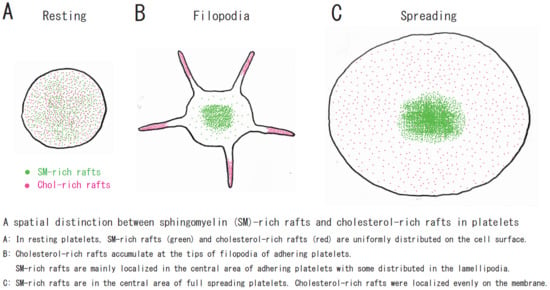
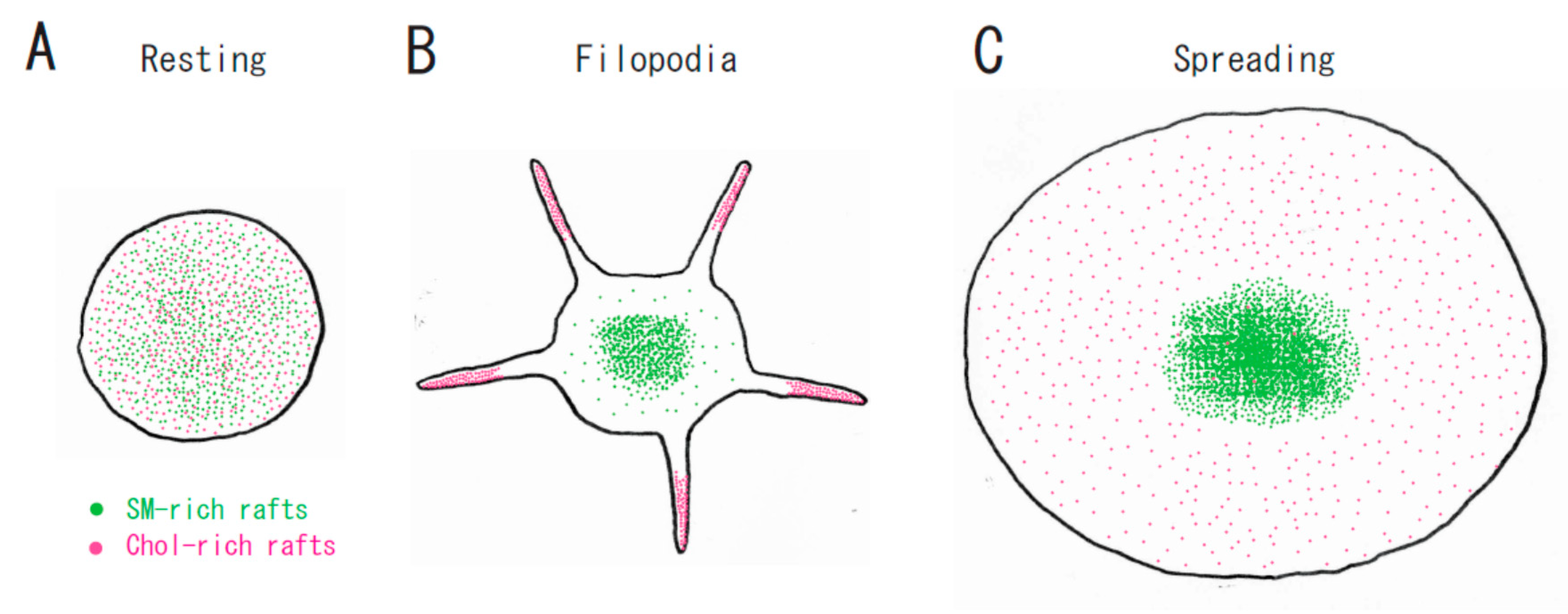
Function of Platelet Glycosphingolipid Microdomains/Lipid Rafts
Abstract
1. Platelet Lipid Rafts
2. Sphingomyelin-Rich Rafts of Platelets
3. Raft Heterogeneity
4. Platelet Glycosphingolipids
5. Platelet Raft-Binding Proteins
5.1. Protein S-Palmitoylation: Lipid Raft Targeting Modification
5.2. G protein-Coupled Receptors (P2Y1, P2Y12, CXCR4)
5.3. Stomatin, Prohibitin, Flotillin, and HflK/C (SPFH)-Domain Protein Family
5.3.1. Flotillin
5.3.2. Stomatin
5.3.3. Prohibitin
5.4. Tetraspanin Family
5.4.1. CD9
5.4.2. CD151
5.4.3. CD63
5.4.4. Tspan32
5.4.5. CD82
5.5. Calcium Channels (Orai 1, STIM, TRPC)
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADP | adenosine diphosphate |
| ANX | annexin |
| APT | acyl protein thioesterase |
| BCθ | biotinylated derivative of perfringolysin O |
| CRAC | cholesterol recognition/interaction amino acid motif |
| Dab2 | disabled-2 |
| DHHC | Asp-His-His-Cys domain |
| DIC | differential interference contrast |
| DRM | detergent-resistant membrane |
| FXIII | coagulation factor XIII |
| GFP | green fluorescent protein |
| GP | glycoprotein |
| MCSP | malaria circumsporozoite protein |
| PAR1 | protease-activated receptor 1 |
| PAR4 | protease-activated receptor 4 |
| PGI2 | prostaglandin I2 |
| PI3K | phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase |
| PPT | palmitoyl protein thioesterase |
| PS | phosphatidylserine |
| S1P | sphingosine-1-phosphate |
| SDF-1α | chemokine stromal cell-derived factor-1α |
| SOCE | store-operated Ca2+ entry |
| SM | sphingomyelin |
| SPFH domain | stomatin, prohibitin, flotillin, and HflK/C |
| STIM | stromal interaction molecule |
| TEM | tetraspanin-enriched microdomain |
| TRAP | thrombin receptor activating peptide |
| TRPC | transient receptor potential canonical |
| TXA2 | stromal interaction molecule |
| vWF | von Willebrand factor |
References
- Simons, K.; Gerl, M.J. Revitalizing membrane rafts: New tools and insights. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Móuton, C.; Abad, J.L.; Mira, E.; Lacalle, R.A.; Gallardo, E.; Jiménez-Baranda, S.; Illa, I.; Bernad, A.; Mañes, S.; Martínez-A, C. Segregation of leading-edge and uropod components into specific lipid rafts during T cell polarization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 9642–9647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorahy, D.J.; Lincz, L.F.; Meldrum, C.J.; Burns, G.F. Biochemical isolation of a membrane microdomain from resting platelets highly enriched in the plasma membrane glycoprotein CD36. Biochem. J. 1996, 319, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrimpton, C.N.; Borthakur, G.; Larrucea, S.; Cruz, M.A.; Dong, J.F.; López, J.A. Localization of the adhesion receptor glycoprotein Ib-IX-V complex to lipid rafts is required for platelet adhesion and activation. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 196, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, W.; Inoue, O.; Tamura, N.; Suzuki-Inoue, K.; Satoh, K.; Berndt, M.C.; Handa, M.; Goto, S.; Ozaki, Y. A role for glycosphingolipid-enriched microdomains in platelet glycoprotein Ib-mediated platelet activation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 1034–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Malcor, J.M.; Harper, M.T. Lipid rafts are essential for release of phosphatidylserine-exposing extracellular vesicles from platelets. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodin, S.; Tronchère, H.; Payrastre, B. Lipid rafts are critical membrane domains in blood platelet activation processes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1610, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.A.; del Conde, I.; Shrimpton, C.N. Receptors, rafts, and microvesicles in thrombosis and inflammation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 3, 1737–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodin, S.; Soulet, C.; Tronchère, H.; Sié, P.; Gachet, C.; Plantavid, M.; Payrastre, B. Integrin-dependent interaction of lipid rafts with the actin cytoskeleton in activated human platelets. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rabani, V.; Montange, D.; Meneveau, N.; Davani, S. Impact of ticagrelor on P2Y1 and P2Y12 localization and on cholesterol levels in platelet plasma membrane. Platelets 2018, 29, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, A.A.; Shimada, Y.; Heijnen, H.F.; Nakamura, M.; Inomata, M.; Hayashi, M.; Iwashita, S.; Slot, J.W.; Ohno-Iwashita, Y. Selective binding of perfringolysin O derivative to cholesterol-rich membrane microdomains (rafts). