The Chloroplast RNA Binding Protein CP31A Has a Preference for mRNAs Encoding the Subunits of the Chloroplast NAD(P)H Dehydrogenase Complex and Is Required for Their Accumulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
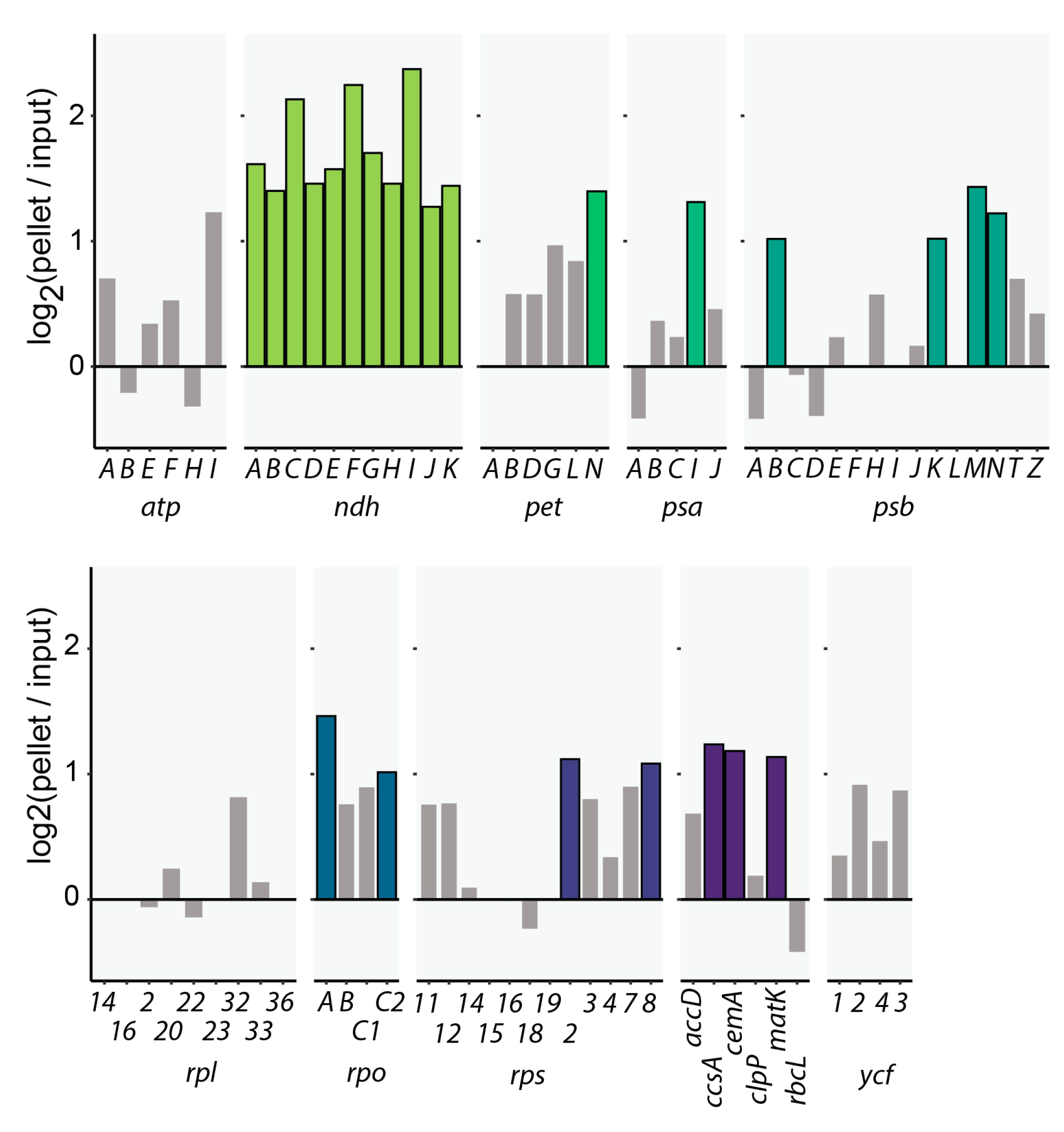
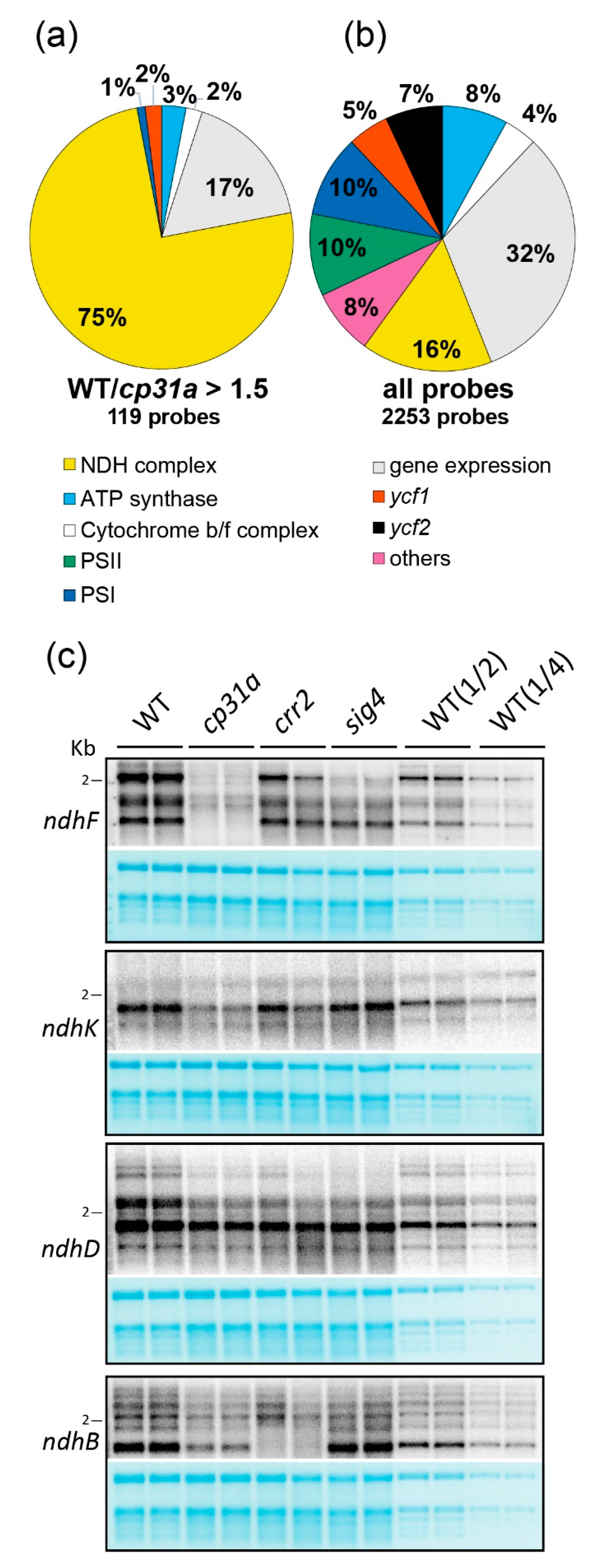
2.1. CP31A Has a Preference for Transcripts Encoding Subunits of the NDH Complex
2.2. NDH mRNAs Are Reduced in cp31a Null Mutants
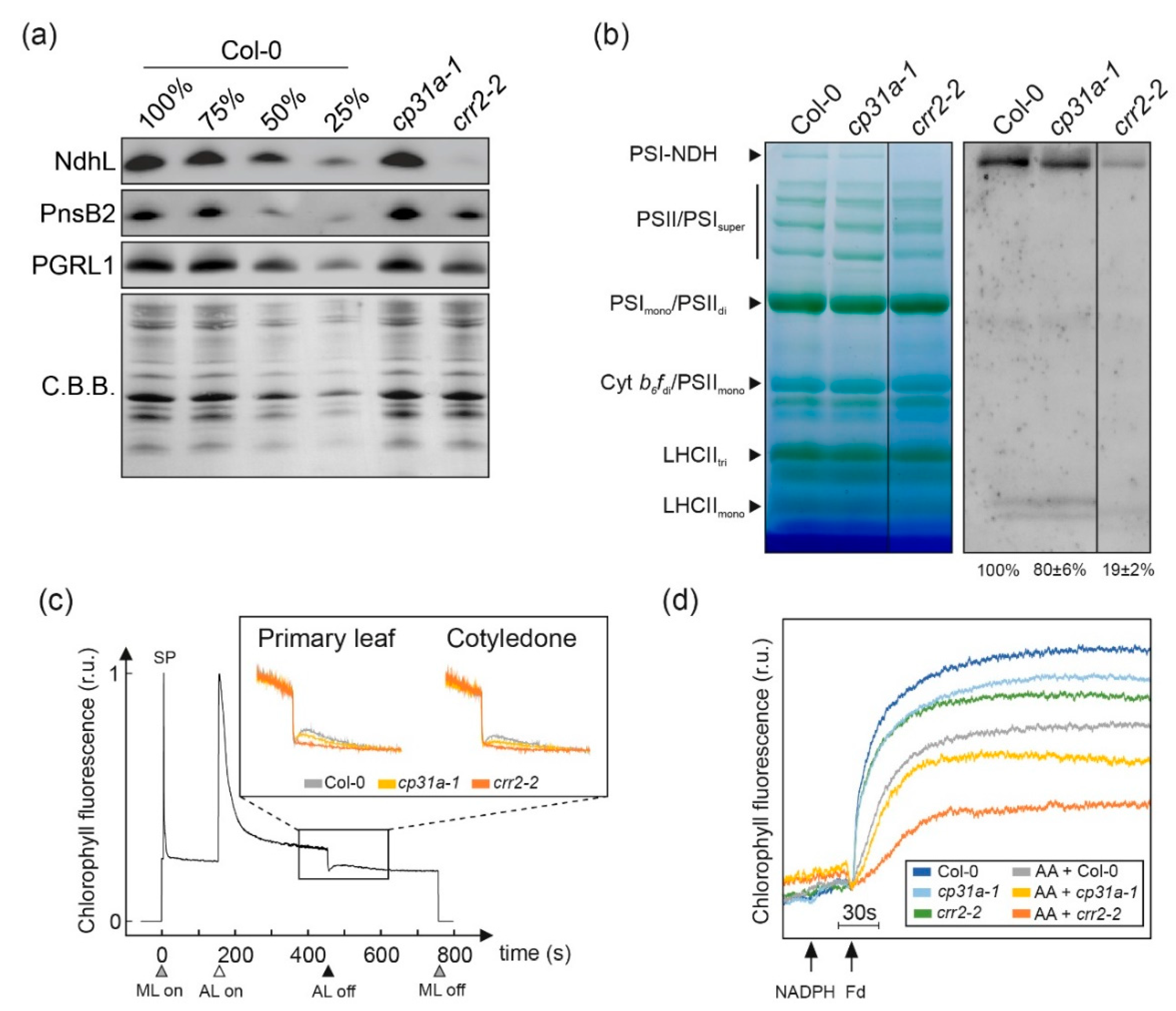
2.3. NDH Complex Activity Is Reduced, but Not Absent, in cp31a Mutants
3. Discussion
3.1. CP31A Co-Regulates ndh Genes
3.2. CP31A Supports NDH Activity
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Growth
4.2. Immunoblot Analysis
4.3. DO-RIP-Seq Analysis
4.4. Microarray Analysis
4.5. RNA Extraction and RNA Gel Blot Analysis
4.6. Analysis of NDH Complex Abundance
4.7. NDH Complex Activity Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RBP | RNA binding protein |
| DO-RIP-Seq | Digestion-optimized RNA co-immunoprecipitation and sequencing |
| cpRNP | Chloroplast ribonucleoprotein |
| NDH complex | NAD(P)H dehydrogenase-like (NDH) complex |
| Fd | ferredoxin |
References
- Barkan, A. Expression of plastid genes: Organelle-specific elaborations on a prokaryotic scaffold. Plant Physiol. 2011, 155, 1520–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsunoyama, Y.; Ishizaki, Y.; Morikawa, K.; Kobori, M.; Nakahira, Y.; Takeba, G.; Toyoshima, Y.; Shiina, T. Blue light-induced transcription of plastid-encoded psbd gene is mediated by a nuclear-encoded transcription initiation factor, atsig5. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 3304–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfannschmidt, T. Chloroplast redox signals: How photosynthesis controls its own genes. Trends Plant Sci. 2003, 8, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhard, S.; Drapier, D.; Wollman, F. Searching limiting steps in the expression of chloroplast-encoded proteins: Relations between gene copy number, transcription, transcript abundance and translation rate in the chloroplast of chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant J. 2002, 31, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udy, D.B.; Belcher, S.; Williams-Carrier, R.; Gualberto, J.M.; Barkan, A. Effects of reduced chloroplast gene copy number on chloroplast gene expression in maize. Plant Physiol. 2012, 160, 1420–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.