Abstract
C-type lectins (CTLs), a superfamily of glycan-binding receptors, play a pivotal role in the host defense against pathogens and the maintenance of immune homeostasis of higher animals and humans. CTLs in innate immunity serve as pattern recognition receptors and often bind to glycan structures in damage- and pathogen-associated molecular patterns. While CTLs are found throughout the whole animal kingdom, their ligand specificities and downstream signaling have mainly been studied in humans and in model organisms such as mice. In this review, recent advancements in CTL research in veterinary species as well as potential applications of CTL targeting in veterinary medicine are outlined.
1. Introduction
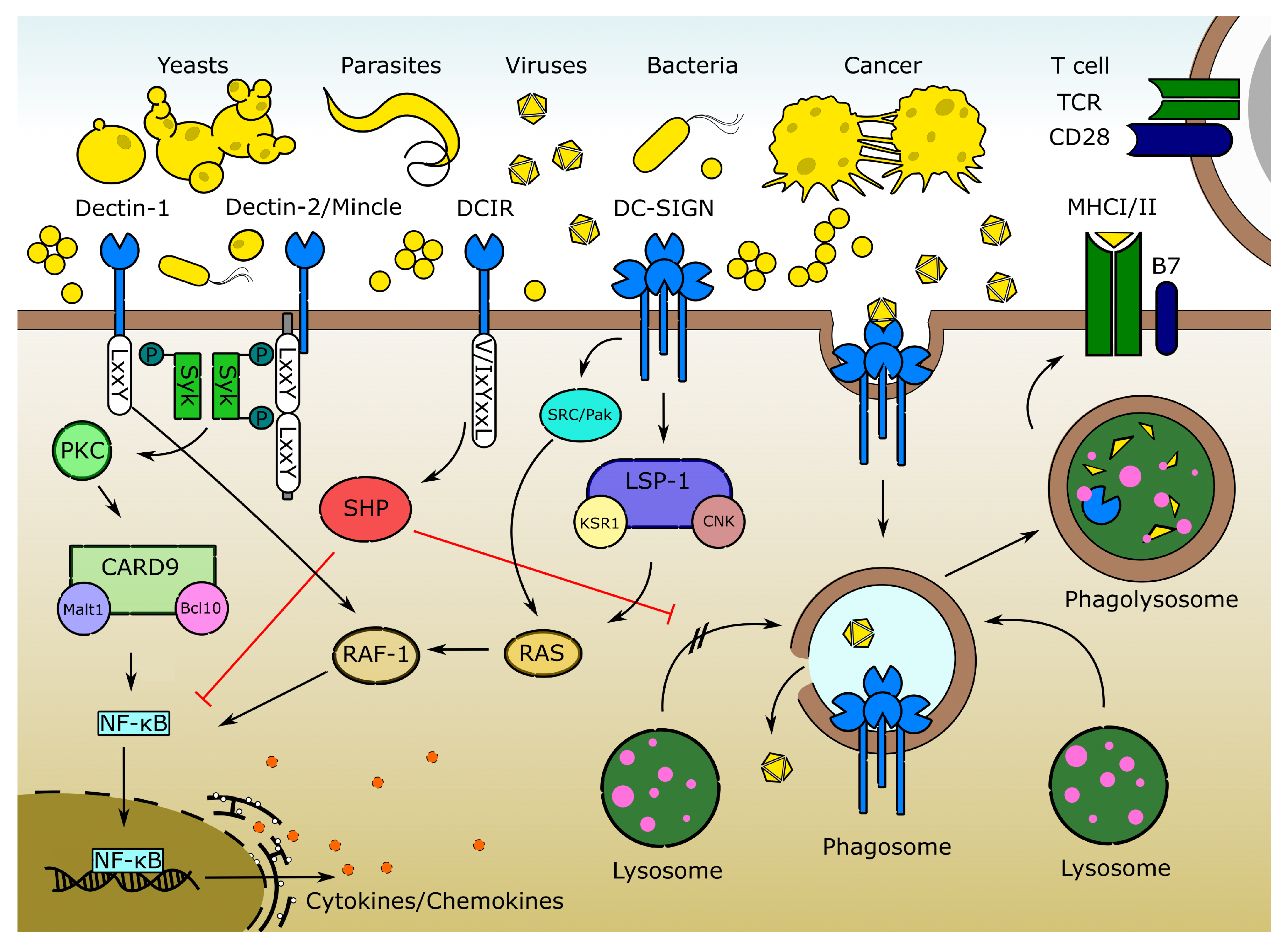
Glycans belong to the most abundant macromolecules constituting all living organisms. In multicellular animals, processes such as cell migration, homeostasis maintenance, and innate immune signaling rely on the ability of cells to recognize glycoconjugates, most often in the form of glycoproteins and glycolipids, via glycan binding proteins, the so-called lectins [1]. In the immune system, lectin receptors are either secreted or found on the cell surface of immune cells [2]. Three major receptor families that are involved in glycan recognition in the immune system include the galectins [3], siglecs [4], and C-type lectins (CTLs) [5]. Among these, the phylogenetically conserved CTLs proved to play a pivotal role in both host–pathogen interactions and homeostasis maintenance in vertebrate and in invertebrate species [5,6,7]. Myeloid CTLs are mainly expressed by antigen-presenting cells (APCs) and act as pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) that bind to pathogen and damage-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs and DAMPs) [5]. Most CTL receptors require Ca2+ ions for binding, hence the “C” in the name. However, some CTLs also bind carbohydrate, peptide, or crystalline ligands in a Ca2+-independent manner [5]. The importance of CTLs for antifungal immunity is well recognized in human medicine [8] (Table 1). For instance, an increased risk for candidiasis [9] and a higher susceptibility to aspergillosis is associated with CTL polymorphisms in human patients [10]. However, CTLs are also chiefly important in the scope of immune homeostasis [11,12,13,14] and protection against bacteria, viruses, parasites, and cancer [15,16,17,18,19] (Figure 1). They induce signal pathways leading to the expression of chemokines and cytokines, and they are involved in phagocytosis and antigen (cross-)presentation by molecules of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) I or II to T-cells, thus bridging innate and adaptive immunity [20] (Figure 1). CTLs associated with an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM), such as the dendritic cell-associated lectin 1 (Dectin-1/Clec7a), and 2 (Dectin-2/Clec6a) and the macrophage-inducible Ca2+-dependent lectin (Mincle/Clec4e), signal upon ligand binding via phosphorylation of the spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk). Syk activates further kinases such as the protein kinase C (PKC), which results in downstream activation and assembly of the caspase recruitment domain-containing protein 9 (CARD9), mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation protein 1 (MALT1), and B-cell lymphoma protein 10 (BCL10) complex. Finally, this leads to phosphorylation of IκB and translocation of the transcription factor NF-κB into the nucleus, where it enhances the transcription of numerous cytokine and chemokine genes [21]. This activation may be counteracted by CTLs such as the DC immunoreceptor (DCIR/Clec4a), which carry an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motif (ITIM) and engage the src homology domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatases (SHP), thus restricting ITAM-mediated signals and limiting inflammation [22,23]. ITAM/ITIM-independent CTLs, such as the dendritic cell-specific ICAM-3-grabbing non-integrin (DC-SIGN/Clec4l/CD209) can also stimulate the activation of NF-κB via steroid receptor coactivator (SRC) and p21-activated kinase (PAK) or via the leukocyte-specific protein 1 (LSP-1), kinase suppressor of RAS 1 (KSR-1), and connector enhancer of kinase suppressor of RAS (CNK) rat sarcoma (RAS) signalosome [22]. However, CTLs were also shown to act as pathogen entry receptors and targets of immune escape [24] and may contribute to immune pathology in several infections [25,26,27,28], as well as in autoimmune diseases and cancer [20,29,30].

Table 1.
Overview of selected human CTLs, including examples of respective ligands and functions.
Figure 1.
CTL functions and signalling pathways. CTLs recognize molecular patterns of fungal, parasitic, bacterial, and viral pathogens (so-called PAMPs) as well as those of dead and malignant cells (DAMPs). Upon pathogen binding, CTL–mediated signalling leads to cytokine and chemokine production and phagocytosis. The latter results in antigen (cross-)presentation and priming of T-cells. However, some viruses, such as the zoonotic Dengue fever virus, developed immune evasion mechanisms and may exploit CTLs such as DC-SIGN to promote viral transmission and dissemination.
