A Survey on Computational Methods for Investigation on ncRNA-Disease Association through the Mode of Action Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Types of ncRNAs and Its Association with Diseases
2.1. miRNA
2.2. lncRNA
2.3. circRNA
2.4. The ceRNA Hypothesis
3. Databases
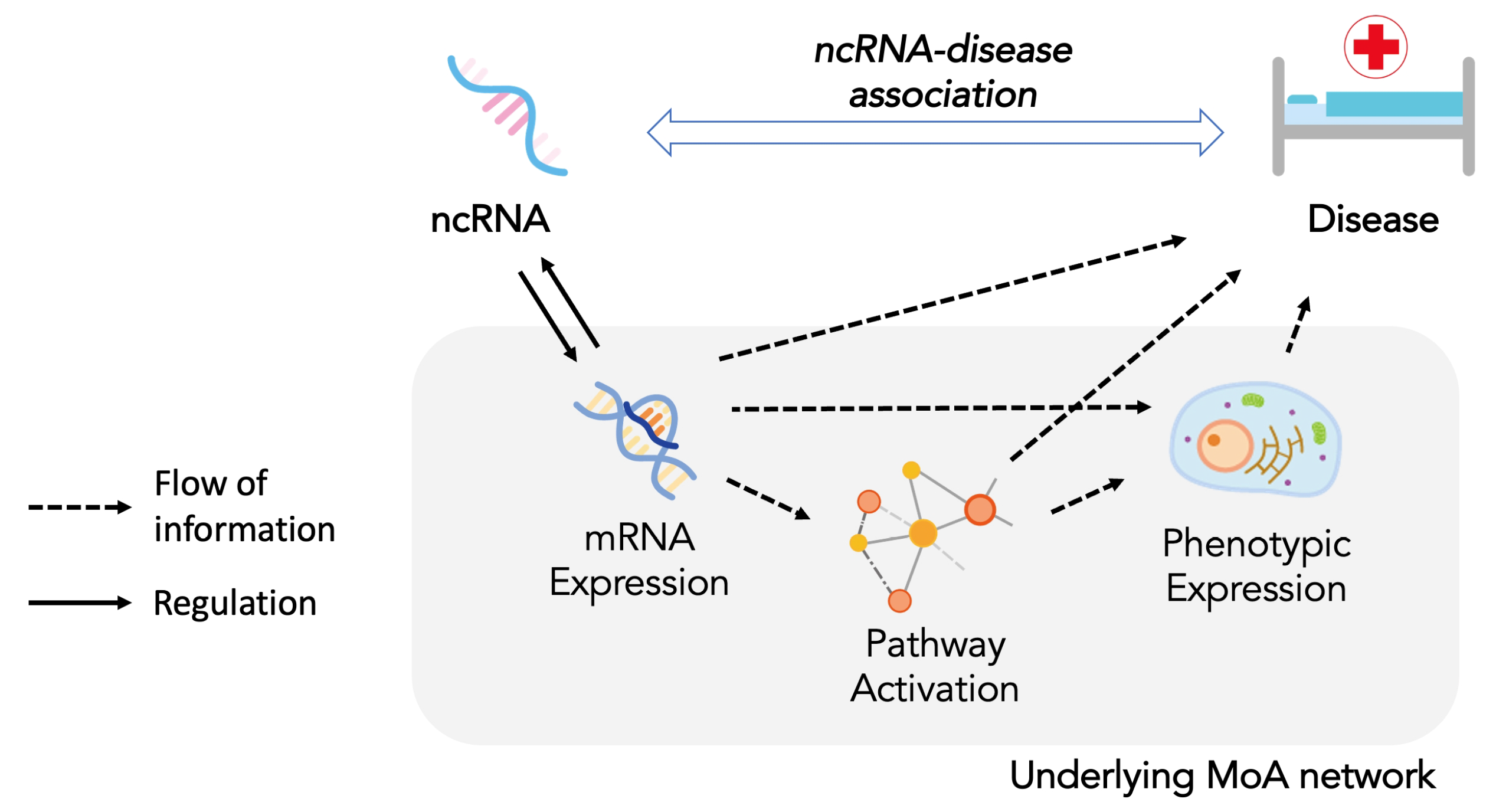
4. The Mode of Action Network for ncRNA-Disease Association
5. Computational Methodologies for Modeling the MoA Network
5.1. Methods for Mining on the MoA Network
5.1.1. Statistical Methods
5.1.2. Network Propagation
5.1.3. Random Walk-Based Methods
5.2. Methods for Learning on the MoA Network
5.2.1. Matrix Factorization
5.2.2. Graph Neural Networks
6. Computational ncRNA-Disease Association Studies
6.1. ncRNA-mRNA-Disease Network
6.1.1. Mining Based Studies
6.1.2. Learning Based Studies
6.2. ncRNA-mRNA-Pathway/Phenotype-Disease Network
Mining Based Studies
7. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ncRNA | non-coding RNA |
| miRNA | micro RNA |
| lncRNA | long non-coding RNA |
| circRNA | circular RNA |
| siRNA | small interfering RNA |
| piRNA | piwi-interacting RNA |
| ceRNA | competing endogenous RNA |
| ncDA | ncRNA-Disease association |
| miDA | miRNA-Disease association |
| lncDA | lncRNA-Disease association |
| circDA | circRNA-Disease association |
| MoA | Mode of Action |
| DE | Differentially Expressed |
| DEG | Differentially Expressed Gene |
| GNN | Graph Neural Network |
| RWR | Random Walk with Restart |
| NPC | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma |
| LUAD | Lung Adenocarcinoma |
| SNP | Single Nucleotide Polymorphism |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
References
- Jarroux, J.; Morillon, A.; Pinskaya, M. History, discovery, and classification of lncRNAs. Long Non Coding RNA Biol. 2017, 1008, 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Mattick, J.S.; Makunin, I.V. Non-coding RNA. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006, 15, R17–R29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, M.; Yang, D. Systematic identification of non-coding pharmacogenomic landscape in cancer. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkle, M.; El-Daly, S.M.; Fabbri, M.; Calin, G.A. Noncoding RNA therapeutics—Challenges and potential solutions. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 629–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.C.; Feinbaum, R.L.; Ambros, V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 1993, 75, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miska, E.A. How microRNAs control cell division, differentiation and death. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2005, 15, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.-Q.; Huang, J.-T.; Xiong, Y.-G.; Yang, X.-Y.; Han, R.; Zhu, W.-W. MicroRNA-96 regulates apoptosis by targeting PDCD4 in human glioma cells. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 16, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahesh, G.; Biswas, R. MicroRNA-155: A master regulator of inflammation. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2019, 39, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulay, P.; Sengupta, S.B. MicroRNA expression and its association with DNA repair in preimplantation embryos. J. Reprod. Dev. 2016, 62, 2015–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Glinge, C.; Clauss, S.; Boddum, K.; Jabbari, R.; Jabbari, J.; Risgaard, B.; Tomsits, P.; Hildebrand, B.; Kääb, S.; Wakili, R.; et al. Stability of circulating blood-based microRNAs–pre-analytic methodological considerations. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0167969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Tuazon, J.P.; Borlongan, C.V.; Yu, G. MicroRNA-133a and myocardial infarction. Cell Transplant. 2019, 28, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Guan, H. Investigating the expression of miRNA-133 in animal models of myocardial infarction and its effect on cardiac function. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 5934. [Google Scholar]
- Chistiakov, D.A.; Orekhov, A.N.; Bobryshev, Y.V. Cardiac-specific miRNA in cardiogenesis, heart function, and cardiac pathology (with focus on myocardial infarction). J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2016, 94, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dooley, J.; Garcia-Perez, J.E.; Sreenivasan, J.; Schlenner, S.M.; Vangoitsenhoven, R.; Papadopoulou, A.S.; Tian, L.; Schonefeldt, S.; Serneels, L.; Deroose, C.; et al. The microRNA-29 family dictates the balance between homeostatic and pathological glucose handling in diabetes and obesity. Diabetes 2016, 65, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Fullwood, M.J. Roles, functions, and mechanisms of long non-coding RNAs in cancer. