Contradictory Effects of NLRP3 Inflammasome Regulatory Mechanisms in Colitis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
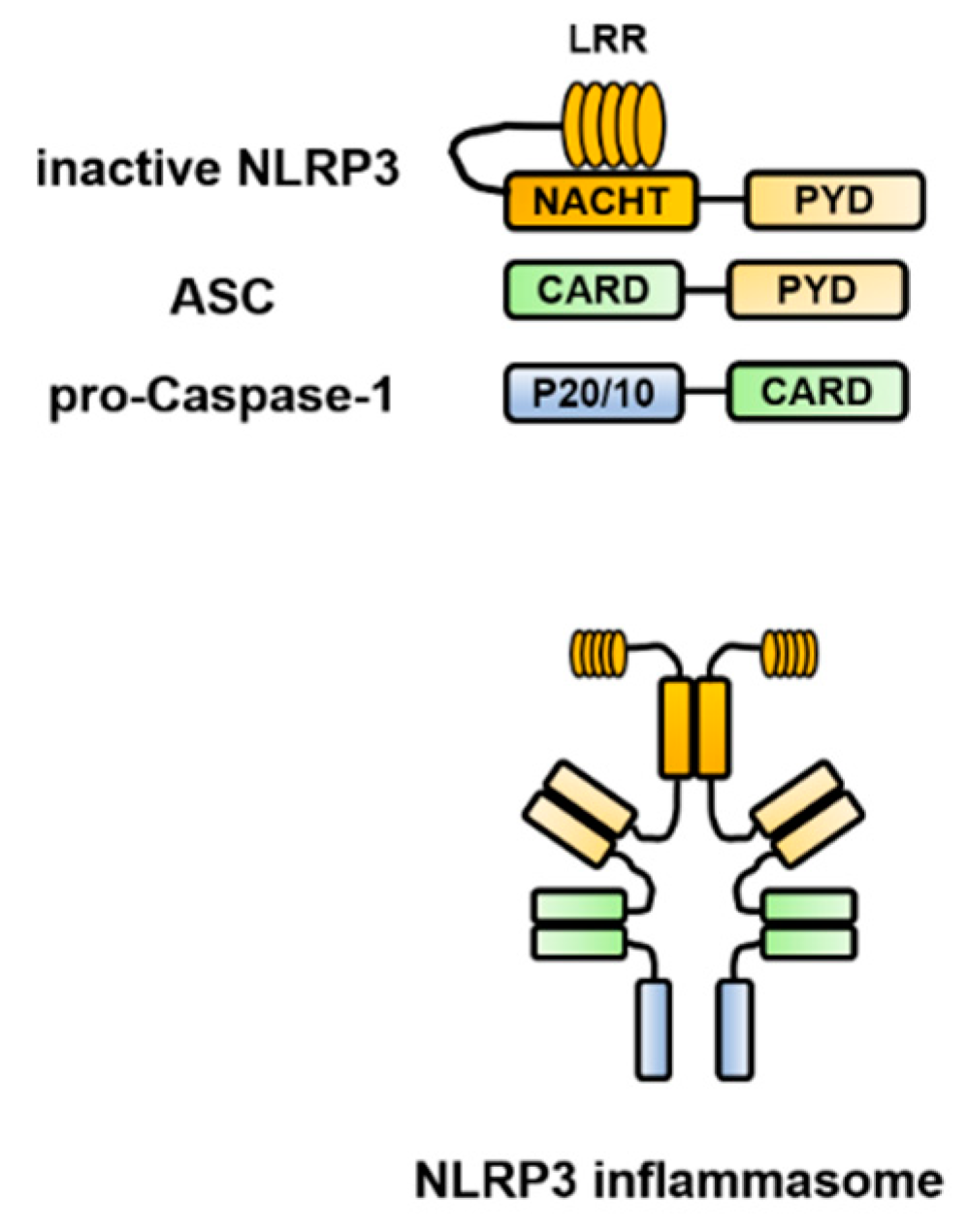
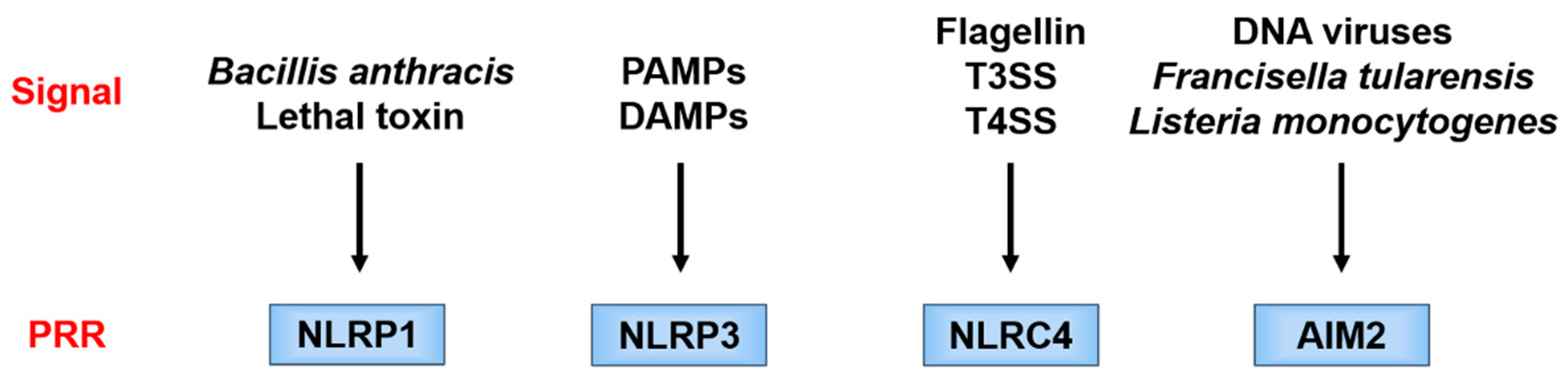
2. Structure of the Inflammasome
3. Control Mechanism of the NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation
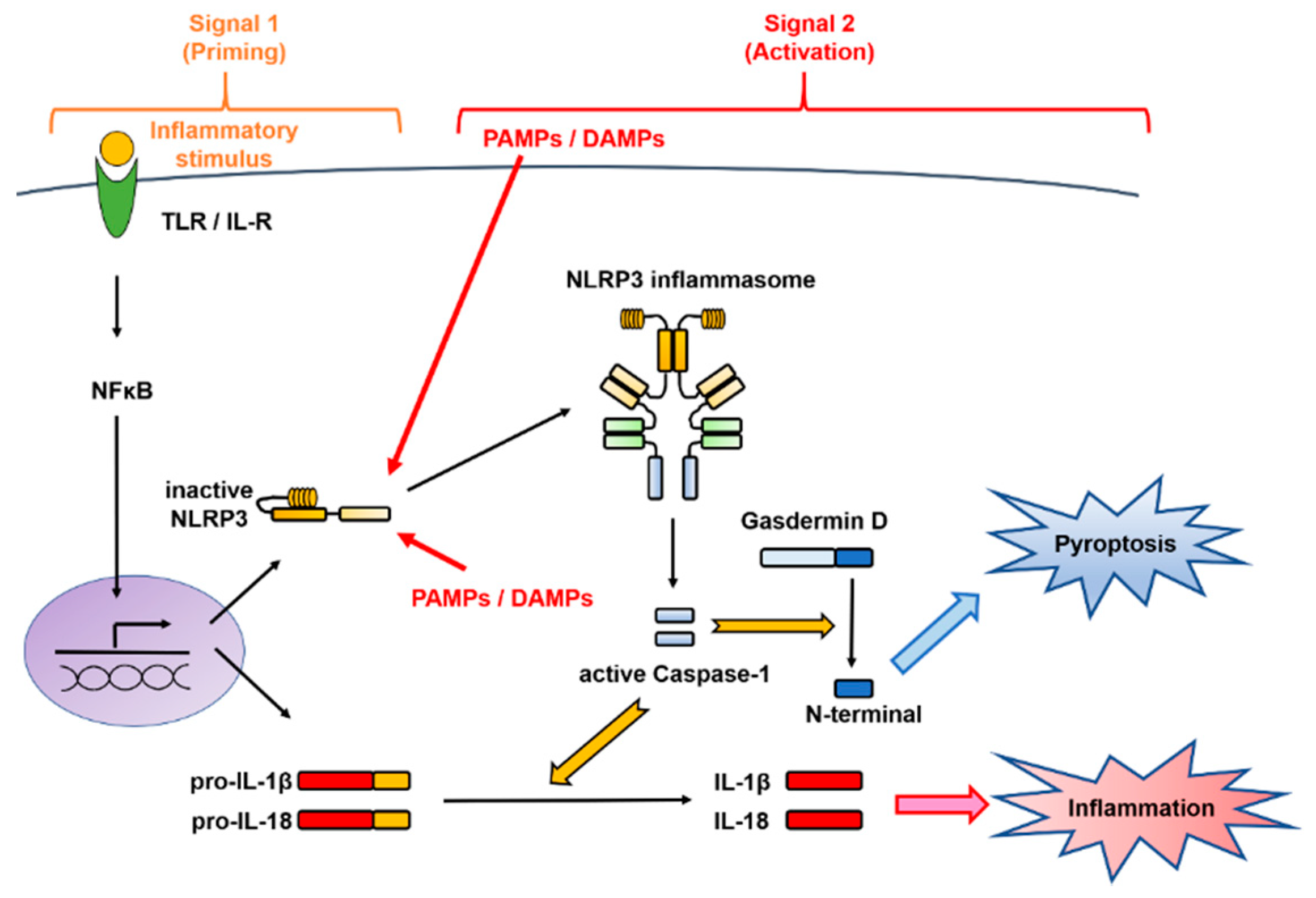
3.1. Two-Signal Control of the NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation
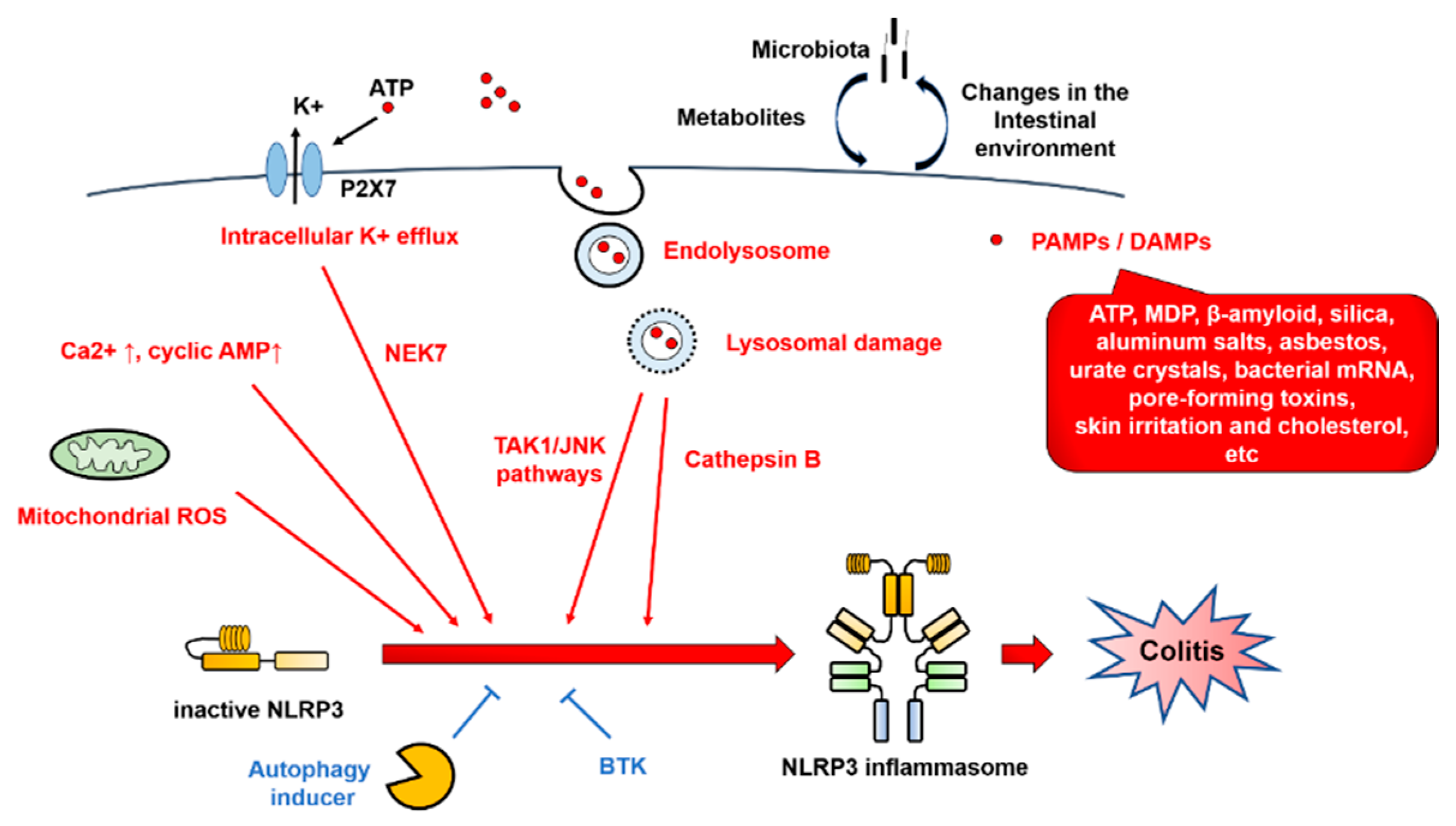
3.2. NLRP3 Inflammasome Regulators
3.3. Non-Canonical Inflammasomes
4. Diseases Associated with Inflammasome Dysfunction
4.1. Autoinflammatory Diseases
4.2. IBD
5. Factors Associated with the NLRP3 Inflammasome in IBD
5.1. Cytokines and Pyroptosis
5.1.1. IL-1β
5.1.2. IL-18
5.1.3. Pyroptosis
5.2. Autophagy
5.3. Microbiota
5.3.1. Involvement of NLRP3 in Intestinal Inflammation via Effects on the Microbiota
5.3.2. Regulation of Intestinal Inflammation by Microbiota via NLRP3
5.3.3. Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)
6. Inflammasome Dysfunction in the Colon
6.1. Colitis
6.1.1. Patients with IBD
6.1.2. Experimental Models
- Caspase-1
- NLRP3
6.1.3. Therapy
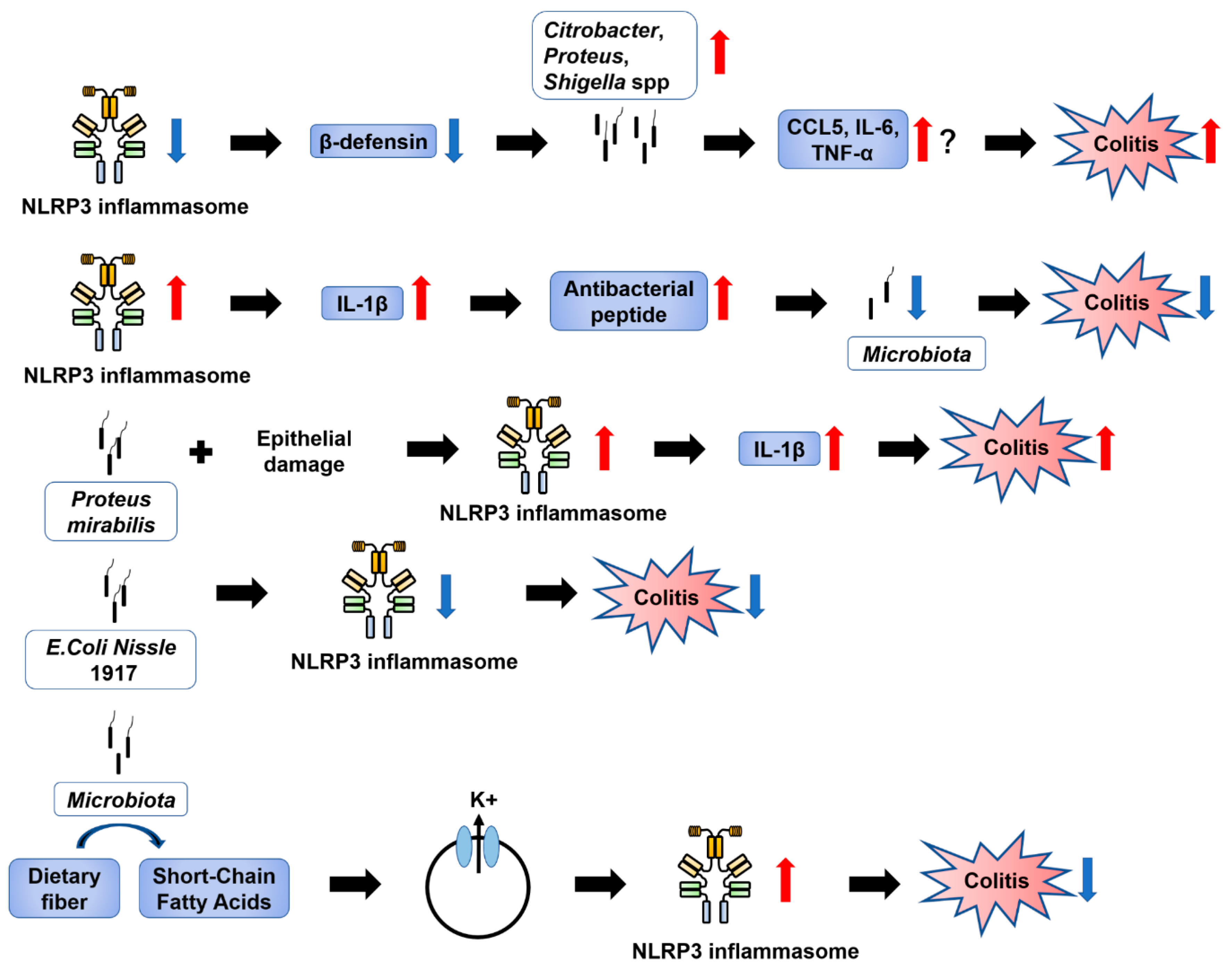
6.2. Contradictory Results on the Role of NLRP3 Inflammasome Regulation in Colitis
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NLRP3, 1, 6, 12 | NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing 3, 1, 6, 12 |
| PRR | Pattern recognition receptor |
| PAMP | Pathogen-associated molecular pattern |
| DAMP | Danger-associated molecular pattern |
| CAPS | Cryopyrin-associated periodic syndrome |
| CARD | Caspase recruitment domain |
| ASC | Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a caspase recruitment domain |
| IL | Interleukin |
| NLR | NOD-like receptor |
| PYD | Pyrin domain |
| IBD | Inflammatory bowel disease |
| KO | Knockout |
| TLR | Toll-like receptor |
| RLR | Retinoic acid-inducible gene-I-like receptor |
| AIM2 | Absent in melanoma 2 |
| ALR | Absent in melanoma 2-like receptor |
| PYHIN | Pyrin and HIN domain |
| NLRC4 | NOD-like receptor family caspase recruitment domain-containing 4 |
| NACHT | Neuronal apoptosis inhibitory protein, MHC class II transcription activator, incompatibility locus protein from Podospora anserina, and telomerase-associated protein |
| NAIP | Neuronal apoptosis inhibitory protein |
| CIITA | MHC class II transcription activator |
| HET-E | Incompatibility locus protein from Podospora anserina |
| TP1 | Telomerase-associated protein |
| LRR | Leucine-rich repeat |
| NAIP | Neuronal apoptosis inhibitory protein |
| IL-1R | Interleukin-1 receptor |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor-kappa B |
| T3SS/T4SS | Type III/IV secretion system |
| MDP | Muramyl dipeptide |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| BTK | Bruton’s tyrosine kinase |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| NEK7 | NIMA-related kinase 7 |
| TAK1 | TGF-β-activated kinase 1 |
| GBP5 | Guanylate-binding protein 5 |
| CaSR | Calcium-sensing receptor |
| CD | Crohn’s disease |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| FMF | Familial Mediterranean fever |
| UC | Ulcerative colitis |
| SNP | Single-nucleotide polymorphism |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor |
| Th | T helper |
| DSS | Dextran sulfate sodium |
| IFN | Interferon |
| IL-18BP | Interleukin-18-binding protein |
| NK | Natural killer |
| IEC | Intestinal epithelial cell |
| ATG | Autophagy-related gene |
| Treg | T regulatory |
| SCFA | Short-chain fatty acid |
| PBMC | Peripheral blood mononuclear cell |
| WT | Wild type |
| AOM | Azoxymethane |
| STAT | Signal transducer and activator of transcription |
| TNBS | 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid |
References
- Martinon, F.; Burns, K.; Tschopp, J. The inflammasome: A molecular platform triggering activation of inflammatory caspases and processing of proIL-beta. Mol. Cell 2002, 10, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinon, F.; Pétrilli, V.; Mayor, A.; Tardivel, A.; Tschopp, J. Gout-associated uric acid crystals activate the NALP3 inflammasome. Nature 2006, 440, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schroder, K.; Tschopp, J. The inflammasomes. Cell 2010, 140, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aguilera, M.; Darby, T.; Melgar, S. The complex role of inflammasomes in the pathogenesis of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases—Lessons learned from experimental models. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014, 25, 715–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A. Immunological and inflammatory functions of the interleukin-1 family. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 519–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latz, E.; Xiao, T.S.; Stutz, A. Activation and regulation of the inflammasomes. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, S.M.; Karki, R.; Kanneganti, T.D. Molecular mechanisms and functions of pyroptosis, inflammatory caspases and inflammasomes in infectious diseases. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 277, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, B.Z.; Xu, Z.Q.; Han, B.Z.; Su, D.F.; Liu, C. NLRP3 inflammasome and its inhibitors: A review. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhen, Y.; Zhang, H. NLRP3 Inflammasome and Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, B.Z.; Wang, S.L.; Pan, P.; Yao, J.; Wu, K.; Li, Z.S.; Bai, Y.; Linghu, E.Q. Targeting NLRP3 Inflammasome in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Putting out the Fire of Inflammation. Inflammation 2019, 42, 1147–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Hara, H.; Núñez, G. Mechanism and Regulation of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Trends. Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 1012–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Broz, P.; Dixit, V.M. Inflammasomes: Mechanism of assembly, regulation and signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranson, N.; Kunde, D.; Eri, R. Regulation and Sensing of Inflammasomes and Their Impact on Intestinal Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelley, N.; Jeltema, D.; Duan, Y.; He, Y. The NLRP3 Inflammasome: An Overview of Mechanisms of Activation and Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Place, D.E.; Kanneganti, T.D. Recent advances in inflammasome biology. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2018, 50, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Kanneganti, T.D. The cell biology of inflammasomes: Mechanisms of inflammasome activation and regulation. J. Cell Biol. 2016, 213, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Opipari, A.; Franchi, L. Role of inflammasomes in intestinal inflammation and Crohn’s disease. Inflamm. Bowel. Dis. 2015, 21, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pétrilli, V.; Papin, S.; Dostert, C.; Mayor, A.; Martinon, F.; Tschopp, J. Activation of the NALP3 inflammasome is triggered by low intracellular potassium concentration. Cell Death Differ. 2007, 14, 1583–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Planillo, R.; Kuffa, P.; Martínez-Colón, G.; Smith, B.L.; Rajendiran, T.M.; Núñez, G. K+ efflux is the common trigger of NLRP3 inflammasome activation by bacterial toxins and particulate matter. Immunity 2013, 38, 1142–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okada, M.; Matsuzawa, A.; Yoshimura, A.; Ichijo, H. The lysosome rupture-activated TAK1-JNK pathway regulates NLRP3 inflammasome activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 32926–32936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hornung, V.; Bauernfeind, F.; Halle, A.; Samstad, E.O.; Kono, H.; Rock, K.L.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Latz, E. Silica crystals and aluminum salts activate the NALP3 inflammasome through phagosomal destabilization. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Z.; Umemura, A.; Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Liang, S.; Shalapour, S.; Wong, J.; He, F.; Boassa, D.; Perkins, G.; Ali, S.R.; et al. NF-κB Restricts Inflammasome Activation via Elimination of Damaged Mitochondria. Cell 2016, 164, 896–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juliana, C.; Fernandes-Alnemri, T.; Kang, S.; Farias, A.; Qin, F.; Alnemri, E.S. Non-transcriptional priming and deubiquitination regulate NLRP3 inflammasome activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 36617–36622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bauernfeind, F.; Bartok, E.; Rieger, A.; Franchi, L.; Núñez, G.; Hornung, V. Cutting edge: Reactive oxygen species inhibitors block priming, but not activation, of the NLRP3 inflammasome. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shenoy, A.R.; Wellington, D.A.; Kumar, P.; Kassa, H.; Booth, C.J.; Cresswell, P.; MacMicking, J.D. GBP5 promotes NLRP3 inflammasome assembly and immunity in mammals. Science 2012, 336, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zeng, M.Y.; Yang, D.; Motro, B.; Núñez, G. NEK7 is an essential mediator of NLRP3 activation downstream of potassium efflux. Nature 2016, 530, 354–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhan, X.; Tang, M.; Fina, M.; Su, L.; Pratt, D.; Bu, C.H.; Hildebrand, S.; et al. NLRP3 activation and mitosis are mutually exclusive events coordinated by NEK7, a new inflammasome component. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, T.; Jiang, W.; Zhou, R. Control of Inflammasome Activation by Phosphorylation. Trends. Biochem. Sci. 2018, 43, 685–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Py, B.F.; Kim, M.S.; Vakifahmetoglu-Norberg, H.; Yuan, J. Deubiquitination of NLRP3 by BRCC3 critically regulates inflammasome activity. Mol. Cell 2013, 49, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, G.S.; Subramanian, N.; Kim, A.I.; Aksentijevich, I.; Goldbach-Mansky, R.; Sacks, D.B.; Germain, R.N.; Kastner, D.L.; Chae, J.J. The calcium-sensing receptor regulates the NLRP3 inflammasome through Ca2+ and cAMP. Nature 2012, 492, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gutiérrez-López, T.Y.; Orduña-Castillo, L.B.; Hernández-Vásquez, M.N.; Vázquez-Prado, J.; Reyes-Cruz, G. Calcium sensing receptor activates the NLRP3 inflammasome via a chaperone-assisted degradative pathway involving Hsp70 and LC3-II. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 505, 1121–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Kitani, A.; Hiejima, E.; Montgomery-Recht, K.; Zhou, W.; Fuss, I.; Wiestner, A.; Strober, W. Bruton tyrosine kinase deficiency augments NLRP3 inflammasome activation and causes IL-1β-mediated colitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 1793–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Mateer, S.W.; Hsu, A.; Goggins, B.J.; Tay, H.; Mathe, A.; Fan, K.; Neal, R.; Bruce, J.; Burns, G.; et al. Platelet activating factor receptor regulates colitis-induced pulmonary inflammation through the NLRP3 inflammasome. Mucosal. Immunol. 2019, 12, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Hu, M.; Zang, X.; Fan, Q.; Liu, Y.; Che, Y.; Guan, X.; Hou, Y.; Wang, G.; Hao, H. Kynurenic acid/GPR35 axis restricts NLRP3 inflammasome activation and exacerbates colitis in mice with social stress. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 79, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayagaki, N.; Warming, S.; Lamkanfi, M.; Vande Walle, L.; Louie, S.; Dong, J.; Newton, K.; Qu, Y.; Liu, J.; Heldens, S.; et al. Non-canonical inflammasome activation targets caspase-11. Nature 2011, 479, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathinam, V.A.; Vanaja, S.K.; Waggoner, L.; Sokolovska, A.; Becker, C.; Stuart, L.M.; Leong, J.M.; Fitzgerald, K.A. TRIF licenses caspase-11-dependent NLRP3 inflammasome activation by gram-negative bacteria. Cell 2012, 150, 606–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yi, Y.S. Caspase-11 Non-Canonical Inflammasome: Emerging Activator and Regulator of Infection-Mediated Inflammatory Responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mangan, M.S.J.; Olhava, E.J.; Roush, W.R.; Seidel, H.M.; Glick, G.D.; Latz, E. Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome in inflammatory diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 588–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, R.; Siracusa, R.; Genovese, T.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Di Paola, R. Focus on the Role of NLRP3 Inflammasome in Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irrera, N.; Russo, M.; Pallio, G.; Bitto, A.; Mannino, F.; Minutoli, L.; Altavilla, D.; Squadrito, F. The Role of NLRP3 Inflammasome in the Pathogenesis of Traumatic Brain Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero-Andrés, A.; Panisello-Roselló, A.; Roselló-Catafau, J.; Folch-Puy, E. NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Inflammation in Acute Pancreatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dostert, C.; Pétrilli, V.; Van Bruggen, R.; Steele, C.; Mossman, B.T.; Tschopp, J. Innate immune activation through Nalp3 inflammasome sensing of asbestos and silica. Science 2008, 320, 674–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.M.; Kim, J.J.; Kim, H.J.; Shong, M.; Ku, B.J.; Jo, E.K. Upregulated NLRP3 inflammasome activation in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2013, 62, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baragetti, A.; Catapano, A.L.; Magni, P. Multifactorial Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasome: Relevance for a Precision Approach to Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Risk and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toldo, S.; Abbate, A. The NLRP3 inflammasome in acute myocardial infarction. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, R.J.; Robinson, J.I.; Battellino, M.; Wong, C.; Taylor, J.C.; Biologics in Rheumatoid Arthritis Genetics and Genomics Study Syndicate (BRAGGSS); Eyre, S.; Churchman, S.M.; Wilson, A.G.; Isaacs, J.D.; et al. Evidence of NLRP3-inflammasome activation in rheumatoid arthritis (RA); genetic variants within the NLRP3-inflammasome complex in relation to susceptibility to RA and response to anti-TNF treatment. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 1202–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneka, M.T.; Kummer, M.P.; Stutz, A.; Delekate, A.; Schwartz, S.; Vieira-Saecker, A.; Griep, A.; Axt, D.; Remus, A.; Tzeng, T.C.; et al. NLRP3 is activated in Alzheimer’s disease and contributes to pathology in APP/PS1 mice. Nature 2013, 493, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M.; Shichita, T.; Okada, M.; Komine, R.; Noguchi, Y.; Yoshimura, A.; Morita, R. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase is essential for NLRP3 inflammasome activation and contributes to ischaemic brain injury. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; MacFadyen, J.G.; Thuren, T.; Everett, B.M.; Libby, P.; Glynn, R.J.; CANTOS Trial Group. Effect of interleukin-1β inhibition with canakinumab on incident lung cancer in patients with atherosclerosis: Exploratory results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 1833–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastner, D.L.; Aksentijevich, I.; Goldbach-Mansky, R. Autoinflammatory disease reloaded: A clinical perspective. Cell 2010, 140, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Picard, C.; Bobby Gaspar, H.; Al-Herz, W.; Bousfiha, A.; Casanova, J.L.; Chatila, T.; Crow, Y.J.; Cunningham-Rundles, C.; Etzioni, A.; Franco, J.L.; et al. International Union of Immunological Societies: 2017 Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases Committee Report on Inborn Errors of Immunity. J. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 38, 96–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peckham, D.; Scambler, T.; Savic, S.; McDermott, M.F. The burgeoning field of innate immune-mediated disease and autoinflammation. J. Pathol. 2017, 241, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.L.; Chae, J.J.; Park, Y.H.; De Nardo, D.; Stirzaker, R.A.; Ko, H.J.; Tye, H.; Cengia, L.; DiRago, L.; Metcalf, D.; et al. Aberrant actin depolymerization triggers the pyrin inflammasome and autoinflammatory disease that is dependent on IL-18, not IL-1β. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 927–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sood, R.; Blake, T.; Aksentijevich, I.; Wood, G.; Chen, X.; Gardner, D.; Shelton, D.A.; Mangelsdorf, M.; Orsborn, A.; Pras, E.; et al. Construction of a 1-Mb restriction-mapped cosmid contig containing the candidate region for the familial Mediterranean fever locus (MEFV) on chromosome 16p 13.3. Genomics 1997, 42, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French FMF Consortium. A candidate gene for familial Mediterranean fever. Nat. Genet. 1997, 17, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, J.J.; Wood, G.; Masters, S.L.; Richard, K.; Park, G.; Smith, B.J.; Kastner, D.L. The B30.2 domain of pyrin, the familial Mediterranean fever protein, interacts directly with caspase-1 to modulate IL-1beta production. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 9982–9987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chae, J.J.; Cho, Y.H.; Lee, G.S.; Cheng, J.; Liu, P.P.; Feigenbaum, L.; Katz, S.I.; Kastner, D.L. Gain-of-function Pyrin mutations induce NLRP3 protein-independent interleukin-1β activation and severe autoinflammation in mice. Immunity 2011, 34, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsumoto, S.; Urayoshi, S.; Yoshida, Y. Familial Mediterranean fever in which Crohn’s disease was suspected: A case report. BMC Res. Notes 2014, 7, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asakura, K.; Yanai, S.; Nakamura, S.; Kawaski, K.; Eizuka, M.; Ishida, K.; Endo, M.; Sugai, T.; Migita, K.; Matsumoto, T. Familial Mediterranean fever mimicking Crohn disease: A case report. Medicine 2018, 97, e9547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitade, T.; Horiki, N.; Katsurahara, M.; Totoki, T.; Harada, T.; Tano, S.; Yamada, R.; Hamada, Y.; Inoue, H.; Tanaka, K.; et al. Usefulness of Small Intestinal Endoscopy in a Case of Adult-onset Familial Mediterranean Fever Associated with Jejunoileitis. Intern. Med. 2015, 54, 1343–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torisu, T.; Kawatoko, S.; Esaki, M. Febrile Attacks With a Refractory Colonic Lesion. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 19–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esaki, M.; Kawano, S.; Matsumoto, T. Rare cause of duodenojejunal pseudopolyposis: Report of a case of adult-onset familial Mediterranean fever. Dig. Endosc. 2017, 29, 394–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, D.; Hibi, N.; Ozaki, R.; Kikuchi, O.; Sato, T.; Tokunaga, S.; Minowa, S.; Ikezaki, O.; Mitsui, T.; Miura, M.; et al. MEFV Gene-Related Enterocolitis Account for Some Cases Diagnosed as Inflammatory Bowel Disease Unclassified. Digestion 2019, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.B.; Xavier, R.J. Pathway paradigms revealed from the genetics of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 2020, 578, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, H.S.; Fiocchi, C. Immunopathogenesis of IBD: Current state of the art. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramsothy, S.; Kamm, M.A.; Kaakoush, N.O.; Walsh, A.J.; van den Bogaerde, J.; Samuel, D.; Leong, R.W.L.; Connor, S.; Ng, W.; Paramsothy, R.; et al. Multidonor intensive faecal microbiota transplantation for active ulcerative colitis: A randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 1218–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungaro, R.; Mehandru, S.; Allen, P.B.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Colombel, J.F. Ulcerative colitis. Lancet 2017, 389, 1756–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranson, N.; Veldhuis, M.; Mitchell, B.; Fanning, S.; Cook, A.L.; Kunde, D.; Eri, R. NLRP3-Dependent and -Independent Processing of Interleukin (IL)-1β in Active Ulcerative Colitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 20, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villani, A.C.; Lemire, M.; Fortin, G.; Louis, E.; Silverberg, M.S.; Collette, C.; Baba, N.; Libioulle, C.; Belaiche, J.; Bitton, A.; et al. Common variants in the NLRP3 region contribute to Crohn’s disease susceptibility. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, B.K.; Pizarro, T.T. Commentary: The role of the IL-18 system and other members of the IL-1R/TLR superfamily in innate mucosal immunity and the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease: Friend or foe? Eur. J. Immunol. 2004, 34, 2347–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jostins, L.; Ripke, S.; Weersma, R.K.; Duerr, R.H.; McGovern, D.P.; Hui, K.Y.; Lee, J.C.; Schumm, L.P.; Sharma, Y.; Anderson, C.A.; et al. Host-microbe interactions have shaped the genetic architecture of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 2012, 491, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, S.; Ding, S.; Wang, P.; Wei, Z.; Pan, W.; Palm, N.W.; Yang, Y.; Yu, H.; Li, H.B.; Wang, G.; et al. Nlrp9b inflammasome restricts rotavirus infection in intestinal epithelial cells. Nature 2017, 546, 667–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, S.; Gagliani, N.; Flavell, R.A. Life, death, and miracles: Th17 cells in the intestine. Eur. J. Immunol. 2012, 42, 2238–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vela, J.M.; Molina-Holgado, E.; Arévalo-Martín, A.; Almazán, G.; Guaza, C. Interleukin-1 regulates proliferation and differentiation of oligodendrocyte progenitor cells. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2002, 20, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guarda, G.; So, A. Regulation of inflammasome activity. Immunology 2010, 130, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, M.; Ceballos-Olvera, I.; del Barrio, L.; Re, F. Role of the inflammasome, IL-1β, and IL-18 in bacterial infections. Sci. World J. 2011, 11, 2037–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coccia, M.; Harrison, O.J.; Schiering, C.; Asquith, M.J.; Becher, B.; Powrie, F.; Maloy, K.J. IL-1β mediates chronic intestinal inflammation by promoting the accumulation of IL-17A secreting innate lymphoid cells and CD4+ Th17 cells. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 1595–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cominelli, F.; Pizarro, T.T. Interleukin-1 and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1996, 10, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAlindon, M.E.; Hawkey, C.J.; Mahida, Y.R. Expression of interleukin 1 beta and interleukin 1 beta converting enzyme by intestinal macrophages in health and inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 1998, 42, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, C.; Duewell, P.; Mayer, C.; Lehr, H.A.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Dauer, M.; Tschopp, J.; Endres, S.; Latz, E.; Schnurr, M. Colitis induced in mice with dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) is mediated by the NLRP3 inflammasome. Gut 2010, 59, 1192–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasegawa, M.; Kamada, N.; Jiao, Y.; Liu, M.Z.; Núñez, G.; Inohara, N. Protective role of commensals against Clostridium difficile infection via an IL-1β-mediated positive-feedback loop. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 3085–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fan, H.; Zhao, G.; Liu, L.; Liu, F.; Gong, W.; Liu, X.; Yang, L.; Wang, J.; Hou, Y. Pre-treatment with IL-1β enhances the efficacy of MSC transplantation in DSS-induced colitis. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2012, 9, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itani, S.; Watanabe, T.; Nadatani, Y.; Sugimura, N.; Shimada, S.; Takeda, S.; Otani, K.; Hosomi, S.; Nagami, Y.; Tanaka, F.; et al. NLRP3 inflammasome has a protective effect against oxazolone-induced colitis: A possible role in ulcerative colitis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.J.; Zhang, L.; Lu, W.; Wang, L.; Chen, L.; Zhu, Z.; Zhu, H.H. Interleukin-18 genetic polymorphisms contribute differentially to the susceptibility to Crohn’s disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 8711–8722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Aleya, W.; Sfar, I.; Habibi, I.; Mouelhi, L.; Aouadi, H.; Makhlouf, M.; Ayed-Jendoubi, S.; Najjar, T.; Ben Abdallah, T.; Ayed, K.; et al. Interleukin-18 gene polymorphisms in tunisian patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Digestion 2011, 83, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Zhang, C.; Xing, Y.; Xue, G.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, F.; Wu, G.; Hu, Y.; Guo, Q.; Lu, A.; et al. Remodelling of the gut microbiota by hyperactive NLRP3 induces regulatory T cells to maintain homeostasis. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okamura, H.; Tsutsi, H.; Komatsu, T.; Yutsudo, M.; Hakura, A.; Tanimoto, T.; Torigoe, K.; Okura, T.; Nukada, Y.; Hattori, K.; et al. Cloning of a new cytokine that induces IFN-gamma production by T cells. Nature 1995, 378, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, S.T.; Messina, I.; Lemberg, D.A.; Novick, D.; Rubenstein, M.; Day, A.S. Local and systemic interleukin-18 and interleukin-18-binding protein in children with inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2008, 14, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteleone, G.; Trapasso, F.; Parrello, T.; Biancone, L.; Stella, A.; Iuliano, R.; Luzza, F.; Fusco, A.; Pallone, F. Bioactive IL-18 expression is up-regulated in Crohn’s disease. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 143–147. [Google Scholar]
- Pizarro, T.T.; Michie, M.H.; Bentz, M.; Woraratanadharm, J.; Smith MFJr Foley, E.; Moskaluk, C.A.; Bickston, S.J.; Cominelli, F. IL-18, a novel immunoregulatory cytokine, is up-regulated in Crohn’s disease: Expression and localization in intestinal mucosal cells. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 6829–6835. [Google Scholar]
- Sivakumar, P.V.; Westrich, G.M.; Kanaly, S.; Garka, K.; Born, T.L.; Derry, J.M.; Viney, J.L. Interleukin 18 is a primary mediator of the inflammation associated with dextran sulphate sodium induced colitis: Blocking interleukin 18 attenuates intestinal damage. Gut 2002, 50, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wirtz, S.; Becker, C.; Blumberg, R.; Galle, P.R.; Neurath, M.F. Treatment of T cell-dependent experimental colitis in SCID mice by local administration of an adenovirus expressing IL-18 antisense mRNA. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nowarski, R.; Jackson, R.; Gagliani, N.; de Zoete, M.R.; Palm, N.W.; Bailis, W.; Low, J.S.; Harman, C.C.; Graham, M.; Elinav, E.; et al. Epithelial IL-18 Equilibrium Controls Barrier Function in Colitis. Cell 2015, 163, 1444–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaki, M.H.; Boyd, K.L.; Vogel, P.; Kastan, M.B.; Lamkanfi, M.; Kanneganti, T.D. The NLRP3 inflammasome protects against loss of epithelial integrity and mortality during experimental colitis. Immunity 2010, 32, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martins, R.P.; Aguilar, C.; Graham, J.E.; Carvajal, A.; Bautista, R.; Claros, M.G.; Garrido, J.J. Pyroptosis and adaptive immunity mechanisms are promptly engendered in mesenteric lymph-nodes during pig infections with Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Vet. Res. 2013, 44, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kayagaki, N.; Stowe, I.B.; Lee, B.L.; O’Rourke, K.; Anderson, K.; Warming, S.; Cuellar, T.; Haley, B.; Roose-Girma, M.; Phung, Q.T.; et al. Caspase-11 cleaves gasdermin D for non-canonical inflammasome signalling. Nature 2015, 526, 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgensen, I.; Miao, E.A. Pyroptotic cell death defends against intracellular pathogens. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 265, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ey, B.; Eyking, A.; Klepak, M.; Salzman, N.H.; Göthert, J.R.; Rünzi, M.; Schmid, K.W.; Gerken, G.; Podolsky, D.K.; Cario, E. Loss of TLR2 worsens spontaneous colitis in MDR1A deficiency through commensally induced pyroptosis. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 5676–5688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulek, K.; Zhao, J.; Liao, Y.; Rana, N.; Corridoni, D.; Antanaviciute, A.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Qian, W.; Miller-Little, W.A.; et al. Epithelial-derived gasdermin D mediates nonlytic IL-1β release during experimental colitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 4218–4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Yang, D.; Wang, B.; Wu, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, X.; Lassen, K.; Dai, L.; Yang, S. Gasdermin D in macrophages restrains colitis by controlling cGAS-mediated inflammation. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz6717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deretic, V.; Saitoh, T.; Akira, S. Autophagy in infection, inflammation, and immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 722–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deretic, V.; Klionsky, D.J. Autophagy and inflammation: A special review issue. Autophagy 2018, 14, 179–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zaki, M.H.; Lamkanfi, M.; Kanneganti, T.D. The Nlrp3 inflammasome: Contributions to intestinal homeostasis. Trends Immunol. 2011, 32, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, C.S.; Shenderov, K.; Huang, N.N.; Kabat, J.; Abu-Asab, M.