Measurements
2.8. ATR-FTIR Measurements
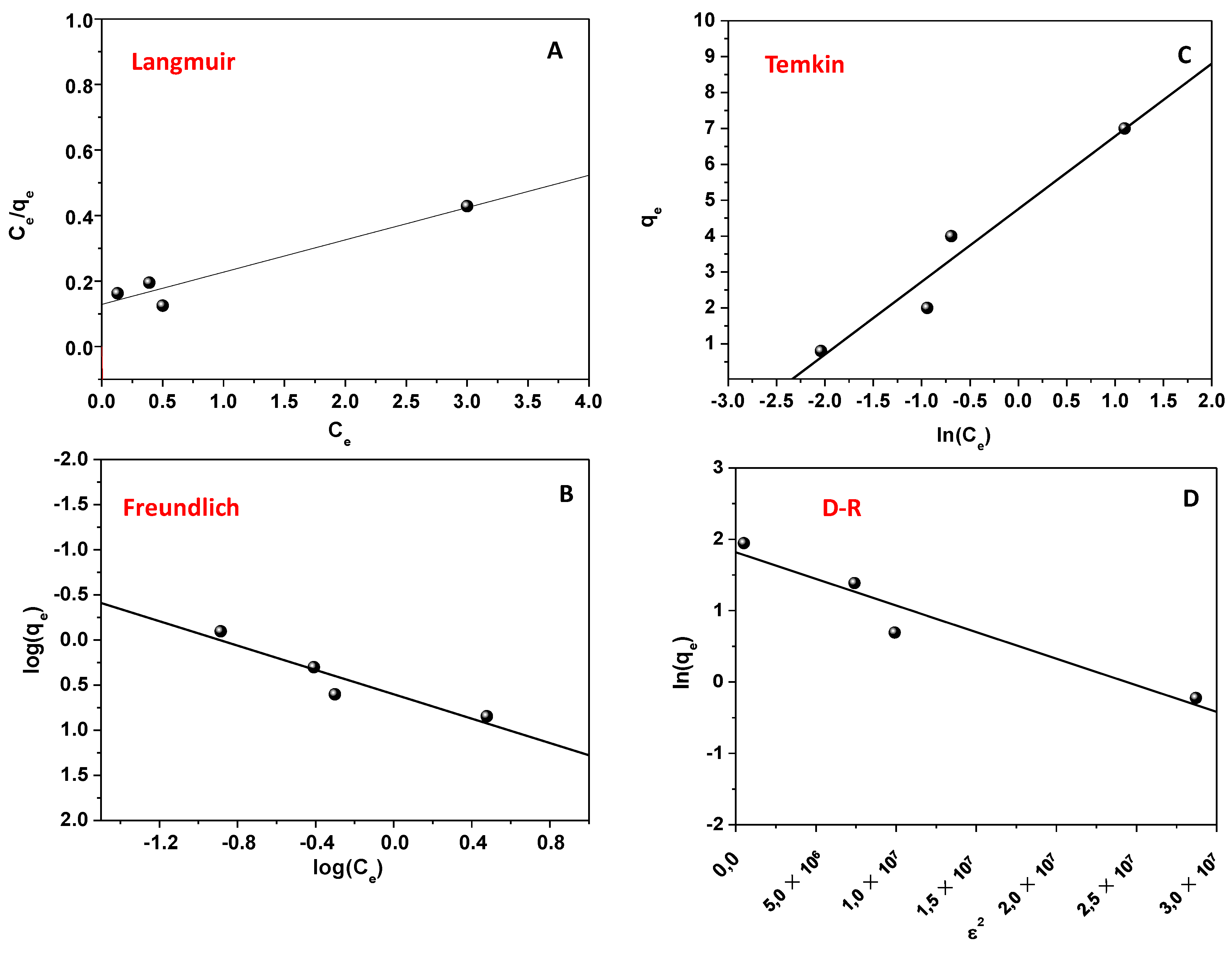
2.9. Isotherms of Adsorption
2.10. CH/TiO2 Regeneration
2.10.1. Desorption of DNP and Reuse of the Adsorbent
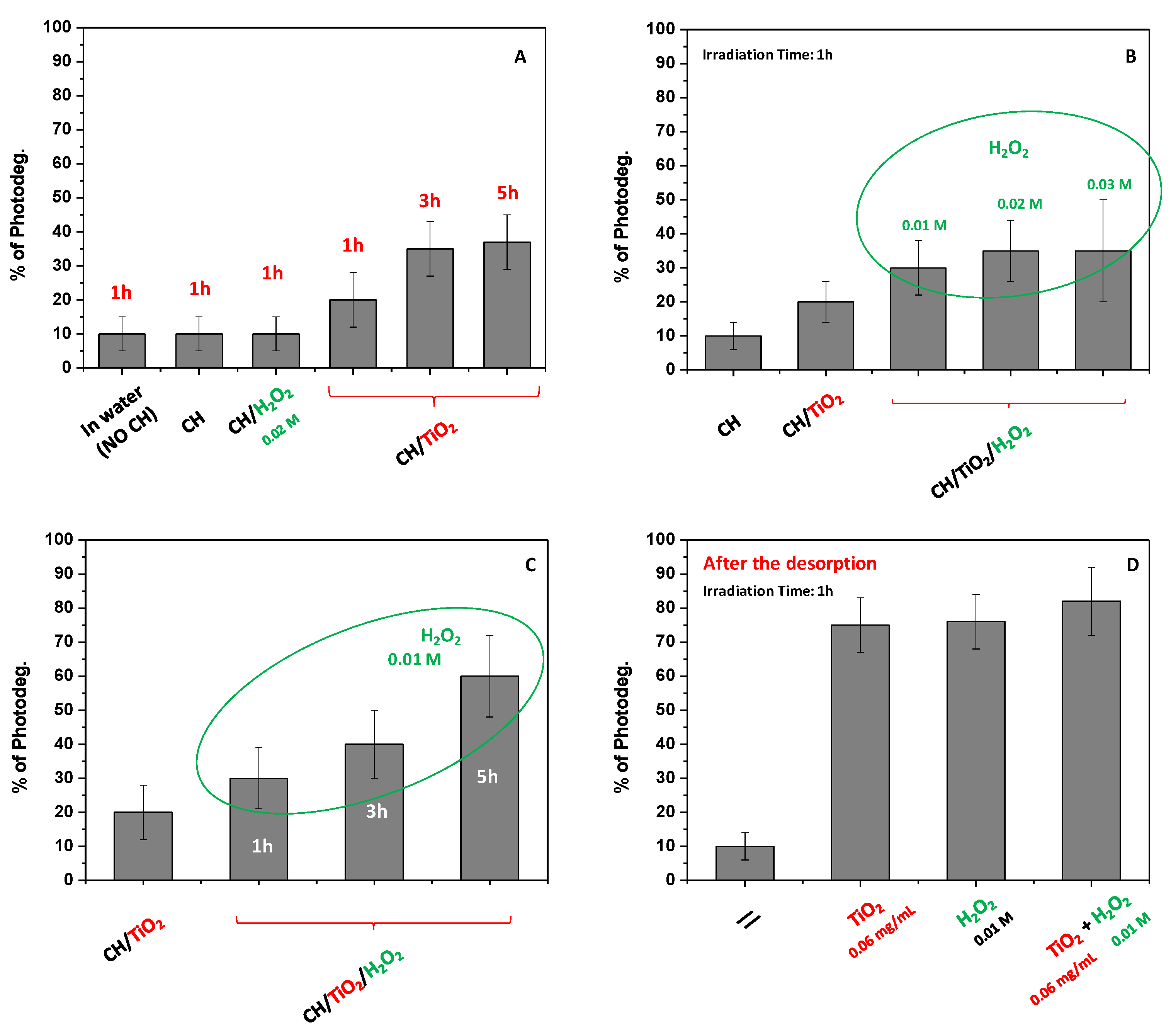
2.10.2. DNP Solid-State Photodegradation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Preparation of Chitosan/TiO2 Films
3.3. UV–Visible Measurements
3.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Investigation
3.5. ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy Measurements
3.6. In Batch Adsorption Experiments
3.7. Adsorption Kinetics
3.8. Thermodynamic Study
3.9. Swelling Ratio Measurements
3.10. Determination of Chitosan/TiO2 Film Zero-Point Charge
3.11. Isotherms of Adsorption
3.12. CH/TiO2 Regeneration: In Batch Desorption Experiments
3.13. CH/TiO2 Regeneration: Solid-State Photocatalytic Experiments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haseena, M.; Malik, M.F.; Javed, A.; Arshad, S.; Asif, N.; Zulfiqar, S.; Hanif, J. Water pollution and human health. Environ. Risk Assess. Remediat. 2017, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Shekhar, S.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, P.; Govarthanan, M.; Chaminda, T. Drinking water treatment and associated toxic byproducts: Concurrence and urgence. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 320, 121009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Yin, M.; Yang, W.; Li, H.; Zhong, Y.; Mo, L.; Liang, Y.; Ma, X.; Sun, X. Emerging pollutants in water environment: Occurrence, monitoring, fate, and risk assessment. Water Environ. Res. 2019, 91, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubitosa, J.; Mongiovi’, C.; Romita, R.; Cosma, P.; Nuzzo, S.; Rizzi, V.; Fini, P. Removal of Emerging Contaminants from Water Using Cyclodextrin-Based Polymers and Advanced Oxidation Processes: The Case of Carbamazepine. Processes 2022, 10, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubitosa, J.; Rizzi, V.; Fini, P.; Nuzzo, S.; Cosma, P. Regenerable Kiwi Peels as an Adsorbent to Remove and Reuse the Emerging Pollutant Propranolol from Water. Processes 2022, 10, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubitosa, J.; Rizzi, V.; Cignolo, D.; Fini, P.; Fanelli, F.; Cosma, P. From agricultural wastes to a resource: Kiwi Peels, as long-lasting, recyclable adsorbent, to remove emerging pollutants from water. The case of Ciprofloxacin removal. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2022, 29, 100749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, V.; Gubitosa, J.; Signorile, R.; Fini, P.; Cecone, C.; Matencio, A.; Trotta, F.; Cosma, P. Cyclodextrin nanosponges as adsorbent material to remove hazardous pollutants from water: The case of ciprofloxacin. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 411, 128514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Yu, W.; Yang, C.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, P.; Zhang, K.; Li, X.; Zhu, G. Highly selective removal of 2,4-dinitrophenol by a surface imprinted sol–gel polymer. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 49236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gziut, T.; Thomas, S.H.L. International trends in systemic human exposures to 2,4 dinitrophenol reported to poisons centres. Clin. Toxicol. 2022, 60, 628–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daraei, H.; Mittal, A.; Toolabian, K.; Mittal, J.; Mariyam, A. Study on the biodegradability improvement of 2,4 dinitrophenol in wastewater using advanced oxidation/reduction process with UV/SO3/ZnO. