Structural Basis for the Functional Diversity of Centrins: A Focus on Calcium Sensing Properties and Target Recognition
Abstract
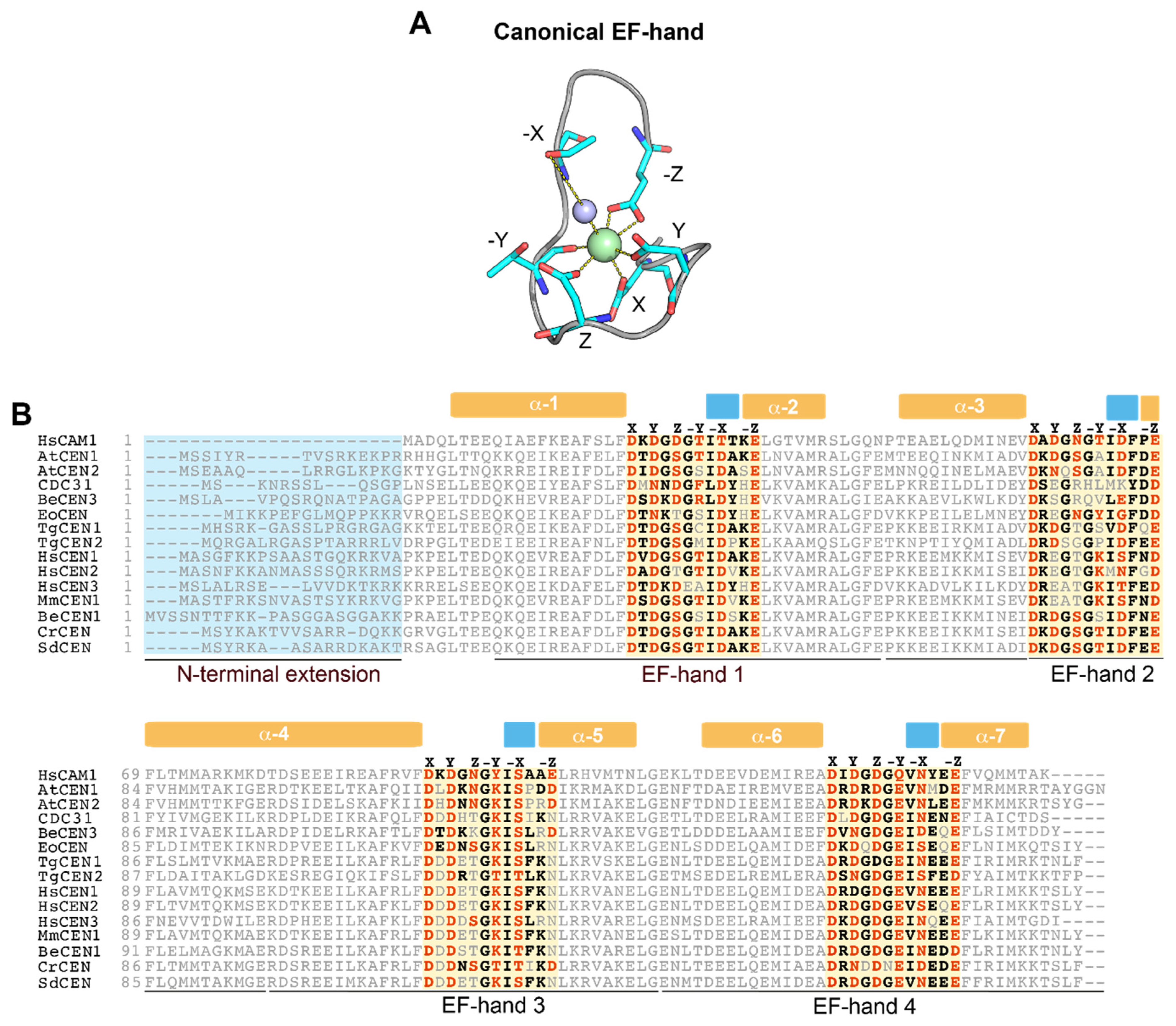
1. Overview of Centrins
2. Centrins Have Large Differences in Their Ability to Sense Ca2+
| Organism | Centrin | UniProt Code | Experimental Ca2+-Binding Sites a | Ca2+ Affinity b | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chlamydomonas reinhardtii | CrCEN | P05434 | 4 | Kd1,2N = 1.2 ± 0.1 × 10−6 M Kd3C = 2 ± 2 × 10−5 M Kd4C = 3 ± 2 × 10−3 M | [64,65,66] |
| Scherffelia dubia | SdCEN | Q06827 | 3 | Ka1N = 2.6 × 105 M−1 Ka2N = 4.3 × 105 M−1 Ka3C = 1.1 × 105 M−1 | [52] |
| Homo sapiens | HsCEN1 | Q12798 | 4 | Ka1,2 = 4.26 × 105 ± 9.5 × 104 M−1 Ka3,4 = 2.73 × 104 ± 2.7 × 103 M−1 | [67,68] |
| Homo sapiens | HsCEN2 | P41208 | 2 | Ka(EF-3) = 8.1 × 103 M−1 Ka(EF-4) = 1.5 × 105 M−1 | [43,48,49,50,62] |
| Homo sapiens | HsCEN3 | O15182 | 3 | Ka1N = 3.3 × 105 M−1 Ka2 = 7.0 × 103 M−1 Ka3 = 7.5 × 103 M−1 | [69] |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae | CDC31 | P06704 | 3 | Ka(EF-1) = 3.0 × 106 M−1 Ka2C = 2.4 × 104 M−1 Ka3C = 3.5 × 104 M−1 | [19,70] |
| Mus musculus | MmCEN1 | P41209 | 4 | Ka1 = 5.23 × 105 M−1 Ka2 = 3.11 × 103 M−1 Ka3 = 2.31 × 105 M−1 Ka4 = 1.59 × 104 M−1 | [51] |
| Arabidopsis thaliana | AtCEN2 | O23184 | 4 | Ka(EF-1) = 2.9 × 105 ± 7.1 × 104 M−1 Ka(EF-2) = 4.1 × 105 ± 6.8 × 104 M−1 Ka(EF-3) = 1.4 × 104 ± 3.8 × 103 M−1 Ka(EF-4) = 3.7 × 103 ± 0.8 × 103 M−1 | [22] |
| Toxoplasma gondii | TgCEN1 | A0A125YHX7 | 2 | Ka(EF-1) = 4.8 × 105 ± 6.1 × 103 M−1 Ka(EF-2) = 3.9 × 104 ± 4.5 × 103 M−1 | [53] |
| Toxoplasma gondii | TgCEN2 | A0A125YZN2 | 1 | Ka(EF-1) = 1.6 × 104 ± 1.5 × 103 M−1 | [53] |
| Trypanosoma brucei | TbCEN4 | A0A3L6L623 | 2 | Ka(EF-3) = 3.18 × 105 ± 4.63 × 104 M−1 Ka(EF-4) = 2.63 × 104 ± 4.37 × 103 M−1 | [14] |
| Trypanosoma brucei | TbCEN5 | Q382E7 | 2 | Kd1,2 = 4.8 µM | [71] |
| Euplotes octocarinatus | EoCEN | Q9XZV2 | 4 | Ka1,2 = 1.12 ± 0.04 × 103 M−1 Ka(EF-4) = 6.82 ± 0.33 × 105 M−1 | [13,72] |
| Blastocladiella emersonii | BeCEN1 | Q4F6W6 | 4 | Kd1 = 6.06 ± 2.26 µM Kd2 = 7.50 ± 0.44 µM Kd3 = 75.20 ± 28.3 µM Kd4 = 9.35 ± 0.93 µM | [73] |
| Blastocladiella emersonii | BeCEN3 | Q4F6W5 | 4 | Kd1 = 2.45 ± 0.04 µM Kd2 = 18.50 ± 0.86 µM Kd3 = 2.11 ± 0.38 µM Kd4 = 38.1 ± 7.46 µM | [73] |
3. Functional Diversity and Specialization of Centrins
| Centrin | Identified Target | Complex Localization | Function/Pathway | Centrin Binding Motif of Targets | Target Binding Affinity a | PDB CODE | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HsCEN2 | XPC | Nucleus | NER | 847-NWKLLAKGLLIRERLKR-863 | with Ca2+, Ka = 170 ± 30 × 106 M−1 without Ca2+, Ka = 8 ± 1 × 106 M−1 | 2GGM, 2OBH, 2A4J | [17,43,49,76,77,87] |
| HsCEN2 | XPA | Nucleus | NER | N/A b | N/A | N/A | [87,88] |
| CDC31 | RAD4 | Nucleus | DNA repair and protein degradation | N/A | N/A | N/A | [28] |
| AtCEN2 | AtRAD4 | Nucleus | NER | 756-EAQAASRWYQLLSSILTR-773 | with Ca2+, Kd = 54 ± 14 nM without Ca2+, Kd = 8 ± 1 µM | N/A | [18,22] |
| HsCEN1 | HsSFI1 (R18) c | Basal body/ centrosome | Centrosome duplication | 670-REVAARESQHNRQLLRGALRRWK-692 | with Ca2+, Ka = 12.03 × 105 M−1 without Ca2+, Ka = 0.03 × 105 M−1 | N/A | [29,89] |
| HsCEN2 | HsSFI1(R17) | Basal body/ centrosome | Centrosome duplication | 641-RADLHHQHSVLHRALQAWVT-660 | with Ca2+, Ka = 6.5 ± 0.9 × 106 M−1 without Ca2+, Ka = 0.25 ± 0.02 × 106 M−1 | 2K2I | [29,78,90] |
| CDC31 | ScSFI1 (R18) | SPB | SPB duplication | 680- IQAISKRNYQLEKMVLKKFR -699 | with Ca2+, Ka = 1 ± 0.03 × 107 M−1 without Ca2+, Ka = 2.4 ± 0.13 × 105 M−1 | 2GV5, 2DOQ | [19,70,74,91] |
| CDC31 | ScSFI1 (R19) | SPB | SPB duplication | 710- ELADEVREEFVLVKTFYIWK -729 | with Ca2+, Ka = 3.5 ± 0.29 × 107 M−1 without Ca2+, Ka = 1.9 ± 0.3 × 105 M−1 | N/A | [19,70,74,91] |
| HsCEN2 HsCEN3 | GANP | Nuclear pore | mRNA export | 1225-IFQTAKETLQELQCFCKYLQRWR-1247 | N/A | N/A | [20,25,92] |
| CDC31 | SAC3 | Nuclear pore | mRNA export | 797-KFFEKWQASYSQAKKNRI-814 | with Ca2+, Ka = 2.2 ± 0.2 × 107 M−1 without Ca2+, Ka = 1.5 ± 0.11 × 106 M−1 | 3FWB, 3FWC, 4MBE | [19,20,24,93,94] |
| AtCEN1 AtCEN2 | SAC3B | Nuclear pore | mRNA export | 1050-AKAKLKLIIRLWKRWSSRQSELRERR-1075 | with Ca2+, Ka = 1.5 x 106 ± 5.5 × 105 M−1 without Ca2+, Ka = 4.1 x 105 ± 8.3 × 104 M−1 | N/A | [21,95,96] |
| CDC31 | KAR1 | SPB | SPB duplication | 237-KKRELIESKWHRLLFHDKK-255 | with Ca2+, Ka = 2.3 ± 0.15 × 107 M−1 without Ca2+, Ka = 4.4 ± 0.1 × 105 M−1 | N/A | [8,19,80,97] |
| HsCEN1 | Transducin β | Photoreceptor Connecting Cilium | Phototransduction | 325-MAVATGSWDSFLKIWN-340 | with Ca2+, Ka = 0.17 ± 0.12 × 106 M−1 | N/A | [23,29,84] |
| HsCEN2 | POC5 | Basal body/ centrosome | Centriole elongation | 156-LQKMENVLDLWSSGLKTN-173 245-KIELMRTFFHWRIGHVRA-262 278-RTLLKKVWKVWRSVVQKQ-295 | N/A | N/A | [98,99] |
