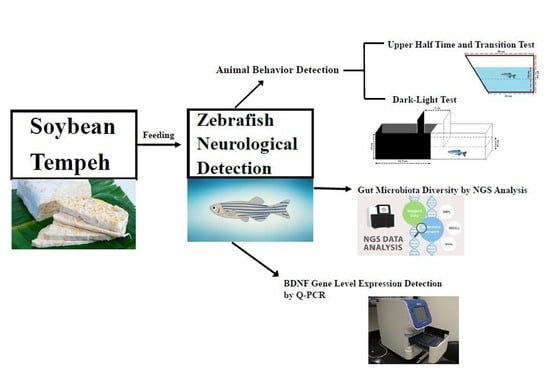
Effect of Tempeh on Gut Microbiota and Anti-Stress Activity in Zebrafish
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Result
2.1. GABA Detection
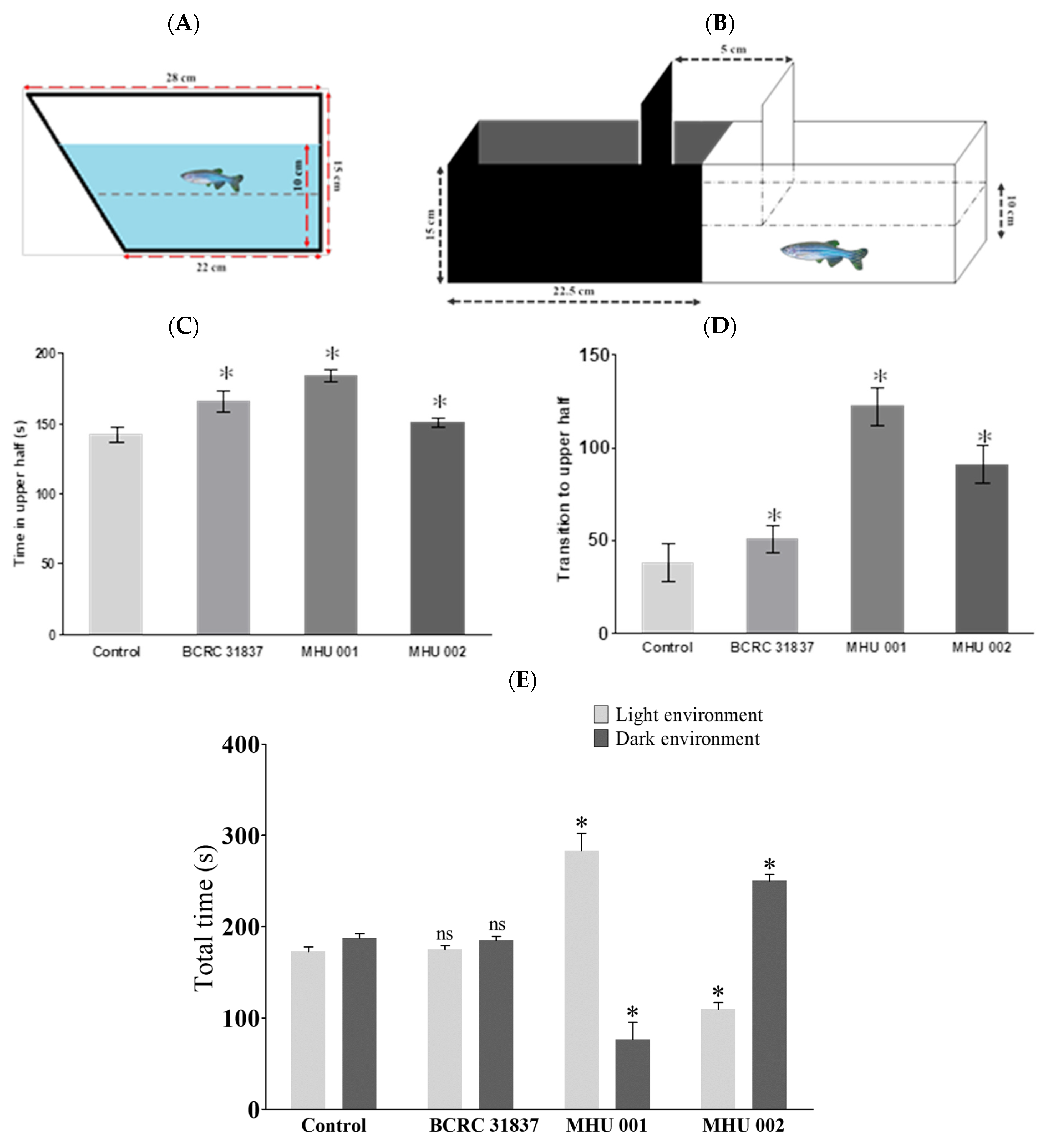
2.2. Novel Tank Diving Test
2.3. Light–Dark Test
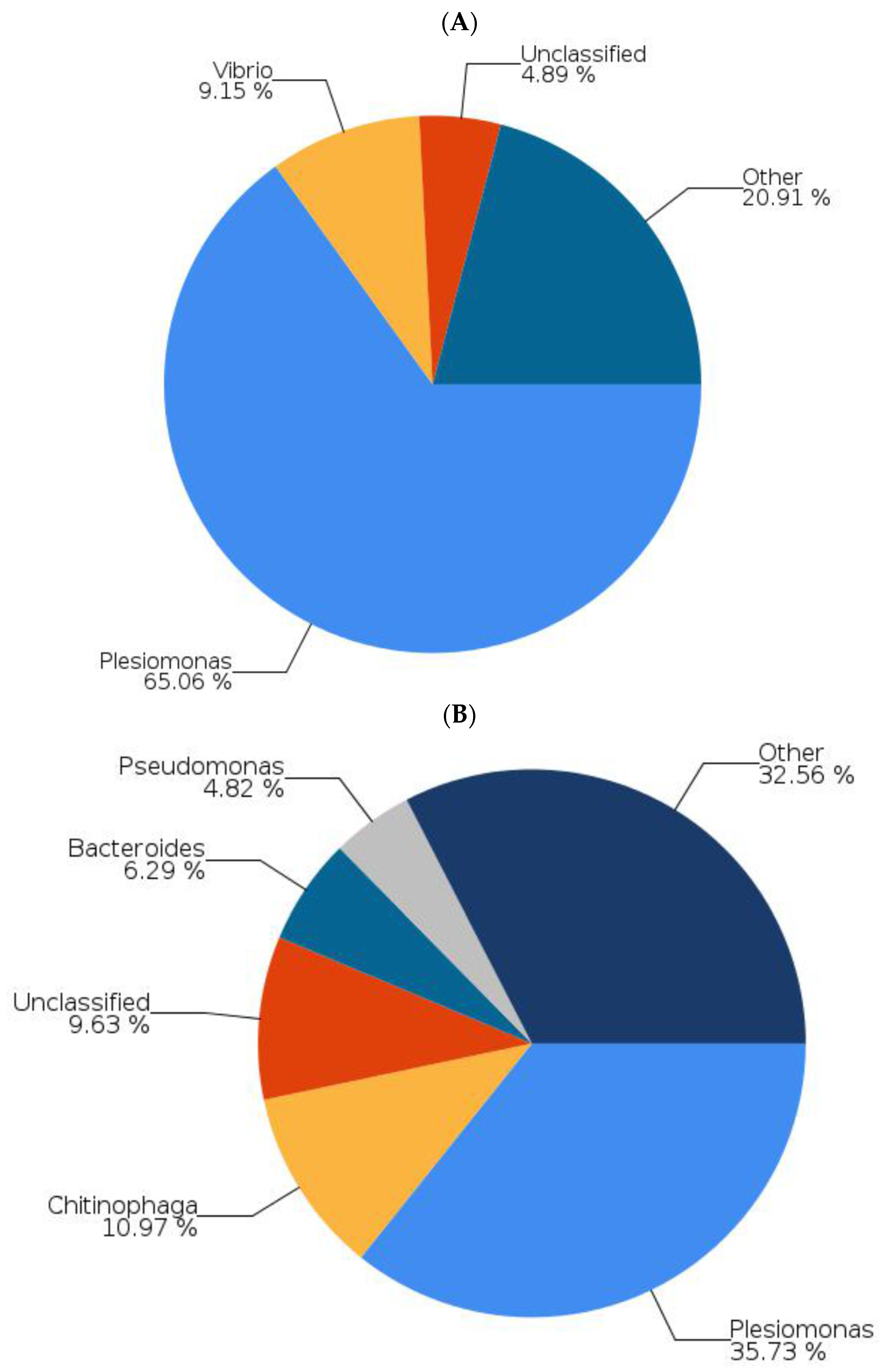
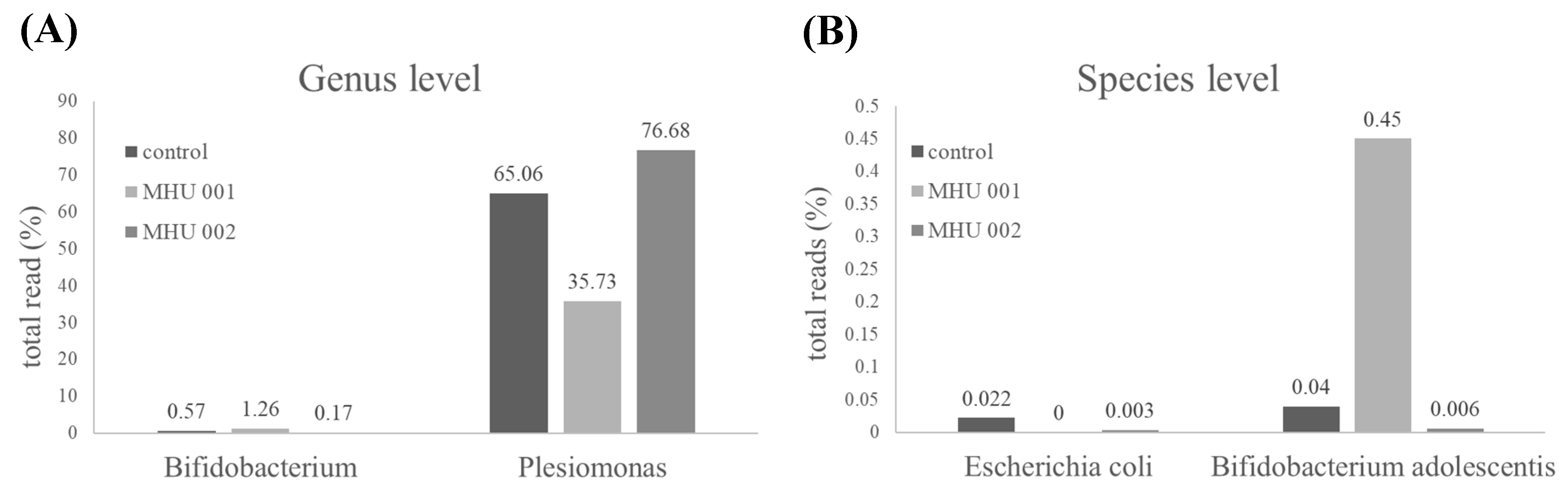
2.4. Tempeh Modulation of Gut Microbial Communities
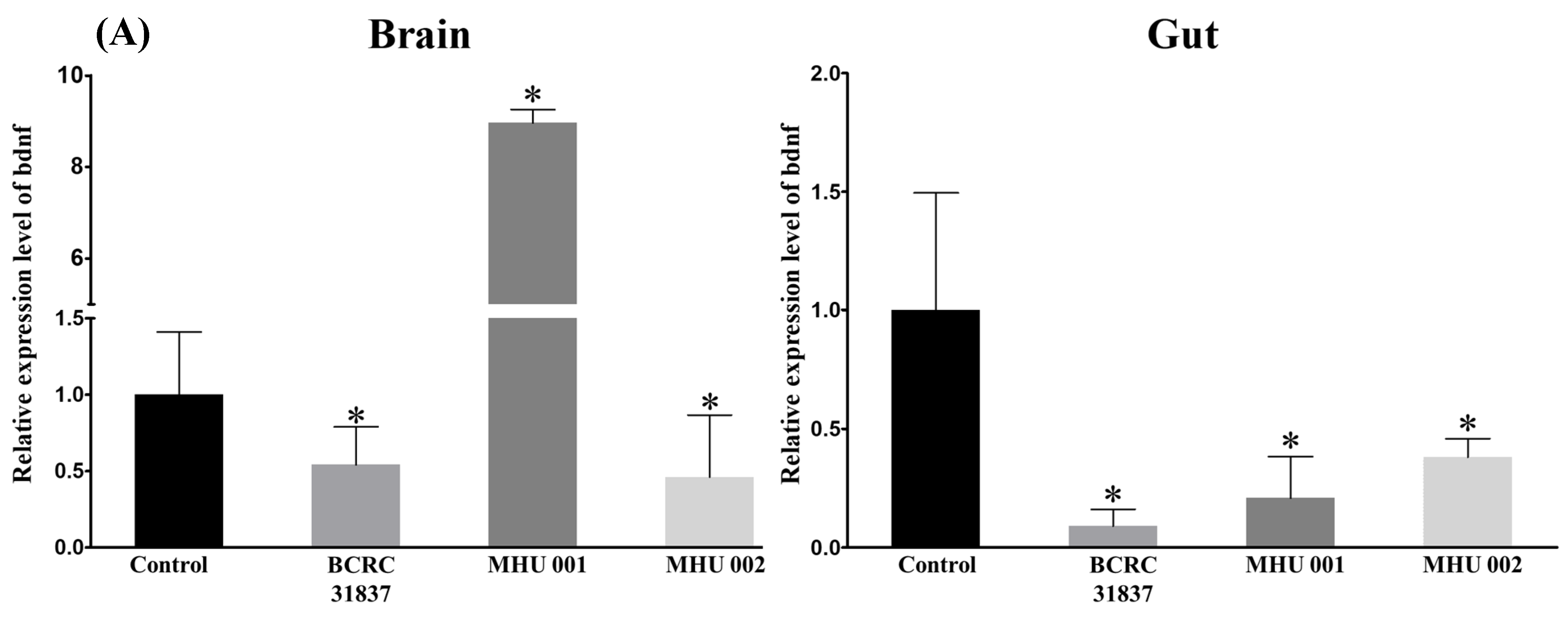
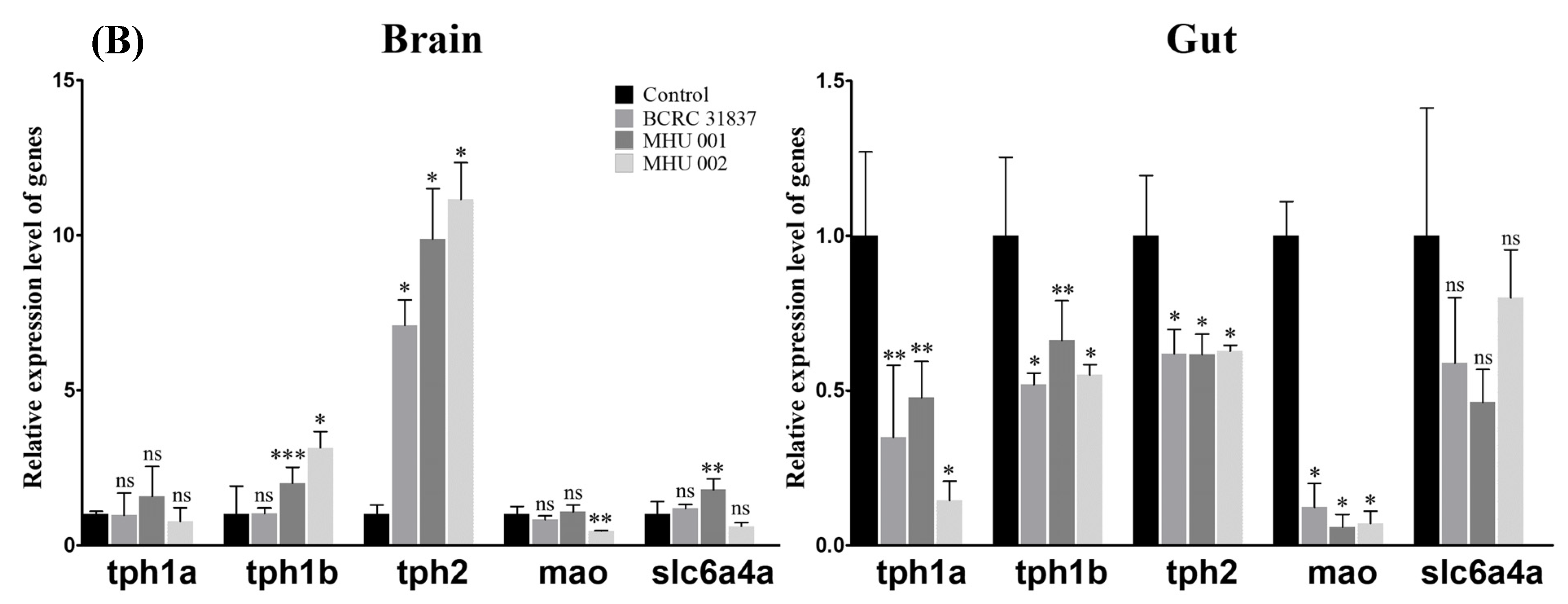
2.5. Tempeh Feeding Induces Changes in Neuronal Gene Expression in Brain and Gut
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Microorganisms
4.2. Tempeh Fermentation
4.3. Aminobutyric Acid Determination
4.4. Animals and Housing
4.5. Behavioral Testing
4.5.1. Novel Tank Diving Test
4.5.2. Light–Dark Test
4.5.3. Euthanasia
4.6. Gut Microbiotal Analysis
4.6.1. Fecal DNA Extraction
4.6.2. PCR Amplification and 16S Sequencing
4.6.3. Bioinformatics Analysis
4.7. RNA Extraction and Expression Analysis
4.7.1. RNA Extraction
4.7.2. cDNA Synthesis
4.7.3. Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nout, M.; Kiers, J. Tempe fermentation, innovation and functionality: Update into the third millenium. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 98, 789–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.M.; Eriksson, A.R.; Schnürer, J. Growth of lactic acid bacteria and Rhizopus oligosporus during barley tempeh fermentation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2005, 104, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Hsieh, S.-L.; Hu, C.-Y. Effects of Red-Bean Tempeh with Various Strains of Rhizopus on GABA Content and Cortisol Level in Zebrafish. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, Y.; Tokumasu, S.; Tubaki, K. An original habitat of tempeh molds. Mycoscience 2004, 45, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Gao, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, O.; Wu, W.