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2016, 14, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatica, A.; Bozzoni, I. Long non-coding RNAs: New players in cell differentiation and development. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Liao, Y.T.; He, J.C.; Xie, C.L.; Chen, S.Y.; Fan, H.H.; Su, Z.P.; Wang, Z. Plasma long non-coding RNA BACE1 as a novel biomarker for diagnosis of Alzheimer disease. BMC Neurol. 2018, 18, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, P.; Luo, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Wu, W.; Du, Y.; Ye, B.; Wang, D.; He, L.; et al. LncRNA HAND2-AS1 promotes liver cancer stem cell self-renewal via BMP signaling. EMBO J. 2019, 38, e101110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, M.T.; Coca-Prados, M. Electron microscopic evidence for the circular form of RNA in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. Nature 1979, 280, 339–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.B.; Jensen, T.I.; Clausen, B.H.; Bramsen, J.B.; Finsen, B.; Damgaard, C.K.; Kjems, J. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 2013, 495, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, K.; Liu, C.; Liu, B.H.; Chen, X.; Dong, R.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Liu, B.; Zhang, S.J.; Wang, J.J.; et al. Circular noncoding RNA HIPK3 mediates retinal vascular dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. Circulation 2017, 136, 1629–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Luo, P.; Jing, W.; Zhou, H.; Liang, C.; Tu, J. circSMAD2 inhibits the epithelial–mesenchymal transition by targeting miR-629 in hepatocellular carcinoma. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enuka, Y.; Lauriola, M.; Feldman, M.E.; Sas-Chen, A.; Ulitsky, I.; Yarden, Y. Circular RNAs are long-lived and display only minimal early alterations in response to a growth factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 1370–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybak-Wolf, A.; Stottmeister, C.; Glažar, P.; Jens, M.; Pino, N.; Giusti, S.; Hanan, M.; Behm, M.; Bartok, O.; Ashwal-Fluss, R.; et al. Circular RNAs in the mammalian brain are highly abundant, conserved, and dynamically expressed. Mol. Cell 2015, 58, 870–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Y.; Chen, B.; Song, X.; Li, Y.; Liang, Y.; Han, D.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, T.; et al. circRNA_0025202 regulates tamoxifen sensitivity and tumor progression via regulating the miR-182-5p/FOXO3a axis in breast cancer. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 1638–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmena, L.; Poliseno, L.; Tay, Y.; Kats, L.; Pandolfi, P.P. A ceRNA hypothesis: The Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell 2011, 146, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poliseno, L.; Salmena, L.; Zhang, J.; Carver, B.; Haveman, W.J.; Pandolfi, P.P. A coding-independent function of gene and pseudogene mRNAs regulates tumour biology. Nature 2010, 465, 1033–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Wang, X.; Shi, H.; Cheng, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, H.; Yang, L.; Sun, J. Characterization of long non-coding RNA-associated ceRNA network to reveal potential prognostic lncRNA biomarkers in human ovarian cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 12598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Feng, L.; Li, F.; Sun, Z.; Wu, T.; Shi, X.; Li, J.; Li, X. Comprehensive characterization of lncRNA-mRNA related ceRNA network across 12 major cancers. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 64148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, R.S.; Zhang, E.X.; Sun, Q.F.; Ye, Z.J.; Liu, J.W.; Zhou, D.H.; Tang, Y. Integrated analysis of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA network in squamous cell carcinoma of tongue. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Shi, J.; Gao, Y.; Cui, C.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, Q. HMDD v3. 0: A database for experimentally supported human microRNA–disease associations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D1013–D1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Hao, Y.; Juan, L.; Teng, M.; Zhang, X.; Li, M.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y. miR2Disease: A manually curated database for microRNA deregulation in human disease. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D98–D104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Wu, L.; Wang, A.; Tang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Teschendorff, A.E. dbDEMC 2.0: Updated database of differentially expressed miRNAs in human cancers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D812–D818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, B.; Ding, Q.; Han, H.; Wu, D. miRCancer: A microRNA–cancer association database constructed by text mining on literature. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.; Yang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, Q.; Dong, D. LncRNADisease 2.0: An updated database of long non-coding RNA-associated diseases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D1034–D1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Shang, S.; Guo, S.; Li, X.; Zhou, H.; Liu, H.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, P.; Zhi, H.; et al. Lnc2Cancer 3.0: An updated resource for experimentally supported lncRNA/circRNA cancer associations and web tools based on RNA-seq and scRNA-seq data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D1251–D1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, L.; Cui, T.; Zheng, B.; Wang, N.; Luo, J.; Yang, B.; Du, M.; Cheng, J.; Dou, Y.; Wang, D. MNDR v3. 0: Mammal ncRNA–disease repository with increased coverage and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D160–D164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, K.; Wu, F.; Wang, W.; Zhang, K.; Hu, H.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, T. circRNA disease: A manually curated database of experimentally supported circRNA-disease associations. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Lei, X.; Tie, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, F.; Pan, Y. CircR2Disease v2. 0: An Updated Web Server for Experimentally Validated circRNA–disease Associations and Its Application. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2021; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rophina, M.; Sharma, D.; Poojary, M.; Scaria, V. Circad: A comprehensive manually curated resource of circular RNA associated with diseases. Database 2020, 2020, baaa019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; He, X.; Zhang, R.; Deng, W. LncR2metasta: A manually curated database for experimentally supported lncRNAs during various cancer metastatic events. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbaa178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Min, Z.; Liang, G.; Mo, J.; Ju, Z.; Zeng, B.; Guan, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; et al. circMine: A comprehensive database to integrate, analyze and visualize human disease–related circRNA transcriptome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D83–D92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Zhan, X.; Xiang, S.; Johnson, T.S.; Helm, B.; Yu, C.Y.; Zhang, J.; Salama, P.; Rizkalla, M.; Han, Z.; et al. SALMON: Survival analysis learning with multi-omics neural networks on breast cancer. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Li, R.; Dudek, S.M.; Ritchie, M.D. ATHENA: Identifying interactions between different levels of genomic data associated with cancer clinical outcomes using grammatical evolution neural network. BioData Min. 2013, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Shannon, C.P.; Gautier, B.; Rohart, F.; Vacher, M.; Tebbutt, S.J.; Lê Cao, K.A. DIABLO: An integrative approach for identifying key molecular drivers from multi-omics assays. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 3055–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Mezlini, A.M.; Demir, F.; Fiume, M.; Tu, Z.; Brudno, M.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Goldenberg, A. Similarity network fusion for aggregating data types on a genomic scale. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Shao, W.; Huang, Z.; Tang, H.; Zhang, J.; Ding, Z.; Huang, K. MOGONET integrates multi-omics data using graph convolutional networks allowing patient classification and biomarker identification. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Principles and Methods for the Risk Assessment of Chemicals in Food; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- Dellarco, V.L.; Wiltse, J.A. US Environmental Protection Agency’s revised guidelines for carcinogen risk assessment: Incorporating mode of action data. Mutat. Res. 1998, 405, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorio, F.; Bosotti, R.; Scacheri, E.; Belcastro, V.; Mithbaokar, P.; Ferriero, R.; Murino, L.; Tagliaferri, R.; Brunetti-Pierri, N.; Isacchi, A.; et al. Discovery of drug mode of action and drug repositioning from transcriptional responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14621–14626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarada, T.N.; Rokne, J.G.; Alhajj, R. A review of computational drug repositioning: Strategies, approaches, opportunities, challenges, and directions. J. Cheminform. 2020, 12, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frazee, A.C.; Pertea, G.; Jaffe, A.E.