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 22273–22283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Shafy, H.I.; Mansour, M.S.M. A review on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Source, environmental impact, effect on human health and remediation. Egypt. J. Pet. 2016, 25, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Huang, H.; Chen, Y. Recent advances in biological removal of nitroaromatics from wastewater. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 307, 119570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, K.; Mohd, N.I.; Raoov, M.; Suah, F.B.M.; Yahaya, N.; Zain, N.N.M. Development of a new efficient and economical magnetic sorbent silicone surfactant-based activated carbon for the removal of chloro-and nitro-group phenolic compounds from contaminated water samples. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 36915–36930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anoop Krishnan, K.; Sini Suresh, S.; Arya, S.; Sreejalekshmi, K.G. Adsorptive removal of 2,4-dinitrophenol using active carbon: Kinetic and equilibrium modeling at solid–liquid interface. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 54, 1850–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettini, S.; Pagano, R.; Bosco, G.; Pal, S.; Ingrosso, C.; Valli, L.; Giancane, G. SiO2 based nanocomposite for simultaneous magnetic removal and discrimination of small pollutants in water. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 633, 127905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walia, S.; Kaur, M.; Kansal, S.K. Adsorptive removal of 2,4-dinitrophenol from aqueous phase using amine functionalized metal organic framework (NH2-MIL-101(Cr)). Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 289, 126493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azari, A.; Yeganeh, M.; Gholami, M.; Salari, M. The superior adsorption capacity of 2,4-Dinitrophenol under ultrasound-assisted magnetic adsorption system: Modeling and process optimization by central composite design. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 418, 126348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, N.A.; Bakhshaei, S.; Kamboh, M.A.; Abdul Manan, N.S.; Mohamad, S.; Yilmaz, M. Adsorption of phenols from contaminated water through titania-silica mixed imidazolium based ionic liquid: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic modeling studies. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 2016, 53, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdy, Y.M.; Altaher, H.; ElQada, E. Removal of three nitrophenols from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto char ash: Equilibrium and kinetic modeling. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thang, P.Q.; Jitae, K.; Giang, B.L.; Viet, N.M.; Huong, P.T. Potential application of chicken manure biochar towards toxic phenol and 2,4-dinitrophenol in wastewaters. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 251, 109556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-L.; Kim, H.; Pan, S.-Y.; Tseng, P.-C.; Lin, Y.-P.; Chiang, P.-C. Implementation of green chemistry principles in circular economy system towards sustainable development goals: Challenges and perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 136998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, S. Low-Cost Adsorbents for the Removal of Phenol/Phenolics, Pesticides, and Dyes from Wastewater Systems: A Review. Water 2022, 14, 3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.