Immunotherapy in Renal Cell Carcinoma: The Future Is Now
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Specificities of the Tumour Microenvironment in Renal Cell Carcinoma
2.1. Vascular Component
2.2. Immune Component
3. Treatment Update in Renal Cell Carcinoma
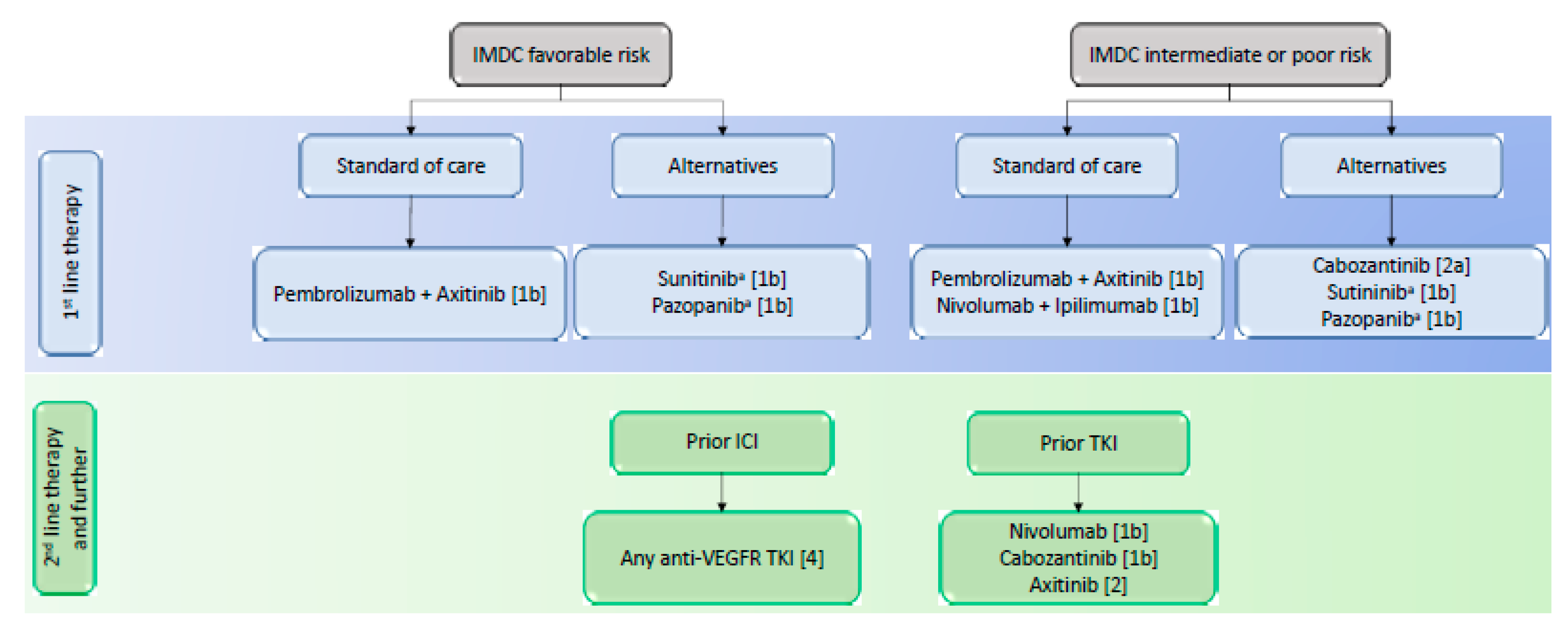
3.1. First-Line Treatment
3.2. Second-Line Treatment
3.3. Adjuvant treatment
3.4. Non-Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
4. Emerging Drugs in Ongoing Trials Include Renal Cell Carcinoma
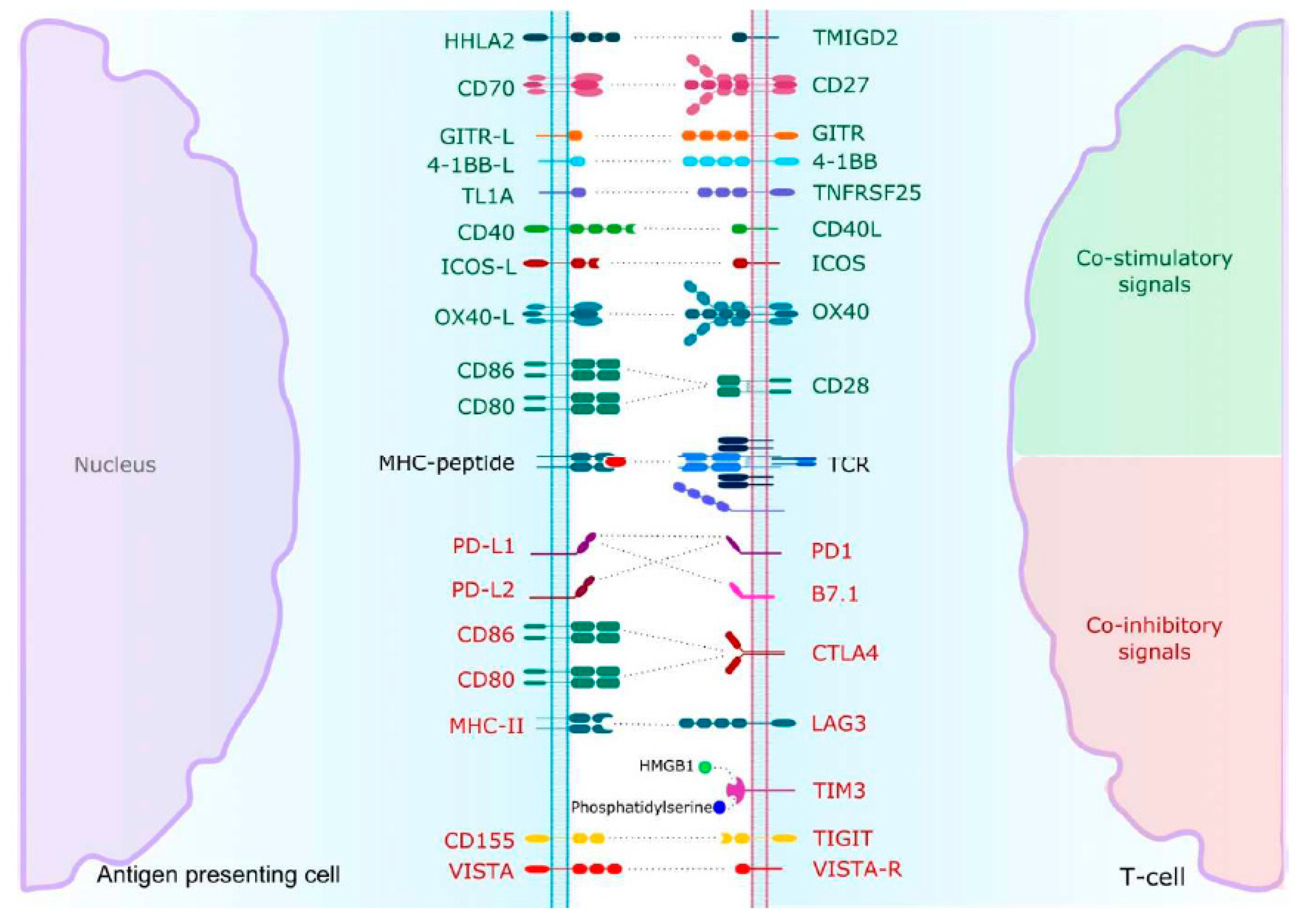
4.1. Inhibitory Immune Checkpoints
4.2. Co-Activating Immune Checkpoints
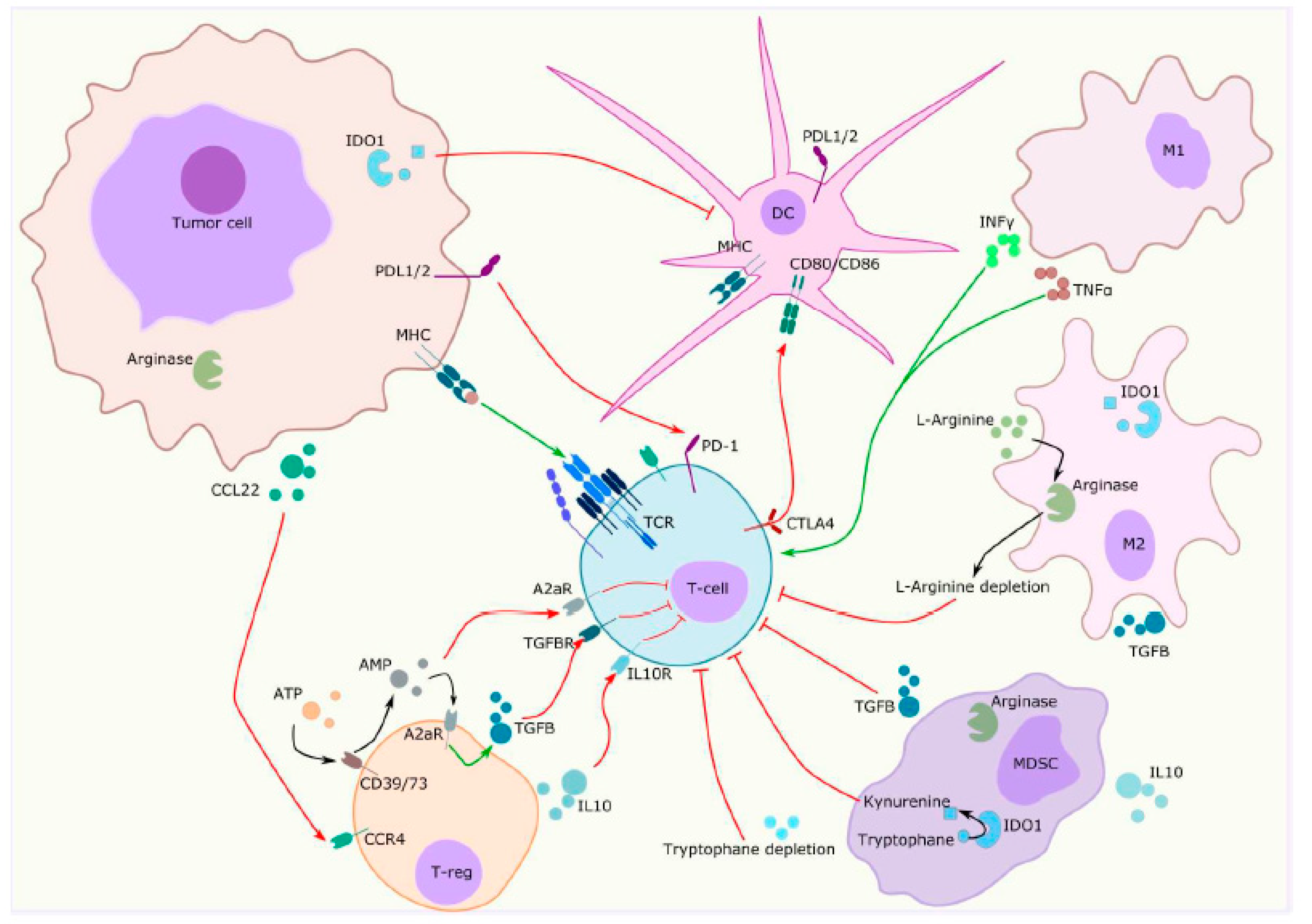
4.3. Metabolic Pathways
4.4. Other Strategies
5. Predictive Biomarkers in RCC
5.1. Clinico-Biological Biomarkers
5.2. Immunohistochemical Biomarkers
5.3. Transcriptomic Analysis
5.4. Tumour Mutational Burden and Mismatch Repair Deficiency
5.5. Gut Microbiome
6. Future Directions
6.1. Microenvironment Cell Population Counter
6.2. Single-Cell Technologies
6.3. 3D Culture Models
6.4. Imaging
6.5. Circulating Tumour Cells
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljungberg, B.; Campbell, S.C.; Choi, H.Y.; Jacqmin, D.; Lee, J.E.; Weikert, S.; Kiemeney, L.A. The epidemiology of renal cell carcinoma. Eur. Urol. 2011, 60, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gossage, L.; Eisen, T.; Maher, E.R. Vhl, the story of a tumour suppressor gene. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akaza, H.; Fukuyama, T. Axitinib for the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2014, 15, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Hutson, T.E.; Cella, D.; Reeves, J.; Hawkins, R.; Guo, J.; Nathan, P.; Staehler, M.; de Souza, P.; Merchan, J.R.; et al. Pazopanib versus sunitinib in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choueiri, T.K.; Escudier, B.; Powles, T.; Mainwaring, P.N.; Rini, B.I.; Donskov, F.; Hammers, H.; Hutson, T.E.; Lee, J.L.; Peltola, K.; et al. Cabozantinib versus everolimus in advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1814–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rini, B.I.; Pal, S.K.; Escudier, B.J.; Atkins, M.B.; Hutson, T.E.; Porta, C.; Verzoni, E.; Needle, M.N.; McDermott, D.F. Tivozanib versus sorafenib in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (tivo-3): A phase 3, multicentre, randomised, controlled, open-label study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moch, H.; Cubilla, A.L.; Humphrey, P.A.; Reuter, V.E.; Ulbright, T.M. The 2016 who classification of tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs-part a: Renal, penile, and testicular tumours. Eur. Urol. 2016, 70, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research, N.; Linehan, W.M.; Spellman, P.T.; Ricketts, C.J.; Creighton, C.J.; Fei, S.S.; Davis, C.; Wheeler, D.A.; Murray, B.A.; Schmidt, L.; et al. Comprehensive molecular characterization of papillary renal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argani, P. Mit family translocation renal cell carcinoma. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 2015, 32, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malouf, G.G.; Monzon, F.A.; Couturier, J.; Molinie, V.; Escudier, B.; Camparo, P.; Su, X.; Yao, H.; Tamboli, P.; Lopez-Terrada, D.; et al. Genomic heterogeneity of translocation renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 4673–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malouf, G.G.; Comperat, E.; Yao, H.; Mouawad, R.; Lindner, V.; Rioux-Leclercq, N.; Verkarre, V.; Leroy, X.; Dainese, L.; Classe, M.; et al. Unique transcriptomic profile of collecting duct carcinomas relative to upper tract urothelial carcinomas and other kidney carcinomas. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlo, M.I.; Chaim, J.; Patil, S.; Kemel, Y.; Schram, A.M.; Woo, K.; Coskey, D.; Nanjangud, G.J.; Voss, M.H.; Feldman, D.R.; et al. Genomic characterization of renal medullary carcinoma and treatment outcomes. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2017, 15, e987–e994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.B.; Brannon, A.R.; Toubaji, A.; Dudas, M.E.; Won, H.H.; Al-Ahmadie, H.A.; Fine, S.W.; Gopalan, A.; Frizzell, N.; Voss, M.H.; et al. Hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell carcinoma syndrome-associated renal cancer: Recognition of the syndrome by pathologic features and the utility of detecting aberrant succination by immunohistochemistry. