Participation of Amyloid and Tau Protein in Post-Ischemic Neurodegeneration of the Hippocampus of a Nature Identical to Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Amyloid Protein Precursor, β-Secretase, Presenilin 1, Presenilin 2, and Tau Protein Genes
3. Amyloid Staining
4. Tau Protein Staining
5. Alpha-Synuclein Staining
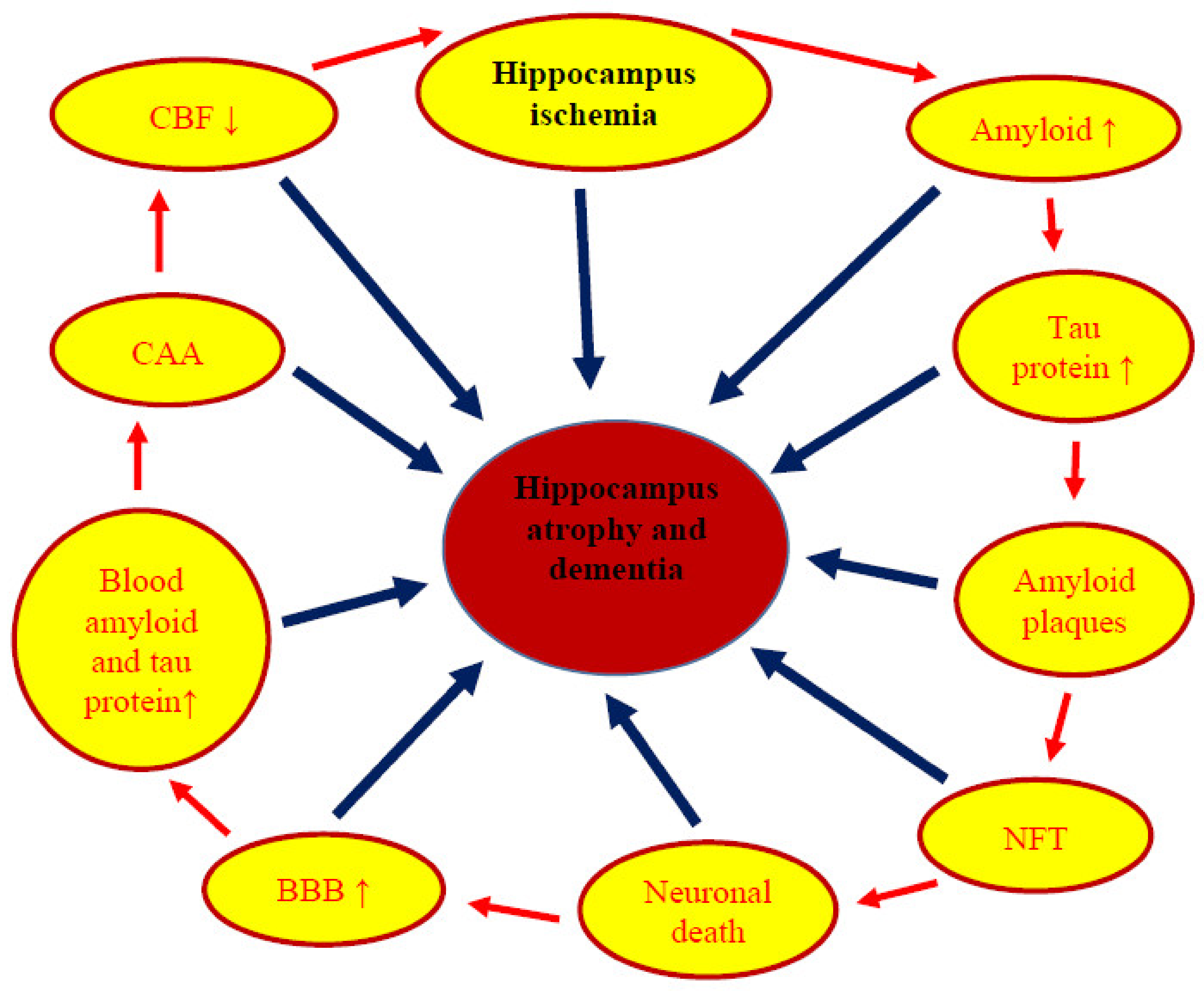
6. Neuropathophysiology and Neuropathology
7. Dementia
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pluta, R. The role of apolipoprotein E in the deposition of β-amyloid peptide during ischemia-reperfusion brain injury. A model of early Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 903, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluta, R.; Ułamek, M.; Jabłoński, M. Alzheimer’s mechanisms in ischemic brain degeneration. Anat. Rec. 2009, 292, 1863–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gemmell, E.; Bosomworth, H.; Allan, L.; Hall, R.; Khundakar, A.; Oakley, A.E.; Deramecourt, V.; Polvikoski, T.M.; O’Brien, J.T.; Kalaria, R.N. Hippocampal neuronal atrophy and cognitive function in delayed poststroke and aging-related dementias. Stroke 2012, 43, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinyemi, R.O.; Allan, L.M.; Oakley, A.; Kalaria, R.N. Hippocampal neurodegenerative pathology in post-stroke dementia compared to other dementias and aging controls. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.B.; Li, Y.; Cai, Y.F.; Huang, Y.; Liu, S.; Yeung, P.K.; Deng, M.Z.; Sun, G.S.; Zilundu, P.L.; Hu, Q.S.; et al. Scutellarin protects oxygen/glucose-deprived astrocytes and reduces focal cerebral ischemic injury. Neural. Regen. Res. 2018, 13, 1396–1407. [Google Scholar]
- Uchida, H.; Fujita, Y.; Matsueda, M.; Umeda, M.; Matsuda, S.; Kato, H.; Kasahara, J.; Araki, T. Damage to neurons and oligodendrocytes in the hippocampal CA1 sector after transient focal ischemia in rats. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2010, 30, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Xu, S. Edaravone alleviates delayed neuronal death and long-dated cognitive dysfunction of hippocampus after transient focal ischemia in Wistar rat brains. Neuroscience 2011, 182, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavaglia, M.; Dombrowski, S.M.; Drazba, J.; Vasanji, A.; Bokesch, P.M.; Janigro, D. Regional variation in brain capillary density and vascular response to ischemia. Brain Res. 2001, 910, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluta, R.; Salińska, E.; Puka, M.; Stafiej, A.; Łazarewicz, J.W. Early changes in extracellular amino acids and calcium concentrations in rabbit hippocampus following complete 15-min cerebral ischemia. Resuscitation 1988, 16, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekeljic, V.; Bataveljic, D.; Stamenkovic, S.; Ułamek, M.; Jabłoński, M.; Radenovic, L.; Pluta, R.; Andjus, P.R. Cellular markers of neuroinflammation and neurogenesis after ischemic brain injury in the long-term survival rat model. Brain Struct. Funct. 2012, 217, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashabi, G.; Khalaj, L.; Khodagholi, F.; Goudarzvand, M.; Sarkaki, A. Pre-treatment with metformin activates Nrf2 antioxidant pathways and inhibits inflammatory responses through induction of AMPK after transient global cerebral ischemia. Metab. Brain Dis. 2015, 30, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Ahn, J.H.; Choi, S.Y.; Hong, S.; Kim, S.K.; Kang, I.J.; Kim, Y.M.; Lee, T.K.; Won, M.H.; et al. Atomoxetine protects against NMDA receptor-mediated hippocampal neuronal death following transient global cerebral ischemia. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2017, 14, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radenovic, L.; Nenadic, M.; Ułamek-Kozioł, M.; Januszewski, S.; Czuczwar, S.J.; Andjus, P.R.; Pluta, R. Heterogeneity in brain distribution of activated microglia and astrocytes in a rat ischemic model of Alzheimer’s disease after 2 years of survival. Aging 2020, 12, 12251–12267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugawara, T.; Lewén, A.; Noshita, N.; Gasche, Y.; Chan, P.H. Effects of global ischemia duration on neuronal, astroglial, oligodendroglial, and microglial reactions in the vulnerable hippocampal CA1 subregion in rats. J. Neurotrauma 2002, 19, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Yoo, K.-Y.; Choi, J.H.; Park, O.K.; Hwang, I.K.; Kim, S.K.; Kang, I.-J.; Kim, Y.-M.; Won, M.-H. Neuronal damage is much delayed and microgliosis is more severe in the aged hippocampus induced by transient cerebral ischemia compared to the adult hippocampus. J. Neurol. Sci. 2010, 294, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedergaard, M.; Kimelberg, H.K. Functions of astrocytes and their potential as therapeutic targets. Neurotherapeutics 2010, 7, 338–353. [Google Scholar]