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Sher, A.; Kehrl, J.H. Activation of autophagy by inflammatory signals limits IL-1β production by targeting ubiquitinated inflammasomes for destruction. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitoh, T.; Fujita, N.; Jang, M.H.; Uematsu, S.; Yang, B.G.; Satoh, T.; Omori, H.; Noda, T.; Yamamoto, N.; Komatsu, M.; et al. Loss of the autophagy protein Atg16L1 enhances endotoxin-induced IL-1beta production. Nature 2008, 456, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassen, K.G.; Kuballa, P.; Conway, K.L.; Patel, K.K.; Becker, C.E.; Peloquin, J.M.; Villablanca, E.J.; Norman, J.M.; Liu, T.C.; Heath, R.J.; et al. Atg16L1 T300A variant decreases selective autophagy, resulting in altered cytokine signaling and decreased antibacterial defense. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7741–7746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ke, P.; Shao, B.Z.; Xu, Z.Q.; Wei, W.; Han, B.Z.; Chen, X.W.; Su, D.F.; Liu, C. Activation of Cannabinoid Receptor 2 Ameliorates DSS-Induced Colitis through Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome in Macrophages. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, R.; Yazdi, A.S.; Menu, P.; Tschopp, J. A role for mitochondria in NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Nature 2011, 469, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macia, L.; Tan, J.; Vieira, A.T.; Leach, K.; Stanley, D.; Luong, S.; Maruya, M.; Ian McKenzie, C.; Hijikata, A.; Wong, C.; et al. Metabolite-sensing receptors GPR43 and GPR109A facilitate dietary fibre-induced gut homeostasis through regulation of the inflammasome. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dupont, N.; Jiang, S.; Pilli, M.; Ornatowski, W.; Bhattacharya, D.; Deretic, V. Autophagy-based unconventional secretory pathway for extracellular delivery of IL-1β. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 4701–4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Kenny, S.J.; Ge, L.; Xu, K.; Schekman, R. Translocation of interleukin-1β into a vesicle intermediate in autophagy-mediated secretion. Elife 2015, 4, e11205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, S.Y.; Yang, C.H.; Chou, C.C.; Chiang, Y.P.; Chuang, T.H.; Hsu, L.C. TLR-induced PAI-2 expression suppresses IL-1β processing via increasing autophagy and NLRP3 degradation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 16079–16084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Requena, T.; Martínez-Cuesta, M.C.; Peláez, C. Diet and microbiota linked in health and disease. Food Funct 2018, 9, 688–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leone, V.; Chang, E.B.; Devkota, S. Diet, microbes, and host genetics: The perfect storm in inflammatory bowel diseases. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 48, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirota, S.A.; Ng, J.; Lueng, A.; Khajah, M.; Parhar, K.; Li, Y.; Lam, V.; Potentier, M.S.; Ng, K.; Bawa, M.; et al. NLRP3 inflammasome plays a key role in the regulation of intestinal homeostasis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2011, 17, 1359–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elinav, E.; Strowig, T.; Kau, A.L.; Henao-Mejia, J.; Thaiss, C.A.; Booth, C.J.; Peaper, D.R.; Bertin, J.; Eisenbarth, S.C.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. NLRP6 inflammasome regulates colonic microbial ecology and risk for colitis. Cell 2011, 145, 745–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, B.; Elinav, E.; Huber, S.; Strowig, T.; Hao, L.; Hafemann, A.; Jin, C.; Wunderlich, C.; Wunderlich, T.; Eisenbarth, S.C.; et al. Microbiota-induced activation of epithelial IL-6 signaling links inflammasome-driven inflammation with transmissible cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9862–9867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seo, S.U.; Kamada, N.; Muñoz-Planillo, R.; Kim, Y.G.; Kim, D.; Koizumi, Y.; Hasegawa, M.; Himpsl, S.D.; Browne, H.P.; Lawley, T.D.; et al. Distinct Commensals Induce Interleukin-1β via NLRP3 Inflammasome in Inflammatory Monocytes to Promote Intestinal Inflammation in Response to Injury. Immunity 2015, 42, 744–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De la Fuente, M.; Franchi, L.; Araya, D.; Díaz-Jiménez, D.; Olivares, M.; Álvarez-Lobos, M.; Golenbock, D.; González, M.J.; López-Kostner, F.; Quera, R.; et al. Escherichia coli isolates from inflammatory bowel diseases patients survive in macrophages and activate NLRP3 inflammasome. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 304, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, J.; Liu, G.; Xing, J.; Song, H.; Wang, Z. Fecal bacteria from Crohn’s disease patients more potently activated NOD-like receptors and Toll-like receptors in macrophages, in an IL-4-repressible fashion. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 121, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, H.M.; Apladas, A.; Scharl, M.; Fried, M.; Rogler, G. Probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 and commensal E. coli K12 differentially affect the inflammasome in intestinal epithelial cells. Digestion 2014, 89, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kruis, W.; Fric, P.; Pokrotnieks, J.; Lukás, M.; Fixa, B.; Kascák, M.; Kamm, M.A.; Weismueller, J.; Beglinger, C.; Stolte, M.; et al. Maintaining remission of ulcerative colitis with the probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 is as effective as with standard mesalazine. Gut 2004, 53, 1617–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Nogales, A.; Algieri, F.; Garrido-Mesa, J.; Vezza, T.; Utrilla, M.P.; Chueca, N.; Fernández-Caballero, J.A.; García, F.; Rodríguez-Cabezas, M.E.; Gálvez, J. The Administration of Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 Ameliorates Development of DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, M.S.; Seekatz, A.M.; Koropatkin, N.M.; Kamada, N.; Hickey, C.A.; Wolter, M.; Pudlo, N.A.; Kitamoto, S.; Terrapon, N.; Muller, A.; et al. A Dietary Fiber-Deprived Gut Microbiota Degrades the Colonic Mucus Barrier and Enhances Pathogen Susceptibility. Cell 2016, 167, 1339–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furusawa, Y.; Obata, Y.; Fukuda, S.; Endo, T.A.; Nakato, G.; Takahashi, D.; Nakanishi, Y.; Uetake, C.; Kato, K.; Kato, T.; et al. Commensal microbe-derived butyrate induces the differentiation of colonic regulatory T cells. Nature 2013, 504, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, H.S.P. Etiopathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease: Today and tomorrow. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2017, 33, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanaei, S.; Sadr, M.; Rezaei, A.; Shahkarami, S.; Ebrahimi Daryani, N.; Bidoki, A.Z.; Rezaei, N. Association of NLRP3 single nucleotide polymorphisms with ulcerative colitis: A case-control study. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2018, 42, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitomi, Y.; Ebisawa, M.; Tomikawa, M.; Imai, T.; Komata, T.; Hirota, T.; Harada, M.; Sakashita, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Shimojo, N.; et al. Associations of functional NLRP3 polymorphisms with susceptibility to food-induced anaphylaxis and aspirin-induced asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 124, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Hara, Y.; Kubota, T. CARD8 is a negative regulator for NLRP3 inflammasome, but mutant NLRP3 in cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes escapes the restriction. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, R52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mao, L.; Kitani, A.; Similuk, M.; Oler, A.J.; Albenberg, L.; Kelsen, J.; Aktay, A.; Quezado, M.; Yao, M.; Montgomery-Recht, K.; et al. Loss-of-function CARD8 mutation causes NLRP3 inflammasome activation and Crohn’s disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 1793–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.K.; Kim, H.; Hong, M.; Lim, J.; Choi, E.; Ye, B.D.; Park, S.K.; Song, K. Association of CARD8 with inflammatory bowel disease in Koreans. J. Hum. Genet 2011, 56, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagnall, R.D.; Roberts, R.G.; Mirza, M.M.; Torigoe, T.; Prescott, N.J.; Mathew, C.G. Novel isoforms of the CARD8 (TUCAN) gene evade a nonsense mutation. Eur. J. Hum. Genet 2008, 16, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.T.; Ma, X.J.; Zong, Y.; Du, X.M.; Hu, J.H.; Lu, G.C. Is the CARD8 rs2043211 polymorphism associated with susceptibility to Crohn’s disease? A meta-analysis. Autoimmunity 2015, 48, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, G.J.; Massey, D.C.; Zhang, H.; Bredin, F.; Tremelling, M.; Lee, J.C.; Berzuini, C.; Parkes, M. Genetic association between NLRP3 variants and Crohn’s disease does not replicate in a large UK panel. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2011, 17, 1387–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, G.P.; Uporova, L.; Halfvarson, J.; Sirsjö, A.; Fransén, K. Polymorphism in the NLRP3 inflammasome-associated EIF2AK2 gene and inflammatory bowel disease. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 4579–4584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.X.; Wang, Z.T.; Lu, X.X.; Wang, Y.G.; Zhong, J.; Liu, J. NLRP3 gene is associated with ulcerative colitis (UC), but not Crohn’s disease (CD), in Chinese Han population. Inflamm. Res. 2014, 63, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaridis, L.D.; Pistiki, A.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Georgitsi, M.; Damoraki, G.; Polymeros, D.; Dimitriadis, G.D.; Triantafyllou, K. Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasome in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Differences Between Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 2348–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegmund, B.; Lehr, H.A.; Fantuzzi, G.; Dinarello, C.A. IL-1 beta -converting enzyme (caspase-1) in intestinal inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 13249–13254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bauer, C.; Loher, F.; Dauer, M.; Mayer, C.; Lehr, H.A.; Schönharting, M.; Hallwachs, R.; Endres, S.; Eigler, A. The ICE inhibitor pralnacasan prevents DSS-induced colitis in C57BL/6 mice and suppresses IP-10 mRNA but not TNF-alpha mRNA expression. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2007, 52, 1642–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Fu, S.; Sun, S.; Li, Z.; Guo, B. Inflammasome activation has an important role in the development of spontaneous colitis. Mucosal. Immunol. 2014, 7, 1139–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dupaul-Chicoine, J.; Yeretssian, G.; Doiron, K.; Bergstrom, K.S.; McIntire, C.R.; LeBlanc, P.M.; Meunier, C.; Turbide, C.; Gros, P.; Beauchemin, N.; et al. Control of intestinal homeostasis, colitis, and colitis-associated colorectal cancer by the inflammatory caspases. Immunity 2010, 32, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mai, C.T.; Wu, M.M.; Wang, C.L.; Su, Z.R.; Cheng, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.J. Palmatine attenuated dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis via promoting mitophagy-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome inactivation. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 105, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wei, Z.; Wang, J.; Kou, J.; Liu, W.; Fu, Y.; Yang, Z. Alpinetin attenuates inflammatory responses by suppressing TLR4 and NLRP3 signaling pathways in DSS-induced acute colitis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, C.; Duewell, P.; Lehr, H.A.; Endres, S.; Schnurr, M. Protective and aggravating effects of Nlrp3 inflammasome activation in IBD models: Influence of genetic and environmental factors. Dig. Dis. 2012, 30, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruiz, P.A.; Morón, B.; Becker, H.M.; Lang, S.; Atrott, K.; Spalinger, M.R.; Scharl, M.; Wojtal, K.A.; Fischbeck-Terhalle, A.; Frey-Wagner, I.; et al. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles exacerbate DSS-induced colitis: Role of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Gut 2017, 66, 1216–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, G.; Zhang, F.; Fuss, I.; Kitani, A.; Strober, W. A mutation in the Nlrp3 gene causing inflammasome hyperactivation potentiates Th17 cell-dominant immune responses. Immunity 2009, 30, 860–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perera, A.P.; Fernando, R.; Shinde, T.; Gundamaraju, R.; Southam, B.; Sohal, S.S.; Robertson, A.A.B.; Schroder, K.; Kunde, D.; Eri, R. MCC950, a specific small molecule inhibitor of NLRP3 inflammasome attenuates colonic inflammation in spontaneous colitis mice. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, X.; Fan, W.; Tan, L.; Shi, Y.; Ding, C.; Liu, S.; Miao, Y.; Luo, Y.; Shi, X.; DeSaeger, S.; et al. Soy isoflavones ameliorate experimental colitis by targeting ERα/NLRP3 inflammasome pathways. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 83, 108438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, R.; Ma, Y.; Li, S.; Shen, D.; Yang, S.; Wang, X.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wei, Y.; Li, S.; et al. 1,25(OH)2D3 alleviates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis via inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 108, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Guo, Q.; Zhu, Q.; Tan, R.; Bai, D.; Bu, X.; Lin, B.; Zhao, K.; Pan, C.; Chen, H.; et al. Flavonoid VI-16 protects against DSS-induced colitis by inhibiting Txnip-dependent NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages via reducing oxidative stress. Mucosal. Immunol. 2019, 12, 1150–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carter, J.D.; Valeriano, J.; Vasey, F.B. Crohn disease worsened by anakinra administration. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2003, 9, 276–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena Rossi, C.; Hanauer, S.B.; Tomasevic, R.; Hunter, J.O.; Shafran, I.; Graffner, H. Interferon beta-1a for the maintenance of remission in patients with Crohn’s disease: Results of a phase II dose-finding study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2009, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Błażejewski, A.J.; Thiemann, S.; Schenk, A.; Pils, M.C.; Gálvez, E.J.C.; Roy, U.; Heise, U.; de Zoete, M.R.; Flavell, R.A.; Strowig, T. Microbiota Normalization Reveals that Canonical Caspase-1 Activation Exacerbates Chemically Induced Intestinal Inflammation. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 2319–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mamantopoulos, M.; Ronchi, F.; Van Hauwermeiren, F.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Yilmaz, B.; Martens, L.; Saeys, Y.; Drexler, S.K.; Yazdi, A.S.; Raes, J.; et al. Nlrp6- and ASC-Dependent Inflammasomes Do Not Shape the Commensal Gut Microbiota Composition. Immunity 2017, 47, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mamantopoulos, M.; Ronchi, F.; McCoy, K.D.; Wullaert, A. Inflammasomes make the case for littermate-controlled experimental design in studying host-microbiota interactions. Gut Microbes. 2018, 9, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Mouse Model | Method to Control Microbiota Composition | Trigger | Effect on Colitis Compared to WT | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NLRP3 KO | Littermate, Cohousing | DSS | Exacerbated | [115] |
| NLRP3 KO | Littermate, Cohousing | TNBS | Exacerbated | [115] |
| NLRP3 KO | Cohousing | oxazolone | Exacerbated | [83] |
| NLRP3 KO | Cohousing | DSS | Ameliorated | [144] |
| NLRP3 KO | Cohousing | TNBS | Ameliorated | [144] |
| NLRP3 KO | None | DSS | Exacerbated | [94] |
| NLRP3 KO | None | DSS | Ameliorated | [80] |
| NLRP3 KO | None | titanium dioxide nanoparticles | Ameliorated | [145] |
| ASC KO | None | DSS | Exacerbated | [94] |
| ASC KO | None | DSS | Exacerbated | [116] |
| ASC KO | None | C. difficile infection | Exacerbated | [81] |
| Caspase-1 KO | Embryo transfer, Cohousing | DSS | Ameliorated | [153] |
| Caspase-1 KO | Cohousing | oxazolone | Exacerbated | [83] |
| Caspase-1 KO | None | DSS | Exacerbated | [94] |
| Caspase-1 KO | None | DSS | Exacerbated | [141] |
| Caspase-1 KO | None | DSS | Ameliorated | [138] |
| IL-18 KO in intestinal epithelial cells | Littermate, Cohousing | DSS | Ameliorated | [93] |
| IL-18r1 KO in intestinal epithelial cells | Littermate, Cohousing | DSS | Ameliorated | [93] |
| Gasdermin D KO | Littermate, Cohousing | DSS | Exacerbated | [100] |
| Gasdermin D KO | Littermate | DSS | Ameliorated (compared to heterozygous control littermates gasdermin D+/−) | [99] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wagatsuma, K.; Nakase, H. Contradictory Effects of NLRP3 Inflammasome Regulatory Mechanisms in Colitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8145. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218145
Wagatsuma K, Nakase H. Contradictory Effects of NLRP3 Inflammasome Regulatory Mechanisms in Colitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(21):8145. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218145
Chicago/Turabian StyleWagatsuma, Kohei, and Hiroshi Nakase. 2020. "Contradictory Effects of NLRP3 Inflammasome Regulatory Mechanisms in Colitis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 21: 8145. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218145
APA StyleWagatsuma, K., & Nakase, H. (2020). Contradictory Effects of NLRP3 Inflammasome Regulatory Mechanisms in Colitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(21), 8145. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218145






