Ceftriaxone Treatment Weakens Long-Term Synaptic Potentiation in the Hippocampus of Young Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
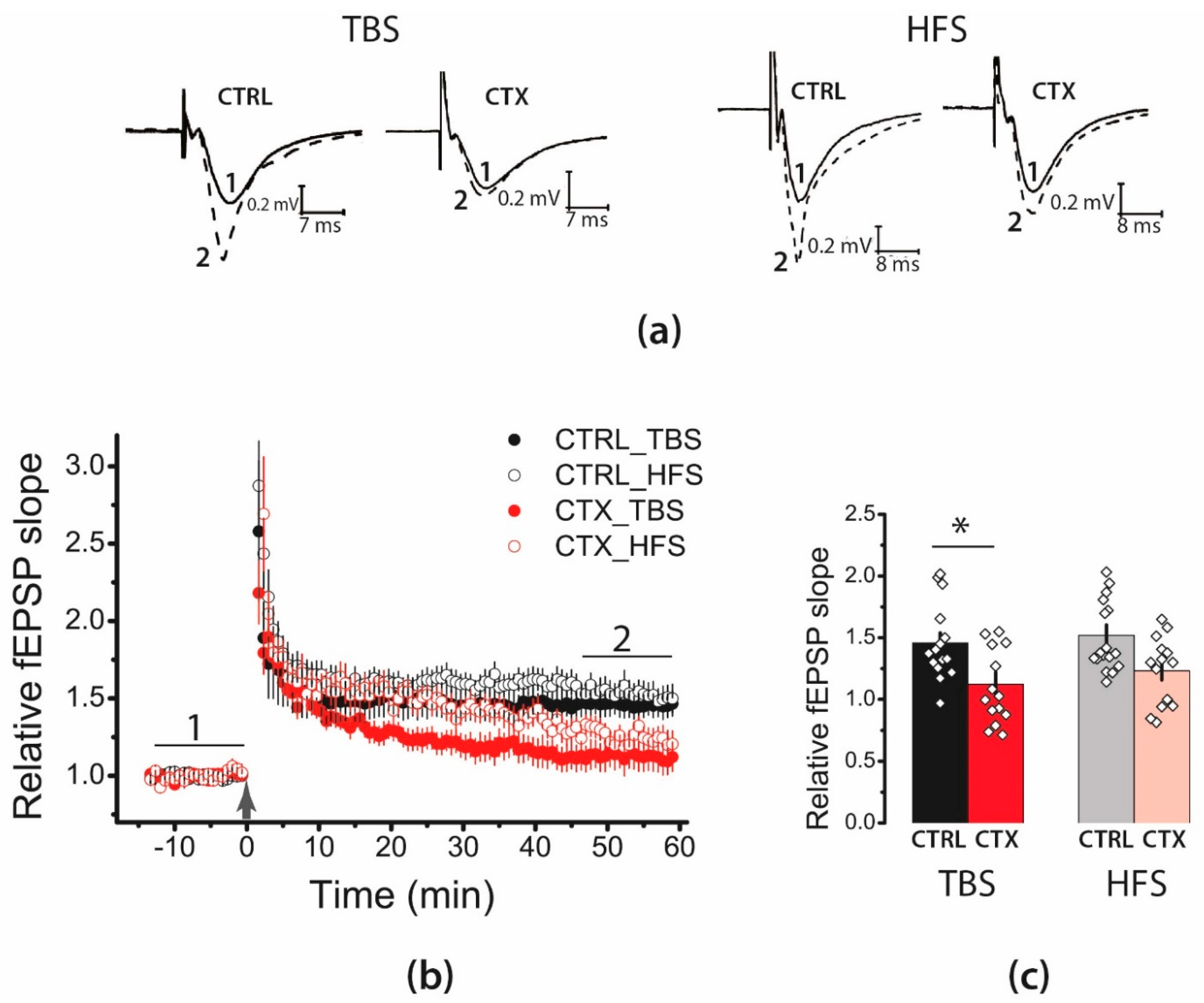
2.1. LTP Was Attenuated in the CA1 Hippocampal Area after CTX Treatment
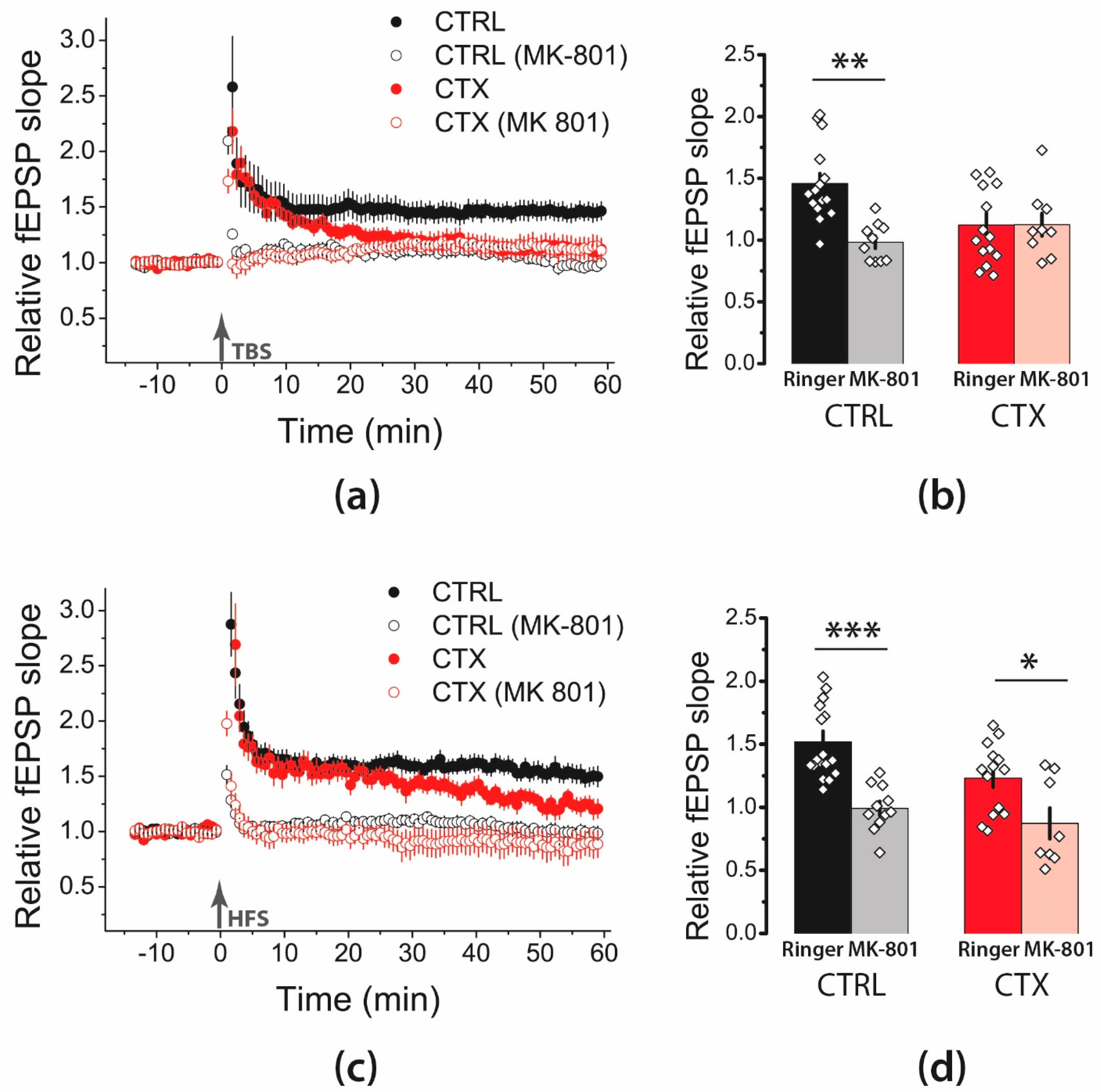
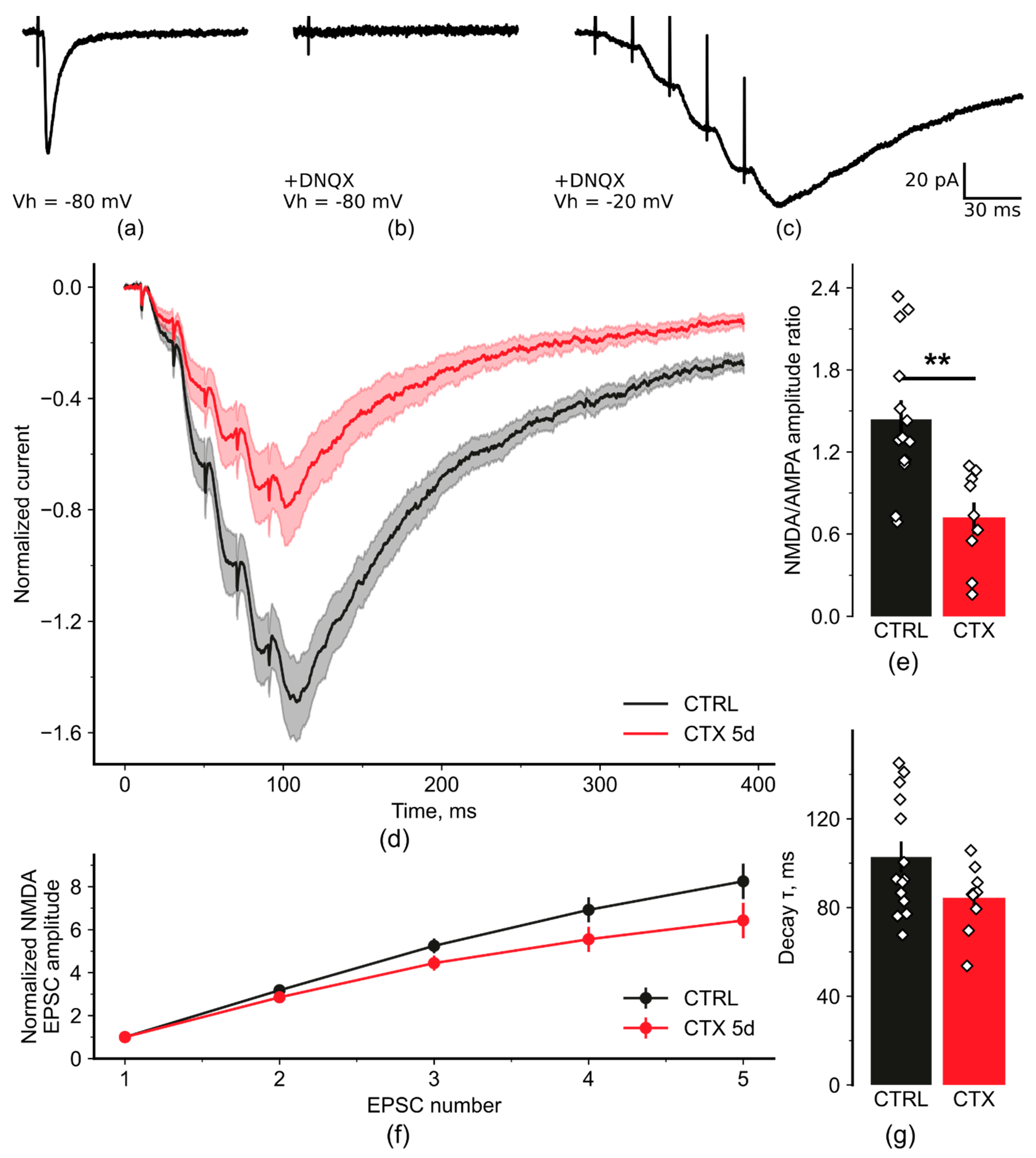
2.2. NMDA-Mediated Signaling during Train Stimulation Was Attenuated after CTX Treatment
2.3. Expression of Glutamate Receptor Subunit Genes Encoding the NMDAR following CTX Treatment
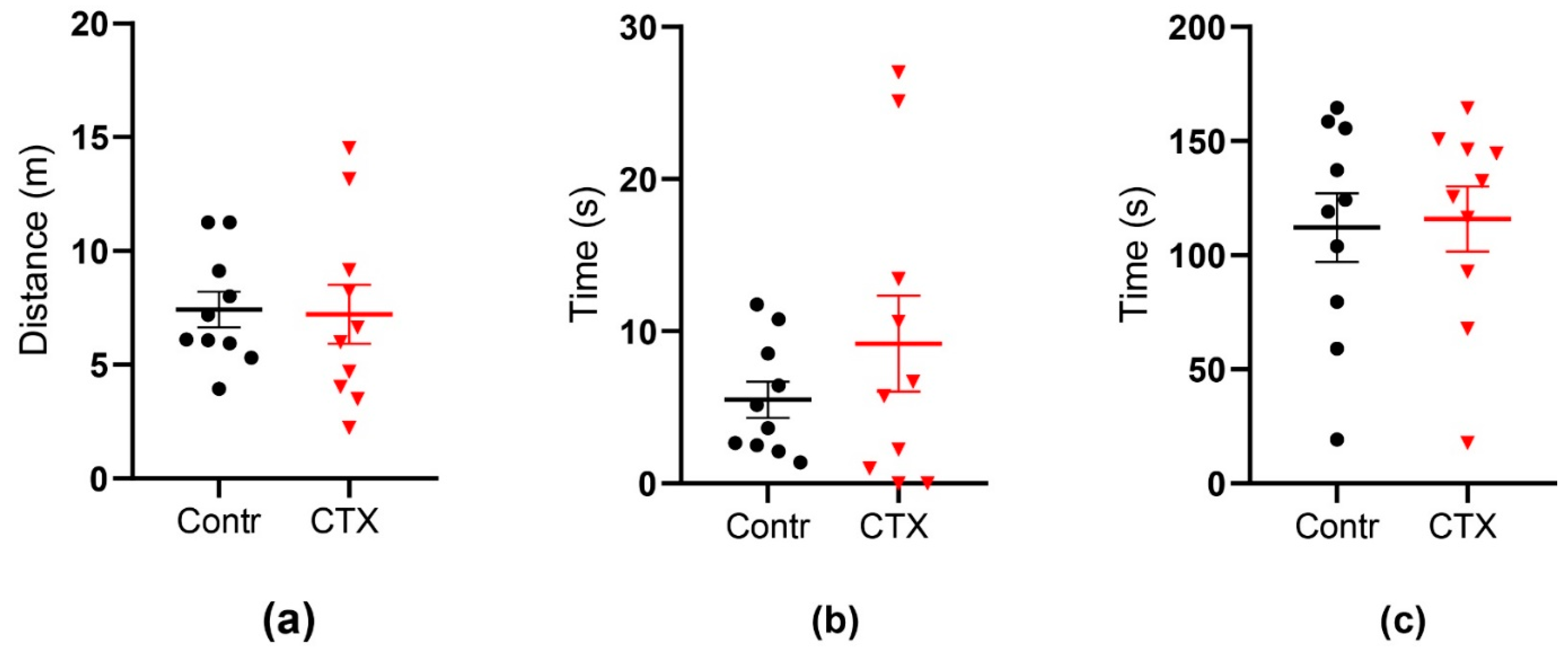
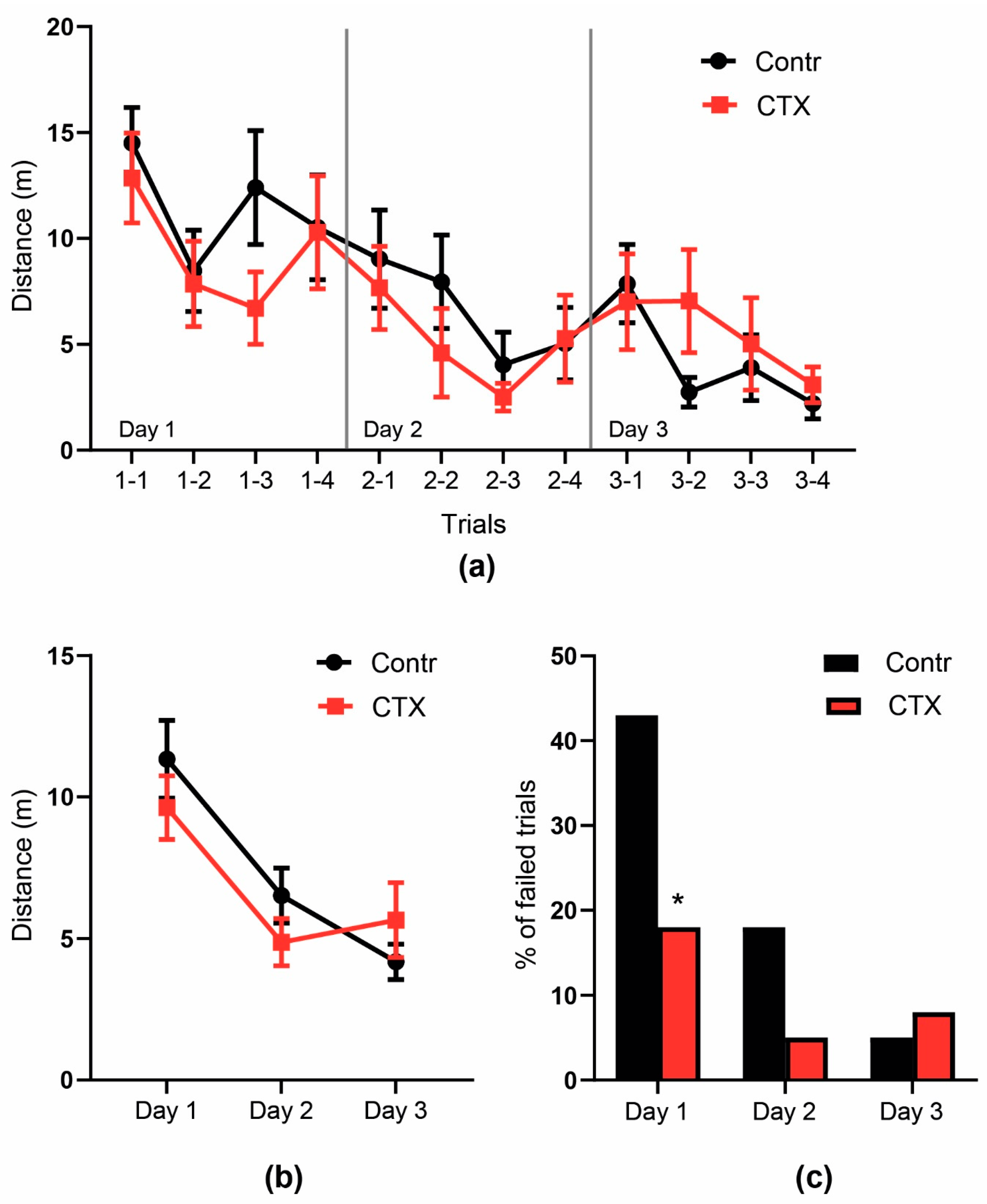
2.4. Rats’ Behavior Is Not Impaired after Ceftriaxone Treatment
2.4.1. Open Field Test
2.4.2. Morris Water Maze
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and CTX Administration
4.2. Slice Preparation
4.3. Field Potential Recordings
4.4. LTP of Excitatory Synaptic Transmission
4.5. Patch-Clamp Recordings
4.6. Drugs
4.7. Quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR)
4.8. Behavioral Tests
4.9. Statistics
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Traynelis, S.F.; Wollmuth, L.P.; McBain, C.J.; Menniti, F.S.; Vance, K.M.; Ogden, K.K.; Hansen, K.B.; Yuan, H.; Myers, S.J.; Dingledine, R. Glutamate Receptor Ion Channels: Structure, Regulation, and Function. Pharmacol. Rev. 2010, 62, 405–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwyl, R. Metabotropic glutamate receptor-dependent long-term potentiation. Neuropharmacology 2009, 56, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volianskis, A.; France, G.; Jensen, M.S.; Bortolotto, Z.A.; Jane, D.E.; Collingridge, G.L. Long-term potentiation and the role of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors. Brain Res. 2015, 1621, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, S.R. The role of glutamate in central nervous system health and disease–A review. Vet. J. 2007, 173, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaitsev, A.V.; Smolensky, I.V.; Jorratt, P.; Ovsepian, S.V. Neurobiology, Functions, and Relevance of Excitatory Amino Acid Transporters (EAATs) to Treatment of Refractory Epilepsy. CNS Drugs 2020, 34, 1089–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehre, K.P.; Levy, L.M.; Ottersen, O.P.; Storm-Mathisen, J.; Danbolt, N.C. Differential expression of two glial glutamate transporters in the rat brain: Quantitative and immunocytochemical observations. