Circulating Tumor Cells in Colorectal Cancer: Detection Systems and Clinical Utility
Abstract
1. Introduction
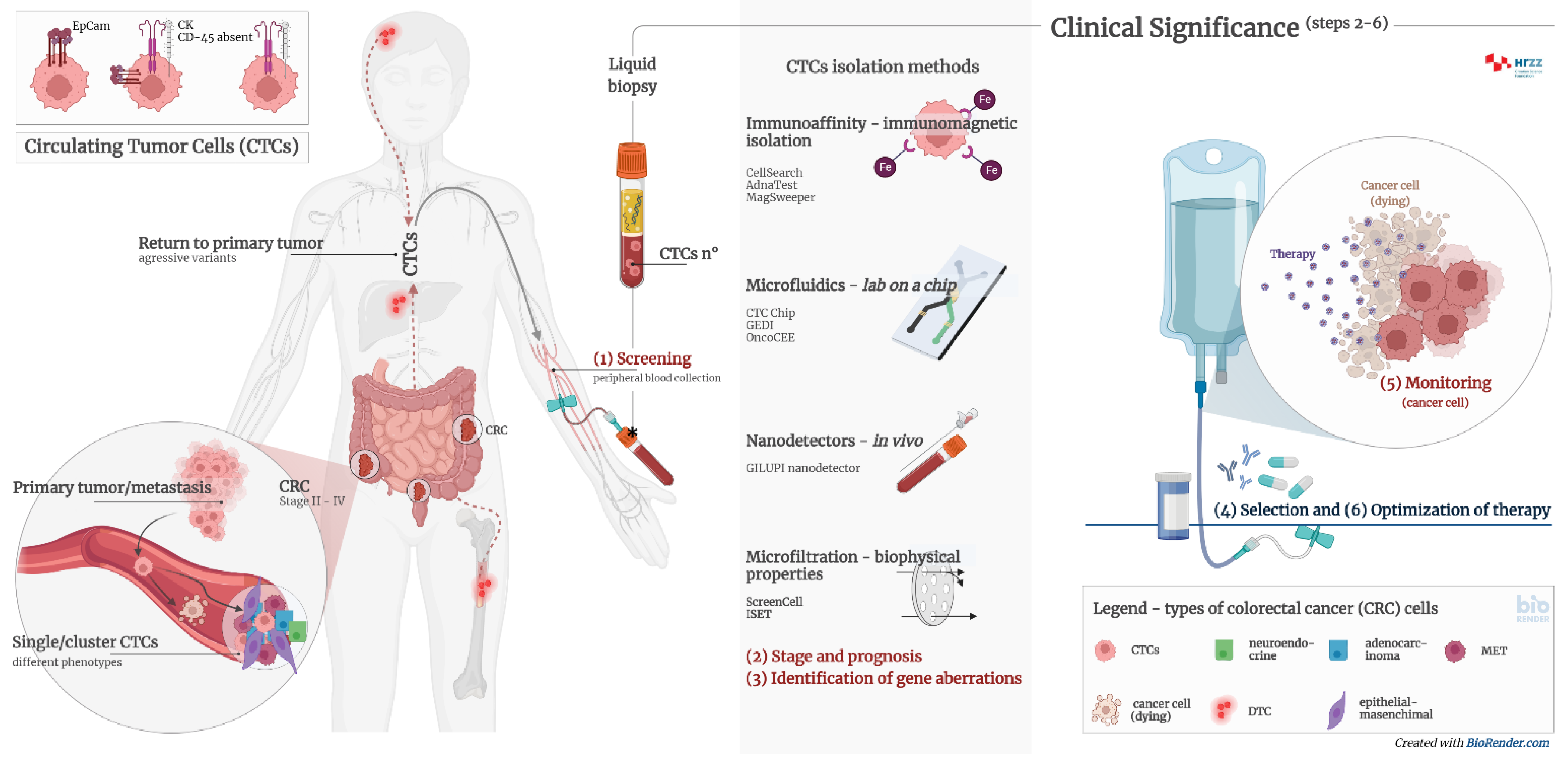
2. Liquid Biopsy
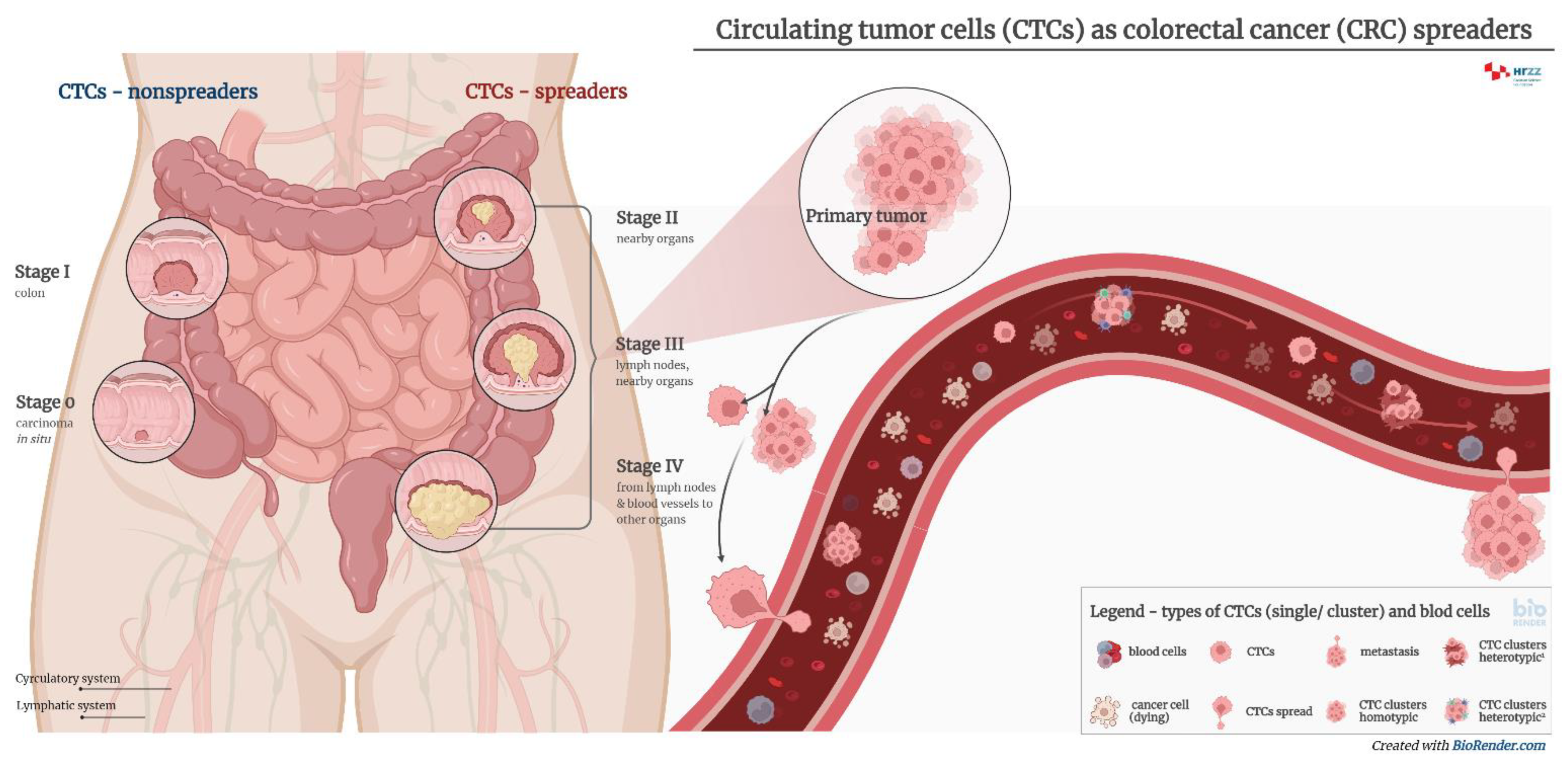
3. Circulating Tumor Cells
4. Diagnostic Significance of Circulating Tumor Cells
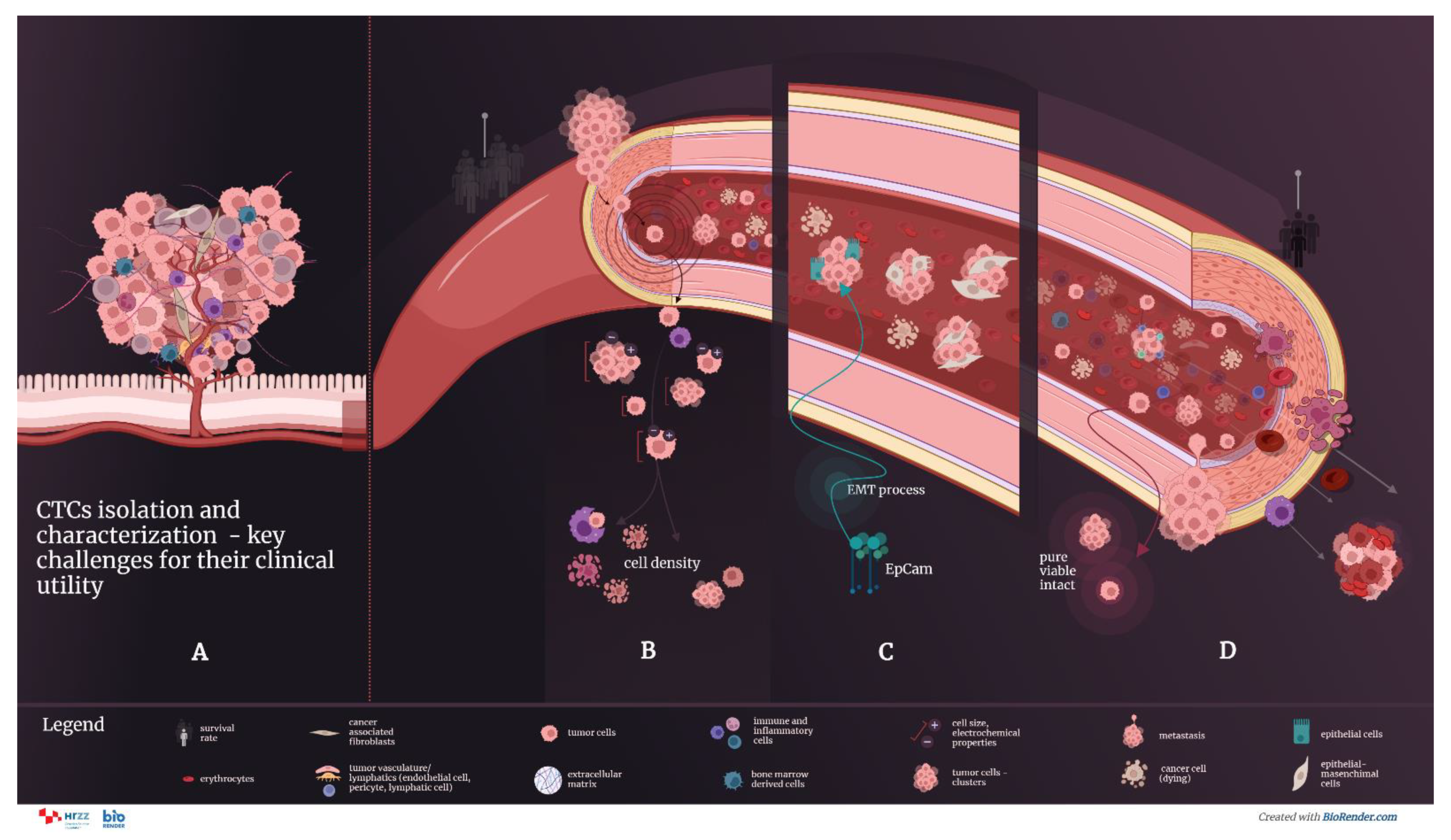
5. Methods and Technologies of Isolation Circulating Tumor Cells
6. Strategies for Characterization of Circulating Tumor Cells
7. Assessment of ScreenCell Cyto Kit
8. Discussion
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALDH1 | aldheyde dehydrogenase 1 |
| BRAF | serine/threonine-protein kinase B-Raf gene |
| CD45 | cluster of differentiation 45 |
| CEA | carcinoembryonic antigen |
| cfNAs | circulating free nucleic acids |
| CK | cytokeratins |
| CONCORD-3 | global surveillance of trends in cancer survival, 2000–2014 |
| cfDNA | cell-free circulating deoxyribonucleic acid |
| CRC | colorectal cancer |
| CTC | circulating tumor cells |
| ctDNA | circulating tumor deoxyribonucleic acid |
| DTC | disseminated tumor cells |
| EpCAM | epithelial cell adhesion molecule |
| FDG-PET | fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography |
| KRAS | c-K-ras protein gene |
