Protein Kinase CK2 Contributes to Glucose Homeostasis by Targeting Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphatase 1
Abstract
1. Introduction
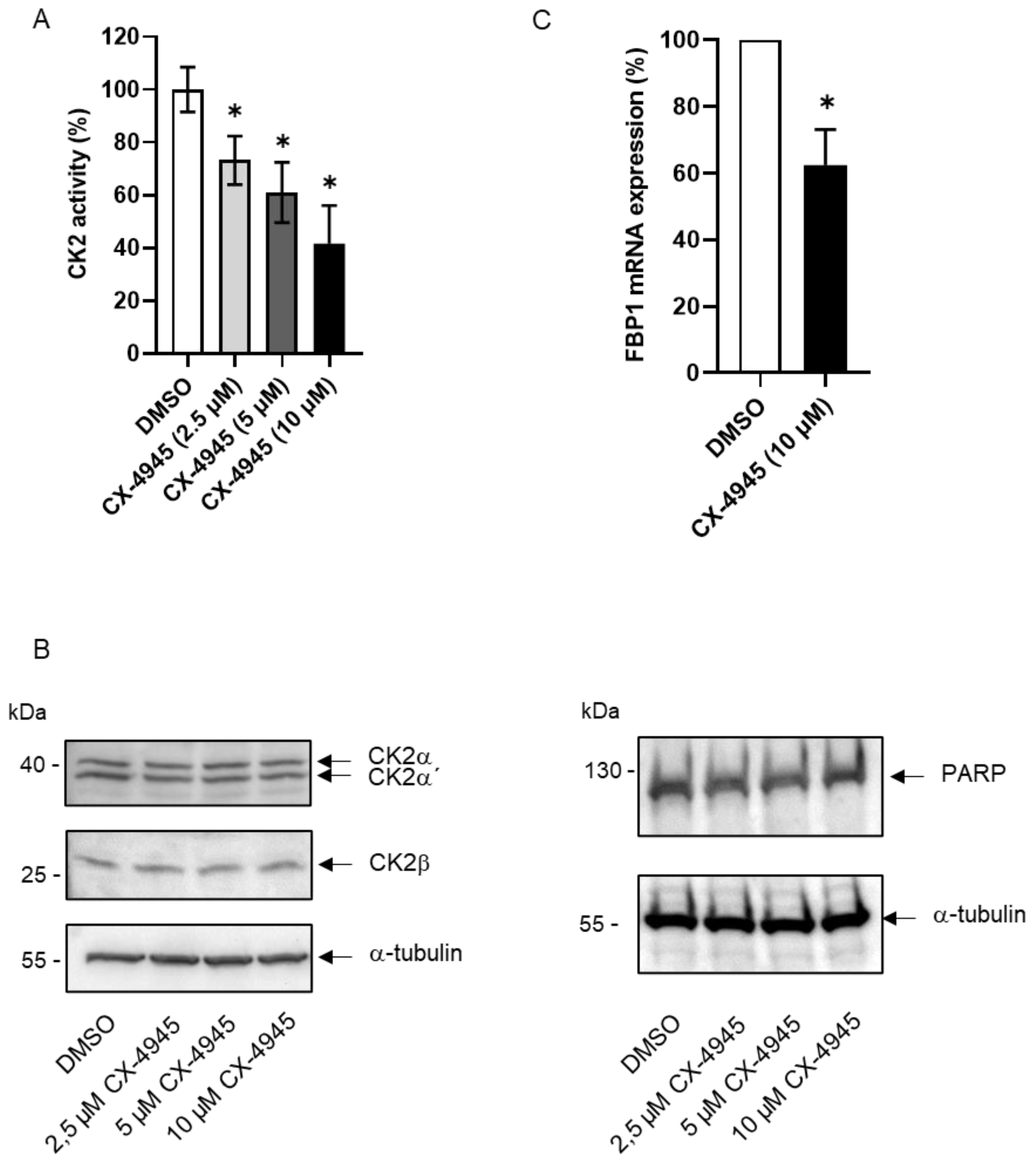
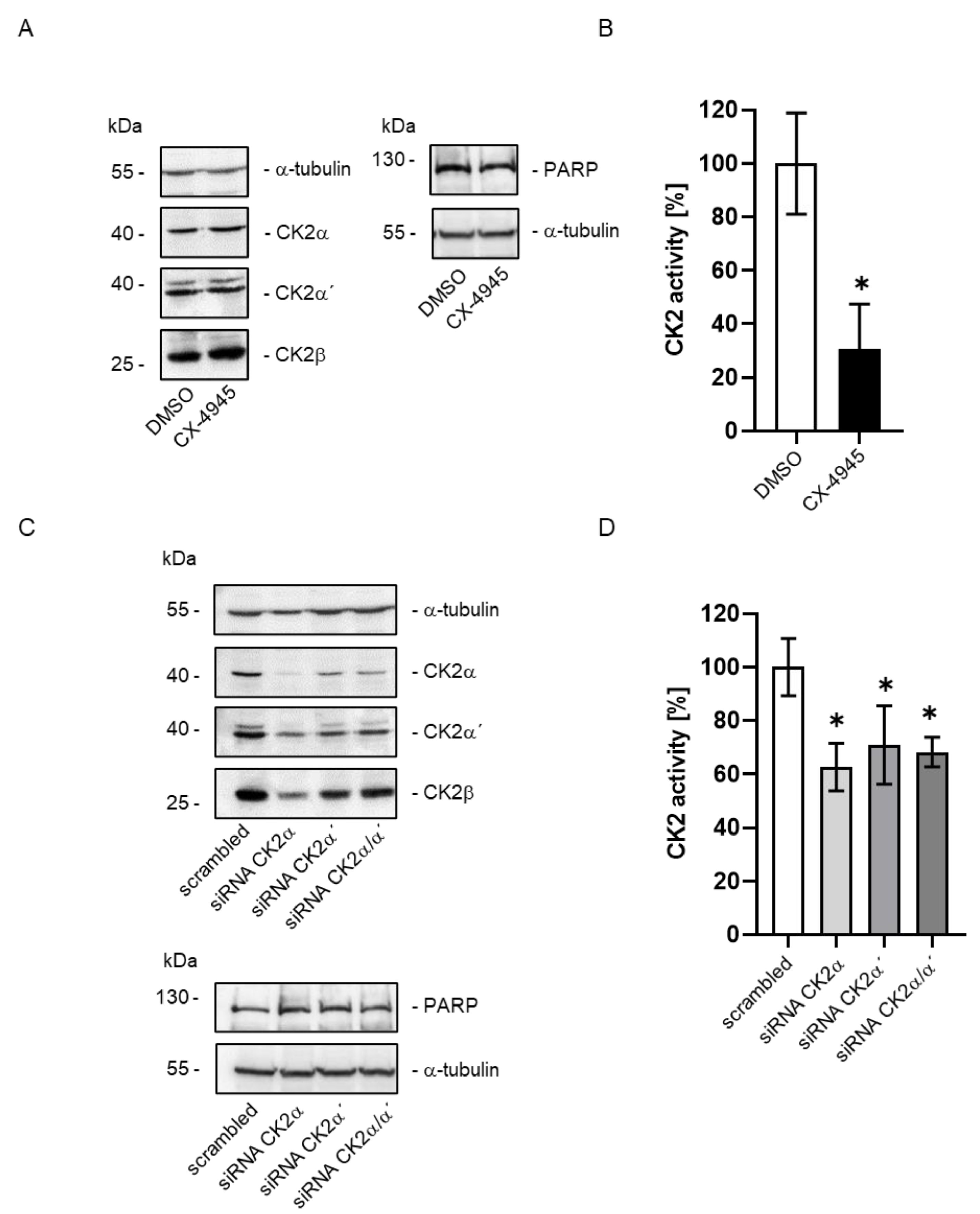
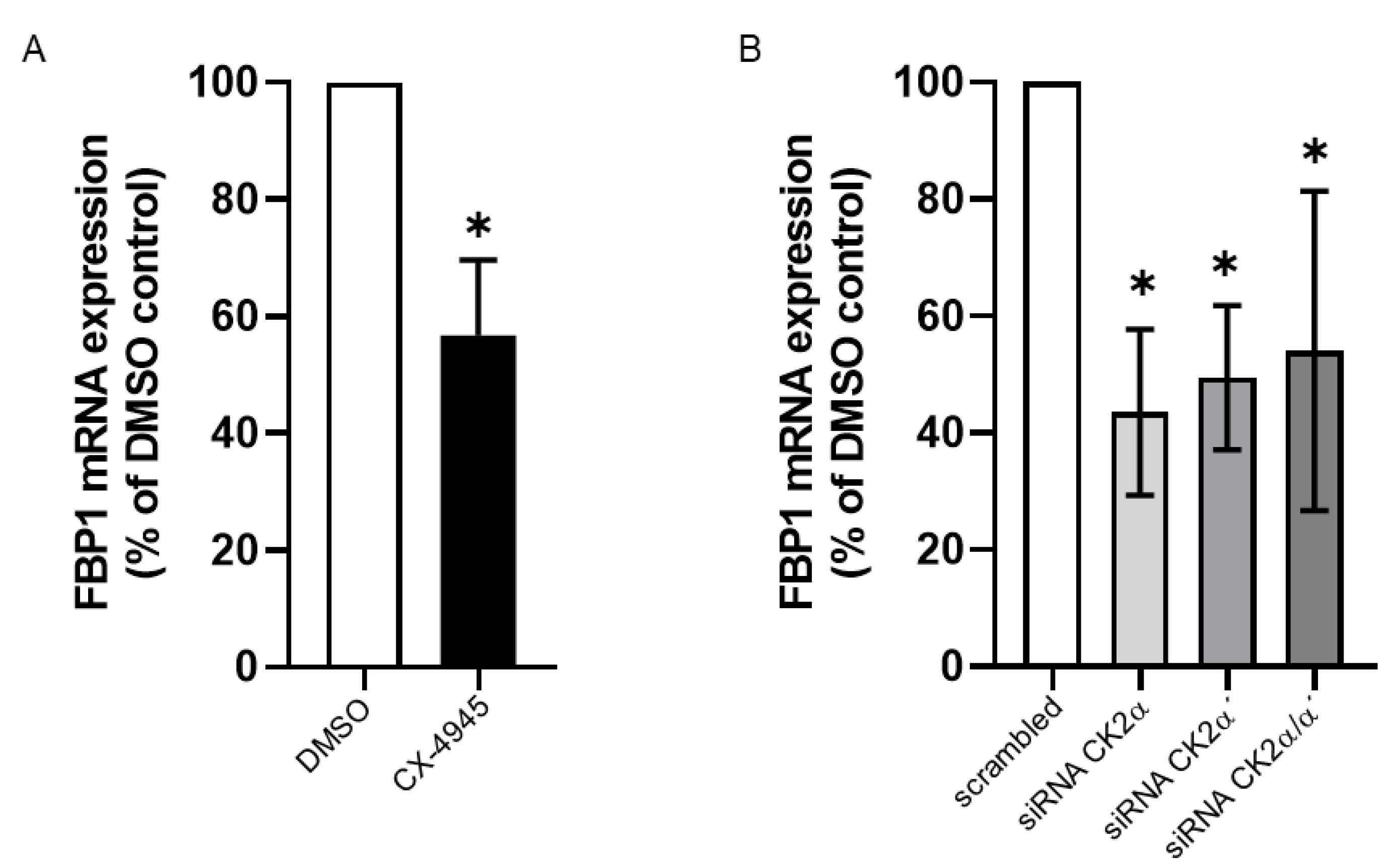
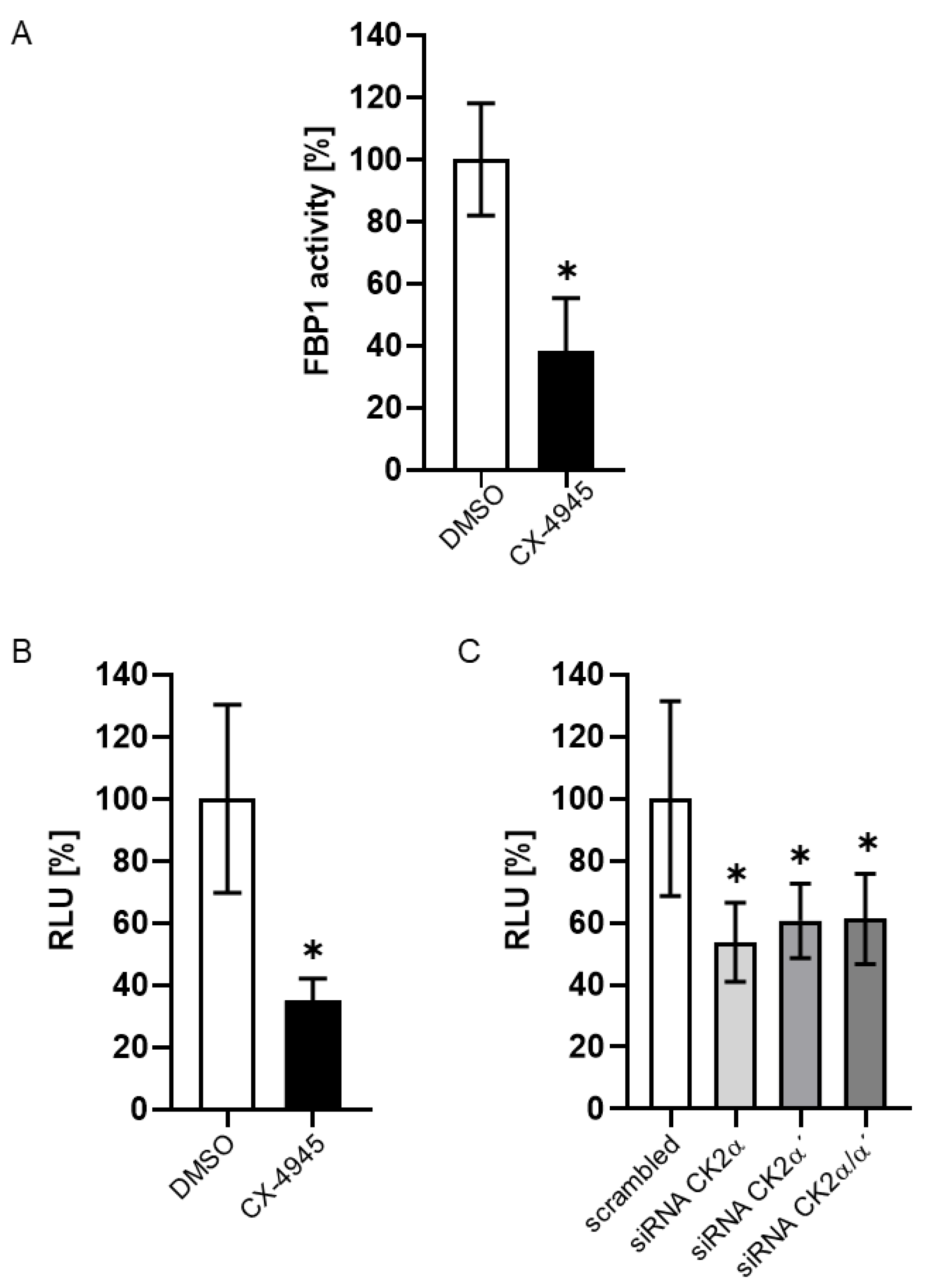
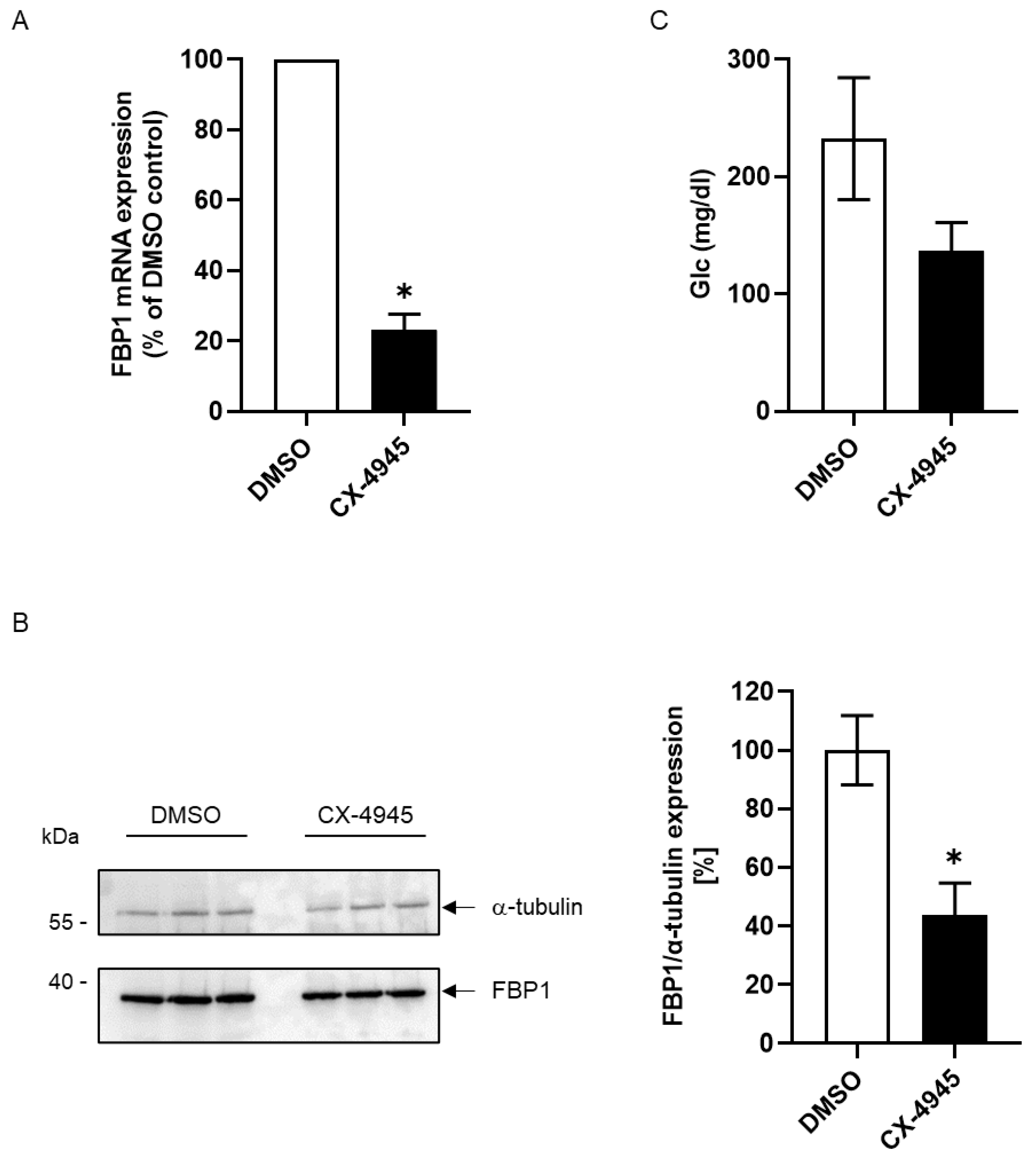
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Treatment of Cells
4.2. Animals and Treatment
4.3. Transfection of McA-RH7777 Cells with siRNA
4.4. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
4.5. qRT PCR Microarray
4.6. Protein Extraction and Immunoblot Analysis
4.7. In Vitro Phosphorylation
4.8. Determination of Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphatase Activity
4.9. Detection of Extracellular Glucose
4.10. Determination of Blood Glucose
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stoffers, D.A.; Thomas, M.K.; Habener, J.F. Homeodomain protein IDX-1: A master regulator of pancreas development and insulin gene expression. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 8, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolensek, J.; Rupnik, M.S.; Stozer, A. Structural similarities and differences between the human and the mouse pancreas. Islets 2015, 7, e1024405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Miyatsuka, T.; Sasaki, S.; Miyashita, K.; Kubo, F.; Shimo, N.; Takebe, S.; Watada, H.; Kaneto, H.; Matsuoka, T.A.; et al. Preserving expression of Pdx1 improves beta-cell failure in diabetic mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 483, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, T. Protein kinases and phosphatases: The yin and yang of protein phosphorylation and signaling. Cell 1995, 80, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ampofo, E.; Nalbach, L.; Menger, M.D.; Montenarh, M.; Götz, C. Protein kinase CK2-A putative target for the therapy of diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Quobaili, F.; Montenarh, M. CK2 and the regulation of the carbohydrate metabolism. Metabolism 2012, 61, 1512–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Quobaili, F.; Montenarh, M. Pancreatic duodenal homeobox factor-1 and diabetes mellitus type 2. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2008, 21, 399–404. [Google Scholar]
