Lipid-Drug Conjugates and Nanoparticles for the Cutaneous Delivery of Cannabidiol
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Lipid-Drug Conjugates
- The traditional pharmaceutical formulas (e.g., creams and ointments) have responded to different pathologies as much as possible;
- Unlike many other structures and organs, the skin’s composition allows a broad absorption of hydrophilic and lipophilic drugs;
- Simply the development of other transport mechanisms, such as the phospholipid micelles.
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Souto, E.B.; Silva, G.F.; Dias-Ferreira, J.; Zielinska, A.; Ventura, F.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Novellino, E.; Santini, A. Nanopharmaceutics: Part I—Clinical Trials Legislation and Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) of Nanotherapeutics in the EU. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souto, E.B.; Silva, G.F.; Dias-Ferreira, J.; Zielinska, A.; Ventura, F.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Novellino, E.; Santini, A. Nanopharmaceutics: Part II-Production Scales and Clinically Compliant Production Methods. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.M.; Lee, S.H.; Sohn, B.H.; Song, O. Micellar nanotubes and AAO nanopores decorated with nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 0957–4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, L.; Dougan, J.A.; Faulds, K.; Graham, D. Stable dye-labelled oligonucleotide-nanoparticle conjugates for nucleic acid detection. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 3221–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betigeri, S.; Zhang, M.; Garbuzenko, O.; Minko, T. Non-viral systemic delivery of siRNA or antisense oligonucleotides targeted to Jun N-terminal kinase 1 prevents cellular hypoxic damage. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2011, 1, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Carlring, J.; Szabo, M.J.; Dickinson, R.; De Leenheer, E.; Heath, A.W. Conjugation of lymphoma idiotype to CD40 antibody enhances lymphoma vaccine immunogenicity and antitumor effects in mice. Blood 2012, 119, 2056–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Wu, J.; Sawa, T.; Matsumura, Y.; Hori, K. Tumor vascular permeability and the EPR effect in macromolecular therapeutics: A review. J. Control. Release 2000, 65, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Akaike, T.; Hayashida, K.; Okamoto, T.; Okuyama, A.; Maeda, H. Enhanced Vascular Permeability in Solid Tumor Involving Peroxynitrite and Matrix Metalloproteinases. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 2001, 92, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmaso, S.; Pappalardo, J.S.; Sawant, R.R.; Musacchio, T.; Rockwell, K.; Caliceti, P.; Torchilin, V.P. Targeting glioma cells in vitro with ascorbate-conjugated pharmaceutical nanocarriers. Bioconjug. Chem. 2009, 20, 2348–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torchilin, V.P. Micellar nanocarriers: Pharmaceutical perspectives. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torchilin, V.P. Polymer-coated long-circulating microparticulate pharmaceuticals. J. Microencapsul. 1998, 15, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Mongayt, D.; Torchilin, V.P. Polymeric micelles for delivery of poorly soluble drugs: Preparation and anticancer activity in vitro of paclitaxel incorporated into mixed micelles based on poly(ethylene glycol)-lipid conjugate and positively charged lipids. J. Drug Target 2005, 13, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Petrenko, V.A.; Torchilin, V.P. Paclitaxel-Loaded Polymeric Micelles Modified with MCF-7 Cell-Specific Phage Protein: Enhanced Binding to Target Cancer Cells and Increased Cytotoxicity. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawant, R.R.; Torchilin, V.P. Design and synthesis of novel functional lipid-based bioconjugates for drug delivery and other applications. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 751, 357–378. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wissing, S.A.; Kayser, O.; Muller, R.H. Solid lipid nanoparticles for parenteral drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 1257–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Date, A.A.; Joshi, M.D.; Patravale, V.B. Parasitic diseases: Liposomes and polymeric nanoparticles versus lipid nanoparticles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 505–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, M.D.; Unger, W.J.; Storm, G.; van Kooyk, Y.; Mastrobattista, E. Targeting tumor antigens to dendritic cells using particulate carriers. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 46, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A. Drug-like properties and the causes of poor solubility and poor permeability. J Pharm. Toxicol Methods 2000, 44, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Yalkowsky, S.H. Solubilization of poorly soluble compounds using 2-pyrrolidone. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 342, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.K.; Chourasia, M.K.; Masuriha, R.; Soni, V.; Jain, A.; Jain, N.K.; Gupta, Y. Solid lipid nanoparticles bearing flurbiprofen for transdermal delivery. Drug Deliv. 2005, 12, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Khare, P.; Jain, A.; Jain, N.K.; Soni, V.; Jain, S.K. Glutamate-conjugated liposomes of dopamine hydrochloride for effective management of parkinsonism’s. PDA J. Pharm. Sci. Technol. 