Preparing for the KIL: Receptor Analysis of Pseudomonas syringae pv. porri Phages and Their Impact on Bacterial Virulence
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
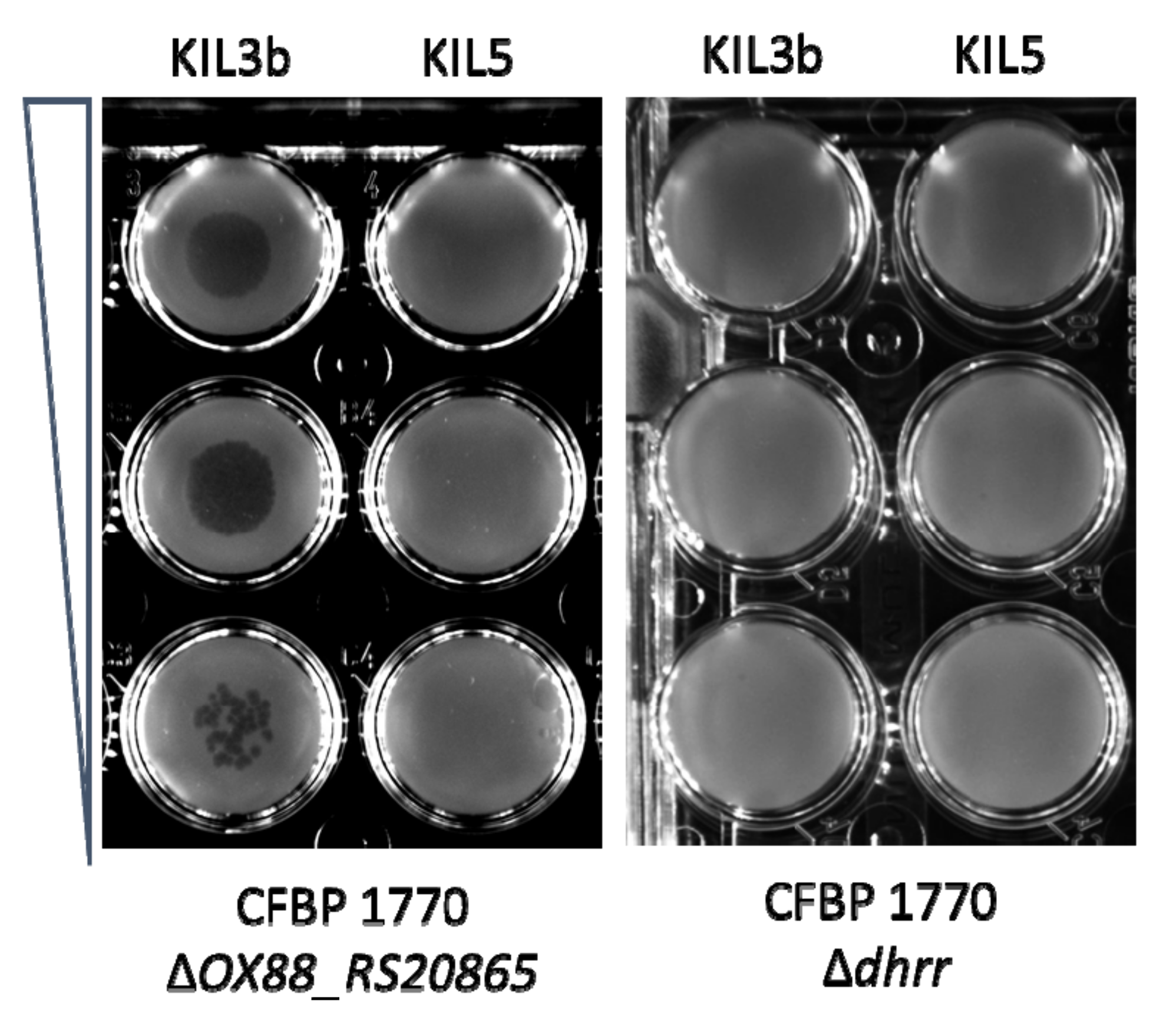
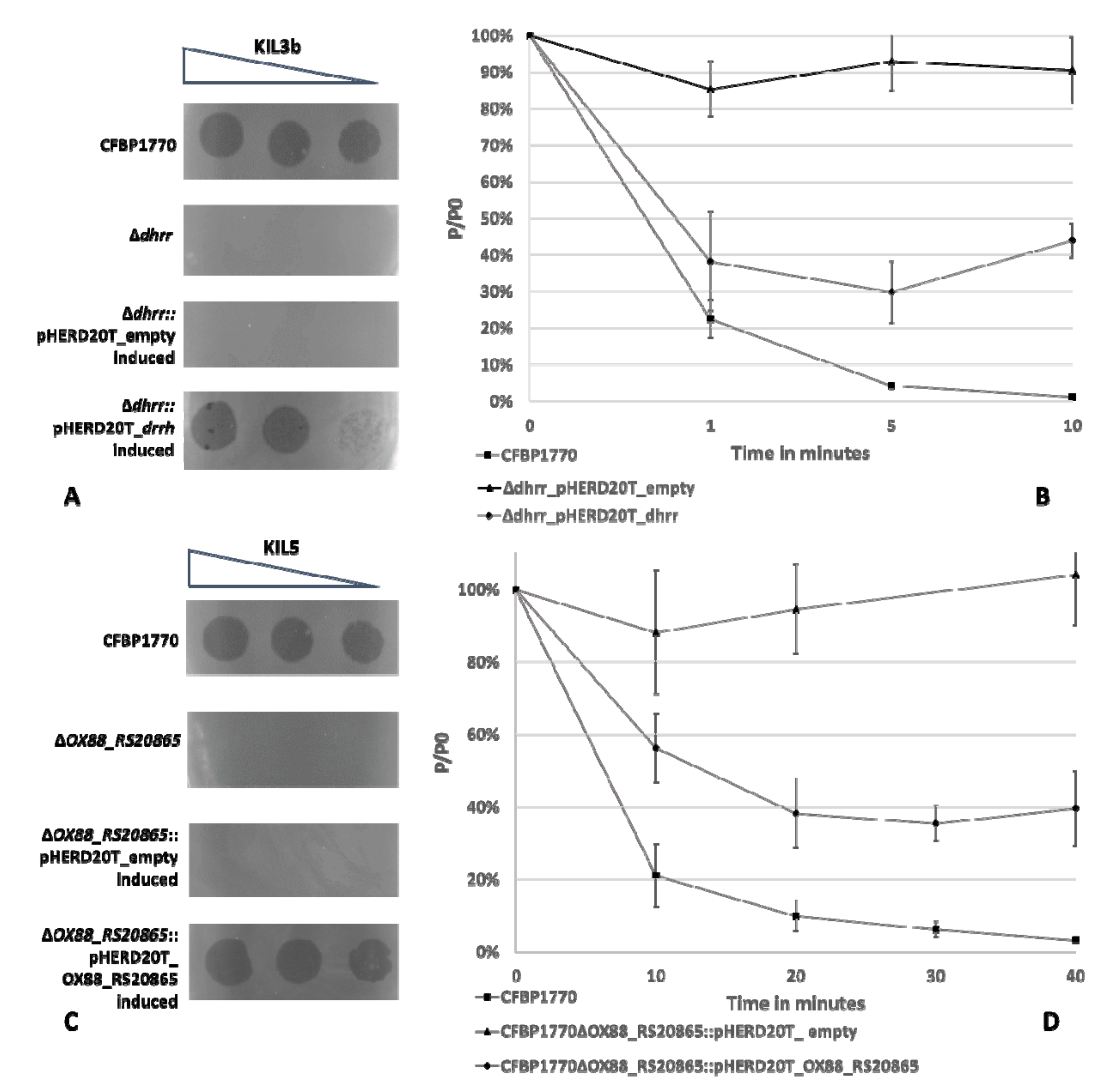
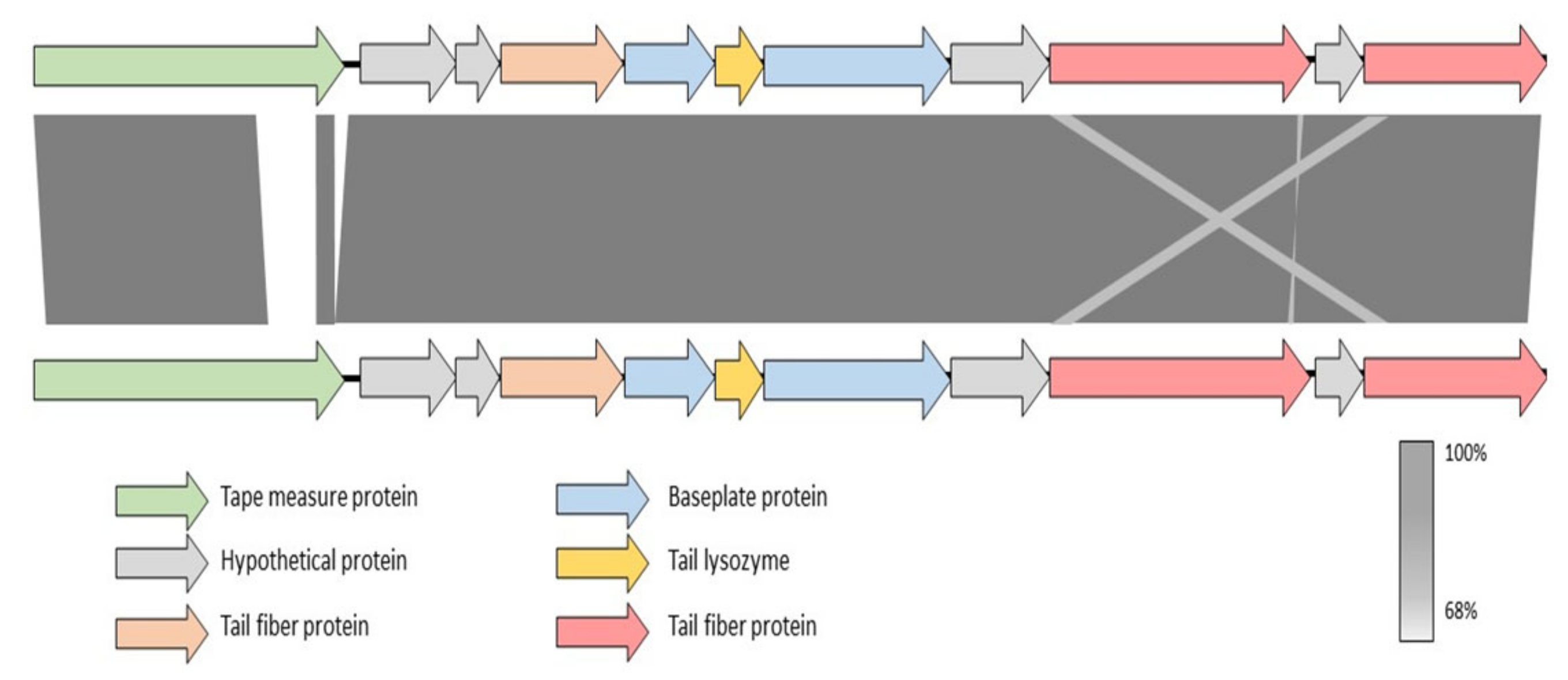
2.1. Subsection Identification of Genes Involved in the Attachment of KIL3b and KIL5 to Pseudomonas syringae pv. porri
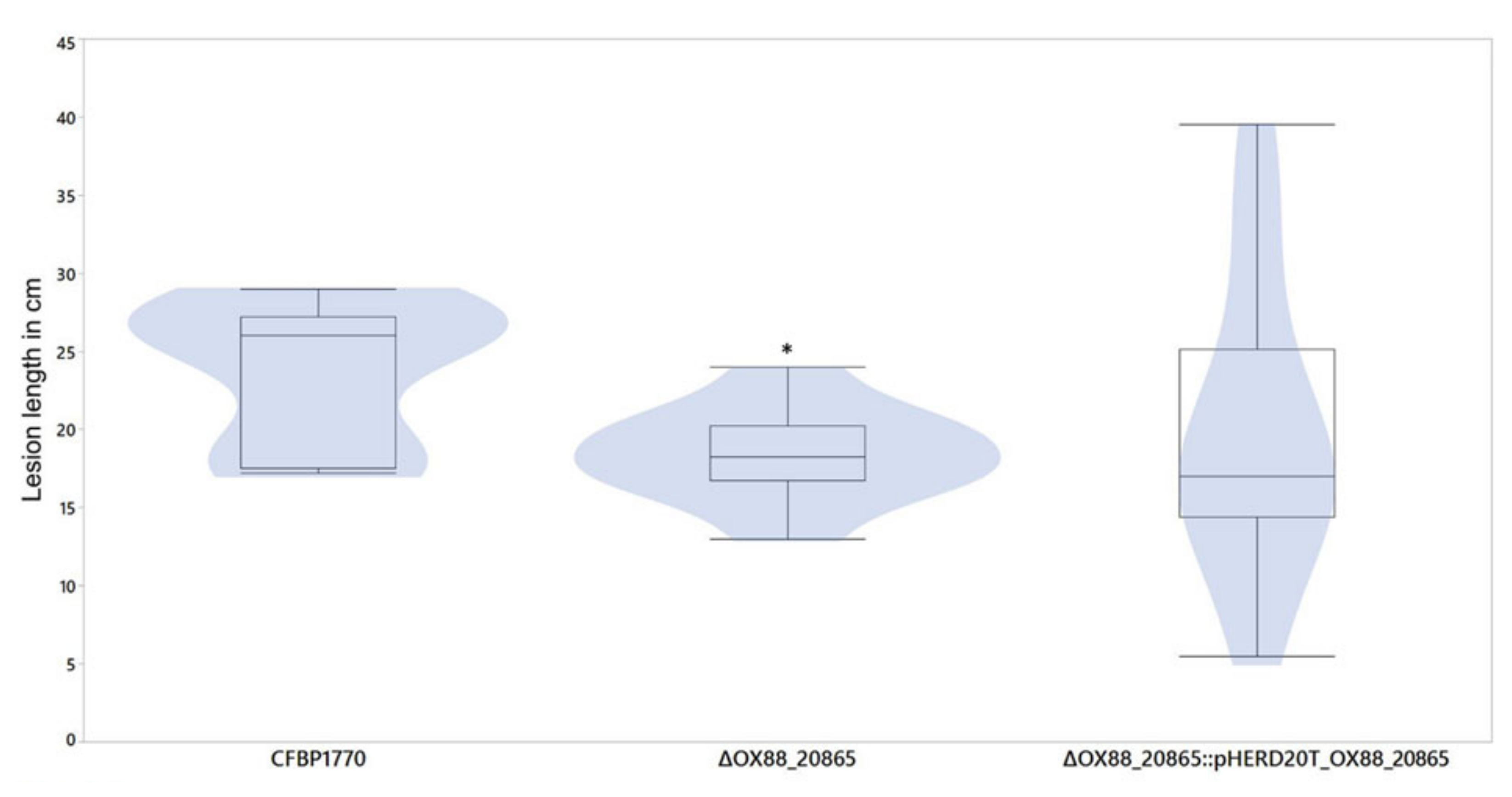
2.2. Phage-Resistant Pspo Mutants Display a Markedly Reduced Virulence
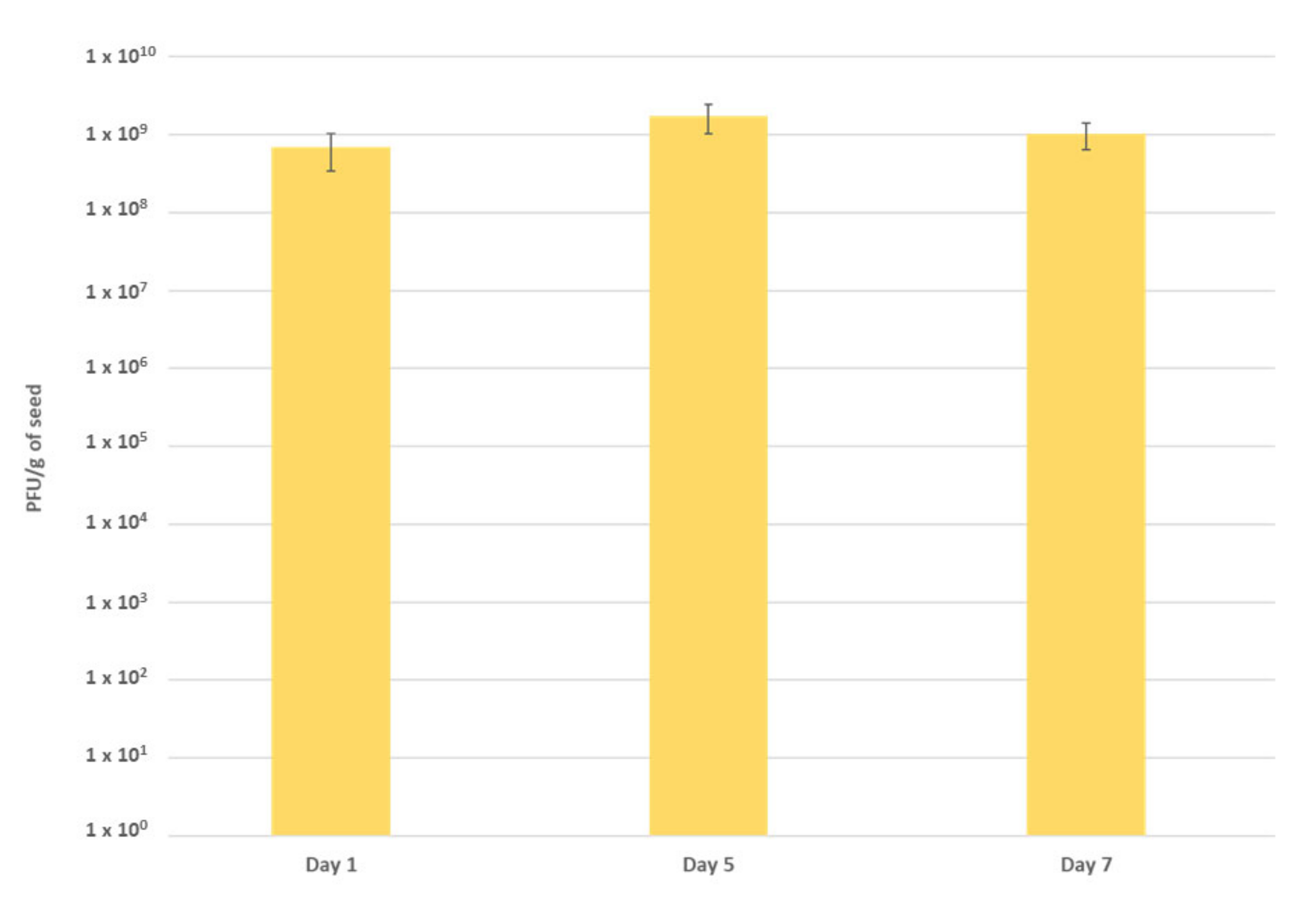
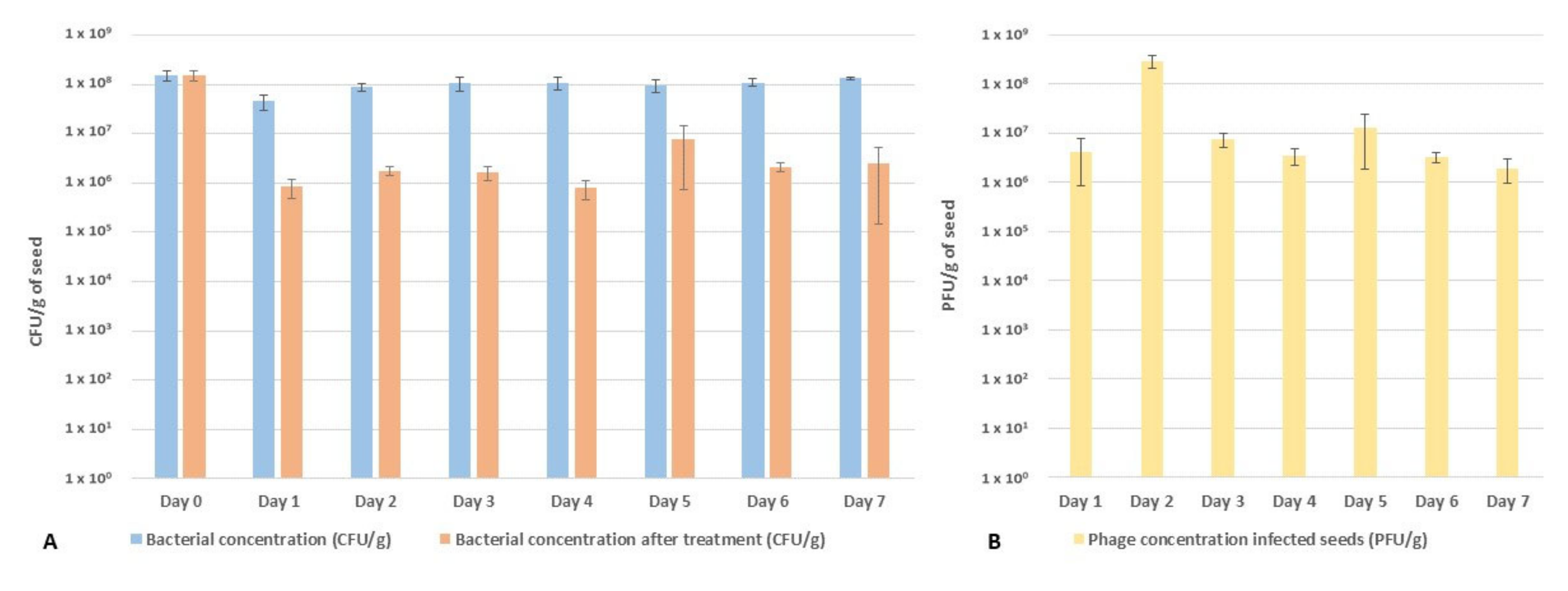
2.3. Performance of the Phage Cocktail in Reducing Pspo Titers during Seed Priming
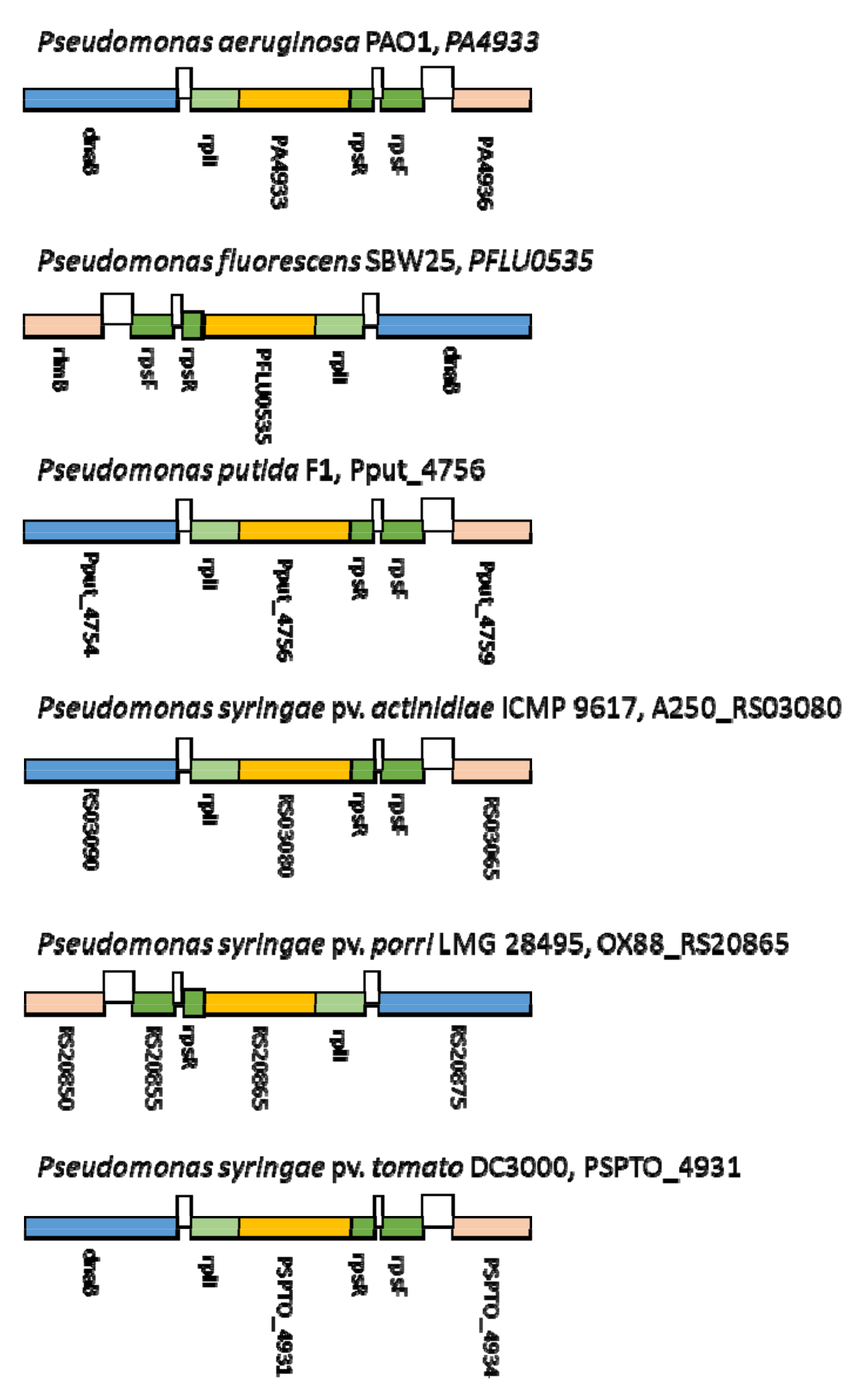
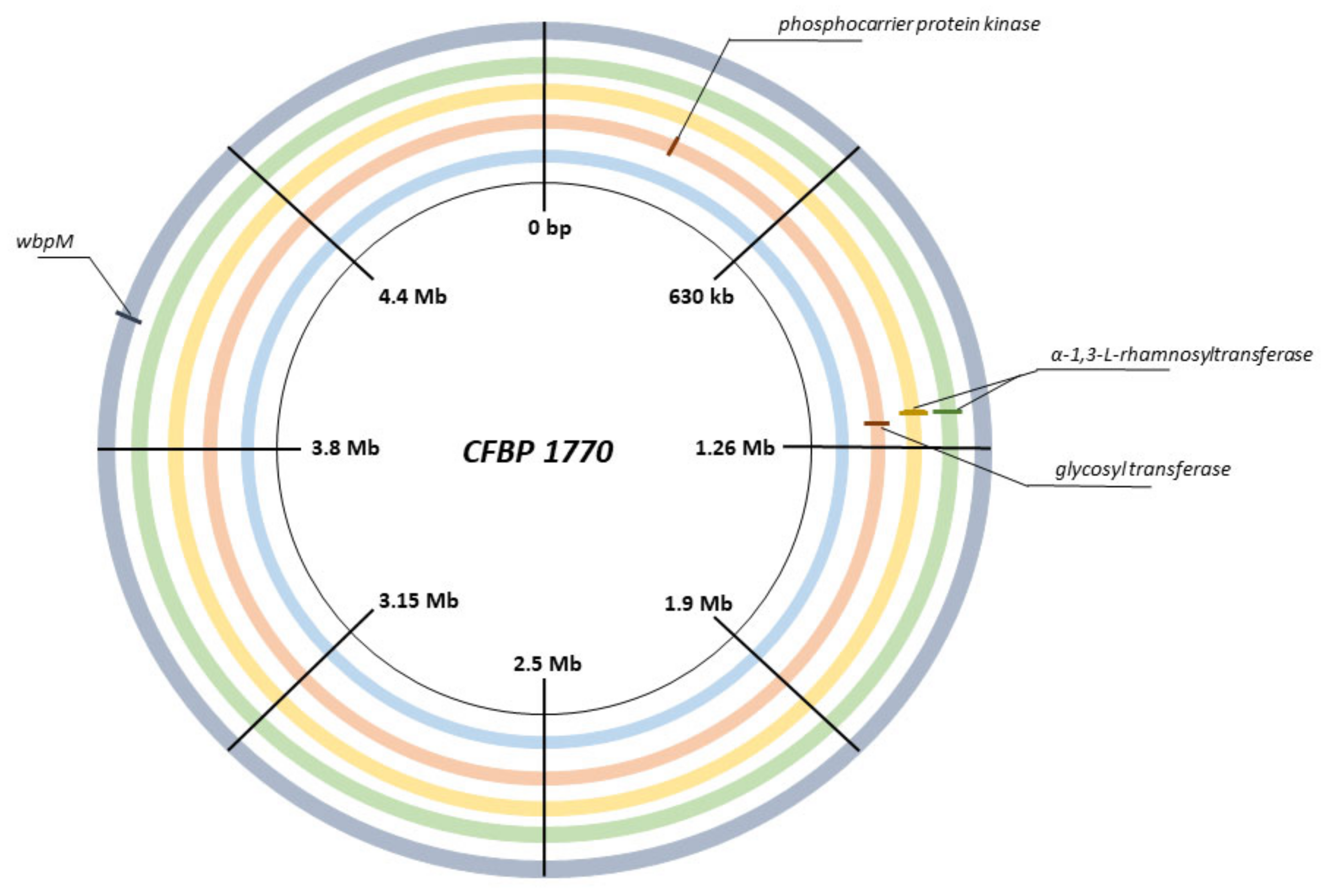
2.4. Screening and Full Genome SNP Analysis of Phage-Resistant Pspo Strains
3. Discussion
3.1. Elucidation of the Differences in Bacterial Receptors for Phages KIL3b and KIL5
3.2. Impact of the Bacterial Receptors on Phage-Based Biocontrol Assays
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Microbiological Manipulations
4.2. Tn5 Knock-Out Mutants of CFBP 1770 and Selection of Phage-Resistant Clones
4.3. Complementation of Phage Resistance and Phage Adsorption Assay
4.4. Virulence Assay in Leek Plants
4.5. Seed Bioassay
4.6. Sequencing of Natural Phage-Resistant Clones of Pseudomonas syringae pv. porri
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Phage | KO Mutant | Protein | Accession Number | e-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KIL3b | CFBP 1770_R3a | dTDP-4-dehydrorhamnose reductase | KPY21988.1 | 6 × 10−144 |
| CFBP 1770_R3b | Carbamoyltransferase | KOP57525.1 | 9 × 10−75 | |
| CFBP 1770_R3c | dTDP-4-dehydrorhamnose reductase | KOP54965.1 | 2 × 10−98 | |
| CFBP 1770_R3d | Carbamoyltransferase | KOP57525.1 | 9 × 10−75 | |
| CFBP 1770_R3e | Carbamoyltransferase | KOP57525.1 | 8 × 10−75 | |
| CFBP 1770_R3f | dTDP-glucose 4,6-dehydratase | KOP54966.1 | 3 × 10−108 | |
