MPA_Pathway_Tool: User-Friendly, Automatic Assignment of Microbial Community Data on Metabolic Pathways
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
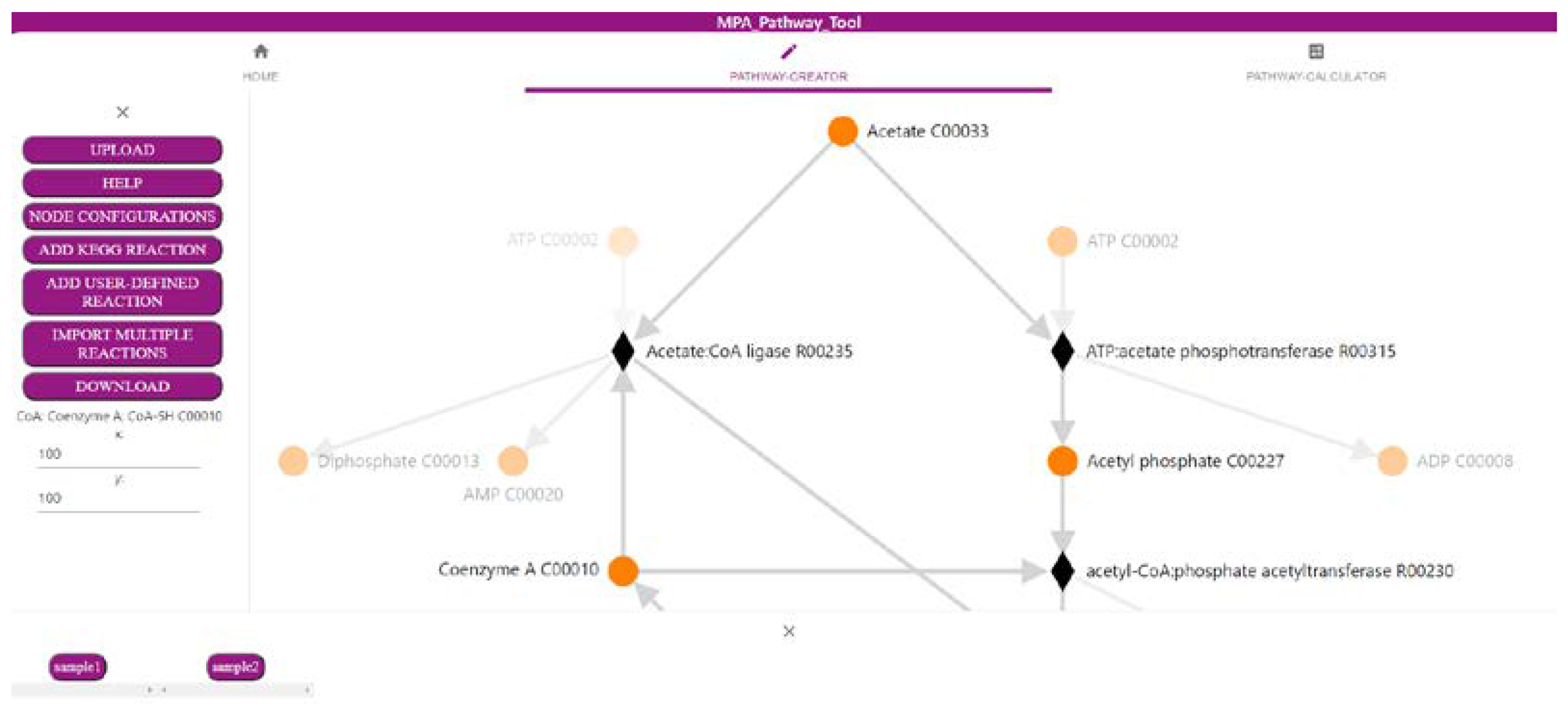
2.1. The ‘Pathway-Creator’ Enables Users to Define Their Own Metabolic Pathways
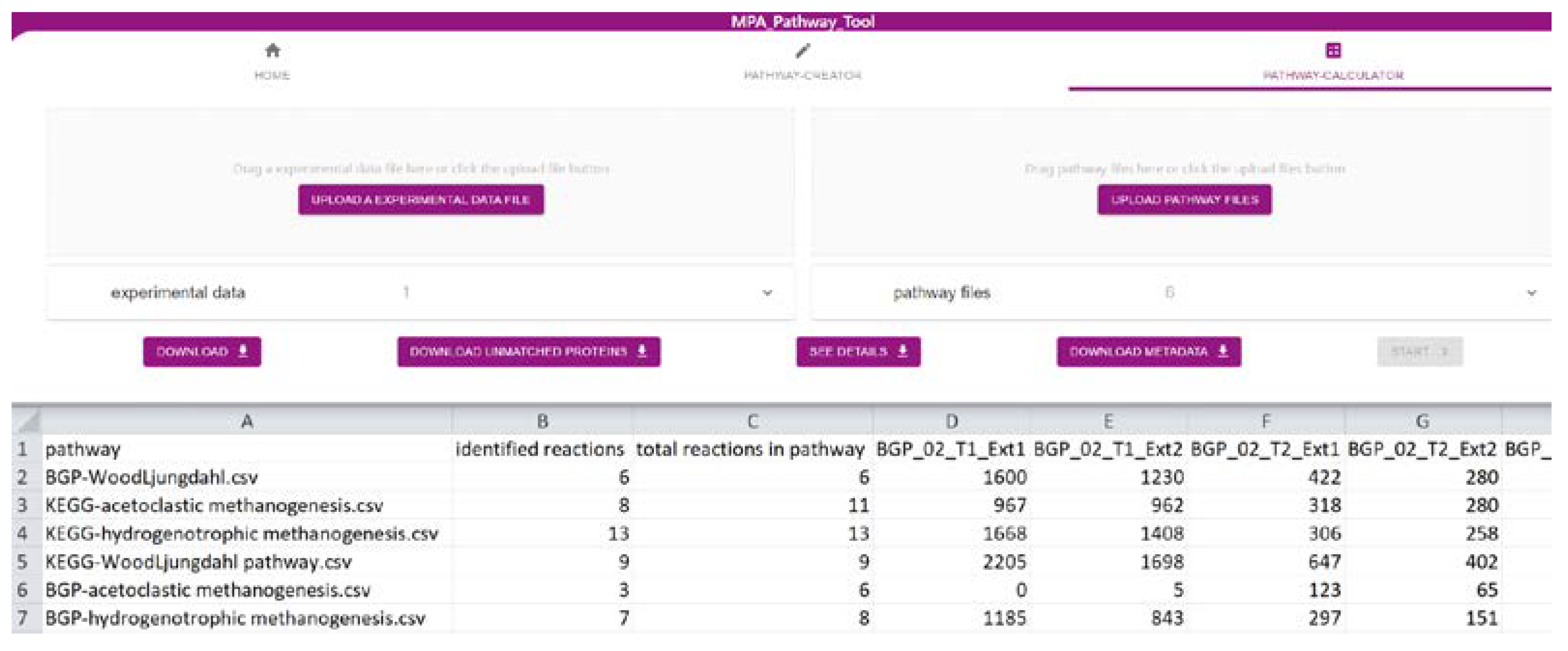
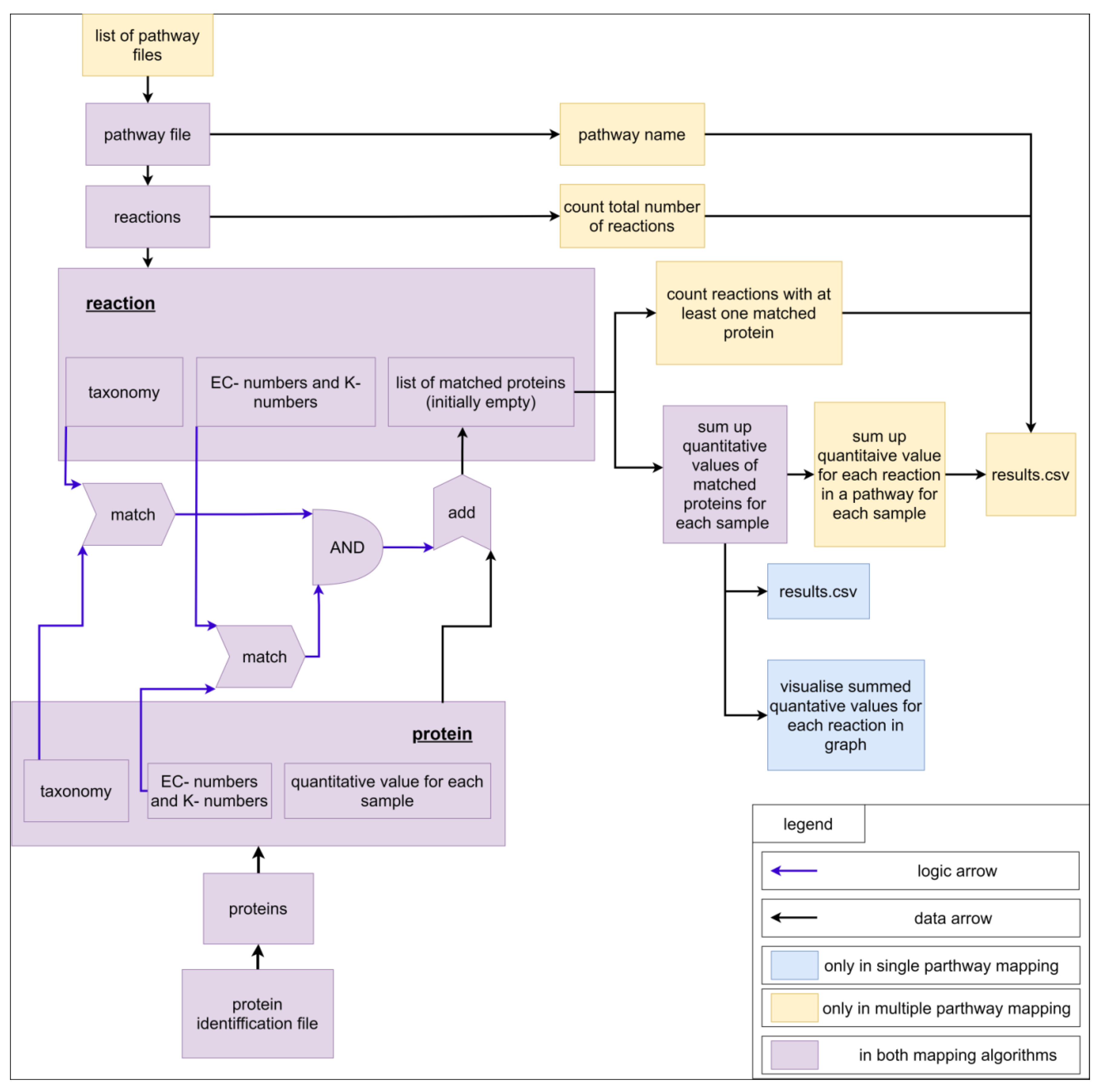
2.2. The ‘Pathway-Calculator’ Enables Automated Mapping of Experimental Data on Multiple Metabolic Pathways
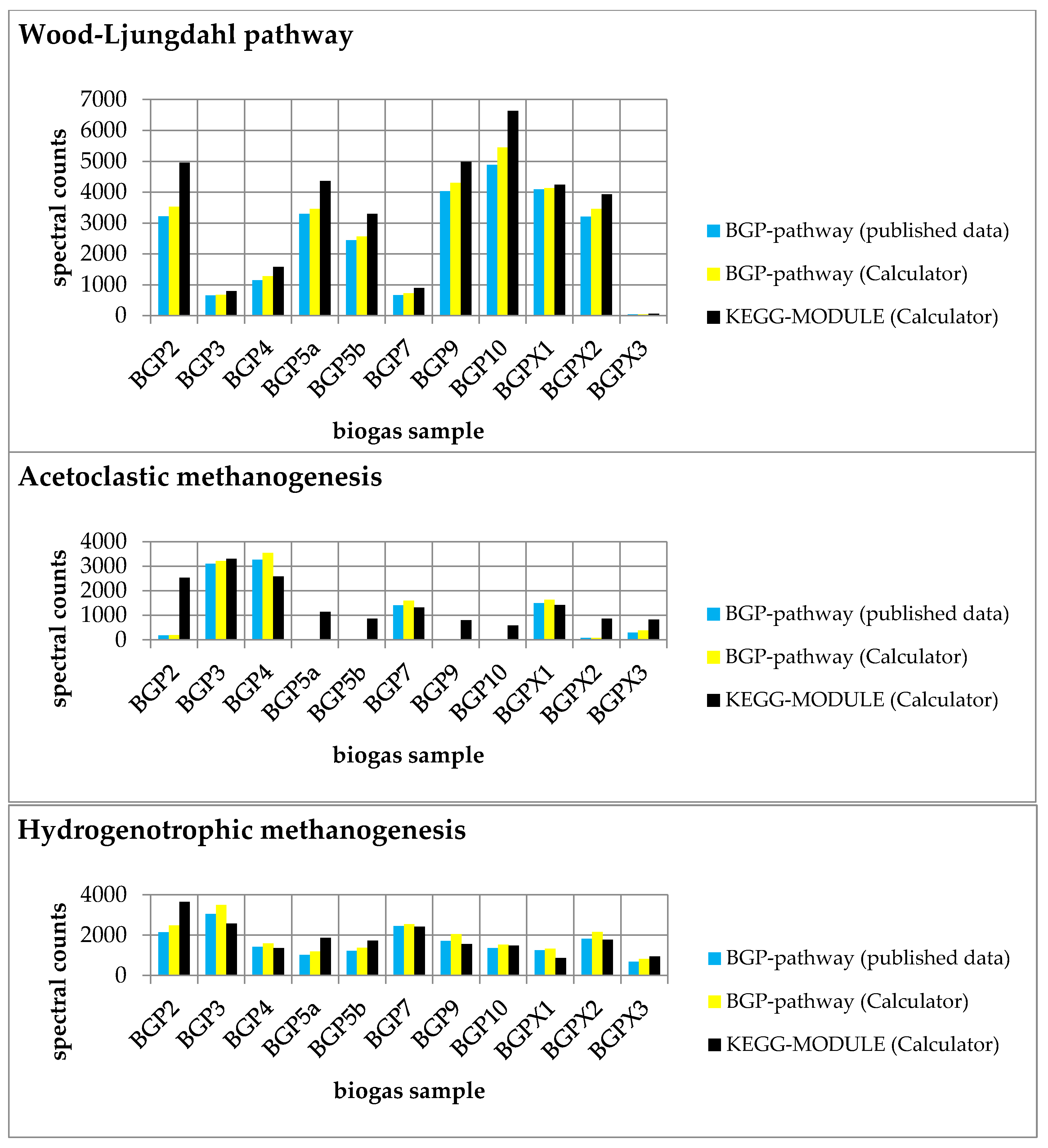
2.3. Tool Validation with Experimental Data
2.4. Conclusion: The MPA_Pathway_Tool Provides An Easy and Fast Option to Set up Multiple Pathways
