Using Probiotics as Supplementation for Helicobacter pylori Antibiotic Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. H. pylori Infection and Antibiotic Therapy
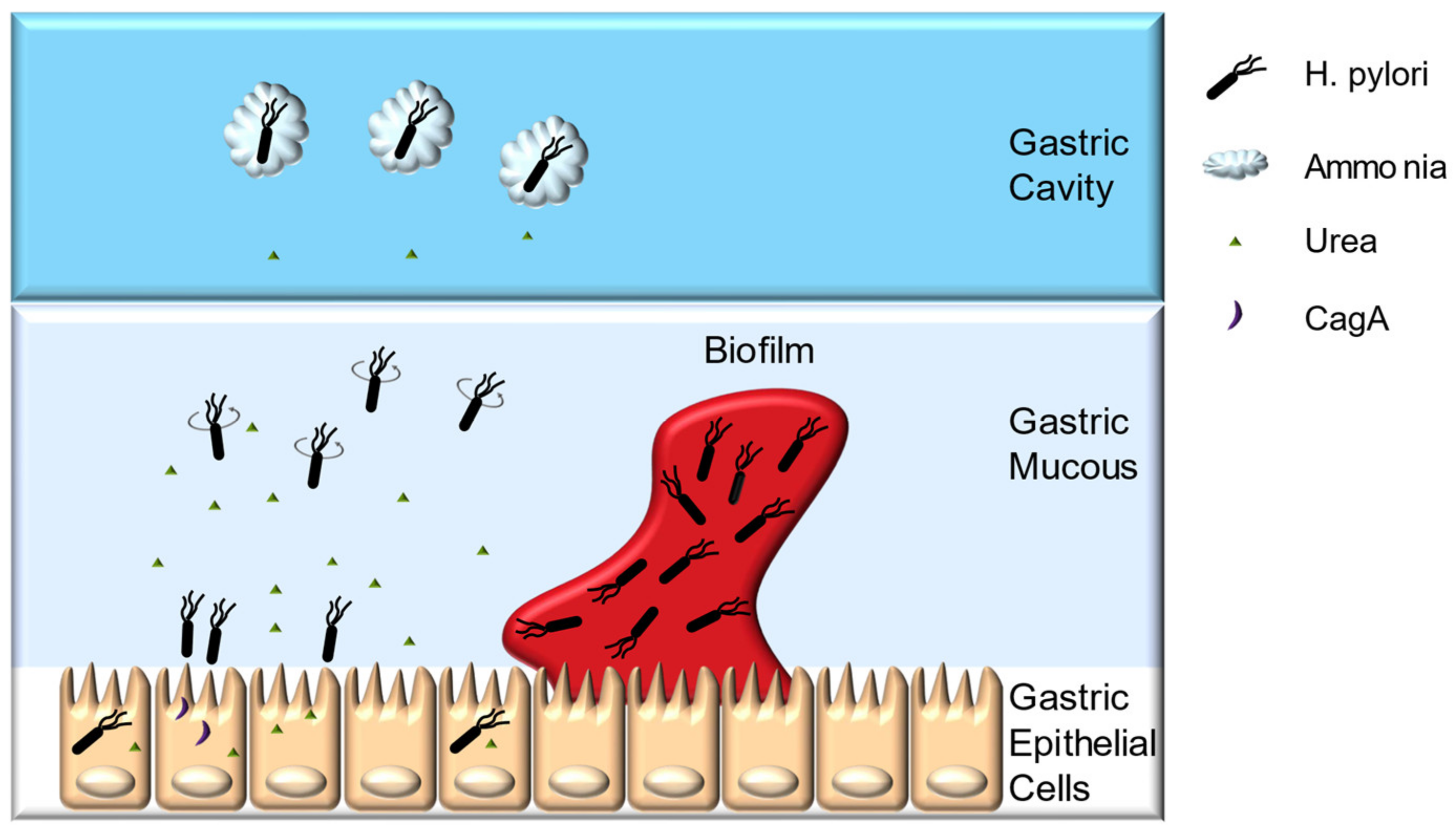
2.1. Colonization Mechanisms
2.2. H. pylori Pathogenesis
2.3. Antibiotic Therapy
3. Probiotic Therapy
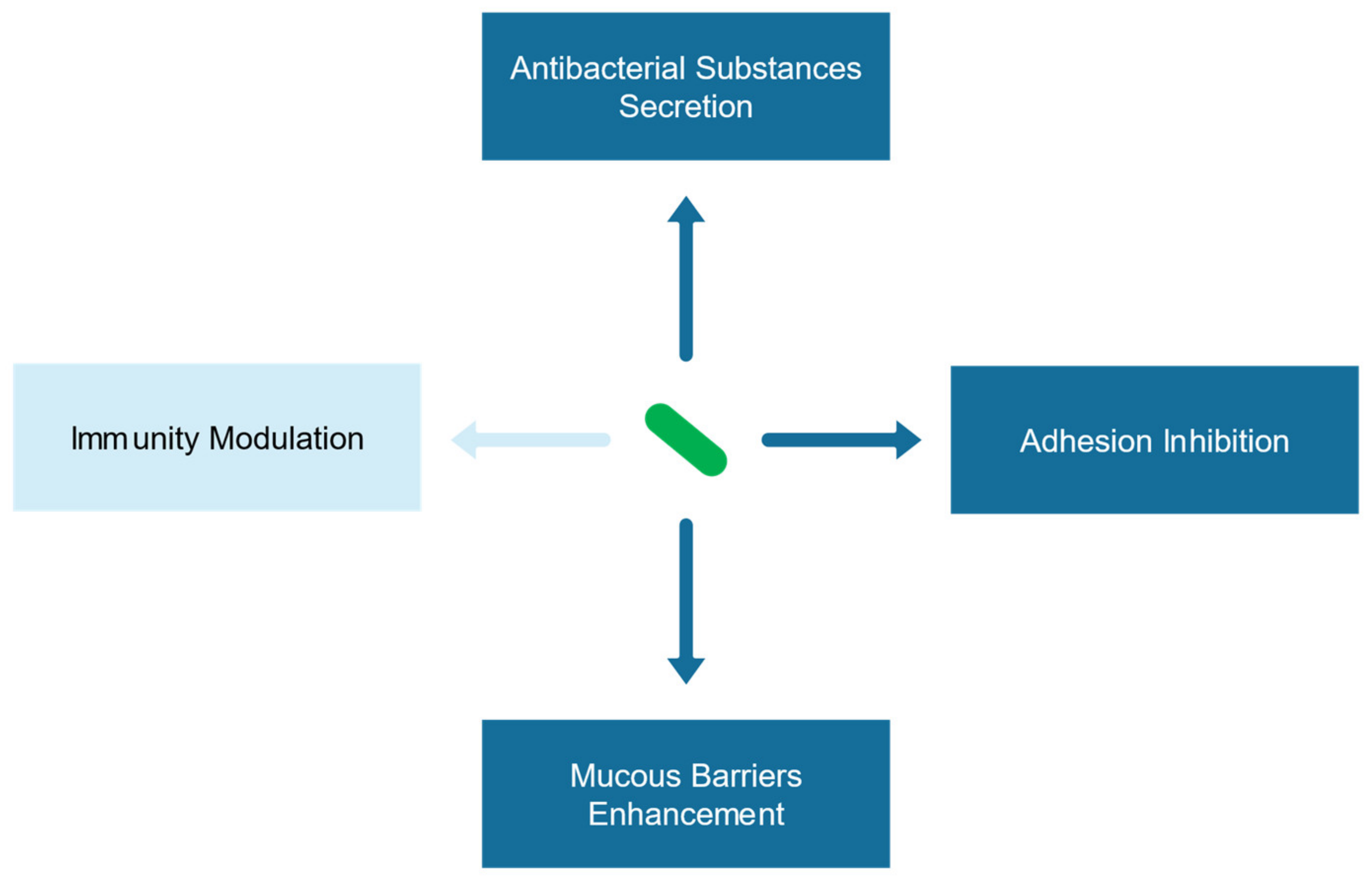
3.1. Antagonistic Mechanism
3.2. Clinical Studies
4. Advantages of Probiotic Supplementation Therapy
4.1. Drug Synergy and Mutant Prevention Theories
4.2. Biofilm Theory
4.3. Gastrointestinal Theory
5. Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Connor, A.; O’Morain, C.A.; Ford, A.C. Population screening and treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thung, I.; Aramin, H.; Vavinskaya, V.; Gupta, S.; Park, J.Y.; Crowe, S.E.; Valasek, M.A. Review article: The global emergence of Helicobacter pylori antibiotic resistance. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 43, 514–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacifico, L.; Osborn, J.F.; Bonci, E.; Romaggioli, S.; Baldini, R.; Chiesa, C. Probiotics for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection in children. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardini, G.; Figura, N.; Ponzetto, A.; Marzocchi, B.; Santucci, A. Application of proteomics to the study of Helicobacter pylori and implications for the clinic. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2017, 14, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Megraud, F.; O’Morain, C.A.; Gisbert, J.P.; Kuipers, E.J.; Axon, A.T.; Bazzoli, F.; Gasbarrini, A.; Atherton, J.; Graham, D.Y.; et al. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection-the Maastricht V/Florence consensus report. Gut 2017, 66, 6–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, S.E.; Choi, K.D.; Choe, J.; Kim, S.O.; Na, H.K.; Choi, J.Y.; Ahn, J.Y.; Jung, K.W.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.H.; et al. The effect of eradication of Helicobacter pylori on gastric cancer prevention in healthy asymptomatic populations. Helicobacter 2018, 23, e12464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Y.; Reinhardt, J.D.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, G. The effect of probiotics supplementation on Helicobacter pylori eradication rates and side effects during eradication therapy: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chey, W.D.; Leontiadis, G.I.; Howden, C.W.; Moss, S.F. ACG Clinical Guideline: Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 112, 212–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dore, M.P.; Bibbò, S.; Pes, G.M.; Francavilla, R.; Graham, D.Y. Role of probiotics in Helicobacter pylori eradication: Lessons from a study of Lactobacillus reuteri strains DSM 17938 and ATCC PTA 6475 (Gastrus®) and a proton-pump inhibitor. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 2019, 3409820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yang, H. Non-antibiotic therapy for Clostridioides difficile infection: A review. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2019, 56, 493–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yang, H. Antibacterial Activity of Bifidobacterium breve Against Clostridioides difficile. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Losurdo, G.; Cubisino, R.; Barone, M.; Principi, M.; Leandro, G.; Ierardi, E.; Di Leo, A. Probiotic monotherapy and Helicobacter pylori eradication: A systematic review with pooled-data analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francavilla, R.; Lionetti, E.; Castellaneta, S.P.; Magistà, A.M.; Maurogiovanni, G.; Bucci, N.; De Canio, A.; Indrio, F.; Cavallo, L.; Ierardi, E.; et al. Inhibition of Helicobacter pylori infection in humans by Lactobacillus reuteri ATCC 55730 and effect on eradication therapy: A pilot study. Helicobacter 2008, 13, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, K.A.; Jayaraman, T.; Daly, P.; Canchaya, C.; Curran, S.; Fang, F.; Quigley, E.M.; O’Toole, P.W. Isolation of lactobacilli with probiotic properties from the human stomach. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 47, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, J.L.; Matsumoto, A.; Tanaka, H.; Matsumura, I. Gastric microbiota: An emerging player in Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric malignancies. Cancer Lett. 2018, 414, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homan, M.; Orel, R. Are probiotics useful in Helicobacter pylori eradication? World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 10644–10653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Zhou, L.; Liu, D.; Ge, L.; Li, Y. Probiotic effect on Helicobacter pylori attachment and inhibition of inflammation in human gastric epithelial cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 1151–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, S.; Bucker, R.; Groll, C.; Azevedo-Vethacke, M.; Garten, D.; Scheid, P.; Friedrich, S.; Gatermann, S.; Josenhans, C.; Suerbaum, S. Rapid loss of motility of Helicobacter pylori in the gastric lumen In Vivo. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 1584–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Meng, X.; Li, Y.; Zhao, C.-N.; Tang, G.-Y.; Li, S.; Gan, R.-Y.; Li, H.-B. Natural Products for the Prevention and Management of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 937–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, N.R.; Hartung, M.L.; Muller, A. Life in the human stomach: Persistence strategies of the bacterial pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathroubi, S.; Servetas, S.L.; Windham, I.; Merrell, D.S.; Ottemann, K.M. Helicobacter pylori biofilm formation and its potential role in pathogenesis. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2018, 82, e00001–e00018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yonezawa, H.; Osaki, T.; Kamiya, S. Biofilm formation by Helicobacter pylori and its involvement for antibiotic resistance. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 914791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attaran, B.; Falsafi, T.; Ghorbanmehr, N. Effect of biofilm formation by clinical isolates of Helicobacter pylori on the efflux-mediated resistance to commonly used antibiotics. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yonezawa, H.; Osaki, T.; Hojo, F.; Kamiya, S. Effect of Helicobacter pylori biofilm formation on susceptibility to amoxicillin, metronidazole and clarithromycin. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 132, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keilberg, D.; Ottemann, K.M. How Helicobacter pylori senses, targets and interacts with the gastric epithelium. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 791–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debowski, A.W.; Walton, S.M.; Chua, E.-G.; Tay, A.C.-Y.; Liao, T.; Lamichhane, B.; Himbeck, R.; Stubbs, K.A.; Marshall, B.J.; Fulurija, A.; et al. Helicobacter pylori gene silencing In Vivo demonstrates urease is essential for chronic infection. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.Y.; Sweeney, E.G.; Sigal, M.; Zhang, H.C.; Remington, S.J.; Cantrell, M.A.; Kuo, C.J.; Guillemin, K.; Amieva, M.R. Chemodetection and destruction of host urea allows Helicobacter pylori to locate the epithelium. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 18, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.S.; Ottemann, K.M. Colonization, localization, and inflammation: The roles of H. pylori chemotaxis In Vivo. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2018, 41, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGee, D.J.; Langford, M.L.; Watson, E.L.; Carter, J.E.; Chen, Y.T.; Ottemann, K.M. Colonization and inflammation deficiencies in Mongolian gerbils infected by Helicobacter pylori chemotaxis mutants. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 1820–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottemann, K.M.; Lowenthal, A.C. Helicobacter pylori uses motility for initial colonization and to attain robust infection. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 1984–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, L.E.; Hardcastle, J.M.; Wang, J.; Pincus, Z.; Tsang, J.; Hoover, T.R.; Bansil, R.; Salama, N.R. Helicobacter pylori strains vary cell shape and flagellum number to maintain robust motility in viscous environments. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 99, 88–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, Q.L.; Cheng, D.D.; Xu, W.T.; Lu, N.H. Adhesion and invasion of gastric mucosa epithelial cells by Helicobacter pylori. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coticchia, J.M.; Sugawa, C.; Tran, V.R.; Gurrola, J.; Kowalski, E.; Carron, M.A. Presence and density of Helicobacter pylori biofilms in human gastric mucosa in patients with peptic ulcer disease. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2006, 10, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bugli, F.; Palmieri, V.; Torelli, R.; Papi, M.; De Spirito, M.; Cacaci, M.; Galgano, S.; Masucci, L.; Paroni Sterbini, F.; Vella, A.; et al. In vitro effect of clarithromycin and alginate lyase against Helicobacter pylori biofilm. Biotechnol. Prog. 2016, 32, 1584–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yonezawa, H.; Osaki, T.; Hanawa, T.; Kurata, S.; Ochiai, K.; Kamiya, S. Impact of Helicobacter pylori Biofilm Formation on Clarithromycin Susceptibility and Generation of Resistance Mutations. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, M.; Suzuki, H.; Suzuki, M.; Kai, A.; Miura, S.; Ishii, H. Catalase and superoxide dismutase secreted from Helicobacter pylori. Helicobacter 1997, 2, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarque, D.; Moran, A.P.; Szepes, Z.; Delchier, J.C.; Whittle, B.J.R. Cytotoxicity associated with induction of nitric oxide synthase in rat duodenal epithelial cells in vivo by lipopolysaccharide of Helicobacter pylori: Inhibition by superoxide dismutase. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 130, 1531–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereswill, S.; Neuner, O.; Strobel, S.; Kist, M. Identification and molecular analysis of superoxide dismutase isoforms in Helicobacter pylori. Fems Microbiol. Lett. 2000, 183, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyler, R.W.; Olson, J.W.; Maier, R.J. Superoxide dismutase-deficient mutants of Helicobacter pylori are hypersensitive to oxidative stress and defective in host colonization. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 4034–4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.L.; Yeh, Y.C.; Sheu, B.S. The impacts of H. pylori virulence factors on the development of gastroduodenal diseases. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018, 25, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, N.; Li, P.; Gu, Q. Probiotic therapy in Helicobacter pylori infection: A potential strategy against a serious pathogen? Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 1573–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nejati, S.; Karkhah, A.; Darvish, H.; Validi, M.; Ebrahimpour, S.; Nouri, H.R. Influence of Helicobacter pylori virulence factors CagA and VacA on pathogenesis of gastrointestinal disorders. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 117, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterbenc, A.; Jarc, E.; Poljak, M.; Homan, M. Helicobacter pylori virulence genes. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 4870–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatakeyama, M. Helicobacter pylori CagA and gastric cancer: A paradigm for hit-and-run carcinogenesis. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 15, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClain, M.S.; Beckett, A.C.; Cover, T.L. Helicobacter pylori vacuolating toxin and gastric cancer. Toxins 2017, 9, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, N.; Tay, A.C.Y.; Marshall, B.J.; Jain, U. Helicobacter pylori VacA, a distinct toxin exerts diverse functionalities in numerous cells: An overview. Helicobacter 2019, 24, e12544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabamba, E.T.; Tuan, V.P.; Yamaoka, Y. Genetic populations and virulence factors of Helicobacter pylori. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 60, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.; Yamaoka, Y. Survival of Helicobacter pylori in gastric acidic territory. Helicobacter 2017, 22, e12386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, M.D.J.; De Moraes, J.A.; Da Silva, V.N.; Helal-Neto, E.; Uberti, A.F.; Scopel-Guerra, A.; Olivera-Severo, D.; Carlini, C.R.; Barja-Fidalgo, C. Helicobacter pylori urease induces pro-inflammatory effects and differentiation of human endothelial cells: Cellular and molecular mechanism. Helicobacter 2019, 24, e12573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebi Bezmin Abadi, A. Helicobacter pylori treatment: New perspectives using current experience. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2017, 8, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami, M.; Yousefi, B.; Kokhaei, P.; Jazayeri Moghadas, A.; Sadighi Moghadam, B.; Arabkari, V.; Niazi, Z. Are probiotics useful for therapy of Helicobacter pylori diseases? Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 64, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, D.Y. Helicobacter pylori update: Gastric cancer, reliable therapy, and possible benefits. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, D.Y.; Lu, H.; Dore, M.P. Relative potency of proton-pump inhibitors, Helicobacter pylori therapy cure rates, and meaning of double-dose PPI. Helicobacter 2019, 24, e12554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, N.H. Novel and Effective Therapeutic Regimens for Helicobacter pylori in an Era of Increasing Antibiotic Resistance. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alba, C.; Blanco, A.; Alarcon, T. Antibiotic resistance in Helicobacter pylori. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 30, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Wang, Z.; Sun, G.; Peng, L.; Lu, Z.; Yan, B.; Huang, K.; Yang, Y. Effects of anti-H. pylori triple therapy and a probiotic complex on intestinal microbiota in duodenal ulcer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olekhnovich, E.I.; Manolov, A.I.; Samoilov, A.E.; Prianichnikov, N.A.; Malakhova, M.V.; Tyakht, A.V.; Pavlenko, A.V.; Babenko, V.V.; Larin, A.K.; Kovarsky, B.A.; et al. Shifts in the human gut microbiota structure caused by quadruple Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornejo-Pareja, I.; Martín-Núñez, G.; Roca-Rodríguez, M.; Cardona, F.; Coin-Aragüez, L.; Sánchez-Alcoholado, L.; Gutiérrez-Repiso, C.; Muñoz-Garach, A.; Fernández-García, J.; Moreno-Indias, I.; et al. H. pylori Eradication treatment alters gut microbiota and GLP-1 secretion in humans. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhann, F.; Bonder, M.J.; Vich Vila, A.; Fu, J.; Mujagic, Z.; Vork, L.; Tigchelaar, E.F.; Jankipersadsing, S.A.; Cenit, M.C.; Harmsen, H.J.M.; et al. Proton pump inhibitors affect the gut microbiome. Gut 2016, 65, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.A.; Goodrich, J.K.; Maxan, M.