2009, 63, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mishra, P.K.; Gulbake, A.; Jain, A.; Vyas, S.P.; Jain, S.K. Targeted delivery of an anti-cancer agent via steroid coupled liposomes. Drug Deliv. 2009, 16, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millard, J.; Alvarez-Nunez, F.; Yalkowsky, S. Solubilization by cosolvents. Establishing useful constants for the log-linear model. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 245, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Y.; Jain, A.; Yalkowsky, S.H. Solubilization and Preformulation Studies on PG-300995 (An Anti-HIV Drug). J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 94, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawat, M.K.; Jain, A.; Singh, S. Studies on binary lipid matrix based solid lipid nanoparticles of repaglinide: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. J. Pharm. Sci 2011, 100, 2366–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musacchio, T.; Vaze, O.; D’Souza, G.; Torchilin, V.P. Effective stabilization and delivery of siRNA: Reversible siRNA-phospholipid conjugate in nanosized mixed polymeric micelles. Bioconjug. Chem. 2010, 21, 1530–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijani, A.O.; Thakur, D.; Mishra, D.; Frempong, D.; Chukwunyere, U.I.; Puri, A. Delivering therapeutic cannabinoids via skin: Current state and future perspectives. J. Control. Release 2021, 334, 427–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudinoodezh, H.; Telukutla, S.R.; Bhangu, S.K.; Bachari, A.; Cavalieri, F.; Mantri, N. The Transdermal Delivery of Therapeutic Cannabinoids. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atalay, S.; Gęgotek, A.; Wroński, A.; Domigues, P.; Skrzydlewska, E. Therapeutic application of cannabidiol on UVA and UVB irradiated rat skin. A proteomic study. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 192, 113656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jastrząb, A.; Jarocka-Karpowicz, I.; Markowska, A.; Wroński, A.; Gęgotek, A.; Skrzydlewska, E. Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Effect of Cannabidiol Contributes to the Decreased Lipid Peroxidation of Keratinocytes of Rat Skin Exposed to UV Radiation. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 6647222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, H.; Xu, F.; Jiang, X.; Ma, H.; Seeram, N.P. Cannabidiol Protects Human Skin Keratinocytes from Hydrogen-Peroxide-Induced Oxidative Stress via Modulation of the Caspase-1–IL-1β Axis. J. Nat. Prod. 2021, 84, 1563–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikarashi, N.; Shiseki, M.; Yoshida, R.; Tabata, K.; Kimura, R.; Watanabe, T.; Kon, R.; Sakai, H.; Kamei, J. Cannabidiol Application Increases Cutaneous Aquaporin-3 and Exerts a Skin Moisturizing Effect. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burch, R.; Mortuza, A.; Blumenthal, E.; Mustafa, A. Effects of cannabidiol (CBD) on the inhibition of melanoma cells in vitro. J. Immunoass. Immunochem. 2021, 42, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelliah, M.P.; Zinn, Z.; Khuu, P.; Teng, J.M.C. Self-initiated use of topical cannabidiol oil for epidermolysis bullosa. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2018, 35, e224–e227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oláh, A.; Tóth, B.I.; Borbíró, I.; Sugawara, K.; Szöllõsi, A.G.; Czifra, G.; Pál, B.; Ambrus, L.; Kloepper, J.; Camera, E.; et al. Cannabidiol exerts sebostatic and antiinflammatory effects on human sebocytes. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 3713–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaneto, M.S.; Gorelick, D.A.; Desrosiers, N.A.; Hartman, R.L.; Pirard, S.; Huestis, M.A. Synthetic cannabinoids: Epidemiology, pharmacodynamics, and clinical implications. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014, 144, 12–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baswan, S.M.; Klosner, A.E.; Glynn, K.; Rajgopal, A.; Malik, K.; Yim, S.; Stern, N. Therapeutic Potential of Cannabidiol (CBD) for Skin Health and Disorders. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2020, 13, 927–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.Y.; Sharan, S.; Woo, S. Model-Based Analysis of Cannabidiol Dose-Exposure Relationship and Bioavailability. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2020, 40, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, S.A.; Maguire, R.F.; Yates, A.S.; O’Sullivan, S.E. Towards better delivery of cannabidiol (CBD). Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodzki, M.; Godin, B.; Rakou, L.; Mechoulam, R.; Gallily, R.; Touitou, E. Cannabidiol—transdermal delivery and anti-inflammatory effect in a murine model. J. Control. Release 2003, 93, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francke, N.M.; Schneider, F.; Baumann, K.; Bunjes, H. Formulation of Cannabidiol in Colloidal Lipid Carriers. Molecules 2021, 26, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharkawy, A.; Silva, A.M.; Rodrigues, F.; Barreiro, F.; Rodrigues, A. Pickering emulsions stabilized with chitosan/collagen peptides nanoparticles as green topical delivery vehicles for cannabidiol (CBD). Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 631, 127677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkawy, A.; Barreiro, F.; Rodrigues, A. Pickering emulsions stabilized with chitosan/gum Arabic particles: Effect of chitosan degree of deacetylation on the physicochemical properties and cannabidiol (CBD) topical delivery. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 355, 118993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanti, G.; Grifoni, L.; Bergonzi, M.C.; Antiga, E.; Montefusco, F.; Caproni, M.; Bilia, A.R. Development and optimisation of biopharmaceutical properties of a new microemulgel of cannabidiol for locally-acting dermatological delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 607, 121036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheriff, T.; Lin, M.J.; Dubin, D.; Khorasani, H. The potential role of cannabinoids in dermatology. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2020, 31, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, C.; Massick, S.; Kaffenberger, B.H.; Kwatra, S.G.; Bechtel, M. Cannabinoids for the treatment of chronic pruritus: A review. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 82, 1205–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muchow, M.; Maincent, P.; Muller, R.H. Lipid nanoparticles with a solid matrix (SLN, NLC, LDC) for oral drug delivery. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2008, 34, 1394–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olbrich, C.; Gessner, A.; Schröder, W.; Kayser, O.; Müller, R.H. Lipid-drug conjugate nanoparticles of the hydrophilic drug diminazene-cytotoxicity testing and mouse serum adsorption. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2004, 96, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, R.H.; Keck, C.M. Drug delivery to the brain--realization by novel drug carriers. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2004, 4, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, R.H.; Maassen, S.; Weyhers, H.; Mehnert, W. Phagocytic uptake and cytotoxicity of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) sterically stabilized with poloxamine 908 and poloxamer 407. J. Drug Target 1996, 4, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyhers, H.; Ehlers, S.; Hahn, H.; Souto, E.B.; Muller, R.H. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN)--effects of lipid composition on in vitro degradation and in vivo toxicity. Pharmazie 2006, 61, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Olbrich, C.; Gessner, A.; Kayser, O.; Muller, R.H. Lipid-drug-conjugate (LDC) nanoparticles as novel carrier system for the hydrophilic antitrypanosomal drug diminazenediaceturate. J. Drug Target 2002, 10, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doktorovova, S.; Shegokar, R.; Rakovsky, E.; Gonzalez-Mira, E.; Lopes, C.M.; Silva, A.M.; Martins-Lopes, P.; Muller, R.H.; Souto, E.B. Cationic solid lipid nanoparticles (cSLN): Structure, stability and DNA binding capacity correlation studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 420, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, E.B.; Muller, R.H. Lipid nanoparticles: Effect on bioavailability and pharmacokinetic changes. Handb. Exp. Pharm. 