2.5. Future Work: Integration to Other Features and Addition of New Functions Will Increase the Flexibility of the MPA_Pathway_Tool
3. Availability and Implementation
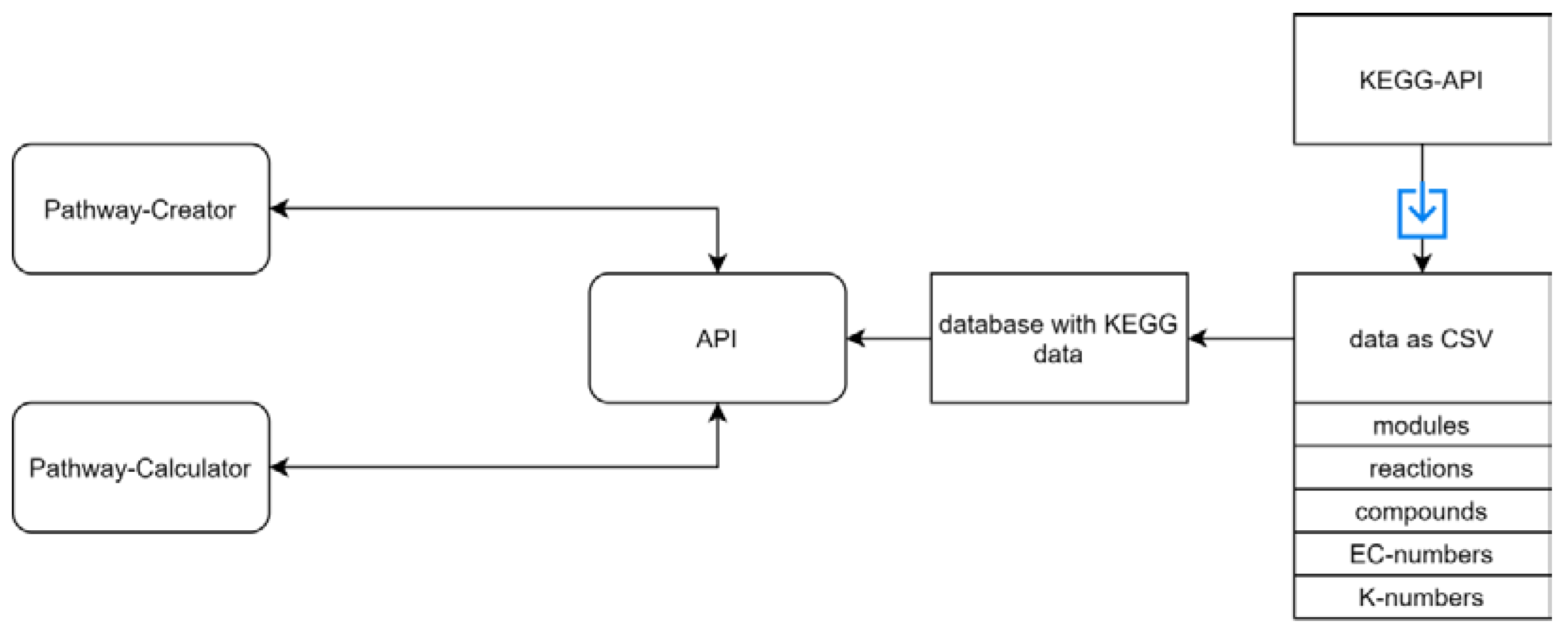
3.1. General Workflow
3.2. Implementation
3.3. Mapping Algorithm
3.4. Experimental Data
3.5. Availability
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, C.L.; Versalovic, J. The human microbiome and its potential importance to pediatrics. Pediatrics 2012, 129, 950–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ursell, L.K.; Metcalf, J.L.; Parfrey, L.W.; Knight, R. Defining the human microbiome. Nutr. Rev. 2012, 70 (Suppl. 