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 1835–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, A.; Asan, E.; Lesch, K.P.; Kugler, P. A splice variant of glutamate transporter GLT1/EAAT2 expressed in neurons: Cloning and localization in rat nervous system. Neuroscience 2002, 109, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmseth, S.; Dehnes, Y.; Huang, Y.H.; Follin-Arbelet, V.V.; Grutle, N.J.; Mylonakou, M.N.; Plachez, C.; Zhou, Y.; Furness, D.N.; Bergles, D.E.; et al. The density of EAAC1 (EAAT3) glutamate transporters expressed by neurons in the mammalian CNS. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 6000–6013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajarillo, E.; Rizor, A.; Lee, J.; Aschner, M.; Lee, E. The role of astrocytic glutamate transporters GLT-1 and GLAST in neurological disorders: Potential targets for neurotherapeutics. Neuropharmacology 2019, 161, 107559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Lee, S.G.; Kegelman, T.P.; Su, Z.Z.; Das, S.K.; Dash, R.; Dasgupta, S.; Barral, P.M.; Hedvat, M.; Diaz, P.; et al. Role of Excitatory Amino Acid Transporter-2 (EAAT2) and glutamate in neurodegeneration: Opportunities for developing novel therapeutics. J. Cell. Physiol. 2011, 226, 2484–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, A.R.; Garcia, T.A.; Cullion, K.; Tiwari-Woodruff, S.K.; Pedapati, E.V.; Binder, D.K. Targeted overexpression of glutamate transporter-1 reduces seizures and attenuates pathological changes in a mouse model of epilepsy. Neurobiol. Dis. 2021, 157, 105443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Sidoryk-Wegrzynowicz, M.; Yin, Z.; Webb, A.; Son, D.-S.; Aschner, M. Transforming growth factor-α mediates estrogen-induced upregulation of glutamate transporter GLT-1 in rat primary astrocytes. Glia 2012, 60, 1024–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothstein, J.D.; Patel, S.; Regan, M.R.; Haenggeli, C.; Huang, Y.H.; Bergles, D.E.; Jin, L.; Hoberg, M.D.; Vidensky, S.; Chung, D.S.; et al. β-Lactam antibiotics offer neuroprotection by increasing glutamate transporter expression. Nature 2005, 433, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitsev, A.V.; Malkin, S.L.; Postnikova, T.Y.; Smolensky, I.V.; Zubareva, O.E.; Romanova, I.V.; Zakharova, M.V.; Karyakin, V.B.; Zavyalov, V. Ceftriaxone treatment affects EAAT2 expression