| HsCEN2 | PRP40A | Nucleus | Pre-mRNA splicing | 524-KQLRKRNWEALKNILDNMANVTYSTTWSEAQQY-556 | with Ca2+, Ka = 3.6 x ± 0.4 × 106 M−1 | N/A | [75] |
| HsCEN2 | NUP107-160 | Nuclear pore | mRNA and protein nuclear export | N/A | N/A | N/A | [25] |
| HsCEN2 | MPS1 | Centrosome | Centriole assembly | N/A | N/A | N/A | [100] |
| HsCEN3 | MPS1 | Centrosome | Inhibition of centrosome duplication | N/A | N/A | N/A | [101] |
| CDC31 | MPS3p | SPB | SPB duplication | N/A | N/A | N/A | [102] |
| HsCEN2 | CP110 | Centrosome | Cytokinesis | N/A | N/A | N/A | [103] |
| HsCEN2 | CDC25B | Centrosome Cytoplasm | Centrosome integrity | N/A | N/A | N/A | [104,105] |
| HsCEN2 | Gelectin-3 | Centrosome | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | [106] |
| CDC31 | KIC1p | N/A | Cell integrity/ morphogenesis | N/A | N/A | N/A | [107,108] |
| CDC31 | 26S proteasome | Cytoplasm/ proteasome | Protein degradation | N/A | N/A | N/A | [28] |
| CDC31 | cytosolic and mitochondrial factors | Mitochondria | Energy metabolism | N/A | N/A | N/A | [109] |
| CDC31 | VPS13 | N/A | TGN (trans-Golgi network) –PVC (prevacuolar compartment) transport and TGN homotypic fusion | N/A | N/A | N/A | [110,111] |
| AtCEN1 | Tonneau1 | Cytoskeleton | microtubule centers organization | N/A | N/A | N/A | [1] |
4. Centrin–Peptide Complexes
4.1. Centrins and Nucleotide Excision Repair
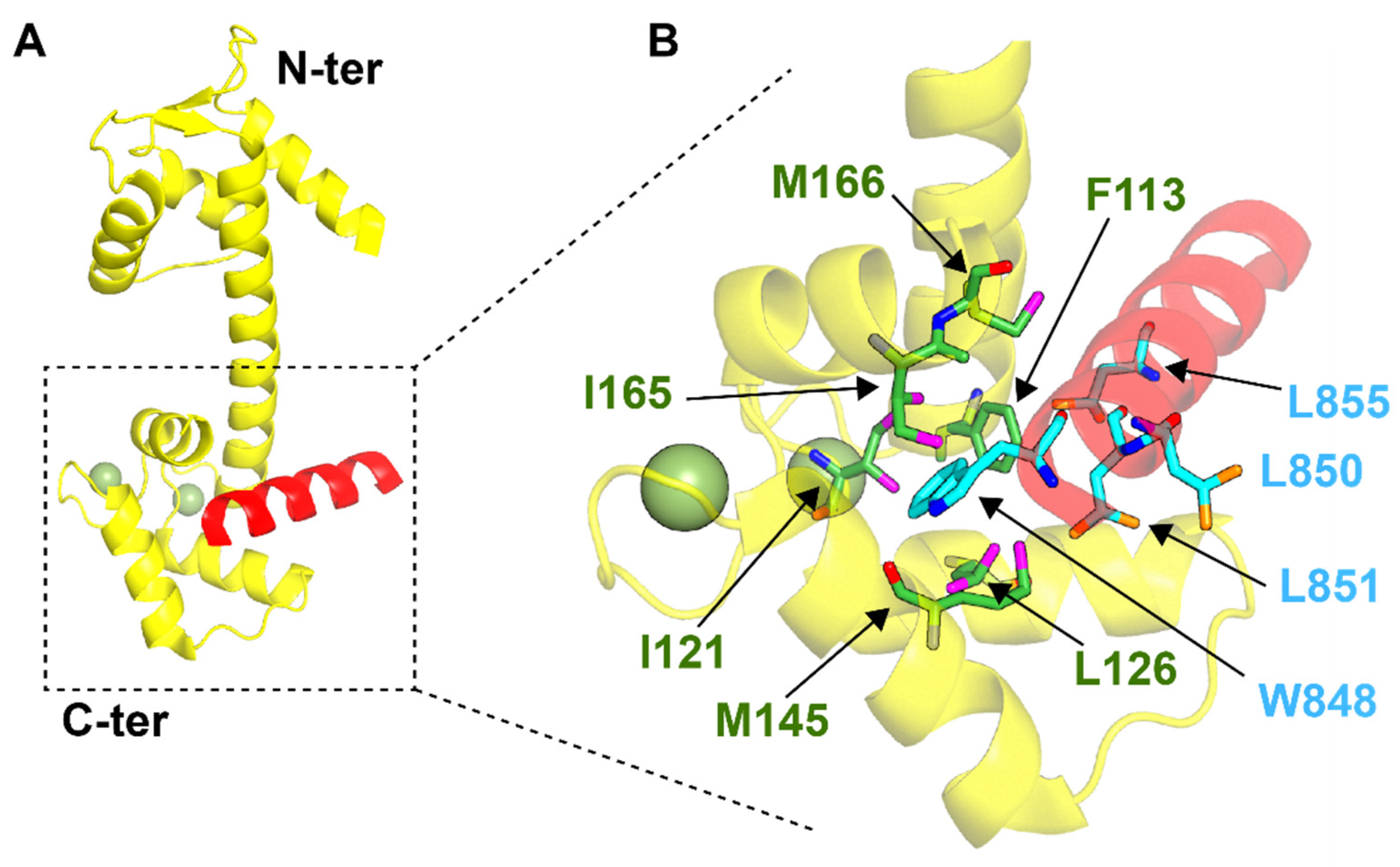
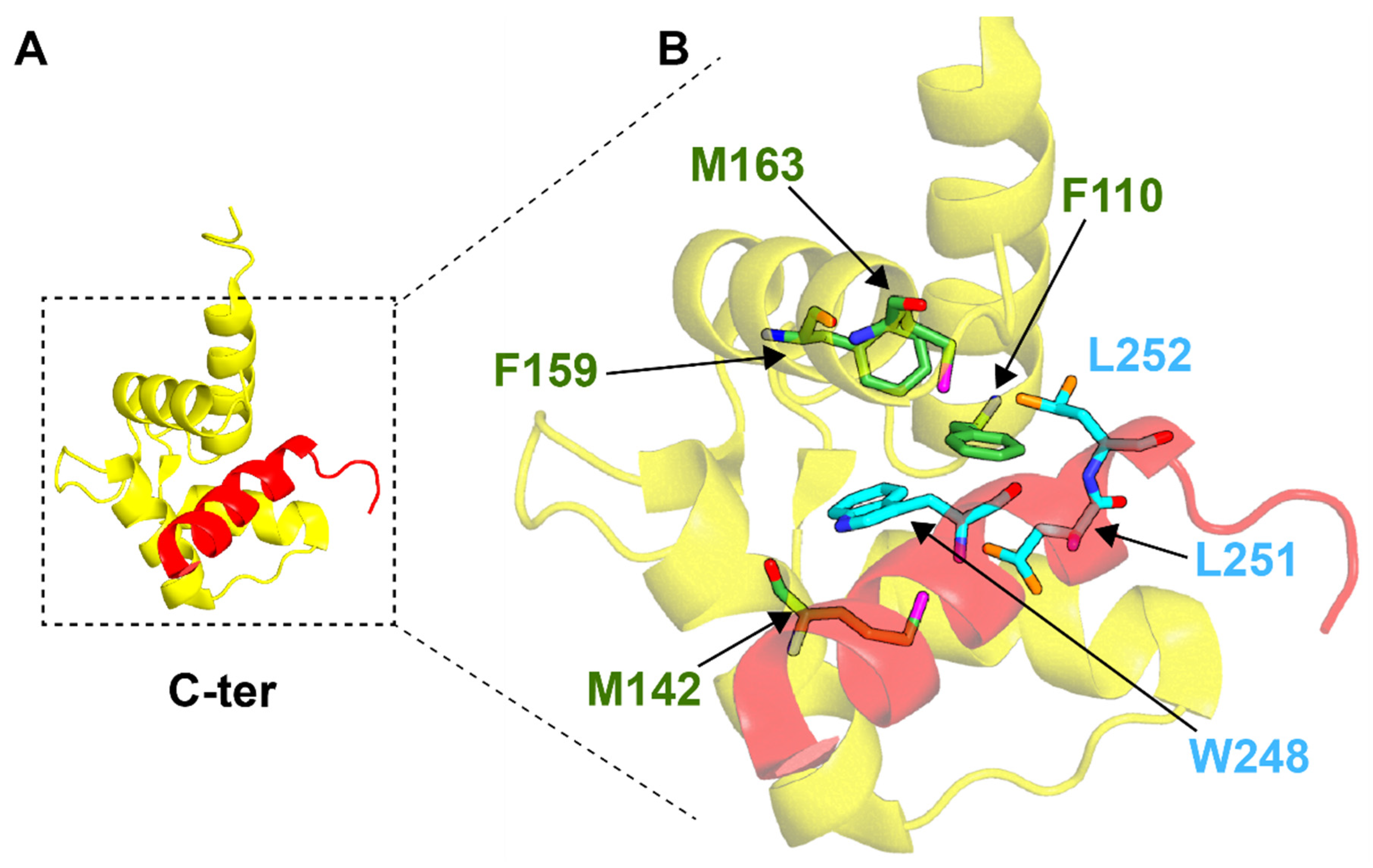
4.2. SFI1 and Centrosome Duplication
4.3. Centrins and mRNA Export
4.4. Centrins and KAR1
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Azimzadeh, J.; Nacry, P.; Christodoulidou, A.; Drevensek, S.; Camilleri, C.; Amiour, N.; Parcy, F.; Pastuglia, M.; Bouchez, D. Arabidopsis TONNEAU1 proteins are essential for preprophase band formation and interact with centrin. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 2146–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Vecchio, A.J.; Harper, J.D.I.; Vaughn, K.C.; Baron, A.T.; Salisbury, J.L.; Overall, R.L. Centrin homologues in higher plants are prominently associated with the developing cell plate. Protoplasma 1997, 196, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugerolle, G.; Bricheux, G.; Coffe, G. Centrin protein and genes in Trichomonas vaginalis and close relatives. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2000, 47, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salisbury, J.L.; Baron, A.; Surek, B.; Melkonian, M. Striated flagellar roots: Isolation and partial characterization of a calcium-modulated contractile organelle. J. Cell Biol. 1984, 99, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errabolu, R.; Sanders, M.A.; Salisbury, J.L. Cloning of a cDNA encoding human centrin, an EF-hand protein of centrosomes and mitotic spindle poles. J. Cell Sci. 1994, 107 Pt 1, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, V.D.; Huang, B. Molecular cloning and centrosomal localization of human caltractin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 11039–11043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, K.; Shimizu, T. cDNA sequence for mouse caltractin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1993, 1216, 126–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spang, A.; Courtney, I.; Fackler, U.; Matzner, M.; Schiebel, E. The calcium-binding protein cell division cycle 31 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a component of the half bridge of the spindle pole body. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 123, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baum, P.; Furlong, C.; Byers, B. Yeast gene required for spindle pole body duplication: Homology of its product with Ca2+-binding proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 5512–5516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Mengersen, A.; Lee, V.D. Molecular cloning of cDNA for caltractin, a basal body-associated Ca2+-binding protein: Homology in its protein sequence with calmodulin and the yeast CDC31 gene product. J. Cell Biol. 1988, 107, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeddu, L.; Klotz, C.; Le Caer, J.P.; Beisson, J. Characterization of centrin genes in Paramecium. Eur. J. Biochem. 1996, 238, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middendorp, S.; Paoletti, A.; Schiebel, E.; Bornens, M. Identification of a new mammalian centrin gene, more closely related to Saccharomyces cerevisiae CDC31 gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 9141–9146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaqin, Z.; Jiuying, F.; Aihua, L.; Binsheng, Y. The characterization for the binding of calcium and terbium to Euplotes octocarinatus centrin. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2009, 71, 1756–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, F.; Ye, K.; Zhang, J.; Liao, S.; Zhang, X.; Xu, C.; Tu, X. Solution structure of TbCentrin4 from Trypanosoma brucei and its interactions with Ca2+ and other centrins. Biochem. J. 2018, 475, 3763–3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, K.; Johnson, J.; Florens, L.; Fraunholz, M.; Suravajjala, S.; DiLullo, C.; Yates, J.; Roos, D.S.; Murray, J.M. Cytoskeletal components of an invasion machine—The apical complex of Toxoplasma gondii. PLoS Pathog. 2006, 2, e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletti, A.; Moudjou, M.; Paintrand, M.; Salisbury, J.L.; Bornens, M. Most of centrin in animal cells is not centrosome-associated and centrosomal centrin is confined to the distal lumen of centrioles. J. Cell Sci. 1996, 109 Pt 13, 3089–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, R.; Okuda, Y.; Watanabe, E.; Mori, T.; Iwai, S.; Masutani, C.; Sugasawa, K.; Hanaoka, F. Centrin 2 stimulates nucleotide excision repair by interacting with xeroderma pigmentosum group C protein. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 5664–5674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.; Flury, S.; Kalck, V.; Hohn, B.; Molinier, J. CENTRIN2 interacts with the Arabidopsis homolog of the human XPC protein (AtRAD4) and contributes to efficient synthesis-dependent repair of bulky DNA lesions. Plant Mol. Biol. 2006, 61, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miron, S.; Durand, D.; Chilom, C.; Perez, J.; Craescu, C.T. Binding of calcium, magnesium, and target peptides to Cdc31, the centrin of yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 6409–6422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jani, D.; Lutz, S.; Marshall, N.J.; Fischer, T.; Kohler, A.; Ellisdon, A.M.; Hurt, E.; Stewart, M. Sus1, Cdc31, and the Sac3 CID region form a conserved interaction platform that promotes nuclear pore association and mRNA export. Mol. Cell 2009, 33, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedretti, M.; Conter, C.; Dominici, P.; Astegno, A. SAC3B is a target of CML19, the centrin 2 of Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochem. J. 2020, 477, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Verde, V.; Trande, M.; D’Onofrio, M.; Dominici, P.; Astegno, A. Binding of calcium and target peptide to calmodulin-like protein CML19, the centrin 2 of Arabidopsis thaliana. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 1289–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giessl, A.; Pulvermüller, A.; Trojan, P.; Park, J.H.; Choe, H.-W.; Ernst, O.P.; Hofmann, K.P.; Wolfrum, U. Differential Expression and Interaction with the Visual G-protein Transducin of Centrin Isoforms in Mammalian Photoreceptor Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 51472–51481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, T.; Rodríguez-Navarro, S.; Pereira, G.; Rácz, A.; Schiebel, E.; Hurt, E. Yeast centrin Cdc31 is linked to the nuclear mRNA export machinery. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004, 6, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resendes, K.K.; Rasala, B.A.; Forbes, D.J. Centrin 2 localizes to the vertebrate nuclear pore and plays a role in mRNA and protein export. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 1755–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, C.Y. Centrins in unicellular organisms: Functional diversity and specialization. Protoplasma 2012, 249, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araki, M.; Masutani, C.; Takemura, M.; Uchida, A.; Sugasawa, K.; Kondoh, J.; Ohkuma, Y.; Hanaoka, F. Centrosome protein centrin 2/caltractin 1 is part of the xeroderma pigmentosum group C complex that initiates global genome nucleotide excision repair. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 18665–18672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Madura, K. Centrin/Cdc31 is a novel regulator of protein degradation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 1829–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grecu, D.; Assairi, L. CK2 phosphorylation of human centrins 1 and 2 regulates their binding to the DNA repair protein XPC, the centrosomal protein Sfi1 and the phototransduction protein transducin β. FEBS Open Bio 2014, 4, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavet, O.; Alvarez, C.; Gaspar, P.; Bornens, M. Centrin4p, a novel mammalian centrin specifically expressed in ciliated cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 1818–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, P.E.; Glantz, J.N.; Orth, J.D.; Poynter, G.M.; Salisbury, J.L. Testis-specific murine centrin, Cetn1: Genomic characterization and evidence for retroposition of a gene encoding a centrosome protein. Genomics 1999, 60, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedberg, F. Centrin isoforms in mammals. Relation to calmodulin. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2006, 33, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubusson-Fleury, A.; Balavoine, G.; Lemullois, M.; Bouhouche, K.; Beisson, J.; Koll, F. Centrin diversity and basal body patterning across evolution: New insights from Paramecium. Biol. Open 2017, 6, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, B.; Selvapandiyan, A.; Gerald, N.J.; Majam, V.; Zheng, H.; Wickramarachchi, T.; Tiwari, J.; Fujioka, H.; Moch, J.K.; Kumar, N.; et al. Centrins, cell cycle regulation proteins in human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 31871–31883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.Y.; Pypaert, M.; Warren, G. Golgi duplication in Trypanosoma brucei requires Centrin2. Science 2005, 310, 1196–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berriman, M.; Ghedin, E.; Hertz-Fowler, C.; Blandin, G.; Renauld, H.; Bartholomeu, D.C.; Lennard, N.J.; Caler, E.; Hamlin, N.E.; Haas, B.; et al. The genome of the African trypanosome Trypanosoma brucei. Science 2005, 309, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bornens, M.; Azimzadeh, J. Origin and Evolution of the Centrosome. In Eukaryotic Membranes and Cytoskeleton: Origins and Evolution; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, F.; Garreau de Loubresse, N.; Klotz, C.; Beisson, J.; Koll, F. Centrin deficiency in Paramecium affects the geometry of basal-body duplication. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, 2097–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonda, K.; Yoshida, A.; Oami, K.; Takahashi, M. Centrin is essential for the activity of the ciliary reversal-coupled voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 323, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogendeau, D.; Klotz, C.; Arnaiz, O.; Malinowska, A.; Dadlez, M.; de Loubresse, N.G.; Ruiz, F.; Koll, F.; Beisson, J. Functional diversification of centrins and cell morphological complexity. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Babu, Y.S.; Bugg, C.E.; Cook, W.J. Structure of calmodulin refined at 2.2 A resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 1988, 204, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuboniwa, H.; Tjandra, N.; Grzesiek, S.; Ren, H.; Klee, C.B.; Bax, A. Solution structure of calcium-free calmodulin. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1995, 2, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.R.; Ryan, Z.C.; Salisbury, J.L.; Kumar, R. The Structure of the Human Centrin 2-Xeroderma Pigmentosum Group C Protein Complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 18746–18752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gifford, J.L.; Walsh, M.P.; Vogel, H.J. Structures and metal-ion-binding properties of the Ca2+-binding helix-loop-helix EF-hand motifs. Biochem. J. 2007, 405, 199–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trande, M.; Pedretti, M.; Bonza, M.C.; Di Matteo, A.; D’Onofrio, M.; Dominici, P.; Astegno, A. Cation and peptide binding properties of CML7, a calmodulin-like protein from Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2019, 199, 110796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, D.; Steinkötter, J.; Melkonian, M. Molecular cloning and evolutionary analysis of the calcium-modulated contractile protein, centrin, in green algae and land plants. Plant Mol. Biol. 1993, 23, 1243–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro, E.; Sigrist, C.J.; Gattiker, A.; Bulliard, V.; Langendijk-Genevaux, P.S.; Gasteiger, E.; Bairoch, A.; Hulo, N. ScanProsite: Detection of PROSITE signature matches and ProRule-associated functional and structural residues in proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, W362–W365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durussel, I.; Blouquit, Y.; Middendorp, S.; Craescu, C.T.; Cox, J.A. Cation- and peptide-binding properties of human centrin 2. FEBS Lett. 2000, 472, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charbonnier, J.B.; Renaud, E.; Miron, S.; Le Du, M.H.; Blouquit, Y.; Duchambon, P.; Christova, P.; Shosheva, A.; Rose, T.; Angulo, J.F.; et al. Structural, thermodynamic, and cellular characterization of human centrin 2 interaction with xeroderma pigmentosum group C protein. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 373, 1032–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matei, E.; Miron, S.; Blouquit, Y.; Duchambon, P.; Durussel, I.; Cox, J.A.; Craescu, C.T. C-terminal half of human centrin 2 behaves like a regulatory EF-hand domain. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 1439–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Kim, D.S.; Hong, J.E.; Park, J.H. Crystal structure of wild-type centrin 1 from Mus musculus occupied by Ca2+. Biochemistry 2017, 82, 1129–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radu, L.; Durussel, I.; Assairi, L.; Blouquit, Y.; Miron, S.; Cox, J.A.; Craescu, C.T. Scherffelia dubia centrin exhibits a specific mechanism for Ca2+-controlled target binding. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 4383–4394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombardi, L.; Pedretti, M.; Conter, C.; Dominici, P.; Astegno, A. Distinct Calcium Binding and Structural Properties of Two Centrin Isoforms from Toxoplasma gondii. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astegno, A.; Bonza, M.C.; Vallone, R.; La Verde, V.; D’Onofrio, M.; Luoni, L.; Molesini, B.; Dominici, P. Arabidopsis calmodulin-like protein CML36 is a calcium (Ca2+) sensor that interacts with the plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase isoform ACA8 and stimulates its activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 15049–15061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallone, R.; La Verde, V.; D’Onofrio, M.; Giorgetti, A.; Dominici, P.; Astegno, A. Metal binding affinity and structural properties of calmodulin-like protein 14 from Arabidopsis thaliana. Protein Sci. 2016, 25, 1461–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogunrinde, A.; Munro, K.; Davidson, A.; Ubaid, M.; Snedden, W.A. Arabidopsis Calmodulin-Like Proteins, CML15 and CML16 Possess Biochemical Properties Distinct from Calmodulin and Show Non-overlapping Tissue Expression Patterns. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Verde, V.; Dominici, P.; Astegno, A. Towards Understanding Plant Calcium Signaling through Calmodulin-Like Proteins: A Biochemical and Structural Perspective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linse, S.; Helmersson, A.; Forsen, S. Calcium binding to calmodulin and its globular domains. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 8050–8054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astegno, A.; La Verde, V.; Marino, V.; Dell’Orco, D.; Dominici, P. Biochemical and biophysical characterization of a plant calmodulin: Role of the N- and C-lobes in calcium binding, conformational change, and target interaction. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Proteins Proteom. 2016, 1864, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiech, H.; Geier, B.M.; Paschke, T.; Spang, A.; Grein, K.; Steinkotter, J.; Melkonian, M.; Schiebel, E. Characterization of green alga, yeast, and human centrins. Specific subdomain features determine functional diversity. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 22453–22461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourbez, M.; Firanescu, C.; Yang, A.; Unipan, L.; Duchambon, P.; Blouquit, Y.; Craescu, C.T. Calcium-dependent Self-assembly of Human Centrin 2. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 47672–47680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Miron, S.; Duchambon, P.; Assairi, L.; Blouquit, Y.; Craescu, C.T. The N-terminal domain of human centrin 2 has a closed structure, binds calcium with a very low affinity, and plays a role in the protein self-assembly. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 880–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conter, C.; Bombardi, L.; Pedretti, M.; Favretto, F.; Di Matteo, A.; Dominici, P.; Astegno, A. The interplay of self-assembly and target binding in centrin 1 from Toxoplasma gondii. Biochem. J. 2021, 478, 2571–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeraraghavan, S.; Fagan, P.A.; Hu, H.; Lee, V.; Harper, J.F.; Huang, B.; Chazin, W.J. Structural independence of the two EF-hand domains of caltractin. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 28564–28571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, C.; Lee, V.D.; Chazin, W.J.; Huang, B. High level expression in Escherichia coli and characterization of the EF-hand calcium-binding protein caltractin. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 15795–15802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Sheehan, J.H.; Chazin, W.J. The Mode of Action of Centrin: Binding of Ca2+ and a peptide fragment of Kar1p to the C-terminal domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 50895–50903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phanindranath, R.; Sudhakar, D.V.S.; Thangaraj, K.; Sharma, Y. Conformational scanning of individual EF-hand motifs of calcium sensor protein centrin-1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 570, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phanindranath, R.; Sudhakar, D.V.; Sharma, A.K.; Thangaraj, K.; Sharma, Y. Optimization of purification method and characterization of recombinant human Centrin-1. Protein Expr. Purif. 