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 4926–4931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heijnen, H.F.; Van Lier, M.; Waaijenborg, S.; Ohno-Iwashita, Y.; Waheed, A.A.; Inomata, M.; Gorter, G.; Möbius, W.; Akkerman, J.W.; Slot, J.W. Concentration of rafts in platelet filopodia correlates with recruitment of c-Src and CD63 to these domains. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2003, 1, 1161–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasahara, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Sanai, Y. Association of Src family tyrosine kinase Lyn with ganglioside GD3 in rat brain. Possible regulation of Lyn by glycosphingolipid in caveolae-like domains. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 29947–29953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasahara, K.; Watanabe, K.; Takeuchi, K.; Kaneko, H.; Oohira, A.; Yamamoto, T.; Sanai, Y. Involvement of gangliosides in glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored neuronal cell adhesion molecule TAG-1 signaling in lipid rafts. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 34701–34709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasahara, K.; Sanai, Y. Functional roles of glycosphingolipids in signal transduction via lipid rafts. Glycoconj. J. 2000, 17, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasahara, K.; Watanabe, K.; Kozutsumi, Y.; Oohira, A.; Yamamoto, T.; Sanai, Y. Association of GPI-anchored protein TAG-1 with src-family kinase Lyn in lipid rafts of cerebellar granule cells. Neurochem. Res. 2002, 27, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuyama, K.; Sekino-Suzuki, N.; Sanai, Y.; Kasahara, K. Translocation of activated heterotrimeric G protein Galpha (o) to ganglioside-enriched detergent-resistant membrane rafts in developing cerebellum. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 26392–26400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekino-Suzuki, N.; Yuyama, K.; Miki, T.; Kaneda, M.; Suzuki, H.; Yamamoto, N.; Yamamoto, T.; Oneyama, C.; Okada, M.; Kasahara, K. Involvement of gangliosides in the process of Cbp/PAG phosphorylation by Lyn in developing cerebellar growth cones. J. Neurochem. 2013, 124, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, T.; Kaneda, M.; Iida, K.; Hasegawa, G.; Murakami, M.; Yamamoto, N.; Asou, H.; Kasahara, K. An anti-sulfatide antibody O4 immunoprecipitates sulfatide rafts including Fyn, Lyn and the G protein α subunit in rat primary immature oligodendrocytes. Glycoconj. J. 2013, 30, 819–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsuka, H.; Iguchi, T.; Hayashi, M.; Kaneda, M.; Iida, K.; Shimonaka, M.; Hara, T.; Arai, M.; Koike, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; et al. SDF-1α/CXCR4 Signaling in Lipid Rafts Induces Platelet Aggregation via PI3 Kinase-Dependent Akt Phosphorylation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
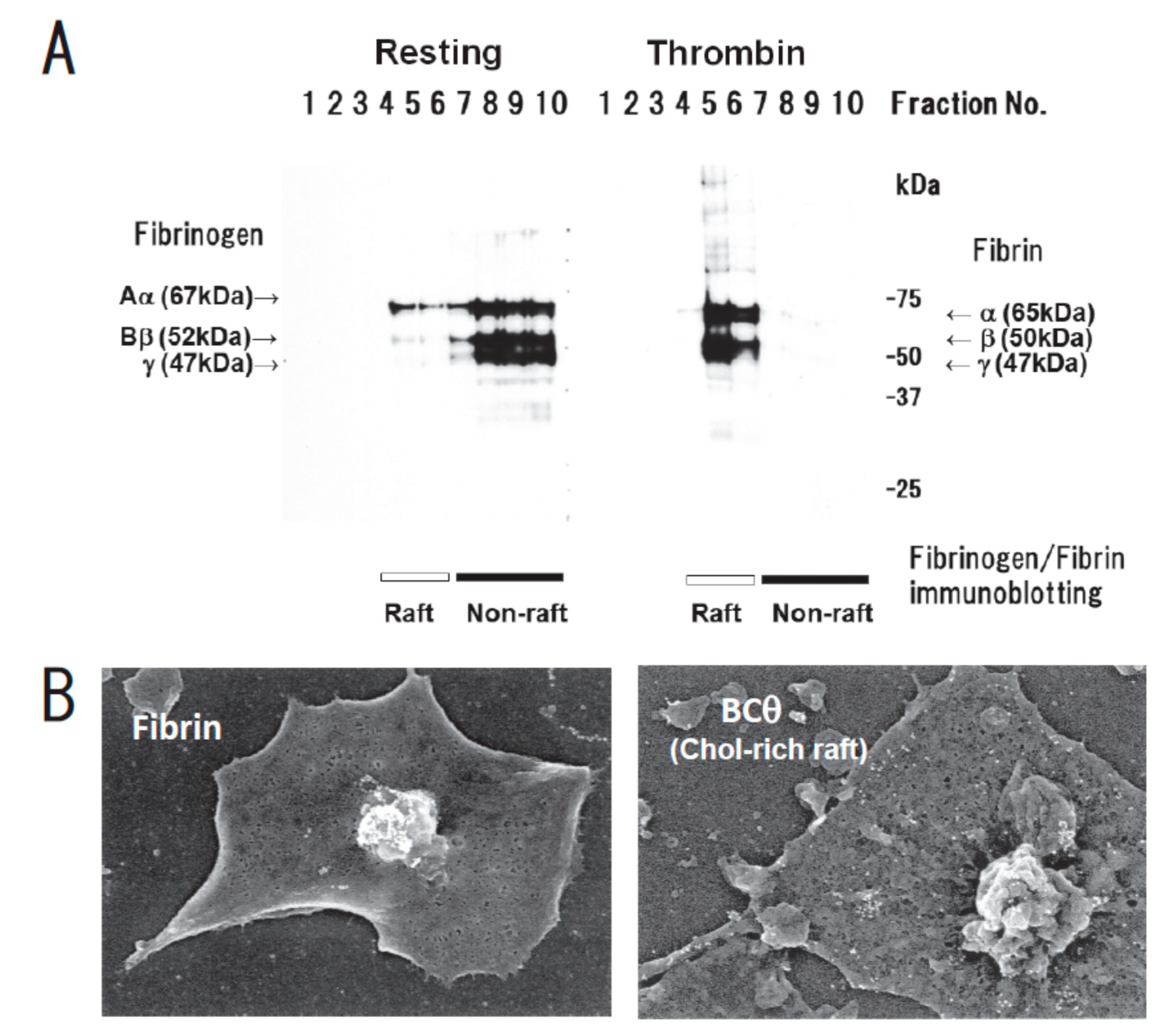
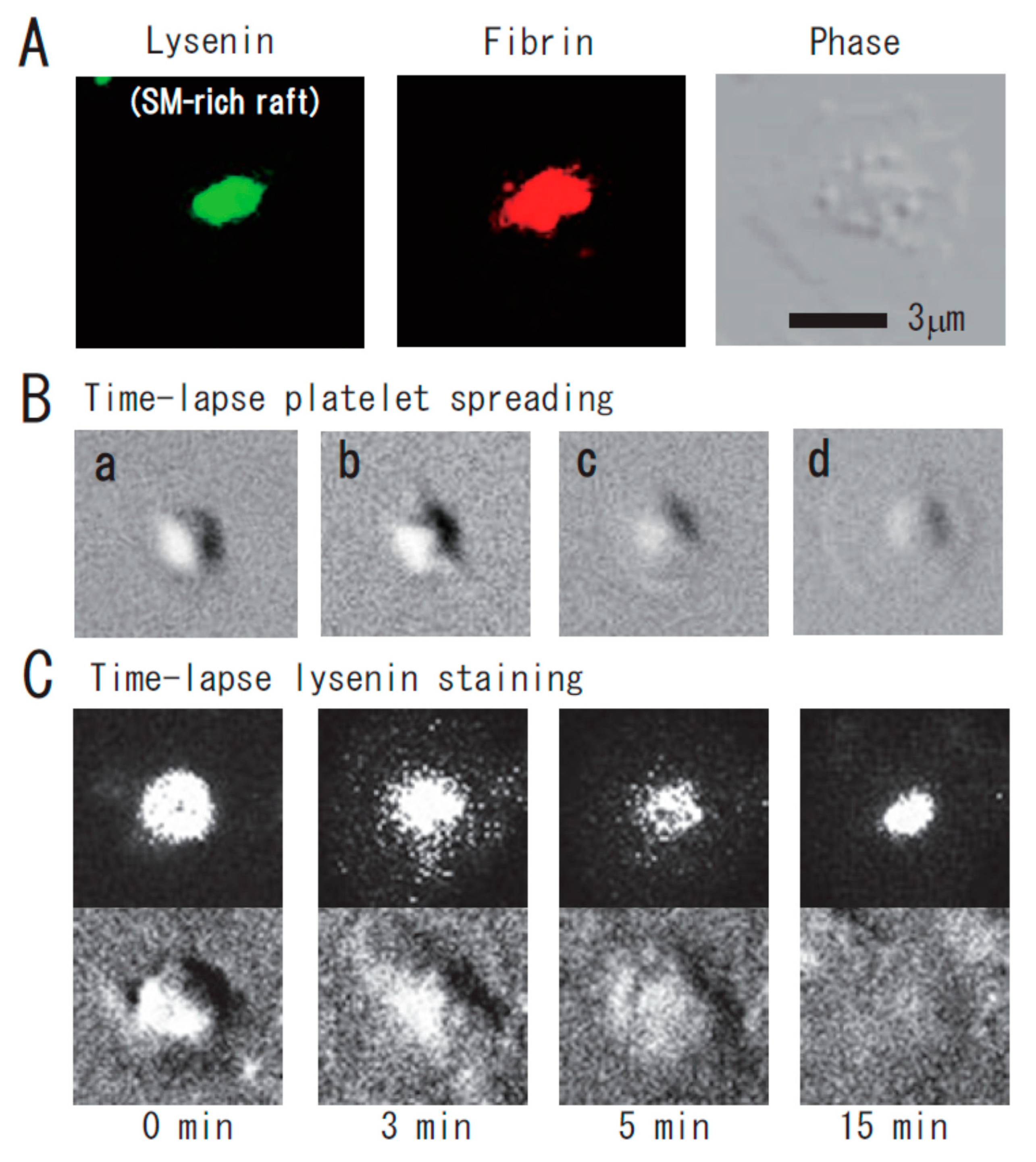
- Kasahara, K.; Kaneda, M.; Miki, T.; Iida, K.; Sekino-Suzuki, N.; Kawashima, I.; Suzuki, H.; Shimonaka, M.; Arai, M.; Ohno-Iwashita, Y.; et al. Clot retraction is mediated by factor XIII-dependent fibrin-αIIbβ3-myosin axis in platelet sphingomyelin-rich membrane rafts. Blood 2013, 122, 3340–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyokawa, E.; Baba, T.; Otsuka, N.; Makino, A.; Ohno, S.; Kobayashi, T. Spatial and functional heterogeneity of sphingolipid-rich membrane domains. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 24072–24084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hullin-Matsuda, F.; Kobayashi, T. Monitoring the distribution and dynamics of signaling microdomains in living cells with lipid-specific probes. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2007, 64, 2492–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasahara, K.; Souri, M.; Kaneda, M.; Miki, T.; Yamamoto, N.; Ichinose, A. Impaired clot retraction in factor XIII A subunit-deficient mice. Blood 2010, 115, 1277–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munday, A.D.; López, J.A. Factor XIII: Sticking it to platelets. Blood 2013, 122, 3246–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrdinka, M.; Otahal, P.; Horejsi, V. The transmembrane region is responsible for targeting of adaptor protein LAX into “heavy rafts”. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkin, E.T.; Turner, A.J.; Hooper, N.M. Isolation and characterization of two distinct low-density, Triton-insoluble, complexes from porcine lung membranes. Biochem. J. 1996, 319, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olive, S.; Dubois, C.; Schachner, M.; Rougon, G. The F3 neuronal glycosylphosphatidylinositol-linked molecule is localized to glycolipid-enriched membrane subdomains and interacts with L1 and fyn kinase in cerebellum. J. Neurochem. 