| MPR5 | multidrug resistance related protein 5 |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| OS | overall survival |
| PBMCs | peripheral blood mononuclear cells |
| PIK3CA | phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha gene |
| PI3K | phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase |
| PFS | progression-free survival |
| TGF-β | transforming growth factor β |
References
- Colorectal Cancer Statistics|WCRF International. Available online: https://www.wcrf.org (accessed on 18 October 2022).
- Epidemiologija Raka Debelog Crijeva U Hrvatskoj|Hrvatski Zavod Za Javno Zdravstvo. Available online: https://www.hzjz.hr/sluzba-epidemiologija-prevencija-nezaraznih-bolesti/epidemiologija-raka-debelog-crijeva-u-hrvatskoj/ (accessed on 29 August 2022).
- Allemani, C.; Matsuda, T.; Di Carlo, V.; Harewood, R.; Melissa Matz, M.; Nikšić, M.; Bonaventure, A.; Valkov, M.; Johnson, C.J.; Estève, J.; et al. Global surveillance of trends in cancer survival: Analysis of individual records for 37,513,025 patients diagnosed with one of 18 cancers during 2000–2014 from 322 population-based registries in 71 countries (CONCORD-3). Lancet 2018, 391, 1023–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konczalla, L.; Wöstemeier, A.; Kemper, M.; Karstens, K.-F.; Izbicki, J.; Reeh, M. Clinical Significance of Circulating Tumor Cells in Gastrointestinal Carcinomas. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Cutsem, E.; Cervantes, A.; Nordlinger, B.; Arnold, D. The ESMO Guidelines Working Group Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, iii1–iii9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptistella, A.R.; Salles Dias, M.V.; Aguiar, S.; Begnami, M.D.; Martins, V.R. Heterogeneous Expression of A33 in Colorectal Cancer. Anticancer Drugs 2016, 27, 734–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheal, S.M.; Fung, E.K.; Patel, M.; Xu, H.; Guo, H.; Zanzonico, P.B.; Monette, S.; Wittrup, K.D.; Cheung, N.-K.V.; Larson, S.M. Curative Multicycle Radioimmunotherapy Monitored by Quantitative SPECT/CT-Based Theranostics, Using Bispecific Antibody Pretargeting Strategy in Colorectal Cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 1735–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colorectal Cancer Antibodies Used in Immunohistochemistry|LSBio. Available online: https://www.lsbio.com/research-areas/colorectal-cancer-ihc-markers (accessed on 30 August 2022).