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2014, 38, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malouf, G.G.; Ali, S.M.; Wang, K.; Balasubramanian, S.; Ross, J.S.; Miller, V.A.; Stephens, P.J.; Khayat, D.; Pal, S.K.; Su, X.; et al. Genomic characterization of renal cell carcinoma with sarcomatoid dedifferentiation pinpoints recurrent genomic alterations. Eur. Urol. 2016, 70, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albiges, L.; Powles, T.; Staehler, M.; Bensalah, K.; Giles, R.H.; Hora, M.; Kuczyk, M.A.; Lam, T.B.; Ljungberg, B.; Marconi, L.; et al. Updated european association of urology guidelines on renal cell carcinoma: Immune checkpoint inhibition is the new backbone in first-line treatment of metastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Eur. Urol. 2019, 76, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Bacik, J.; Murphy, B.A.; Russo, P.; Mazumdar, M. Interferon-alfa as a comparative treatment for clinical trials of new therapies against advanced renal cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fyfe, G.; Fisher, R.I.; Rosenberg, S.A.; Sznol, M.; Parkinson, D.R.; Louie, A.C. Results of treatment of 255 patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma who received high-dose recombinant interleukin-2 therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 1995, 13, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Hutson, T.E.; Tomczak, P.; Michaelson, M.D.; Bukowski, R.M.; Rixe, O.; Oudard, S.; Negrier, S.; Szczylik, C.; Kim, S.T.; et al. Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Tannir, N.M.; McDermott, D.F.; Aren Frontera, O.; Melichar, B.; Choueiri, T.K.; Plimack, E.R.; Barthelemy, P.; Porta, C.; George, S.; et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib in advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1277–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Escudier, B.; McDermott, D.F.; George, S.; Hammers, H.J.; Srinivas, S.; Tykodi, S.S.; Sosman, J.A.; Procopio, G.; Plimack, E.R.; et al. Nivolumab versus everolimus in advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1803–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite, K.R.; Reis, S.T.; Junior, J.P.; Zerati, M.; Gomes Dde, O.; Camara-Lopes, L.H.; Srougi, M. Pd-l1 expression in renal cell carcinoma clear cell type is related to unfavorable prognosis. Diagn. Pathol. 2015, 10, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, R.H.; Dong, H.; Kwon, E.D. Implications of b7-h1 expression in clear cell carcinoma of the kidney for prognostication and therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 709s–715s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.H.; Dong, H.; Lohse, C.M.; Leibovich, B.C.; Blute, M.L.; Cheville, J.C.; Kwon, E.D. Pd-1 is expressed by tumor-infiltrating immune cells and is associated with poor outcome for patients with renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 1757–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Penkov, K.; Haanen, J.; Rini, B.; Albiges, L.; Campbell, M.T.; Venugopal, B.; Kollmannsberger, C.; Negrier, S.; Uemura, M.; et al. Avelumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1103–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rini, B.I.; Plimack, E.R.; Stus, V.; Gafanov, R.; Hawkins, R.; Nosov, D.; Pouliot, F.; Alekseev, B.; Soulieres, D.; Melichar, B.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Hu-Lieskovan, S.; Wargo, J.A.; Ribas, A. Primary, adaptive, and acquired resistance to cancer immunotherapy. Cell 2017, 168, 707–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, G.P.; Bruce, A.T.; Ikeda, H.; Old, L.J.; Schreiber, R.D. Cancer immunoediting: From immunosurveillance to tumor escape. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.C.; Joller, N.; Kuchroo, V.K. Lag-3, tim-3, and tigit: Co-inhibitory receptors with specialized functions in immune regulation. Immunity 2016, 44, 989–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrechts, D.; Wauters, E.; Boeckx, B.; Aibar, S.; Nittner, D.; Burton, O.; Bassez, A.; Decaluwe, H.; Pircher, A.; Van den Eynde, K.; et al. Phenotype molding of stromal cells in the lung tumor microenvironment. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1277–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akino, T.; Hida, K.; Hida, Y.; Tsuchiya, K.; Freedman, D.; Muraki, C.; Ohga, N.; Matsuda, K.; Akiyama, K.; Harabayashi, T.; et al. Cytogenetic abnormalities of tumor-associated endothelial cells in human malignant tumors. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 175, 2657–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edeline, J.; Mottier, S.; Vigneau, C.; Jouan, F.; Perrin, C.; Zerrouki, S.; Fergelot, P.; Patard, J.J.; Rioux-Leclercq, N. Description of 2 angiogenic phenotypes in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 2012, 43, 1982–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufies, M.; Giuliano, S.; Ambrosetti, D.; Claren, A.; Ndiaye, P.D.; Mastri, M.; Moghrabi, W.; Cooley, L.S.; Ettaiche, M.; Chamorey, E.; et al. Sunitinib stimulates expression of vegfc by tumor cells and promotes lymphangiogenesis in clear cell renal cell carcinomas. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 1212–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, R.H.; Kuntz, S.M.; Leibovich, B.C.; Dong, H.; Lohse, C.M.; Webster, W.S.; Sengupta, S.; Frank, I.; Parker, A.S.; Zincke, H.; et al. Tumor b7-h1 is associated with poor prognosis in renal cell carcinoma patients with long-term follow-up. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 3381–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choueiri, T.K.; Fay, A.P.; Gray, K.P.; Callea, M.; Ho, T.H.; Albiges, L.; Bellmunt, J.; Song, J.; Carvo, I.; Lampron, M.; et al. Pd-l1 expression in nonclear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 2178–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Cheville, J. C.; Jungbluth, A. A.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y. B.; Tickoo, S. K.; Fine, S. W.; Gopalan, A.; Al-Ahmadie, H. A.; et al. JAK2/PD-L1/PD-L2 (9p24.1) amplifications in renal cell carcinomas with sarcomatoid transformation: Implications for clinical management. Mod. Pathol. 2019, 32, 1344–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevrier, S.; Levine, J.H.; Zanotelli, V.R.T.; Silina, K.; Schulz, D.; Bacac, M.; Ries, C.H.; Ailles, L.; Jewett, M.A.S.; Moch, H.; et al. An immune atlas of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cell 2017, 169, 736–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldo, N.A.; Becht, E.; Vano, Y.; Petitprez, F.; Lacroix, L.; Validire, P.; Sanchez-Salas, R.; Ingels, A.; Oudard, S.; Moatti, A.; et al. Tumor-infiltrating and peripheral blood t-cell immunophenotypes predict early relapse in localized clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 4416–4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjoberg, E.; Frodin, M.; Lovrot, J.; Mezheyeuski, A.; Johansson, M.; Harmenberg, U.; Egevad, L.; Sandstrom, P.; Ostman, A. A minority-group of renal cell cancer patients with high infiltration of cd20 + b-cells is associated with poor prognosis. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 119, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choueiri, T.K.; Fishman, M.N.; Escudier, B.; McDermott, D.F.; Drake, C.G.; Kluger, H.; Stadler, W.M.; Perez-Gracia, J.L.; McNeel, D.G.; Curti, B.; et al. Immunomodulatory activity of nivolumab in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 5461–5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirotake, S.; Kaneko, G.; Nagata, K.; Oyama, M.; Nishimoto, K. Histological complete response with nivolumab for renal cell carcinoma with multiple metastases: A case report. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 10, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rini, B.I.; Powles, T.; Atkins, M.B.; Escudier, B.; McDermott, D.F.; Suarez, C.; Bracarda, S.; Stadler, W.M.; Donskov, F.; Lee, J.L.; et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab versus sunitinib in patients with previously untreated metastatic renal cell carcinoma (immotion151): A multicentre, open-label, phase 3, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 2404–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Rini, B.I.; McDermott, D.F.; Aren Frontera, O.; Hammers, H.J.; Carducci, M.A.; Salman, P.; Escudier, B.; Beuselinck, B.; Amin, A.; et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib in first-line treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma: Extended follow-up of efficacy and safety results from a randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1370–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalani, A.A.; McGregor, B.A.; Albiges, L.; Choueiri, T.K.; Motzer, R.; Powles, T.; Wood, C.; Bex, A. Systemic treatment of metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma in 2018: Current paradigms, use of immunotherapy, and future directions. Eur. Urol. 2019, 75, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, Y.; Fukasawa, S.; Shinohara, N.; Kitamura, H.; Oya, M.; Eto, M.; Tanabe, K.; Kimura, G.; Yonese, J.; Yao, M.; et al. Nivolumab versus everolimus in advanced renal cell carcinoma: Japanese subgroup analysis from the checkmate 025 study. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 47, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravaud, A.; Motzer, R.J.; Pandha, H.S.; George, D.J.; Pantuck, A.J.; Patel, A.; Chang, Y.H.; Escudier, B.; Donskov, F.; Magheli, A.; et al. Adjuvant sunitinib in high-risk renal-cell carcinoma after nephrectomy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 2246–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Jonasch, E.; Michaelson, M.D.; Nandagopal, L.; Gore, J.L.; George, S.; Alva, A.; Haas, N.; Harrison, M.R.; Plimack, E.R.; et al. Nccn guidelines insights: Kidney cancer, version 2.2020. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2019, 17, 1278–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera-Badillo, F.E.; Templeton, A.J.; Duran, I.; Ocana, A.; de Gouveia, P.; Aneja, P.; Knox, J.J.; Tannock, I.F.; Escudier, B.; Amir, E. Systemic therapy for non-clear cell renal cell carcinomas: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Urol. 2015, 67, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshkin, V.S.; Barata, P.C.; Zhang, T.; George, D.J.; Atkins, M.B.; Kelly, W.J.; Vogelzang, N.J.; Pal, S.K.; Hsu, J.; Appleman, L.J.; et al. Clinical activity of nivolumab in patients with non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benci, J.L.; Xu, B.; Qiu, Y.; Wu, T.J.; Dada, H.; Twyman-Saint Victor, C.; Cucolo, L.; Lee, D.S.M.; Pauken, K.E.; Huang, A.C.; et al. Tumor interferon signaling regulates a multigenic resistance program to immune checkpoint blockade. Cell 2016, 167, 1540–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhu, Y.; Li, G.; Huang, H.; Zhang, G.; Wang, F.; Sun, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Lu, B. Tim-3 expression characterizes regulatory t cells in tumor tissues and is associated with lung cancer progression. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakuishi, K.; Apetoh, L.; Sullivan, J.M.; Blazar, B.R.; Kuchroo, V.K.; Anderson, A.C. Targeting tim-3 and pd-1 pathways to reverse t cell exhaustion and restore anti-tumor immunity. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 2187–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casado, J.G.; Pawelec, G.; Morgado, S.; Sanchez-Correa, B.; Delgado, E.; Gayoso, I.; Duran, E.; Solana, R.; Tarazona, R. Expression of adhesion molecules and ligands for activating and costimulatory receptors involved in cell-mediated cytotoxicity in a large panel of human melanoma cell lines. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2009, 58, 1517–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inamura, K.; Amori, G.; Yuasa, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Yonese, J.; Ishikawa, Y. Relationship of b7-h3 expression in tumor cells and tumor vasculature with foxp3+ regulatory t cells in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 7021–7030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Rubinstein, R.; Lines, J.L.; Wasiuk, A.; Ahonen, C.; Guo, Y.; Lu, L.F.; Gondek, D.; Wang, Y.; Fava, R.A.; et al. Vista, a novel mouse ig superfamily ligand that negatively regulates t cell responses. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 577–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Mercier, I.; Chen, W.; Lines, J.L.; Day, M.; Li, J.; Sergent, P.; Noelle, R.J.; Wang, L. Vista regulates the development of protective antitumor immunity. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 1933–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fos, C.; Salles, A.; Lang, V.; Carrette, F.; Audebert, S.; Pastor, S.; Ghiotto, M.; Olive, D.; Bismuth, G.; Nunes, J.A. Icos ligation recruits the p50alpha pi3k regulatory subunit to the immunological synapse. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 1969–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspeslagh, S.; Postel-Vinay, S.; Rusakiewicz, S.; Soria, J.C.; Zitvogel, L.; Marabelle, A. Rationale for anti-ox40 cancer immunotherapy. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 52, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevach, E.M.; Stephens, G.L. The gitr-gitrl interaction: Co-stimulation or contrasuppression of regulatory activity? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramapriyan, R.; Caetano, M.S.; Barsoumian, H.B.; Mafra, A.C.P.; Zambalde, E.P.; Menon, H.; Tsouko, E.; Welsh, J.W.; Cortez, M.A. Altered cancer metabolism in mechanisms of immunotherapy resistance. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 195, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y.; Li, C.F.; Kuo, C.C.; Tsai, K.K.; Hou, M.F.; Hung, W.C. Cancer/stroma interplay via cyclooxygenase-2 and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase promotes breast cancer progression. Breast Cancer Res. 2014, 16, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheong, J.E.; Sun, L. Targeting the ido1/tdo2-kyn-ahr pathway for cancer immunotherapy—challenges and opportunities. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 39, 307–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, R.D.; Emens, L.A. Targeting adenosine for cancer immunotherapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linnemann, C.; Schildberg, F.A.; Schurich, A.; Diehl, L.; Hegenbarth, S.I.; Endl, E.; Lacher, S.; Muller, C.E.; Frey, J.; Simeoni, L.; et al. Adenosine regulates cd8 t-cell priming by inhibition of membrane-proximal t-cell receptor signalling. Immunology 2009, 128, e728–e737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananieva, E. Targeting amino acid metabolism in cancer growth and anti-tumor immune response. World J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 6, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, M.A.; Kouzarides, T. Cancer epigenetics: From mechanism to therapy. Cell 2012, 150, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckschlager, T.; Plch, J.; Stiborova, M.; Hrabeta, J. Histone deacetylase inhibitors as anticancer drugs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, R.Y.; Chung, W.H.; Chu, M.T.; Chen, S.J.; Chen, H.C.; Zheng, L.; Hung, S.I. Recent development and clinical application of cancer vaccine: Targeting neoantigens. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 4325874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ding, J.; Lu, M.; Liu, H.; Miao, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, G.; Zheng, J.; Pei, D.; Zhang, Q. Caix-specific car-t cells and sunitinib show synergistic effects against metastatic renal cancer models. J. Immunother. 