Most insights into animal CTLs functions were gained in studies performed with model organisms, predominantly mice. In vitro CTL–ligand screenings using murine [31,32,33] or human [34,35] recombinant CTL hFc-fusion protein libraries (Figure 2) allowed for the identification of novel CTL/pathogen interactions and CTL ligands [34,36]. Further studies analyzed ligand binding and downstream signal transduction of mouse and human CTL using APCs [21,37,38,39,40,41] or CTL expressing reporter cell systems [42,43,44,45]. Data from human patients [46] and studies performed in CTL−/− mice or mice that were deficient for CTL-mediated signaling [47,48] depict the effects of particular CTLs in vivo. However, ligand specificities of CTL orthologues, downstream signaling pathways, and effector functions may significantly vary among different species [44,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59], thus emphasizing the need for CTL investigations performed in a species-specific manner (Figure 3). In particular, there is a knowledge gap regarding CTL function in veterinary species. In the following sections, we will discuss recent studies in this field and briefly highlight potential applications of CTL targeting in veterinary medicine.
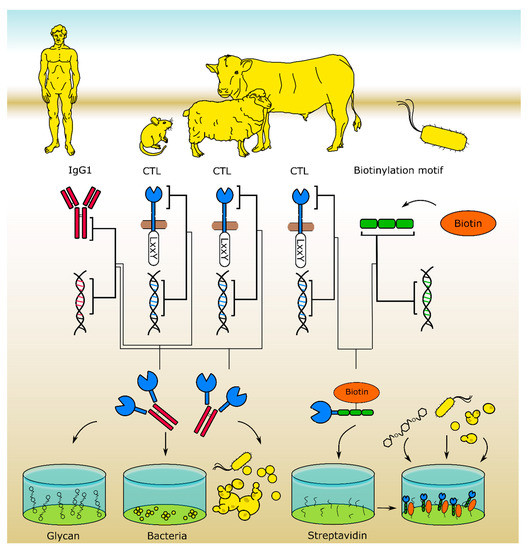
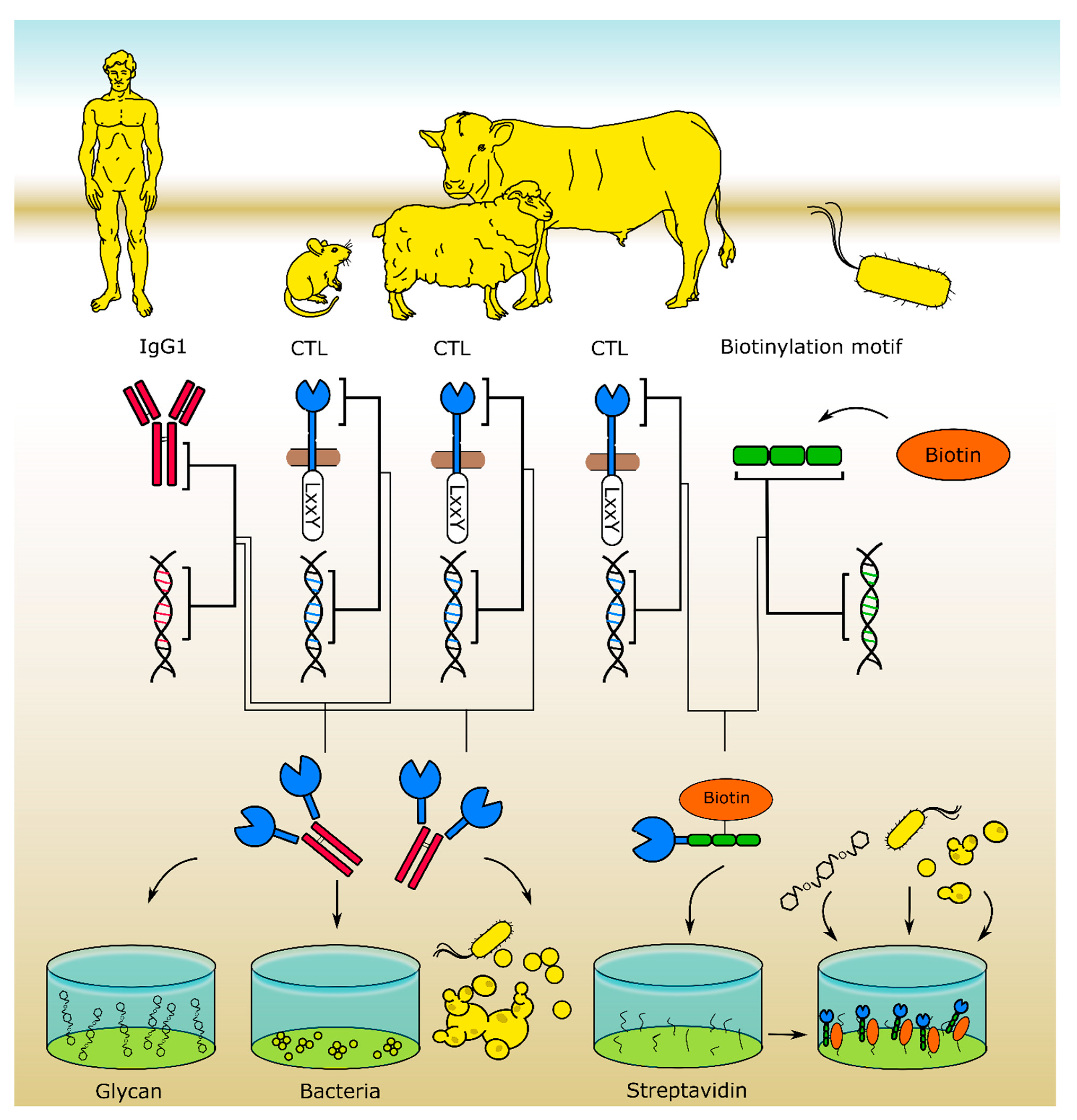
Figure 2.
Recombinant CTL libraries for in vitro screenings allow for the identification of CTL ligands. The murine [31] and ovine [60] CTL libraries were expressed as CTL-Fc fusion proteins. For the bovine [61] library, cow CTL and bacterial biotinylation site coding DNA fragments were fused and expressed in E. coli, yielding biotinylated fusion proteins that can be used for glycan array- and ELISA-based binding studies and high throughput pull-down assays.
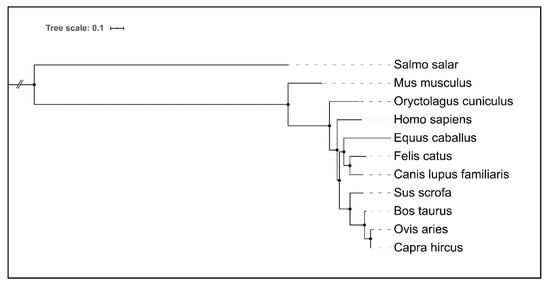
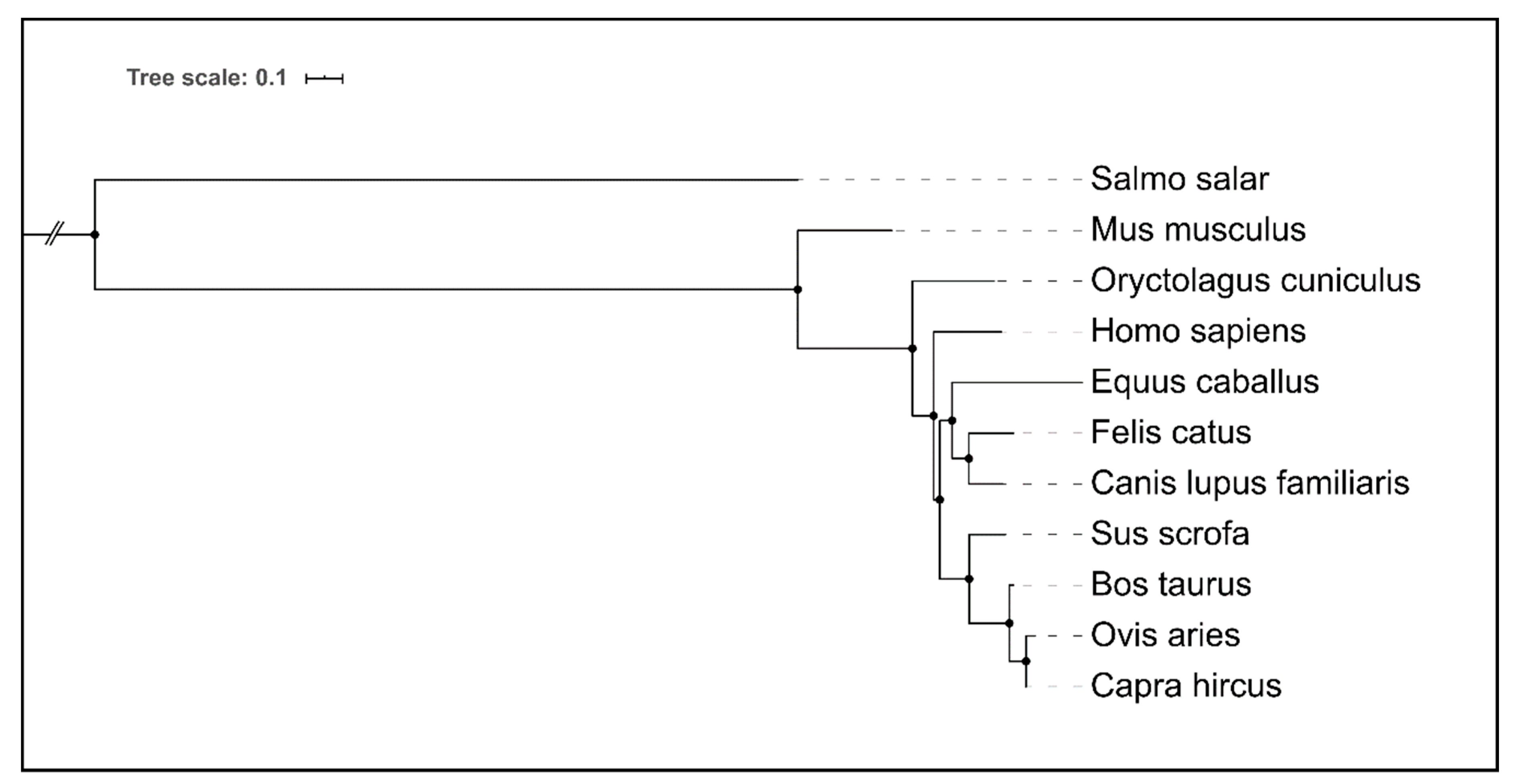
Figure 3.