- Micalizzi, D.S.; Maheswaran, S.; Haber, D.A. A Conduit to Metastasis: Circulating Tumor Cell Biology. Genes Dev. 2017, 31, 1827–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.; Shen, L.; Luo, M.; Zhang, K.; Li, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, F.; Zhou, D.; Zheng, S.; Chen, Y.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cells: Biology and Clinical Significance. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasseur, A.; Kiavue, N.; Bidard, F.; Pierga, J.; Cabel, L. Clinical Utility of Circulating Tumor Cells: An Update. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 1647–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbanac, D.; Čeri, A.; Hlapčić, I.; Shakibaei, M.; Brockmueller, A.; Krušlin, B.; Ljubičić, N.; Baršić, N.; Detel, D.; Batičić, L.; et al. Profiling Colorectal Cancer in the Landscape Personalized Testing—Advantages of Liquid Biopsy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Ding, P.; Pei, R.; Wang, Q.; Xing, C. Circulating Tumor Cells in Colorectal Cancer in the Era of Precision Medicine. J. Mol. Med. 2022, 100, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciardiello, F.; Ciardiello, D.; Martini, G.; Napolitano, S.; Tabernero, J.; Cervantes, A. Clinical Management of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer in the Era of Precision Medicine. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 372–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baghban, R.; Roshangar, L.; Jahanban-Esfahlan, R.; Seidi, K.; Ebrahimi-Kalan, A.; Jaymand, M.; Kolahian, S.; Javaheri, T.; Zare, P. Tumor Microenvironment Complexity and Therapeutic Implications at a Glance. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaath, H.; Toor, S.; Nair, V.S.; Elkord, E.; Alajez, N.M. Transcriptomic Analyses Revealed Systemic Alterations in Gene Expression in Circulation and Tumor Microenvironment of Colorectal Cancer Patients. Cancers 2019, 11, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biller, L.H.; Schrag, D. Diagnosis and Treatment of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. JAMA 2021, 325, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcuello, M.; Vymetalkova, V.; Neves, R.P.L.; Duran-Sanchon, S.; Vedeld, H.M.; Tham, E.; van Dalum, G.; Flügen, G.; Garcia-Barberan, V.; Fijneman, R.J.; et al. Circulating Biomarkers for Early Detection and Clinical Management of Colorectal Cancer. Mol. Aspects Med. 2019, 69, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Ljubimov, V.A.; Zhou, C.; Tong, Y.; Liang, J. Cell-Free Circulating Tumor DNA in Cancer. Chin. J. Cancer 2016, 35, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sai, B.; Xiang, J. Disseminated Tumour Cells in Bone Marrow Are the Source of Cancer Relapse after Therapy. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 5776–5786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Stoecklein, N.H.; Lin, P.P.; Gires, O. Circulating and Disseminated Tumor Cells: Diagnostic Tools and Therapeutic Targets in Motion. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 1884–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alix-Panabières, C.; Pantel, K. Circulating Tumor Cells: Liquid Biopsy of Cancer. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandel, P.; Metais, P. Les Acides Nucléiques Du Plasma Sanguin Chez L’homme [Nuclear Acids In Human Blood Plasma]. C. R. Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1948, 142, 241–243. (in French). [Google Scholar]
- Pantel, K.; Alix-Panabières, C. Circulating Tumour Cells in Cancer Patients: Challenges and Perspectives. Trends Mol. Med. 2010, 16, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alix-Panabières, C.; Pantel, K. Liquid Biopsy: From Discovery to Clinical Application. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 858–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmirotta, R.; Lovero, D.; Cafforio, P.; Felici, C.; Mannavola, F.; Pellè, E.; Quaresmini, D.; Tucci, M.; Silvestris, F. Liquid Biopsy of Cancer: A Multimodal Diagnostic Tool in Clinical Oncology. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2018, 10, 175883591879463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, M.H.D.; Bender, S.; Krahn, T.; Schlange, T. ctDNA and CTCs in Liquid Biopsy—Current Status and Where We Need to Progress. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmiegel, W.; Scott, R.J.; Dooley, S.; Lewis, W.; Meldrum, C.J.; Pockney, P.; Draganic, B.; Smith, S.; Hewitt, C.; Philimore, H.; et al. Blood-Based Detection of RAS Mutations to Guide Anti-EGFR Therapy in Colorectal Cancer Patients: Concordance of Results from Circulating Tumor DNA and Tissue-Based RAS Testing. Mol. Oncol. 