S100A9 Alters the Pathway of Alpha-Synuclein Amyloid Aggregation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
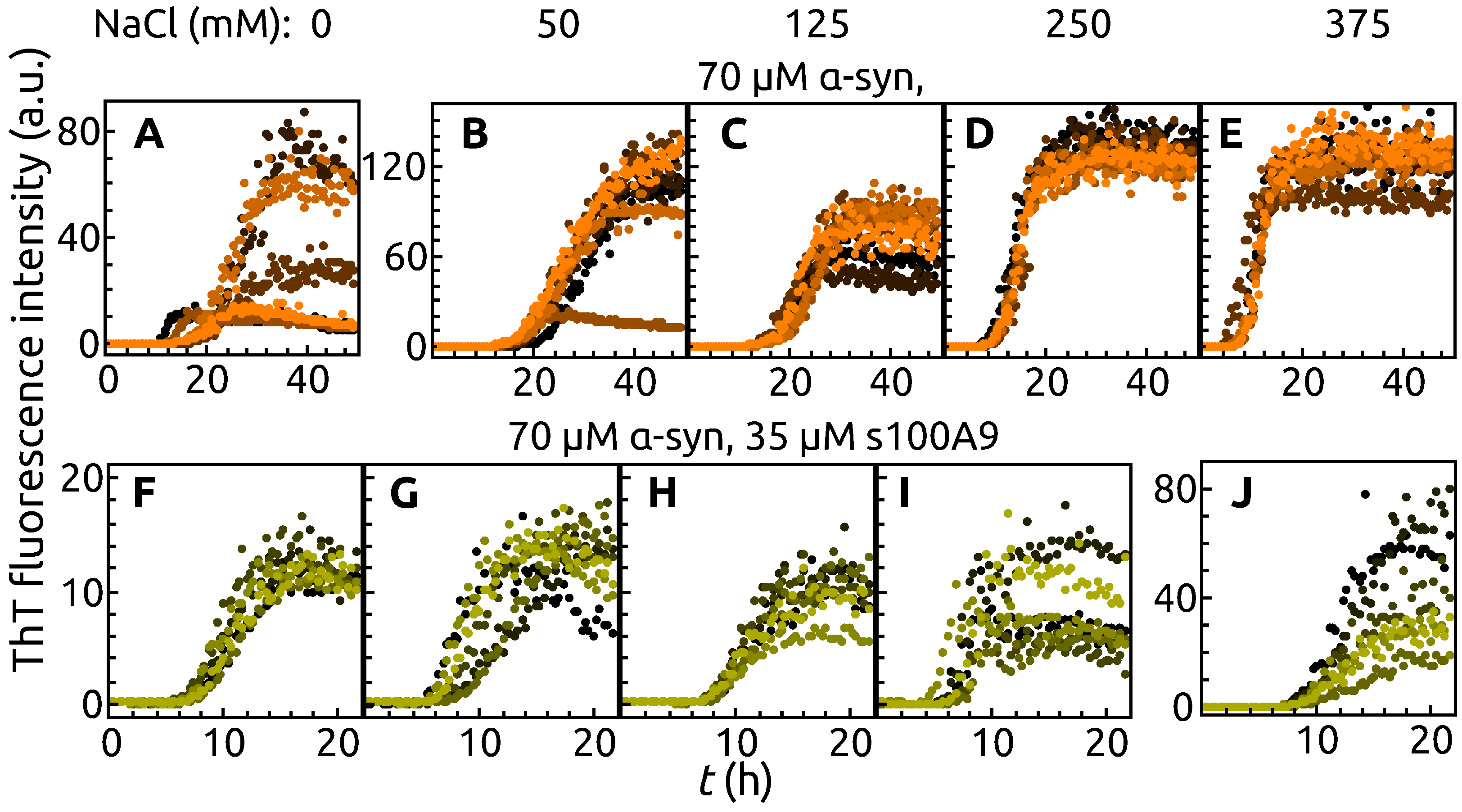
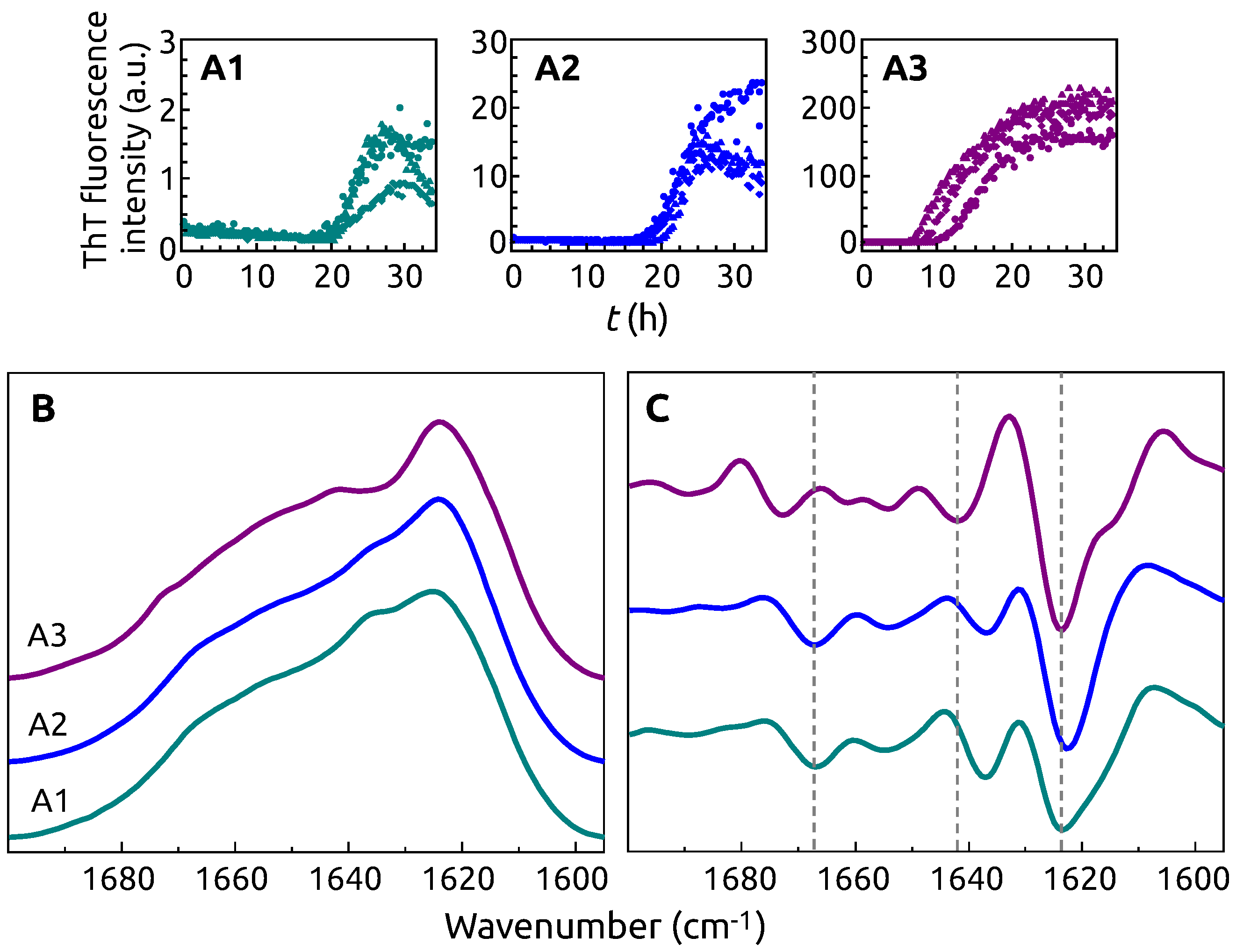
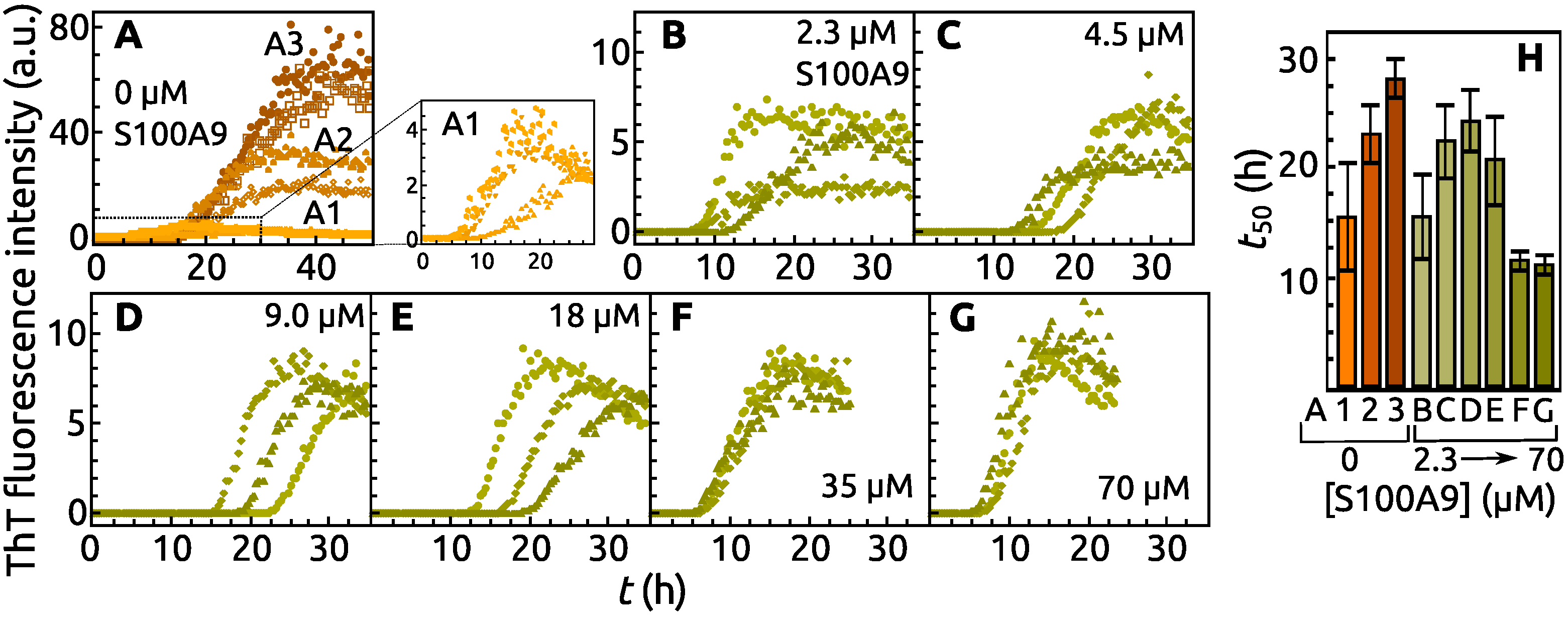
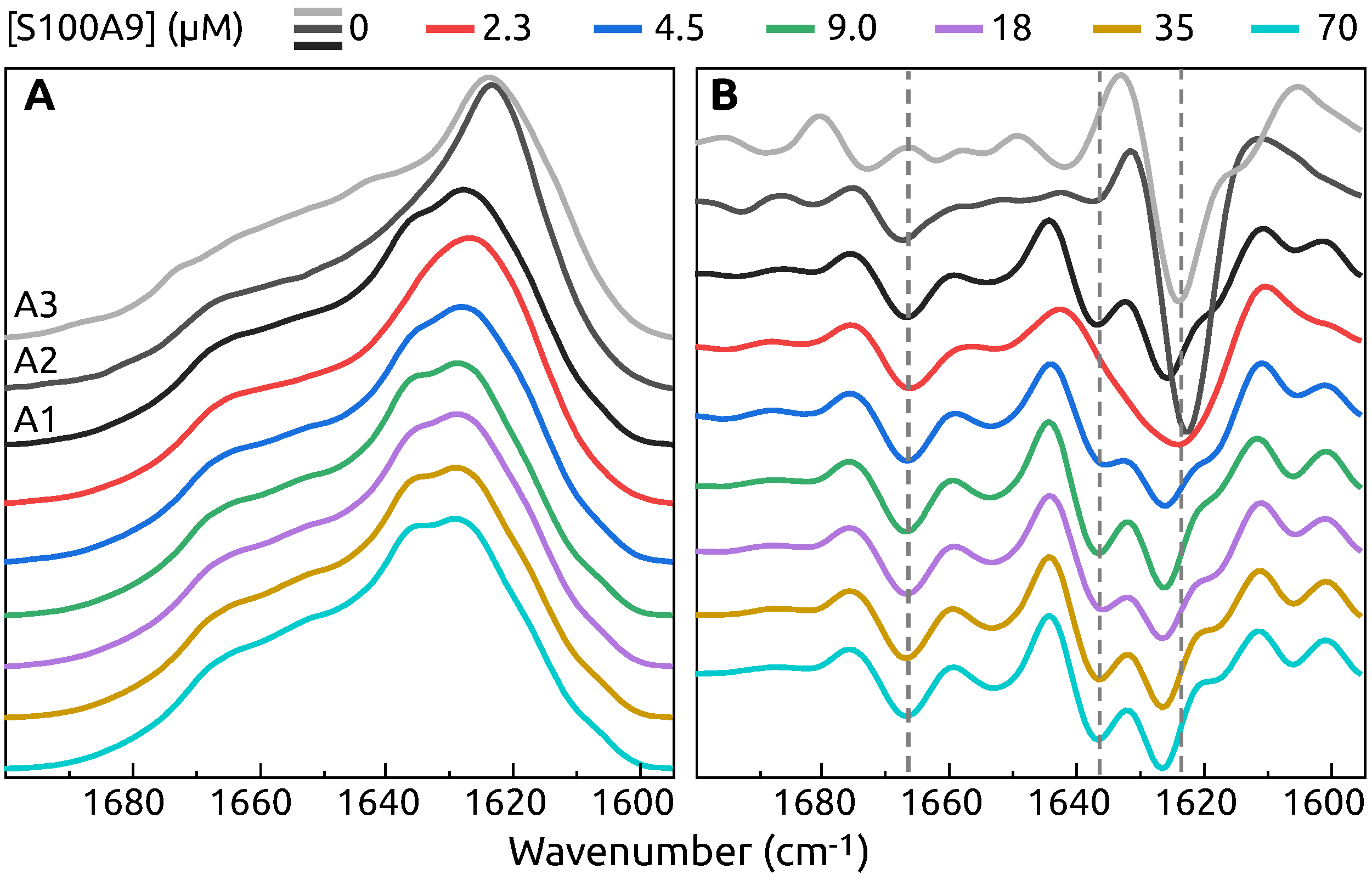
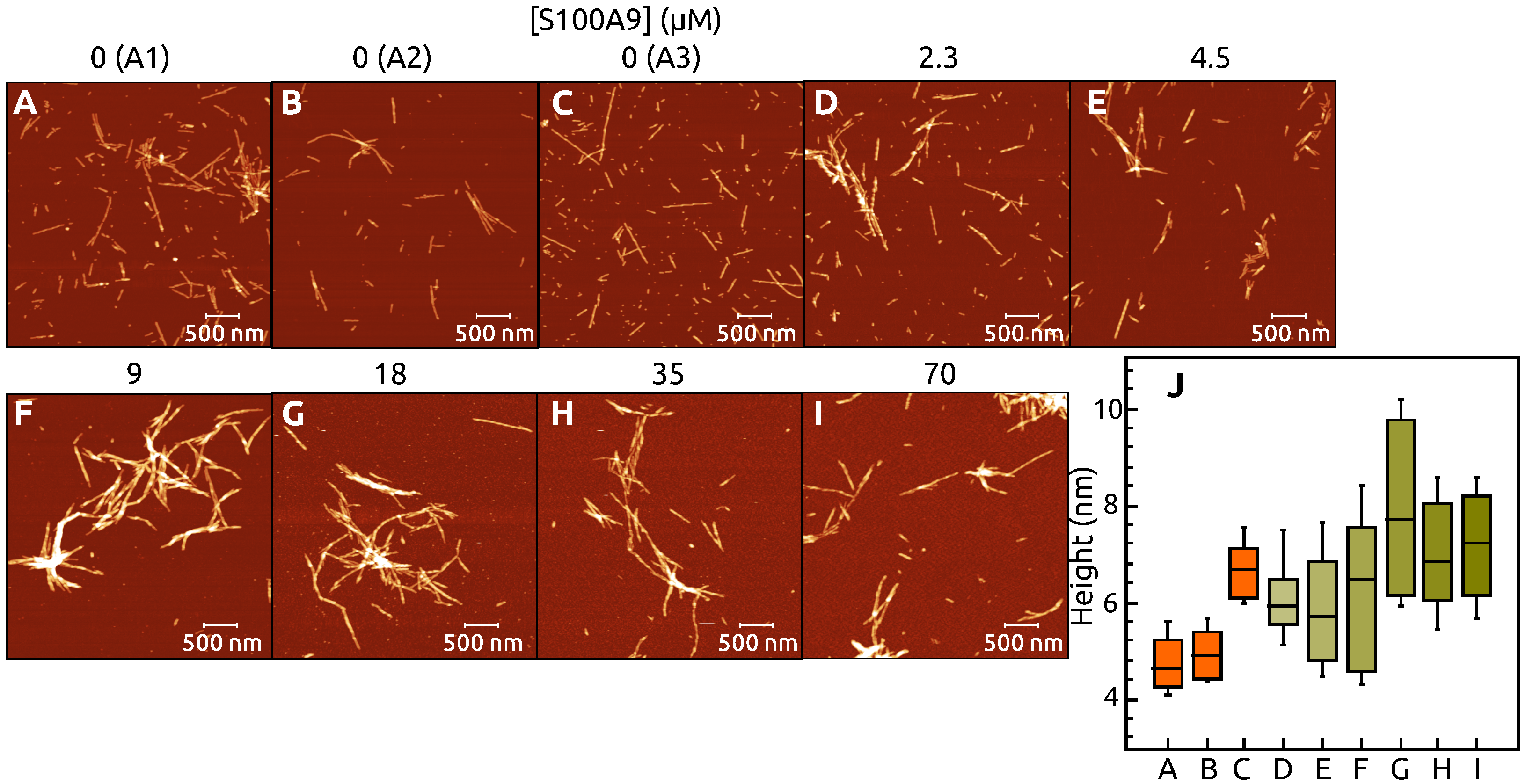
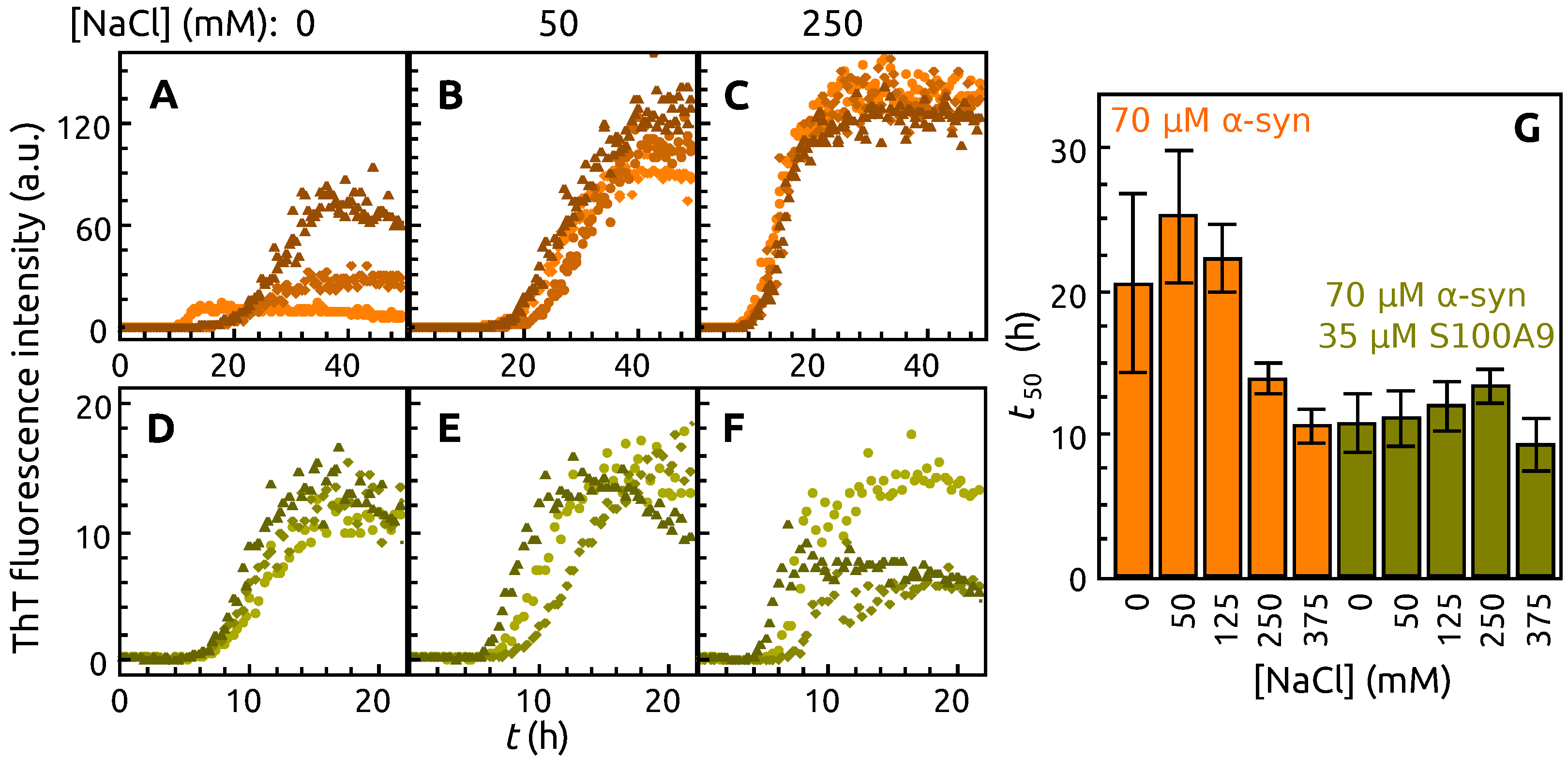
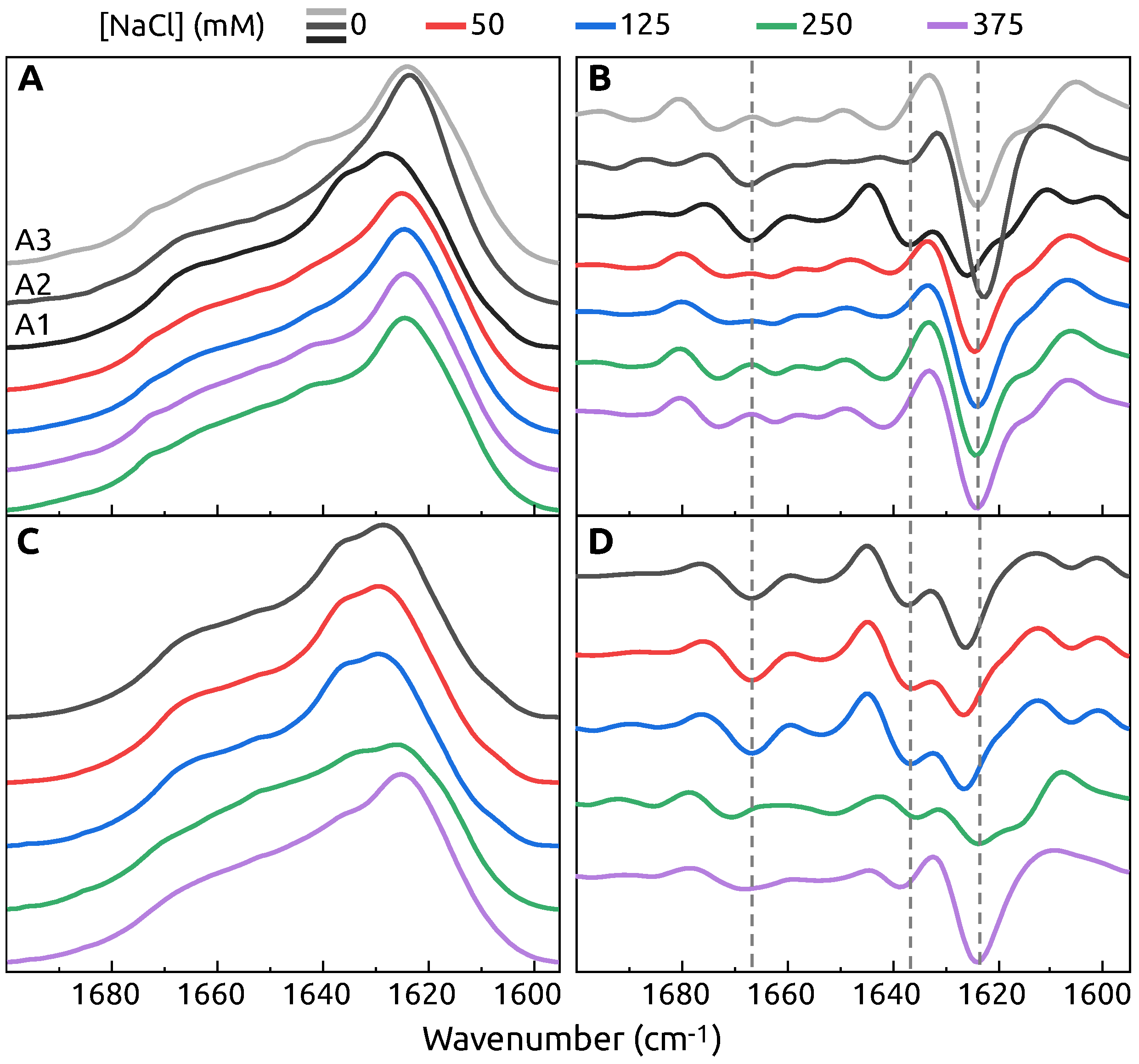
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Protein Production
4.2. ThT Assay
4.3. FTIR Spectroscopy
4.4. Atomic Force Microscopy
4.5. SDS-PAGE
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Knowles, T.P.J.; Vendruscolo, M.; Dobson, C.M. The Amyloid State and Its Association with Protein Misfolding Diseases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, K.R.; Rice, L. The Amyloidoses: Clinical Features, Diagnosis and Treatment. Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc. J. 2012, 8, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiti, F.; Dobson, C.M. Protein Misfolding, Amyloid Formation, and Human Disease: A Summary of Progress Over the Last Decade. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017, 86, 27–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, D.; Jackson, R.; Paul, G.; Shi, J.; Sabbagh, M. Why Do Trials for Alzheimer’s Disease Drugs Keep Failing? A Discontinued Drug Perspective for 2010–2015. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2017, 26, 735–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Egolum, U.; Parker, S.; Andrews, E.; Ombengi, D.; Ling, H. Tafamidis: A First-in-Class Transthyretin Stabilizer for Transthyretin Amyloid Cardiomyopathy. Ann. Pharmacother. 2020, 54, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, J.; Lee, G.; Ritter, A.; Sabbagh, M.; Zhong, K. Alzheimer’s Disease Drug Development Pipeline: 2020. Alzheimer Dement. Transl. Res. Clin. Interv. 