- Pekny, M.; Pekna, M. Astrocyte reactivity and reactive astrogliosis: Costs and benefits. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 1077–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, Y.-B.; Voloboueva, L.A.; Xu, L.-J.; Giffard, R.G. Selective dysfunction of hippocampal CA1 astrocytes contributes to delayed neuronal damage after transient forebrain ischemia. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 4253–4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richmond, T.S. Cerebral resuscitation after global brain ischemia: Linking research to practice. AACN Clin. Issue 1997, 8, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.; Alexander, M.P.; LaFleche, G. The neurological and cognitive sequelae of cardiac arrest. Neurology 2004, 63, 1774–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Park, J.H.; Maharjan, S.; Park, J.A.; Choi, K.S.; Park, H.; Jeong, Y.; Ahn, J.H.; Kim, I.H.; Lee, J.C.; et al. Sac-1004, a vascular leakage blocker, reduces cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by suppressing blood-brain barrier disruption and inflammation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zheng, D.; Shui, M.; Yu, K.; Liu, X.; Lin, Y.; Su, L.; Yang, W.; Wang, Y. Design and evaluation of EphrinA1 mutants with cerebral protective effect. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rother, J. Neuroprotection does not work! Stroke 2008, 39, 523–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, T.; Park, Y.; Sun, X.; Liu, C.; Hu, B. Protein misfolding, aggregation, and autophagy after brain ischemia. Transl. Stroke Res. 2013, 4, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, Z.G.; Lu, X.H.; Kong, X.X.; Wu, F.Z.; Lin, L.; Tan, X.; Ye, L.B.; Xiao, J. Endoplasmic reticulum stress: Relevance and therapeutics in central nervous system diseases. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 51, 1343–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.J.; Li, X.N.; Liu, W.L.; Yuan, H.Y.; Gao, Y.; Wang, K.; Tang, B.; Pang, D.W.; Chen, J.; Liang, Y. Neutralizing mutations significantly inhibit amyloid formation by human prion protein and decrease its cytotoxicity. J. Mol. Biol. 2020, 432, 828–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, S.; Trindade, D.; Martins, T.; Rosa, I.M.; Delgadillo, I.; Goodfellow, B.J.; Da Cruz e Silva, O.A.B.; Henriques, A.G.; Nunes, A. Monitoring plasma protein aggregation during aging using conformation-specific antibodies and FTIR spectroscopy. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 502, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wesen, E.; Kumar, R.; Bernson, D.; Gallud, A.; Paul, A.; Wittung-Stafshede, P.; Esbjörner, E.K. Correlation between cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of fragmented alpha-synuclein amyloid fibrils suggests intracellular basis for toxicity. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.R.; Janelidze, S.; Ginsberg, M.D.; Busto, R.; Perez-Pinzon, M.; Sick, T.J.; Siesjö, B.K.; Liu, C.L. Protein aggregation after focal brain ischemia and reperfusion. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2001, 21, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Liu, C.L.; Hu, B.R. Irreversible aggregation of protein synthesis machinery after focal brain ischemia. J. Neurochem. 2006, 98, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluta, R.; Kida, E.; Lossinsky, A.S.; Golabek, A.A.; Mossakowski, M.J.; Wisniewski, H.M. Complete cerebral ischemia with short-term survival in rats induced by cardiac arrest. I. Extracellular accumulation of Alzheimer’s β-amyloid protein precursor in the brain. Brain Res. 1994, 649, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocki, J.; Ułamek-Kozioł, M.; Bogucka-Kocka, A.; Januszewski, S.; Jabłoński, M.; Gil-Kulik, P.; Brzozowska, J.; Petniak, A.; Furmaga-Jabłońska, W.; Bogucki, J.; et al. Dysregulation of amyloid precursor protein, β-secretase, presenilin 1 and 2 genes in the rat selectively vulnerable CA1 subfield of hippocampus following transient global brain ischemia. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2015, 47, 1047–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluta, R.; Ułamek-Kozioł, M.; Januszewski, S.; Czuczwar, S.J. Tau protein dysfunction after brain ischemia. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 66, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluta, R.; Bogucka-Kocka, A.; Ułamek-Kozioł, M.; Bogucki, J.; Czuczwar, S.J. Ischemic tau protein gene induction as an additional key factor driving development of Alzheimer’s phenotype changes in CA1 area of hippocampus in an ischemic model of Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmacol. Rep. 2018, 70, 881–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, E.D.; Oostveen, J.A.; Dunn, E.; Carter, D.B. Increased amyloid protein precursor and apolipoprotein E immunoreactivity in the selectively vulnerable hippocampus following transient forebrain ischemia in gerbils. Exp. Neurol. 1995, 135, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishimaru, H.; Ishikawa, K.; Haga, S.; Shoji, M.; Ohe, Y.; Haga, C.; Sasaki, A.; Takashashi, A.; Maruyama, Y. Accumulation of apolipoprotein E and β-amyloid-like protein in a trace of the hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cell layer after ischaemic delayed neuronal death. NeuroReport 1996, 7, 3063–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, M.; Saido, T.C.; Tani, E.; Yamaura, I.; Minami, N. Cytotoxic fragment of amyloid precursor protein accumulates in hippocampus after global forebrain ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1996, 16, 1219–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluta, R.; Barcikowska, M.; Dębicki, G.; Ryba, M.; Januszewski, S. Changes in amyloid precursor protein and apolipoprotein E immunoreactivity following ischemic brain injury in rat with long-term survival: Influence of idebenone treatment. Neurosci. Lett. 1997, 232, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluta, R.; Barcikowska, M.; Mossakowski, M.J.; Zelman, I. Cerebral accumulation of beta-amyloid following ischemic brain injury with long-term survival. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 1998, 71, 206–208. [Google Scholar]