| CFBP 1770_R3g | GDP-6-deoxy-D-lyxo-4-hexulose reductase | KPY25409.1 | 2 × 10−8 | |
| KIL5 | CFBP 1770_R5a | Hypothetical protein ALP22_101621 | RMU82419.1 | 5 × 10−91 |
| CFBP 1770_R5b | Hypothetical membrane protein | KOP53361.1 | 4 × 10−57 | |
| CFBP 1770_R5c | Hypothetical membrane protein | KOP53361.1 | 5 × 10−50 | |
| CFBP 1770_R5d | Hypothetical membrane protein | KOP53361.1 | 6 × 10−64 |
References
- Mallmann, W.; Hemstreet, C. Isolation ofan inhibitory substance from plants. Agric. Res. 1924, 28, 599–602. [Google Scholar]
- Buttimer, C.; McAuliffe, O.; Ross, R.P.; Hill, C.; O’Mahony, J.; Coffey, A. Bacteriophages and bacterial plant diseases. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holtappels, D.; Lavigne, R.; Huys, I.; Wagemans, J. Protection of Phage Applications in Crop Production: A Patent Landscape. Viruses 2019, 11, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellington, E.M.; Boxall, A.B.; Cross, P.; Feil, E.J.; Gaze, W.H.; Hawkey, P.M.; Johnson-Rollings, A.S.; Jones, D.L.; Lee, N.M.; Otten, W.; et al. The role of the natural environment in the emergence of antibiotic resistance in Gram-negative bacteria. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenni, P.; Ancona, V.; Barra Caracciolo, A. Ecological effects of antibiotics on natural ecosystems: A review. Microchem. J. 2018, 136, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondarczuk, K.; Piotrowska-Seget, Z. Molecular basis of active copper resistance mechanisms in Gram-negative bacteria. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2013, 29, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, J.K.; Király, L.; Schwarczinger, I. Phage therapy for plant disease control with a focus on fire blight. Cent. Eur. J. Biol. 2011, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteil, C.L.; Yahara, K.; Studholme, D.J.; Mageiros, L.; Méric, G.; Swingle, B.; Morris, C.E.; Vinatzer, B.A.; Sheppard, S.K. Population-genomic insights into emergence, crop adaptation and dissemination of Pseudomonas syringae pathogens. Microb. Genom. 