2020, 6, e12050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, L.E.; Weuve, J.; Scherr, P.A.; Evans, D.A. Alzheimer Disease in the United States (2010–2050) Estimated Using the 2010 Census. Neurology 2013, 80, 1778–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Das, U.; Scott, D.A.; Tang, Y.; McLean, P.J.; Roy, S. α-Synuclein Multimers Cluster Synaptic Vesicles and Attenuate Recycling. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, 2319–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Schmidt, M.L.; Lee, V.M.Y.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Jakes, R.; Goedert, M. α-Synuclein in Lewy Bodies. Nature 1997, 388, 839–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakabayashi, K.; Hayashi, S.; Kakita, A.; Yamada, M.; Toyoshima, Y.; Yoshimoto, M.; Takahashi, H. Accumulation of α-Synuclein/NACP Is a Cytopathological Feature Common to Lewy Body Disease and Multiple System Atrophy. Acta Neuropathol. 1998, 96, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakabayashi, K.; Yoshimoto, M.; Tsuji, S.; Takahashi, H. α-Synuclein Immunoreactivity in Glial Cytoplasmic Inclusions in Multiple System Atrophy. Neurosci. Lett. 1998, 249, 180–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousset, L.; Pieri, L.; Ruiz-Arlandis, G.; Gath, J.; Jensen, P.H.; Habenstein, B.; Madiona, K.; Olieric, V.; Böckmann, A.; Meier, B.H.; et al. Structural and Functional Characterization of Two Alpha-Synuclein Strains. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gath, J.; Bousset, L.; Habenstein, B.; Melki, R.; Böckmann, A.; Meier, B.H. Unlike Twins: An NMR Comparison of Two α-Synuclein Polymorphs Featuring Different Toxicity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strohäker, T.; Jung, B.C.; Liou, S.H.; Fernandez, C.O.; Riedel, D.; Becker, S.; Halliday, G.M.; Bennati, M.; Kim, W.S.; Lee, S.J.; et al. Structural Heterogeneity of α-Synuclein Fibrils Amplified from Patient Brain Extracts. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Perren, A.; Gelders, G.; Fenyi, A.; Bousset, L.; Brito, F.; Peelaerts, W.; Van den Haute, C.; Gentleman, S.; Melki, R.; Baekelandt, V. The Structural Differences between Patient-Derived α-Synuclein Strains Dictate Characteristics of Parkinson’s Disease, Multiple System Atrophy and Dementia with Lewy Bodies. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 139, 977–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giehm, L.; Lorenzen, N.; Otzen, D.E. Assays for α-Synuclein Aggregation. Methods 2011, 53, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, A.M.; Finke, R.G. α-Synuclein Aggregation Variable Temperature and Variable pH Kinetic Data: A Re-Analysis Using the Finke–Watzky 2-Step Model of Nucleation and Autocatalytic Growth. Biophys. Chem. 2009, 140, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeters, S.J.; Iyer, A.; Pletikapić, G.; Kogan, V.; Subramaniam, V.; Woutersen, S. Evidence for Intramolecular Antiparallel Beta-Sheet Structure in Alpha-Synuclein Fibrils from a Combination of Two-Dimensional Infrared Spectroscopy and Atomic Force Microscopy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afitska, K.; Fucikova, A.; Shvadchak, V.V.; Yushchenko, D.A. α-Synuclein Aggregation at Low Concentrations. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Proteins Proteom. 2019, 1867, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Zhang, S.; Ma, X.; Jia, C.; Liu, Z.; Huang, C.; Liu, C.; Li, D. Structural Basis of the Interplay between α-Synuclein and Tau in Regulating Pathological Amyloid Aggregation. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 7470–7480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Köppen, J.; Schulze, A.; Machner, L.; Wermann, M.; Eichentopf, R.; Guthardt, M.; Hähnel, A.; Klehm, J.; Kriegeskorte, M.C.; Hartlage-Rübsamen, M.; et al. Amyloid-Beta Peptides Trigger Aggregation of Alpha-Synuclein In Vitro. Molecules 2020, 25, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rösener, N.S.; Gremer, L.; Wördehoff, M.M.; Kupreichyk, T.; Etzkorn, M.; Neudecker, P.; Hoyer, W. Clustering of Human Prion Protein and α-Synuclein Oligomers Requires the Prion Protein N-Terminus. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, D.G.; Temido-Ferreira, M.; Vicente Miranda, H.; Batalha, V.L.; Coelho, J.E.; Szegö, É.M.; Marques-Morgado, I.; Vaz, S.H.; Rhee, J.S.; Schmitz, M.; et al. α-Synuclein Interacts with PrP C to Induce Cognitive Impairment through mGluR5 and NMDAR2B. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 1569–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masliah, E.; Rockenstein, E.; Inglis, C.; Adame, A.; Bett, C.; Lucero, M.; Sigurdson, C.J. Prion Infection Promotes Extensive Accumulation of α-Synuclein in Aged Human α-Synuclein Transgenic Mice. Prion 2012, 6, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Horvath, I.; Iashchishyn, I.A.; Moskalenko, R.A.; Wang, C.; Wärmländer, S.K.T.S.; Wallin, C.; Gräslund, A.; Kovacs, G.G.; Morozova-Roche, L.A. Co-Aggregation of pro-Inflammatory S100A9 with α-Synuclein in Parkinson’s Disease: Ex Vivo and in Vitro Studies. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellomo, G.; Bologna, S.; Cerofolini, L.; Paciotti, S.; Gatticchi, L.; Ravera, E.; Parnetti, L.; Fragai, M.; Luchinat, C. Dissecting the Interactions between Human Serum Albumin and α-Synuclein: New Insights on the Factors Influencing α-Synuclein Aggregation in Biological Fluids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 