2010, 197, 115–141. [Google Scholar]
- Durán, N.; Durán, M.; Tasic, L.; Marcato, P.D. Tecnologia de nanocristais em fármacos. Química Nova 2010, 33, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Marcato, P.D.; Caverzan, J.; Rossi-Bergmann, B.; Pinto, E.F.; Machado, D.; Silva, R.A.; Justo, G.Z.; Ferreira, C.V.; Durán, N. Nanostructured Polymer and Lipid Carriers for Sunscreen. Biological Effects and Skin Permeation. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 11, 1880–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessner, A.; Olbrich, C.; Schröder, W.; Kayser, O.; Müller, R.H. The role of plasma proteins in brain targeting: Species dependent protein adsorption patterns on brain-specific lipid drug conjugate (LDC) nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 214, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, J.A. Estradiol in micellar nanoparticles: The efficacy and safety of a novel transdermal drug-delivery technology in the management of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms. Menopause 2006, 13, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egusquiaguirre, S.P.; Igartua, M.; Hernandez, R.M.; Pedraz, J.L. Nanoparticle delivery systems for cancer therapy: Advances in clinical and preclinical research. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2012, 14, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Maghraby, G.M.; Barry, B.W.; Williams, A.C. Liposomes and skin: From drug delivery to model membranes. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 34, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Maghraby, G.M.; Campbell, M.; Finnin, B.C. Mechanisms of action of novel skin penetration enhancers: Phospholipid versus skin lipid liposomes. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 305, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Maghraby, G.M.; Williams, A.C.; Barry, B.W. Skin delivery of 5-fluorouracil from ultradeformable and standard liposomes in-vitro. J. Pharm. Pharm. 2001, 53, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Maghraby, G.M.; Williams, A.C.; Barry, B.W. Oestradiol skin delivery from ultradeformable liposomes: Refinement of surfactant concentration. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 196, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukyanov, A.N.; Gao, Z.; Torchilin, V.P. Micelles from polyethylene glycol/phosphatidylethanolamine conjugates for tumor drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2003, 91, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukyanov, A.N.; Torchilin, V.P. Micelles from lipid derivatives of water-soluble polymers as delivery systems for poorly soluble drugs. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 1273–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katragadda, U.; Teng, Q.; Rayaprolu, B.M.; Chandran, T.; Tan, C. Multi-drug delivery to tumor cells via micellar nanocarriers. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 419, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.H.; Jin, S.E.; Lee, M.K.; Lim, S.J.; Park, J.S.; Kim, B.G.; Ahn, W.S.; Kim, C.K. Novel cationic solid lipid nanoparticles enhanced p53 gene transfer to lung cancer cells. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 68, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, K.K.; Rousing, M.L.; Jensen, C.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Gazerani, P. Effect of local controlled heat on transdermal delivery of nicotine. Int. J. Physiol. Pathophysiol. Pharm. 2011, 3, 236–242. [Google Scholar]
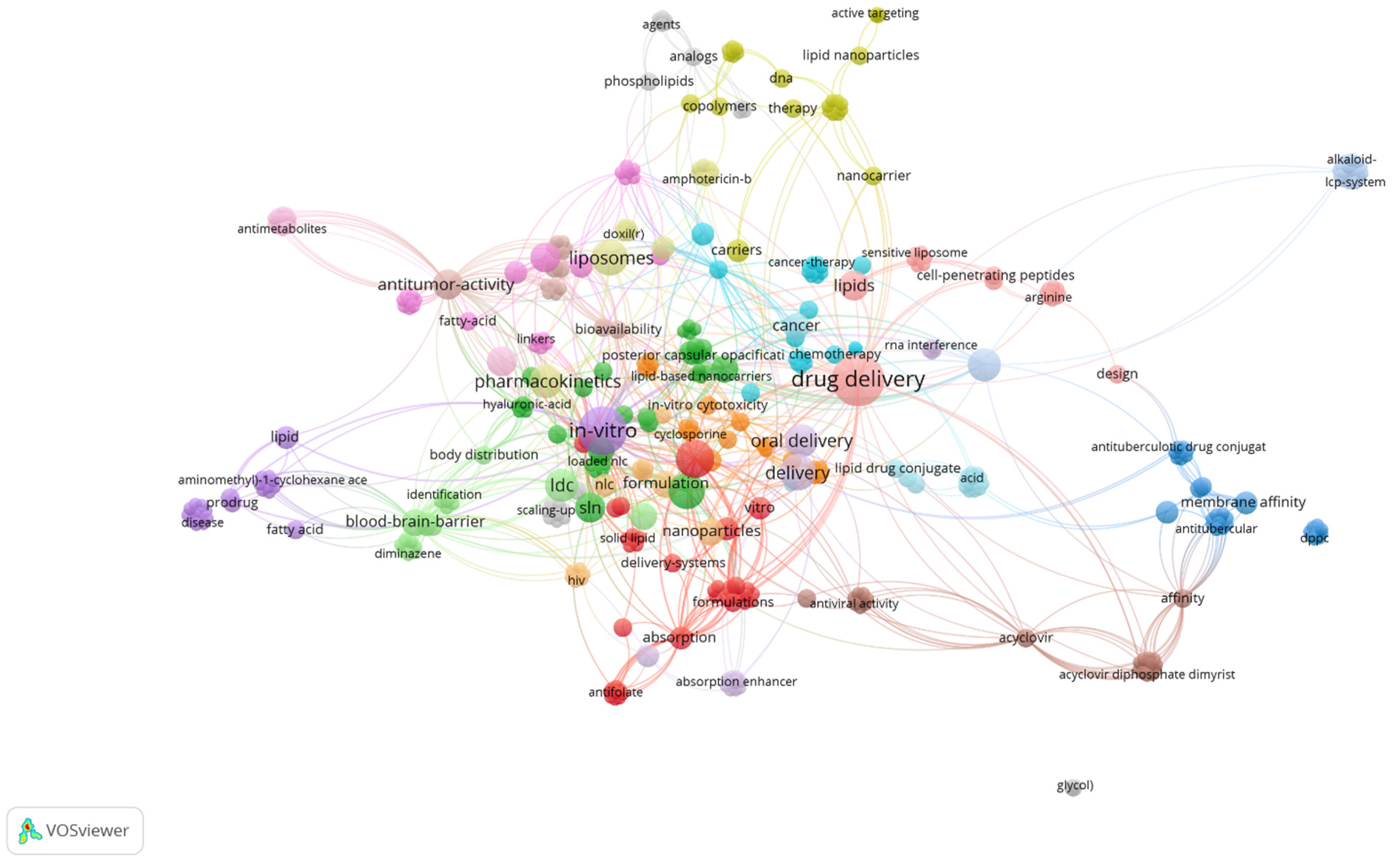
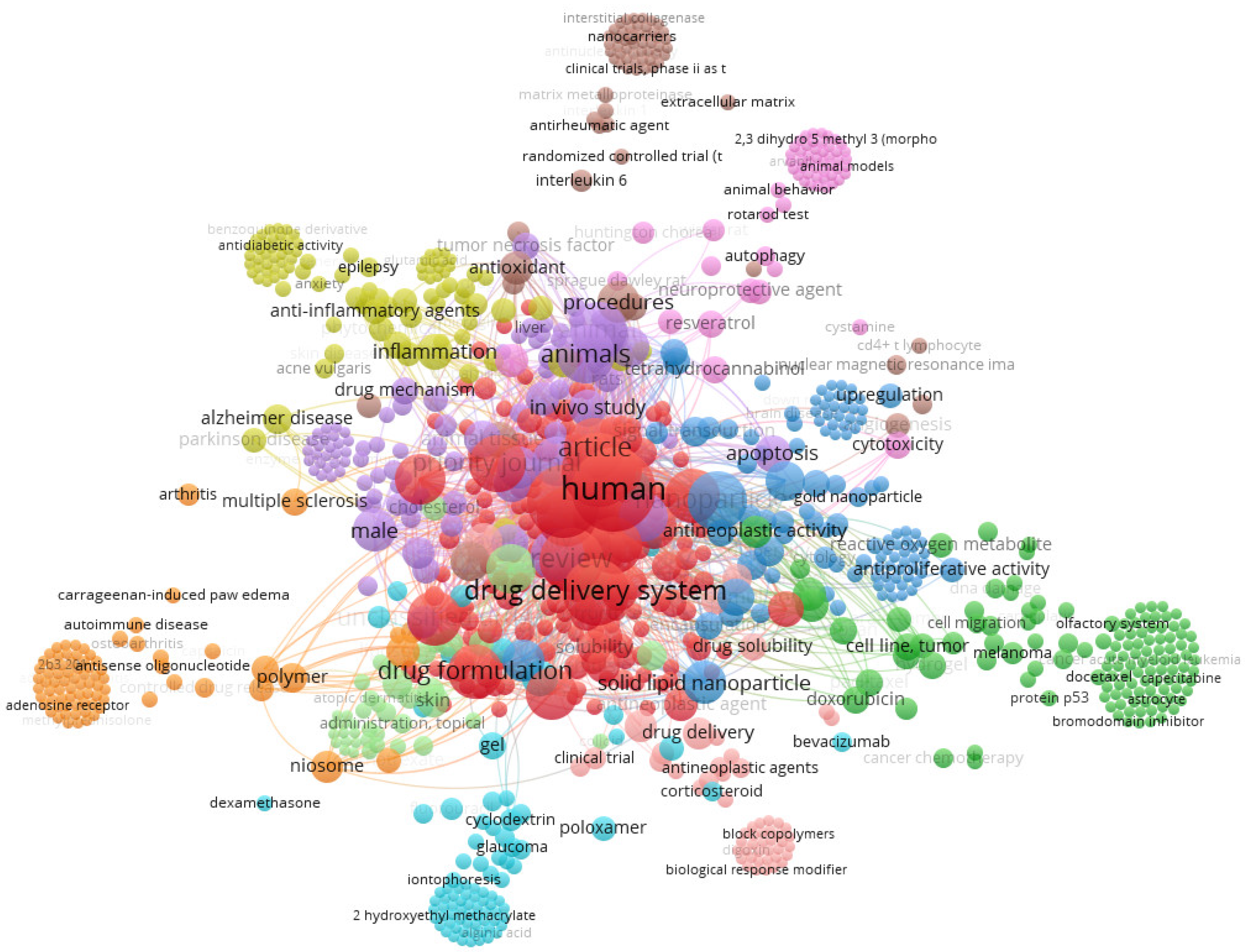

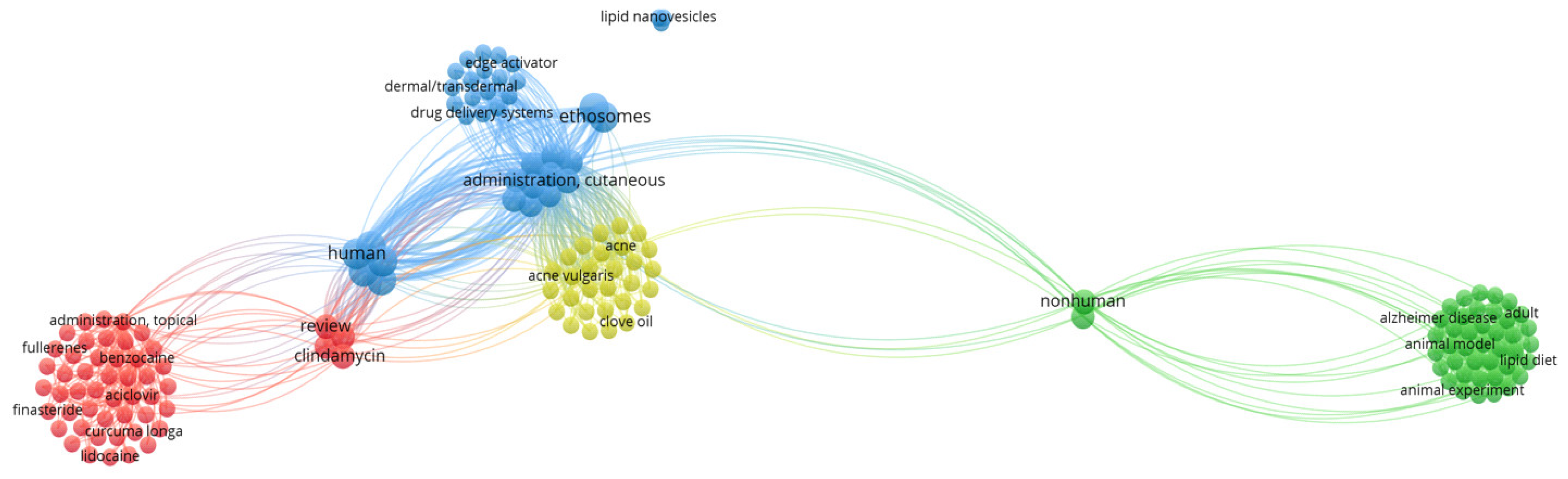

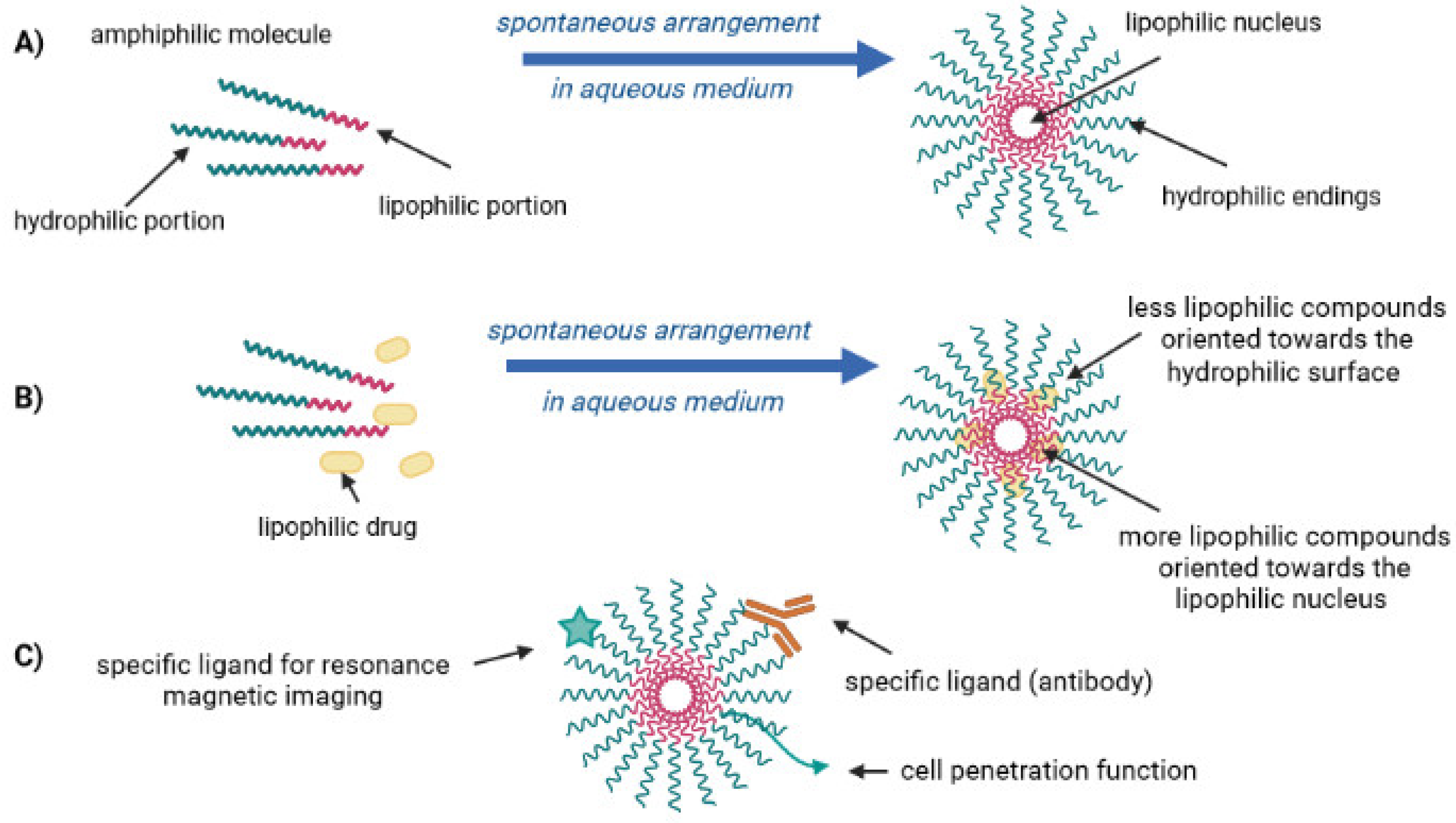

| CBD Formulation | Experimental Model | Bioactivity | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.5% | Rat | Prevent protein modulation by UVA and UVB exposure | [31] |
| 2.5% | Rat | Protection against UV-induced damage | [32] |
| 10 µM | Human keratinocyte cell model (HaCaT) | Protection against H2O2- induced oxidative damage | [33] |
| 1% | Mice | Moisturizing activity | [34] |
| 0.04–0.2 mg/mL | Mice melanoma cell line (B16-F) | Anti-proliferative activity | [35] |
| n.s. | Human clinical case studies | Treatment of Epidermolysis bullosa | [36] |
| 10 µM | Human immortalized SZ95 sebocytes | Treatment of acne vulgaris Anti-inflammatory activity Sebostatic activity | [37] |
| Formulation | Composition | Size | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethosome | CBD, EtOH, Phospholipon 90 | 300–400 nm | Increased skin permeation Anti-inflammatory activity | [42] |
| Emulsion | CBD, Oil phase (Soybean oil, rapeseed oil, Trimyristin or Miglyol 812), Poloxamer (188 or 407), Sodium azide | 69–233 nm | Increased drug loading | [43] |
| Emulsion | CBD, chitosan, collagen, oil phase (olive oil or liquid paraffin) | n.s. | Increased delivery and deposition in the stratum corneum | [44] |
| Emulsion | CBD, chitosan (various deacetylation degrees), gum Arabic, olive oil | 45–787 nm | Higher skin absorption | [45] |