2016, 2, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelliott, R.A. A New Bacterial Disease of Leeks. Plant Pathol. 1952, 1, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rombouts, S.; Van Vaerenbergh, J.; Volckaert, A.; Baeyen, S.; De Langhe, T.; Declercq, B.; Lavigne, R.; Maes, M. Isolation and characterization of Pseudomonas syringae pv. porri from leek in Flanders. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2016, 144, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson, R.; Shafik, H.; Benjama, A.; Gardan, L. Description of the bacterium causing blight of leek as Pseudomonas syringae pv. porri (pv. nov.). Phytopathology 1998, 88, 844–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noble, D.H.; Cother, E.J.; Hailstones, D.L.; Flack, M.; Oxspring, L.; Hall, B. Characterisation of Pseudomonas syringae strains associated with a leaf disease of leek in Australia. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2006, 115, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rombouts, S.; Volckaert, A.; Venneman, S.; Declercq, B.; Vandenheuvel, D.; Allonsius, C.N.; Van Malderghem, C.; Jang, H.B.; Briers, Y.; Noben, J.P.; et al. Characterization of novel bacteriophages for biocontrol of bacterial blight in leek caused by Pseudomonas syringae pv. porri. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, A.; Ward, S.; Hyman, P. More is better: Selecting for broad host range bacteriophages. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyman, P.; Abedon, S.T. Bacteriophage Host Range and Bacterial Resistance. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 70, 217–248. [Google Scholar]