and glutamatergic neurotransmission and exerts a weak anticonvulsant effect in young rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, A.M.; Ghalwash, M.; Magdy, K.; Abulseoud, O.A. Beta Lactams Antibiotic Ceftriaxone Modulates Seizures, Oxidative Stress and Connexin 43 Expression in Hippocampus of Pentylenetetrazole Kindled Rats. J. Epilepsy Res. 2016, 6, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uyanikgil, Y.; Özkeşkek, K.; Çavuşoğlu, T.; Solmaz, V.; Tümer, M.K.; Erbas, O. Positive effects of ceftriaxone on pentylenetetrazol-induced convulsion model in rats. Int. J. Neurosci. 2016, 126, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hameed, M.Q.; Hsieh, T.H.; Morales-Quezada, L.; Lee, H.H.C.; Damar, U.; MacMullin, P.C.; Hensch, T.K.; Rotenberg, A. Ceftriaxone Treatment Preserves Cortical Inhibitory Interneuron Function via Transient Salvage of GLT-1 in a Rat Traumatic Brain Injury Model. Cereb. Cortex 2019, 29, 4506–4518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.-Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, D.; Li, L.; Li, W.-B. Ceftriaxone modulates uptake activity of glial glutamate transporter-1 against global brain ischemia in rats. J. Neurochem. 2015, 132, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos-Ocasio, F.; Hernández-López, A.; Thompson, K.J. Ceftriaxone, a GLT-1 transporter activator, disrupts hippocampal learning in rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2014, 122, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omrani, A.; Melone, M.; Bellesi, M.; Safiulina, V.; Aida, T.; Tanaka, K.; Cherubini, E.; Conti, F. Up-regulation of GLT-1 severely impairs LTD at mossy fibre-CA3 synapses. J. Physiol. 2009, 587, 4575–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bliss, T.V.P.; Collingridge, G.L. A synaptic model of memory: Long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 1993, 361, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citri, A.; Malenka, R.C. Synaptic Plasticity: Multiple Forms, Functions, and Mechanisms. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008, 33, 18–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postnikova, T.Y.; Trofimova, A.M.; Ergina, J.L.; Zubareva, O.E.; Kalemenev, S.V.; Zaitsev, A.V. Transient Switching of NMDA-Dependent Long-Term Synaptic Potentiation in CA3-CA1 Hippocampal Synapses to mGluR1-Dependent Potentiation After Pentylenetetrazole-Induced Acute Seizures in Young Rats. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 39, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.G.; Su, Z.Z.; Emdad, L.; Gupta, P.; Sarkar, D.; Borjabad, A.; Volsky, D.J.; Fisher, P.B. Mechanism of ceftriaxone induction of excitatory amino acid transporter-2 expression and glutamate uptake in primary human astrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 13116–13123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodrich, G.S.; Kabakov, A.Y.; Hameed, M.Q.; Dhamne, S.C.; Rosenberg, P.A.; Rotenberg, A. Ceftriaxone treatment after traumatic brain injury restores expression of the glutamate transporter, GLT-1, reduces regional gliosis, and reduces post-traumatic seizures in the rat. J. Neurotrauma 2013, 30, 1434–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soni, N.; Koushal, P.; Reddy, B.V.K.; Deshmukh, R.; Kumar, P. Effect of GLT-1 modulator and P2X7 antagonists alone and in combination in the kindling model of epilepsy in rats. Epilepsy Behav. 2015, 48, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, S.-C.; Hsu, C.-C.; Pawlak, C.R.; Tikhonova, M.A.; Lai, T.-J.; Amstislavskaya, T.G.; Ho, Y.-J. Effects of ceftriaxone on the behavioral and neuronal changes in an MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease rat model. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 268, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koomhin, P.; Tilokskulchai, K.; Tapechum, S. Ceftriaxone improves spatial learning and memory in chronic cerebral hypoperfused rats. ScienceAsia 2012, 38, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Li, M.X.; Luo, Y.; Chen, T.; Liu, J.; Fang, P.; Jiang, B.; Hu, Z.L.; Jin, Y.; Chen, J.G.; et al. Chronic ceftriaxone treatment rescues hippocampal memory deficit in AQP4 knockout mice via activation of GLT-1. Neuropharmacology 2013, 75, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventura, R.; Harris, K.M. Three-dimensional relationships between hippocampal synapses and astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 6897–6906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzingounis, A.V.; Wadiche, J.I. Glutamate transporters: Confining runaway excitation by shaping synaptic transmission. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 935–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusakov, D.A.; Kullmann, D.M.; Stewart, M.G. Hippocampal synapses: Do they talk to their neighbours? Trends Neurosci. 1999, 22, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusakov, D.A.; Kullmann, D.M. Extrasynaptic glutamate diffusion in the hippocampus: Ultrastructural constraints, uptake, and receptor activation. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 3158–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amakhin, D.V.; Malkin, S.L.; Ergina, J.L.; Kryukov, K.A.; Veniaminova, E.A.; Zubareva, O.E.; Zaitsev, A.V. Alterations in Properties of Glutamatergic Transmission in the Temporal Cortex and Hippocampus Following Pilocarpine-Induced Acute Seizures in Wistar Rats. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozovaya, N.A.; Kopanitsa, M.V.; Boychuk, Y.A.; Krishtal, O.A. Enhancement of glutamate release uncovers spillover-mediated transmission by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in the rat hippocampus. Neuroscience 1999, 91, 1321–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berberich, S.; Jensen, V.; Hvalby, Ø.; Seeburg, P.H.; Köhr, G. The role of NMDAR subtypes and charge transfer during hippocampal LTP induction. Neuropharmacology 2007, 52, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, K.B.; Yi, F.; Perszyk, R.E.; Furukawa, H.; Wollmuth, L.P.; Gibb, A.J.; Traynelis, S.F. Structure, function, and allosteric modulation of NMDA receptors. J. Gen. Physiol. 2018, 150, 1081–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchini, L.; Carrano, N.; Di Luca, M.; Gardoni, F. Synaptic GluN2A-Containing NMDA Receptors: From Physiology to Pathological Synaptic Plasticity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletti, P.; Bellone, C.; Zhou, Q. NMDA receptor subunit diversity: Impact on receptor properties, synaptic plasticity and disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 383–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erreger, K.; Geballe, M.T.; Kristensen, A.; Chen, P.E.; Hansen, K.B.; Lee, C.J.; Yuan, H.; Le, P.; Lyuboslavsky, P.N.; Micale, N.; et al. Subunit-specific agonist activity at NR2A-, NR2B-, NR2C-, and NR2D-containing N-methyl-D-aspartate glutamate receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 72, 907–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakimura, K.; Kutsuwada, T.; Ito, I.; Manabe, T.; Takayama, C.; Kushiya, E.; Yagi, T.; Aizawa, S.; Inoue, Y.; Sugiyama, H.; et