Hierarchical clustering of amino acid sequences comprising Dectin-1 (Clec7a) CTLs of selected animal species, and humans. For the Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar), missing a corresponding ortholog Dectin-1 encoding gene, a functional ortholog C-type lectin receptor C was chosen. Remarkably, the degree of similarity in the Dectin-1 amino acid sequences mirrors the phylogenetic relationships between the respective species. Visualization and clustering were performed with NGPhylogeny.fr suite [62].
2. Protective Role of Veterinary Relevant CTLs
Most often, CTL functions in veterinary species were investigated in population screening studies. These studies correlated the course of infection- or general susceptibility-associated phenotypes with specific CTL genotypes, thus allowing for conclusions concerning the functions of individual CTLs in health and disease [63,64]. By using such strategies, implications of CTLs in antimicrobial immunity were recently described. For instance, a link between different single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the bovine Dectin-1 encoding gene and the susceptibility to Johne’s disease caused by Mycobacterium avium ssp. paratuberculosis (MAP) was found in screening studies in Canadian [65] and in Indian cattle [66]. Similarly, multiple SNPs were described in the Dectin-1 encoding gene in pigs [67]. All SNPs discovered in commercial pig lines proved to be neutral when compared to the reference pig Dectin-1 in a NF-κB driven reporter system using the Dectin-1 ligand zymosan [67]. In contrast, the Dectin-1 isoform found exclusively in wild boars displayed a markedly enhanced activatory capability upon ligand stimulation. This augmented Dectin-1 signaling was suggested to negatively influence the overall fitness of its carriers, possibly leading to overshooting immune responses to pathogenic and commensal fungi [67]. A SNP in the gene encoding for the humoral mannose binding lectin A (MBL1), on the other hand, was hypothesized to result in a loss-of-function type of mutation and in an increased shedding of Salmonella sp. in fattened pigs [68]. Consistently, a negative correlation between the concentration of the orthologous MBL and Salmonella susceptibility was observed in chicken [69]. However, multiple SNPs in the non-coding intron parts of the MBL gene were shown to correlate with varying serum MBL levels in Chinese Hu sheep [70], demonstrating that SNPs that do not directly affect the CTL protein sequence may nevertheless influence CTL levels in vivo.
The antimicrobial effects of several CTLs were recently shown for both sweet water [71] and salt water [72] fish species. In carp, a number of CTLs were identified to be downregulated on macrophages upon stimulation with the ß-glucan curdlan [73], which is a well-known ligand of Dectin-1 in mammals [74]. This surprising effect may represent a negative feedback mechanism preventing an over-stimulation of the carp immune cells in the course of bacterial and fungal infections [73]. In contrast, several salmon genes encoding signaling molecules downstream of CTL receptors SCRLA, SCRLB, and SCRLC (Salmon C-type lectins A,B,C), such as the one encoding the fish analogue of the mammalian tyrosine kinase Syk, were significantly upregulated following ß-glucan stimulation. These findings suggest an involvement of CTLs in pathogen recognition and signal transduction in salmon [75].
A strong correlation between the protective Th1 response and Dectin-1 engagement was recently shown in mouse Leishmania spp. infections models [76,77], demonstrating a crucial role of this specific CTL in anti-Leishmania immunity. The site-specific expansion of Dectin-1 expressing DCs following intradermal injection of the specific Dectin-1 agonist curdlan sufficed to protect wild-type mice from illness following transdermal Leishmania infection, whereas Dectin-1−/− mice succumbed to the disease [76]. Leishmaniosis is an important and life-threatening disease in dogs; an insufficient Th1 response in favor of the detrimental Th2 response [78] in clinically affected canids renders vaccine development a significant challenge [79,80]. However, the function of canine Dectin-1 during Leishmania spp. infection in dogs is yet unknown.
The influence of different CTL-associated alleles on anti-parasitic immunity was described in wild Soay sheep on the St Kilda archipelago, Scotland [81]. In this study, SNPs in the presumed cis-regulatory element of the clec16a gene, a CTL-encoding gene associated with immunoglobulin isotype deficiency disorders in humans and mice [82], strongly correlated with specific IgA levels against the intestinal roundworm Telodorsagia circumcincta in lambs as well as in mature sheep [81]. In fish, CTLs may also contribute to protective immune responses against parasites as suggested by a positive correlation between macrophage mannose receptor 1 (MRC1/Clec13d) expression levels and the relative resistance of Atlantic [83] and pink salmon toward sea lice infestation [84]. These findings indicate that the selective breeding or genetic engineering introducing desirable CTL alleles into veterinary species might be a means to improve their performance and disease resistance in the future.
3. Detrimental Role of Veterinary Relevant CTLs
3.1. Pathological Inflammation
Dysregulation in CTL signaling can lead to sterile inflammation in the absence of any pathogen [29]. For instance, a possible involvement of Dectin-1 in sterile inflammation and postpartum placenta retention was suggested in cows, since higher numbers of Dectin-1-expressing uterine macrophages were detected in retention-affected cows compared to cows with a regular afterbirth [85]. Allergic hypersensitivity and immunopathology can also be mediated by CTLs: in horses, Dectin-1, Dectin-2, and macrophage lectin 2 (MGL/Clec10a) may contribute to severe allergic dermatitis following insect bites [86]. Similar findings were also obtained for mice and men, as Dectin-1−/− mice were largely protected against Aspergillus fumigatus-initiated corneal keratitis [87] and Dectin-1 blockade using the antagonist laminarin alleviated the severity of fungal keratitis in human patients [28]. Other CTLs may also be involved in immune pathology upon CTL engagement during infections. For instance, the myeloid C-type lectin-like receptor (MICL/Clec12a) was shown to cross-prime CD8+ T-cells contributing to the development of experimental cerebral malaria [26] and to promote murine viral lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) infections by hampering pathogen clearance [88]. To date, there is a knowledge gap on how CTLs may contribute to immune pathology in veterinary species, thus highlighting the need for further research in this field.
3.2. Exploitation of CTLs by Pathogens
Numerous viral pathogens, among them arthropod-borne phleboviruses, such as Dengue virus and Rift Valley Fever virus, specifically target CTLs such as the human DC-SIGN to establish infections [89]. Similarly, the feline corona virus, a close relative of both the canine coronaviruses (CCoVs) and the porcine transmissible gastroenteritis virus (TGEV) [90], establish infection by exploiting the cat DC-SIGN [91]. Heterologous expression of human DC-SIGN in otherwise resistant cells rendered them susceptible for infection with an avian corona virus, chicken Infectious Bronchitis virus (IBV) [92]. These studies on viral/DC-SIGN interactions indicate that CTLs represent relevant receptors for viral entry into host cells; thus, they may play a crucial role in the cross-species transmission of viruses.
However, not only viruses, but also bacteria and parasites were reported to highjack DC-SIGN or its orthologues, as recently demonstrated for the bacterium Yersinia pestis [93] and the apicomplexan parasite Toxoplasma gondii [94]. For the ruminant trematode parasite Fasciola hepatica, a strong downregulation of host DC effector functions via DC-SIGN was observed, finally leading to immune dysregulation and T-cell anergy [95]. The apicomplexan parasite Neospora caninum circulating between canine definitive hosts and bovine intermediate hosts causes large losses in dairy and beef production worldwide by inducing abortions [96]. In a murine model, N. caninum engaged Dectin-1 and thereby inhibited DC effector functions in wild-type mice compared to Dectin-1−/− mice [97]. Further helminths, such as the nematode Toxocara canis, were shown to synthesize a repertoire of mammalian-like CTLs [98,99] and unusual glycans [100], which might interfere with and subvert CTL-based glycan recognition in vivo [100]. In conclusion, the examples highlighted here demonstrate a variety of immune evasion strategies of parasites to interfere with mammalian CTL-mediated immunity [101].