- Bertozzi Silva, J.; Storms, Z.; Sauvageau, D. Host receptors for bacteriophage adsorption. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2016, 363, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, M.; Bai, J.; Lim, J.-A.; Heu, S.; Ryu, S. Colanic Acid Is a Novel Phage Receptor of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum Phage POP72. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roach, D.R.; Sjaarda, D.R.; Castle, A.J.; Svircev, A.M. Host exopolysaccharide quantity and composition impact erwinia: Amylovora bacteriophage pathogenesis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 3249–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.-H.; Wu, H.-C.; Tseng, Y.-H. Mutation in the Xanthomonas campestris xanA Gene Required for Synthesis of Xanthan and Lipopolysaccharide Drastically Reduces the Efficiency of Bacteriophage φL7 Adsorption. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 291, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narulita, E.; Addy, H.S.; Kawasaki, T.; Fujie, M.; Yamada, T. The involvement of the PilQ secretin of type IV pili in phage infection in Ralstonia solanacearum. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 469, 868–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epicentre EZ-Tn5TM <KAN-2> Tnp TransposomeTM Kit. 2012, pp. 1–9. Available online: https://www.lucigen.com/docs/manuals/MA138E-EZ-Tn5-KAN-2-Transposome.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2020).
- Zdorovenko, E.L.; Zatonskii, G.V.; Kocharova, N.A.; Shashkov, A.S.; Knirel, Y.A.; Ovod, V.V. Structure of the O polysaccharides and serological classification of Pseudomonas syringae pv. porri from genomospecies 4. Eur. J. Biochem. 2003, 270, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koskella, B.; Brockhurst, M.A. Bacteria–phage coevolution as a driver of ecological and evolutionary processes in microbial communities. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 38, 916–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creuzenet, C.; Lam, J.S. Topological and functional characterization of WbpM, an inner membrane UDP-GlcNAc C6 dehydratase essential for lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 41, 1295–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoonejans, E.; Expert, D.; Toussaint, A. Characterization and virulence properties of Erwinia chrysanthemi lipopolysaccharide-defective, phi EC2-resistant mutants. J. Bacteriol. 