Abstract
Vitamin K (VK) is a key nutrient for several biological processes (e.g., blood clotting and bone metabolism). To fulfill VK nutritional requirements, VK action as an activator of pregnane X receptor (Pxr) signaling pathway, and as a co-factor of γ-glutamyl carboxylase enzyme, should be considered. In this regard, VK recycling through vitamin K epoxide reductases (Vkors) is essential and should be better understood. Here, the expression patterns of vitamin K epoxide reductase complex subunit 1 (vkorc1) and vkorc1 like 1 (vkorc1l1) were determined during the larval ontogeny of Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis), and in early juveniles cultured under different physiological conditions. Full-length transcripts for ssvkorc1 and ssvkorc1l1 were determined and peptide sequences were found to be evolutionarily conserved. During larval development, expression of ssvkorc1 showed a slight increase during absence or low feed intake. Expression of ssvkorc1l1 continuously decreased until 24 h post-fertilization, and remained constant afterwards. Both ssvkors were ubiquitously expressed in adult tissues, and highest expression was found in liver for ssvkorc1, and ovary and brain for ssvkorc1l1. Expression of ssvkorc1 and ssvkorc1l1 was differentially regulated under physiological conditions related to fasting and re-feeding, but also under VK dietary supplementation and induced deficiency. The present work provides new and basic molecular clues evidencing how VK metabolism in marine fish is sensitive to nutritional and environmental conditions.
1. Introduction
Increasing a sustainable animal production is essential to warrant world food security and nutrition in the nearest future [1,2]. Animal protein sources of aquatic origin are generally healthier (richer in n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids [3]), cheaper to produce and more sustainable (with better feed conversion rates) than those from the terrestrial livestock [4]. Several factors determine the world production of animal protein of aquatic origin. On the one hand, the loss of natural habitats, its degradation and pollution, and the reduction of biodiversity, reduce the productivity and profitability of ecosystem services and affect the well-being of human population [5,6]. On the other hand, the aquaculture sector, representing more than 50% of the total fish production, largely depends on genetic selection, husbandry practices and nutrition [1]. Regarding nutrition, fulfilling nutritional requirements is a cornerstone for aquaculture development [7,8], being critical for fish survival, growth potential, feed conversion efficiency and product quality, mainly during early development (i.e., embryonic, larval and early juvenile stages).
Nutritional requirements for micronutrients (minerals and vitamins) have still to be fine-tuned for marine fish larvae [9]. Their amount and chemical form depend on factors such as fish species, developmental phase, physiological stage, environmental conditions and nutritional approach used, among others (reviewed in [10]). Regarding vitamin K (VK), our understanding of VK metabolism and VK-dependent molecular pathways has increased during the last decade (reviewed in [10,11,12,13]). Three chemical VK forms exist: phylloquinone (VK1, from vegetable origin), menaquinones (VK2 or MK, from bacterial or animal origin) and menadione (VK3, synthetic). VK requirements are strongly dependent on the chemical form and fish species considered, ranging from 0.1 mg to 20 mg kg−1. In this sense, although VK3 has a limited bioavailability, it is the most common source of VK in aquafeeds (reviewed in [12]). In general, VK nutritional requirements were considered to be low, as VK was thought to be mainly involved in blood coagulation, and no major signs of bleeding disorders were observed in fish with low VK dietary levels [12]. In fish species, the key role of VK in biological processes, such as sex hormone synthesis/release and reproductive performance [14], skeletal development and maintenance [15,16,17,18], neural development and cognitive capacities [19], and redox system homeostasis, vasculogenesis and visual phototransduction [18], has been evidenced, and higher VK nutritional requirements during early developmental stages than previously thought were suggested [15,16,18].