| Emulsion | CBD, isopropyl myristate, Solutol HS 15 and Transcutol P | 35 nm | Development of a microemulgel for the treatment of skin disorders | [46] |
| Micelles | Mean Vesicle Size (mm) |
|---|---|
| PEG750-DSPE | 7–15 |
| PEG2000-DSPE | 7–20 |
| PEG5000-DSPE | 10–40 |
| PEG2000-DOPE | 7–20 |
| PEG5000-DOPE | 10–35 |
| PVP1500-P | 5–15 |
| PVP8000-P | 7–20 |
| PVP15000-P | - |
| PVP1500-S | 5–15 |
| PVP8000-S | 10–20 |
| PVP15000-S | - |
| Patent | Application |
|---|---|
| CA2760460C | CBD transdermal formulation with enhanced penetration to be used in inflammation and pain treatment |
| WO2019244160A1 | Anti-microbial hyperosmotic formulation containing CBD |
| USRE47885E1 | CBD-containing hydrogel developed for transdermal (microneedle) or topical application |
| US11260033B2 | CBD-loaded lipid nanoparticles for increased stability and bioavailability |
| US8435556B2 | Transdermal formulation containing CBD and diethylene glycol monoethyl ether as penetration enhancer |
| US20210244680A1 | Wearable transdermal patch with CBD-loaded liposomes |
| BR112020003025A2 | Transdermal gel containing CBD for osteoarthritis treatment |
| US10842758B1 | Transdermal delivery formulation containing CBD, phosphatidylcholine, safflower oil, oleic acid, stearic acid, and isopropyl palmitate |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zielińska, A.; Cano, A.; Andreani, T.; Martins-Gomes, C.; Silva, A.M.; Szalata, M.; Słomski, R.; Souto, E.B. Lipid-Drug Conjugates and Nanoparticles for the Cutaneous Delivery of Cannabidiol. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6165. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23116165
Zielińska A, Cano A, Andreani T, Martins-Gomes C, Silva AM, Szalata M, Słomski R, Souto EB. Lipid-Drug Conjugates and Nanoparticles for the Cutaneous Delivery of Cannabidiol. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(11):6165. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23116165
Chicago/Turabian StyleZielińska, Aleksandra, Amanda Cano, Tatiana Andreani, Carlos Martins-Gomes, Amélia M. Silva, Marlena Szalata, Ryszard Słomski, and Eliana B. Souto. 2022. "Lipid-Drug Conjugates and Nanoparticles for the Cutaneous Delivery of Cannabidiol" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 11: 6165. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23116165
APA StyleZielińska, A., Cano, A., Andreani, T., Martins-Gomes, C., Silva, A. M., Szalata, M., Słomski, R., & Souto, E. B. (2022). Lipid-Drug Conjugates and Nanoparticles for the Cutaneous Delivery of Cannabidiol. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(11), 6165. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23116165