1987, 169, 4011–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumrall, E.T.; Shen, Y.; Keller, A.P.; Rismondo, J.; Pavlou, M.; Eugster, M.R.; Boulos, S.; Disson, O.; Thouvenot, P.; Kilcher, S.; et al. Phage resistance at the cost of virulence: Listeria monocytogenes serovar 4b requires galactosylated teichoic acids for InlB-mediated invasion. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippov, A.A.; Sergueev, K.V.; He, Y.; Huang, X.-Z.; Gnade, B.T.; Mueller, A.J.; Fernandez-Prada, C.M.; Nikolich, M.P. Bacteriophage-Resistant Mutants in Yersinia pestis: Identification of Phage Receptors and Attenuation for Mice. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszak, T.; Danis-Wlodarczyk, K.; Arabski, M.; Gula, G.; Maciejewska, B.; Wasik, S.; Lood, C.; Higgins, G.; Harvey, B.J.; Lavigne, R.; et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA5oct jumbo phage impacts planktonic and biofilm population and reduces its host virulence. Viruses 2019, 11, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumby, N.; Reimer, K.; Mengin-Lecreulx, D.; Davidson, A.R.; Maxwell, K.L. The phage tail tape measure protein, an inner membrane protein and a periplasmic chaperone play connected roles in the genome injection process of E.coli phage HK97. Mol. Microbiol. 2015, 96, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, N.; Fox, D.K.; Shea, C.; Roseman, S. Pel, the protein that permits lambda DNA penetration of Escherichia coli, is encoded by a gene in ptsM and is required for mannose utilization by the phosphotransferase system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 8934–8938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scandella, D.; Arber, W. Phage λ DNA injection into Escherichia coli pel− mutants