-C.; Juang, R.-S.; Huq, M.M.; Hsieh, C.-T. Enhanced adsorption and photodegradation of phenol in aqueous suspensions of titania/graphene oxide composite catalysts. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 67, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sescu, A.M.; Favier, L.; Lutic, D.; Soto-Donoso, N.; Ciobanu, G.; Harja, M. TiO2 Doped with Noble Metals as an Efficient Solution for the Photodegradation of Hazardous Organic Water Pollutants at Ambient Conditions. Water 2021, 13, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Lai, C.; Huang, D.; Zeng, G.; Chen, L.; Qin, L.; Xu, P.; Cheng, M.; Huang, C.; Zhang, C.; et al. Preparation of water-compatible molecularly imprinted thiol-functionalized activated titanium dioxide: Selective adsorption and efficient photodegradation of 2, 4-dinitrophenol in aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 346, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Oda, Y.; Shiraishi, F. Photocatalytic and adsorptive treatment of 2,4-dinitrophenol using a TiO2 film covering activated carbon surface. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, H.-L.; Jiang, W.-F.; Li, Z.-Q. Photocatalytic degradation of 2,4-dinitrophenol (DNP) by multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs)/TiO2 composite in aqueous solution under solar irradiation. Water Res. 2009, 43, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MirzaHedayat, B.; Noorisepehr, M.; Dehghanifard, E.; Esrafili, A.; Norozi, R. Evaluation of photocatalytic degradation of 2,4-Dinitrophenol from synthetic wastewater using Fe3O4@SiO2@TiO2/rGO magnetic nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 264, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad AlGarni, T.; Ali, M.H.H.; Al-Mohaimeed, A.M. Green biosynthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles using Chlorella vulgaris extract for enhancing degradation of 2,4 dinitrophenol. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2023, 35, 102426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-J.; Yang, Y.-L.; Zou, X.-X.; Shi, X.-L.; Chen, Z.-G. Flexible hollow TiO2@CMS/carbon-fiber van der Waals heterostructures for simulated-solar light photocatalysis and photoelectrocatalysis. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 98, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raizada, P.; Sudhaik, A.; Singh, P.; Shandilya, P.; Thakur, P.; Jung, H. Visible light assisted photodegradation of 2,4-dinitrophenol using Ag2CO3 loaded phosphorus and sulphur co-doped graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets in simulated wastewater. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 3196–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, V.; Gubitosa, J.; Fini, P.; Romita, R.; Nuzzo, S.; Cosma, P. Chitosan Biopolymer from Crab Shell as Recyclable Film to Remove/Recover in Batch Ketoprofen from Water: Understanding the Factors Affecting the Adsorption Process. Materials 2019, 12, 3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, V.; Romanazzi, F.; Gubitosa, J.; Fini, P.; Romita, R.; Agostiano, A.; Petrella, A.; Cosma, P. Chitosan Film as Eco-Friendly and Recyclable Bio-Adsorbent to Remove/Recover Diclofenac, Ketoprofen, and their Mixture from Wastewater. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, V.; Longo, A.; Placido, T.; Fini, P.; Gubitosa, J.; Sibillano, T.; Giannini, C.; Semeraro, P.; Franco, E.; Ferrandiz, M.; et al. A comprehensive investigation of dye–chitosan blended films for green chemistry applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 45945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, V.; Gubitosa, J.; Fini, P.; Romita, R.; Nuzzo, S.; Gabaldón, J.A.; Gorbe, M.I.F.; Gómez-Morte, T.; Cosma, P. Chitosan film as recyclable adsorbent membrane to remove/recover hazardous pharmaceutical pollutants from water: The case of the emerging pollutant Furosemide. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2021, 56, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebello, S.; Sali, S.; Jisha, M.S.; Reshmy, R.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Madhavan, A.; Binod, P.; Awasthi, M.K.; Pandey, A.; Sindhu, R. Chitosan a versatile adsorbent in environmental remediation in the era of circular economy-a mini review. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2023, 32, 101004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, A.; Appunni, S.; Chinthala, M.; Jacob, M.M.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Reddy, S.S.; Kunnel, E.S. Chitosan-based beads as sustainable adsorbents for wastewater remediation: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordin, A.H.; Ngadi, N.; Ilyas, R.A.; Abd Latif, N.A.F.; Nordin, M.L.; Mohd Syukri, M.S.; Nabgan, W.; Paiman, S.H. Green surface functionalization of chitosan with spent tea waste extract for the development of an efficient adsorbent for aspirin removal. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.N.A.; Shah, Z.; Hussain, M.; Khan, M. Hazardous Effects of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles in Ecosystem. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2017, 2017, 4101735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, K.; Stalin, T.; Sivakumar, K. Spectral and electrochemical study of host–guest inclusion complex between 2,4-dinitrophenol and β-cyclodextrin. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2012, 94, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerelbaatar, K.; Tsogoo, A.; Dashzeveg, R.; Tsedev, N.; Ganbold, E.O. Reduction of 2,4-Dinitrophenol to 2,4-Diaminophenol Using AuNPs and AgNPs as Catalyst. Solid State Phenom. 2018, 271, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinrichs, R.Z.; Buczek, P.; Trivedi, J.J. Solar Absorption by Aerosol-Bound Nitrophenols Compared to Aqueous and Gaseous Nitrophenols. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5661–5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dotto, G.L.; Pinto, L.A.A. Adsorption of food dyes acid blue 9 and food yellow 3 onto chitosan: Stirring rate effect in kinetics and mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 187, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girish, C.R.; Murty, V.R. Mass Transfer Studies on Adsorption of Phenol from Wastewater Using Lantana camara, Forest Waste. Int. J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 2016, 5809505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotto, G.L.; Buriol, C.; Pinto, L.A.A. Diffusional mass transfer model for the adsorption of food dyes on chitosan films. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2014, 92, 2324–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglezakis, V.J.; Balsamo, M.; Montagnaro, F. Liquid–Solid Mass Transfer in Adsorption Systems—An Overlooked Resistance? Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 22007–22016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglezakis, V.J.; Fyrillas, M.M.; Park, J. Variable diffusivity homogeneous surface diffusion model and analysis of merits and fallacies of simplified adsorption kinetics equations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 367, 224–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, V.V.L.; Pinto, D.; Salau, N.P.G.; Pinto, L.A.A.; Cadaval, T.R.S., Jr.; Silva, L.F.O.; Lopes, T.J.; Dotto, G.L. Modeling of anthocyanins adsorption onto chitosan films: An approach using the pore volume and surface diffusion model. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 292, 121062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furusawa, T.; Smith, J.M. Fluid-Particle and Intraparticle Mass Transport Rates in Slurries. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1973, 12, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Chen, T. A new simplified method for estimating film mass transfer and surface diffusion coefficients from batch adsorption kinetic data. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 265, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocampo-Perez, R.; Leyva-Ramos, R.; Alonso-Davila, P.; Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Sanchez-Polo, M. Modeling adsorption rate of pyridine onto granular activated carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 165, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuśmierek, K.; Świątkowski, A. The influence of different agitation techniques on the adsorption kinetics of 4-chlorophenol on granular activated carbon. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2015, 116, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotto, G.L.; Ocampo-Pérez, R.; Moura, J.M.; Cadaval, T.R.S.; Pinto, L.A.A. Adsorption rate of Reactive Black 5 on chitosan based materials: Geometry and swelling effects. Adsorption 2016, 22, 973–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, V.; Lacalamita, D.; Gubitosa, J.; Fini, P.; Petrella, A.; Romita, R.; Agostiano, A.; Gabaldón, J.A.; Gorbe, M.I.F.; Gómez-Morte, T.; et al. Removal of tetracycline from polluted water by chitosan-olive pomace adsorbing films. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 693, 133620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, V.; Gubitosa, J.; Fini, P.; Romita, R.; Agostiano, A.; Nuzzo, S.; Cosma, P. Commercial bentonite clay as low-cost and recyclable “natural” adsorbent for the Carbendazim removal/recover from water: Overview on the adsorption process and preliminary photodegradation considerations. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 602, 125060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, V.; Fini, P.; Fanelli, F.; Placido, T.; Semeraro, P.; Sibillano, T.; Fraix, A.; Sortino, S.; Agostiano, A.; Giannini, C.; et al. Molecular interactions, characterization and photoactivity of Chlorophyll a/chitosan/2-HP-?-cyclodextrin composite films as functional and active surfaces for ROS production. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 58, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papac, J.; Ballesteros, S.G.; Tonkovic, S.; Kovacic, M.; Tomic, A.; Cvetnić, M.; Kusic, H.; Senta, I.; Terzić, S.; Ahel, M.; et al. Degradation of pharmaceutical memantine by photo-based advanced oxidation processes: Kinetics, pathways and environmental aspects. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagal, M.V.; Gogate, P.R. Degradation of 2,4-dinitrophenol using a combination of hydrodynamic cavitation, chemical and advanced oxidation processes. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2013, 20, 1226–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.S.; Dorris, K.L.; Chikkaveeraiah, B. V Photocatalytic degradation of 2,4-dinitrophenol. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadimoghaddam, M.; Mesdaghinia, A.; Naddafi, K.; Nasseri, S.; Mahvi, A.H.; Vaezi, F.; Nabizadeh, R. Degradation of 2,4-Dinitrophenol by Photo Fenton Process. Asian J. Chem. 2010, 22, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar]