- Pluta, R. No effect of anti-oxidative therapy on cerebral amyloidosis following ischemia-reperfusion brain injury. Folia Neuropathol. 2000, 38, 188–190. [Google Scholar]
- Sinigaglia-Coimbra, R.; Cavalheiro, E.A.; Coimbra, C.G. Postischemic hypertermia induces Alzheimer-like pathology in the rat brain. Acta Neuropathol. 2002, 103, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banati, R.B.; Gehrmann, J.; Wießner, C.; Hossmann, K.A.; Kreutzberg, G.W. Glial expression of the β-amyloid precursor protein (APP) in global ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1995, 15, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, G.; Mengod, G.; Tortosa, A.; Ferrer, I.; Palacios, J.M. Increased β-amyloid precursor protein expression in astrocytes in the gerbil hippocampus following ischaemia: Association with proliferation of astrocytes. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1995, 7, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badan, I.; Dinca, I.; Buchhold, B.; Suofu, Y.; Walker, L.; Gratz, M.; Platt, D.; Kessler, C.H.; Popa-Wagner, A. Accelerated accumulation of N- and C-terminal beta APP fragments and delayed recovery of microtubule-associated protein 1B expression following stroke in aged rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 19, 2270–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabłoński, M.; Maciejewski, R.; Januszewski, S.; Ułamek, M.; Pluta, R. One year follow up in ischemic brain injury and the role of Alzheimer factors. Physiol. Res. 2011, 60 (Suppl. S1), 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takuma, K.; Baba, A.; Matsuda, T. Astrocyte apoptosis: Implications for neuroprotection. Prog. Neurobiol. 2004, 72, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Groen, T.; Puurunen, K.; Maki, H.M.; Sivenius, J.; Jolkkonen, J. Transformation of diffuse beta-amyloid precursor protein and beta-amyloid deposits to plaques in the thalamus after transient occlusion of the middle cerebral artery in rats. Stroke 2005, 36, 1551–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluta, R. Glial expression of the β-amyloid peptide in cardiac arrest. J. Neurol. Sci. 2002, 203–204, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluta, R. Astroglial expression of the beta-amyloid in ischemia-reperfusion brain injury. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2002, 977, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiryk, A.; Pluta, R.; Figiel, I.; Mikosz, M.; Ułamek, M.; Niewiadomska, G.; Jabłoński, M.; Kaczmarek, L. Transient brain ischemia due to cardiac arrest causes irreversible long-lasting cognitive injury. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 219, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluta, R.; Jabłoński, M.; Czuczwar, S.J. Postischemic dementia with Alzheimer phenotype: Selectively vulnerable versus resistant areas of the brain and neurodegeneration versus β-amyloid peptide. Folia Neuropathol. 2012, 50, 101–109. [Google Scholar]
- Ułamek-Kozioł, M.; Czuczwar, S.J.; Januszewski, S.; Pluta, R. Proteomic and genomic changes in tau protein, which are associated with Alzheimer’s disease after ischemia-reperfusion brain injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jendroska, K.; Poewe, W.; Daniel, S.E.; Pluess, J.; Iwerssen-Schmidt, H.; Paulsen, J.; Barthel, S.; Schelosky, L.; Cervos-Navarr, J.; DeArmond, S.J. Ischemic stress induces deposition of amyloid beta immunoreactivity in human brain. Acta Neuropathol. 1995, 90, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisniewski, H.M.; Maslinska, D. Beta-protein immunoreactivity in the human brain after cardiac arrest. Folia Neuropathol. 1996, 34, 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Jendroska, K.; Hoffmann, O.M.; Patt, S. Amyloid β peptide and precursor protein (APP) in mild and severe brain ischemia. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1997, 826, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Wu, H.; Yang, Y.; Wand, D.; Chen, Y.; Gu, Y.; Liu, T. Cerebral ischemia and Alzheimer’s disease: The expression of amyloid-β and apolipoprotein E in human hippocampus. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2007, 12, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geddes, J.W.; Schwab, C.; Craddock, S.; Wilson, J.L.; Pettigrew, L.C. Alterations in tau immunostaining in the rat hippocampus following transient cerebral ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1994, 14, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majd, S.; Power, J.H.; Koblar, S.A.; Grantham, H.J. Early glycogen synthase kinase-3 and protein phosphatase 2A independent tau dephosphorylation during global brain ischaemia and reperfusion following cardiac arrest and the role of the adenosine monophosphate kinase pathway. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2016, 44, 1987–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.; Takahashi, T.; Mukai, T.; Tanaka, S.; Hosomi, N.; Maruyama, H.; Sakai, N.; Matsumoto, M. Modifications of tau protein after cerebral ischemia and reperfusion in rats are similar to those occurring in Alzheimer’s disease—Hyperphosphorylation and cleavage of 4- and 3-repeat tau. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2017, 37, 2441–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamer, K.; Vogel, R.; Thies, E.; Mandelkow, E.; Mandelkow, E.M. Tau blocks traffic of organelles, neurofilaments, and APP vesicles in neurons and enhances oxidative stress. J. Cell. Biol. 2002, 156, 1051–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Yang, S.; Liu, R.; Simpkins, J.W. Transient cerebral ischemia induces site-specific hyperphosphorylation of tau protein. Brain Res. 2004, 1022, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Yang, S.; Liu, R.; Brun-Zinkernagel, A.M.; Koulen, P.; Simpkins, J.W. Transient cerebral ischemia induces aberrant neuronal cell cycle re-entry and Alzheimer’s disease-like tauopathy in female rats. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 22684–22692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Yang, S.H.; Liu, R.; Perez, E.J.; Brun-Ziukemagel, A.M.; Koulen, P.; Simpkins, J.W. Cdk5 is involved in NFT-like tauopathy induced by transient cerebral ischemia in female rats. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1772, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Yuldasheva, N.Y.; Batten, T.F.C.; Pickles, A.R.; Kellett, K.A.B.; Saha, S. Tau pathology and neurochemical changes associated with memory dysfunction in an optimized murine model of global cerebral ischaemia—A potential model for vascular dementia? Neurochem. Int. 2018, 118, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, T.; Hirano, A.; Katagiri, T.; Sasaki, H.; Yamada, S. Neurofibrillary tangle formation in the nucleus basalis of Meynert ipsilateral to a massive cerebral infarct. Ann. Neurol. 1988, 23, 620–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatsuta, H.; Takao, M.; Nogami, A.; Uchino, A.; Sumikura, H.; Takata, T.; Morimoto, S.; Kanemaru, K.; Adachi, T.; Arai, T.; et al. Tau and TDP-43 accumulation of the basal nucleus of Meynert in individuals with cerebral lobar infarcts or hemorrhage. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2019, 7, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, M.; Gladbach, A.; Van Eersel, J.; Ittner, A.; Przybyla, M.; Van Hummel, A.; Chua, S.W.; Van der Hoven, J.; Lee, W.S.; Muller, J.; et al. Tau exacerbates excitotoxic brain damage in an animal model of stroke. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuo, Q.Z.; Lei, P.; Jackman, K.A.; Li, X.L.; Xiong, H.; Li, X.L.; Liuyang, Z.Y.; Roisman, L.; Zhang, S.T.; Ayton, S.; et al. Tau-mediated iron export prevents ferroptotic damage after ischemic stroke. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 1520–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basurto-Islas, G.; Gu, J.H.; Tung, Y.C.; Liu, F.; Iqbal, K. Mechanism of tau hyperphosphorylation involving lysosomal enzyme asparagine endopeptidase in a mouse model of brain ischemia. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 63, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishimaru, H.; Ueda, K.; Takashashi, A.; Maruyama, Y. Changes in presynaptic protein NACP/alpha-synuclein in an ischemic gerbil hippocampus. Brain Res. 1998, 788, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, Y.; Ishida, Y.; Takata, K.; Kakimura, J.; Mizutani, H.; Shimohama, S.; Akaike, A.; Taniguchi, T. Alpha-synuclein protein is not scavenged in neuronal loss induced by kainic acid or focal ischemia. Brain Res. 2001, 898, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedert, M. Alpha-synuclein and neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 2, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, M.; Masliah, E. Alpha-synuclein in Lewy body disease and Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Pathol. 1999, 9, 707–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirino, T. Delayed neuronal death in the gerbil hippocampus following ischemia. Brain Res. 1982, 239, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulsinelli, W.A.; Brierley, J.B.; Plum, F. Temporal profile of neuronal damage in a model of transient forebrain ischemia. Ann. Neurol. 1982, 11, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluta, R.; Salińska, E.; Lazarewicz, J.W. Prostacyclin reduces early ischemic changes in central nervous system. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 1990, 50, 295–302. [Google Scholar]
- Pluta, R.; Salińska, E.; Lazarewicz, J.W. Prostacyclin attenuates in the rabbit hippocampus early consequences of transient complete cerebral ischemia. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1991, 83, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluta, R. Complete cerebral ischemia, prostacyclin deficiency, and therapeutic possibilities. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 1994, 60, 303–306. [Google Scholar]