2017, 11, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murtaza, M.; Dawson, S.-J.; Tsui, D.W.Y.; Gale, D.; Forshew, T.; Piskorz, A.M.; Parkinson, C.; Chin, S.-F.; Kingsbury, Z.; Wong, A.S.C.; et al. Non-Invasive Analysis of Acquired Resistance to Cancer Therapy by Sequencing of Plasma DNA. Nature 2013, 497, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, H.; Chung, J.; Issadore, D. Diagnostic Technologies for Circulating Tumour Cells and Exosomes. Biosci. Rep. 2016, 36, e00292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arneth, B. Update on the Types and Usage of Liquid Biopsies in the Clinical Setting: A Systematic Review. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulet, G.; Massias, J.; Taly, V. Liquid Biopsy: General Concepts. Acta Cytol. 2019, 63, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashworth, T. A Case of Cancer in Which Cells Similar to Those in the Tumours Were Seen in the Blood after Death. Aust. Med. J. 1869, 14, 146–147. [Google Scholar]
- De Wit, S.; van Dalum, G.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. Detection of Circulating Tumor Cells. Scientifica 2014, 2014, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhe, X.; Cher, M.L.; Bonfil, R.D. Circulating Tumor Cells: Finding the Needle in the Haystack. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2011, 1, 740–751. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lozar, T.; Gersak, K.; Cemazar, M.; Kuhar, C.G.; Jesenko, T. The Biology and Clinical Potential of Circulating Tumor Cells. Radiol. Oncol. 2019, 53, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzagalli, M.; Fontana, F.; Raimondi, M.; Limonta, P. Cancer Stem Cells—Key Players in Tumor Relapse. Cancers 2021, 13, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, S.; Tripathy, D.; Frenkel, E.P.; Shete, S.; Naftalis, E.Z.; Huth, J.F.; Beitsch, P.D.; Leitch, M.; Hoover, S.; Euhus, D.; et al. Circulating tumor cells in patients with breast cancer dormancy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 8152–8162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aramini, B.; Masciale, V.; Arienti, C.; Dominici, M.; Stella, F.; Martinelli, G.; Fabbri, F. Cancer Stem Cells (CSCs), Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs) and Their Interplay with Cancer Associated Fibroblasts (CAFs): A New World of Targets and Treatments. Cancers 2022, 14, 2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Pestell, T.G.; Lisanti, M.P.; Pestell, R.G. Cancer stem cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 44, 2144–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Ramena, G.; Elble, R.C. The role of cancer stem cells in relapse of solid tumors. Front. Biosci. 2012, 4, 1528–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.M.; Ramani, V.C.; Jeffrey, S.S. Circulating Tumor Cell Technologies. Mol. Oncol. 2016, 10, 374–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, M.G.; Hou, J.-M.; Ward, T.H.; Blackhall, F.H.; Dive, C. Circulating Tumour Cells: Their Utility in Cancer Management and Predicting Outcomes. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2010, 2, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.L.; Liu, X.; Suhaimi, N.-A.M.; Koh, K.J.H.; Hu, M.; Lee, D.Y.S.; Cima, I.; Phyo, W.M.; Lee, E.X.W.; Tai, J.A.; et al. Molecular Characterization of Circulating Colorectal Tumor Cells Defines Genetic Signatures for Individualized Cancer Care. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 68026–68037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchetti, A.; Del Grammastro, M.; Felicioni, L.; Malatesta, S.; Filice, G.; Centi, I.; De Pas, T.; Santoro, A.; Chella, A.; Brandes, A.A.; et al. Assessment of EGFR Mutations in Circulating Tumor Cell Preparations from NSCLC Patients by Next Generation Sequencing: Toward a Real-Time Liquid Biopsy for Treatment. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wechsler, J.; Benali-Furet, N.; Ye, F.; Avril, M.-F.; Boitier, F.; Carlotti, A.; Clauser, E.; North, M.-O.; Paraiso, I.; Cayre, Y.E. Analysis of BRAF Mutations in Circulating Tumor Cells Selected by Size from Patients with Melanoma and Comparision to the Primary Tumor. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, e21014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CELLSEARCH®|Home. Available online: https://www.cellsearchctc.com/ (accessed on 29 August 2022).