1995, 65, 2307–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knorr, R.; Karacsonyi, C.; Lindner, R. Endocytosis of MHC molecules by distinct membrane rafts. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 1584–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Kwon, H.; Jeong, K.; Lee, J.; Pak, Y. Essential role of flotillin-1 palmitoylation in the intracellular localization and signaling function of IGF-1 receptor. J. Cell Sci. 2015, 128, 2179–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferroni, P.; Lenti, L.; Martini, F.; Ciatti, F.; Pontieri, G.M.; Gazzaniga, P.P. Ganglioside content of human platelets–differences in resting and activated platelets. Thromb. Haemost. 1997, 77, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martini, F.; Riondino, S.; Pignatelli, P.; Gazzaniga, P.P.; Ferroni, P.; Lenti, L. Involvement of GD3 in platelet activation. A novel association with Fcgamma receptor. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1583, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nara, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Maruyama, K.; Kasahara, K.; Nagai, Y.; Sanai, Y. Expression cloning of a CMP-NeuAc: NeuAc alpha 2-3Gal beta 1-4Glc beta 1-1’Cer alpha 2,8-sialyltransferase (GD3 synthase) from human melanoma cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 7952–7956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.T.; Schick, P.K. The effect of thrombin on the organization of human platelet membrane glycosphingolipids. The sphingosine composition of platelet glycolipids and ceramides. J. Biol. Chem. 1981, 256, 752–756. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tao, R.V.; Sweeley, C.C.; Jamieson, G.A. Sphingolipid composition of human platelets. J. Lipid Res. 1973, 14, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kyogashima, M.; Taketomi, T. Lipids from human platelets in primary thrombocythemia. Jpn. J. Exp. Med. 1986, 56, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kushi, Y.; Arita, M.; Ishizuka, I.; Kasama, T.; Fredman, P.; Handa, S. Sulfatide is expressed in both erythrocytes and platelets of bovine origin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1304, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdebska, E.; Soszyńska, B.; Dobrowolski, Z.; Kościelak, J. The levels of glycosphingolipids, ceramides, sialic acid and glycogen are changed in plasma membranes of rat platelets harvested during recovery from immune-mediated thrombocytopenia. Acta Biochim. Pol. 1996, 43, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, K.; Tan, L.; Chen, Y.H.; Cao, Y.P. Alterations in cholesterol and ganglioside GM1 content of lipid rafts in platelets from patients with Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2015, 29, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooling, L.L.; Walker, K.E.; Gille, T.; Koerner, T.A. Shiga toxin binds human platelets via globotriaosylceramide (Pk antigen) and a novel platelet glycosphingolipid. Infect. Immun. 1998, 66, 4355–4366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooling, L.L.; Zhang, D.; Koerner, T.A. Human platelets express gangliosides with LKE activity and ABH blood group activity. Transfusion 2001, 41, 504–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, D.D.; Williams, S.B.; Gralnick, H.R.; Ginsburg, V. von Willebrand factor binds specifically to sulfated glycolipids. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 3306–3309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ginsburg, V.; Roberts, D.D. Glycoconjugates and cell adhesion: The adhesive proteins laminin, thrombospondin and von Willebrand’s factor bind specifically to sulfated glycolipids. Biochimie 1988, 70, 1651–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guchhait, P.; Shrimpton, C.N.; Honke, K.; Rumbaut, R.E.; Lopez, J.A.; Thiagarajan, P. Effect of an anti-sulfatide single-chain antibody probe on platelet function. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 99, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Merten, M.; Thiagarajan, P. Role for sulfatides in platelet aggregation. Circulation 2001, 104, 2955–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Borthakur, G.; Cruz, M.A.; Dong, J.F.; McIntire, L.; Li, F.; López, J.A.; Thiagarajan, P. Sulfatides inhibit platelet adhesion to von Willebrand factor in flowing blood. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2003, 1, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drahos, K.E.; Welsh, J.D.; Finkielstein, C.V.; Capelluto, D.G. Sulfatides partition disabled-2 in response to platelet activation. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e8007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.J.; Tseng, C.P. The adaptor protein Disabled-2: New insights into platelet biology and integrin signaling. Thromb. J. 2016, 14 (Suppl. 1), 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, J.D.; Charonko, J.J.; Salmanzadeh, A.; Drahos, K.E.; Shafiee, H.; Stremler, M.A.; Davalos, R.V.; Capelluto, D.G.; Vlachos, P.P.; Finkielstein, C.V. Disabled-2 modulates homotypic and heterotypic platelet interactions by binding to sulfatides. Br. J. Haematol. 2011, 154, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Charonko, J.J.; Fu, X.; Salmanzadeh, A.; Davalos, R.V.; Vlachos, P.P.; Finkielstein, C.V.; Capelluto, D.G. Structure, sulfatide binding properties, and inhibition of platelet aggregation by a disabled-2 protein-derived peptide. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 37691–37702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.J.; Huang, C.L.; Chang, Y.W.; Huang, D.Y.; Lin, C.C.; Cooper, J.A.; Cheng, J.C.; Tseng, C.P. Disabled-2 is required for efficient hemostasis and platelet activation by thrombin in mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 2404–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ida, M.; Satoh, A.; Matsumoto, I.; Kojima-Aikawa, K. Human annexin V binds to sulfatide: Contribution to regulation of blood coagulation. J. Biochem. 2004, 135, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, M.; Miyagawa, H.; Kuranami, Y.; Tsunooka-Ota, M.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Kojima-Aikawa, K. Annexin A4 inhibits sulfatide-induced activation of coagulation factor XII. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1357–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, J.; Sullam, P.M. Streptococcus mitis phage-encoded adhesins mediate attachment to {alpha} 2-8-linked sialic acid residues on platelet membrane gangliosides. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 3485–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpman, D.; Papadopoulou, D.; Nilsson, K.; Sjögren, A.C.; Mikaelsson, C.; Lethagen, S. Platelet activation by Shiga toxin and circulatory factors as a pathogenetic mechanism in the hemolytic uremic syndrome. Blood 2001, 97, 3100–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raslan, Z.; Naseem, K.M. Compartmentalisation of cAMP-dependent signalling in blood platelets: The role of lipid rafts and actin polymerisation. Platelets 2015, 26, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerecedo, D.; Martínez-Vieyra, I.; Maldonado-García, D.; Hernández-González, E.; Winder, S.J. Association of membrane/lipid rafts with the platelet cytoskeleton and the caveolin PY14: Participation in the adhesion process. J. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 116, 2528–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israels, S.J.; McMillan-Ward, E.M. Platelet tetraspanin complexes and their association with lipid rafts. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 98, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar]
- Mairhofer, M.; Steiner, M.; Mosgoeller, W.; Prohaska, R.; Salzer, U. Stomatin is a major lipid-raft component of platelet alpha granules. Blood 2002, 100, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollitt, A.Y.; Grygielska, B.; Leblond, B.; Désiré, L.; Eble, J.A.; Watson, S.P. Phosphorylation of CLEC-2 is dependent on lipid rafts, actin polymerization, secondary mediators, and Rac. Blood 2010, 115, 2938–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reineri, S.; Bertoni, A.; Sanna, E.; Baldassarri, S.; Sarasso, C.; Zanfa, M.; Canobbio, I.; Torti, M.; Sinigaglia, F. Membrane lipid rafts coordinate estrogen-dependent signaling in human platelets. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1773, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baglia, F.A.; Shrimpton, C.N.; López, J.A.; Walsh, P.N. The glycoprotein Ib-IX-V complex mediates localization of factor XI to lipid rafts on the platelet membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 21744–21750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, F.A.; van Lier, M.; Relou, I.A.; Foley, L.; Akkerman, J.W.; Heijnen, H.F.; Farndale, R.W. Lipid rafts facilitate the interaction of PECAM-1 with the glycoprotein VI-FcR gamma-chain complex in human platelets. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 39330–39338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vial, C.; Fung, C.Y.; Goodall, A.H.; Mahaut-Smith, M.P.; Evans, R.J. Differential sensitivity of human platelet P2X1 and P2Y1 receptors to disruption of lipid rafts. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 343, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinton, T.M.; Kim, S.; Jin, J.; Kunapuli, S.P. Lipid rafts are required in Galpha (i) signaling downstream of the P2Y12 receptor during ADP-mediated platelet activation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 3, 1036–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houck, K.L.; Yuan, H.; Tian, Y.; Solomon, M.; Cramer, D.; Liu, K.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, X.; Zhang, J.; Oehler, V.; et al. Physical proximity and functional cooperation of glycoprotein 130 and glycoprotein VI in platelet membrane lipid rafts. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 17, 1500–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Lier, M.; Lee, F.; Farndale, R.W.; Gorter, G.; Verhoef, S.; Ohno-Iwashita, Y.; Akkerman, J.W.; Heijnen, H.F. Adhesive surface determines raft composition in platelets adhered under flow. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 3, 2514–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezumi, Y.; Kodama, K.; Uchiyama, T.; Takayama, H. Constitutive and functional association of the platelet collagen receptor glycoprotein VI-Fc receptor gamma-chain complex with membrane rafts. Blood 2002, 99, 3250–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorahy, D.J.; Burns, G.F. Active Lyn protein tyrosine kinase is selectively enriched within membrane microdomains of resting platelets. Biochem. J. 1998, 333, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dionisio, N.; Galán, C.; Jardín, I.; Salido, G.M.; Rosado, J.A. Lipid rafts are essential for the regulation of SOCE by plasma membrane resident STIM1 in human platelets. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, S.; Vijayan, K.V. Lipid rafts contribute to agonist-induced serine/threonine phosphatase activation and platelet aggregation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 11, 1612–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Lee, W. Prohibitins are involved in protease-activated receptor 1-mediated platelet aggregation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 10, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouckova, A.; Holada, K. Cellular prion protein in blood platelets associates with both lipid rafts and the cytoskeleton. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 102, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canobbio, I.; Trionfini, P.; Guidetti, G.F.; Balduini, C.; Torti, M. Targeting of the small GTPase Rap2b, but not Rap1b, to lipid rafts is promoted by palmitoylation at Cys176 and Cys177 and is required for efficient protein activation in human platelets. Cell. Signal. 2008, 20, 1662–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurice, P.; Waeckel, L.; Pires, V.; Sonnet, P.; Lemesle, M.; Arbeille, B.; Vassy, J.; Rochette, J.; Legrand, C.; Fauvel-Lafève, F. The platelet receptor for type III collagen (TIIICBP) is present in platelet membrane lipid microdomains (rafts). Histochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 125, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownlow, S.L.; Sage, S.O. Transient receptor potential protein subunit assembly and membrane distribution in human platelets. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 94, 839–845. [Google Scholar]
- Moscardó, A.; Vallés, J.; Latorre, A.; Santos, M.T. The association of thromboxane A2 receptor with lipid rafts is a determinant for platelet functional responses. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 3154–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gitz, E.; Koekman, C.A.; van den Heuvel, D.J.; Deckmyn, H.; Akkerman, J.W.; Gerritsen, H.C.; Urbanus, R.T. Improved platelet survival after cold storage by prevention of glycoprotein Ibα clustering in lipid rafts. Haematologica 2012, 97, 1873–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwanaga, T.; Tsutsumi, R.; Noritake, J.; Fukata, Y.; Fukata, M. Dynamic protein palmitoylation in cellular signaling. Prog. Lipid Res. 2009, 48, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, P.J.; Dixon, S.J. Protein palmitoylation and cancer. EMBO Rep. 2018, 19, e46666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladygina, N.; Martin, B.R.; Altman, A. Dynamic palmitoylation and the role of DHHC proteins in T cell activation and anergy. Adv. Immunol. 2011, 109, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Hao, J.W.; Wang, X.; Guo, H.; Sun, H.H.; Lai, X.Y.; Liu, L.Y.; Zhu, M.; Wang, H.Y.; Li, Y.F.; et al. DHHC4 and DHHC5 Facilitate Fatty Acid Uptake by Palmitoylating and Targeting CD36 to the Plasma Membrane. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 209–221.e205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Martin, B.R.; Cravatt, B.F.; Hofmann, S.L. DHHC5 protein palmitoylates flotillin-2 and is rapidly degraded on induction of neuronal differentiation in cultured cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, C.; Yang, X.H.; Hemler, M.E. DHHC2 affects palmitoylation, stability, and functions of tetraspanins CD9 and CD151. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 3415–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorent, J.H.; Levental, I. Structural determinants of protein partitioning into ordered membrane domains and lipid rafts. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2015, 192, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luiken, J.J.; Chanda, D.; Nabben, M.; Neumann, D.; Glatz, J.F. Post-translational modifications of CD36 (SR-B2): Implications for regulation of myocellular fatty acid uptake. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1862, 2253–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parton, R.G.; Hanzal-Bayer, M.; Hancock, J.F. Biogenesis of caveolae: A structural model for caveolin-induced domain formation. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowal, L.; Yang, W.; Freeman, M.R.; Steen, H.; Flaumenhaft, R. Proteomic analysis of palmitoylated platelet proteins. Blood 2011, 118, e62–e73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savi, P.; Zachayus, J.L.; Delesque-Touchard, N.; Labouret, C.; Hervé, C.; Uzabiaga, M.F.; Pereillo, J.M.; Culouscou, J.M.; Bono, F.; Ferrara, P.; et al. The active metabolite of Clopidogrel disrupts P2Y12 receptor oligomers and partitions them out of lipid rafts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 11069–11074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, M.; Gawaz, M. Platelet-derived CXCL12 (SDF-1α): Basic mechanisms and clinical implications. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 11, 1954–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, M.A.; Ratajczak, J.; Hoxie, J.; Brass, L.F.; Gewirtz, A.; Poncz, M.; Ratajczak, M.Z. Megakaryocyte precursors, megakaryocytes and platelets express the HIV co-receptor CXCR4 on their surface: Determination of response to stromal-derived factor-1 by megakaryocytes and platelets. Br. J. Haematol. 1999, 104, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalska, M.A.; Ratajczak, M.Z.; Majka, M.; Jin, J.; Kunapuli, S.; Brass, L.; Poncz, M. Stromal cell-derived factor-1 and macrophage-derived chemokine: 2 chemokines that activate platelets. Blood 2000, 96, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, M.; Seizer, P.; Borst, O.; Schönberger, T.; Mack, A.; Geisler, T.; Langer, H.F.; May, A.E.; Vogel, S.; Lang, F.; et al. SDF-1α induces differential trafficking of CXCR4-CXCR7 involving cyclophilin A, CXCR7 ubiquitination and promotes platelet survival. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 2864–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, T.G.; Harper, M.T.; Poole, A.W. SDF-1α is a novel autocrine activator of platelets operating through its receptor CXCR4. Cell. Signal. 2015, 27, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abi-Younes, S.; Sauty, A.; Mach, F.; Sukhova, G.K.; Libby, P.; Luster, A.D. The stromal cell-derived factor-1 chemokine is a potent platelet agonist highly expressed in atherosclerotic plaques. Circ. Res. 2000, 86, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geisler, T.; Fekecs, L.; Wurster, T.; Chiribiri, A.; Schuster, A.; Nagel, E.; Miller, S.; Gawaz, M.; Stellos, K.; Bigalke, B. Association of platelet-SDF-1 with hemodynamic function and infarct size using cardiac MR in patients with AMI. Eur. J. Radiol. 2012, 81, e486–e490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, H.; Matsui, I. The lipid raft markers stomatin, prohibitin, flotillin, and HflK/C (SPFH)-domain proteins form an operon with NfeD proteins and function with apolar polyisoprenoid lipids. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 46, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatkowska, K.; Matveichuk, O.V.; Fronk, J.; Ciesielska, A. Flotillins: At the Intersection of Protein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatomi, Y.; Ruan, F.; Hakomori, S.; Igarashi, Y. Sphingosine-1-phosphate: A platelet-activating sphingolipid released from agonist-stimulated human platelets. Blood 1995, 86, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatomi, Y.; Ozaki, Y.; Ohmori, T.; Igarashi, Y. Sphingosine 1-phosphate: Synthesis and release. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2001, 64, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, H.; Yatomi, Y.; Ohmori, T.; Satoh, K.; Matsumoto, Y.; Ozaki, Y. Sphingosine 1-phosphate stimulates G (i)- and Rho-mediated vascular endothelial cell spreading and migration. Thromb. Res. 2000, 99, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riento, K.; Zhang, Q.; Clark, J.; Begum, F.; Stephens, E.; Wakelam, M.J.; Nichols, B.J. Flotillin proteins recruit sphingosine to membranes and maintain cellular sphingosine-1-phosphate levels. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rungaldier, S.; Umlauf, E.; Mairhofer, M.; Salzer, U.; Thiele, C.; Prohaska, R. Structure-function analysis of human stomatin: A mutation study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Hsieh, C.F.; Liu, H.W.; Chen, C.Y.; Wu, S.C.; Chen, T.W.; Hsu, C.S.; Liao, Y.H.; Yang, C.Y.; Shyu, J.F.; et al. Lipid raft-associated stomatin enhances cell fusion. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrow, I.C.; Parton, R.G. Flotillins and the PHB domain protein family: Rafts, worms and anaesthetics. Traffic 2005, 6, 725–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ande, S.R.; Mishra, S. Palmitoylation of prohibitin at cysteine 69 facilitates its membrane translocation and interaction with Eps 15 homology domain protein 2 (EHD2). Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 88, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemler, M.E. Tetraspanin proteins mediate cellular penetration, invasion, and fusion events and define a novel type of membrane microdomain. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2003, 19, 397–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Deventer, S.J.; Dunlock, V.E.; van Spriel, A.B. Molecular interactions shaping the tetraspanin web. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2017, 45, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odintsova, E.; Butters, T.D.; Monti, E.; Sprong, H.; van Meer, G.; Berditchevski, F. Gangliosides play an important role in the organization of CD82-enriched microdomains. Biochem. J. 2006, 400, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakomori Si, S.I. The glycosynapse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, G.L.; Remenyi, G.; Friese, P. Tetraspanin CD9 is required for microparticle release from coated-platelets. Platelets 2009, 20, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangin, P.H.; Kleitz, L.; Boucheix, C.; Gachet, C.; Lanza, F. CD9 negatively regulates integrin alphaIIbbeta3 activation and could thus prevent excessive platelet recruitment at sites of vascular injury. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 7, 900–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- .Charrin, S.; Manié, S.; Oualid, M.; Billard, M.; Boucheix, C.; Rubinstein, E. Differential stability of tetraspanin/tetraspanin interactions: Role of palmitoylation. FEBS Lett. 2002, 516, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, L.M.; Wee, J.L.; Wright, M.D.; Moseley, G.W.; Hogarth, P.M.; Ashman, L.K.; Jackson, D.E. The tetraspanin superfamily member CD151 regulates outside-in integrin alphaIIbbeta3 signaling and platelet function. Blood 2004, 104, 2368–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, M.D.; Geary, S.M.; Fitter, S.; Moseley, G.W.; Lau, L.M.; Sheng, K.C.; Apostolopoulos, V.; Stanley, E.G.; Jackson, D.E.; Ashman, L.K. Characterization of mice lacking the tetraspanin superfamily member CD151. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 5978–5988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berditchevski, F.; Odintsova, E.; Sawada, S.; Gilbert, E. Expression of the palmitoylation-deficient CD151 weakens the association of alpha 3 beta 1 integrin with the tetraspanin-enriched microdomains and affects integrin-dependent signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 36991–37000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, J.; Lüllmann-Rauch, R.; Himmerkus, N.; Pleines, I.; Nieswandt, B.; Orinska, Z.; Koch-Nolte, F.; Schröder, B.; Bleich, M.; Saftig, P. Deficiency of the tetraspanin CD63 associated with kidney pathology but normal lysosomal function. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 1083–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goschnick, M.W.; Lau, L.M.; Wee, J.L.; Liu, Y.S.; Hogarth, P.M.; Robb, L.M.; Hickey, M.J.; Wright, M.D.; Jackson, D.E. Impaired “outside-in” integrin alphaIIbbeta3 signaling and thrombus stability in TSSC6-deficient mice. Blood 2006, 108, 1911–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchtmann, K.; Park, E.R.; Bergsma, A.; Segula, J.; Edick, M.J.; Miranti, C.K. Homozygous loss of mouse tetraspanin CD82 enhances integrin αIIbβ3 expression and clot retraction in platelets. Exp. Cell Res. 2015, 339, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, F.; Münzer, P.; Gawaz, M.; Borst, O. Regulation of STIM1/Orai1-dependent Ca2+ signalling in platelets. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 110, 925–930. [Google Scholar]
