Alcohol Addiction, Gut Microbiota, and Alcoholism Treatment: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Alcohol Use Disorder and Cognition Impairment
3. Thiamine Deficiency and Alcohol Encephalopathy (Wernicke–Korsakoff Syndrome)
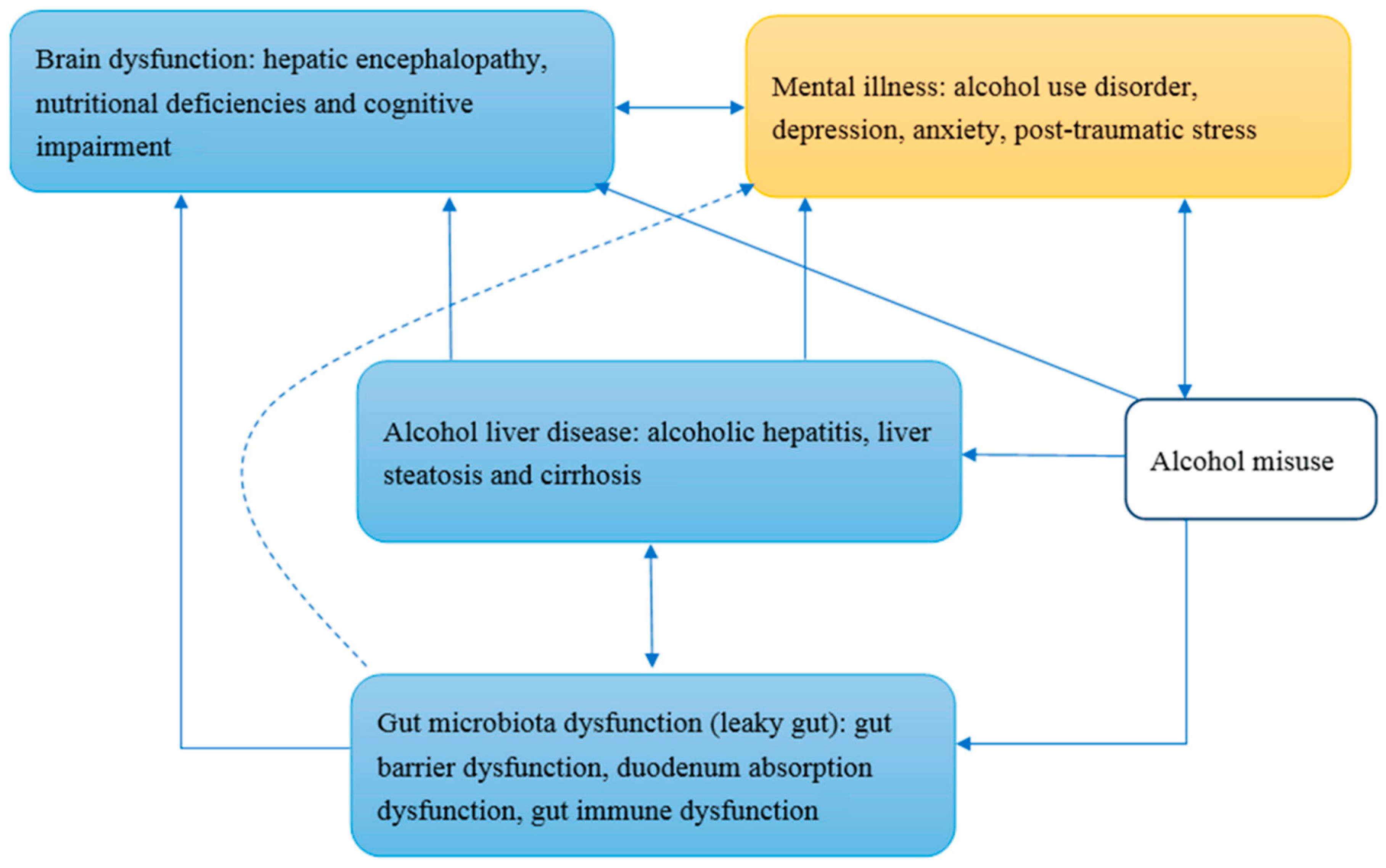
4. Alcohol Addiction and the Gut–Brain–Liver Axis
5. Current and Potential Medical Treatment for Alcohol Addiction
6. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rehm, J.; Mathers, C.; Popova, S.; Thavorncharoensap, M.; Teerawattananon, Y.; Patra, J. Global burden of disease and injury and economic cost attributable to alcohol use and alcohol-use disorders. Lancet 2009, 373, 2223–2233. [Google Scholar]
- Griswold, M.G.; Fullman, N.; Hawley, C.; Arian, N.; Zimsen, S.R.; Tymeson, H.D.; Venkateswaran, V.; Tapp, A.D.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Salama, J.S. Alcohol use and burden for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2018, 392, 1015–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Mathurin, P.; Bataller, R. Trends in the management and burden of alcoholic liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, S38–S46. [Google Scholar]
- Gilpin, N.W.; Koob, G.F. Neurobiology of alcohol dependence: Focus on motivational mechanisms. Alcohol Res. Health 2008, 31, 185. [Google Scholar]
- McLellan, A.T.; Lewis, D.C.; O’brien, C.P.; Kleber, H.D. Drug dependence, a chronic medical illness: Implications for treatment, insurance, and outcomes evaluation. JAMA 2000, 284, 1689–1695. [Google Scholar]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5®); American Psychiatric Pub: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kandel, D.B. Stages and Pathways of Drug Involvement: Examining the Gateway Hypothesis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Jonas, D.E.; Amick, H.R.; Feltner, C.; Bobashev, G.; Thomas, K.; Wines, R.; Kim, M.M.; Shanahan, E.; Gass, C.E.; Rowe, C.J. Pharmacotherapy for adults with alcohol use disorders in outpatient settings: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2014, 311, 1889–1900. [Google Scholar]
- Maisel, N.C.; Blodgett, J.C.; Wilbourne, P.L.; Humphreys, K.; Finney, J.W. Meta-analysis of naltrexone and acamprosate for treating alcohol use disorders: When are these medications most helpful? Addiction 2013, 108, 275–293. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S. Historical review: Opiate addiction and opioid receptors. Cell Transplant. 2019, 28, 233–238. [Google Scholar]
- Bajaj, J.S. Alcohol, liver disease and the gut microbiota. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 235–246. [Google Scholar]
- Day, E.; Bentham, P.; Callaghan, R.; Kuruvilla, T.; George, S. Thiamine for Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome in people at risk from alcohol abuse. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclercq, S.; Stärkel, P.; Delzenne, N.M.; de Timary, P. The gut microbiota: A new target in the management of alcohol dependence? Alcohol 2019, 74, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- National Institute for Clinical Excellence (NICE). Alcohol Use Disorders: Diagnosis and Clinical Management of Alcohol-related Physical Complications; NICE: Nice, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ries, R.K.; Miller, S.C.; Fiellin, D.A. Principles of Addiction Medicine; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Malenka, R.C.; Nestler, E.; Hyman, S.; Sydor, A.; Brown, R. Molecular Neuropharmacology: A Foundation for Clinical Neuroscience; McGraw-Hill Medical: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, A.D. Mechanisms of vitamin deficiency in chronic alcohol misusers and the development of the Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome. Alcohol Alcohol. 