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L.; Leek, J.T. Ballgown bridges the gap between transcriptome assembly and expression analysis. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, N.; Dawson, J.A.; Thomson, J.A.; Ruotti, V.; Rissman, A.I.; Smits, B.M.; Haag, J.D.; Gould, M.N.; Stewart, R.M.; Kendziorski, C. EBSeq: An empirical Bayes hierarchical model for inference in RNA-seq experiments. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tibshirani, R. Finding consistent patterns: A nonparametric approach for identifying differential expression in RNA-Seq data. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 2013, 22, 519–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarazona, S.; Furió-Tarí, P.; Turrà, D.; Pietro, A.D.; Nueda, M.J.; Ferrer, A.; Conesa, A. Data quality aware analysis of differential expression in RNA-seq with NOISeq R/Bioc package. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, F.; Li, M.; Balch, C.; Thomson, M.; Fan, M.; Liu, Y.; Hammond, S.M.; Kim, S.; Nephew, K.P. Computational analysis of microRNA profiles and their target genes suggests significant involvement in breast cancer antiestrogen resistance. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowen, L.; Ideker, T.; Raphael, B.J.; Sharan, R. Network propagation: A universal amplifier of genetic associations. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2017, 18, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, M.; Jeong, D.; Moon, J.H.; Ann, H.; Hur, B.; Lee, S.; Kim, S. Network Propagation for the Analysis of Multi-omics Data. In Recent Advances in Biological Network Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 185–217. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.Y.; Yang, H.J.; Faloutsos, C.; Duygulu, P. Automatic multimedia cross-modal correlation discovery. In Proceedings of the Tenth ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Seattle, WA, USA, 22–25 August 2004; pp. 653–658. [Google Scholar]
- Valdeolivas, A.; Tichit, L.; Navarro, C.; Perrin, S.; Odelin, G.; Levy, N.; Cau, P.; Remy, E.; Baudot, A. Random walk with restart on multiplex and heterogeneous biological networks. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolov, T.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.; Dean, J. Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1301.3781. [Google Scholar]
- Grover, A.; Leskovec, J. node2vec: Scalable feature learning for networks. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 855–864. [Google Scholar]
- Koren, Y.; Bell, R.; Volinsky, C. Matrix factorization techniques for recommender systems. Computer 2009, 42, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, W.L.; Ying, R.; Leskovec, J. Representation learning on graphs: Methods and applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1709.05584. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, M.; Miao, J.; Guo, Y.; Gao, W.; Cui, Q. An analysis of human microRNA and disease associations. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Liu, M.X.; Yan, G.Y. RWRMDA: Predicting novel human microRNA–disease associations. Mol. BioSyst. 2012, 8, 2792–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, P.; Han, K.; Guo, Y.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, J. Prediction of potential disease-associated microRNAs based on random walk. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1805–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Gao, L.; Guo, X.; Shi, X.; Wu, H.; Song, F.; Wang, B. A network based method for analysis of lncRNA-disease associations and prediction of lncRNAs implicated in diseases. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Qu, J.; Guan, N.N.; Li, J.Q. Predicting miRNA–disease association based on inductive matrix completion. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 4256–4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X. Predicting lncRNA-disease associations and constructing lncRNA functional similarity network based on the information of miRNA. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yan, G.Y. Semi-supervised learning for potential human microRNA-disease associations inference. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yan, C.C.; Zhang, X.; You, Z.H.; Huang, Y.A.; Yan, G.Y. HGIMDA: Heterogeneous graph inference for miRNA-disease association prediction. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 65257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; You, Z.H.; Yan, G.Y.; Gong, D.W. IRWRLDA: Improved random walk with restart for lncRNA-disease association prediction. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 57919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Z.H.; Huang, Z.A.; Zhu, Z.; Yan, G.Y.; Li, Z.W.; Wen, Z.; Chen, X. PBMDA: A novel and effective path-based computational model for miRNA-disease association prediction. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, Y. ELLPMDA: Ensemble learning and link prediction for miRNA-disease association prediction. RNA Biol. 2018, 15, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Le, T.T.K.; Than, K.; Tran, D.H. Predicting miRNA–disease associations using improved random walk with restart and integrating multiple similarities. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, P.; Pan, S.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Y.; Sun, H. Graph convolutional network and convolutional neural network based method for predicting lncRNA-disease associations. Cells 2019, 8, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; You, Z.H.; Li, Y.M.; Zheng, K.; Huang, Y.A. GCNCDA: A new method for predicting circRNA-disease associations based on graph convolutional network algorithm. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2020, 16, e1007568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, N.; Huang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xuan, P.; Gao, L.; Cao, Y. Multi-channel graph attention autoencoders for disease-related lncRNAs prediction. Brief. Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbab604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Huang, Z.A.; Gu, W.; Han, K.; Pan, W.; Yang, X.; Zhu, Z. Prediction of biomarker–disease associations based on graph attention network and text representation. Brief. Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbac298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Yoon, W.; Kim, S.; Kim, D.; Kim, S.; So, C.H.; Kang, J. BioBERT: A pre-trained biomedical language representation model for biomedical text mining. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 1234–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, T.; Ning, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, W. Neural inductive matrix completion with graph convolutional networks for miRNA-disease association prediction. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 2538–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Gao, Z.; Ma, X.; Wu, Q.; Ni, J.; Zheng, C. AEMDA: Inferring miRNA–disease associations based on deep autoencoder. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Q.; Zhong, J.; Tang, X.; Luo, J. iCDA-CMG: Identifying circRNA-disease associations by federating multi-similarity fusion and collective matrix completion. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2021, 296, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, W.; Dong, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zheng, R.; Liu, J.; Pan, Y.; Chen, Y.P.P. KGANCDA: Predicting circRNA-disease associations based on knowledge graph attention network. Brief. Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbab494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Pan, H.; Qi, H.p.; Cao, Y.g.; Zhao, J.m.; Li, S.; Guo, J.; Sun, H.l.; et al. Construction and analysis of cardiac hypertrophy-associated lncRNA-mRNA network based on competitive endogenous RNA reveal functional lncRNAs in cardiac hypertrophy. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 10827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Chen, S.; Zhang, C.; Li, M.; Zheng, H. MYC and hsa-miRNA-423-5p as biomarkers in nasopharyngeal carcinoma revealed by miRNA-mRNA-pathway network integrated analysis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Ping, Y.; Zhao, H.; Ning, S.; Xia, P.; Wang, W.; Wan, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Yu, L.; et al. LncNetP, a systematical lncRNA prioritization approach based on ceRNA and disease phenotype association assumptions. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 114603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ding, L.; Wang, M.; Sun, D.; Li, A. TPGLDA: Novel prediction of associations between lncRNAs and diseases via lncRNA-disease-gene tripartite graph. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilk, G.; Braun, R. Integrative analysis reveals disrupted pathways regulated by microRNAs in cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 1089–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.-G.; Huang, X.-L.; Liang, S.-Y.; Tang, S.-M.; Wu, S.-K.; Huang, T.-T.; Mo, Z.-N.; Wang, Q.-Y. Identifying miRNA and gene modules of colon cancer associated with pathological stage by weighted gene co-expression network analysis. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Shukla, M.; Brettin, T.; Garcia-Cardona, C.; Cohn, J.; Allen, J.E.; Maslov, S.; Holbeck, S.L.; Doroshow, J.H.; Evrard, Y.A.; et al. Predicting tumor cell line response to drug pairs with deep learning. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, K.; Ran, L.; Song, F. Identification of functional lncRNAs in gastric cancer by integrative analysis of GEO and TCGA data. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 17898–17911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, G.; Kong, W.; Mou, X.; Wang, S. A new method for excavating feature lncRNA in lung adenocarcinoma based on pathway crosstalk analysis. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 9034–9046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhr, K.; Prager-van der Smissen, W.J.; Heine, A.A.; Ozturk, B.; van Jaarsveld, M.T.; Boersma, A.W.; Jager, A.; Wiemer, E.A.; Smid, M.; Foekens, J.A.; et al. MicroRNAs as possible indicators of drug sensitivity in breast cancer cell lines. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Zhu, N.; Guo, W.; Wang, X.; Li, K.; Yan, J.; Jiang, C.; Han, S.; Xiang, H.; Wu, X.; et al. RNA-Seq revealed a circular RNA-microRNA-mRNA regulatory network in Hantaan virus infection. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Yang, Y.; Yin, M. MHRWR: Prediction of lncRNA-disease associations based on multiple heterogeneous networks. IEEE/Acm Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2020, 18, 2577–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, D.H.; Tran, T.T. RWRMTN: A tool for predicting disease-associated microRNAs based on a microRNA-target gene network. BMC Bioinform. 2020, 21, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, T.; Zhou, W.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Wang, Q.; Jin, X.; Yin, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Pan-cancer characterization of immune-related lncRNAs identifies potential oncogenic biomarkers. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Shen, K.; Yin, N.; Jiang, M. Comprehensive transcriptomic analysis reveals dysregulated competing endogenous RNA network in endocrine resistant breast cancer cells. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 600487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Chen, H.Y.; Wang, L.; Song, S.J.; You, Z.H.; Yan, X.; Yu, J.Q. A structural deep network embedding model for predicting associations between miRNA and disease based on molecular association network. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Zhao, J.; Sun, T.; Shen, Z. A machine learning framework that integrates multi-omics data predicts cancer-related LncRNAs. BMC Bioinform. 2021, 22, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Ma, X. Predicting lincRNA-disease association in heterogeneous networks using co-regularized non-negative matrix factorization. Front. Genet. 2021, 11, 622234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Xu, S.; Zhang, H.; Lu, X.; Li, S.; Liu, L.; Kong, X.; Gao, H.; Wang, X.; Ning, S.; et al. Competitive endogenous RNA network and pathway-based analysis of LncRNA single-nucleotide polymorphism in myasthenia gravis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Cui, Y.; Ding, X.; Liu, S.; Han, B.; Duan, X.; Zhang, H.; Sun, T. Analysis of mRNA-lncRNA and mRNA-lncRNA-pathway co-expression networks based on WGCNA in developing pediatric sepsis. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 1457–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evangelista, A.F.; Oliveira, R.J.; Silva, V.A.O.; Vieira, R.A.D.C.; Reis, R.M.; Marques, M.M.C. Integrated analysis of mRNA and miRNA profiles revealed the role of miR-193 and miR-210 as potential regulatory biomarkers in different molecular subtypes of breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ai, H.; Li, B.; Zhang, C.; Meng, F.; Ai, Y. MIMRDA: A Method Incorporating the miRNA and mRNA Expression Profiles for Predicting miRNA-Disease Associations to Identify Key miRNAs (microRNAs). Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 825318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Gao, L. MiRNA–disease association prediction based on meta-paths. Brief. Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbab571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabaie, H.; Moghaddam, M.M.; Moghaddam, M.M.; Ahangar, N.K.; Asadi, M.R.; Hussen, B.M.; Taheri, M.; Rezazadeh, M. Bioinformatics analysis of long non-coding RNA-associated competing endogenous RNA network in schizophrenia. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shang, M.; Dai, Q.; He, P.A. Prediction of lncRNA-disease association based on a Laplace normalized random walk with restart algorithm on heterogeneous networks. BMC Bioinform. 2022, 23, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousef, M.; Goy, G.; Bakir-Gungor, B. miRModuleNet: Detecting miRNA-mRNA regulatory modules. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 767455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Duan, L.; Zheng, H.; Li-Ling, J.; Song, L.; Li, L. Graph convolutional network approach to discovering disease-related circRNA-miRNA-mRNA axes. Methods 2022, 198, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. WGCNA: An R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, W.; Jiang, X.X.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Y.R.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, D.M. Comprehensive analysis of the ceRNA network in coronary artery disease. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Ding, Z.; Tao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Fu, Y. Generative multi-view human action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6212–6221. [Google Scholar]