- Burnett, G.; Kennedy, E.P. The enzymatic phosphorylation of proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1954, 211, 969–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, G.; Whyte, D.B.; Martinez, R.; Hunter, T.; Sudarsanam, S. The protein kinase complement of the human genome. Science 2002, 298, 1912–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinna, L.A.; Meggio, F. Protein kinase CK2 (“casein kinase-2”) and its implication in cell division and proliferation. Prog. Cell Cycle Res. 1997, 3, 77–97. [Google Scholar]
- Litchfield, D.W. Protein kinase CK2: Structure, regulation and role in cellular decisions of life and death. Biochem. J. 2003, 369, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trembley, J.H.; Wang, G.; Unger, G.; Slaton, J.; Ahmed, K. CK2: A key player in cancer biology. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 1858–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montenarh, M. Protein kinase CK2 and angiogenesis. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 23, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götz, C.; Montenarh, M. Protein kinase CK2 in development and differentiation. Biomed. Rep. 2016, 6, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montenarh, M.; Götz, C. Protein kinase CK2 and ion channels. Biomed. Rep. 2020, 13, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götz, C.; Montenarh, M. Protein kinase CK2 in the ER stress response. Ad. Biol. Chem. 2013, 3A, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenarh, M. Protein kinase CK2 in DNA damage and repair. Transl. Cancer Res. 2016, 5, 49–63. [Google Scholar]
- Salvi, M.; Sarno, S.; Marin, O.; Meggio, F.; Itarte, E.; Pinna, L.A. Discrimination between the activity of protein kinase CK2 holoenzyme and its catalytic subunits. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 3948–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, R.; Al-Quobaili, F.; Müller, I.; Götz, C.; Thiel, G.; Montenarh, M. CK2 phosphorylation of Pdx-1 regulates its transcription factor activity. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 2481–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, R.; Götz, C.; Montenarh, M. The role of protein kinase CK2 in the regulation of the insulin production of pancreatic islets. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 401, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spohrer, S.; Gross, R.; Nalbach, L.; Schwind, L.; Stumpf, H.; Menger, M.D.; Ampofo, E.; Montenarh, M.; Götz, C. Functional interplay between the transcription factors USF1 and PDX-1 and protein kinase CK2 in pancreatic b-cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheuer, R.; Philipp, S.E.; Becker, A.; Nalbach, L.; Ampofo, E.; Montenarh, M.; Götz, C. Protein Kinase CK2 Controls CaV2.1-Dependent Calcium Currents and Insulin Release in Pancreatic b-Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, A.; Götz, C.; Montenarh, M.; Philipp, S.E. Control of TRPM3 ion channels by protein kinase Ck2-mediated phosphorylation in pancreatic β-cells of the line INS-1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, M.; Takihara, Y.; Yasunaga, T.; Shimada, K. One of the retinoic acid-inducible cDNA clones in mouse embryonal carcinoma F9 cells encodes a novel isoenzyme of fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase. FEBS Lett. 1994, 348, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohmeier, H.E.; Mulder, H.; Chen, G.; Henkel-Rieger, R.; Prentki, M.; Newgard, C.B. Isolation of INS-1-derived cell lines with robust ATP-sensitive K+ channel-dependent and -independent glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Diabetes 2000, 49, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierre, F.; Chua, P.C.; O’Brien, S.E.; Siddiqui-Jain, A.; Bourbon, P.; Haddach, M.; Michaux, J.; Nagasawa, J.; Schwaebe, M.K.; Stefan, E.; et al. Pre-clinical characterization of CX-4945, a potent and selective small molecule inhibitor of CK2 for the treatment of cancer. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2011, 356, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, K.S.; Rho, J.K.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Choi, C.M.; Chun, Y.J.; Lee, J.C. AKT/mTOR down-regulation by CX-4945, a CK2 inhibitor, promotes apoptosis in chemorefractory non-small cell lung cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 1537–1542. [Google Scholar]