is restored by mutations in phage genes V or H. Virology 1976, 69, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Barceló, C. Phage Therapy Faces Evolutionary Challenges. Viruses 2018, 10, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svircev, A.; Roach, D.; Castle, A. Framing the future with bacteriophages in agriculture. Viruses 2018, 10, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.B.; Jackson, L.E.; Balogh, B.; Obradovic, A.; Iriarte, F.B.; Momol, M.T. Bacteriophages for plant disease control. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2007, 45, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, Y.E.; Saleh, A.A.; Al-Saleh, M.A. Management of asiatic citrus canker under field conditions in Saudi Arabia using bacteriophages and acibenzolar-s-methyl. Plant Dis. 2017, 101, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, S.T.; Barak, J.D.; Henderson, D.M.; Gilbertson, R.L. Bacterial blight of leek: A new disease in California caused by Pseudomonas syringae. Plant Dis. 1999, 83, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, R.C.T.; Friman, V.P.; Smith, M.C.M.; Brockhurst, M.A. Resistance evolution against phage combinations depends on the timing and order of exposure. MBio 2019, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kropinski, A.M.; Adriaenssens, E.M.; Klumpp, J.; Lavigne, R. Flaumdravirus; International committee on Taxonomy of Viruses: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wagemans, J.; Blasdel, B.G.; Van den Bossche, A.; Uytterhoeven, B.; De Smet, J.; Paeshuyse, J.; Cenens, W.; Aertsen, A.; Uetz, P.; Delattre, A.-S.; et al. Functional elucidation of antibacterial phage ORFans targeting Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Cell. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 1822–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, T.; Burke, E. High-Throughput TAIL-PCR as a Tool to Identify DNA Flanking Insertions. In Methods in Molecular Biology, vol. 236: Plant Functional Genomics: Methods and Protocols; Grotewold, E., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 241–271. [Google Scholar]