-E.; Freedberg, D.E.; Abrams, J.A.; Poole, A.C.; Sutter, J.L.; Welter, D.; Ley, R.E.; Bell, J.T.; et al. Proton pump inhibitors alter the composition of the gut microbiota. Gut 2016, 65, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Tsai, W.H.; Wu, H.Y.; Chen, C.Y.; Yeh, W.L.; Chen, Y.H.; Hsu, H.Y.; Chen, W.W.; Chen, Y.W.; Chang, W.W.; et al. Probiotic Lactobacillus spp. act Against Helicobacter pylori-induced Inflammation. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Xie, Q.; Xu, D.; Guo, Y.; Tao, X.; Wei, H.; Wan, C. Antagonistics of Lactobacillus plantarum ZDY2013 against Helicobacter pylori SS1 and its infection in vitro in human gastric epithelial AGS cells. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2018, 126, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Zhao, H.; Liu, L.; Wu, X.; Gao, Q.; Zhao, Y. Effects of Lactobacillus on the inhibition of Helicobacter pylori growth. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2018, 32, 1533–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiba, Y.; Nakano, Y.; Koga, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Komatsu, Y. A highly acid-resistant novel strain of Lactobacillus johnsonii No. 1088 has antibacterial activity, including that against Helicobacter pylori, and inhibits gastrin-mediated acid production in mice. Microbiologyopen 2015, 4, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiba, Y.; Ishikawa, H.; Tokunaga, M.; Komatsu, Y. Anti-Helicobacter pylori activity of non-living, heat-killed form of lactobacilli including Lactobacillus johnsonii No.1088. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2017, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poppi, L.B.; Rivaldi, J.D.; Coutinho, T.S.; Astolfi-Ferreira, C.S.; Ferreira, A.J.P.; Mancilha, I.M. Effect of Lactobacillus sp isolates supernatant on Escherichia coli O157:H7 enhances the role of organic acids production as a factor for pathogen control. Pesqui. Veterinária Bras. 2015, 35, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.X.; Fang, H.Y.; Yang, H.B.; Tien, N.Y.; Wang, M.C.; Wu, J.J. Lactobacillus pentosus strain LPS16 produces lactic acid, inhibiting multidrug-resistant Helicobacter pylori. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2016, 49, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesbros-Pantoflickova, D.; Corthesy-Theulaz, I.; Blum, A.L. Helicobacter pylori and probiotics. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 812S–818S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batdorj, B.; Trinetta, V.; Dalgalarrondo, M.; Prevost, H.; Dousset, X.; Ivanova, I.; Haertle, T.; Chobert, J.M. Isolation, taxonomic identification and hydrogen peroxide production by Lactobacillys delbrueckii subsp lactis T31, isolated from Mongolian yoghurt: Inhibitory activity on food-borne pathogens fool-borne pathogens. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 103, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.-N.; Kim, W.J.; Kang, S.-S. Anti-biofilm effect of crude bacteriocin derived from Lactobacillus brevis DF01 on Escherichia coli and Salmonella Typhimurium. Food Control 2019, 98, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.S.; Hur, J.W.; Yu, M.A.; Cheigh, C.I.; Kim, K.N.; Hwang, J.K.; Pyun, Y.R. Antagonism of Helicobacter pylori by bacteriocins of lactic acid bacteria. J. Food Prot. 2003, 66, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyanova, L.; Gergova, G.; Markovska, R.; Yordanov, D.; Mitov, I. Bacteriocin-like inhibitory activities of seven Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus strains against antibiotic susceptible and resistant Helicobacter pylori strains. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 65, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urrutia-Baca, V.H.; Escamilla-Garcia, E.; de la Garza-Ramos, M.A.; Tamez-Guerra, P.; Gomez-Flores, R.; Urbina-Rios, C.S. In Vitro antimicrobial activity and downregulation of virulence gene expression on Helicobacter pylori by reuterin. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2018, 10, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukai, T.; Asasaka, T.; Sato, E.; Mori, K.; Matsumoto, M.; Ohori, H. Inhibition of binding of Helicobacter pylori to the glycolipid receptors by probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri. Fems Immunol. Med Microbiol. 2002, 32, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Klerk, N.; Maudsdotter, L.; Gebreegziabher, H.; Saroj, S.D.; Eriksson, B.; Eriksson, O.S.; Roos, S.; Lindén, S.; Sjölinder, H.; Jonsson, A.-B. Lactobacilli reduce Helicobacter pylori attachment to host gastric epithelial cells by inhibiting adhesion gene expression. Infect. Immun. 2016, 84, 1526–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakarya, S.; Gunay, N. Saccharomyces boulardii expresses neuraminidase activity selective for alpha2,3-linked sialic acid that decreases Helicobacter pylori adhesion to host cells. APMIS 2014, 122, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.C.; Yunker, C.K.; Xu, Q.S.; Sternberg, L.R.; Bresalier, R.S. Inhibition of gastric mucin synthesis by Helicobacter pylori. Gastroenterology 2000, 118, 1072–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suez, J.; Zmora, N.; Segal, E.; Elinav, E. The pros, cons, and many unknowns of probiotics. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 716–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-J.; Chuang, C.-C.; Yang, H.-B.; Lu, C.-C.; Sheu, B.-S. Lactobacillus acidophilus ameliorates H. pylori-induced gastric inflammation by inactivating the Smad7 and NFΚB pathways. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiraworawong, T.; Spinler, J.K.; Werawatganon, D.; Klaikeaw, N.; Venable, S.F.; Versalovic, J.; Tumwasorn, S. Anti-inflammatory properties of gastric-derived Lactobacillus plantarum XB7 in the context of Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter 2014, 19, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, E.M.M. Prebiotics and probiotics in digestive health. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotteland, M.; Poliak, L.; Cruchet, S.; Brunser, O. Effect of regular ingestion of Saccharomyces boulardii plus inulin or Lactobacillus acidophilus LB in children colonized by Helicobacter pylori. Acta Paediatr. 2005, 94, 1747–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, J.D.; Fernandes, C.C.; Cunha, L.F.; Zung, S. Efficacy and Safety of Lactobacillus reuteri in Helicobacter pylori Infection. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, S531–S532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykora, J.; Valeckova, K.N.; Amlerova, J.; Siala, K.; Dedek, P.; Watkins, S.; Varvarovska, J.; Stozicky, F.; Pazdiora, P.; Schwarz, J. Effects of a specially designed fermented milk product containing probiotic Lactobacillus casei DN-114 001 and the eradication of H-pylori in children—A prospective randomized double-blind study. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2005, 39, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deguchi, R.; Nakaminami, H.; Rimbara, E.; Noguchi, N.; Sasatsu, M.; Suzuki, T.; Matsushima, M.; Koike, J.; Igarashi, M.; Ozawa, H.; et al. Effect of pretreatment with Lactobacillus gasseri OLL2716 on first-line Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 27, 888–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdeva, A.; Nagpal, J. Effect of fermented milk-based probiotic preparations on Helicobacter pylori eradication: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized-controlled trials. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 21, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNicholl, A.G.; Molina-Infante, J.; Lucendo, A.J.; Calleja, J.L.; Pérez-Aisa, Á.; Modolell, I.; Aldeguer, X.; Calafat, M.; Comino, L.; Ramas, M.; et al. Probiotic supplementation with Lactobacillus plantarum and Pediococcus acidilactici for Helicobacter pylori therapy: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Helicobacter 2018, 23, e12529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcusson, L.L.; Olofsson, S.K.; Lindgren, P.K.; Cars, O.; Hughes, D. Mutant prevention concentrations of ciprofloxacin for urinary tract infection isolates of Escherichia coli. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2005, 55, 938–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.-H.; Fan, L.; Yang, J.; Huo, X.-Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lan, C.-H. Mutant selection window of clarithromycin for clinical isolates of Helicobacter pylori. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, B.D.; Brooks, A.E. Therapeutic strategies to combat antibiotic resistance. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 78, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemaiswarya, S.; Kruthiventi, A.K.; Doble, M. Synergism between natural products and antibiotics against infectious diseases. Phytomedicine 2008, 15, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caesar, L.K.; Cech, N.B. Synergy and antagonism in natural product extracts: When 1 + 1 does not equal 2. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 869–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, J.; Zhu, F.; Ma, X.; Cao, Z.W.; Li, Y.X.; Chen, Y.Z. Mechanisms of drug combinations: Interaction and network perspectives. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleymanzadeh Moghadam, S.; Khodaii, Z.; Fathi Zadeh, S.; Ghooshchian, M.; Fagheei Aghmiyuni, Z.; Mousavi Shabestari, T. Synergistic or antagonistic effects of probiotics and antibiotics-alone or in combination- on antimicrobial-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from burn wounds. Arch. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 13, e63121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yang, H. Effect of Bifidobacterium breve in Combination With Different Antibiotics on Clostridium difficile. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Fuente-Núñez, C.; Reffuveille, F.; Fernández, L.; Hancock, R.E. Bacterial biofilm development as a multicellular adaptation: Antibiotic resistance and new therapeutic strategies. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2013, 16, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzato, C.; Torres, J.; Kasamatsu, E.; Camorlinga-Ponce, M.; Bravo, M.M.; Canzian, F.; Kato, I. Potential Role of Biofilm Formation in the Development of Digestive Tract Cancer With Special Reference to Helicobacter pylori Infection. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Cai, Y.; Chen, Z.; Gao, S.; Geng, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Jia, J.; Sun, Y. Bifunctional enzyme spot is involved in biofilm formation of Helicobacter pylori with multidrug resistance by upregulating efflux pump Hp1174 (gluP). Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e00957-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bińkowska, A.; Biernat, M.; Duś, I.; Gościniak, G. The role of biofilm formation in pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori infections. Prz. Gastroenterol. 2013, 1, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathroubi, S.; Zerebinski, J.; Ottemann, K.M. Helicobacter pylori biofilm involves a multigene stress-biased response, including a structural role for flagella. mBio 2018, 9, e01973-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammarota, G.; Branca, G.; Ardito, F.; Sanguinetti, M.; Ianiro, G.; Cianci, R.; Torelli, R.; Masala, G.; Gasbarrini, A.; Fadda, G.; et al. Biofilm demolition and antibiotic treatment to eradicate resistant Helicobacter pylori: A Clinical Trial. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 8, 817–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Zhang, J.; Qu, J.; Liu, J.; Yin, P.; Zhang, G.; Shang, D. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG microcapsules inhibit Escherichia coli biofilm formation in coculture. Biotechnol. Lett. 2019, 41, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merino, L.; Trejo, F.M.; De Antoni, G.; Golowczyc, M.A. Lactobacillus strains inhibit biofilm formation of Salmonella sp. isolates from poultry. Food Res. Int. 2019, 123, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.; Park, O.J.; Kim, A.R.; Ahn, K.B.; Lee, D.; Kum, K.Y.; Yun, C.H.; Han, S.H. Lipoteichoic acids of lactobacilli inhibit Enterococcus faecalis biofilm formation and disrupt the preformed biofilm. J. Microbiol. 2019, 57, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez Moreno, M.; Trampuz, A.; Di Luca, M. Synergistic antibiotic activity against planktonic and biofilm-embedded Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus pyogenes and Streptococcus oralis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 3085–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butel, M.J. Probiotics, gut microbiota and health. Med. Mal. Infect. 2014, 44, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooks, M.G.; Garrett, W.S. Gut microbiota, metabolites and host immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E.; Kinross, J.; Burcelin, R.; Gibson, G.; Jia, W.; Pettersson, S. Host-gut microbiota metabolic interactions. Science 2012, 336, 1262–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, J.C.; Ursell, L.K.; Parfrey, L.W.; Knight, R. The impact of the gut microbiota on human health: An integrative view. Cell 2012, 148, 1258–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kienesberger, S.; Laura Livanos, A.; Zhang, X.-S.; Chung, J.; Guillermo, I.; Gorkiewicz, G.; Ellen, L.; Martin, I. Helicobacter pylori infection affects local and distant microbial populations and host responses. Cell Rep. 2016, 14, 1395–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, C.M.; Kim, N.; Lee, D.H. Changes of gastric corpus microbiota after Helicobacter Pylori eradication: A long term follow up study. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, S535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gareau, M.G.; Sherman, P.M.; Walker, W.A. Probiotics and the gut microbiota in intestinal health and disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 7, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunathilake, M.N.; Lee, J.; Choi, I.J.; Kim, Y.-I.; Ahn, Y.; Park, C.; Kim, J. Assoc. between the relative abundance of gastric microbiota and the risk of gastric cancer: A case-control study. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, J.; Yang, H. Using Probiotics as Supplementation for Helicobacter pylori Antibiotic Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21031136
Ji J, Yang H. Using Probiotics as Supplementation for Helicobacter pylori Antibiotic Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(3):1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21031136
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Jianfu, and Hong Yang. 2020. "Using Probiotics as Supplementation for Helicobacter pylori Antibiotic Therapy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 3: 1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21031136
APA StyleJi, J., & Yang, H. (2020). Using Probiotics as Supplementation for Helicobacter pylori Antibiotic Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(3), 1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21031136