2020, 43, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, D.Y.; Xie, W.; Regan, M.M.; Harshman, L.C.; Bjarnason, G.A.; Vaishampayan, U.N.; Mackenzie, M.; Wood, L.; Donskov, F.; Tan, M.H.; et al. External validation and comparison with other models of the international metastatic renal-cell carcinoma database consortium prognostic model: A population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroeger, N.; Klatte, T.; Chamie, K.; Rao, P.N.; Birkhauser, F.D.; Sonn, G.A.; Riss, J.; Kabbinavar, F.F.; Belldegrun, A.S.; Pantuck, A.J. Deletions of chromosomes 3p and 14q molecularly subclassify clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer 2013, 119, 1547–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kammerer-Jacquet, S.F.; Deleuze, A.; Saout, J.; Mathieu, R.; Laguerre, B.; Verhoest, G.; Dugay, F.; Belaud-Rotureau, M.A.; Bensalah, K.; Rioux-Leclercq, N. Targeting the pd-1/pd-l1 pathway in renal cell carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeber, A.; Klinglmair, G.; Fritz, J.; Steinkohl, F.; Zimmer, K.C.; Aigner, F.; Horninger, W.; Gastl, G.; Zelger, B.; Brunner, A.; et al. High ido-1 expression in tumor endothelial cells is associated with response to immunotherapy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 1583–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beuselinck, B.; Job, S.; Becht, E.; Karadimou, A.; Verkarre, V.; Couchy, G.; Giraldo, N.; Rioux-Leclercq, N.; Molinie, V.; Sibony, M.; et al. Molecular subtypes of clear cell renal cell carcinoma are associated with sunitinib response in the metastatic setting. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 1329–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakimi, A.A.; Voss, M.H.; Kuo, F.; Sanchez, A.; Liu, M.; Nixon, B.G.; Vuong, L.; Ostrovnaya, I.; Chen, Y.B.; Reuter, V.; et al. Transcriptomic profiling of the tumor microenvironment reveals distinct subgroups of clear cell renal cell cancer—data from a randomized phase iii trial. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 510–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDermott, D.F.; Huseni, M.A.; Atkins, M.B.; Motzer, R.J.; Rini, B.I.; Escudier, B.; Fong, L.; Joseph, R.W.; Pal, S.K.; Reeves, J.A.; et al. Clinical activity and molecular correlates of response to atezolizumab alone or in combination with bevacizumab versus sunitinib in renal cell carcinoma. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, R.W.; Millis, S.Z.; Carballido, E.M.; Bryant, D.; Gatalica, Z.; Reddy, S.; Bryce, A.H.; Vogelzang, N.J.; Stanton, M.L.; Castle, E.P.; et al. Pd-1 and pd-l1 expression in renal cell carcinoma with sarcomatoid differentiation. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2015, 3, 1303–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamoun, A.; de Reynies, A.; Allory, Y.; Sjodahl, G.; Robertson, A.G.; Seiler, R.; Hoadley, K.A.; Groeneveld, C.S.; Al-Ahmadie, H.; Choi, W.; et al. A consensus molecular classification of muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Eur. Urol. 2019, 77, 420–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmers, Z.R.; Connelly, C.F.; Fabrizio, D.; Gay, L.; Ali, S.M.; Ennis, R.; Schrock, A.; Campbell, B.; Shlien, A.; Chmielecki, J.; et al. Analysis of 100,000 human cancer genomes reveals the landscape of tumor mutational burden. Genome Med. 2017, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Velasco, G.; Miao, D.; Voss, M.H.; Hakimi, A.A.; Hsieh, J.J.; Tannir, N.M.; Tamboli, P.; Appleman, L.J.; Rathmell, W.K.; Van Allen, E.M.; et al. Tumor mutational load and immune parameters across metastatic renal cell carcinoma risk groups. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2016, 4, 820–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, D.; Margolis, C.A.; Gao, W.; Voss, M.H.; Li, W.; Martini, D.J.; Norton, C.; Bosse, D.; Wankowicz, S.M.; Cullen, D.; et al. Genomic correlates of response to immune checkpoint therapies in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Science 2018, 359, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudley, J.C.; Lin, M.T.; Le, D.T.; Eshleman, J.R. Microsatellite instability as a biomarker for pd-1 blockade. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derosa, L.; Hellmann, M.D.; Spaziano, M.; Halpenny, D.; Fidelle, M.; Rizvi, H.; Long, N.; Plodkowski, A.J.; Arbour, K.C.; Chaft, J.E.; et al. Negative association of antibiotics on clinical activity of immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with advanced renal cell and non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1437–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becht, E.; Giraldo, N.A.; Lacroix, L.; Buttard, B.; Elarouci, N.; Petitprez, F.; Selves, J.; Laurent-Puig, P.; Sautes-Fridman, C.; Fridman, W.H.; et al. Estimating the population abundance of tissue-infiltrating immune and stromal cell populations using gene expression. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlinger, M.; Catto, J.W.; Orntoft, T.F.; Real, F.X.; Zwarthoff, E.C.; Swanton, C. Intratumour heterogeneity in urologic cancers: From molecular evidence to clinical implications. Eur. Urol. 2015, 67, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suva, M.L.; Tirosh, I. Single-cell rna sequencing in cancer: Lessons learned and emerging challenges. Mol. Cell 2019, 75, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.T.; Lee, H.W.; Lee, H.O.; Song, H.J.; Jeong da, E.; Shin, S.; Kim, H.; Shin, Y.; Nam, D.H.; Jeong, B.C.; et al. Application of single-cell rna sequencing in optimizing a combinatorial therapeutic strategy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelants, C.; Pillet, C.; Franquet, Q.; Sarrazin, C.; Peilleron, N.; Giacosa, S.; Guyon, L.; Fontanell, A.; Fiard, G.; Long, J.A.; et al. Ex-vivo treatment of tumor tissue slices as a predictive preclinical method to evaluate targeted therapies for patients with renal carcinoma. Cancers (Basel) 2020, 12, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, T.G.; Naipal, K.A.; Jager, A.; van Gent, D.C. Ex vivo tumor culture systems for functional drug testing and therapy response prediction. Future Sci. OA 2017, 3, FSO190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.D.; Jiang, X.; Sullivan, K.M.; Jalikis, F.G.; Smythe, K.S.; Abbasi, A.; Vignali, M.; Park, J.O.; Daniel, S.K.; Pollack, S.M.; et al. Mobilization of cd8( + ) t cells via cxcr4 blockade facilitates pd-1 checkpoint therapy in human pancreatic cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3934–3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, K.K.; Cattaneo, C.M.; Weeber, F.; Chalabi, M.; van de Haar, J.; Fanchi, L.F.; Slagter, M.; van der Velden, D.L.; Kaing, S.; Kelderman, S.; et al. Generation of tumor-reactive t cells by co-culture of peripheral blood lymphocytes and tumor organoids. Cell 2018, 174, 1586–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bensch, F.; van der Veen, E.L.; Lub-de Hooge, M.N.; Jorritsma-Smit, A.; Boellaard, R.; Kok, I.C.; Oosting, S.F.; Schroder, C.P.; Hiltermann, T.J.N.; van der Wekken, A.J.; et al. (89)zr-atezolizumab imaging as a non-invasive approach to assess clinical response to pd-l1 blockade in cancer. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1852–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Limkin, E.J.; Vakalopoulou, M.; Dercle, L.; Champiat, S.; Han, S.R.; Verlingue, L.; Brandao, D.; Lancia, A.; Ammari, S.; et al. A radiomics approach to assess tumour-infiltrating cd8 cells and response to anti-pd-1 or anti-pd-l1 immunotherapy: An imaging biomarker, retrospective multicohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1180–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradilone, A.; Iacovelli, R.; Cortesi, E.; Raimondi, C.; Gianni, W.; Nicolazzo, C.; Petracca, A.; Palazzo, A.; Longo, F.; Frati, L.; et al. Circulating tumor cells and “suspicious objects” evaluated through cellsearch(r) in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Anticancer. Res. 2011, 31, 4219–4221. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Magi-Galluzzi, C. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in renal neoplasms. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2014, 21, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, L.; Hou, S.; Hu, S.; Wu, J.; Jing, Y.; Sun, H.; Yu, F.; Zhao, L.; et al. Combined cell surface carbonic anhydrase 9 and cd147 antigens enable high-efficiency capture of circulating tumor cells in clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 59877–59891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoni, M.; Cimadamore, A.; Cheng, L.; Lopez-Beltran, A.; Battelli, N.; Massari, F.; Scarpelli, M.; Galosi, A.B.; Bracarda, S.; Montironi, R. Circulating tumor cells in renal cell carcinoma: Recent findings and future challenges. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study Name | Tested Drugs | Comparison | Phase | Histology | Therapy Setting | OS (HR, 95% CI, p) | Median PFS (HR, 95% CI) | ORR (%) | CR (%) | Grade 3 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Javelin Renal 101 | avelumab + axitinib | sunitinib | III | ccRCC | First line | 12-mo: 86% vs. 83% (0.78; 0.55–1.08; p = 0.14) | 13.8 vs. 7.2 mo (0.61) | 55.2 vs. 25,5 | 3.4 vs. 1.8 | 71.2 vs. 71.5 |
| Keynote 426 | pembrolizumab + axitinib | sunitinib | III | ccRCC | First line | 12-mo: 90% vs. 78% (0.53; 0.38–0.74; p < 0.0001) | 15.1 vs. 11.1 mo (0.69; 0.57–0.84) | 59.3 vs. 35.7 | 5.8 vs. 1.9 | 75.8 vs. 70.6 |
| CheckMate 214 | nivolumab + ipilimumab | sunitinib | III | ccRCC | First line | 30-mo : 60% vs, 47% (0.66; 0.54–0.80; p < 0.0001) | 11.6 vs. 8.4 mo (0.82; 0.64–1,05) | 42 vs. 29 | 9 vs. 1 | 47 vs. 64 |
| Immotion 151 | atezolizumab + bevacizumab | sunitinib | III | ccRCC | First line | 24 mo : 63% vs. 60% (0.93; 0.76–1.14; p = 0·4751) | 11.2 vs. 7.7 mo (0.74; 0.57–0.96) | 43 vs. 25 | 9 vs. 4 | 40 vs. 54 |
| NCT number | Targeting Agents | Comparison | Phase | Histology | Primary Endpoint | Therapy Setting | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT03260894 | pembrolizumab + epacadostat | sunitinib or pazopanib | III | ccRCC | ORR | First line | Active not recruiting |
| NCT02811861 | lenvatinib + everolimus or pembrolizumab | sunitinib | III | ccRCC | PFS | First line | Active not recruiting |
| NCT03141177 | nivolumab + cabozantinib | sunitinib | III | ccRCC | PFS | First line | Active not recruiting |