- Lankiewicz, S.; Zimmermann, S.; Hollmann, C.; Hillemann, T.; Greten, T.F. Circulating Tumour Cells as a Predictive Factor for Response to Systemic Chemotherapy in Patients with Advanced Colorectal Cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2008, 2, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnar, B.; Floro, L.; Sipos, F.; Toth, B.; Sreter, L.; Tulassay, Z. Elevation in Peripheral Blood Circulating Tumor Cell Number Correlates with Macroscopic Progression in UICC Stage IV Colorectal Cancer Patients. Dis. Markers 2008, 24, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzaniga, P.; Gradilone, A.; Petracca, A.; Nicolazzo, C.; Raimondi, C.; Iacovelli, R.; Naso, G.; Cortesi, E. Molecular Markers in Circulating Tumour Cells from Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Patients. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 2073–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tol, J.; Koopman, M.; Miller, M.C.; Tibbe, A.; Cats, A.; Creemers, G.J.M.; Vos, A.H.; Nagtegaal, I.D.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M.; Punt, C.J.A. Circulating Tumour Cells Early Predict Progression-Free and Overall Survival in Advanced Colorectal Cancer Patients Treated with Chemotherapy and Targeted Agents. Ann. Oncol. 2010, 21, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.-Y.; Uen, Y.-H.; Tsai, H.-L.; Chuang, S.-C.; Hou, M.-F.; Wu, D.-C.; Hank Juo, S.-H.; Lin, S.-R.; Wang, J.-Y. Molecular Detection of Persistent Postoperative Circulating Tumour Cells in Stages II and III Colon Cancer Patients via Multiple Blood Sampling: Prognostic Significance of Detection for Early Relapse. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 104, 1178–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neki, K.; Kawahara, H.; Watanabe, K.; Toyama, Y.; Akiba, T.; Yanaga, K. Usefulness of Circulating Tumor Cells after Preliminary Chemotherapy for Prediction of Response to Further Anticancer Therapy in Patients with Initially Unresectable Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 1769–1772. [Google Scholar]
- Krebs, M.G.; Renehan, A.G.; Backen, A.; Gollins, S.; Chau, I.; Hasan, J.; Valle, J.W.; Morris, K.; Beech, J.; Ashcroft, L.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cell Enumeration in a Phase II Trial of a Four-Drug Regimen in Advanced Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2015, 14, 115–122.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, Y.; Hayashi, K.; Kawakami, K.; Miwa, Y.; Hayashi, H.; Yamamoto, M. KRAS Mutation Analysis of Single Circulating Tumor Cells from Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wan, L.; Wu, S.; Yang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, F.; Wu, Z.; Cheng, Y. Mesenchymal Marker and LGR5 Expression Levels in Circulating Tumor Cells Correlate with Colorectal Cancer Prognosis. Cell. Oncol. 2018, 41, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Shi, D.; Wang, S.; Wei, C.; Zhang, C.; Xiong, B. Prognostic Value of Pre- and Post-Operative Circulating Tumor Cells Detection in Colorectal Cancer Patients Treated with Curative Resection: A Prospective Cohort Study Based on ISET Device. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 4135–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Huang, L.; Huang, J.; Kang, L.; Lin, H.; Huang, P.; Zhu, P.; Wang, J.; Dong, J.; Wang, L.; et al. Associations between the cyclooxygenase-2 Expression in Circulating Tumor Cells and the Clinicopathological Features of Patients with Colorectal Cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 4935–4941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, K.; Yamada, T.; Takahashi, G.; Iwai, T.; Ueda, K.; Kuriyama, S.; Koizumi, M.; Matsuda, A.; Shinji, S.; Ohta, R.; et al. Analysis of Colorectal Cancer-related Mutations by Liquid Biopsy: Utility of Circulating Cell-free DNA and Circulating Tumor. Cells Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 3497–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yang, Y.; Jin, L.; Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; Wu, G.; Zhang, J.; Kou, T.; Yao, H.; Zhang, Z. Prognostic Models Based on Postoperative Circulating Tumor Cells Can Predict Poor Tumor Recurrence-Free Survival in Patients with Stage II-III Colorectal Cancer. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 4552–4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadagni, S.; Clementi, M.; Mackay, A.R.; Ricevuto, E.; Fiorentini, G.; Sarti, D.; Palumbo, P.; Apostolou, P.; Papasotiriou, I.; Masedu, F.; et al. Real-Life Multidisciplinary Treatment for Unresectable Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastases Including Hepatic Artery Infusion with Chemo-Filtration and Liquid Biopsy Precision Oncotherapy: Observational Cohort Study. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 146, 1273–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendricks, A.; Brandt, B.; Geisen, R.; Dall, K.; Röder, C.; Schafmayer, C.; Becker, T.; Hinz, S.; Sebens, S. Isolation and Enumeration of CTC in Colorectal Cancer Patients: Introduction of a Novel Cell Imaging Approach and Comparison to Cellular and Molecular Detection Techniques. Cancers 2020, 12, 2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsusaka, S.; Hann, D.L.; Ning, Y.; Yang, D.; Cao, S.; Berger, M.D.; Miyamoto, Y.; Suenaga, M.; Dan, S.; Mashima, T.; et al. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor mRNA Expression: A Potential Molecular Escape Mechanism from Regorafenib. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastre, J.; Orden, V.d.l.; Martínez, A.; Bando, I.; Balbín, M.; Bellosillo, B.; Palanca, S.; Peligros Gomez, M.I.; Mediero, B.; Llovet, P.; et al. Association Between Baseline Circulating Tumor Cells, Molecular Tumor Profiling, and Clinical Characteristics in a Large Cohort of Chemo-Naïve Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Patients Prospectively Collected. Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2020, 19, e110–e116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francescangeli, F.; Magri, V.; De Angelis, M.L.; De Renzi, G.; Gandini, O.; Zeuner, A.; Gazzaniga, P.; Nicolazzo, C. Sequential Isolation and Characterization of Single CTCs and Large CTC Clusters in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Patients. Cancers 2021, 13, 6362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabisiewicz, A.; Grzybowska, E. CTC Clusters in Cancer Progression and Metastasis. Med. Oncol. 2017, 34, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swennenhuis, J.F.; van Dalum, G.; Zeune, L.L.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. Improving the CellSearch® System. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2016, 16, 1291–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazard, T.; Cayrefourcq, L.; Perriard, F.; Senellart, H.; Linot, B.; de la Fouchardière, C.; Terrebonne, E.; François, E.; Obled, S.; Guimbaud, R.; et al. Clinical Relevance of Viable Circulating Tumor Cells in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: The COLOSPOT Prospective Study. Cancers 2021, 13, 2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soler, A.; Cayrefourcq, L.; Mazel, M.; Alix-Panabières, C. EpCAM-Independent Enrichment and Detection of Viable Circulating Tumor Cells Using the EPISPOT Assay. In Circulating Tumor Cells; Magbanua, M.J.M., Park, J.W., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 1634, pp. 263–276. [Google Scholar]
- DeNeve, E.; Riethdorf, S.; Ramos, J.; Nocca, D.; Coffy, A.; Daurès, J.-P.; Maudelonde, T.; Fabre, J.-M.; Pantel, K.; Alix-Panabières, C. Capture of Viable Circulating Tumor Cells in the Liver of Colorectal Cancer Patients. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 1384–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talasaz, A.H.; Powell, A.A.; Huber, D.E.; Berbee, J.G.; Roh, K.-H.; Yu, W.; Xiao, W.; Davis, M.M.; Pease, R.F.; Mindrinos, M.N.; et al. Isolating Highly Enriched Populations of Circulating Epithelial Cells and Other Rare Cells from Blood Using a Magnetic Sweeper Device. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3970–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, B.J.; Jodari, M.; Loftus, M.S.; Gakhar, G.; Pratt, E.D.; Chanel-Vos, C.; Gleghorn, J.P.; Santana, S.M.; Liu, H.; Smith, J.P.; et al. Functional Characterization of Circulating Tumor Cells with a Prostate-Cancer-Specific Microfluidic Device. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saucedo-Zeni, N.; Mewes, S.; Niestroj, R.; Gasiorowski, L.; Murawa, D.; Nowaczyk, P.; Tomasi, T.; Weber, E.; Dworacki, G.; Morgenthaler, N.G.; et al. A Novel Method for the in Vivo Isolation of Circulating Tumor Cells from Peripheral Blood of Cancer Patients Using a Functionalized and Structured Medical Wire. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 41, 1241–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowes, L.E.; Allan, A.L. Circulating Tumor Cells and Implications of the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2018, 83, 121–181. [Google Scholar]
- Powell, A.A.; Talasaz, A.H.; Zhang, H.; Coram, M.A.; Reddy, A.; Deng, G.; Telli, M.L.; Advani, R.H.; Carlson, R.W.; Mollick, J.A.; et al. Single Cell Profiling of Circulating Tumor Cells: Transcriptional Heterogeneity and Diversity from Breast Cancer Cell Lines. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, G.; Ignatiadis, M. Promises and Pitfalls of Using Liquid Biopsy for Precision Medicine. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 2798–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Rachel Zhuang, R.; Long, M.; Mirjana Pavlovic, M.; Kang, Z.; Ilyas, A.; Waseem Asghar, W. Circulating Tumor Cell Isolation, Culture, and Downstream Molecular Analysis. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 1063–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, K.; Fan, Z.H. Circulating Tumor Cell Isolation and Analysis. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2016, 75, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]


| Number of Patients | Detection Method | CTC No. (%) | Clinical Significance | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 34 | Multiplex PCR | 20 (59) | Therapy alignment and monitoring; CTCs could predict chemotherapy response; moreover, EGFR status of CTCs could predict the likelihood of targeted therapy response. | [48] |