- States, D.J.; Gish, W. Comined use of sequence similarity and codon bias for coding region identification. J. Comput. Biol. 1994, 1, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, D.; Damron, F.H.; Mima, T.; Schweizer, H.P.; Yu, H.D. PBAD-based shuttle vectors for functional analysis of toxic and highly regulated genes in Pseudomonas and Burkholderia spp. and other bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 7422–7426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriaenssens, E.M.; Edwards, R.; Nash, J.H.E.; Mahadevan, P.; Seto, D.; Ackermann, H.-W.; Lavigne, R.; Kropinski, A.M. Integration of genomic and proteomic analyses in the classification of the Siphoviridae family. Virology 2015, 477, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Linden, I.; Cottyn, B.; Uyttendaele, M.; Vlaemynck, G.; Maes, M.; Heyndrickx, M. Long-term survival of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella enterica on butterhead lettuce seeds, and their subsequent survival and growth on the seedlings. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 161, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Holt, K.E. Performance of neural network basecalling tools for Oxford Nanopore sequencing. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Gorrie, C.L.; Holt, K.E. Completing bacterial genome assemblies with multiplex MinION sequencing. Microb. Genom. 2017, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Gorrie, C.L.; Holt, K.E. Unicycler: Resolving bacterial genome assemblies from short and long sequencing reads. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, R.R.; Schultz, M.B.; Zobel, J.; Holt, K.E. Bandage: Interactive visualization of de novo genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3350–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wattam, A.R.; Davis, J.J.; Assaf, R.; Boisvert, S.; Brettin, T.; Bun, C.; Conrad, N.; Dietrich, E.M.; Disz, T.; Gabbard, J.L.; et al. Improvements to PATRIC, the all-bacterial Bioinformatics Database and Analysis Resource Center. Nucl. Acids Res. 2017, 45, D535–D542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seemann, T. Snippy: Fast Bacterial Variant Calling from NGS Reads. Available online: https://github.com/tseemann/snippy (accessed on 3 March 2020).
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Holtappels, D.; Kerremans, A.; Busschots, Y.; Van Vaerenbergh, J.; Maes, M.; Lavigne, R.; Wagemans, J. Preparing for the KIL: Receptor Analysis of Pseudomonas syringae pv. porri Phages and Their Impact on Bacterial Virulence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2930. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082930
Holtappels D, Kerremans A, Busschots Y, Van Vaerenbergh J, Maes M, Lavigne R, Wagemans J. Preparing for the KIL: Receptor Analysis of Pseudomonas syringae pv. porri Phages and Their Impact on Bacterial Virulence. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(8):2930. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082930
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoltappels, Dominique, Alison Kerremans, Yoni Busschots, Johan Van Vaerenbergh, Martine Maes, Rob Lavigne, and Jeroen Wagemans. 2020. "Preparing for the KIL: Receptor Analysis of Pseudomonas syringae pv. porri Phages and Their Impact on Bacterial Virulence" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 8: 2930. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082930
APA StyleHoltappels, D., Kerremans, A., Busschots, Y., Van Vaerenbergh, J., Maes, M., Lavigne, R., & Wagemans, J. (2020). Preparing for the KIL: Receptor Analysis of Pseudomonas syringae pv. porri Phages and Their Impact on Bacterial Virulence. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(8), 2930. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082930