4. Harnessing the Power of CTLs
CTLs represent attractive targets for immune modulation, not only in mice and humans, but also in veterinary species as they hold promise of novel and/or improved diagnostic, prophylactic, and therapeutic applications. In the following, we will briefly highlight some recent examples.
4.1. General Aspects
In veterinary research, cell-surface expressed CTLs can be used as cell-specific markers, thus allowing for the discrimination of immune cell subsets to elucidate specific functions. For instance, the analysis of antiviral effector functions of porcine DCs was performed in Clec13B/LY75/CD205 positive DCs [102]. Accordingly, the in vitro characterization of rainbow trout immune cell subpopulations was performed by staining Clec4t1 positive monocyte-derived macrophage and DC precursor cells with CTL-specific antibodies [71]. Plate-bound or soluble recombinant CTL-based fusion proteins can in turn be used for binding studies with bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites in order to identify interactions of CTLs with PAMPs [103]. In this regard, the lectin array technology offers excellent opportunities for the diagnosis of blood and urine infections [61] or protein glycosylation-associated disorders [104] in animal or human patients.
4.2. Prophylaxis
CTL-targeting adjuvants, for instance the Mincle glycolipid ligand trehalose-6,6-dimycolate (TDM) derived from the M. tuberculosis cell wall and its synthetic analogue trehelose-6,6-dibehenate (TDB) [105], were recently evaluated for their immunogenic properties in mouse models [106,107]. In veterinary research, this approach was adopted for the development of a bovine tuberculosis vaccine [108]. In addition, the co-application of TDB and furfurman (targeting Dectin-2) in pigs as well as TDB and curdlan (targeting Dectin-1) along with further PRR targeting ligands in cattle markedly enhanced vaccination efficacy against Foot-and-Mouth Disease by providing robust and long-lasting effects in vivo [53]. Similarly, a TDB-based experimental liposomal vaccine adjuvant, CAF01, was shown to mediate long-lived M. tuberculosis-specific T-cell responses in humans [109] and enhanced the efficacy of a commercially available inactivated influenza vaccine in ferret models [110]. This adjuvant system was also used for rainbow trout immunization against Aeromonas salmonicida and induced enhanced cellular immunity in comparison to formulation with the standard adjuvant mineral oil [111]. Further trehalose-based CTL-targeting compounds, such as the 2-hydroxy benzoic acid coupled trehalose compound 6,6′-bis-(3,5-di-tert-butylsalisate)-α,α-trehalose (UM1024), demonstrated high Mincle targeting specificity and low cytotoxicity in mouse and human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) in vitro and robust immunogenicity in a mouse model [112]. In pigs, a recently characterized MICL ortholog was proposed as a selective antigen delivery target, since it mediated antigen uptake by pig dendritic cells in vitro [113]. In poultry, novel CTL-targeting compounds such as pustulan [114], as well as other promising CTL immunization targets, namely Clec13B [115,116], Clec17AL-A, and –B [117], the bird homologues of the mammalian Prolectin/Clec17A, were described. These studies indicate that CTLs in veterinary species are indeed promising targets to enhance vaccine efficacy; however, further research is needed to evaluate the potential of the respective adjuvant candidates in vivo.
4.3. Therapeutic Applications
CTL targeting can not only enhance the efficacy of vaccines, but it can also be adapted to metaphylaxis and therapy. As a potential treatment of parasitic infections, T-cell modulation toward the favorable T helper type 1 response was achieved via the metaphylactic curdlan stimulation of Dectin-1 expressing DCs in the mouse model of cutaneous leishmaniosis. In this model, the co-injection of curdlan along with infectious L. major promastigotes resulted in a resistant phenotype observed in the otherwise highly susceptible BALB/c mouse strain [76]. This finding matches the protective properties of yeast glucans that had previously been described in murine leishmaniosis models [118,119]. The utility of this approach for leishmaniosis treatment in other species, such as the domestic and feral dogs [120], cats [121], and foxes [122] remains to be investigated.
DC-SIGN can serve as an adhesion and dissemination receptor for cat-born Toxoplasma gondii infection [94]. Therefore, the specific antibody- or glycan-mediated blocking of paralogues could possibly be applied to prevent toxoplasmosis in chicken [123], thus reducing the risk of alimentary infections in poultry meat consumers. Additionally, selective blocking of the corresponding DC-SIGN orthologue might be applied to limit IBV spread in chickens. Although no chicken DC-SIGN orthologue has been identified yet [92], it is probable to exist due to the engagement of human DC-SIGN and the DC-SIGN-related protein L-SIGN (CD209L/Clec4m) by IBV to establish experimental infections in vitro [92].
Furthermore, CTLs represent important therapeutic targets in immune-mediated diseases. As such, isolated helminth immunomodulatory compounds mimicking an infestation might be used to suppress autoimmunity in human patients [124]. Consistently, a desensitizing DC targeting construct composed of the mite allergoid and mannan, a ligand of the murine [125], ovine [60], and human [126] CTL Dectin-2, was described as a potential allergy treatment in dogs [127]. Another potential therapeutic CTL target is Mincle. The expression of Mincle along with Syk and CARD9 adapter proteins was described in cattle papillomavirus-associated urothelial tumor cells, suggesting their phagocytotic capacity and rendering Mincle a promising target in veterinary oncology [128].
5. Conclusions
Along with other PRRs, CTLs also are important constituents of the host–microbiome communication interface: symbiotic microbes interact with CTLs [129] and affect host cytokine production and CTL expression in trained innate immunity [130] and homeostasis [131] by epigenetic mechanisms. For the Dectin-1 targeting mushroom glucans lentinan [132] and proteo-β-glucan [133], a robust Dectin-1-mediated antidepressant-like effect was demonstrated in mouse models [133,134], illustrating the influence that CTLs may have upon animal and human cerebral functions via the microbiota–gut–brain signaling axis [135]. Many veterinary and human nutraceuticals, or pharmacologically active nutrition additives [136,137], are also likely to exhibit their respective immune stimulating and/or modulatory functions via CTL-mediated signalling. Such an effect was also observed in a study performed in crayfish: crayfish susceptibility to the viral White-spot disease was reduced while the expression of hemocyte-associated crayfish CTL (X2C306-1) was simultaneously upregulated following the probiotic gavage of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens [138]. Further positive effects of carbohydrate supplements were demonstrated in lentinan-rich shiitake mushrooms gavage in a rat model of human dyslipidemia [139], probiotic glucan gavage in carp [140], and mannoprotein supplementation in adult and aging dogs [141].
Finally, functions of CTLs in intrauterine immunity and maternal–fetal tolerance [142], as well as in parturition [143], were shown in humans. Initial studies suggest a possible involvement of CTLs in veterinary species in these processes. For instance, a microarray-based differential gene expression investigation in pregnant sheep yielded several candidate CTLs, such as the DCAR/Clec4b, that were upregulated during the early gestation phase in the endometrium [144]. However, the impact of the respective CTLs on the placenta immunity in vivo is an open question for future research.
In conclusion, advancements in the understanding of CTL functions in veterinary species will open up new applications in veterinary medicine; yet, the current lack of knowledge clearly highlights the need for further research. To bridge this knowledge gap between model and target species, novel tools, such as recombinant bovine [61] and ovine [60] CTL receptor libraries, were recently generated. The role of the identified CTL interactions of veterinary relevant species with pathogens will be unravelled in further studies.