2000, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, M.; Adams, R.D.; Collins, G.H. The Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome. A clinical and pathological study of 245 patients, 82 with post-mortem examinations. Contemp. Neurol. Ser. 1971, 7, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Kessels, R.P.; Kortrijk, H.E.; Wester, A.J.; Nys, G.M. Confabulation behavior and false memories in Korsakoff’s syndrome: Role of source memory and executive functioning. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2008, 62, 220–225. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, K.; Agartz, I.; Harper, C.; Shoaf, S.; Rawlings, R.R.; Momenan, R.; Hommer, D.W.; Pfefferbaum, A.; Sullivan, E.V.; Anton, R.F. Neuroimaging in alcoholism: Ethanol and brain damage. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2001, 25, 104S–109S. [Google Scholar]
- Roger, F.B. Pathophysiology of cerebellar dysfunction in the Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 1993, 20, S123–S126. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, P.R.; Singleton, C.K.; Hiller-Sturmhöfel, S. The role of thiamine deficiency in alcoholic brain disease. Alcohol Res. Health 2003, 27, 134. [Google Scholar]
- Osiezagha, K.; Ali, S.; Freeman, C.; Barker, N.C.; Jabeen, S.; Maitra, S.; Olagbemiro, Y.; Richie, W.; Bailey, R.K. Thiamine deficiency and delirium. Innov. Clin. Neurosci. 2013, 10, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Sechi, G.; Serra, A. Wernicke’s encephalopathy: New clinical settings and recent advances in diagnosis and management. Lancet Neurol. 2007, 6, 442–455. [Google Scholar]
- Rehm, J.; Samokhvalov, A.V.; Shield, K.D. Global burden of alcoholic liver diseases. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 160–168. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, S.J.; Harrison, S.A. Comparison of the natural history of alcoholic and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2005, 7, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. Alcohol Facts and Statistics; NIAAA, National Institutes of Health, US Department of Health and Human: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mutlu, E.A.; Gillevet, P.M.; Rangwala, H.; Sikaroodi, M.; Naqvi, A.; Engen, P.A.; Kwasny, M.; Lau, C.K.; Keshavarzian, A. Colonic microbiome is altered in alcoholism. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 302, G966–G978. [Google Scholar]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Ridlon, J.M.; Hylemon, P.B.; Thacker, L.R.; Heuman, D.M.; Smith, S.; Sikaroodi, M.; Gillevet, P.M. Linkage of gut microbiome with cognition in hepatic encephalopathy. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 302, G168–G175. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.H.; Suk, K.T.; Kim, D.J.; Kim, M.Y.; Baik, S.K.; Kim, Y.D.; Cheon, G.J.; Choi, D.H.; Ham, Y.L.; Shin, D.H. Effects of probiotics (cultured Lactobacillus subtilis/Streptococcus faecium) in the treatment of alcoholic hepatitis: Randomized-controlled multicenter study. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 27, 1300–1306. [Google Scholar]