2016, 124, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.A.; Tirone, F.; Durussel, I.; Firanescu, C.; Blouquit, Y.; Duchambon, P.; Craescu, C.T. Calcium and magnesium binding to human centrin 3 and interaction with target peptides. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 840–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Sandercock, A.M.; Conduit, P.; Robinson, C.V.; Williams, R.L.; Kilmartin, J.V. Structural role of Sfi1p–centrin filaments in budding yeast spindle pole body duplication. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 173, 867–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, F.; Yang, X.; Diwu, Y.; Ma, H.; Tu, X. Trypanosoma brucei centrin5 is enriched in the flagellum and interacts with other centrins in a calcium-dependent manner. FEBS Open Bio 2019, 9, 1421–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.-J.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Ren, L.-X.; Li, G.-T.; Liang, A.-H.; Yang, B.-S. Spectral study on the interaction of ciliate Euplotes octocarinatus centrin and metal ions. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2007, 186, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, A.I.; Wiggers, H.J.; Damalio, J.C.P.; Araujo, A.P.U.; Ribichich, K.F.; de Camargo, P.C. Structural and thermodynamic studies of two centrin isoforms from Blastocladiella emersonii upon calcium binding. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Proteins Proteom. 2013, 1834, 2823–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilmartin, J.V. Sfi1p has conserved centrin-binding sites and an essential function in budding yeast spindle pole body duplication. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 162, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz Casas, A.; Chazin, W.J.; Pastrana-Ríos, B. Prp40 Homolog A Is a Novel Centrin Target. Biophys. J. 2017, 112, 2529–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Popescu, A.; Miron, S.; Blouquit, Y.; Duchambon, P.; Christova, P.; Craescu, C.T. Xeroderma pigmentosum group C protein possesses a high affinity binding site to human centrin 2 and calmodulin. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 40252–40261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Miron, S.; Mouawad, L.; Duchambon, P.; Blouquit, Y.; Craescu, C.T. Flexibility and Plasticity of Human Centrin 2 Binding to the Xeroderma Pigmentosum Group C Protein (XPC) from Nuclear Excision Repair. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 3653–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Sanz, J.; Kateb, F.; Assairi, L.; Blouquit, Y.; Bodenhausen, G.; Abergel, D.; Mouawad, L.; Craescu, C.T. Structure, dynamics and thermodynamics of the human centrin 2/hSfi1 complex. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 395, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Chazin, W.J. Unique features in the C-terminal domain provide caltractin with target specificity. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 330, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggins, S.; Rose, M.D. Direct interaction between yeast spindle pole body components: Kar1p is required for Cdc31p localization to the spindle pole body. J. Cell Biol. 1994, 125, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Pan, J. Regulation of flagellar biogenesis by a calcium dependent protein kinase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukasiewicz, K.B.; Greenwood, T.M.; Negron, V.C.; Bruzek, A.K.; Salisbury, J.L.; Lingle, W.L. Control of centrin stability by Aurora A. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lingle, W.L.; Lutz, W.H.; Ingle, J.N.; Maihle, N.J.; Salisbury, J.L. Centrosome hypertrophy in human breast tumors: Implications for genomic stability and cell polarity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 2950–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trojan, P.; Krauss, N.; Choe, H.W.; Giessl, A.; Pulvermüller, A.; Wolfrum, U. Centrins in retinal photoreceptor cells: Regulators in the connecting cilium. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2008, 27, 237–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyn, S.M.; Seda, C.; Campbell, M.; Weiss, K.L.; Hu, H.; Pastrana-Rios, B.; Chazin, W.J. The biochemical effect of Ser167 phosphorylation on Chlamydomonas reinhardtii centrin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 342, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanoguet, Z.; Campbell, M.; Ramos, S.; Seda, C.; Moreno, L.P.; Pastrana-Rios, B. Effects of Phosphorylation in Chlamydomonas Centrin Ser 167. Calcium Bind Proteins 2006, 1, 108–114. [Google Scholar]