- Pluta, R.; Tomida, S.; Ikeda, J.; Nowak, T.S., Jr.; Klatzo, I. Cerebral vascular volume after repeated ischemic insults in the gerbil: Comparison with changes in CBF and brain edema. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1989, 9, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathmell, J.C.; Thompson, C.B. The central effectors of cell death in the immune system. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1999, 17, 781–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Saikumar, P.; Weinberg, J.M.; Venkatachalam, M.A. Internucleosomal DNA cleavage triggered by plasma membrane damage during necrotic cell death. Involvement of serine but not cysteine proteases. Am. J. Pathol. 1997, 151, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar]
- Nitatori, T.; Sato, N.; Waguri, S.; Karasawa, Y.; Araki, H.; Shibanai, K.; Kominami, E.; Uchiyama, Y. Delayed neuronal death in the CA1 pyramidal cell layer of the gerbil hippocampus following transient ischemia is apoptosis. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 1001–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimura, M.; Morita-Fujimura, Y.; Murakami, K.; Kawase, M.; Chan, P.H. Cytosolic redistribution of cytochrome c after transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1998, 18, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, T.; Fujimura, M.; Morita-Fujimura, Y.; Kawase, M.; Chan, P.H. Mitochondrial release of cytochrome c corresponds to the selective vulnerability of hippocampus CA1 neurons in rats after transient global cerebral ischemia. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, RC39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, T.; Fujimura, M.; Noshita, N.; Kim, G.W.; Saito, A.; Hayashi, T.; Narasimhan, P.; Maier, C.M.; Chan, P.H. Neuronal death/survival signaling pathways in cerebral ischemia. NeuroRx 2004, 1, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ułamek-Kozioł, M.; Kocki, J.; Bogucka-Kocka, A.; Petniak, A.; Gil-Kulik, P.; Januszewski, S.; Bogucki, J.; Jabłoński, M.; Furmaga-Jabłońska, W.; Brzozowska, J.; et al. Dysregulation of autophagy, mitophagy and apoptotic genes in the medial temporal lobe cortex in an ischemic model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2016, 54, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluta, R.; Ułamek-Kozioł, M.; Januszewski, S.; Czuczwar, S.J. Dysregulation of Alzheimer’s disease-related genes and proteins following cardiac arrest. Folia Neuropathol. 2017, 55, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ułamek-Kozioł, M.; Kocki, J.; Bogucka-Kocka, A.; Januszewski, S.; Bogucki, J.; Czuczwar, S.J.; Pluta, R. Autophagy, mitophagy and apoptotic gene changes in the hippocampal CA1 area in a rat ischemic model of Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmacol. Rep. 2017, 69, 1289–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenbaum, D.M.; Gupta, G.; D’Amore, J.; Sinhg, M.; Weidenheim, K.; Zhang, H.; Kessler, J.A. Fas(CD95/APO-1) plays a role in the pathophysiology of focal cerebral ischemia. J. Neurosci. Res. 2000, 61, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degterev, A.; Huang, Z.; Boyce, M.; Li, Y.; Jagtap, P.; Mizushima, N.; Cuny, G.D.; Mitachison, T.J.; Moskowitz, M.A.; Yuan, J. Chemical inhibitor of nonapoptotic cell death with therapeutic potential for ischemic brain injury. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2005, 1, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unal-Cevik, I.; Kilinc, M.; Can, A.; Gursoy-Ozdemir, Y.; Dalkara, T. Apoptotic and necrotic death mechanisms are concomitantly activated in the same cell after cerebral ischemia. Stroke 2004, 35, 2189–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsujimoto, Y.; Shimizu, S. Another way to die: Autophagic programmed cell death. Cell Death Differ. 2005, 12, 1528–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Shao, B.Z.; Deng, Z.; Chen, S.; Yue, Z.; Miao, C.Y. Autophagy in ischemic stroke. Prog Neurobiol. 2018, 163–164, 98–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ułamek-Kozioł, M.; Czuczwar, S.J.; Kocki, J.; Januszewski, S.; Bogucki, J.; Bogucka-Kocka, A.; Pluta, R. Dysregulation of autophagy, mitophagy, and apoptosis genes in the CA3 region of the hippocampus in the ischemic model of Alzheimer’s disease in the rat. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2019, 72, 1279–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhami, F.; Schloemer, A.; Kuan, C.Y. The roles of autophagy in cerebral ischemia. Autophagy 2007, 3, 42–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheff, S.W.; Price, D.A.; Schmitt, F.A.; Scheff, M.A.; Mufson, E.J. Synaptic loss in the inferior temporal gyrus in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2011, 24, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orzyłowska, O.; Oderfeld-Nowak, B.; Zaremba, M.; Januszewski, S.; Mossakowski, M.J. Prolonged and concomitant induction of astroglial immunoreactivity of interleukin-1 beta and interleukin-6 in the rat hippocampus after transient global ischemia. Neurosci. Lett. 1999, 263, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touzani, O.; Boutin, H.; LeFeuvre, R.; Parker, L.; Miller, A.; Luheshi, G.; Rothwell, N. Interleukin-1 influences ischemic brain damage in the mouse independently of the interleukin-1 type I receptor. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, W.S.; Sheng, J.G.; Royston, M.C.; Gentleman, S.M.; McKenzie, J.E.; Graham, D.I.; Roberts, G.W.; Mrak, R.E. Glial-neuronal interactions in Alzheimer’s disease: The potential role of a “Cytokine Cycle” in disease progression. Brain Pathol. 1998, 8, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giulian, D.; Haverkamp, L.J.; Li, J.; Karshin, W.L.; Yu, J.; Tom, D.; Li, X.; Kirkpatrick, J.B. Senile plaques stimulate microglia to release a neurotoxin found in Alzheimer brain. Neurochem. Int. 1995, 27, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, J.T.; Cohan, C.H.; Dave, K.R.; Wright, C.B.; Perez-Pinzon, M.A. Global cerebral ischemia: Synaptic and cognitive dysfunction. Curr. Drug Targets 2013, 14, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, Y.W.; Han, X.J.; Shi, Z.S.; Lei, Z.G.; Xu, Z.C. Remodeling of synapses in the CA1 area of the hippocampus after transient global ischemia. Neuroscience 2012, 218, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ułamek-Kozioł, M.; Furmaga-Jabłońska, W.; Januszewski, S.; Brzozowska, J.; Sciślewska, M.; Jabłoński, M.; Pluta, R. Neuronal autophagy: Self-eating or self-cannibalism in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem. Res. 2013, 38, 1769–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curcio, M.; Salazar, I.L.; Mele, M.; Canzoniero, L.M.; Duarte, C.B. Calpains and neuronal damage in the ischemic brain: The swiss knife in synaptic injury. Prog. Neurobiol. 2016, 143, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossakowski, M.J.; Lossinsky, A.S.; Pluta, R.; Wisniewski, H.M. Changes in cerebral microcirculation system following experimentally induced cardiac arrest: A SEM and TEM study. In Microcirculatory Stasis in the Brain; Tomita, M., Ed.; Elsevier Science Publishers B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1993; pp. 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Mossakowski, M.J.; Lossinsky, A.S.; Pluta, R.; Wisniewski, H.M. Abnormalities of the blood-brain barrier in global cerebral ischemia in rats due to experimental cardiac arrest. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 1994, 60, 274–276. [Google Scholar]
- Pluta, R.; Lossinsky, A.S.; Wiśniewski, H.M.; Mossakowski, M.J. Early blood-brain barrier changes in the rat following transient complete cerebral ischemia induced by cardiac arrest. Brain Res. 1994, 633, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisniewski, H.M.; Pluta, R.; Lossinsky, A.S.; Mossakowski, M.J. Ultrastructural studies of cerebral vascular spasm after cardiac arrest-related global cerebral ischemia in rats. Acta Neuropathol. 1995, 90, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, M.; Akiguchi, I.; Hosokawa, M.; Shinnou, M.; Sakamoto, H.; Takemura, M.; Higuchi, K. Age-related changes in the brain transfer of blood-borne horseradish peroxidase in the hippocampus of senescence-accelerated mouse. Acta Neuropathol. 1997, 93, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinnou, M.; Ueno, M.; Sakamoto, H.; Ide, M. Blood-brain barrier damage in reperfusion following ischemia in the hippocampus of the Mongolian gerbil brain. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1998, 98, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippoldt, A.; Kniesel, U.; Liebner, S.; Kalbacher, H.; Kirsch, T.; Wolburg, H.; Haller, H. Structural alterations of tight junctions are associated with loss of polarity in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rat blood-brain barrier endothelial cells. Brain Res. 2000, 885, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, M.; Tomimoto, H.; Akiguchi, I.; Wakita, H.; Sakamoto, H. Blood-brain barrier disruption in white matter lesions in a rat model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2002, 22, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, M.; Sakamoto, H.; Liao, Y.J.; Onodera, M.; Huang, C.L.; Miyanaka, H.; Nakagawa, T. Blood-brain barrier disruption in the hypothalamus of young adult spontaneously hypertensive rats. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 122, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluta, R. Blood–brain barrier dysfunction and amyloid precursor protein accumulation in microvascular compartment following ischemia–reperfusion brain injury with 1-year survival. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2003, 86, 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Pluta, R. Pathological opening of the blood-brain barrier to horseradish peroxidase and amyloid precursor protein following ischemia-reperfusion brain injury. Chemotherapy 2005, 51, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluta, R.; Ułamek, M.; Januszewski, S. Micro-blood-brain barrier openings and cytotoxic fragments of amyloid precursor protein accumulation in white matter after ischemic brain injury in long-lived rats. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2006, 96, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pluta, R. Role of ischemic blood-brain barrier on amyloid plaques development in Alzheimer’s disease brain. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2007, 4, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluta, R.; Januszewski, S.; Ułamek, M. Ischemic blood-brain barrier and amyloid in white matter as etiological factors in leukoaraiosis. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2008, 102, 353–356. [Google Scholar]