- Leclercq, S.; Matamoros, S.; Cani, P.D.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Jamar, F.; Stärkel, P.; Windey, K.; Tremaroli, V.; Bäckhed, F.; Verbeke, K. Intestinal permeability, gut-bacterial dysbiosis, and behavioral markers of alcohol-dependence severity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E4485–E4493. [Google Scholar]
- Kirpich, I.A.; Solovieva, N.V.; Leikhter, S.N.; Shidakova, N.A.; Lebedeva, O.V.; Sidorov, P.I.; Bazhukova, T.A.; Soloviev, A.G.; Barve, S.S.; McClain, C.J. Probiotics restore bowel flora and improve liver enzymes in human alcohol-induced liver injury: A pilot study. Alcohol 2008, 42, 675–682. [Google Scholar]
- Keshavarzian, A.; Choudhary, S.; Holmes, E.W.; Yong, S.; Banan, A.; Jakate, S.; Fields, J.Z. Preventing gut leakiness by oats supplementation ameliorates alcohol-induced liver damage in rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 299, 442–448. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrier, L.; Bérard, F.; Debrauwer, L.; Chabo, C.; Langella, P.; Buéno, L.; Fioramonti, J. Impairment of the intestinal barrier by ethanol involves enteric microflora and mast cell activation in rodents. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 168, 1148–1154. [Google Scholar]
- Forsyth, C.B.; Farhadi, A.; Jakate, S.M.; Tang, Y.; Shaikh, M.; Keshavarzian, A. Lactobacillus GG treatment ameliorates alcohol-induced intestinal oxidative stress, gut leakiness, and liver injury in a rat model of alcoholic steatohepatitis. Alcohol 2009, 43, 163–172. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, G.; Zhong, W.; Zheng, X.; Li, Q.; Qiu, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, H.; Zhou, Z.; Jia, W. Chronic ethanol consumption alters mammalian gastrointestinal content metabolites. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 3297–3306. [Google Scholar]
- Bull-Otterson, L.; Feng, W.; Kirpich, I.; Wang, Y.; Qin, X.; Liu, Y.; Gobejishvili, L.; Joshi-Barve, S.; Ayvaz, T.; Petrosino, J. Metagenomic analyses of alcohol induced pathogenic alterations in the intestinal microbiome and the effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG treatment. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53028. [Google Scholar]
- Leclercq, S.; De Saeger, C.; Delzenne, N.; de Timary, P.; Stärkel, P. Role of inflammatory pathways, blood mononuclear cells, and gut-derived bacterial products in alcohol dependence. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 76, 725–733. [Google Scholar]
- Felger, J.C.; Lotrich, F.E. Inflammatory cytokines in depression: Neurobiological mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Neuroscience 2013, 246, 199–229. [Google Scholar]
- Ashwood, P.; Krakowiak, P.; Hertz-Picciotto, I.; Hansen, R.; Pessah, I.; Van de Water, J. Elevated plasma cytokines in autism spectrum disorders provide evidence of immune dysfunction and are associated with impaired behavioral outcome. Brain Behav. Immun. 2011, 25, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Hasin, D.S.; Stinson, F.S.; Ogburn, E.; Grant, B.F. Prevalence, correlates, disability, and comorbidity of DSM-IV alcohol abuse and dependence in the United States: Results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2007, 64, 830–842. [Google Scholar]
