Sorafenib Treatment and Modulation of the Sphingolipid Pathway Affect Proliferation and Viability of Hepatocellular Carcinoma In Vitro
Abstract
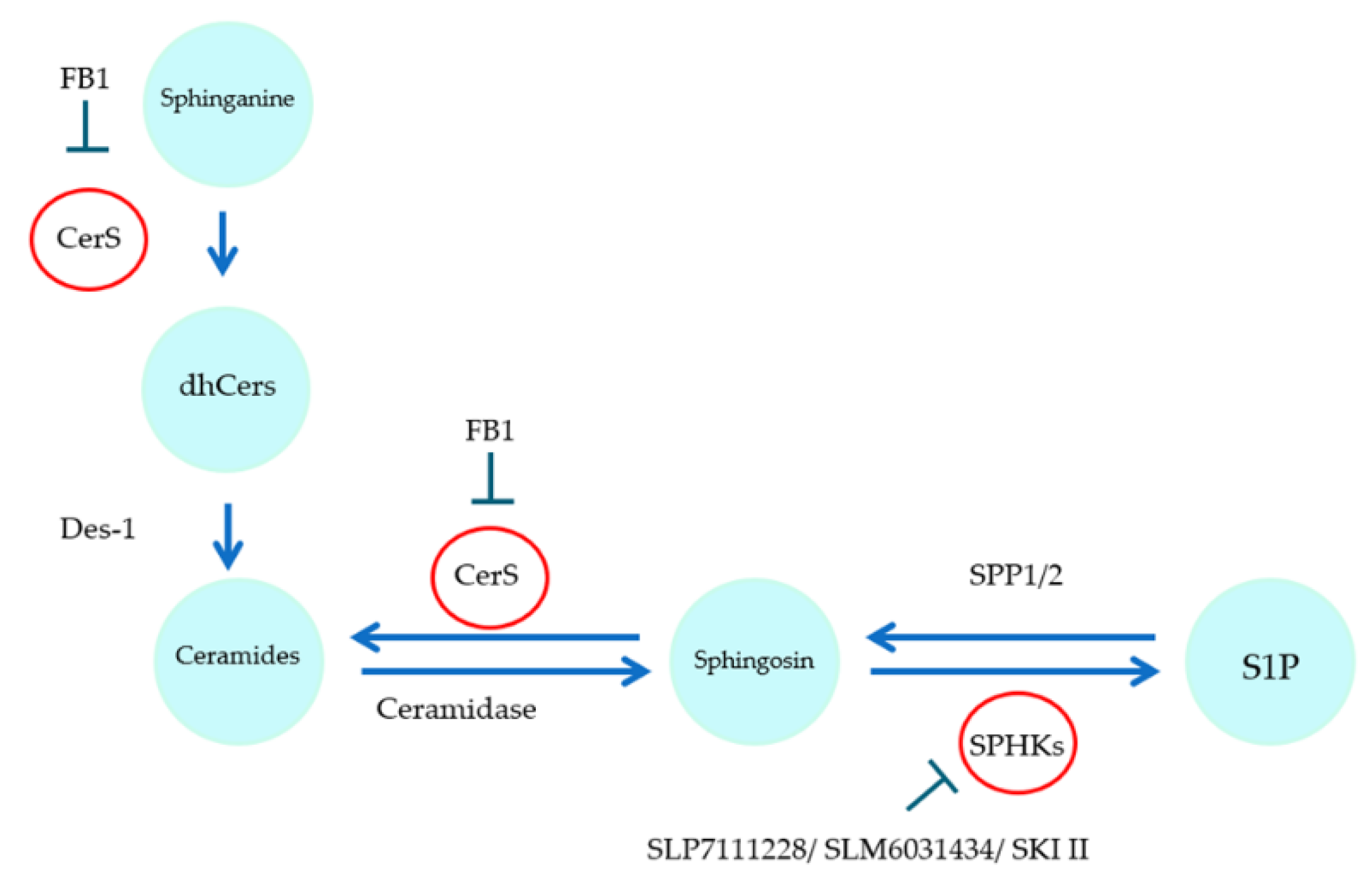
1. Introduction
2. Results
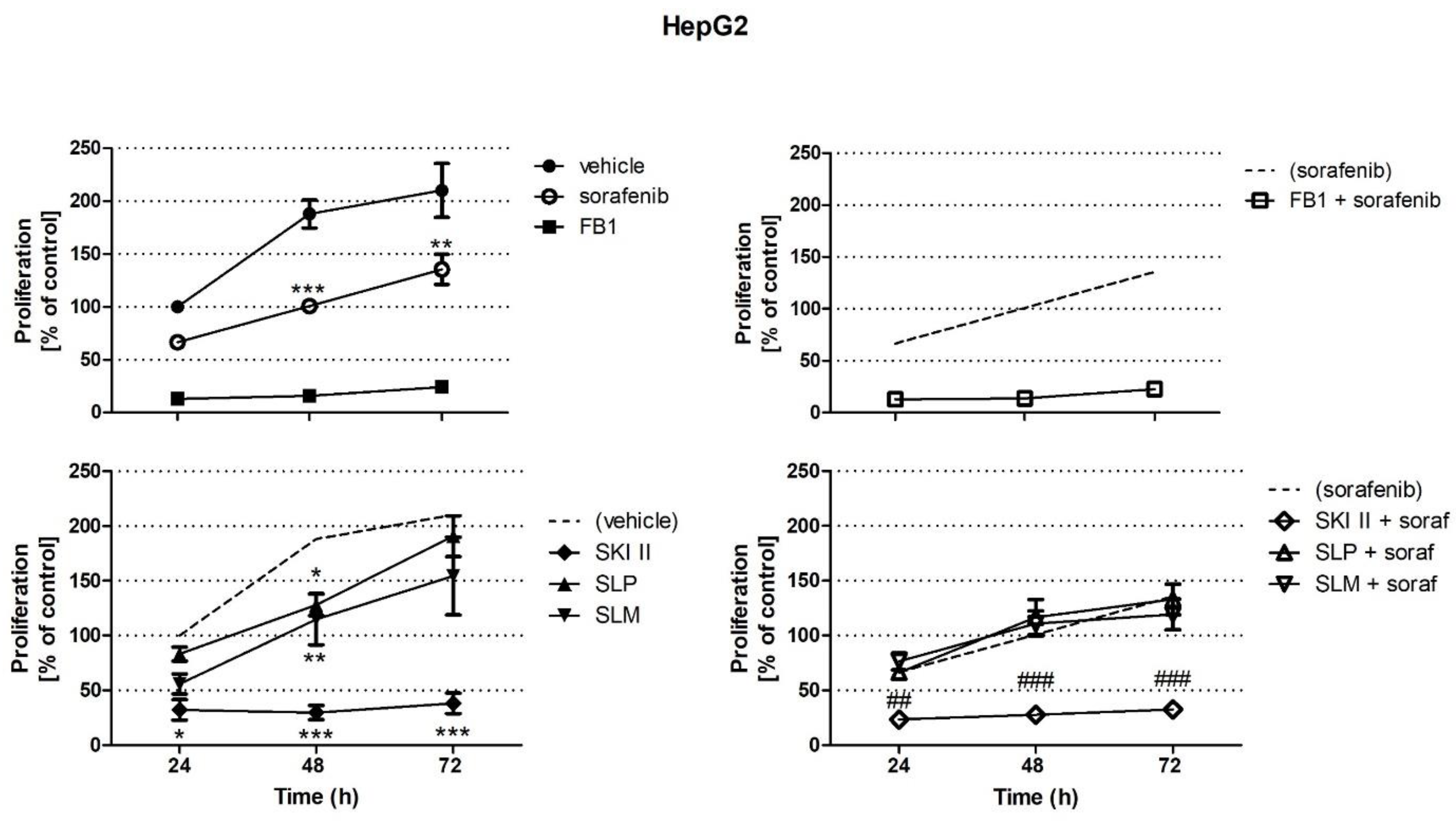
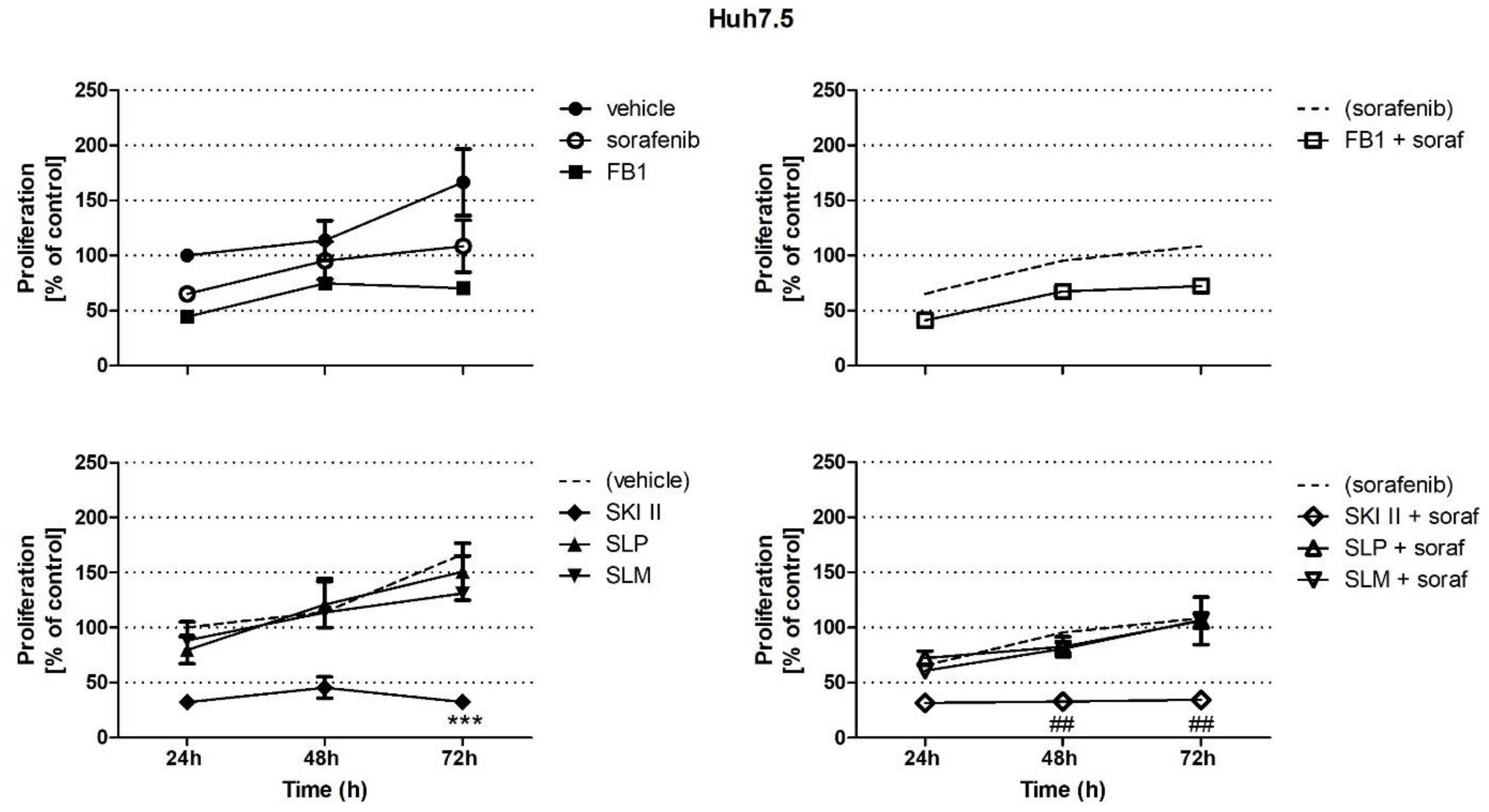
2.1. Effects of Sorafenib, FB1, and SPHK Inhibitors on Cell Proliferation
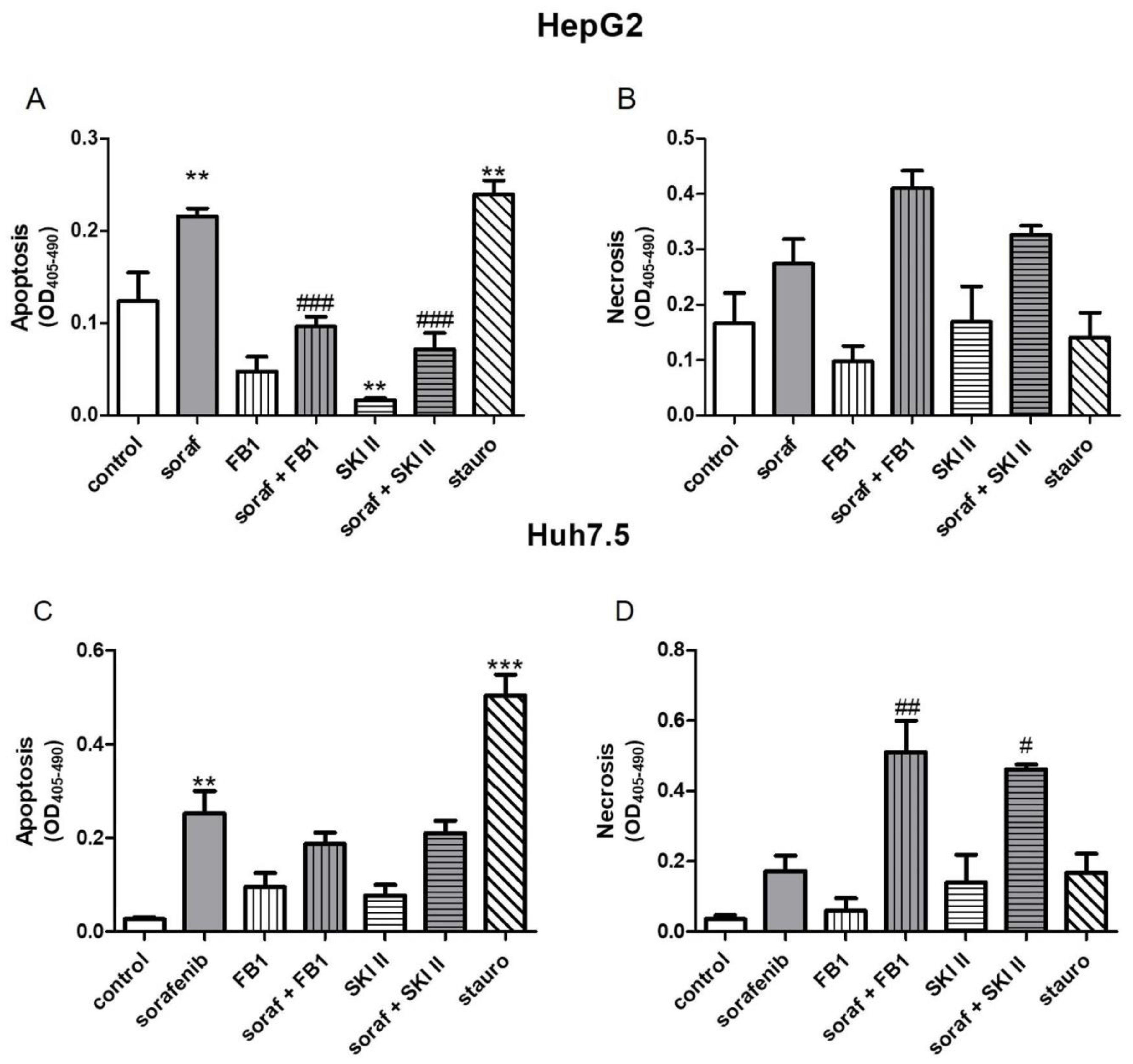
2.2. Influence of Sorafenib, FB1, and SKI II on Apoptosis and Necrosis
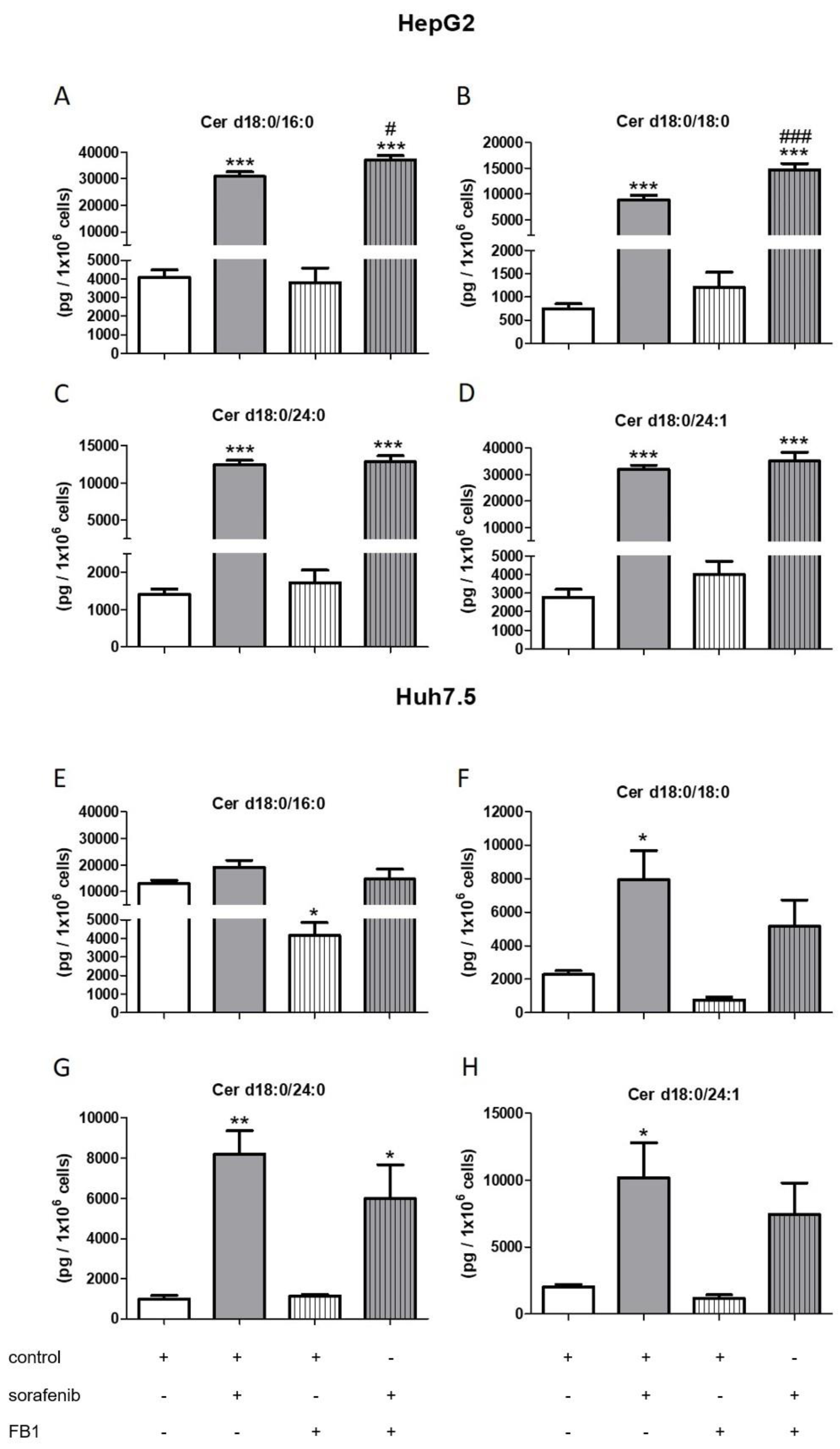
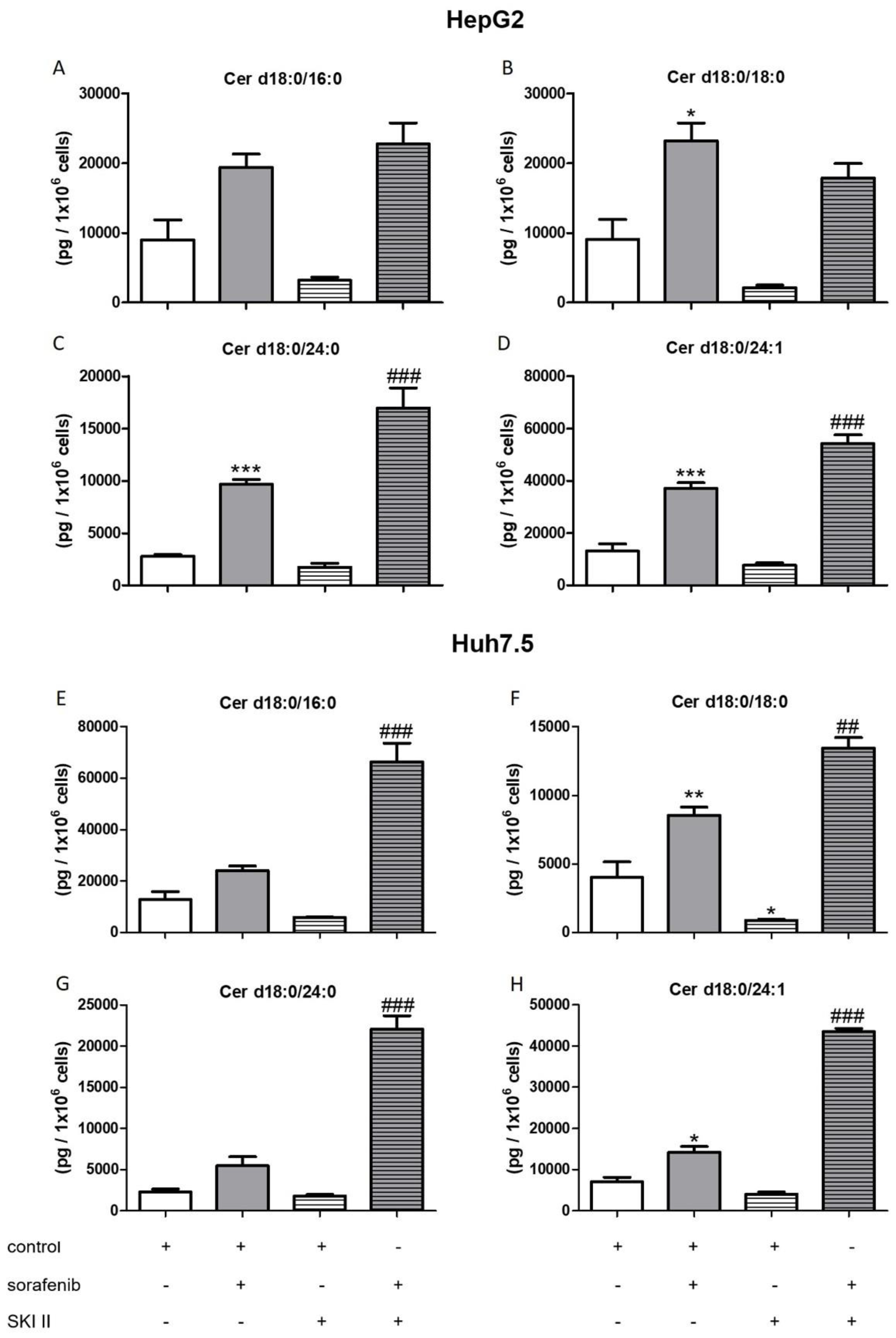
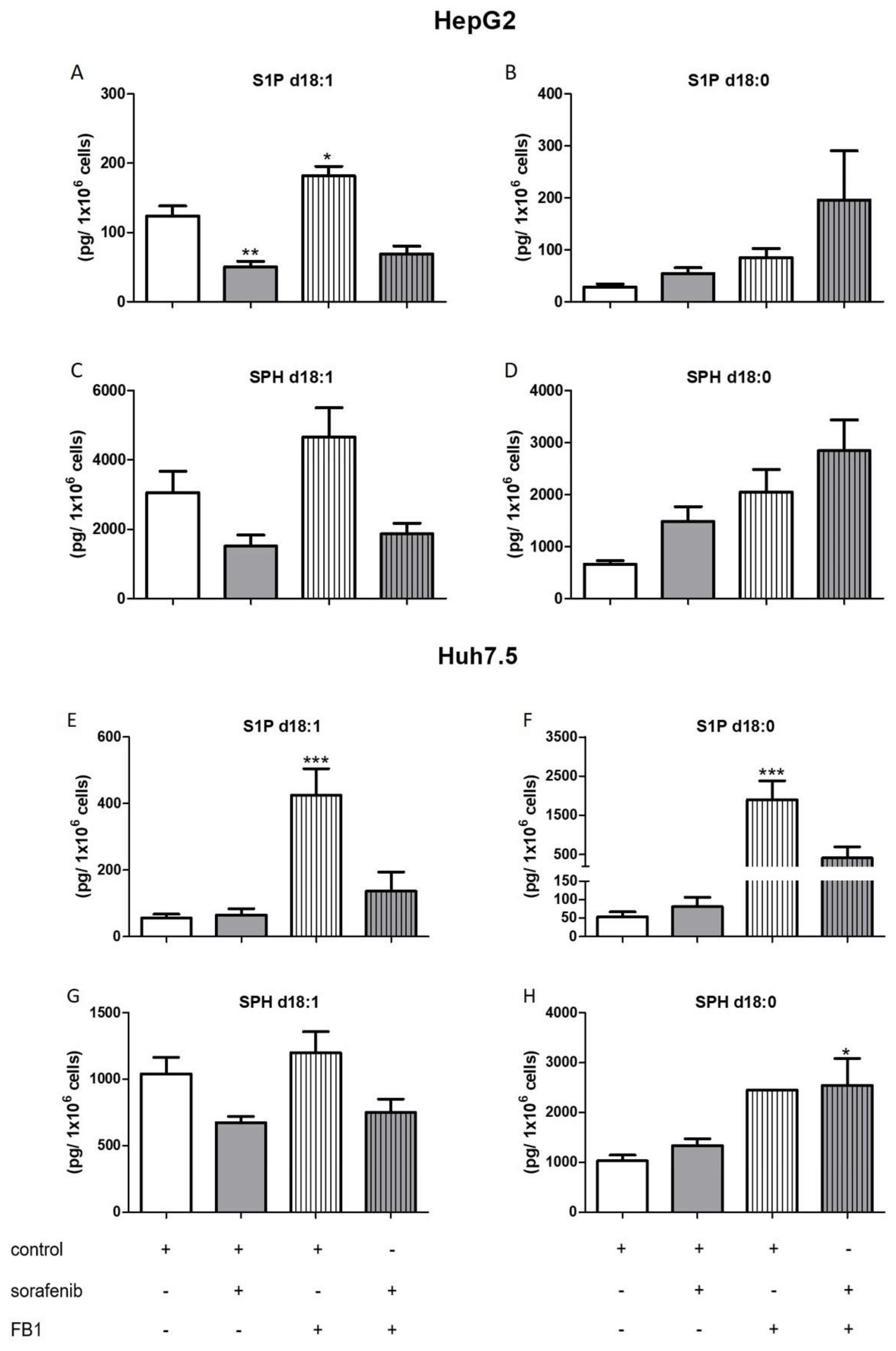
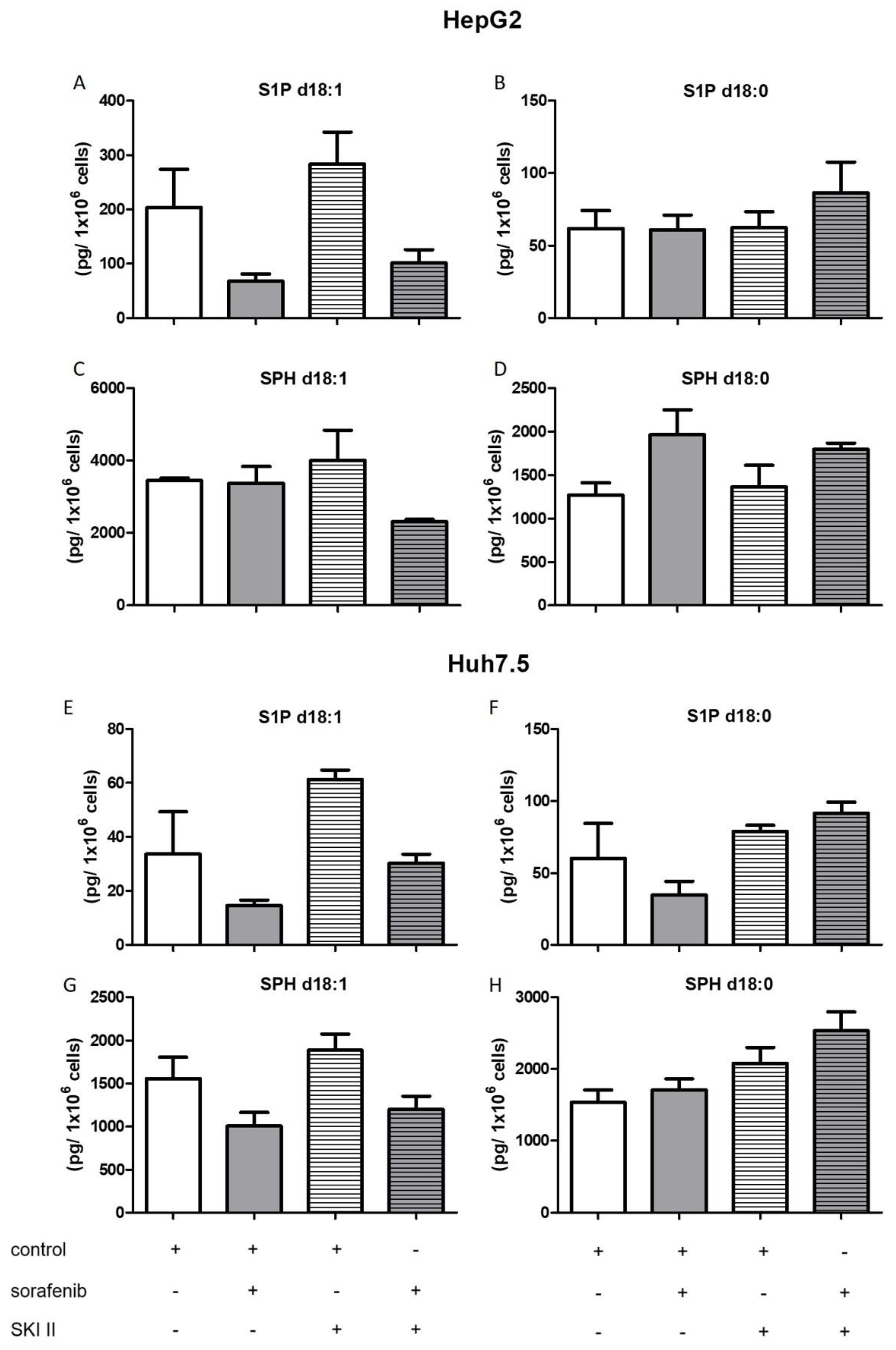
2.3. Influence of Sorafenib, FB1, and SKI II on Levels of Bioactive Sphingolipids
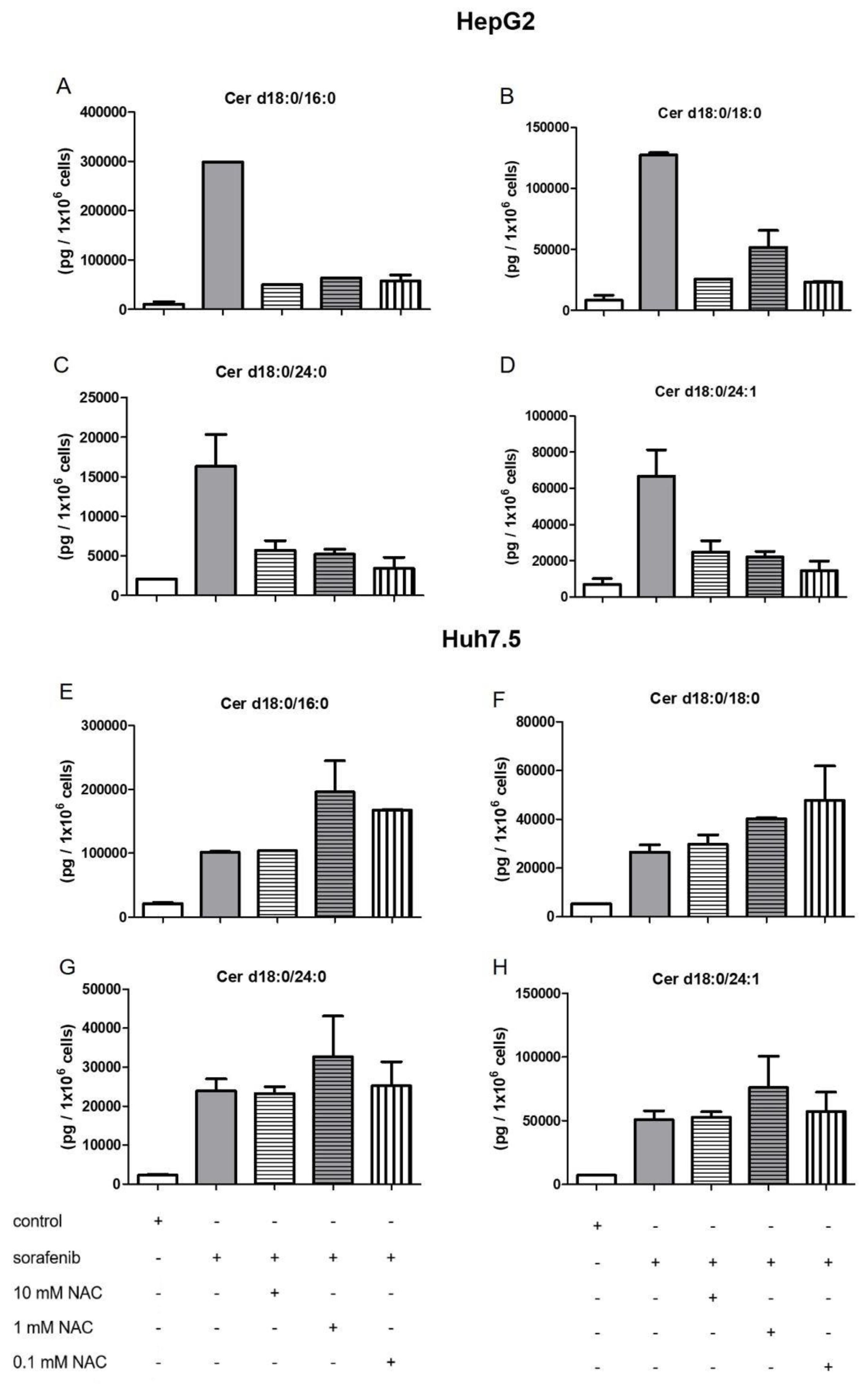
2.4. Influence of NAC on the Formation of Dihydroceramides
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Proliferation Assay
4.4. DNA Fragmentation ELISA
4.5. Cell Viability
4.6. Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DMSO | dimethylsulfoxid |
| FB1 | fumonisin B1 |
| HCC | hepatocellular carcinoma |
| LC-MS/MS | liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry |
| NAC | N-acetyl-cysteine |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| SPHK1 | sphingosine kinase 1 |
| SPHK2 | sphingosine kinase 2 |
| SPHKs | sphingosine kinases |
| SLP | SLP7111228 |
| SLM | SLM6031434 |
| S1P | sphingosine 1-phosphate |
| TCA | trichloroacetic acid |
References
- Torre, L.A.; Bray, F.; Siegel, R.L.; Ferlay, J.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forner, A.; Da Fonseca, L.G.; Díaz-González, Á.; Sanduzzi-Zamparelli, M.; Reig, M.; Bruix, J. Controversies in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma. JHEP Rep. 2019, 1, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Ricci, S.; Mazzaferro, V.; Hilgard, P.; Gane, E.; Blanc, J.F.; De Oliveira, A.C.; Santoro, A.; Raoul, J.L.; Forner, A.; et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, J.; Lima, S.; Maceyka, M.; Spiegel, S. Revisiting the sphingolipid rheostat: Evolving concepts in cancer therapy. Exp. Cell Res. 2015, 333, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogretmen, B. Sphingolipid metabolism in cancer signalling and therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruangsiriluk, W.; Grosskurth, S.E.; Ziemek, D.; Kuhn, M.; des Etages, S.G.; Francone, O.L. Silencing of enzymes involved in ceramide biosynthesis causes distinct global alterations of lipid homeostasis and gene expression. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 1459–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marí, M.; Fernández-Checa, J.C. Sphingolipid signalling and liver diseases. Liver Int. 2007, 27, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friemel, J.; Rechsteiner, M.; Frick, L.; Böhm, F.; Struckmann, K.; Egger, M.; Moch, H.; Heikenwalder, M.; Weber, A. Intratumor heterogeneity in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 1951–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Liu, D.; Kimchi, E.T.; Kaifi, J.T.; Qi, X.; Manjunath, Y.; Liu, X.; Deering, T.; Avella, D.M.; Fox, T.; et al. Nanoliposome C6-Ceramide Increases the Anti-tumor Immune Response and Slows Growth of Liver Tumors in Mice. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 1024–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkal, C.E.; Ponnusamy, S.; Bielawski, J.; Hannun, Y.A.; Ogretmen, B. Antiapoptotic roles of ceramide-synthase-6-generated C16-ceramide via selective regulation of the ATF6/CHOP arm of ER-stress-response pathways. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.H.; Chen, M.B.; Liu, Y.Y.; Wu, M.H.; Li, W.T.; Wei, M.X.; Liu, C.Y.; Qin, S.K. Identification of sphingosine kinase 1 (SphK1) as a primary target of icaritin in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 22800–22810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pewzner-Jung, Y.; Brenner, O.; Braun, S.; Laviad, E.L.; Ben-Dor, S.; Feldmesser, E.; Horn-Saban, S.; Amann-Zalcenstein, D.; Raanan, C.; Berkutzki, T.; et al. A critical role for ceramide synthase 2 in liver homeostasis: II. Insights into molecular changes leading to hepatopathy. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 10911–10923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- French, K.J.; Upson, J.J.; Keller, S.N.; Zhuang, Y.; Yun, J.K.; Smith, C.D. Antitumor activity of sphingosine kinase inhibitors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 318, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, C.X.; Ma, Y.; He, H.W.; Wang, J.P.; Shao, R.G. SphK1 inhibitor SKI II inhibits the proliferation of human hepatoma HepG2 cells via the Wnt5A/β-catenin signaling pathway. Life Sci. 2016, 151, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beljanski, V.; Lewis, C.S.; Smith, C.D. Antitumor activity of sphingosine kinase 2 inhibitor ABC294640 and sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma xenografts. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2011, 11, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grbčić, P.; Tomljanović, I.; Klobučar, M.; Pavelić, S.K.; Lučin, K.; Sedić, M. Dual sphingosine kinase inhibitor SKI-II enhances sensitivity to 5-fluorouracil in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via suppression of osteopontin and FAK/IGF-1R signalling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 487, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savić, R.; He, X.; Fiel, I.; Schuchman, E.H. Recombinant human acid sphingomyelinase as an adjuvant to sorafenib treatment of experimental liver cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Xiao, Y.; Han, L.; Zhang, B.; Wang, T.; Su, Z.; Zhang, N. Ceramide-Fabricated Co-Loaded Liposomes for the Synergistic Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 2133–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.A.; Mitchell, C.; Zhang, G.; Yacoub, A.; Allegood, J.; Häussinger, D.; Reinehr, R.; Larner, A.; Spiegel, S.; Fisher, P.B.; et al. Vorinostat and sorafenib increase CD95 activation in gastrointestinal tumor cells through a Ca2+-de novo ceramide-PP2A-reactive oxygen species-dependent signaling pathway. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 6313–6324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.A.; Zhang, G.; Martin, A.P.; Hamed, H.; Mitchell, C.; Hylemon, P.B.; Graf, M.; Rahmani, M.; Ryan, K.; Liu, X.; et al. Vorinostat and sorafenib increase ER stress, autophagy and apoptosis via ceramide-dependent CD95 and PERK activation. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2008, 7, 1648–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanovic, M.; Tutusaus, A.; Martinez-Nieto, G.A.; Bárcena, C.; de Gregorio, E.; Moutinho, C.; Barbero-Camps, E.; Villanueva, A.; Colell, A.; Marí, M.; et al. Targeting glucosylceramide synthase upregulation reverts sorafenib resistance in experimental hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 8253–8267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arumugam, T.; Pillay, Y.; Ghazi, T.; Nagiah, S.; Abdul, N.S.; Chuturgoon, A.A. Fumonisin B1-induced oxidative stress triggers Nrf2-mediated antioxidant response in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) cells. Mycotoxin Res. 2019, 35, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, K.S.; Tang, L.; Cai, Q.; Shen, Y.; Su, J.; Wang, J.S. Mitigation of Fumonisin Biomarkers by Green Tea Polyphenols in a High-Risk Population