- Kendall, J.J.; Chaney, K.E.; Patel, A.V.; Rizvi, T.A.; Largaespada, D.A.; Ratner, N. CK2 blockade causes MPNST cell apoptosis and promotes degradation of beta-catenin. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 53191–53203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; McFarland, B.C.; Drygin, D.; Yu, H.; Bellis, S.L.; Kim, H.; Bredel, M.; Benveniste, E.N. Targeting protein kinase CK2 suppresses prosurvival signaling pathways and growth of glioblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 6484–6494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, S.H. Druggability of the CK2 inhibitor CX-4945 as an anticancer drug and beyond. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2012, 35, 1293–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui-Jain, A.; Drygin, D.; Streiner, N.; Chua, P.; Pierre, F.; O’Brien, S.E.; Bliesath, J.; Omori, M.; Huser, N.; Ho, C.; et al. CX-4945, an Orally Bioavailable Selective Inhibitor of Protein Kinase CK2, Inhibits Prosurvival and Angiogenic Signaling and Exhibits Antitumor Efficacy. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 10288–10298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.S.; Lee, S.; Kim, C.; Kim, D.; Kim, K.P.; Yoo, C. The Casein Kinase 2 Inhibitor CX-4945 Promotes Cholangiocarcinoma Cell Death Through PLK1. Anticancer Res. 2022, 42, 3435–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamzina, L.; Eraiser, T.; Borgeat, P. Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) expression in clones of McA-RH 7777 rat hepatoma: Correlation with the occurrence of homogeneously staining regions on chromosome 14. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 3615–3622. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Becker, J.E.; de Nechaud, E.; Potter, V.R. The new hepatoma cell lines for studying the unbalance blocked ontogeny hypothesis. In Onco-Developmental Gene Expression; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1976; pp. 259–270. [Google Scholar]