1), S38–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, W.; Abraham, P.E.; Li, Z.; Pan, C.; Hettich, R.L. Microbial metaproteomics for characterizing the range of metabolic functions and activities of human gut microbiota. Proteomics 2015, 15, 3424–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Deeke, S.A.; Ning, Z.; Starr, A.E.; Butcher, J.; Li, J.; Mayne, J.; Cheng, K.; Liao, B.; Li, L.; et al. Metaproteomics reveals associations between microbiome and intestinal extracellular vesicle proteins in pediatric inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biemann, R.; Buß, E.; Benndorf, D.; Lehmann, T.; Schallert, K.; Püttker, S.; Reichl, U.; Isermann, B.; Schneider, J.G.; Saake, G.; et al. Fecal Metaproteomics Reveals Reduced Gut Inflammation and Changed Microbial Metabolism Following Lifestyle-Induced Weight Loss. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Liu, T.; Müller, B.; Schnürer, A. The microbial community structure in industrial biogas plants influences the degradation rate of straw and cellulose in batch tests. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2016, 9, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kohrs, F.; Wolter, S.; Benndorf, D.; Heyer, R.; Hoffmann, M.; Rapp, E.; Bremges, A.; Sczyrba, A.; Schlüter, A.; Reichl, U. Fractionation of biogas plant sludge material improves metaproteomic characterization to investigate metabolic activity of microbial communities. Proteomics 2015, 15, 3585–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heyer, R.; Schallert, K.; Siewert, C.; Kohrs, F.; Greve, J.; Maus, I.; Klang, J.; Klocke, M.; Heiermann, M.; Hoffmann, H.; et al. Metaproteome Analysis Reveals That Syntrophy, Competition, and Phage-Host Interaction Shape Microbial Communities in Biogas Plants. 2019. Available online: https://microbiomejournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40168-019-0673-y (accessed on 8 October 2021).
