AI-Based Protein Interaction Screening and Identification (AISID)
Abstract
1. Introduction
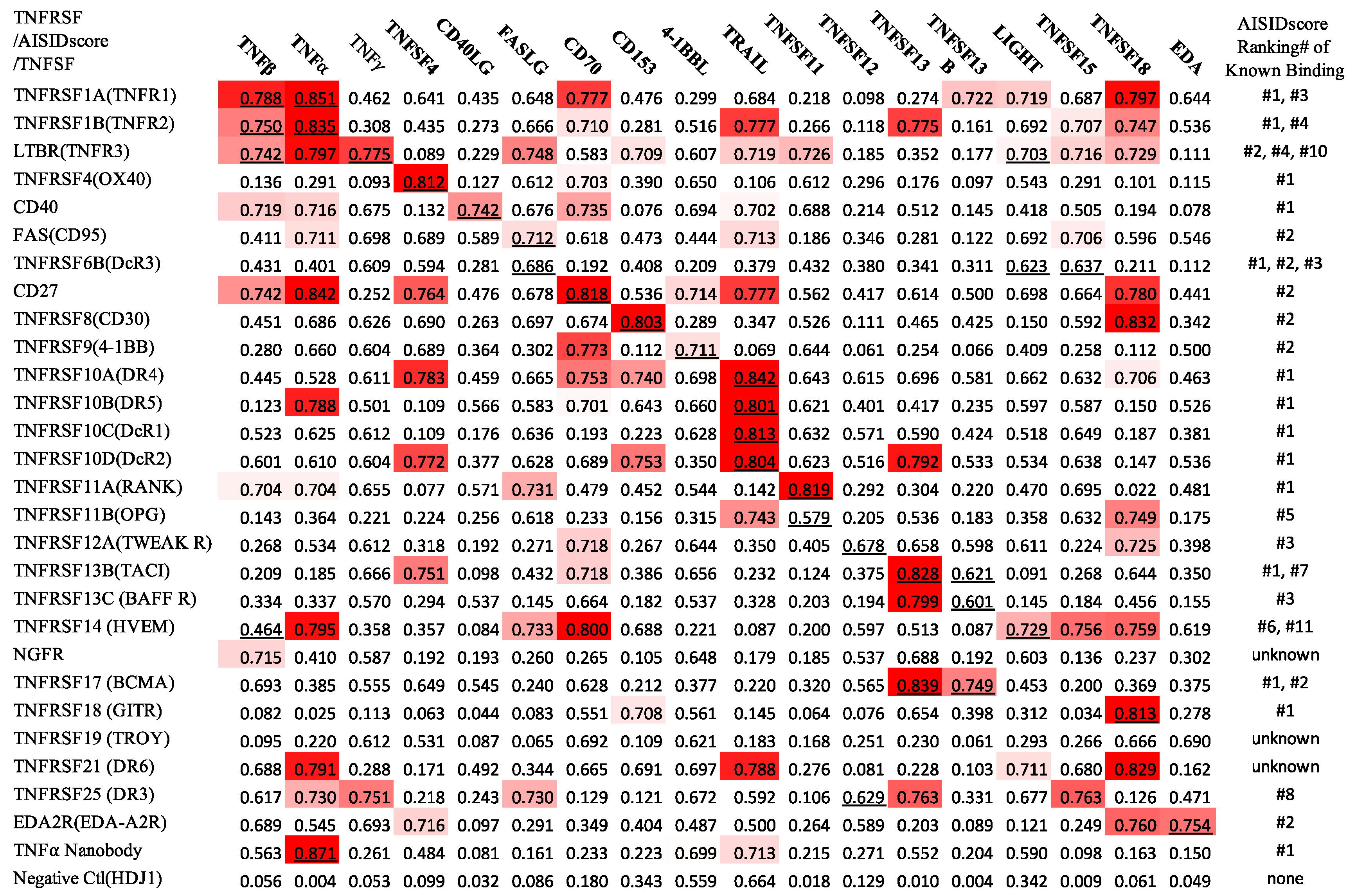
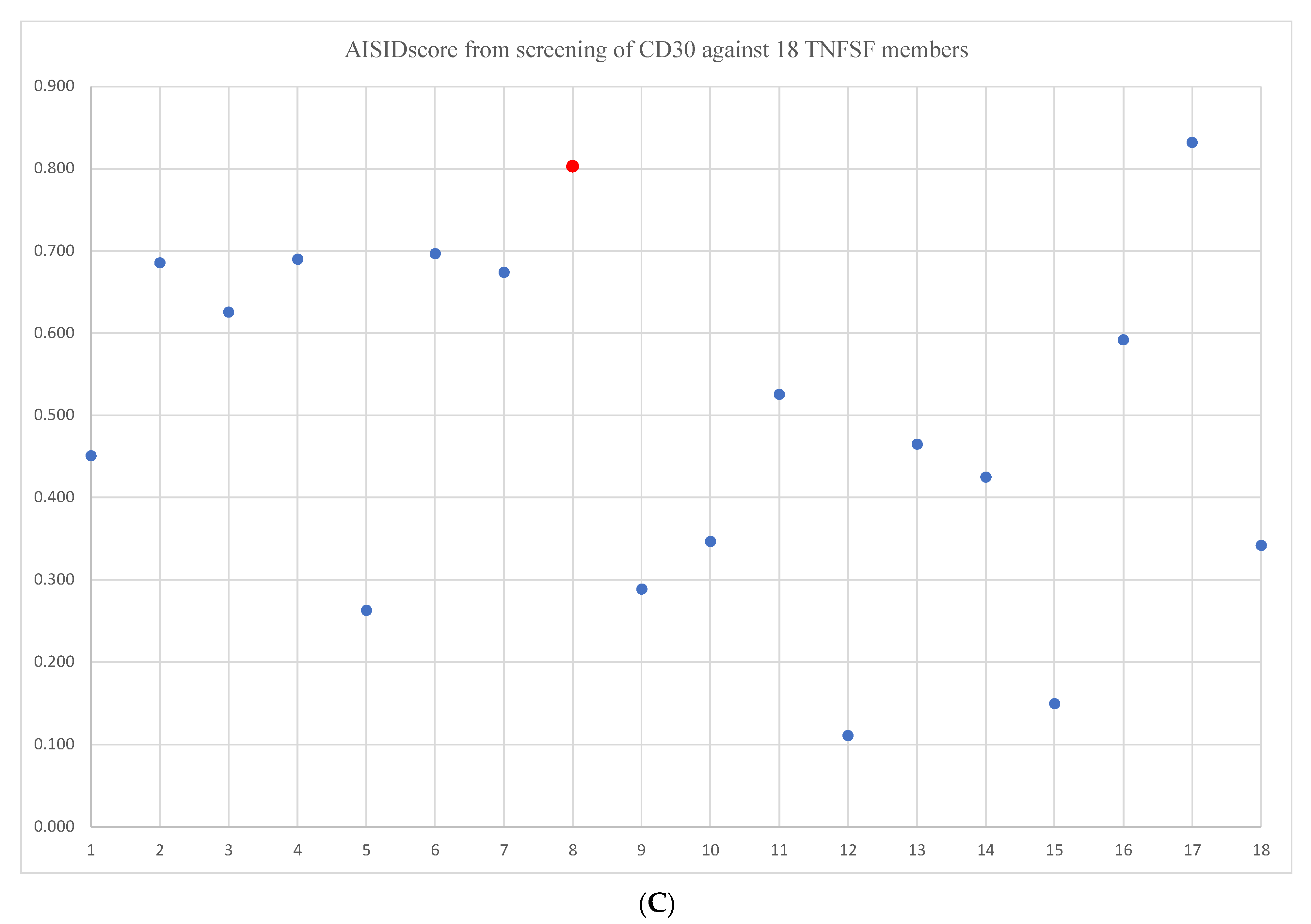
2. Results and Discussions
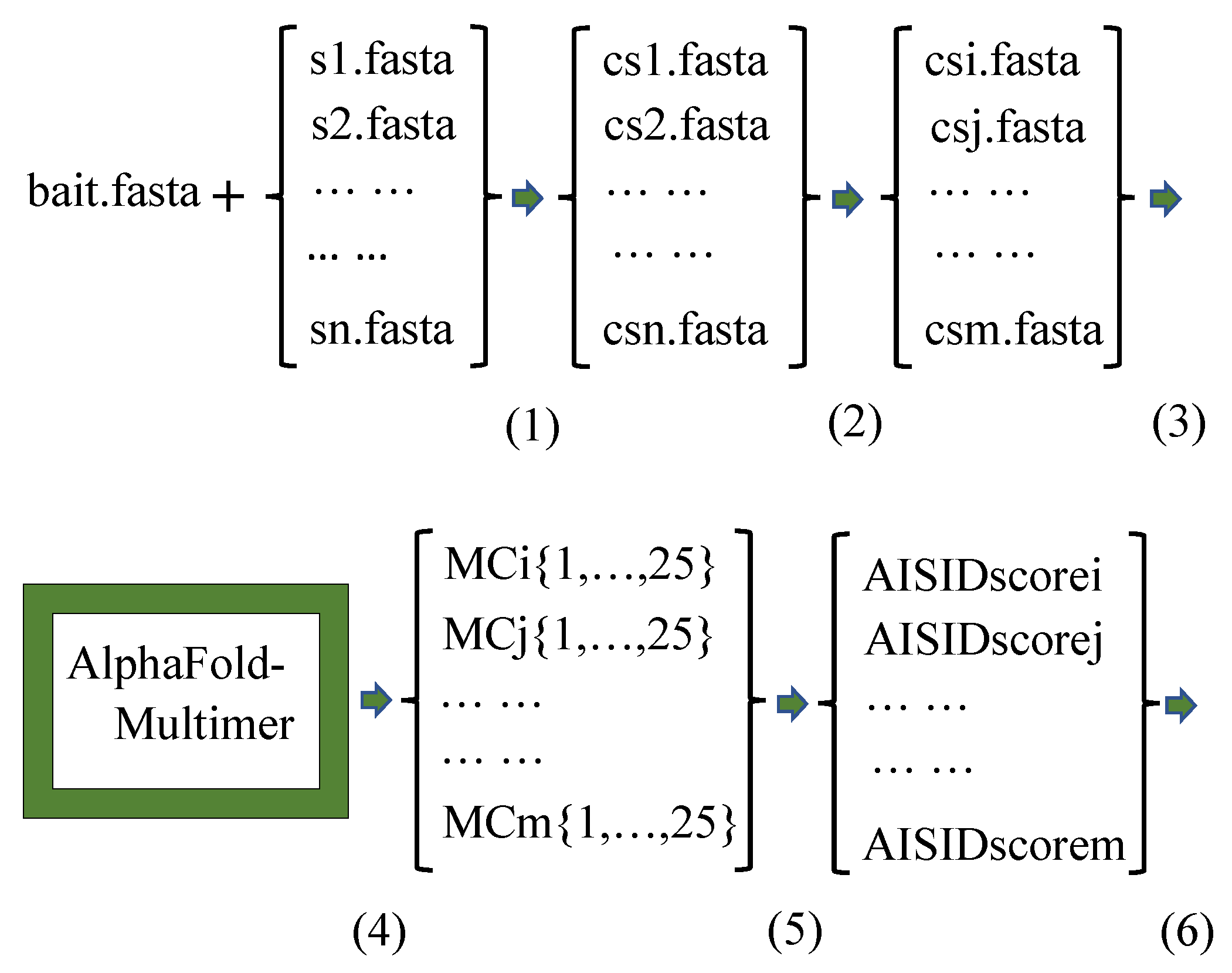
3. Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kryshtafovych, A.; Schwede, T.; Topf, M.; Fidelis, K.; Moult, J. Critical assessment of methods of protein structure prediction (CASP)-Round XIV. Proteins 2021, 89, 1607–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, M.; DiMaio, F.; Anishchenko, I.; Dauparas, J.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Lee, G.R.; Wang, J.; Cong, Q.; Kinch, L.N.; Schaeffer, R.D.; et al. Accurate prediction of protein structures and interactions using a three-track neural network. Science 2021, 373, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirdita, M.; Schutze, K.; Moriwaki, Y.; Heo, L.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Steinegger, M. ColabFold: Making protein folding accessible to all. Nat. Methods 2022, 19, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, P.; Pozzati, G.; Elofsson, A. Improved prediction of protein-protein interactions using AlphaFold2. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, I.R.; Pei, J.; Baek, M.; Krishnakumar, A.; Anishchenko, I.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Zhang, J.; Ness, T.J.; Banjade, S.; Bagde, S.R.; et al. Computed structures of core eukaryotic protein complexes. Science 2021, 374, eabm4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, N.Q.K.; Ho, Q.T.; Ou, Y.Y. Using two-dimensional convolutional neural networks for identifying GTP binding sites in Rab proteins. J. Bioinform. Comput. Biol. 2019, 17, 1950005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, N.Q.K.; Sandag, G.A.; Ou, Y.Y. Incorporating post translational modification information for enhancing the predictive performance of membrane transport proteins. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2018, 77, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R.; O’Neill, M.; Pritzel, A.; Antropova, N.; Senior, A.W.; Green, T.; Žídek, A.; Bates, R.; Blackwell, S.; Yim, J.; et al. Protein complex prediction with AlphaFold-Multimer. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Nakajima An, D.; Parks, J.M.; Skolnick, J. AF2Complex predicts direct physical interactions in multimeric proteins with deep learning. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tordai, H.; Suhajda, E.; Sillitoe, I.; Nair, S.; Varadi, M.; Hegedus, T. Comprehensive Collection and Prediction of ABC Transmembrane Protein Structures in the AI Era of Structural Biology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, R.; Feng, B.Y.; Varshney, A.; Pierce, B.G. Benchmarking AlphaFold for protein complex modeling reveals accuracy determinants. Protein Sci. 2022, 31, e4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verburgt, J.; Zhang, Z.; Kihara, D. Multi-level analysis of intrinsically disordered protein docking methods. Methods 2022, 204, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, Y.D.; Taldaev, A.; Lisitsa, A.V.; Ponomarenko, E.A.; Archakov, A.I. Prediction of Monomeric and Dimeric Structures of CYP102A1 Using AlphaFold2 and AlphaFold Multimer and Assessment of Point Mutation Effect on the Efficiency of Intra- and Interprotein Electron Transfer. Molecules 2022, 27, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UniProt, C. UniProt: The universal protein knowledgebase in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D480–D489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dostert, C.; Grusdat, M.; Letellier, E.; Brenner, D. The TNF Family of Ligands and Receptors: Communication Modules in the Immune System and Beyond. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 115–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucka, K.; Wajant, H. Receptor Oligomerization and Its Relevance for Signaling by Receptors of the Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Superfamily. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 615141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degli-Esposti, M.A.; Dougall, W.C.; Smolak, P.J.; Waugh, J.Y.; Smith, C.A.; Goodwin, R.G. The novel receptor TRAIL-R4 induces NF-kappaB and protects against TRAIL-mediated apoptosis, yet retains an incomplete death domain. Immunity 1997, 7, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery, J.G.; McDonnell, P.; Burke, M.B.; Deen, K.C.; Lyn, S.; Silverman, C.; Dul, E.; Appelbaum, E.R.; Eichman, C.; DiPrinzio, R.; et al. Osteoprotegerin is a receptor for the cytotoxic ligand TRAIL. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 14363–14367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, P.G.; Al-Shamkhani, A. Soluble CD30 binds to CD153 with high affinity and blocks transmembrane signaling by CD30. Eur. J. Immunol. 2002, 32, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beirnaert, E.; Desmyter, A.; Spinelli, S.; Lauwereys, M.; Aarden, L.; Dreier, T.; Loris, R.; Silence, K.; Pollet, C.; Cambillau, C.; et al. Bivalent Llama Single-Domain Antibody Fragments against Tumor Necrosis Factor Have Picomolar Potencies due to Intramolecular Interactions. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toto, A.; Malagrino, F.; Visconti, L.; Troilo, F.; Pagano, L.; Brunori, M.; Jemth, P.; Gianni, S. Templated folding of intrinsically disordered proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 6586–6593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| TNFSF/AISIDscore | Default | Cutoff Date 1 January 2016 |
|---|---|---|
| TNFα | 0.871 | 0.869 |
| TRAIL | 0.713 | 0.705 |
| 4-1BBL | 0.699 | 0.392 |
| LIGHT | 0.590 | 0.709 |
| TNFβ | 0.563 | 0.515 |
| TNFSF13 | 0.552 | 0.454 |
| TNFSF4 | 0.484 | 0.118 |
| TNFSF12 | 0.271 | 0.101 |
| TNFγ | 0.261 | 0.311 |
| CD70 | 0.233 | 0.353 |
| CD153 | 0.223 | 0.096 |
| TNFSF11 | 0.215 | 0.265 |
| TNFSF13B | 0.204 | 0.253 |
| TNFSF18 | 0.163 | 0.276 |
| FASLG | 0.161 | 0.155 |
| EDA | 0.150 | 0.158 |
| TNFSF15 | 0.098 | 0.089 |
| CD40LG | 0.081 | 0.082 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, Z.-Q.; Sha, H.L.; Sha, B. AI-Based Protein Interaction Screening and Identification (AISID). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11685. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911685
Fu Z-Q, Sha HL, Sha B. AI-Based Protein Interaction Screening and Identification (AISID). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(19):11685. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911685
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Zheng-Qing, Hansen L. Sha, and Bingdong Sha. 2022. "AI-Based Protein Interaction Screening and Identification (AISID)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 19: 11685. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911685
APA StyleFu, Z.-Q., Sha, H. L., & Sha, B. (2022). AI-Based Protein Interaction Screening and Identification (AISID). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(19), 11685. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911685