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, F.; Ji, B. Evaluation of γ-aminobutyric acid, phytate and antioxidant activity of tempeh-like fermented oats (Avena sativa L.) prepared with different filamentous fungi. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 2544–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astuti, M.; Meliala, A.; Dalais, F.S.; Wahlqvist, M.L. Tempe, a nutritious and healthy food from Indonesia. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 9, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutabarat, L.; Greenfield, H.; Mulholland, M. Isoflavones and coumestrol in soybeans and soybean products from Australia and Indonesia. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2001, 14, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, H.; Furuya, Y.; Endo, Y.; Fujimoto, K. Effect of γ-aminobutyric acid-enriched tempeh-like fermented soybean (GABA-tempeh) on the blood pressure of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2003, 67, 1806–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsuzaki, N.; Shima, J.; Kawamoto, S.; Momose, H.; Kimura, T. Production of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) by Lactobacillus paracasei isolated from traditional fermented foods. Food Microbiol. 2005, 22, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Asmakh, M.; Anuar, F.; Zadjali, F.; Rafter, J.; Pettersson, S. Gut microbial communities modulating brain development and function. Gut Microbes 2012, 3, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinan, T.G.; Stilling, R.; Stanton, C.; Cryan, J. Collective unconscious: How gut microbes shape human behavior. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2015, 63, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinan, T.G.; Stanton, C.; Cryan, J.F. Psychobiotics: A novel class of psychotropic. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 74, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messaoudi, M.; Violle, N.; Bisson, J.