-W.; Gruissem, W. Control of plastid gene expression during development: The limited role of transcriptional regulation. Cell 1987, 49, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentzen, W.I.; Wurtele, E.S. Regulon organization of arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol. 2008, 8, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, W.K.; Geimer, S.; Meurer, J. Cluster analysis and comparison of various chloroplast transcriptomes and genes in arabidopsis thaliana. DNA Res. 2009, 16, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Favory, J.J.; Kobayshi, M.; Tanaka, K.; Peltier, G.; Kreis, M.; Valay, J.G.; Lerbs-Mache, S. Specific function of a plastid sigma factor for ndhf gene transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 5991–5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanamaru, K.; Nagashima, A.; Fujiwara, M.; Shimada, H.; Shirano, Y.; Nakabayashi, K.; Shibata, D.; Tanaka, K.; Takahashi, H. An arabidopsis sigma factor (sig2)-dependent expression of plastid-encoded trnas in chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol. 2001, 42, 1034–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selinger, D.W.; Saxena, R.M.; Cheung, K.J.; Church, G.M.; Rosenow, C. Global rna half-life analysis in escherichia coli reveals positional patterns of transcript degradation. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaff, P.; Gruissem, W. Changes in chloroplast mrna stability during leaf development. Plant Cell 1991, 3, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germain, A.; Kim, S.H.; Gutierrez, R.; Stern, D.B. Ribonuclease ii preserves chloroplast rna homeostasis by increasing mrna decay rates, and cooperates with polynucleotide phosphorylase in 3’ end maturation. Plant J. 2012, 72, 960–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkan, A.; Small, I. Pentatricopeptide repeat proteins in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2014, 65, 415–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruwe, H.; Kupsch, C.; Teubner, M.; Schmitz-Linneweber, C. The rna-recognition motif in chloroplasts. J. Plant Physiol. 2011, 168, 1361–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimmer, J.; Rodiger, A.; Hoehenwarter, W.; Helm, S.; Baginsky, S. The rna-binding protein rnp29 is an unusual toc159 transport substrate. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Q.; Sugiura, M. Three distinct ribonucleoproteins from tobacco chloroplasts: Each contains a unique amino terminal acidic domain and two ribonucleoprotein consensus motifs. Embo J. 1990, 9, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillich, M.; Hardel, S.L.; Kupsch, C.; Armbruster, U.; Delannoy, E.; Gualberto, J.M.; Lehwark, P.; Leister, D.; Small, I.D.; Schmitz-Linneweber, C. Chloroplast