- Detho, A.; Memon, A.A.; Memon, A.H.; Almohana, A.I.; Daud, Z.; Rosli, M.A. Sorption Kinetics, Isotherm Studies and Mechanism of Removal of Organic and Inorganic by Adsorption onto Renewable Biomineral. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2022, 234, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, V.; Fiorini, F.; Lamanna, G.; Gubitosa, J.; Prasetyanto, E.A.; Fini, P.; Fanelli, F.; Nacci, A.; De Cola, L.; Cosma, P. Polyamidoamine-Based Hydrogel for Removal of Blue and Red Dyes from Wastewater. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2018, 2, 1700146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Adsorbent | qmax (mg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Active carbon | 277.78 | [14] |
| SiO2-based nanocomposite | Not available. % removal: 58.66% at pH 6.4 | [15] |
| Amine-functionalized metal-organic framework | Not available. % removal: 99% at pH 4 | [16] |
| Ultrasound-assisted magnetic adsorption graphene oxide-Fe3O4-based system | 425.58 | [17] |
| A polymer obtained by loading ionic liquids on silica | 114.7 | [8] |
| Sol–gel Titania-silica-mixed imidazolium-based ionic liquid | 7.78 | [18] |
| Char ash | 7.55 | [19] |
| Chicken manure biochar | 148.1 | [20] |
| Chitosan/TiO2 film | 900 | This work |
| Adsorbent | Reference |
|---|---|
| Water-compatible molecularly imprinted thiol-functionalized activated titanium dioxide | Zhou et al. [25] |
| TiO2/activated carbon | Cao et al. [26] |
| Multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs)/TiO2 composite | Wang et al. [27] |
| Fe3O4@SiO2@TiO2/rGO magnetic nanoparticles | Hedayat et al. [28] |
| Fe3O4 nanoparticles using Chlorella vulgaris extract | Al Garni et al. [29] |
| Flexible hollow TiO2@CMS/carbon-fiber van der Waals heterostructures | Chen et al. [30] |
| Ag2CO3-loaded phosphorus and sulfur co-doped graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets | Raizada et al. [31] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gubitosa, J.; Rizzi, V.; Fini, P.; Nuzzo, S.; Cosma, P. The Adsorption Efficiency of Regenerable Chitosan-TiO2 Composite Films in Removing 2,4-Dinitrophenol from Water. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108552
Gubitosa J, Rizzi V, Fini P, Nuzzo S, Cosma P. The Adsorption Efficiency of Regenerable Chitosan-TiO2 Composite Films in Removing 2,4-Dinitrophenol from Water. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(10):8552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108552
Chicago/Turabian StyleGubitosa, Jennifer, Vito Rizzi, Paola Fini, Sergio Nuzzo, and Pinalysa Cosma. 2023. "The Adsorption Efficiency of Regenerable Chitosan-TiO2 Composite Films in Removing 2,4-Dinitrophenol from Water" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 10: 8552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108552
APA StyleGubitosa, J., Rizzi, V., Fini, P., Nuzzo, S., & Cosma, P. (2023). The Adsorption Efficiency of Regenerable Chitosan-TiO2 Composite Films in Removing 2,4-Dinitrophenol from Water. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(10), 8552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108552