Author Contributions
Original draft preparation and visualization, D.L.L.; review and editing, B.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Nationale Forschungsplattform für Zoonosen (DLR/BMBF, Fkz. 01KI1724). We also acknowledge support from the Niedersachsen-Research Network on Neuroinfectiology (NRENNT-2). This publication was supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft and the University of Veterinary Medicine Hannover, Foundation, within the funding programme Open Access Publishing.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cummings, R.D. Stuck on sugars—how carbohydrates regulate cell adhesion, recognition, and signaling. Glycoconj. J. 2019, 36, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Kooyk, Y.; Rabinovich, A.G. Protein-glycan interactions in the control of innate and adaptive immune responses. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaltner, H.; Toegel, S.; Caballero, G.G.; Manning, J.C.; Ledeen, R.W.; Gabius, H.-J. Galectins: Their network and roles in immunity/tumor growth control. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 147, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macauley, M.S.; Crocker, P.R.; Paulson, J.C. Siglec-mediated regulation of immune cell function in disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 653–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, S.; Raulf, M.-K.; Lepenies, B. C-type lectins: Their network and roles in pathogen recognition and immunity. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 147, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-W.; Vasta, G.R.; Wang, J.-X. The functional relevance of shrimp C-type lectins in host-pathogen interactions. Dev. Com. Immunol. 2020, 109, 103708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; You, M.; Rao, X.-J.; Yu, X.-Q. Insect C-type lectins in innate immunity. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 83, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speakman, E.A.; Dambuza, I.M.; Salazar, F.; Brown, G.D. T Cell Antifungal Immunity and the Role of C-Type Lectin Receptors. Trends Immunol. 2020, 41, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plantinga, T.; Van Der Velden, W.J.F.M.; Ferwerda, B.; Van Spriel, A.B.; Adema, G.; Feuth, T.; Donnelly, J.P.; Brown, G.D.; Kullberg, B.-J.; Blijlevens, N.M.A.; et al. Early Stop Polymorphism in Human DECTIN-1 is Associated with Increased Candida Colonization in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 49, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, C.; Di Ianni, M.; Bozza, S.; Giovannini, G.; Zagarella, S.; Zelante, T.; D’Angelo, C.; Pierini, A.; Pitzurra, L.; Falzetti, F.; et al. Dectin-1 Y238X polymorphism associates with susceptibility to invasive aspergillosis in hematopoietic transplantation through impairment of both recipient- and donor-dependent mechanisms of antifungal immunity. Blood 2010, 116, 5394–5402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Fresno, C.; Saz-Leal, P.; Enamorado, M.; Wculek, S.K.; Martínez-Cano, S.; Blanco-Menéndez, N.; Schulz, O.; Gallizioli, M.; Miró-Mur, F.; Cano, E.; et al. DNGR-1 in dendritic cells limits tissue damage by dampening neutrophil recruitment. Science 2018, 362, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Tang, N.; Guo, H.; Zhang, J. C-Type Lectin Receptor Dectin-1 Suppresses the Development of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. J. Immunol. 2020, 204 (Suppl. 1), 150.19. [Google Scholar]
- Sancho, D.; Sousa, E.C.R. Signaling by myeloid C-type lectin receptors in immunity and homeostasis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 30, 491–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Vallejo, J.-J.; Van Kooyk, Y. Endogenous ligands for C-type lectin receptors: The true regulators of immune homeostasis. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 230, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta, M.P.; Lepenies, B. Bacterial glycans and their interactions with lectins in the innate immune system. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2019, 47, 1569–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, J.G.T.; Lepenies, B. Myeloid C-Type Lectin Receptors in Viral Recognition and Antiviral Immunity. Viruses 2017, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez, A.; Carrero, J.C.; Rodriguez-Sosa, M. Parasitic Infections: A Role for C-Type Lectins Receptors. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, Y.; Inoue, A.; Hangai, S.; Saijo, S.; Negishi, H.; Nishio, J.; Yamasaki, S.; Iwakura, Y.; Yanai, H.; Taniguchi, T. The innate immune receptor Dectin-2 mediates the phagocytosis of cancer cells by Kupffer cells for the suppression of liver metastasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 14097–14102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dambuza, I.M.; Brown, G.D. C-type lectins in immunity: Recent developments. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2014, 32, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.D.; Willment, J.A.; Whitehead, L. C-type lectins in immunity and homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 374–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrop, J.; Lang, R. Contact, Collaboration, and Conflict: Signal Integration of Syk-Coupled C-Type Lectin Receptors. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 1403–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Fresno, C.; Iborra, S.; Saz-Leal, P.; Martínez-López, M.; Sancho, D. Flexible Signaling of Myeloid C-Type Lectin Receptors in Immunity and Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redelinghuys, P.; Whitehead, L.; Augello, A.; Drummond, R.; Levesque, J.-M.; Vautier, S.; Reid, D.M.; Kerscher, B.; Taylor, A.J.; Nigrovic, A.P.; et al. MICL controls inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 75, 1386–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermejo-Jambrina, M.; Eder, J.; Helgers, L.C.; Hertoghs, N.; Nijmeijer, B.M.; Stunnenberg, M.; Geijtenbeek, T.B.H. C-Type Lectin Receptors in Antiviral Immunity and Viral Escape. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalantari, P.; Bunnell, S.C.; Stadecker, M.J. The C-type Lectin Receptor-Driven, Th17 Cell-Mediated Severe Pathology in Schistosomiasis: Not All Immune Responses to Helminth Parasites Are Th2 Dominated. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raulf, M.-K.; Johannssen, T.; Matthiesen, S.; Neumann, K.; Hachenberg, S.; Mayer-Lambertz, S.; Steinbeis, F.; Hegermann, J.; Seeberger, P.H.; Baumgärtner, W.; et al. The C-type Lectin Receptor CLEC12A Recognizes Plasmodial Hemozoin and Contributes to Cerebral Malaria Development. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maglinao, M.; Klopfleisch, R.; Seeberger, P.H.; Lepenies, B. The C-Type Lectin Receptor DCIR Is Crucial for the Development of Experimental Cerebral Malaria. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 2551–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Huang, W.; Deng, Q.; Wu, M.; Jiang, H.; Lin, X.; Sun, Y.; Huang, X.; Yuan, J. Inhibition of TREM-1 and Dectin-1 Alleviates the Severity of Fungal Keratitis by Modulating Innate Immune Responses. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiffoleau, E. C-Type Lectin-Like Receptors as Emerging Orchestrators of Sterile Inflammation Represent Potential Therapeutic Targets. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Su, C.; Zhang, Y. C-type lectins facilitate tumor metastasis. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 13, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Maglinao, M.; Eriksson, M.; Schlegel, M.K.; Zimmermann, S.; Johannssen, T.; Götze, S.; Seeberger, P.H.; Lepenies, B. A platform to screen for C-type lectin receptor-binding carbohydrates and their potential for cell-specific targeting and immune modulation. J. Control. Release 2014, 175, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.; Streng-Ouwehand, I.; Litjens, M.; Weelij, D.R.; García-Vallejo, J.-J.; Van Vliet, S.J.; Saeland, E.; Van Kooyk, Y. Characterization of murine MGL1 and MGL2 C-type lectins: Distinct glycan specificities and tumor binding properties. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 1240–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, M.; Omahdi, Z.; Yamasaki, S. Direct Binding Analysis Between C-Type Lectins and Glycans Using Immunoglobulin Receptor Fusion Proteins. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer Science and Business Media LLC Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 119–128. [Google Scholar]