| 30 | Density gradient centrifugation, CK20 qRT-PCR and immunomagnetic CTC number determination | 30 (100) | CTC number reflects the chemotherapeutic sensitivity of CRC patients. Microscopic CTC single-cell, doublet, and cluster numbers were found in correlation with CK20 qRT-PCR results. | [49] |
| 40 | CELLection Dynabeads® | 27 (68) | Therapy alignment and monitoring. Significant shorter progression-free survival (PFS) was found in patients with CTCs positive for the expression of ALDH1, survivin and MRP5. | [50] |
| 467 | CellSearch | 467 (100) | Therapy alignment and monitoring; CTC count provides additional information to CT imaging for early recurrence monitoring. | [51] |
| 141 | RT-PCR | 141 (100) | Therapy alignment and monitoring; CTC persistence after surgical resection was a significant marker for early recurrence. | [52] |
| 14 | CellSearch | 14; 4 (29) after chemotherapy | Therapy alignment and monitoring; CTC-negative patients after chemotherapy had significantly better treatment response. | [53] |
| 42 | CellSearch | 22 (52.3) | Patients with CTCs ≥3/7.5 mL may benefit from the intensive 4-drug regimen (irinotecan, oxaliplatin, and tegafur-uracil with leucovorin and cetuximab). | [54] |
| 61 | CellSearch | 27 (44.3) | CTC heterozygosity and heterogeneity exist in KRAS status among CTCs within all patients and between CTCs and tumor tissues. | [55] |
| 66 | CanPatrol Multiplex mRNA-ISH | 57 (86.4) | CTC count ≥6/5 mL was associated with decreased PFS and OS. LGR5 expression in CTCs may serve as a marker for CRC metastasis. | [56] |
| 138 | ISET device-CTCBIOPSY | 63 (45.7) | Postcurative resection CTC count > 1/2.5 mL was associated with shorter 3-year RFS rate. | [57] |
| 91 | CanPatrol mRNA-ISH | 51 CTC (56.0); 46 mCTC (50.5) | Mesenchymal CTC count ≥1/5 mL and COX-2 expression in mCTCs were associated with distance metastasis. | [58] |
| 34 | Microfluidic chips | 34 (100) | Therapy alignment and monitoring; comparison of mutational status of CTCs, ctDNA, and primary tumor tissue revealed great heterogeneity. | [59] |
| 130 | MACS | 67 (51.54) | Postoperative CTC count ≥2/3.2 mL in non-mCRC was associated with decreased RFS. | [60] |
| 106 | MACS | 100 (94) | HAI/target therapy with drugs selected by liquid biopsy precision oncotherapy is a safe and efficacious alternative therapeutic strategy for unresectable colorectal liver metastases patients. | [61] |
| 21 | ScreenCell® | 21 (100) | Isolation of CTCs by size (as a label-free technique with subsequent immunofluorescence labeling) gives a very high detection rate. | [62] |
| 21 | CK20 RT-qPCR | 15 (71.4) | The CK20 RT-qPCR method gives a relatively high detection rate. | [62] |
| 21 | NYONE® | 11 (52.4) | Application of a semiautomated microscopic approach with NYONE®, an examiner-independent procedure for CTC detection. | [62] |
| 50 | CellSearch | 46 (92) | CTC counts ≥3/7.5 mL at baseline and day 21 after initiation of regorafenib were associated with decreased PFS and OS. Patients had significantly increased EGFR expression at day 21 and/or PD compared to baseline. | [63] |
| 589 | CellSearch | 241 (41) | Baseline CTC counts ≥3/7.5 mL were associated with clinical or pathologic features associated with poor prognosis. | [64] |
| 7 | ScreenCell®, Immunofluorescence Staining | 7 (100) | Promising test for the future isolation and characterization of different CTC subtypes, including clusters. | [65] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petrik, J.; Verbanac, D.; Fabijanec, M.; Hulina-Tomašković, A.; Čeri, A.; Somborac-Bačura, A.; Petlevski, R.; Grdić Rajković, M.; Rumora, L.; Krušlin, B.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cells in Colorectal Cancer: Detection Systems and Clinical Utility. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13582. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113582
Petrik J, Verbanac D, Fabijanec M, Hulina-Tomašković A, Čeri A, Somborac-Bačura A, Petlevski R, Grdić Rajković M, Rumora L, Krušlin B, et al. Circulating Tumor Cells in Colorectal Cancer: Detection Systems and Clinical Utility. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(21):13582. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113582
Chicago/Turabian StylePetrik, József, Donatella Verbanac, Marija Fabijanec, Andrea Hulina-Tomašković, Andrea Čeri, Anita Somborac-Bačura, Roberta Petlevski, Marija Grdić Rajković, Lada Rumora, Božo Krušlin, and et al. 2022. "Circulating Tumor Cells in Colorectal Cancer: Detection Systems and Clinical Utility" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 21: 13582. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113582
APA StylePetrik, J., Verbanac, D., Fabijanec, M., Hulina-Tomašković, A., Čeri, A., Somborac-Bačura, A., Petlevski, R., Grdić Rajković, M., Rumora, L., Krušlin, B., Štefanović, M., Ljubičić, N., Baršić, N., Hanžek, A., Bočkor, L., Ćelap, I., Demirović, A., & Barišić, K. (2022). Circulating Tumor Cells in Colorectal Cancer: Detection Systems and Clinical Utility. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(21), 13582. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113582