For a proper estimation of VK nutritional requirements throughout larval development, a detailed molecular characterization of the main VK gene networks and pathways, and how they respond under changing physiological conditions, is fundamental. VK exerts its biological functions through two main pathways: as an agonist of the pregnane X receptor (Pxr), which has transcriptional activity [20,21], and as a co-factor of the γ-glutamyl carboxylase (Ggcx) enzyme, which promotes the conversion of glutamate (Glu) into γ-carboxyglutamate (Gla) residues in VK-dependent proteins (VKDPs; reviewed by Oldenburg et al. [22]). Carboxylation requires the abstraction of a proton from the 4-carbon of the glutamate residue by reduced VK and results in the conversion of VK into VK epoxide. The VK epoxide must be recycled into VK before it can be reused, a reaction that is catalyzed by two VK 2,3-epoxide reductases (Vkors), the Vkor complex subunit 1 (Vkorc1) and Vkorc1-like 1 (Vkorc1l1), which probably arose from the duplication of a Vkor ancestor gene [23,24,25,26,27,28].
Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis) is a marine flatfish used to understand the molecular mechanisms of asymmetrical morphology [29,30], to conduct biomonitoring programs of coastal ecosystems [31,32], and is an important fish species for European aquaculture diversification [33]. As a result of the interest of both the industry and academia, the knowledge on optimal husbandry practices and environmental conditions, genetic background, and/or nutrition, has recently been improved (reviewed in Muñoz-Cueto et al. [34]). Nevertheless, its production has been hampered by problems in the reproduction of F1 broodstocks [14,35,36,37,38] and the high incidence of skeletal deformities [39,40,41,42,43,44,45], among other factors.
Early during their development, Senegalese sole larvae undergo metamorphosis, a highly complex transition process that involves deep morphological, biochemical and physiological transformations that allow pelagic larvae to become juveniles with a benthic behavior [46]; a phase where the onset of many skeletal deformities might occur [45]. Indeed, Senegalese sole larval performance and skeletal