- Andreasen, A.; Skovgaard, K.; Klaver, E.; Van Die, I.; Mejer, H.; Thamsborg, S.M.; Kringel, H. Comparison of innate and Th1-type host immune responses in Oesophagostomum dentatum and Trichuris suis infections in pigs. Parasite Immunol. 2015, 38, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaver, E.; Kuijk, L.M.; Laan, L.C.; Kringel, H.; Van Vliet, S.J.; Bouma, G.; Cummings, R.D.; Kraal, G.; Van Die, I. Trichuris suis-induced modulation of human dendritic cell function is glycan-mediated. Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, S.; Moeller, R.; Monteiro, J.G.T.; Ellrott, K.; Josenhans, C.; Lepenies, B. C-Type Lectin Receptor (CLR)–Fc Fusion Proteins As Tools to Screen for Novel CLR/Bacteria Interactions: An Exemplary Study on Preselected Campylobacter jejuni Isolates. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, Y.; Oh-Hora, M.; Yamasaki, S. C-Type Lectin Receptor MCL Facilitates Mincle Expression and Signaling through Complex Formation. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 5366–5374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, T.; Itoh, F.; Yoshida, S.; Saijo, S.; Matsuzawa, T.; Gonoi, T.; Saito, T.; Okawa, Y.; Shibata, N.; Miyamoto, T.; et al. Identification of Distinct Ligands for the C-type Lectin Receptors Mincle and Dectin-2 in the Pathogenic Fungus Malassezia. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 13, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Liempt, E.; Van Vliet, S.J.; Engering, A.; García-Vallejo, J.-J.; Bank, C.M.; Sanchez-Hernandez, M.; Van Kooyk, Y.; Van Die, I. Schistosoma mansoni soluble egg antigens are internalized by human dendritic cells through multiple C-type lectins and suppress TLR-induced dendritic cell activation. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 2605–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preite, N.W.; Feriotti, C.; De Lima, D.S.; Da Silva, B.B.; Condino-Neto, A.; Pontillo, A.; Calich, V.L.G.; Loures, F. The Syk-Coupled C-Type Lectin Receptors Dectin-2 and Dectin-3 Are Involved in Paracoccidioides brasiliensis Recognition by Human Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schick, J.; Etschel, P.; Bailo, R.; Ott, L.; Bhatt, A.; Lepenies, B.; Kirschning, C.; Burkovski, A.; Lang, R. Toll-Like Receptor 2 and Mincle Cooperatively Sense Corynebacterial Cell Wall Glycolipids. Infect. Immun. 2017, 85, e00075-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, E.; Ishikawa, T.; Morita, Y.S.; Toyonaga, K.; Yamada, H.; Takeuchi, O.; Kinoshita, T.; Akira, S.; Yoshikai, Y.; Yamasaki, S. Direct recognition of the mycobacterial glycolipid, trehalose dimycolate, by C-type lectin Mincle. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 2879–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, K.; Castineiras-Vilarino, M.; Höckendorf, U.; Hannesschläger, N.; Lemeer, S.; Kupka, D.; Meyermann, S.; Lech, M.; Anders, H.-J.; Kuster, B.; et al. Clec12a Is an Inhibitory Receptor for Uric Acid Crystals that Regulates Inflammation in Response to Cell Death. Immunity 2014, 40, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyotake, R.; Oh-Hora, M.; Ishikawa, E.; Miyamoto, T.; Ishibashi, T.; Yamasaki, S. Human Mincle Binds to Cholesterol Crystals and Triggers Innate Immune Responses. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 25322–25332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyonaga, K.; Torigoe, S.; Motomura, Y.; Kamichi, T.; Hayashi, J.; Morita, Y.; Noguchi, N.; Chuma, Y.; Kiyohara, H.; Matsuo, K.; et al. C-Type Lectin Receptor DCAR Recognizes Mycobacterial Phosphatidyl-Inositol Mannosides to Promote a Th1 Response during Infection. Immunity 2016, 45, 1245–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, R.; Lionakis, M.S. Mechanistic Insights into the Role of C-Type Lectin Receptor/CARD9 Signaling in Human Antifungal Immunity. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, G.J.; Marakalala, M.J.; Hoving, J.C.; van Laarhoven, A.; Drummond, R.A.; Kerscher, B.; Keeton, R.; van de Vosse, E.; Platinga, T.S.; Ottenhoff, T.H.M.; et al. The C-type lectin receptor CLECSF8/CLEC4D is a key component of anti-mycobacterial immunity. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Lin, G.; Langdon, W.Y.; Tao, L.; Zhang, J. Regulation of C-Type Lectin Receptor-Mediated Antifungal Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto-Pelegrín, E.; Toki, D.; Poderoso, T.; Revilla, C.; Ezquerra, A.; Uenishi, H.; de la Riva, P.M.; Álvarez, B.; Domínguez, J. Porcine CLEC12B is expressed on alveolar macrophages and blood dendritic cells. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2020, 111, 103767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baert, K.; Sonck, E.; Goddeeris, B.; Devriendt, B.; Cox, E. Cell type-specific differences in β-glucan recognition and signalling in porcine innate immune cells. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 48, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoccola, E.; Kellie, S.; Barnes, A. Immune transcriptome reveals the mincle C-type lectin receptor acts as a partial replacement for TLR4 in lipopolysaccharide-mediated inflammatory response in barramundi (Lates calcarifer). Mol. Immunol. 2017, 83, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerren, J.R.; Kogut, M.H. The selective Dectin-1 agonist, curdlan, induces an oxidative burst response in chicken heterophils and peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2009, 127, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.J.; Jo, H.; Shin, S.H.; Kim, S.-M.; Kim, B.; Shim, H.S.; Park, J.-H. Mincle and STING-Stimulating Adjuvants Elicit Robust Cellular Immunity and Drive Long-Lasting Memory Responses in a Foot-and-Mouth Disease Vaccine. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jégouzo, S.A.F.; Feinberg, H.; Morrison, A.G.; Holder, A.; May, A.; Huang, Z.; Jiang, L.; Lasanajak, Y.; Smith, D.F.; Werling, D.; et al. CD23 is a glycan-binding receptor in some mammalian species. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 14845–14859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanske, J.; Schulze, J.; Aretz, J.; McBride, R.; Loll, B.; Schmidt, H.; Knirel, Y.; Rabsch, W.; Wahl, M.C.; Paulson, J.C.; et al. Bacterial Polysaccharide Specificity of the Pattern Recognition Receptor Langerin Is Highly Species-dependent. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 292, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, M.B.; Torigoe, S.; Yamasaki, S.; Williams, S.J. Mycobacterium tuberculosis β-gentiobiosyl diacylglycerides signal through the pattern recognition receptor Mincle: Total synthesis and structure activity relationships. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 15027–15030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drickamer, K.; Taylor, M.E. Recent insights into structures and functions of C-type lectins in the immune system. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2015, 34, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, Y.; Morita, D.; Fujiwara, N.; Mori, D.; Nakamura, T.; Harashima, H.; Yamasaki, S.; Sugita, M. Glycerol Monomycolate Is a Novel Ligand for the Human, but Not Mouse Macrophage Inducible C-type Lectin, Mincle. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 15405–15412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Ao, D.; Ni, J.; Chen, N.; Meurens, F.; Zhu, J. The signaling relations between three adaptors of porcine C-type lectin receptor pathway. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2020, 104, 103555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindenwald, D.L.; Monteiro, J.T.; Rautenschlein, S.; Meens, J.; Jung, K.; Becker, S.C.; Lepenies, B. Ovine C-type lectin receptor hFc-fusion protein library—A novel platform to screen for host-pathogen interactions. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2020, 224, 110047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jégouzo, S.A.F.; Nelson, C.; Hardwick, T.; Wong, S.T.A.; Lau, N.K.K.; Neoh, G.K.E.; Castellanos-Rueda, R.; Huang, Z.; Mignot, B.; Hirdaramani, A.; et al. Mammalian lectin arrays for screening host-microbe interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 4541–4555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemoine, F.; Correia, D.; Lefort, V.; Doppelt-Azeroual, O.; Mareuil, F.; Cohen-Boulakia, S.; Gascuel, O. NGPhylogeny.fr: New generation phylogenetic services for non-specialists. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W260–W265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopi, B.; Singh, R.V.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, S.; Chauhan, A.; Kumar, A.; Singh, S.V. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in CLEC7A, CD209 and TLR4 gene and their association with susceptibility to paratuberculosis in Indian cattle. J. Genet. 2020, 99, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, L.A.; Kirkpatrick, B.; Rosa, G.J.M.; Gianola, D.; Valente, B.; Sumner, J.P.; Baltzer, W.; Hao, Z.; Binversie, E.E.; Volstad, N.; et al. Genome-wide association analysis in dogs implicates 99 loci as risk variants for anterior cruciate ligament rupture. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pant, S.; Verschoor, C.; Schenkel, F.; You, Q.; Kelton, D.; Karrow, N.A. Bovine CLEC7A genetic variants and their association with seropositivity in Johne’s disease ELISA. Gene 2014, 537, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, S.; Singh, R.V.; Chauhan, A.; Kumar, A.; Bharati, J.; Singh, S. Association of Bovine CLEC7A gene polymorphism with host susceptibility to paratuberculosis disease in Indian cattle. Res. Vet. Sci. 2019, 123, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinkai, H.; Toki, D.; Okumura, N.; Takenouchi, T.; Kitani, H.; Uenishi, H. Polymorphisms of the immune-modulating receptor dectin-1 in pigs: Their functional influence and distribution in pig populations. Immunogenetics 2016, 68, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainslie-Garcia, M.H.; Farzan, A.; Jafarikia, M.; Lillie, B.N. Single nucleotide variants in innate immune genes associated with Salmonella shedding and colonization in swine on commercial farms. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 219, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich-Lynge, S.L.; Juul-Madsen, H.R.; Kjærup, R.B.; Okimoto, R.; Abrahamsen, M.S.; Maurischat, S.; Sørensen, P.; Dalgaard, T.S. Broilers with low serum Mannose-binding Lectin show increased fecal shedding of Salmonella enterica serovar Montevideo. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 1779–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Zhao, Z.; Yan, G.; Wang, D.; Ban, Q.; Yu, P.; Zhang, W.; Luo, Y. Polymorphisms in mannose-binding lectin (MBL) gene and their association with MBL protein levels in serum in the Hu sheep. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2011, 140, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, P.; Wang, T.; Collet, B.; Corripio-Miyar, Y.; Monte, M.; Secombes, C.J.; Zou, J. Identification and expression modulation of a C-type lectin domain family 4 homologue that is highly expressed in monocytes/macrophages in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 54, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Hu, S.; Wu, T.; Zhao, Z. Characterization and Functional Analysis of Two Transmembrane C-Type Lectins in Obscure Puffer (Takifugu obscurus). Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, J.; Bailey, E.C.; Wheeler, R.T.; de Oliveira, C.A.F.; Forlenza, M.; Wiegertjes, G.F. Studies Into β-Glucan Recognition in Fish. Suggests a Key Role for the C-Type Lectin Pathway. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodridge, H.S.; Wolf, A.J.; Underhill, D.M. Beta-glucan recognition by the innate immune system. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 230, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiron, V.; Kulkarni, A.; Dahle, D.; Vasanth, G.; Lokesh, J.; Elvebo, O. Recognition of purified beta 1,3/1,6 glucan and molecular signalling in the intestine of Atlantic salmon. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 56, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimara, N.; Chanyalew, M.; Aseffa, A.; Van Zandbergen, G.; Lepenies, B.; Schmid, M.; Weiss, R.; Rascle, A.; Wege, A.K.; Jantsch, J.; et al. Dectin-1 Positive Dendritic Cells Expand after Infection with Leishmania major Parasites and Represent Promising Targets for Vaccine Development. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima-Junior, D.S.; Mineo, T.W.P.; Calich, V.L.G.; Zamboni, D.S. Dectin-1 Activation during Leishmania amazonensis Phagocytosis Prompts Syk-Dependent Reactive Oxygen Species Production to Trigger Inflammasome Assembly and Restriction of Parasite Replication. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 2055–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitdidier, E.; Pagniez, J.; Papierok, G.; Vincendeau, P.; Lemesre, J.-L.; Bras-Gonçalves, R. Recombinant Forms of Leishmania amazonensis Excreted/Secreted Promastigote Surface Antigen (PSA) Induce Protective Immune Responses in Dogs. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olías-Molero, A.I.; Corral, M.J.; Jiménez-Antón, M.D.; Alunda, J.M. Early antibody response and clinical outcome in experimental canine leishmaniasis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, J. Assessment of Vaccine-Induced Immunity Against Canine Visceral Leishmaniasis. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, A.M.; Watt, K.; Sinclair, R.; Pilkington, J.G.; Pemberton, J.M.; McNeilly, T.N.; Nussey, D.H.; Johnston, E.S. The genetic architecture of helminth-specific immune responses in a wild population of Soay sheep (Ovis aries). PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1008461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Jørgensen, S.F.; Maggadottir, S.M.; Bakay, M.; Warnatz, K.; Glessner, J.T.; Pandey, R.; Salzer, U.; Schmidt, R.E.; Pérez, E.; et al. Association of CLEC16A with human common variable immunodeficiency disorder and role in murine B cells. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robledo, D.; Gutiérrez, A.P.; Barría, A.; Yáñez, J.M.; Houston, R.D. Gene Expression Response to Sea Lice in Atlantic Salmon Skin: RNA Sequencing Comparison Between Resistant and Susceptible Animals. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, B.J.G.; Koczka, K.W.; Yasuike, M.; Jantzen, S.G.; Yazawa, R.; Koop, B.F.; Jones, S. Comparative transcriptomics of Atlantic Salmo salar, chum Oncorhynchus keta and pink salmon O. gorbuscha during infections with salmon lice Lepeophtheirus salmonis. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelli, R.; De Koster, J.; Roberts, J.N.; De Souza, J.; Lock, A.L.; Raphael, W.; Agnew, D.; Contreras, G.A. Impact of uterine macrophage phenotype on placental retention in dairy cows. Theriogenology 2019, 127, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvitas, I.; Oberhänsli, S.; Leeb, T.; Dettwiler, M.; Müller, E.; Bruggman, R.; Marti, E.I. Investigating the epithelial barrier and immune signatures in the pathogenesis of equine insect bite hypersensitivity. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, S.M., Jr.; Sun, Y.; Pearlman, E. An Essential Role for Dectin 1 in the Pathogenesis of Aspergillus fumigatus Keratitis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 2400. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Neumann, K.; Duhan, V.; Namineni, S.; Hansen, A.L.; Wartewig, T.; Kurgyis, Z.; Holm, C.K.; Heikenwalder, M.; Lang, K.S.; et al. The uric acid crystal receptor Clec12A potentiates type I interferon responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 18544–18549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozach, P.-Y.; Kühbacher, A.; Meier, R.; Mancini, R.; Bitto, D.; Bouloy, M.; Helenius, A. DC-SIGN as a Receptor for Phleboviruses. Cell Host Microbe 2011, 10, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekes, G.; Thiel, H.J. Chapter Six–Feline Coronaviruses: Pathogenesis of Feline Infectious Peritonitis. In Advanced Virus Research; Ziebuhr, J., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; Volume 96, pp. 193–218. [Google Scholar]
- Regan, A.D.; Ousterout, D.G.; Whittaker, G.R. Feline Lectin Activity Is Critical for the Cellular Entry of Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 7917–7921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Buckles, E.; Whittaker, G.R. Expression of the C-type lectins DC-SIGN or L-SIGN alters host cell susceptibility for the avian coronavirus, infectious bronchitis virus. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 157, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; He, Y.; Park, C.G.; Kang, Y.S.; Zhang, P.; Han, Y.; Cui, Y.; Bulgheresi, S.; Anisimov, A.P.; Dentovskaya, S.V.; et al. Yersinia pestis Interacts With SIGNR1 (CD209b) for Promoting Host Dissemination and Infection. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njiri, O.A.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, B.; Jiang, L.; Li, Q.; Liu, W.; Chen, T. CD209 C-Type Lectins Promote Host Invasion, Dissemination, and Infection of Toxoplasma gondii. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, E.; Kalay, H.; Noya, V.; Brossard, N.; Giacomini, C.; Van Kooyk, Y.; García-Vallejo, J.J.; Freire, T. Fasciola hepatica glycoconjugates immuneregulate dendritic cells through the Dendritic Cell-Specific Intercellular adhesion molecule-3-Grabbing Non-integrin inducing T cell anergy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, C.; Reichel, M.P.; Ellis, J. Neospora abortions in dairy cattle: Diagnosis, mode of transmission and control. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 128, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, M.V.; França, F.B.F.; Mota, C.M.; Junior, A.G.D.M.; Ramos, E.L.P.; Santiago, F.M.; Mineo, J.R.; Mineo, T.W.P. Dectin-1 Compromises Innate Responses and Host Resistance against Neospora caninum Infection. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loukas, A.; Doedens, A.; Hintz, M.; Maizels, R.M. Identification of a new C-type lectin, TES-70, secreted by infective larvae of Toxocara canis, which binds to host ligands. Parasitology 2000, 121, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loukas, A.; Mullin, N.; Tetteh, K.K.; Moens, L.; Maizels, R.M. A novel C-type lectin secreted by a tissue-dwelling parasitic nematode. Curr. Biol. 1999, 9, 825–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Die, I.; Cummings, R.D. Glycan gimmickry by parasitic helminths: A strategy for modulating the host immune response? Glycobiology 2009, 20, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokke, C.H.; van Diepen, A. Helminth glycomics—glycan repertoires and host-parasite interactions. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2017, 215, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra-Sánchez, H.; Bustamante-Córdova, L.; Reséndiz, M.; Mata-Haro, V.; Pinelli-Saavedra, A.; Hernández, J. Analysis of Swine Conventional Dendritic Cells, DEC205+CD172a+/-CADM1+, from Blood and Spleen in Response to PRRSV and PEDV. Viruses 2019, 11, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, J.; Day, C.J.; Von Itzstein, M.; Paton, J.C.; Jennings, M.P. Glycointeractions in bacterial pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 16, 440–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Shu, J.; Li, Z. Lectin microarrays for glycoproteomics: An overview of their use and potential. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2020, 17, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenen, H.; Bodendorfer, B.; Hitchens, K.; Manzanero, S.; Werninghaus, K.; Nimmerjahn, F.; Agger, E.M.; Stenger, S.; Andersen, P.; Ruland, J.; et al. Cutting edge: Mincle is essential for recognition and adjuvanticity of the mycobacterial cord factor and its synthetic analog trehalose-dibehenate. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 2756–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decout, A.; Silva-Gomes, S.; Drocourt, D.; Barbe, S.; André, I.; Cueto, F.J.; Lioux, T.; Sancho, D.; Pérouzel, E.; Vercellone, A.; et al. Rational design of adjuvants targeting the C-type lectin Mincle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 2675–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, R.; Schoenen, H.; Desel, C. Targeting Syk-Card9-activating C-type lectin receptors by vaccine adjuvants: Findings, implications and open questions. Immunobiology 2011, 216, 1184–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, A.; Andrea, A.; Mikkelsen, H.; Woodworth, J.S.; Andersen, P.; Jungersen, G.; Aagaard, C. Targeting the Mincle and TLR3 receptor using the dual agonist cationic adjuvant formulation 9 (CAF09) induces humoral and polyfunctional memory T cell responses in calves. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dissel, J.T.; Joosten, S.A.; Hoff, S.T.; Soonawala, D.; Prins, C.; Hokey, D.; O’Dee, D.M.; Graves, A.J.; Thierry-Carstensen, B.; Andreasen, L.V.; et al. A novel liposomal adjuvant system, CAF01, promotes long-lived Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific T-cell responses in human. Vaccine 2014, 32, 7098–7107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martel, C.J.-M.; Agger, E.M.; Poulsen, J.J.; Jensen, T.H.; Andresen, L.; Christensen, D.; Nielsen, L.P.; Blixenkrone-Møller, M.; Andersen, P.; Aasted, B. CAF01 Potentiates Immune Responses and Efficacy of an Inactivated Influenza Vaccine in Ferrets. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villumsen, K.R.; Kania, P.W.; Christensen, D.; Koppang, E.O.; Bojesen, A.M. Injection Vaccines Formulated with Nucleotide, Liposomal or Mineral Oil Adjuvants Induce Distinct Differences in Immunogenicity in Rainbow Trout. Vaccines 2020, 8, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryter, K.T.; Ettenger, G.; Rasheed, O.K.; Buhl, C.; Child, R.; Miller, S.M.; Holley, D.; Smith, A.J.; Evans, J.T. Aryl Trehalose Derivatives as Vaccine Adjuvants for Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 63, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, B.; Nieto-Pelegrín, E.; De La Riva, P.M.; Toki, D.; Poderoso, T.; Revilla, C.; Uenishi, H.; Ezquerra, A.; Domínguez, J. Characterization of the Porcine CLEC12A and Analysis of Its Expression on Blood Dendritic Cell Subsets. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, F.T.; Guldbrandtsen, B.; Christensen, D.; Pitcovski, J.; Kjærup, R.B.; Dalgaard, T.S. Pustulan Activates Chicken Bone Marrow-Derived Dendritic Cells In Vitro and Promotes Ex Vivo CD4+ T Cell Recall Response to Infectious Bronchitis Virus. Vaccines 2020, 8, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jáuregui-Zúñiga, D.; Pedraza, M.; Espino-Solis, G.P.; Quintero-Hernández, V.; Olvera-Rodríguez, A.; Díaz-Salinas, M.A.; López, S.; Possani, L.D. Targeting antigens to Dec-205 on dendritic cells induces a higher immune response in chickens: Hemagglutinin of avian influenza virus example. Res. Vet. Sci. 2017, 111, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jáuregui-Zúñiga, D.; Pedraza, M.; Merino-Guzman, R.; Possani, L.D. Construction and expression of a single-chain variable fragment antibody against chicken DEC 205 for targeting the bacterial expressed hemagglutinin-neuraminidase of Newcastle disease virus. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2019, 212, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, F.T.; Bed’Hom, B.; Guldbrandtsen, B.; Dalgaard, T.S. Identification and tissue-expression profiling of novel chicken c-type lectin-like domain containing proteins as potential targets for carbohydrate-based vaccine strategies. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 114, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, R.; Jaffe, C.L. Administration of β-glucan following Leishmania major infection suppresses disease progression in mice. Parasite Immunol. 1991, 13, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbrook, T.W.; Cook, A.J. Non-specific and specific stimulation of resistance against Leishmania donovani in C57BL/6 mice. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 1983, 13, 411–417. [Google Scholar]
- Alanazi, A.D.; Puschendorf, R.; Alyousif, M.S.; Al-Khalifa, M.S.; Alharbi, S.A.; Al-Shehri, Z.S.; Said, A.E.; Alanazi, I.O.; Al-Mohammed, H.I.; Alraey, Y.A. Molecular Detection of Leishmania spp. in Skin and Blood of Stray Dogs from Endemic Areas of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Saudi Arabia. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2019, 14, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.; Parreira, R.; Cristóvão, J.M.; Castelli, G.; Bruno, F.; Vitale, F.; Campino, L.; Maia, C. Phylogenetic insights on Leishmania detected in cats as revealed by nucleotide sequence analysis of multiple genetic markers. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 77, 104069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medkour, H.; Laidoudi, Y.; Marié, J.-L.; Fenollar, F.; Davoust, B.; Mediannikov, O. Molecular investigation of vector-borne pathogens in red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) from southern France. J. Wildl. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar Khan, M.; Khan, S.; Rafiq, K.; Khan, S.N.; Attaullah, S.; Ali, I. Molecular identification of Toxoplasma gondii in domesticated and broiler chickens (Gallus domesticus) that possibly augment the pool of human toxoplasmosis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnett, W.; Harnett, M.M. Helminth-derived immunomodulators: Can understanding the worm produce the pill? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGreal, E.P.; Rosas, M.; Brown, G.D.; Zamze, S.; Wong, S.Y.; Gordon, S.; Martinez-Pomares, L.; Taylor, P.R. The carbohydrate-recognition domain of Dectin-2 is a C-type lectin with specificity for high mannose. Glycobiology 2006, 16, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feinberg, H.; Jégouzo, S.A.F.; Rex, M.J.; Drickamer, K.; Weis, W.I.; Taylor, M.E. Mechanism of pathogen recognition by human dectin-2. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 13402–13414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soria, I.; Alvarez, J.; Manzano, A.I.; López-Relaño, J.; Cases, B.; Mas-Fontao, A.; Cañada, F.J.; Fernández-Caldas, E.; Casanovas, M.; Jiménez-Barbero, J.; et al. Mite allergoids coupled to nonoxidized mannan from Saccharomyces cerevisae efficiently target canine dendritic cells for novel allergy immunotherapy in veterinary medicine. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2017, 190, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roperto, S.; Russo, V.; Esposito, I.; Ceccarelli, D.M.; Paciello, O.; Avallone, L.; Capparelli, R.; Roperto, F. Mincle, an Innate Immune Receptor, Is Expressed in Urothelial Cancer Cells of Papillomavirus-Associated Urothelial Tumors of Cattle. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cash, H.L.; Whitham, C.V.; Behrendt, C.L.; Hooper, L.V. Symbiotic Bacteria Direct Expression of an Intestinal Bactericidal Lectin. Science 2006, 313, 1126–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, V.; Eshleman, E.M.; Rice, T.; Whitt, J.; Vallance, B.A.; Alenghat, T. Microbiota Inhibit Epithelial Pathogen Adherence by Epigenetically Regulating C-Type Lectin Expression. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.-H.; Liu, L.; Hou, Y.-Y.; Shen, S.-N.; Wang, T.-T. C-type lectin receptor-mediated immune recognition and response of the microbiota in the gut. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2019, 7, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, X.-L.; Ye, Z.-Y. The Effects of Lentinan on the Expression Patterns of β-Catenin, Bcl-2, and Bax in Murine Bone Marrow Cells Are Associated with Enhancing Dectin-1. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2019, 21, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Ran, P.; Zhu, M.; Sun, L.; Li, B.; Hou, Y.; Nie, J.; Shan, L.; Li, H.; Zheng, S.; et al. The Prefrontal Dectin-1/AMPA Receptor Signaling Pathway Mediates the Robust and Prolonged Antidepressant Effect of Proteo-β-Glucan from Maitake. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Sun, L.; Zhu, Y.; Ran, P.; Hu, W.; Zhu, K.; Li, B.; Hou, Y.; Nie, J.; Gao, T.; et al. Lentinan produces a robust antidepressant-like effect via enhancing the prefrontal Dectin-1/AMPA receptor signaling pathway. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 317, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosi, A.; Banfi, D.; Bistoletti, M.; Giaroni, C.; Baj, A. Tryptophan Metabolites Along the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis: An Interkingdom Communication System Influencing the Gut in Health and Disease. Int. J. Tryptophan Res. 2020, 13, 1178646920928984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlando, J.M. Behavioral Nutraceuticals and Diets. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2018, 48, 473–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballou, M.A.; Davis, E.M.; Kasl, B.A. Nutraceuticals: An. Alternative Strategy for the Use of Antimicrobials. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food. Anim. Pract. 2019, 35, 507–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Luo, M.; Zhu, F. Dietary Bacillus amyloliquefaciens enhance survival of white spot syndrome virus infected crayfish. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2020, 102, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, H.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Ullah, M.I.; Hussain, G.; Shabbir, M.Z.; Mustafa, I.; Sohail, M.U. Shiitake Culinary-Medicinal Mushroom, Lentinus edodes (Agaricomycetes), Supplementation Alters Gut Microbiome and Corrects Dyslipidemia in Rats. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2019, 21, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrzak, E.; Mazurkiewicz, J.; Slawinska, A. Innate Immune Responses of Skin Mucosa in Common Carp (Cyprinus Carpio) Fed a Diet Supplemented with Galactooligosaccharides. Animals 2020, 10, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, F.; Putarov, T.; Zaine, L.; Venturini, K.; Aoki, C.; Santos, J.; Pedrinelli, V.; Vendramini, T.; Brunetto, M.A.; Carciofi, A. Active fractions of mannoproteins derived from yeast cell wall stimulate innate and acquired immunity of adult and elderly dogs. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2020, 261, 114392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Qiu, T.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, W. Expression of C-type lectin receptors and Toll-like receptors in decidua of patients with unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2017, 29, 1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, R.; Lappas, M. Expression and function of macrophage-inducible C-type lectin (Mincle) in inflammation driven parturition in fetal membranes and myometrium. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2019, 197, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satterfield, M.C.; Song, G.; Kochan, K.J.; Riggs, P.; Simmons, R.M.; Elsik, C.G.; Adelson, D.L.; Bazer, F.W.; Zhou, H.; Spencer, T. Discovery of candidate genes and pathways in the endometrium regulating ovine blastocyst growth and conceptus elongation. Physiol. Genom. 2009, 39, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).