4380–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaari, A.; Eliezer, D.; Ladjimi, M. The C-Terminal α-Helices of Mammalian Hsc70 Play a Critical Role in the Stabilization of α-Synuclein Binding and Inhibition of Aggregation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 83, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hessian, P.A.; Edgeworth, J.; Hogg, N. MRP-8 and MRP-14, Two Abundant Ca2+-Binding Proteins of Neutrophils and Monocytes. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1993, 53, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogl, T.; Gharibyan, A.L.; Morozova-Roche, L.A. Pro-Inflammatory S100A8 and S100A9 Proteins: Self-Assembly into Multifunctional Native and Amyloid Complexes. IJMS 2012, 13, 2893–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Markowitz, J.; Carson, W.E. Review of S100A9 Biology and Its Role in Cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1835, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iashchishyn, I.A.; Sulskis, D.; Nguyen Ngoc, M.; Smirnovas, V.; Morozova-Roche, L.A. Finke–Watzky Two-Step Nucleation–Autocatalysis Model of S100A9 Amyloid Formation: Protein Misfolding as “Nucleation” Event. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 2152–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Klechikov, A.G.; Gharibyan, A.L.; Wärmländer, S.K.T.S.; Jarvet, J.; Zhao, L.; Jia, X.; Shankar, S.K.; Olofsson, A.; Brännström, T.; et al. The Role of Pro-Inflammatory S100A9 in Alzheimer’s Disease Amyloid-Neuroinflammatory Cascade. Acta Neuropathol. 2014, 127, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horvath, I.; Jia, X.; Johansson, P.; Wang, C.; Moskalenko, R.; Steinau, A.; Forsgren, L.; Wågberg, T.; Svensson, J.; Zetterberg, H.; et al. Pro-Inflammatory S100A9 Protein as a Robust Biomarker Differentiating Early Stages of Cognitive Impairment in Alzheimer’s Disease. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2016, 7, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Iashchishyn, I.A.; Pansieri, J.; Nyström, S.; Klementieva, O.; Kara, J.; Horvath, I.; Moskalenko, R.; Rofougaran, R.; Gouras, G.; et al. S100A9-Driven Amyloid-Neuroinflammatory Cascade in Traumatic Brain Injury as a Precursor State for Alzheimer’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Iashchishyn, I.A.; Kara, J.; Foderà, V.; Vetri, V.; Sancataldo, G.; Marklund, N.; Morozova-Roche, L.A. Proinflammatory and Amyloidogenic S100A9 Induced by Traumatic Brain Injury in Mouse Model. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 699, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pansieri, J.; Iashchishyn, I.A.; Fakhouri, H.; Ostojić, L.; Malisauskas, M.; Musteikyte, G.; Smirnovas, V.; Schneider, M.M.; Scheidt, T.; Xu, C.K.; et al. Templating S100A9 Amyloids on Aβ Fibrillar Surfaces Revealed by Charge Detection Mass Spectrometry, Microscopy, Kinetic and Microfluidic Analyses. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 7031–7039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, A. Infrared Spectroscopy of Proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Bioenerg. 2007, 1767, 1073–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ziaunys, M.; Sneideris, T.; Smirnovas, V. Formation of Distinct Prion Protein Amyloid Fibrils under Identical Experimental Conditions. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowther, R.A.; Jakes, R.; Spillantini, M.G.; Goedert, M. Synthetic Filaments Assembled from C-Terminally Truncated Alpha-Synuclein. FEBS Lett. 1998, 436, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertoncini, C.W.; Jung, Y.S.; Fernandez, C.O.; Hoyer, W.; Griesinger, C.; Jovin, T.M.; Zweckstetter, M. Release