- Gavin, R.L.; Koo, C.Z.; Tomlinson, M.G. Tspan18 is a novel regulator of thrombo-inflammation. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, C.; Choi, S.H.; Kwak, M.; Jeong, B.; Ko, J.; Park, H.J.; Choi, S.; Jun, J.Y.; So, I. TRPC5 channel instability induced by depalmitoylation protects striatal neurons against oxidative stress in Huntington’s disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2020, 1867, 118620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Molecules | Function | Localization in Rafts | Moves into Rafts | Palmitoylation | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actin | Cytoskeleton | + | [9] | ||
| ACV/VI | Adenylyl cyclase | PGI2 | 〇 | [56] | |
| Akt2 | Ser/Thr kinase | + | [20] | ||
| Arp3 | Actin nucleator | TRAP | [9] | ||
| Caveolin-1 | Integral scaffolding protein | ++ | 〇 | [57] | |
| CD9 | Tetraspanin | ++ | 〇 | [58] | |
| CD36 | Scavenger receptor | +++ | 〇 | [59] | |
| CD63 | Tetraspanin | ++ | 〇 | [58] | |
| Cdc42 | Small G protein | TRAP | 〇 | [9] | |
| CLEC-2 | Podoplanin receptor | Rhodocytin | [60] | ||
| c-Src | Tyr kinase | ++ | [12] | ||
| CXCR4 | Chemokine receptor | + | [20] | ||
| Estrogen receptor | Hormone receptor | Estradiol | [61] | ||
| Factor XI | Plasma thromboplastin | ++ | [62] | ||
| Factor XIII | Transglutaminase | Thrombin | [21] | ||
| Fc receptor g | Immunoglobulin G receptor | ++ | [63] | ||
| Fibrin | Major component of blood clot | Thrombin | [21] | ||
| Flotillin-1 | SPFH-domain scaffolding protein | +++ | 〇 | [59] | |
| Flotillin-2 | SPFH-domain scaffolding protein | +++ | 〇 | [64] | |
| Gia | Trimeric G protein | ++ | 〇 | [65] | |
| GLUT-3 | Glucose transporter | ++ | [59] | ||
| GP130 | IL6 receptor | ++ | [66] | ||
| GPIb/IX/V | vWF receptor | vWF | 〇 | [4] | |
| GPVI | Collagen receptor | Collagen | [67] | ||
| Integrin aIIbb3 | Fibrinogen receptor | + | [21] | ||
| LAT | Linker for activation of T cells | +++ | 〇 | [68] | |
| Lyn | Tyr kinase | ++ | 〇 | [69] | |
| Moesin | ERM family | TRAP | [9] | ||
| Myosin | Cytoskeleton | Thrombin | [21] | ||
| Orai1 | Store-operated Ca2+ entry | ++ | [70] | ||
| P2X1 | ATP receptor | ++ | [64] | ||
| P2Y1 | ADP receptor | ADP | [10] | ||
| P2Y12 | ADP receptor | ADP | [10] | ||
| PECAM-1 | Adhesion molecule | ++ | 〇 | [63] | |
| PI3Kb | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase | + | [20] | ||
| PI4K55 | Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase | ++ | 〇 | [58] | |
| PKA-I | Ser/Thr kinase | PGI2 | [56] | ||
| PP1c | Protein phosphatase | Thrombin | [71] | ||
| PP2Ac | Protein phosphatase | Thrombin | [71] | ||
| Prohibitin | SPFH-domain scaffolding protein | ++ | 〇 | [72] | |
| PrPc | Prion | + | [73] | ||
| Pyk2 | Tyr kinase | ++ | [61] | ||
| Rap2b | Small G protein | ++ | 〇 | [74] | |
| STIM1 | Store-operated Ca2+ entry | ++ | [70] | ||
| Stomatin | SPFH-domain scaffolding protein | ++ | 〇 | [59] | |
| TIIICBP | Collagen receptor | ++ | [75] | ||
| TRPC1,4,5 | Store-operated Ca2+ entry | ++ | 〇 | [76] | |
| TXA2 receptor | Prostanoid receptor | ++ | 〇 | [77] | |
| VASP | Actin filament elongation | TRAP | [9] | ||
| vWF | Molecular glue of platelet plug | ++ | [4] | ||
| 14-3-3ζ | pSer/pThr binding protein | Cold shock | [78] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Komatsuya, K.; Kaneko, K.; Kasahara, K. Function of Platelet Glycosphingolipid Microdomains/Lipid Rafts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5539. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155539
Komatsuya K, Kaneko K, Kasahara K. Function of Platelet Glycosphingolipid Microdomains/Lipid Rafts. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(15):5539. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155539
Chicago/Turabian StyleKomatsuya, Keisuke, Kei Kaneko, and Kohji Kasahara. 2020. "Function of Platelet Glycosphingolipid Microdomains/Lipid Rafts" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 15: 5539. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155539
APA StyleKomatsuya, K., Kaneko, K., & Kasahara, K. (2020). Function of Platelet Glycosphingolipid Microdomains/Lipid Rafts. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(15), 5539. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155539