- Krasikova, Y.S.; Rechkunova, N.I.; Maltseva, E.A.; Craescu, C.T.; Petruseva, I.O.; Lavrik, O.I. Influence of centrin 2 on the interaction of nucleotide excision repair factors with damaged DNA. Biochemistry. 2012, 77, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, R.; Sakai, W.; Tone, D.; Hanaoka, F.; Sugasawa, K. Structure-function analysis of the EF-hand protein centrin-2 for its intracellular localization and nucleotide excision repair. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 6917–6929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Guo, X.; Yang, B. Calcium-induced human centrin 1 self-assembly and double-regulating the binding with peptide R18-Sfi1p. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 128, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Sanz, J.; Yang, A.; Blouquit, Y.; Duchambon, P.; Assairi, L.; Craescu, C.T. Binding of human centrin 2 to the centrosomal protein hSfi1. FEBS J 2006, 273, 4504–4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rüthnick, D.; Vitale, J.; Neuner, A.; Schiebel, E. The N-terminus of Sfi1 and yeast centrin Cdc31 provide the assembly site for a new spindle pole body. J. Cell Biol. 2021, 220, e202004196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jani, D.; Lutz, S.; Hurt, E.; Laskey, R.A.; Stewart, M.; Wickramasinghe, V.O. Functional and structural characterization of the mammalian TREX-2 complex that links transcription with nuclear messenger RNA export. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 4562–4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Aguilera, C.; Tous, C.; Gómez-González, B.; Huertas, P.; Luna, R.; Aguilera, A. The THP1-SAC3-SUS1-CDC31 complex works in transcription elongation-mRNA export preventing RNA-mediated genome instability. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 4310–4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jani, D.; Valkov, E.; Stewart, M. Structural basis for binding the TREX2 complex to nuclear pores, GAL1 localisation and mRNA export. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 6686–6697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Tang, X.; Tian, G.; Wang, F.; Liu, K.; Nguyen, V.; Kohalmi, S.E.; Keller, W.A.; Tsang, E.W.T.; Harada, J.J.; et al. Arabidopsis homolog of the yeast TREX-2 mRNA export complex: Components and anchoring nucleoporin. Plant J. 2010, 61, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; La, H.; Tang, K.; Miki, D.; Yang, L.; Wang, B.; Duan, C.-G.; Nie, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; et al. SAC3B, a central component of the mRNA export complex TREX-2, is required for prevention of epigenetic gene silencing in Arabidopsis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Geier, B.M.; Wiech, H.; Schiebel, E. Binding of Centrins and Yeast Calmodulin to Synthetic Peptides Corresponding to Binding Sites in the Spindle Pole Body Components Kar1p and Spc110p*. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 28366–28374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azimzadeh, J.; Hergert, P.; Delouvée, A.; Euteneuer, U.; Formstecher, E.; Khodjakov, A.; Bornens, M. hPOC5 is a centrin-binding protein required for assembly of full-length centrioles. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 185, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas, T.J.; Daly, O.M.; Conroy, P.C.; Tomas, M.; Wang, Y.; Lalor, P.; Dockery, P.; Ferrando-May, E.; Morrison, C.G. Calcium-binding capacity of centrin2 is required for linear POC5 assembly but not for nucleotide excision repair. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-H.; Kasbek, C.; Majumder, S.; Yusof, A.M.; Fisk, H.A. Mps1 Phosphorylation Sites Regulate the Function of Centrin 2 in Centriole Assembly. Mol. Biol. Cell 2010, 21, 4361–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawant, D.B.; Majumder, S.; Perkins, J.L.; Yang, C.H.; Eyers, P.A.; Fisk, H.A. Centrin 3 is an inhibitor of centrosomal Mps1 and antagonizes centrin 2 function. Mol. Biol. Cell 2015, 26, 3741–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaspersen, S.L.; Giddings, T.H., Jr.; Winey, M. Mps3p is a novel component of the yeast spindle pole body that interacts with the yeast centrin homologue Cdc31p. J. Cell Biol. 2002, 159, 945–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, W.Y.; Spektor, A.; Luciano, D.J.; Indjeian, V.B.; Chen, Z.; Salisbury, J.L.; Sánchez, I.; Dynlacht, B.D. CP110 cooperates with two calcium-binding proteins to regulate cytokinesis and genome stability. Mol. Biol. Cell 2006, 17, 3423–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutros, R.; Lorenzo, C.; Mondesert, O.; Jauneau, A.; Oakes, V.; Dozier, C.; Gabrielli, B.; Ducommun, B. CDC25B associates with a centrin 2-containing complex and is involved in maintaining centrosome integrity. Biol. Cell 2011, 103, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutros, R.; Mondesert, O.; Lorenzo, C.; Astuti, P.; McArthur, G.; Chircop, M.; Ducommun, B.; Gabrielli, B. CDC25B overexpression stabilises centrin 2 and promotes the formation of excess centriolar foci. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, A.; Poirier, F.; Jacob, R.; Delacour, D. Galectin-3, a novel centrosome-associated protein, required for epithelial morphogenesis. Mol. Biol. Cell 2010, 21, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, D.S.; Biggins, S.; Rose, M.D. The yeast centrin, cdc31p, and the interacting protein kinase, Kic1p, are required for cell integrity. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 143, 751–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanovska, I.; Rose, M.D. Fine structure analysis of the yeast centrin, Cdc31p, identifies residues specific for cell morphology and spindle pole body duplication. Genetics 2001, 157, 503–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Bian, S.; Li, H.; Madura, K. A role for Saccharomyces cerevisiae Centrin (Cdc31) in mitochondrial function and biogenesis. Mol. Microbiol. 2018, 110, 831–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, M.D.; Payne, G.S. Vps13 and Cdc31/centrin: Puzzling partners in membrane traffic. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 216, 299–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, M.; Oleskie, A.N.; Ayyash, M.; Dutta, S.; Mancour, L.; Abazeed, M.E.; Brace, E.J.; Skiniotis, G.; Fuller, R.S. The Vps13p–Cdc31p complex is directly required for TGN late endosome transport and TGN homotypic fusion. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 216, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molinier, J.; Ramos, C.; Fritsch, O.; Hohn, B. CENTRIN2 modulates homologous recombination and nucleotide excision repair in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 1633–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Winderickx, J.; Nauwelaers, D.; Dumortier, F.; De Doncker, A.; Thevelein, J.M.; Van Dijck, P. Deletion of SFI1, a novel suppressor of partial Ras-cAMP pathway deficiency in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, causes G(2) arrest. Yeast 1999, 15, 1097–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, M.; Sato, M.; Yamamoto, M. Spindle pole body components are reorganized during fission yeast meiosis. Mol. Biol. Cell 2012, 23, 1799–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grecu, D.; Blouquit, Y.; Assairi, L. The E144 residue of Scherffelia dubia centrin discriminates between the DNA repair protein XPC and the centrosomal protein Sfi1. FEBS Open Bio 2014, 4, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, T.; Strässer, K.; Rácz, A.; Rodriguez-Navarro, S.; Oppizzi, M.; Ihrig, P.; Lechner, J.; Hurt, E. The mRNA export machinery requires the novel Sac3p-Thp1p complex to dock at the nucleoplasmic entrance of the nuclear pores. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 5843–5852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurshakova, M.M.; Krasnov, A.N.; Kopytova, D.V.; Shidlovskii, Y.V.; Nikolenko, J.V.; Nabirochkina, E.N.; Spehner, D.; Schultz, P.; Tora, L.; Georgieva, S.G. SAGA and a novel Drosophila export complex anchor efficient transcription and mRNA export to NPC. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 4956–4965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spang, A.; Courtney, I.; Grein, K.; Matzner, M.; Schiebel, E. The Cdc31p-binding protein Kar1p is a component of the half bridge of the yeast spindle pole body. J. Cell Biol. 1995, 128, 863–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pedretti, M.; Bombardi, L.; Conter, C.; Favretto, F.; Dominici, P.; Astegno, A. Structural Basis for the Functional Diversity of Centrins: A Focus on Calcium Sensing Properties and Target Recognition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12173. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212173
Pedretti M, Bombardi L, Conter C, Favretto F, Dominici P, Astegno A. Structural Basis for the Functional Diversity of Centrins: A Focus on Calcium Sensing Properties and Target Recognition. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(22):12173. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212173
Chicago/Turabian StylePedretti, Marco, Luca Bombardi, Carolina Conter, Filippo Favretto, Paola Dominici, and Alessandra Astegno. 2021. "Structural Basis for the Functional Diversity of Centrins: A Focus on Calcium Sensing Properties and Target Recognition" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 22: 12173. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212173
APA StylePedretti, M., Bombardi, L., Conter, C., Favretto, F., Dominici, P., & Astegno, A. (2021). Structural Basis for the Functional Diversity of Centrins: A Focus on Calcium Sensing Properties and Target Recognition. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(22), 12173. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212173