al. Reduced hippocampal LTP and spatial learning in mice lacking NMDA receptor ε1 subunit. Nature 1995, 373, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigman, J.L.; Wright, T.; Talani, G.; Prasad-Mulcare, S.; Jinde, S.; Seabold, G.K.; Mathur, P.; Davis, M.I.; Bock, R.; Gustin, R.M.; et al. Loss of GluN2B-Containing NMDA Receptors in CA1 Hippocampus and Cortex Impairs Long-Term Depression, Reduces Dendritic Spine Density, and Disrupts Learning. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 4590–4600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wong, T.P.; Pozza, M.F.; Lingenhoehl, K.; Wang, Y.T.; Sheng, M.; Auberson, Y.P.; Wang, Y.T. Role of NMDA Receptor Subtypes in Governing the Direction of Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity. Science 2004, 304, 1021–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, C.J.; Russell, K.I.; Wang, Y.T.; Christie, B.R. Contribution of NR2A and NR2B NMDA subunits to bidirectional synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus in vivo. Hippocampus 2006, 16, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartlett, T.E.; Bannister, N.J.; Collett, V.J.; Dargan, S.L.; Massey, P.V.; Bortolotto, Z.A.; Fitzjohn, S.M.; Bashir, Z.I.; Collingridge, G.L.; Lodge, D. Differential roles of NR2A and NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in LTP and LTD in the CA1 region of two-week old rat hippocampus. Neuropharmacology 2007, 52, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Chen, R.Q.; Gu, Q.H.; Yan, J.Z.; Wang, S.H.; Liu, S.Y.; Lu, W. Metaplastic regulation of long-term potentiation/long-term depression threshold by activity-dependent changes of NR2A/NR2B ratio. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 8764–8773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaman, I.; Kizilay-Ozfidan, G.; Karadag, C.H.; Ulugol, A. Lack of effect of ceftriaxone, a GLT-1 transporter activator, on spatial memory in mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2013, 108, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramandi, D.; Elahdadi Salmani, M.; Moghimi, A.; Lashkarbolouki, T.; Fereidoni, M. Pharmacological upregulation of GLT-1 alleviates the cognitive impairments in the animal model of temporal lobe epilepsy. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hota, S.K.; Barhwal, K.; Ray, K.; Singh, S.B.; Ilavazhagan, G. Ceftriaxone rescues hippocampal neurons from excitotoxicity and enhances memory retrieval in chronic hypobaric hypoxia. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2008, 89, 522–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postnikova, T.Y.; Amakhin, D.V.; Trofimova, A.M.; Smolensky, I.V.; Zaitsev, A.V. Changes in Functional Properties of Rat Hippocampal Neurons Following Pentylenetetrazole-induced Status Epilepticus. Neuroscience 2019, 399, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski, P.; Sacchi, N. The single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction: Twenty-something years on. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 581–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, A.P.; Malygina, D.A.; Kovalenko, A.A.; Trofimov, A.N.; Zaitsev, A.V. Multiplex qPCR assay for assessment of reference gene expression stability in rat tissues/samples. Mol. Cell. Probes 2020, 53, 101611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonefeld, B.E.; Elfving, B.; Wegener, G. Reference genes for normalization: A study of rat brain tissue. Synapse 2008, 62, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Burks, C.A.; Hansen, D.R.; Kinnamon, S.C.; Gilbertson, T.A. Taste receptor cells express pH-sensitive leak K+ channels. J. Neurophysiol. 2004, 92, 2909–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giza, C.C.; Maria, N.S.S.; Hovda, D.A. N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit changes after traumatic injury to the developing brain. J. Neurotrauma 2006, 23, 950–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floyd, D.W.; Jung, K.-Y.; McCool, B.A. Chronic ethanol ingestion facilitates N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor function and expression in rat lateral/basolateral amygdala neurons. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003, 307, 1020–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proudnikov, D.; Yuferov, V.; Zhou, Y.; LaForge, K.S.; Ho, A.; Kreek, M.J. Optimizing primer--probe design for fluorescent PCR. J. Neurosci. Methods 2003, 123, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolensky, I.V.; Zubareva, O.E.; Kalemenev, S.V.; Lavrentyeva, V.V.; Dyomina, A.V.; Karepanov, A.A.; Zaitsev, A.V. Impairments in cognitive functions and emotional and social behaviors in a rat lithium-pilocarpine model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Gene Symbol RefSeq Accession Number | Nucleotide Sequences (Forward, Reverse, TaqMan-Probe) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Actb NM_031144 | TGTCACCAACTGGGACGATA | [55] (primers) [54] (probe) |