quality improvement through dietary VK1 supplementation was previously suggested [15]. We also observed Senegalese sole pxr gene expression dependent on the developmental-stage and tissue considered, suggesting a variable VK requirement for its ligand transactivation [19]. Here we hypothesized that vkorc1 and vkorc1l1 gene expression might be altered through larval development and will be tissue-specific, reflecting that dietary VK requirement might depend on fish development and biological process considered. The present work aims at getting full-length transcript sequences of Senegalese sole vkors, at studying their evolutionary conservation, and at determining their expression patterns during larval development and adult tissues, but also under relevant physiological conditions, in order to understand how VK recycling is vital to promoting good growth and normal development in fish.
2. Results
2.1. Senegalese Sole vkorc1 and vkorc1l1 Full-Length cDNA Sequences and Common Protein Sequence Features with Vertebrate Vkors
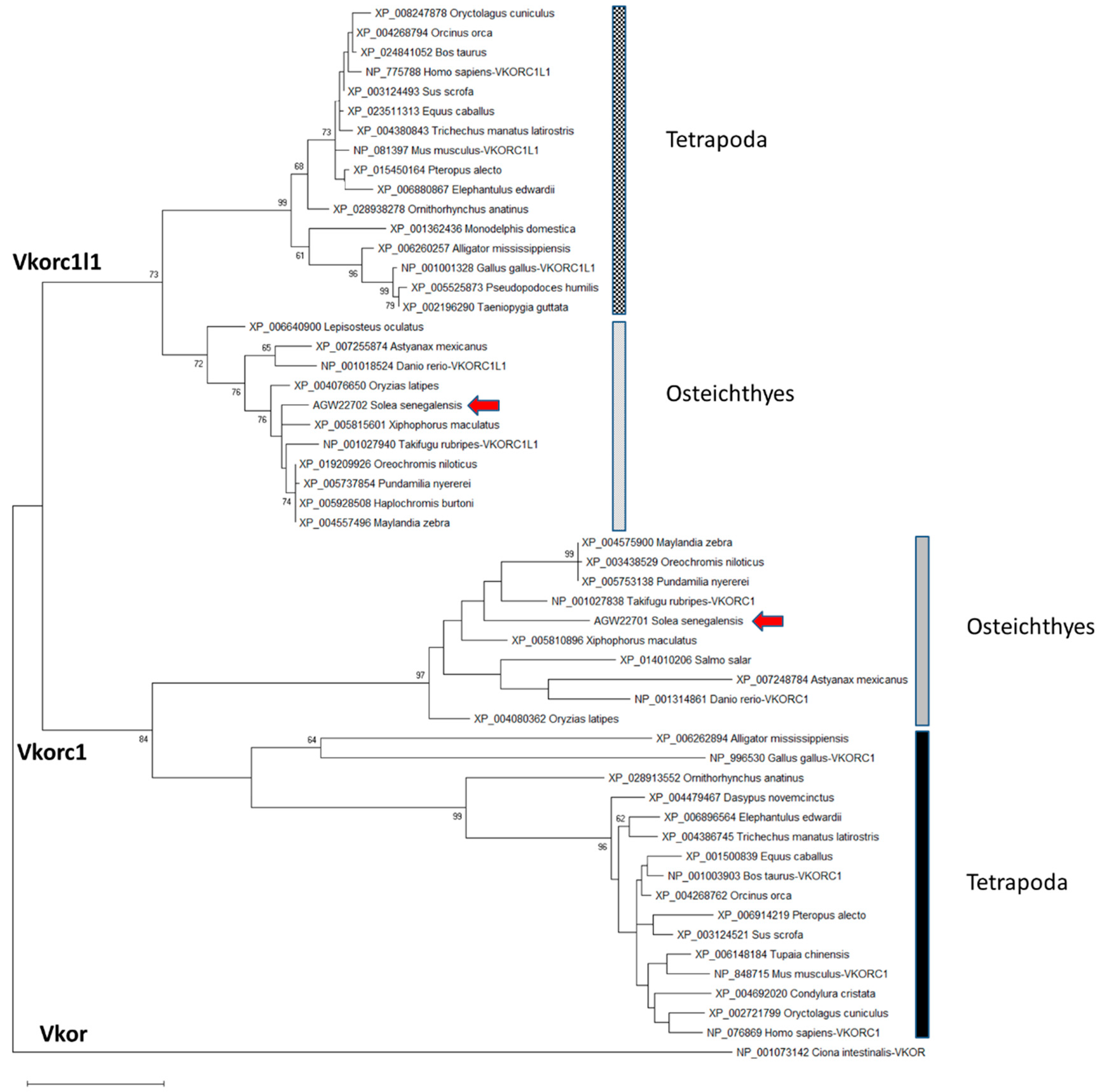
Partial nucleotide sequences for Senegalese sole vkors published by Richard et al. [15]—a 489 bp fragment for vkorc1l1 and a 201 bp fragment for vkor-1—were used to get 5’ and 3’ transcript ends by Rapid Amplification of Complementary deoxyribonucleic acid (cDNA) Ends (RACE) polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Using available cDNA fragments, the full-length transcripts for ssvkorc1l1 (1168 bp; GenBank accession no. KC108910) and ssvkor-1 (748 bp; GenBank accession no. KC108911) were reconstructed and later confirmed by PCR. Deduced peptides ssVkorc1l1 (GenBank accession no. AGW22701) and ssVkorc1 (GenBank accession no. AGW22702) were 175 amino acids (aa) and 161 aa long, respectively. The phylogenetic analysis of 54 vertebrate Vkor protein sequences (see species and GenBank accession no. in Table S1) revealed that AGW22701 and AGW22702 clustered with annotated sequences of Vkorc1 and Vkorc1l1, respectively, and had highest homology with teleost sequences, confirming their identity as Senegalese sole orthologues ssVkorc1 and ssVkorc1l1, respectively (Figure 1).
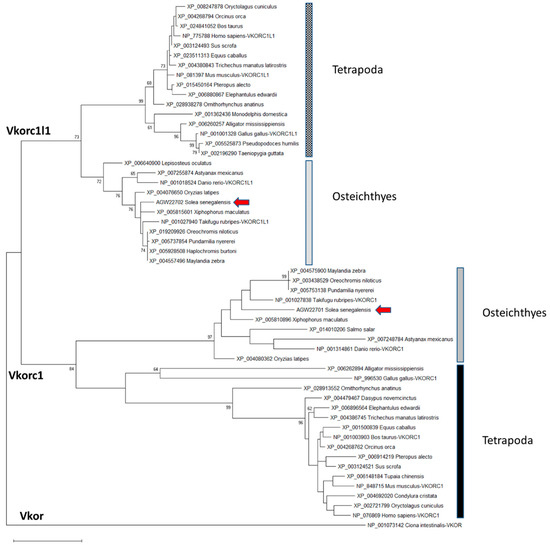
Figure 1.
Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of vitamin K epoxide reductases (Vkors). The evolutionary history was inferred by using the Maximum Likelihood method and Le and Gascuel model [47]. The percentage of trees in which the associated taxa clustered together is shown next to the branches. Initial tree(s) for the heuristic search were obtained by applying the Neighbor Joining method to a matrix of pairwise distances estimated using a Jones-Taylor-Thornton (JTT) model. A discrete Gamma distribution was used to model evolutionary rate differences among sites (5 categories (+G, parameter = 0.7756)). The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths measured in the number of substitutions per site. This analysis involved 54 amino acid sequences. All positions with less than 95% site coverage were eliminated, i.e., fewer than 5% alignment gaps, missing data, and ambiguous bases were allowed at any position (partial deletion option). There was a total of 150 positions in the final dataset. Evolutionary analyses were conducted in MEGA X [48]. Ciona intestinalis Vkor sequence was used as outgroup to root the tree. Scale bar represents nº of substitutions per site.
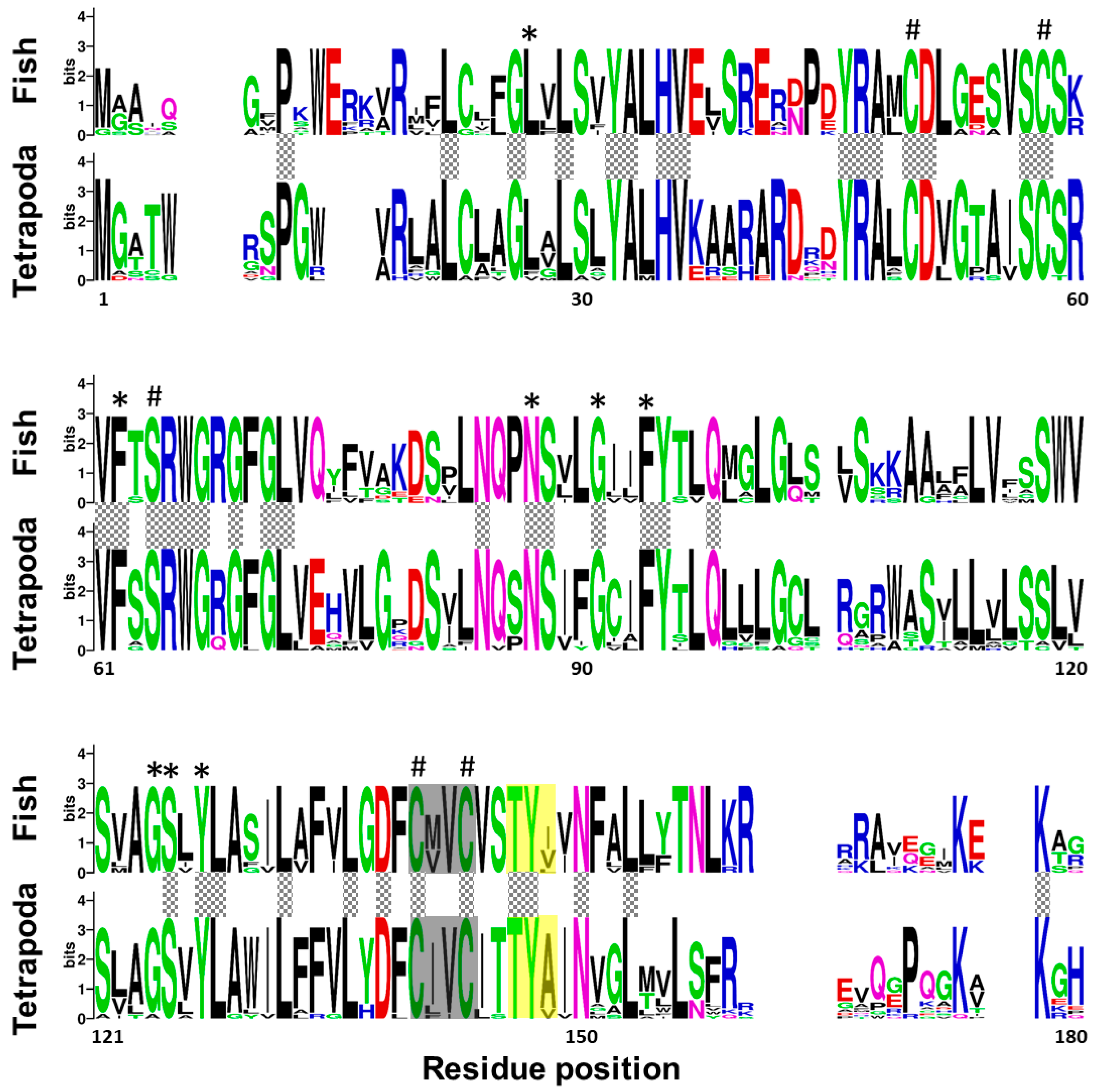
A multi-sequence alignment, using T-coffee platform, of 7 protein sequences corresponding to Vkor sequence from sea squirt (Ciona intestinalis), and Vkorc1 and Vkorc1l1 sequences from Senegalese sole, human (Homo sapiens) and mouse (Mus musculus), showed a high degree of conservation of the characteristic four cysteines and the