- Pluta, R.; Barcikowska, M.; Januszewski, S.; Misicka, A.; Lipkowski, A.W. Evidence of blood-brain barrier permeability/leakage for circulating human Alzheimer’s β-amyloid-(1–42)-peptide. NeuroReport 1996, 7, 1261–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluta, R.; Misicka, A.; Januszewski, J.; Barcikowska, M.; Lipkowski, A.W. Transport of human β-amyloid peptide through the rat blood-brain barrier after global cerebral ischemia. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 1997, 70, 247–249. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pluta, R.; Barcikowska, M.; Misicka, A.; Lipkowski, A.W.; Spisacka, S.; Januszewski, S. Ischemic rats as a model in the study of the neurobiological role of human β-amyloid peptide. Time-dependent disappearing diffuse amyloid plaques in brain. NeuroReport 1999, 10, 3615–3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluta, R.; Misicka, A.; Barcikowska, M.; Spisacka, S.; Lipkowski, A.W.; Januszewski, S. Possible reverse transport of β-amyloid peptide across the blood-brain barrier. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2000, 76, 73–77. [Google Scholar]
- Pluta, R.; Lossinsky, A.S.; Walski, M.; Wiśniewski, H.M.; Mossakowski, M.J. Platelet occlusion phenomenon after short- and long-term survival following complete cerebral ischemia in rats produced by cardiac arrest. J. Hirnforsch. 1994, 35, 463–471. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, P.D.; Prittila, T. Biological markers of Alzheimer’s disease. Drug Dev. Res. 2002, 56, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowska, S.; Andrzejewska, A.; Lukomska, B.; Jankowski, M. Neuroinflammation as a target for treatment of stroke using mesenchymal stem cells and extracellular vesicles. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Dar, N.J.; Bhat, Z.S.; Hussain, A.; Shah, A.; Liu, H.; Graham, S.H. Inflammation in ischemic stroke: Mechanisms, consequences and possible drug targets. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2014, 13, 1378–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Benveniste, E.N. Immune function of astrocytes. Glia 2001, 36, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasko, I.; Veerhuis, R.; Stampfer-Kountchev, M.; Saurwein-Teissl, M.; Eikelenboom, P.; Grubeck-Loebenstein, B. Costimulatory effects of interferon-gamma and interleukin-1beta or tumor necrosis factor alpha on the synthesis of Abeta1–40 and Abeta1–42 by human astrocytes. Neurobiol. Dis. 2000, 7, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Raven, F.; Ward, J.F.; Zhen, S.; Zhang, S.; Sun, H.; Miller, S.J.; Choi, S.H.; Tanzi, R.E.; Zhang, C. Upregulation of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid-β protein precursor in astrocytes both in vitro and in vivo. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2020, 76, 1071–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amantea, D.; Bagetta, G.; Tassorelli, C.; Mercuri, N.B.; Corasaniti, M.T. Identification of distinct cellular pools of interleukin-1beta during the evolution of the neuroinflammatory response induced by transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in the brain of rat. Brain Res. 2010, 1313, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amantea, D.; Micieli, G.; Tassorelli, C.; Cuartero, M.I.; Ballesteros, I.; Certo, M.; Moro, M.A.; Lizasoain, I.; Bagetta, G. Rational modulation of the innate immune system for neuroprotection in ischemic stroke. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denes, A.; Vidyasagar, R.; Feng, J.; Narvainen, J.; McColl, B.W.; Kauppinen, R.A.; Allan, S.M. Proliferating resident microglia after focal cerebral ischaemia in mice. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2007, 27, 1941–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bivard, A.; Lillicrap, T.; Maréchal, B.; Garcia-Esperon, C.; Holliday, E.; Krishnamurthy, V.; Levi, C.R.; Parsons, M. Transient ischemic attack results in delayed brain atrophy and cognitive decline. Stroke 2018, 49, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossmann, K.A.; Schmidt-Kastner, R.; Ophoff, B.G. Recovery of integrative central nervous function after one hour global cerebro-circulatory arrest in normothermic cat. J. Neurol. Sci. 1987, 77, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluta, R.; Januszewski, S.; Jabłoński, M.; Ułamek, M. Factors in creepy delayed neuronal death in hippocampus following brain ischemia-reperfusion injury with long-term survival. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2010, 106, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- De la Tremblaye, P.B.; Plamondon, H. Impaired conditioned emotional response and object recognition are concomitant to neuronal damage in the amygdale and perirhinal cortex in middle-aged ischemic rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 219, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, M.; Fang, C.Q.; Zhou, H.D. Cerebral ischemia aggravates cognitive impairment in a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Life Sci. 2011, 89, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluta, R.; Jolkkonen, J.