| GGGGTGTTGAAGGTCTCAAA | ||
| FAM-CGTGTGGCCCCTGAGGAGCAC-BHQ1 | ||
| Gapdh NM_017008 | TGCACCACCAACTGCTTAG | [56] |
| GGATGCAGGGATGATGTTC | ||
| R6G-ATCACGCCACAGCTTTCCAGAGGG-BHQ2 | ||
| Grin1 NM_017010 | GTTCTTCCGCTCAGGCTTTG | [57] |
| AGGGAAACGTTCTGCTTCCA | ||
| FAM-CGGCATGCGCAAGGACAGCC-BHQ1 | ||
| Grin2a NM_012573 | GCTACACACCCTGCACCAATT | [58] |
| CACCTGGTAACCTTCCTCAGTGA | ||
| FAM-TGGTCAATGTGACTTGGGATGGCAA-BHQ1 | ||
| Grin2b NM_012574 | CCCAACATGCTCTCTCCCTTAA | [58] |
| CAGCTAGTCGGCTCTCTTGGTT | ||
| FAM-GACGCCAAACCTCTAGGCGGACAG-BHQ1 | ||
| Gria1 NM_031608 | TCAGAACGCCTCAACGCC | [59] |
| TGTAGTGGTACCCGATGCCA | ||
| ROX-TCCTGGGCCAGATCGTGAAGCTAGAAAA-BHQ1 | ||
| Gria2 NM_017261 | CAGTGCATTTCGGGTAGGGA | [59] |
| TGCGAAACTGTTGGCTACCT | ||
| FAM-TCGGAGTTCAGACTGACACCCCA-BHQ1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Postnikova, T.Y.; Malkin, S.L.; Zakharova, M.V.; Smolensky, I.V.; Zubareva, O.E.; Zaitsev, A.V. Ceftriaxone Treatment Weakens Long-Term Synaptic Potentiation in the Hippocampus of Young Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8417. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22168417
Postnikova TY, Malkin SL, Zakharova MV, Smolensky IV, Zubareva OE, Zaitsev AV. Ceftriaxone Treatment Weakens Long-Term Synaptic Potentiation in the Hippocampus of Young Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(16):8417. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22168417
Chicago/Turabian StylePostnikova, Tatyana Y., Sergey L. Malkin, Maria V. Zakharova, Ilya V. Smolensky, Olga E. Zubareva, and Aleksey V. Zaitsev. 2021. "Ceftriaxone Treatment Weakens Long-Term Synaptic Potentiation in the Hippocampus of Young Rats" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 16: 8417. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22168417
APA StylePostnikova, T. Y., Malkin, S. L., Zakharova, M. V., Smolensky, I. V., Zubareva, O. E., & Zaitsev, A. V. (2021). Ceftriaxone Treatment Weakens Long-Term Synaptic Potentiation in the Hippocampus of Young Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(16), 8417. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22168417