- de Timary, P.; Stärkel, P.; Delzenne, N.M.; Leclercq, S. A role for the peripheral immune system in the development of alcohol use disorders? Neuropharmacology 2017, 122, 148–160. [Google Scholar]
- Dantzer, R.; Kelley, K.W. Twenty years of research on cytokine-induced sickness behavior. Brain Behav. Immun. 2007, 21, 153–160. [Google Scholar]
- Dantzer, R.; O’Connor, J.C.; Freund, G.G.; Johnson, R.W.; Kelley, K.W. From inflammation to sickness and depression: When the immune system subjugates the brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 46–56. [Google Scholar]
- Koob, G.F.; Le Moal, M. Plasticity of reward neurocircuitry and the ‘dark side’ of drug addiction. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 1442–1444. [Google Scholar]
- Stokes, M.; Abdijadid, S. Disulfiram; NCBI: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.-C.; Chen, Y.-C.; Lee, C.-H.; Cheng, C.-M. Opioid Addiction, Genetic Susceptibility, and Medical Treatments: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4294. [Google Scholar]
- Ogborne, A.C. Identifying and treating patients with alcohol-related problems. CMAJ 2000, 162, 1705–1708. [Google Scholar]
- Soyka, M.; Müller, C.A. Pharmacotherapy of alcoholism—An update on approved and off-label medications. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2017, 18, 1187–1199. [Google Scholar]
- Anton, R.F.; Latham, P.; Voronin, K.; Book, S.; Hoffman, M.; Prisciandaro, J.; Bristol, E. Efficacy of Gabapentin for the Treatment of Alcohol Use Disorder in Patients With Alcohol Withdrawal Symptoms: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 728–736. [Google Scholar]
- Stadlbauer, V.; Mookerjee, R.P.; Hodges, S.; Wright, G.A.; Davies, N.A.; Jalan, R. Effect of probiotic treatment on deranged neutrophil function and cytokine responses in patients with compensated alcoholic cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2008, 48, 945–951. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.-C. Introductory Chapter: Gene Editing Technologies and Applications. In Gene Editing-Technologies and Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Horvath, P.; Barrangou, R. CRISPR/Cas, the immune system of bacteria and archaea. Science 2010, 327, 167–170. [Google Scholar]
- DiCarlo, J.E.; Norville, J.E.; Mali, P.; Rios, X.; Aach, J.; Church, G.M. Genome engineering in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using CRISPR-Cas systems. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 4336–4343. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Sheng, J.; Trang, P.; Liu, F. Potential application of the CRISPR/Cas9 system against herpesvirus infections. Viruses 2018, 10, 291. [Google Scholar]
- ENOCH, M.A. Genetic and environmental influences on the development of alcoholism: Resilience vs. risk. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1094, 193–201. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, D.M.; Taylor, R.E. Health-related effects of genetic variations of alcohol-metabolizing enzymes in African Americans. Alcohol Res. Health 2007, 30, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Edenberg, H.J. The genetics of alcohol metabolism: Role of alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase variants. Alcohol Res. Health 2007, 30, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. The Birth of CRISPR Inc.; American Association for the Advancement of Science: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