of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grammatikos, G.; Mühle, C.; Ferreiros, N.; Schroeter, S.; Bogdanou, D.; Schwalm, S.; Hintereder, G.; Kornhuber, J.; Zeuzem, S.; Sarrazin, C.; et al. Serum acid sphingomyelinase is upregulated in chronic hepatitis C infection and non alcoholic fatty liver disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1841, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grammatikos, G.; Schoell, N.; Ferreirós, N.; Bon, D.; Herrmann, E.; Farnik, H.; Köberle, V.; Piiper, A.; Zeuzem, S.; Kronenberger, B.; et al. Serum sphingolipidomic analyses reveal an upregulation of C16-ceramide and sphingosine-1-phosphate in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 18095–18105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mücke, V.T.; Gerharz, J.; Jakobi, K.; Thomas, D.; Ferreirós Bouzas, N.; Mücke, M.M.; Trötschler, S.; Weiler, N.; Welker, M.W.; Zeuzem, S.; et al. Low Serum Levels of (Dihydro-)Ceramides Reflect Liver Graft Dysfunction in a Real-World Cohort of Patients Post Liver Transplantation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Ikeda, M.; Kojima, Y.; Hosoi, H.; Saito, Y.; Kondo, S. Lipid profiling of pre-treatment plasma reveals biomarker candidates associated with response rates and hand-foot skin reactions in sorafenib-treated patients. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2018, 82, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojima, H.; Freeman, C.M.; Gulbins, E.; Lentsch, A.B. Sphingolipids in liver injury, repair and regeneration. Biol. Chem. 2015, 396, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maceyka, M.; Rohrbach, T.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. Role of Sphingosine Kinase 1 and Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Axis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2019, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, M.; Chen, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zha, R.; Huang, S.; Liu, L.; Chen, T.; Li, J.; Tu, H.; et al. Sphingosine kinase 1 promotes tumour cell migration and invasion via the S1P/EDG1 axis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 2012, 32, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ma, Y.; He, H.W.; Zhao, W.L.; Shao, R.G. SPHK1 (sphingosine kinase 1) induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition by promoting the autophagy-linked lysosomal degradationn of CDH1/E-cadherin in hepatoma cells. Autophagy 2017, 13, 900–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Chaiteerakij, R.; Moser, C.D.; Shaleh, H.; Boakye, J.; Chen, G.; Ndzengue, A.