ribonucleoprotein cp31a is required for editing and stability of specific chloroplast mrnas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 6002–6007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupsch, C.; Ruwe, H.; Gusewski, S.; Tillich, M.; Small, I.; Schmitz-Linneweber, C. Arabidopsis chloroplast rna binding proteins cp31a and cp29a associate with large transcript pools and confer cold stress tolerance by influencing multiple chloroplast rna processing steps. Plant Cell 2012, 10, 4266–4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, C.O.; Friedersdorf, M.; Keene, J.D. Quantifying rna binding sites transcriptome-wide using do-rip-seq. RNA 2017, 23, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, M.; Endo, T.; Peltier, G.; Tasaka, M.; Shikanai, T. A nucleus-encoded factor, crr2, is essential for the expression of chloroplast ndhb in arabidopsis. Plant J. 2003, 36, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meurer, J.; Berger, A.; Westhoff, P. A nuclear mutant of arabidopsis with impaired stability on distinct transcripts of the plastid psbb, psbd/c, ndhh, and ndhc operons. Plant Cell 1996, 8, 1193–1207. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Otani, T.; Kato, Y.; Shikanai, T. Specific substitutions of light-harvesting complex i proteins associated with photosystem i are required for supercomplex formation with chloroplast nadh dehydrogenase-like complex. Plant J. 2018, 94, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shikanai, T.; Endo, T.; Hashimoto, T.; Yamada, Y.; Asada, K.; Yokota, A. Directed disruption of the tobacco ndhb gene impairs cyclic electron flow around photosystem i. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 9705–9709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munekage, Y.; Hojo, M.; Meurer, J.; Endo, T.; Tasaka, M.; Shikanai, T. Pgr5 is involved in cyclic electron flow around photosystem i and is essential for photoprotection in arabidopsis. Cell 2002, 110, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armbruster, U.; Zuhlke, J.; Rengstl, B.; Kreller, R.; Makarenko, E.; Ruhle, T.; Schunemann, D.; Jahns, P.; Weisshaar, B.; Nickelsen, J.; et al. The arabidopsis thylakoid protein pam68 is required for efficient d1 biogenesis and photosystem ii assembly. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 3439–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoschke, R.; Bock, R. Chloroplast translation: Structural and functional organization, operational control, and regulation. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 745–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, K.; Koster, T.; Nolte, C.; Weinholdt, C.; Lewinski, M.; Grosse, I.; Staiger, D. Adaptation of iclip to plants determines the binding landscape of the clock-regulated rna-binding protein atgrp7. Genome Biol. 2017, 18, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Sugiura, M. Domains required for nucleic acid binding activities in chloroplast ribonucleoproteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992, 20, 6275–6279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Q.; Sugiura, M. Nucleic acid-binding specificities of tobacco chloroplast ribonucleoproteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991, 19, 2893–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Ohta, M.; Sugiura, M.; Sugita, M. Chloroplast ribonucleoproteins function as a stabilizing factor of ribosome-free mrnas in the stroma. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choquet, Y.; Wostrikoff, K.; Rimbault, B.; Zito, F.; Girard-Bascou, J.; Drapier, D.; Wollman, F.A. Assembly-controlled regulation of chloroplast gene translation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2001, 29, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keene, J.D. Rna regulons: Coordination of post-transcriptional events. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townley-Tilson, W.H.; Pendergrass, S.A.; Marzluff, W.F.; Whitfield, M.L. Genome-wide analysis of mrnas bound to the histone stem-loop binding protein. RNA 2006, 12, 1853–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lykke-Andersen, J.; Wagner, E. Recruitment and activation of mrna decay enzymes by two are-mediated decay activation domains in the proteins ttp and brf-1. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, A.P.; Herschlag, D.; Brown, P.O. Extensive association of functionally and cytotopically related mrnas with puf family rna-binding proteins in yeast. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, E79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shikanai, T. Chloroplast ndh: A different enzyme with a structure similar to that of respiratory nadh dehydrogenase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1857, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, T.; Shikanai, T.; Takabayashi, A.; Asada, K.; Sato, F. The role of chloroplastic nad(p)h dehydrogenase in photoprotection. FEBS Lett. 1999, 457, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takabayashi, A.; Endo, T.; Shikanai, T.; Sato, F. Post-illumination reduction of the plastoquinone pool in chloroplast transformants in which chloroplastic nad(p)h dehydrogenase was inactivated. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2002, 66, 2107–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, N.; Endo, T.; Sato, F. Electron transport activities of arabidopsis thaliana mutants with impaired chloroplastic nad(p)h dehydrogenase. J. Plant Res. 2008, 121, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, C.; Krause, G.H. Study of tobacco transformants to assess the role of chloroplastic nad(p)h dehydrogenase in photoprotection of photosystems i and ii. Planta 2002, 216, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strand, D.D.; Livingston, A.K.; Satoh-Cruz, M.; Froehlich, J.E.; Maurino, V.G.; Kramer, D.M. Activation of cyclic electron flow by hydrogen peroxide in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5539–5544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikkanen, L.; Toivola, J.; Trotta, A.; Diaz, M.G.; Tikkanen, M.; Aro, E.M.; Rintamaki, E. Regulation of cyclic electron flow by chloroplast nadph-dependent thioredoxin system. Plant Direct 2018, 2, e00093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamori, W.; Shikanai, T. Physiological functions of cyclic electron transport around photosystem i in sustaining photosynthesis and plant growth. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2016, 67, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, C.O.; Friedersdorf, M.B.; Bisogno, L.S.; Keene, J.D. Do-rip-seq to quantify rna binding sites transcriptome-wide. Methods 2017, 118–119, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoschke, R.; Watkins, K.P.; Barkan, A. A rapid ribosome profiling method elucidates chloroplast ribosome behavior in vivo. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 2265–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, M.; Ruwe, H.; Miranda, R.G.; Zoschke, R.; Hase, N.; Schmitz-Linneweber, C.; Barkan, A. Unexpected functional versatility of the pentatricopeptide repeat proteins pgr3, ppr5 and ppr10. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvi, S.; Suorsa, M.; Paakkarinen, V.; Aro, E.M. Optimized native gel systems for separation of thylakoid protein complexes: Novel super- and mega-complexes. Biochem. J. 2011, 439, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porra, R.J.; Thompson, W.A.; Kriedemann, P.E. Determination of accurate extinction coefficients and simultaneous equations for assaying chlorophylls a and b extracted with four different solvents: Verification of the concentration of chlorophyll standards by atomic absorption spectroscopy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 1989, 975, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grahl, S.; Reiter, B.; Gugel, I.L.; Vamvaka, E.; Gandini, C.; Jahns, P.; Soll, J.; Leister, D.; Ruhle, T. The arabidopsis protein cgld11 is required for chloroplast atp synthase accumulation. Mol. Plant 2016, 9, 885–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertle, A.P.; Blunder, T.; Wunder, T.; Pesaresi, P.; Pribil, M.; Armbruster, U.; Leister, D. Pgrl1 is the elusive ferredoxin-plastoquinone reductase in photosynthetic cyclic electron flow. Mol. Cell 2013, 49, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, T.; Shikanai, T.; Fumihiko, S.; Asada, K. Nad(p)h dehydrogenase-dependent, antimycin a-sensitive electron donation to plastoquinone in tobacco chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol. 1998, 39, 1226–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lenzen, B.; Rühle, T.; Lehniger, M.-K.; Okuzaki, A.; Labs, M.; Muino, J.M.; Ohler, U.; Leister, D.; Schmitz-Linneweber, C. The Chloroplast RNA Binding Protein CP31A Has a Preference for mRNAs Encoding the Subunits of the Chloroplast NAD(P)H Dehydrogenase Complex and Is Required for Their Accumulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5633. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21165633
Lenzen B, Rühle T, Lehniger M-K, Okuzaki A, Labs M, Muino JM, Ohler U, Leister D, Schmitz-Linneweber C. The Chloroplast RNA Binding Protein CP31A Has a Preference for mRNAs Encoding the Subunits of the Chloroplast NAD(P)H Dehydrogenase Complex and Is Required for Their Accumulation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(16):5633. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21165633
Chicago/Turabian StyleLenzen, Benjamin, Thilo Rühle, Marie-Kristin Lehniger, Ayako Okuzaki, Mathias Labs, Jose M. Muino, Uwe Ohler, Dario Leister, and Christian Schmitz-Linneweber. 2020. "The Chloroplast RNA Binding Protein CP31A Has a Preference for mRNAs Encoding the Subunits of the Chloroplast NAD(P)H Dehydrogenase Complex and Is Required for Their Accumulation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 16: 5633. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21165633
APA StyleLenzen, B., Rühle, T., Lehniger, M.-K., Okuzaki, A., Labs, M., Muino, J. M., Ohler, U., Leister, D., & Schmitz-Linneweber, C. (2020). The Chloroplast RNA Binding Protein CP31A Has a Preference for mRNAs Encoding the Subunits of the Chloroplast NAD(P)H Dehydrogenase Complex and Is Required for Their Accumulation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(16), 5633. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21165633