- Morris, S.J.; Blackwood, C.B. The Ecology of the Soil Biota and their Function. In Soil Microbiology, Ecology and Biochemistry, 4th ed.; Paul, E.A., Ed.; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2015; ISBN 9780124159556. [Google Scholar]
- McGuire, K.L.; Treseder, K.K. Microbial communities and their relevance for ecosystem models: Decomposition as a case study. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heyer, R.; Schallert, K.; Büdel, A.; Zoun, R.; Dorl, S.; Behne, A.; Kohrs, F.; Püttker, S.; Siewert, C.; Muth, T.; et al. A Robust and Universal Metaproteomics Workflow for Research Studies and Routine Diagnostics Within 24 h Using Phenol Extraction, FASP Digest, and the MetaProteomeAnalyzer. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giardine, B.; Riemer, C.; Hardison, R.C.; Burhans, R.; Elnitski, L.; Shah, P.; Zhang, Y.; Blankenberg, D.; Albert, I.; Taylor, J.; et al. Galaxy: A platform for interactive large-scale genome analysis. Genome Res. 2005, 15, 1451–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muth, T.; Behne, A.; Heyer, R.; Kohrs, F.; Benndorf, D.; Hoffmann, M.; Lehtevä, M.; Reichl, U.; Martens, L.; Rapp, E. The MetaProteomeAnalyzer: A powerful open-source software suite for metaproteomics data analysis and interpretation. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 1557–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, E.; Reinert, K.; Groepl, C.; Kohlbacher, O.; Sturm, M.; Hildebrandt, A. OPENMS; A Generic Open Source Framework for Chromatography/MS-Based Proteomics. 2005. Available online: http://publications.imp.fu-berlin.de/352/ (accessed on 8 October 2021).
- Leipzig, J. A review of bioinformatic pipeline frameworks. Brief. Bioinform. 2017, 18, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blank, C.; Easterly, C.; Gruening, B.; Johnson, J.; Kolmeder, C.A.; Kumar, P.; May, D.; Mehta, S.; Mesuere, B.; Brown, Z.; et al. Disseminating Metaproteomic Informatics Capabilities and Knowledge Using the Galaxy-P Framework. Proteomes 2018, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S.; Sato, Y.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M. KEGG for integration and interpretation of large-scale molecular data sets. Nucleic Acids Research 2012, 40, D109–D114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joshi-Tope, G.; Gillespie, M.; Vastrik, I.; D’Eustachio, P.; Schmidt, E.; de Bono, B.; Jassal, B.; Gopinath, G.R.; Wu, G.R.; Matthews, L.; et al. Reactome: A knowledgebase of biological pathways. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, D428–D432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- King, Z.A.; Dräger, A.; Ebrahim, A.; Sonnenschein, N.; Lewis, N.E.; Palsson, B.O. Escher: A Web Application for Building, Sharing, and Embedding Data-Rich Visualizations of Biological Pathways. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11, e1004321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karp, P.D.; Paley, S.M.; Midford, P.E.; Krummenacker, M.; Billington, R.; Kothari, A.; Ong, W.K.; Subhraveti, P.; Keseler, I.M.; Caspi, R. Pathway Tools version 24.0: Integrated Software for Pathway/Genome Informatics and Systems Biology. 2015. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1510.03964 (accessed on 8 October 2021).
- Mao, X.; Cai, T.; Olyarchuk, J.G.; Wei, L. Automated genome annotation and pathway identification using the KEGG Orthology (KO) as a controlled vocabulary. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3787–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Campanaro, S.; Treu, L.; Seshadri, R.; Ivanova, N.; Kougias, P.G.; Kyrpides, N.; Angelidaki, I. Metabolic dependencies govern microbial syntrophies during methanogenesis in an anaerobic digestion ecosystem. Microbiome 2020, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, T.; Watanabe, T.; Shima, S. Hydrogenotrophic Methanogenesis. In Biogenesis of Hydrocarbons; Stams, A.J., Sousa, D., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; ISBN 978-3-319-53114-4. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, M.D.; Dumontier, M.; Aalbersberg, I.J.J.; Appleton, G.; Axton, M.; Baak, A.; Blomberg, N.; Boiten, J.-W.; da Silva Santos, L.B.; Bourne, P.E.; et al. The FAIR Guiding Principles for scientific data management and stewardship. Sci Data 2016, 3, 160018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vangay, P.; Burgin, J.; Johnston, A.; Beck, K.L.; Berrios, D.C.; Blumberg, K.; Canon, S.; Chain, P.; Chandonia, J.-M.; Christianson, D.; et al. Microbiome Metadata Standards: Report of the National Microbiome Data Collaborative’s Workshop and Follow-On Activities. mSystems 2021, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesuere, B.; Devreese, B.; Debyser, G.; Aerts, M.; Vandamme, P.; Dawyndt, P. Unipept: Tryptic peptide-based biodiversity analysis of metaproteome samples. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 5773–5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiebenhoefer, H.; Schallert, K.; Renard, B.Y.; Trappe, K.; Schmid, E.; Benndorf, D.; Riedel, K.; Muth, T.; Fuchs, S. A complete and flexible workflow for metaproteomics data analysis based on MetaProteomeAnalyzer and Prophane. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 3212–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klamt, S.; Saez-Rodriguez, J.; Gilles, E.D. Structural and functional analysis of cellular networks with CellNetAnalyzer. BMC Syst. Biol. 2007, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ebrahim, A.; Lerman, J.A.; Palsson, B.O.; Hyduke, D.R. COBRApy: COnstraints-Based Reconstruction and Analysis for Python. BMC Syst. Biol. 2013, 7, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Orth, J.D.; Thiele, I.; Palsson, B.Ø. What is flux balance analysis? Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- React – A JavaScript library for building user interfaces. Available online: https://reactjs.org/ (accessed on 8 October 2021).