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, S.; et al. Antitumor effect of the novel sphingosine kinase 2 inhibitor ABC294640 is enhanced by inhibition of autophagy and by sorafenib in human cholangiocarcinoma cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 20080–20092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beljanski, V.; Knaak, C.; Zhuang, Y.; Smith, C.D. Combined anticancer effects of sphingosine kinase inhibitors and sorafenib. Investig. New Drugs 2011, 29, 1132–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Cao, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhang, X.; McNabola, A.; Wilkie, D.; Wilhelm, S.; Lynch, M.; Carter, C. Sorafenib blocks the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway, inhibits tumor angiogenesis, and induces tumor cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma model PLC/PRF/5. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 11851–11858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Wang, R.; Chen, C.; Ma, W.; Cai, H. Cytokine augments the sorafenib-induced apoptosis in Huh7 liver cancer cell by inducing mitochondrial fragmentation and activating MAPK-JNK signalling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 110, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garten, A.; Grohmann, T.; Kluckova, K.; Lavery, G.G.; Kiess, W.; Penke, M. Sorafenib-Induced Apoptosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Is Reversed by SIRT1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seefelder, W. Induction of apoptosis in cultured human proximal tubule cells by fumonisins and fumonisin metabolites. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2003, 192, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.B.; Phulukdaree, A.; Chuturgoon, A.A. Concentration-dependent effect of fumonisin B1 on apoptosis in oesophageal cancer cells. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2018, 37, 762–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Jia, B.; Yang, Y.; Liu, N.; Wu, A. Involvement of PERK-CHOP pathway in fumonisin B1-induced cytotoxicity in human gastric epithelial cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 136, 111080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Weng, W.; Sun, Z.X.; Fu, X.J.; Ma, J.; Zhuang, W.F. SphK1 inhibitor II (SKI-II) inhibits acute myelogenous leukemia cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 460, 903–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBlanc, F.R.; Liu, X.; Hengst, J.; Fox, T.; Calvert, V.; Petricoin, E.F., III; Yun, J.; Feith, D.J.; Loughran, T.P., Jr. Sphingosine kinase inhibitors decrease viability and induce cell death in natural killer-large granular lymphocyte leukemia. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2015, 16, 1830–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Yoon, G.; Ryu, J.Y.; Cho, Y.J.; Choi, J.J.; Lee, Y.Y.; Kim, T.J.; Choi, C.H.; Song, S.Y.; Kim, B.G.; et al. Sphingosine kinase 1 is a reliable prognostic factor and a novel therapeutic target for uterine cervical cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 26746–26756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciacci-Zanella, J.R.; Merrill, A.H., Jr.; Wang, E.; Jones, C. Characterization of Cell-cycle Arrest by Fumonisin B1 in CV-1 Cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1998, 36, 791–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondy, G.S.; Barker, M.G.; Lombaert, G.A.; Armstrong, C.L.; Fernie, S.M.; Gurofsky, S.; Huzel, V.; Savard, M.E.; Curran, I.H. A comparison of clinical, histopathological and cell-cycle markers in rats receiving the fungal toxins fumonisin B1 or fumonisin B2 by intraperitoneal injection. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2000, 38, 873–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobio, T.A.; Anane, R.; Baudrimont, I.; Carratú, M.R.; Shier, T.W.; Dano, S.D.; Ueno, Y.; Creppy, E.E. Epigenetic properties of fumonisin B1: Cell cycle arrest and DNA base modification in C6 glioma cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2000, 164, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mary, V.S.; Arias, S.L.; Otaiza, S.N.; Velez, P.A.; Rubinstein, H.R.; Theumer, M.G. The aflatoxin B1 -fumonisin B1 toxicity in BRL-3A hepatocytes is associated to induction of cytochrome P450 activity and arachidonic acid metabolism. Environ. Toxicol. 2017, 32, 1711–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.H.; Wu, J.X.; Zheng, J.N.; Pei, D.S. A sphingosine kinase-1 inhibitor, SKI-II, induces growth inhibition and apoptosis in human gastric cancer cells. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 10381–10385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Peterson, Y.K.; Smith, R.A.; Smith, C.D. Characterization of isoenzyme-selective inhibitors of human sphingosine kinases. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, B.; Wong, N.; Lo, A.W.; To, K.F.; Chan, A.W.; Ng, M.H.; Ho, C.Y.; Cheng, S.H.; Lai, P.B.; et al. Sirtuin 1 is upregulated in a subset of hepatocellular carcinomas where it is essential for telomere maintenance and tumor cell growth. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 4138–4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.N.; Bae, J.S.; Jamiyandorj, U.; Noh, S.J.; Park, H.S.; Jang, K.Y.; Chung, M.J.; Kang, M.J.; Lee, D.G.; Moon, W.S. Expression and role of SIRT1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 26, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Hao, K.; Qin, C.; Xie, K.; Xie, X.; Yang, Y. Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor promotes the growth and chemoresistance of pancreatic cancer. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2013, 58, 2705–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Dong, L.; Lu, B.; Wu, G.; Xu, D.; Chen, J.; Li, K.; Tong, X.; Dai, J.; Yao, S.; et al. Down-regulation of osteopontin suppresses growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma via induction of apoptosis. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 956–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.; Li, Y.; Cao, J.; Fan, S.; Wen, J.; Zhu, G.; Du, H.; Liang, Y. Overexpression of osteopontin in hepatocellular carcinoma and its relationships with metastasis, invasion of tumor cells. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 38, 5205–5210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plastaras, J.P.; Kim, S.H.; Liu, Y.Y.; Dicker, D.T.; Dorsey, J.F.; McDonough, J.; Cerniglia, G.; Rajendran, R.R.; Gupta, A.; Rustgi, A.K.; et al. Cell cycle dependent and schedule-dependent antitumor effects of sorafenib combined with radiation. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 9443–9454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idkowiak-Baldys, J.; Apraiz, A.; Li, L.; Rahmaniyan, M.; Clarke, C.J.; Kraveka, J.M.; Asumendi, A.; Hannun, Y.A. Dihydroceramide desaturase activity is modulated by oxidative stress. Biochem. J. 2010, 427, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Ma, Y.; Lei, H.; Su, J. Fumonisin B1 Induces Oxidative Stress and Breaks Barrier Functions in Pig Iliac Endothelium Cells. Toxins 2019, 11, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Singh, M.P.; Sharma, C.; Kang, S.C. Fumonisin B1 actuates oxidative stress-associated colonic damage via apoptosis and autophagy activation in murine model. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2018, 32, e22161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, R.; Li, R.; Guo, H.; Guo, L.; Su, Z.; Ni, X.; Qi, L.; Zhang, T.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Variable Intra-Tumor Genomic Heterogeneity of Multiple Lesions in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.X.; He, M.H.; Dai, Z.H.; Yu, J.; Wang, J.G.; Li, X.C.; Jiang, B.B.; Ke, Z.F.; Su, T.H.; Peng, Z.W.; et al. Genomic and transcriptional heterogeneity of multifocal hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 990–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurke, R.; Etyemez, S.; Prvulovic, D.; Thomas, D.; Fleck, S.C.; Reif, A.; Geisslinger, G.; Lötsch, J. A Data Science-Based Analysis Points at Distinct Patterns of Lipid Mediator Plasma Concentrations in Patients with Dementia. Front. Psychiatr. 2019, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jakobi, K.; Beyer, S.; Koch, A.; Thomas, D.; Schwalm, S.; Zeuzem, S.; Pfeilschifter, J.; Grammatikos, G. Sorafenib Treatment and Modulation of the Sphingolipid Pathway Affect Proliferation and Viability of Hepatocellular Carcinoma In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2409. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21072409
Jakobi K, Beyer S, Koch A, Thomas D, Schwalm S, Zeuzem S, Pfeilschifter J, Grammatikos G. Sorafenib Treatment and Modulation of the Sphingolipid Pathway Affect Proliferation and Viability of Hepatocellular Carcinoma In Vitro. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(7):2409. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21072409
Chicago/Turabian StyleJakobi, Katja, Sandra Beyer, Alexander Koch, Dominique Thomas, Stephanie Schwalm, Stefan Zeuzem, Josef Pfeilschifter, and Georgios Grammatikos. 2020. "Sorafenib Treatment and Modulation of the Sphingolipid Pathway Affect Proliferation and Viability of Hepatocellular Carcinoma In Vitro" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 7: 2409. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21072409
APA StyleJakobi, K., Beyer, S., Koch, A., Thomas, D., Schwalm, S., Zeuzem, S., Pfeilschifter, J., & Grammatikos, G. (2020). Sorafenib Treatment and Modulation of the Sphingolipid Pathway Affect Proliferation and Viability of Hepatocellular Carcinoma In Vitro. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(7), 2409. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21072409