-F.; Desor, D.; Javelot, H.; Rougeot, C. Beneficial psychological effects of a probiotic formulation (Lactobacillus helveticus R0052 and Bifidobacterium longum R0175) in healthy human volunteers. Gut Microbes 2011, 2, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kali, A. Psychobiotics: An emerging probiotic in psychiatric practice. Biomed. J. 2016, 39, 223–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Angelo, L.; De Girolamo, P.; Lucini, C.; Terzibasi, E.T.; Baumgart, M.; Castaldo, L.; Cellerino, A. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor: mRNA expression and protein distribution in the brain of the teleost Nothobranchius furzeri. J. Comp. Neurol. 2014, 522, 1004–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Felice, E.; Porreca, I.; Alleva, E.; De Girolamo, P.; Ambrosino, C.; Ciriaco, E.; Germana, A.; Sordino, P. Localization of BDNF expression in the developing brain of zebrafish. J. Anat. 2014, 224, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, G.; Pagtakhan, C.J. Both 5′ and 3′ flanks regulate Zebrafish brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene expression. BMC Neurosci. 2004, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germanà, A.; Laurà, R.; Montalbano, G.; Guerrera, M.C.; Amato, V.; Zichichi, R.; Campo, S.; Ciriaco, E.; Vega, J.A. Expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and TrkB in the lateral line system of zebrafish during development. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2010, 30, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventriglia, M.; Zanardini, R.; Bonomini, C.; Zanetti, O.; Volpe, D.; Pasqualetti, P.; Gennarelli, M.; Bocchio-Chiavetto, L. Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in different neurological diseases. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 901082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlai, R. Social behavior of zebrafish: From synthetic images to biological mechanisms of shoaling. J. Neurosci. Methods 2014, 234, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, R.; Gerlach, G.; Lawrence, C.; Smith, C. The behaviour and ecology of the zebrafish, Danio rerio. Biol. Rev. 2008, 83, 13–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bencan, Z.; Sledge, D.; Levin, E.D. Buspirone, chlordiazepoxide and diazepam effects in a zebrafish model of anxiety. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2009, 94, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, A.; Kadri, F.; DiLeo, J.; Min Chung, K.; Cachat, J.; Goodspeed, J.; Suciu, C.; Roy, S.; Gaikwad, S.; Wong, K.; et al. The developing utility of zebrafish in modeling neurobehavioral disorders. Int. J. Comp. Psychol. 2010, 23, 104–120. [Google Scholar]
- Kashyap, B.; Pegorsch, L.; Frey, R.A.; Sun, C.; Shelden, E.A.; Stenkamp, D.L. Eye-specific gene expression following embryonic ethanol exposure in zebrafish: Roles for heat shock factor 1. Reprod. Toxicol. 2014, 43, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Alia, A.O.; Petrunich-Rutherford, M.L. Anxiety-like behavior and whole-body cortisol responses to components of energy drinks in zebrafish (Danio rerio). PeerJ 2019, 7, e7546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, S.; Chatterjee, D.; Gerlai, R. Chronic social isolation affects thigmotaxis and whole-brain serotonin levels in adult zebrafish. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 292, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, J.M.; Yu, K.; Donaldson, G.P.; Shastri, G.G.; Ann, P.; Ma, L.; Nagler, C.R.; Ismagilov, R.F.; Mazmanian, S.K.; Hsiao, E.Y. Indigenous bacteria from the gut microbiota regulate host serotonin biosynthesis. Cell 2015, 161, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseka, T.M.; Wen, X.-Y.; Foster, J.A.; Kennedy, S.H. Zebrafish models of major depressive disorders. J. Neurosci. Res. 2016, 94, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, J.R.; Jobin, C. Think small: Zebrafish as a model system of human pathology. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 817341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groves, J. Is it time to reassess the BDNF hypothesis of depression? Mol. Psychiatry 2007, 12, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghoubfar, R.; Behrouzi, A.; Ashrafian, F.; Shahryari, A.; Moradi, H.R.; Choopani, S.; Hadifar, S.; Vaziri, F.; Nojoumi, S.A.; Fateh, A.; et al. Modulation of serotonin signaling/metabolism by Akkermansia muciniphila and its extracellular vesicles through the gut-brain axis in mice. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 22119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrelli, L.; Aceto, S.; Agnisola, C.; De Paolo, S.; Dipineto, L.; Stilling, R.M.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F.; Menna, L.F.; Fioretti, A. Probiotic modulation of the microbiota-gut-brain axis and behaviour in zebrafish. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, E.A.; Knight, R.; Mazmanian, S.K.; Cryan, J.F.; Tillisch, K. Gut microbes and the brain: Paradigm shift in neuroscience. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 15490–15496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, M.; Morici, J.F.; Zanoni, M.B.; Bekinschtein, P. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor: A key molecule for memory in the healthy and the pathological brain. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bercik, P.; Denou, E.; Collins, J.; Jackson, W.; Lu, J.; Jury, J.; Deng, Y.; Blennerhassett, P.; Macri, J.; McCoy, K.D.; et al. The intestinal microbiota affect central levels of brain-derived neurotropic factor and behavior in mice. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 599–609.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duranti, S.; Ruiz, L.; Lugli, G.A.; Tames, H.; Milani, C.; Mancabelli, L.; Mancino, W.; Longhi, G.; Carnevali, L.; Sgoifo, A.; et al. Bifidobacterium adolescentis as a key member of the human gut microbiota in the production of GABA. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeselers, G.; Mittge, E.K.; Stephens, W.Z.; Parichy, D.M.; Cavanaugh, C.M.; Guillemin, K.; Rawls, J.F. Evidence for a core gut microbiota in the zebrafish. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1595–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcinelli, S.; Picchietti, S.; Rodiles, A.; Cossignani, L.; Merrifield, D.; Taddei, A.R.; Maradonna, F.; Olivotto, I.; Gioacchini, G.; Carnevali, O. Lactobacillus rhamnosus lowers zebrafish lipid content by changing gut microbiota and host transcription of genes involved in lipid metabolism. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wang, L.; Wang, F.; Wang, C.; Tang, C.; Li, Q.; Li, J.; Zhao, Q. Microbial fingerprinting detects intestinal microbiota dysbiosis in Zebrafish models with chemically-induced enterocolitis. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audira, G.; Sampurna, B.P.; Juniardi, S.; Liang, S.-T.; Lai, Y.-H.; Hsiao, C.-D. A versatile setup for measuring multiple behavior endpoints in zebrafish. Inventions 2018, 3, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, G.-J.; Granato, M.; Haffter, P. A polymorphic zebrafish line for genetic mapping using SSLPs on high-percentage agarose gels. Tech. Tips Online 1997, 2, 148–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cachat, J.; Stewart, A.; Grossman, L.; Gaikwad, S.; Kadri, F.; Chung, K.M.; Wu, N.; Wong, K.; Roy, S.; Suciu, C.; et al. Measuring behavioral and endocrine responses to novelty stress in adult zebrafish. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 1786–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maximino, C.; de Brito, T.M.; Dias, C.A.G.; Gouveia, A., Jr.; Morato, S. Scototaxis as anxiety-like behavior in fish. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Muinck, E.J.; Trosvik, P.; Gilfillan, G.D.; Hov, J.R.; Sundaram, A.Y. A novel ultra high-throughput 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing library preparation method for the Illumina HiSeq platform. Microbiome 2017, 5, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlidis, M.; Theodoridi, A.; Tsalafouta, A. Neuroendocrine regulation of the stress response in adult zebrafish, Danio rerio. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 60, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Composition | Volume (µL) |
|---|---|
| RNA sample (1 µg/µL) | 1 µL |
| 5× iScript Reaction Mix | 4 µL |
| iScript Reverse Transcriptase | 1 µL |
| Nuclear-free water | To 20 µL |
| Gene | GenBank Accession Number | Forward | Reverse |
|---|---|---|---|
| β-actin | NM_131031 | CACAGATCATGTTCGAGACC | GGTCAGGATCTTCATCAGGT |
| bdnf | U42489 | GCTCAGTCATGGGAGTCC | ATAGTAACGAACAGGATGG |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.-C.; Tao, N.-L.; Hu, S.-Y.; Tsai, H.-Y.; Liao, S.-C.; Tsai, W.-L.; Hu, C.-Y. Effect of Tempeh on Gut Microbiota and Anti-Stress Activity in Zebrafish. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12660. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312660
Chen Y-C, Tao N-L, Hu S-Y, Tsai H-Y, Liao S-C, Tsai W-L, Hu C-Y. Effect of Tempeh on Gut Microbiota and Anti-Stress Activity in Zebrafish. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(23):12660. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312660
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yo-Chia, Nha-Linh Tao, Shao-Yang Hu, Hui-Yun Tsai, Sin-Chung Liao, Wei-Lun Tsai, and Chun-Yi Hu. 2021. "Effect of Tempeh on Gut Microbiota and Anti-Stress Activity in Zebrafish" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 23: 12660. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312660
APA StyleChen, Y.-C., Tao, N.-L., Hu, S.-Y., Tsai, H.-Y., Liao, S.-C., Tsai, W.-L., & Hu, C.-Y. (2021). Effect of Tempeh on Gut Microbiota and Anti-Stress Activity in Zebrafish. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(23), 12660. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312660