| NCT03793166 | nivolumab, ipilimumab, cabozantinib | nivolumab or nivolumab + cabozantinib | III | ccRCC | OS | First line | Recruiting |
| NCT03937219 | nivolumab + ipilimumab + cabozantinib | nivolumab + ipilimumab + placebo | III | ccRCC | DFS | First line | Recruiting |
| NCT03680521 | sitravatinib + nivolumab | _ | II | ccRCC | ORR | First line | Recruiting |
| NCT02960906 | nivolumab, ipilimumab, VEGFR-TKI | _ | II | ccRCC | ORR | First line | Recruiting |
| NCT03736330 | axitinib + pembrolizumab + D-CIK | _ | II | ccRCC | ORR | At least second line | Recruiting |
| NCT02819596 | savolitinib, durvalumab, tremelimumab | _ | II | ccRCC, pRCC | DLT, ORR | At least second line | Unknown |
| NCT02964078 | pembrolizumab + interleukin-2 | _ | II | ccRCC | ORR | Any | Active not recruiting |
| NCT03092856 | anti-OX40 agonist antibody + axitinib | _ | II | ccRCC | PFS | No standard anymore available | Recruiting |
| NCT02724878 | atezolizumab + bevacizumab | _ | II | nccRCC | ORR | Any | Active not recruiting |
| NCT03635892 | nivolumab + cabozantinib | _ | II | nccRCC | ORR | Any | Recruiting |
| NCT03595124 | nivolumab + axitinib | _ | II | tRCC | PFS | Any | Recruiting |
| NCT02493751 | avelumab + axitinib | _ | I/II | ccRCC | DLT | First line | Published |
| NCT02899078 | ibrutinib + nivolumab | _ | I/II | ccRCC, nccRCC | PFS | At least second line | Recruiting |
| NCT02348008 | pembrolizumab + bevacizumab | _ | I/II | ccRCC | Safety, efficacy | At least second line | Active not recruiting |
| NCT03172754 | nivolumab + axitinib | _ | I/II | ccRCC | Safety | At least second line | Recruiting |
| NCT03024437 | atezolizumab + entinostat + bevacizumab | atezolizumab + entinostat | I/II | ccRCC | Safety, ORR | At least second line | Recruiting |
| NCT02501096 | pembrolizumab + lenvatinib | _ | I/II | ccRCC | DLT, ORR | No standard anymore available | Active not recruiting |
| NCT01472081 | nivolumab + sunitinib or pazopanib | nivolumab | I | ccRCC | Safety | At least second line | Published |
| NCT03307785 | TSR-022 (anti-TIM3)/niraparib/TSR-042 (anti-PD1)/chemotherapy/bevacizumab | _ | I | RCC and others | Safety | At least second line | Active not recruiting |
| NCT03200587 | avelumab + cabozantinib | _ | Ib | ccRCC | Safety | Any | Recruiting |
| NCT Number | Targeting Agents | Comparison | Phase | Histology | Primary Endpoint | Therapy Setting | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT03729245 | NKTR-214 (IL2R agonist) + nivolumab | sunitinib or cabozantinib | III | ccRCC | ORR, OS | First line | Recruiting |
| NCT03873402 | nivolumab + ipilimumab | nivolumab | III | ccRCC | PFS, ORR | First line | Recruiting |
| NCT01668784 | nivolumab | everolimus | III | ccRCC | OS | At least second line | Published |
| NCT03055013 | nivolumab | observation | III | ccRCC | DFS | Peri-operative | Recruiting |
| NCT03024996 | atezolizumab | placebo | III | ccRCC | DFS | Adjuvant | Active not recruiting |
| NCT03138512 | nivolumab + ipilimumab | placebo | III | ccRCC | DFS | Adjuvant | Recruiting |
| NCT03142334 | pembrolizumab | placebo | III | ccRCC | DFS | Adjuvant | Active not recruiting |
| NCT03288532 | nivolumab, tremelimumab | _ | III | ccRCC | DFS | Adjuvant | Recruiting |
| NCT02996110 | BMS-986205 (IDO1 oral inhibitor) +/− nivolumab +/− ipilimumab | nivolumab +/− ipilimumab | II | ccRCC, nccRCC | ORR, PFS | First line | Recruiting |
| NCT03552380 | nivolumab + ipilimumab + entinostat | _ | II | ccRCC | Safety | At least second line | Recruiting |
| NCT03501381 | entinostat + IL2 | IL2 | II | ccRCC | PFS | At least second line | Recruiting |
| NCT03469713 | nivolumab + SBRT | _ | II | ccRCC | ORR | At least second line | Recruiting |
| NCT03177239 | nivolumab + ipilimumab | _ | II | nccRCC | ORR | Any | Active, not recruiting |
| NCT04262375 | oleclumab (anti-CD73 antagonist mAb) + durvalumab | _ | II | RCC and others | ORR, PFS | Any | Not yet recruiting |
| NCT03207867 | NIR178 (A2aR antagonist) + spartalizumab (anti-PD1) | _ | II | RCC and others | ORR | At least second line | Recruiting |
| NCT03693612 | GSK3359609 (anti-ICOS) + tremelimumab | chemotherapies | II | RCC and others | DLT | No standard anymore available | Recruiting |
| NCT03693612 | anti-ICOS + tremelimumab | _ | II | RCC and others | Safety, DLT | No standard anymore available | Recruiting |
| NCT01038778 | entinostat + aldesleukin | _ | I/II | ccRCC | Dose, ORR | At least second line | Active, not recruiting |
| NCT03308396 | durvalumab + guadecitabine | _ | I/II | ccRCC | Safe dose/ORR | At least second line | Recruiting |
| NCT02989714 | nivolumab + interleukin-2 | - | I/II | ccRCC | Safety | Third line | Active not recruiting |
| NCT02460224 | LAG525 (anti-LAG3) + spartalizumab (anti-PD1) | _ | I/II | RCC and others | DLT, ORR | At least second line | Active, not recruiting |
| NCT03652077 | anti-TIM3 | _ | I/II | RCC and others | Safety | No standard anymore available | Recruiting |
| NCT02608268 | MBG453 (anti-TIM3) + spartalizumab (anti-PD1) | spartalizumab anti-PD1 | I/II | RCC and others | Safety, ORR, DLT | No standard anymore available | Recruiting |