| Treatments | Indication/Authorities Approval | Mechanisms of Action |
|---|---|---|
| current pharmacological treatments | ||
| Use ONLY as adjunct to supportive and psychotherapeutic treatment, in motivated patients /FDA approved | Aversive agent, ALDH inhibitor (blocks the metabolism of alcohol’s primary metabolite acetaldehyde) |
| Treatment in patients who have been able to abstain from alcohol, decrease the desire, the amount and the frequency of drinking before treatment initiation /FDA approved | μ-opioid receptor antagonist, blocks β-endorphin release induced by alcohol |
| reduce alcohol consumption in combination with psychological support for people who drink heavily /EMA approved | μ and δ-opioid receptor antagonist; κ-opioid receptor partial agonist |
| Indicated for maintenance of alcohol abstinence in patients who are abstinent at treatment initiation /FDA approved | Acts on GABA and glutamate neurotransmitter systems; still under investigation |
| Reduce symptoms of alcohol withdrawal, alcohol dependence, and craving /Still under investigation | GABA inhibitor and calcium channel blocker |
| Still under investigation /Temporary recommendation issued by the French drug agency ANSM | GABA receptor agonist |
| current diet supplements | ||
| Treat and prevent thiamine deficiency and disorders that result from it, such as Wernicke encephalopathy /Diet supplement | Vitamin B1 supplement |
| Improve intestinal barrier integrity and ameliorates alcohol-induced liver damage /Diet supplement | Alteration of the gut microbiota by changing secretion of specific metabolites involved in gut barrier dysfunction, might improve vitamin B1 absorption; still under investigation |
| potential treatments | ||
| Still under investigation | Might target the gene related to ADH and ALDH, the major enzymes involved in alcohol metabolism |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.-C.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chen, S.-J.; Lee, C.-H.; Cheng, C.-M. Alcohol Addiction, Gut Microbiota, and Alcoholism Treatment: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6413. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176413
Wang S-C, Chen Y-C, Chen S-J, Lee C-H, Cheng C-M. Alcohol Addiction, Gut Microbiota, and Alcoholism Treatment: A Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(17):6413. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176413
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shao-Cheng, Yuan-Chuan Chen, Shaw-Ji Chen, Chun-Hung Lee, and Ching-Ming Cheng. 2020. "Alcohol Addiction, Gut Microbiota, and Alcoholism Treatment: A Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 17: 6413. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176413
APA StyleWang, S.-C., Chen, Y.-C., Chen, S.-J., Lee, C.-H., & Cheng, C.-M. (2020). Alcohol Addiction, Gut Microbiota, and Alcoholism Treatment: A Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(17), 6413. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176413