- Pack, M.; Gotz, C.; Wrublewsky, S.; Montenarh, M. SGC-CK2-1 Is an Efficient Inducer of Insulin Production and Secretion in Pancreatic beta-Cells. Pharmaceutics 2021, 14, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welker, S.; Götz, C.; Servas, C.; Laschke, M.W.; Menger, M.D.; Montenarh, M. Glucose regulates protein kinase CK2 in pancreatic ß-cells and its interaction with PDX-1. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 2786–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marselli, L.; Thorne, J.; Dahiya, S.; Sgroi, D.C.; Sharma, A.; Bonner-Weir, S.; Marchetti, P.; Weir, G.C. Gene expression profiles of Beta-cell enriched tissue obtained by laser capture microdissection from subjects with type 2 diabetes. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.C.; Wang, Y.H.; Chen, H.H.; Lo, S.F.; Chen, S.Y.; Tsai, F.J. Effects of Casein Kinase 2 Alpha 1 Gene Expression on Mice Liver Susceptible to Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Obesity. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 17, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijarnia-Mahay, S.; Bhatia, S.; Arora, V. Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphatase Deficiency. GeneReviews® 1993. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK550349/ (accessed on 25 October 2022).
- Yanez, A.J.; Nualart, F.; Droppelmann, C.; Bertinat, R.; Brito, M.; Concha, I.I.; Slebe, J.C. Broad expression of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase provide evidence for gluconeogenesis in human tissues other than liver and kidney. J. Cell. Physiol. 2003, 197, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanez, A.J.; Bertinat, R.; Spichiger, C.; Carcamo, J.G.; de Los Angeles, G.M.; Concha, I.I.; Nualart, F.; Slebe, J.C. Novel expression of liver FBPase in Langerhans islets of human and rat pancreas. J. Cell. Physiol. 2005, 205, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebede, M.; Favaloro, J.; Gunton, J.E.; Laybutt, D.R.; Shaw, M.; Wong, N.; Fam, B.C.; Aston-Mourney, K.; Rantzau, C.; Zulli, A.; et al. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase overexpression in pancreatic beta-cells results in reduced insulin secretion: A new mechanism for fat-induced impairment of beta-cell function. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1887–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, H.; Lu, J.; Zhang, W.J. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase regulates glucose-stimulated insulin secretion of mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 4688–4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busch, A.K.; Cordery, D.; Denyer, G.S.; Biden, T.J. Expression profiling of palmitate- and oleate-regulated genes provides novel insights into the effects of chronic lipid exposure on pancreatic beta-cell function. Diabetes 2002, 51, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Gregersen, S.; Kruhoffer, M.; Pedersen, S.B.; Orntoft, T.F.; Hermansen, K. The effect of chronic exposure to fatty acids on gene expression in clonal insulin-producing cells: Studies using high density oligonucleotide microarray. Endocrinology 2001, 142, 4777–4784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Dahiya, L.; Kumar, M. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase inhibitors: A new valid approach for management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 141, 473–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Poelje, P.D.; Potter, S.C.; Erion, M.D. Fructose-1, 6-bisphosphatase inhibitors for reducing excessive endogenous glucose production in type 2 diabetes. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2011, 203, 279–301. [Google Scholar]
- DePaoli-Roach, A.A.; Roach, P.J.; Pham, K.; Kramer, G.; Hardesty, B. Phosphorylation of glycogen synthase and of the beta subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor two by a common protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1981, 256, 8871–8874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz-Claret, C.; Jolivet, P.; Chardot, T.; Bergeron, E.; Meunier, J.C. Time-co-ordinated control of glycogen synthase, protein phosphatase 2A and protein kinase CK2 during culture growth in Yarrowia lipolytica in relation to glycogen metabolism. C. R. Acad. Sci. III 2000, 323, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagawa, T.; Funasaka, T.; Tsutsumi, S.; Raz, T.; Tanaka, N.; Raz, A. Differential regulation of phosphoglucose isomerase/autocrine motility factor activities by protein kinase CK2 phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 10419–10426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, B.; Waltner-Law, M.; Scott, D.K.; Eschrich, K.; Granner, D.K. Characterization of the human liver fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase gene promoter. Biochem. J. 2000, 351 Pt 2, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirito, M.; Walker, S.; Lin, Q.; Kozlowski, M.T.; Klein, W.H.; Sawadogo, M. Members of the USF family of helix-loop-helix proteins bind DNA as homo- as well as heterodimers. Gene Expr. 1992, 2, 231–240. [Google Scholar]
- Lupp, S.; Götz, C.; Khadouma, S.; Horbach, T.; Dimova, E.Y.; Bohrer, A.-M.; Kietzmann, T.; Montenarh, M. The upstream stimulatory factor USF1 is regulated by protein kinase CK2 phosphorylation. Cell Signal. 2014, 26, 2809–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romieu-Mourez, R.; Landesman-Bollag, E.; Seldin, D.C.; Sonenshein, G.E. Protein kinase CK2 promotes aberrant activation of nuclear factor-kappaB, transformed phenotype, and survival of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 6770–6778. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kato, T., Jr.; Delhase, M.; Hoffmann, A.; Karin, M. CK2 is a C-terminal IkappaB kinase responsible for NF-kappaB activation during the UV response. Mol. Cell 2003, 12, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantome, A.; Pance, A.; Gauthier, N.; Vandroux, D.; Chenu, J.; Solary, E.; Jeannin, J.F.; Reveneau, S. Casein kinase II-mediated phosphorylation of NF-kappaB p65 subunit enhances inducible nitric-oxide synthase gene transcription in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 23953–23960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Westerheide, S.D.; Hanson, J.L.; Baldwin, A.S., Jr. Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced phosphorylation of RelA/p65 on Ser529 is controlled by casein kinase II. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 32592–32597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.S.; Diallo, O.T.; Hu, M.; Ehsanian, R.; Yang, X.; Arun, P.; Lu, H.; Korman, V.; Unger, G.; Ahmed, K.; et al. CK2 modulation of NF-kappaB, TP53, and the malignant phenotype in head and neck cancer by anti-CK2 oligonucleotides in vitro or in vivo via sub-50-nm nanocapsules. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 2295–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, S.A.; Barry, D.A.; Leggett, R.W.; Mueller, C.R. Casein kinase II-mediated phosphorylation of the C terminus of spl decreases its DNA binding activity. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 13489–13495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Target | Direction | Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| FBP1 | forward | 5′-CATCTGGAAAGCTGCGGCTGCTGTACG -3′ |
| FBP1 | reverse | 5′-AGGGACGGCCTTGATTTGGCTTTGTCC -3′ |
| Actin | forward | 5′-CCT CTG AAC CCT AAG GCC AAC CGT GA -3′ |
| Actin | reverse | 5′-GGA CAA CAC AGC CTG GAT GGC TAC G -3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pack, M.; Gulde, T.N.; Völcker, M.V.; Boewe, A.S.; Wrublewsky, S.; Ampofo, E.; Montenarh, M.; Götz, C. Protein Kinase CK2 Contributes to Glucose Homeostasis by Targeting Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphatase 1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010428
Pack M, Gulde TN, Völcker MV, Boewe AS, Wrublewsky S, Ampofo E, Montenarh M, Götz C. Protein Kinase CK2 Contributes to Glucose Homeostasis by Targeting Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphatase 1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(1):428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010428
Chicago/Turabian StylePack, Mandy, Tim Nikolai Gulde, Michelle Victoria Völcker, Anne S. Boewe, Selina Wrublewsky, Emmanuel Ampofo, Mathias Montenarh, and Claudia Götz. 2023. "Protein Kinase CK2 Contributes to Glucose Homeostasis by Targeting Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphatase 1" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 1: 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010428
APA StylePack, M., Gulde, T. N., Völcker, M. V., Boewe, A. S., Wrublewsky, S., Ampofo, E., Montenarh, M., & Götz, C. (2023). Protein Kinase CK2 Contributes to Glucose Homeostasis by Targeting Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphatase 1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(1), 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010428