| NCT01968109 | relatlimab (anti-LAG3) + nivolumab | relatlimab | I/II | RCC and others | Safety, ORR, DLT | No standard anymore available | Recruiting |
| NCT03126110 | INCAGN01876 (anti-GITR) + nivolumab + ipilimumab | _ | I/II | RCC and others | Safety, tolerability | No standard anymore available | Recruiting |
| NCT02335918 | varlilumab (anti-CD27) + nivolumab | _ | I/II | RCC and others | DLT, ORR | At least second line | Completed |
| NCT02718066 | HBI-8000 (HDACi) + nivolumab | _ | I/II | RCC and others | RP2D | At least second line | Recruiting |
| NCT02890069 | spartalizumab + LCL16 (IAP inhibitor) + everolimus + panobinostat | _ | I/II | RCC and others | DLT | At least second line | Recruiting |
| NCT02771626 | CB-839 (glutaminase inhibitor) + nivolumab | _ | I/II | RCC and others | Safety, efficacy | At least second line | Recruiting |
| NCT02817633 | TSR-022 (anti-TIM3)/TSR-042 (anti-PD1)/TSR-033 (anti-LAG3) | _ | I | RCC and others | Safety, tolerability | No standard anymore available | Recruiting |
| NCT03119428 | OMP-31M32 (anti-TIGIT) + nivolumab | _ | I | RCC and others | DLT | No standard anymore available | Terminated |
| NCT00351949 | IMP321 (anti-LAG3) | _ | I | RCC and others | Safety, tolerability | No standard anymore available | Completed |
| NCT02386111 | varlilumab (anti-CD27) | _ | I | RCC and others | Safety, tolerability | At least second line | Terminated |
| NCT03343613 | LY3300054 (IDO1 inhibitor) + PD-L1 inhibitor | _ | I | RCC and others | DLT | No standard anymore available | Recruiting |
| NCT02812875 | CA-170 (VISTA antagonist) | _ | I | RCC and others | DLT | No standard anymore available | Active not recruiting |
| NCT02655822 | ciforadenant (A2aR antagonist) +/- atezolizumab | _ | I | RCC and others | DLT | At least second line | Recruiting |
| NCT04198766 | anti-OX40 + pembrolizumab | _ | I | RCC and others | Safety | No standard anymore available | Recruiting |
| NCT Number | Targeting Agents | Comparison | Phase | Histology | Primary Endpoint | Therapy Setting | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT00458536 | dendritic cell tumor fusion vaccine + GM-CSF | _ | I/II | ccRCC, nccRCC | Safety | Any | Active not recruiting |
| NCT03633110 | GEN-009 Adjuvanted Vaccine + nivolumab + pembrolizumab | _ | I/II | RCC and others | Safety | At least second line | Recruiting |
| NCT00722228 | Autologous or Allogeneic tumor cells | _ | I/II | RCC and others | Safety, efficacy | At least second line | Recruiting |
| NCT03393936 | anti-ROR2 CAR-T or anti AXL CART-T | _ | I/II | ccRCC, nccRCC | Safety | No standard available | Recruiting |
| NCT02830724 | anti-CD70 CAR-T | _ | I/II | RCC and others | Safety | At least second line | Recruiting |
| NCT01218867 | anti-VEGFR2 CAR-T | _ | I/II | RCC and others | ORR | At least second line | Terminated |
| NCT03638206 | anti-C-MET CAR-T | _ | I/II | RCC and others | Safety | At least second line | Recruiting |
| NCT02950766 | neovax vaccine + ipilimumab | _ | I | ccRCC | DLT | At least second line | Recruiting |
| NCT00096629 | PSMA DNA vaccine | _ | I | ccRCC, nccRCC | Safety | Adjuvant | Completed |
| NCT03548467 | VB10.NEO vaccine +/- bempegaldesleukin (NKTR-214) | _ | I | RCC and others | Safety | At least second line | Recruiting |
| NCT03294083 | pexastimogene devacirepvec (Pexa-Vec) | _ | I | ccRCC, nccRCC | Safety, efficacy | At least second line | Recruiting |
| NCT03715985 | EVAX-01-CAF09b (peptide-based vaccine) +/- anti-PD1 or anti-PD-L1 | _ | I | RCC and others | Safety, efficacy | First line | Recruiting |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deleuze, A.; Saout, J.; Dugay, F.; Peyronnet, B.; Mathieu, R.; Verhoest, G.; Bensalah, K.; Crouzet, L.; Laguerre, B.; Belaud-Rotureau, M.-A.; et al. Immunotherapy in Renal Cell Carcinoma: The Future Is Now. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2532. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21072532
Deleuze A, Saout J, Dugay F, Peyronnet B, Mathieu R, Verhoest G, Bensalah K, Crouzet L, Laguerre B, Belaud-Rotureau M-A, et al. Immunotherapy in Renal Cell Carcinoma: The Future Is Now. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(7):2532. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21072532
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeleuze, Antoine, Judikaël Saout, Frédéric Dugay, Benoit Peyronnet, Romain Mathieu, Gregory Verhoest, Karim Bensalah, Laurence Crouzet, Brigitte Laguerre, Marc-Antoine Belaud-Rotureau, and et al. 2020. "Immunotherapy in Renal Cell Carcinoma: The Future Is Now" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 7: 2532. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21072532
APA StyleDeleuze, A., Saout, J., Dugay, F., Peyronnet, B., Mathieu, R., Verhoest, G., Bensalah, K., Crouzet, L., Laguerre, B., Belaud-Rotureau, M.-A., Rioux-Leclercq, N., & Kammerer-Jacquet, S.-F. (2020). Immunotherapy in Renal Cell Carcinoma: The Future Is Now. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(7), 2532. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21072532