of Long-Range Tertiary Interactions Potentiates Aggregation of Natively Unstructured α-Synuclein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 1430–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoyer, W.; Cherny, D.; Subramaniam, V.; Jovin, T.M. Impact of the acidic C-terminal region comprising amino acids 109–140 on α-synuclein aggregation in vitro. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 16233–16242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, M.; Nakajo, S.; Tu, P.H.; Tomita, T.; Nakaya, K.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Iwatsubo, T. Aggregation of Alpha-Synuclein in Lewy Bodies of Sporadic Parkinson’s Disease and Dementia with Lewy Bodies. Am. J. Pathol. 1998, 152, 879–884. [Google Scholar]
- Šneideris, T.; Baranauskienė, L.; Cannon, J.G.; Rutkienė, R.; Meškys, R.; Smirnovas, V. Looking for a Generic Inhibitor of Amyloid-like Fibril Formation among Flavone Derivatives. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Studier, F.W. Protein Production by Auto-Induction in High-Density Shaking Cultures. Protein Expr. Purif. 2005, 41, 207–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, M.J.; Chazin, W.J. High level expression and dimer characterization of the S100 EF-hand proteins, migration inhibitory factor-related proteins 8 and 14. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 12427–12435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gade Malmos, K.; Blancas-Mejia, L.M.; Weber, B.; Buchner, J.; Ramirez-Alvarado, M.; Naiki, H.; Otzen, D. ThT 101: A Primer on the Use of Thioflavin T to Investigate Amyloid Formation. Amyloid 2017, 24, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikalauskaite, K.; Ziaunys, M.; Sneideris, T.; Smirnovas, V. Effect of Ionic Strength on Thioflavin-T Affinity to Amyloid Fibrils and Its Fluorescence Intensity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneideris, T.; Sakalauskas, A.; Sternke-Hoffmann, R.; Peduzzo, A.; Ziaunys, M.; Buell, A.K.; Smirnovas, V. The Environment Is a Key Factor in Determining the Anti-Amyloid Efficacy of EGCG. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shlyakhtenko, L.S.; Gall, A.A.; Lyubchenko, Y.L. Mica Functionalization for Imaging of DNA and Protein-DNA Complexes with Atomic Force Microscopy. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nečas, D.; Klapetek, P. Gwyddion: An Open-Source Software for SPM Data Analysis. Open Phys. 2012, 10, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toleikis, Z.; Ziaunys, M.; Baranauskiene, L.; Petrauskas, V.; Jaudzems, K.; Smirnovas, V. S100A9 Alters the Pathway of Alpha-Synuclein Amyloid Aggregation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7972. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22157972
Toleikis Z, Ziaunys M, Baranauskiene L, Petrauskas V, Jaudzems K, Smirnovas V. S100A9 Alters the Pathway of Alpha-Synuclein Amyloid Aggregation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(15):7972. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22157972
Chicago/Turabian StyleToleikis, Zigmantas, Mantas Ziaunys, Lina Baranauskiene, Vytautas Petrauskas, Kristaps Jaudzems, and Vytautas Smirnovas. 2021. "S100A9 Alters the Pathway of Alpha-Synuclein Amyloid Aggregation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 15: 7972. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22157972
APA StyleToleikis, Z., Ziaunys, M., Baranauskiene, L., Petrauskas, V., Jaudzems, K., & Smirnovas, V. (2021). S100A9 Alters the Pathway of Alpha-Synuclein Amyloid Aggregation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(15), 7972. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22157972