- Mens, M.M.; Maas, S.C.; Klap, J.; Weverling, G.J.; Klatser, P.; Brakenhoff, J.P.; van Meurs, J.B.; Uitterlinden, A.G.; Ikram, M.A.; Kavousi, M.; et al. Multi-omics analysis reveals microRNAs associated with cardiometabolic traits. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Jing, Y.; Wei, F.; Tang, Y.; Yang, L.; Luo, J.; Yang, P.; Ni, Q.; Pang, J.; Liao, Q.; et al. Long non-coding RNA PVT1 predicts poor prognosis and induces radioresistance by regulating DNA repair and cell apoptosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuenzi, B.M.; Park, J.; Fong, S.H.; Sanchez, K.S.; Lee, J.; Kreisberg, J.F.; Ma, J.; Ideker, T. Predicting drug response and synergy using a deep learning model of human cancer cells. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 672–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, M.; Park, S.; Lee, S.; Lee, D.; Lim, S.; Jeong, D.; Jo, K.; Jung, I.; Kim, S. DRIM: A web-based system for investigating drug response at the molecular level by condition-specific multi-omics data integration. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Database | ncRNA Type | Description | URL |
|---|---|---|---|
| HMDD v3.2 [31] | miRNA | This database contains experimentally supported, manually curated evidence for the associations between human miRNAs and diseases. | https://www.cuilab.cn/hmdd, accessed on 26 August 2022 |
| miR2Disease [32] | miRNA | This database is a manually curated database providing a comprehensive resource of miRNA deregulation in human diseases. | http://www.mir2disease.org/, accessed on 26 August 2022 |
| dbDEMC [33] | miRNA | This database is an integrated database designed to retain and show differentially expressed miRNAs in cancers detected by high-throughput and low-throughput methods. | https://www.biosino.org/dbDEMC/index, accessed on 26 August 2022 |
| miRCancer [34] | miRNA | This database provides a comprehensive collection of miRNA expression profiles from various human cancers. | http://mircancer.ecu.edu/, accessed on 26 August 2022 |
| LncRNADisease v2.0 [35] | lncRNA circRNA | This database integrated comprehensive experimentally supported and predicted lncRNA- and circRNA-disease associations curated from manual literatures and other resources. | http://www.rnanut.net/lncrnadisease/index.php/home, accessed on 26 August 2022 |
| Lnc2Cancer 3.0 [36] | lncRNA circRNA | This database is a manually curated database that provides comprehensive experimentally supported associations between lncRNA or circRNA and human cancer, with regulatory mechanisms, biological function, and clinical application. | http://bio-bigdata.hrbmu.edu.cn/lnc2cancer/, accessed on 26 August 2022 |
| MNDR v3.1 [37] | miRNA lncRNA circRNA | This database integrated various kinds of mammalian ncDA through manual curation and prediction algorithms. | https://www.rna-society.org/mndr/home.html, accessed on 26 August 2022 |
| CircRNADisease [38] | circRNA | This database contains a manually curated experimentally supported human circRNA-disease association. | http://cgga.org.cn:9091/circRNADisease/, accessed on 26 August 2022 |
| CircR2Disease v2.0 [39] | circRNA | This database provides experimentally validated circRNA-disease association. | http://bioinfo.snnu.edu.cn/CircR2Disease_v2.0/, accessed on 26 August 2022 |
| circAD [40] | circRNA | This database is a manually curated resource for dysregulated circRNAs in disease, with primer details for respective circRNAs and information about related genes. | https://clingen.igib.res.in/circad/, accessed on 26 August 2022 |
| LncR2metasta [41] | lncRNA | This database is a manually curated database providing experimentally supported lncRNAs that are deregulated in cancer metastatic events, such as cancer cell invasion, proliferation and so on. | http://lncr2metasta.wchoda.com/, accessed on 26 August 2022 |
| CircMine [42] | circRNA | This database provides comprehensive interactions between circRNAs and diseases with various physiological and pathological phenotypes, including drug resistance, disease stage, and so on. | http://www.biomedical-web.com/circmine/home, accessed on 26 August 2022 |