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Pedata, F.; Cechetto, D.; PopaWagner, A. Cognitive impairment with vascular impairment and degeneration. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2011, 8, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohan, C.H.; Neumann, J.T.; Dave, K.R.; Alekseyenko, A.; Binkert, M.; Stransky, K.; Lin, H.W.; Barnes, C.A.; Wright, C.B.; Perez-Pinzon, M.A. Effect of cardiac arrest on cognitive impairment and hippocampal plasticity in middle-aged rats. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa-Wagner, A. Alzheimer’s disease pathological factors in ischemic aged brain. In Ischemia-Reperfusion Pathways in Alzheimer’s Disease; Pluta, R., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 51–84. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.H.; Simpkins, J.W. Ischemia-reperfusion promotes tau and beta-amyloid pathology and a progressive cognictive impairment. In Ischemia-Reperfusion Pathways in Alzheimer’s Disease; Pluta, R., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 113–138. [Google Scholar]
- Kuroiwa, T.; Bonnekoh, P.; Hossmann, K.A. Locomotor hyperactivity and hippocampal CA1 injury after transient forebrain ischemia in gerbils. Neurosci. Lett. 1991, 122, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasawa, Y.; Araki, H.; Otomo, S. Changes in locomotor activity and passive avoidance task performance induced by cerebral ischemia in mongolian gerbils. Stroke 1994, 25, 645–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishibashi, S.; Kuroiwa, T.; LiYuan, S.; Katsumata, N.; Li, S.; Endo, S.; Mizusawa, H. Long-term cognitive and neuropsychological symptoms after global cerebral ischemia in Mongolian gerbils. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2006, 96, 299–302. [Google Scholar]
- Langdon, K.D.; Granter-Button, S.; Corbett, D. Persistent behavioral impairments and neuroinflammation following global ischemia in the rat. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 2310–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karhunen, H.; Pitkanen, A.; Virtanen, T.; Gureviciene, I.; Pussinen, R.; Ylinen, A.; Sivenius, J.; Nissinen, J.; Jolkkonen, J. Long-term functional consequences of transient occlusion of the middle cerebral artery in rats: A 1-year follow-up of the development of epileptogenesis and memory impairment in relation to sensorimotor deficits. Epilepsy Res. 2003, 54, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluta, R.; Ułamek-Kozioł, M.; Januszewski, S.; Ściślewska, M.; Bogucka-Kocka, A.; Kocki, J. Alzheimer’s factors in postischemic dementia. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2012, 53, 461–466. [Google Scholar]
- Pluta, R.; Kocki, J.; Maciejewski, R.; Ułamek-Kozioł, M.; Jabłoński, M.; Bogucka-Kocka, A.; Czuczwar, S.J. Ischemia signaling to Alzheimer-related genes. Folia Neuropathol. 2012, 50, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Back, D.B.; Choi, B.-R.; Han, J.-S.; Kwon, K.J.; Choi, D.-H.; Shin, C.Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.Y. Characterization of tauopathy in a rat model of post-stroke dementia combining acute infarct and chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Genes | APP | BACE1 | PSEN1 | PSEN2 | MAPT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Survival | ||||||
| 2 days | ↓ | ↑↑ | ↑ | ↑↑ | ↑↑ | |
| 7 days | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ | |
| 30 days | ↑ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | |
| Genes | BECN1 | BNIP3 | CASP3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Survival | ||||
| 2 days | ↔ | ↑ | ↑↑↑ | |
| 7 days | ↔ | ↔ | ↑ | |
| 30 days | ↔ | ↔ | ↓ | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pluta, R.; Ouyang, L.; Januszewski, S.; Li, Y.; Czuczwar, S.J. Participation of Amyloid and Tau Protein in Post-Ischemic Neurodegeneration of the Hippocampus of a Nature Identical to Alzheimer's Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2460. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052460
Pluta R, Ouyang L, Januszewski S, Li Y, Czuczwar SJ. Participation of Amyloid and Tau Protein in Post-Ischemic Neurodegeneration of the Hippocampus of a Nature Identical to Alzheimer's Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(5):2460. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052460
Chicago/Turabian StylePluta, Ryszard, Liang Ouyang, Sławomir Januszewski, Yang Li, and Stanisław J. Czuczwar. 2021. "Participation of Amyloid and Tau Protein in Post-Ischemic Neurodegeneration of the Hippocampus of a Nature Identical to Alzheimer's Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 5: 2460. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052460
APA StylePluta, R., Ouyang, L., Januszewski, S., Li, Y., & Czuczwar, S. J. (2021). Participation of Amyloid and Tau Protein in Post-Ischemic Neurodegeneration of the Hippocampus of a Nature Identical to Alzheimer's Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(5), 2460. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052460