- McCurdy, N. Getting Started | Create React App. Available online: https://create-react-app.dev/docs/getting-started/ (accessed on 30 March 2021).
- GitHub. reduxjs/redux. Available online: https://github.com/reduxjs/redux (accessed on 30 March 2021).
- GitHub. mobxjs/mobx. Available online: https://github.com/mobxjs/mobx (accessed on 30 March 2021).
- GitHub. danielcaldas/react-d3-graph. Available online: https://github.com/danielcaldas/react-d3-graph (accessed on 30 March 2021).
- GitHub. axios/axios. Available online: https://github.com/axios/axios (accessed on 30 March 2021).
- Material-UI: A popular React UI framework. Available online: https://material-ui.com/ (accessed on 30 March 2021).
- GitHub. lodash/lodash. Available online: https://github.com/lodash/lodash (accessed on 30 March 2021).
- GitHub. Infinidat/file-saver. Available online: https://github.com/Infinidat/file-saver (accessed on 30 March 2021).
- GitHub. google/gson. Available online: https://github.com/google/gson (accessed on 30 March 2021).
- GitHub. sbmlteam/jsbml. Available online: https://github.com/sbmlteam/jsbml (accessed on 6 May 2021).


| Experimental Data | 1 Pathway | 10 Pathways | 100 Pathways |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10,000 proteins | 5 s | 5 s | 6 s |
| 100,000 proteins | 5 s | 10 s | 36 s |
| 1,000,000 proteins | 192 s | 244 s | 712 s |
| Pathway | Added Taxonomic Requirement |
|---|---|
| BGP-hydrogenotrophic methanogenesis (user-defined) | only Archaea |
| KEGG-hydrogenotrophic methanogenesis (KEGG-MODULE) | only Archaea |
| BGP-acetoclastic methanogenesis (user-defined) | only Archaea |
| KEGG-acetoclastic methanogenesis (KEGG-MODULE) | only Archaea |
| BGP-Wood–Ljungdahl pathway (user-defined) | all except Archaea |
| KEGG-Wood–Ljungdahl pathway (KEGG-MODULE) | all except Archaea |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Walke, D.; Schallert, K.; Ramesh, P.; Benndorf, D.; Lange, E.; Reichl, U.; Heyer, R. MPA_Pathway_Tool: User-Friendly, Automatic Assignment of Microbial Community Data on Metabolic Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10992. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222010992
Walke D, Schallert K, Ramesh P, Benndorf D, Lange E, Reichl U, Heyer R. MPA_Pathway_Tool: User-Friendly, Automatic Assignment of Microbial Community Data on Metabolic Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(20):10992. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222010992
Chicago/Turabian StyleWalke, Daniel, Kay Schallert, Prasanna Ramesh, Dirk Benndorf, Emanuel Lange, Udo Reichl, and Robert Heyer. 2021. "MPA_Pathway_Tool: User-Friendly, Automatic Assignment of Microbial Community Data on Metabolic Pathways" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 20: 10992. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222010992
APA StyleWalke, D., Schallert, K., Ramesh, P., Benndorf, D., Lange, E., Reichl, U., & Heyer, R. (2021). MPA_Pathway_Tool: User-Friendly, Automatic Assignment of Microbial Community Data on Metabolic Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(20), 10992. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222010992