| Direct ncRNA-Disease Association | ncRNA-mRNA-Disease | ncRNA-mRNA-Pathway /Phenotype-Disease | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Mining | Learning | Mining | Learning | Mining | Learning |
| ∼ 2017 | RWRMDA [69] RLSMDA [74] Yang et al. [71] HGLDA [73] MIDP [70] HGIMDA [75] IRWRLDA [76] PBMDA [77] | Song et al. [89] | Tian et al. [90] LncNetP [91] | |||
| 2018 | ELLPMDA [78] | TPGLDA [92] | Wilk et al. [93] Zhou et al. [94] Xia et al. [95] | |||
| 2019 | Xuan et al. [80] | Zhang et al. [96] | DIABLO [45] Qi et al. [97] Uhr et al. [98] | |||
| 2020 | GCNCDA [81] Li et al. [85] | Lu et al. [99] MHRWR [100] RWRMTN [101] | ImmLnc [102] Gao et al. [103] | |||
| 2021 | Nguyen et al. [79] | AEMDA [86] iCDA-CMG [87] | SDNE-MDA [104] | MOGONET [47] LGDLDA [105] Cr-NMF [106] | Wang et al. [107] Zhang et al. [108] Evangelista et al. [109] | |
| 2022 | MGATE [82] GTGenie [83] KGANCDA [88] | MIMRDA [110] MDPBMP [111] Sabaie et al. [112] LRWRHLDA [113] | miRModuleNet [114] DRAMA [115] | |||
| Tool | Year | Method | Software Language | Input | Output | Performance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RWRMDA [69] | 2012 | RWR | N/A | known miDA, mi-mi | predicted miDA | AUROC | 0.8617 |
| MIDP [70] | 2015 | RWR | N/A | known miDA, D-D | predicted miDA | AUROC | 0.862 |
| HGLDA [73] | 2015 | Statistical | N/A | known lncDA, , | predicted lncDA | AUROC | 0.7621 |
| IMCMDA [72] | 2018 | MF | Matlab | known miDA, , mi-mi | predicted miDA | AUROC | 0.8034 |
| GCNCDA [81] | 2020 | GNN | Matlab | known circDA, D-D | predicted circDA | AUROC Accuracy | 0.9090 0.9278 |
| Nguyen et al. [79] | 2021 | RWR | N/A | known miDA, | predicted miDA | AUROC AUPR | 0.9882 0.9066 |
| MGATE [82] | 2022 | GNN | Python | known lncDA, , , | predicted lncDA | AUROC AUPR | 0.964 0.413 |
| GTGenie [83] | 2022 | GNN | Python | known miDA, Text decription of ncDA, D-D , nc-nc | predicted ncDA | miDA AUROC lncDA AUROC | 0.9755 0.9810 |
| Tool | Year | Method | Software Language | Input | Output | Performance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MOGONET [47] | 2021 | GNN | Python | Multi-omics profile | Predicted phenotype Rank of biomarkers | - | |
| MHRWR [100] | 2021 | RWR | Python | known lncDA, , | Predicted lncDA | AUROC | 0.9134 |
| MIMRDA [110] | 2022 | Statistical | R | DE miRNA, DE mRNA, | Rank of miRNAs | - | |
| MDPBMP [111] | 2022 | GNN | Python | known miDA, , | Predicted miDA | AUROC | 0.9214 |
| miRModuleNet [114] | 2022 | Statistical | Python | known miDA, miRNA Exp, mRNA Exp, | Predicted phenotype Rank of miRNA modules | - | |
| LGDLDA [105] | 2021 | GNN | Matlab | known lncDA, lncRNA expression, , , , , | Predicted lncDA | AUROC | 0.9352 |
| Tool | Year | Method | Software Language | Input | Output |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wilk et al. [93] | 2018 | Statistical | R | mRNA Exp, miRNA Exp, | Disease-related miRNA-pathway pair |
| Xia et al. [95] | 2018 | Deep learning | Python | mRNA Exp, miRNA Exp, Protein abundance, Drug descriptors | Predicted drug response Gene, protein, miRNA biomarkers |
| DIABLO [45] | 2019 | Statistical | R | Multi-omics profiles | Predicted phenotype Rank of biomarkers |
| ImmLnc [102] | 2020 | Statistical | Web page | mRNA Exp, lncRNA Exp | Predicted phenotype Rank of lncRNAs |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bang, D.; Gu, J.; Park, J.; Jeong, D.; Koo, B.; Yi, J.; Shin, J.; Jung, I.; Kim, S.; Lee, S. A Survey on Computational Methods for Investigation on ncRNA-Disease Association through the Mode of Action Perspective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11498. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911498
Bang D, Gu J, Park J, Jeong D, Koo B, Yi J, Shin J, Jung I, Kim S, Lee S. A Survey on Computational Methods for Investigation on ncRNA-Disease Association through the Mode of Action Perspective. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(19):11498. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911498
Chicago/Turabian StyleBang, Dongmin, Jeonghyeon Gu, Joonhyeong Park, Dabin Jeong, Bonil Koo, Jungseob Yi, Jihye Shin, Inuk Jung, Sun Kim, and Sunho Lee. 2022. "A Survey on Computational Methods for Investigation on ncRNA-Disease Association through the Mode of Action Perspective" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 19: 11498. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911498
APA StyleBang, D., Gu, J., Park, J., Jeong, D., Koo, B., Yi, J., Shin, J., Jung, I., Kim, S., & Lee, S. (2022). A Survey on Computational Methods for Investigation on ncRNA-Disease Association through the Mode of Action Perspective. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(19), 11498. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911498