serine residues, the four transmembrane domains, the thiol redox (CXXC) site, and the warfarin binding motif (TYX; Figure S1). A weblogo comparative analysis of fish and tetrapod Vkorc1 and Vkorc1l1 peptides also revealed the conservation of important amino acids related to Vkors protein function in a broader context. Fish and tetrapod Vkorc1 protein sequences (Figure 2) have 44 amino acid residues fully conserved, including the previously reported and characteristic four cysteines and the serine, as well as the CXXC site of known hydrophobic environment. Fish Vkorc1 protein sequences showed a higher conservation degree than tetrapods, with 99 amino acid residues fully conserved. Furthermore, in both taxonomic groups the warfarin binding motif was identified, although not fully conserved, with a lower degree of conservation on the third amino acid residue in fish species.
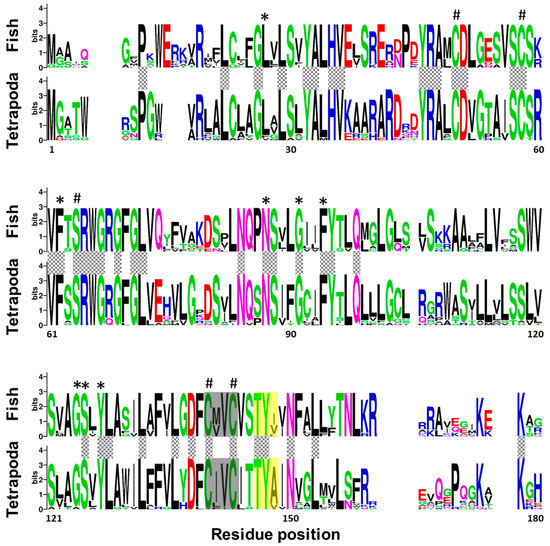
Figure 2.
Conservation of amino acid residues in vitamin K epoxide reductase complex subunit 1 (Vkorc1) between fish and tetrapods. Logos were constructed from isoform-specific alignments of mature peptides. The height of the letters is directly proportional to their frequency. Asterisks indicate amino acids fully conserved within fish species; hashes indicate Vkor active sites (four cysteines and one serine); yellow box, warfarin binding motif (TYX); grey box, hydrophobic environment of the thiol redox site of the enzyme; grey squared boxes between alignments, amino acids with full conservation between both taxa: fish and tetrapoda.
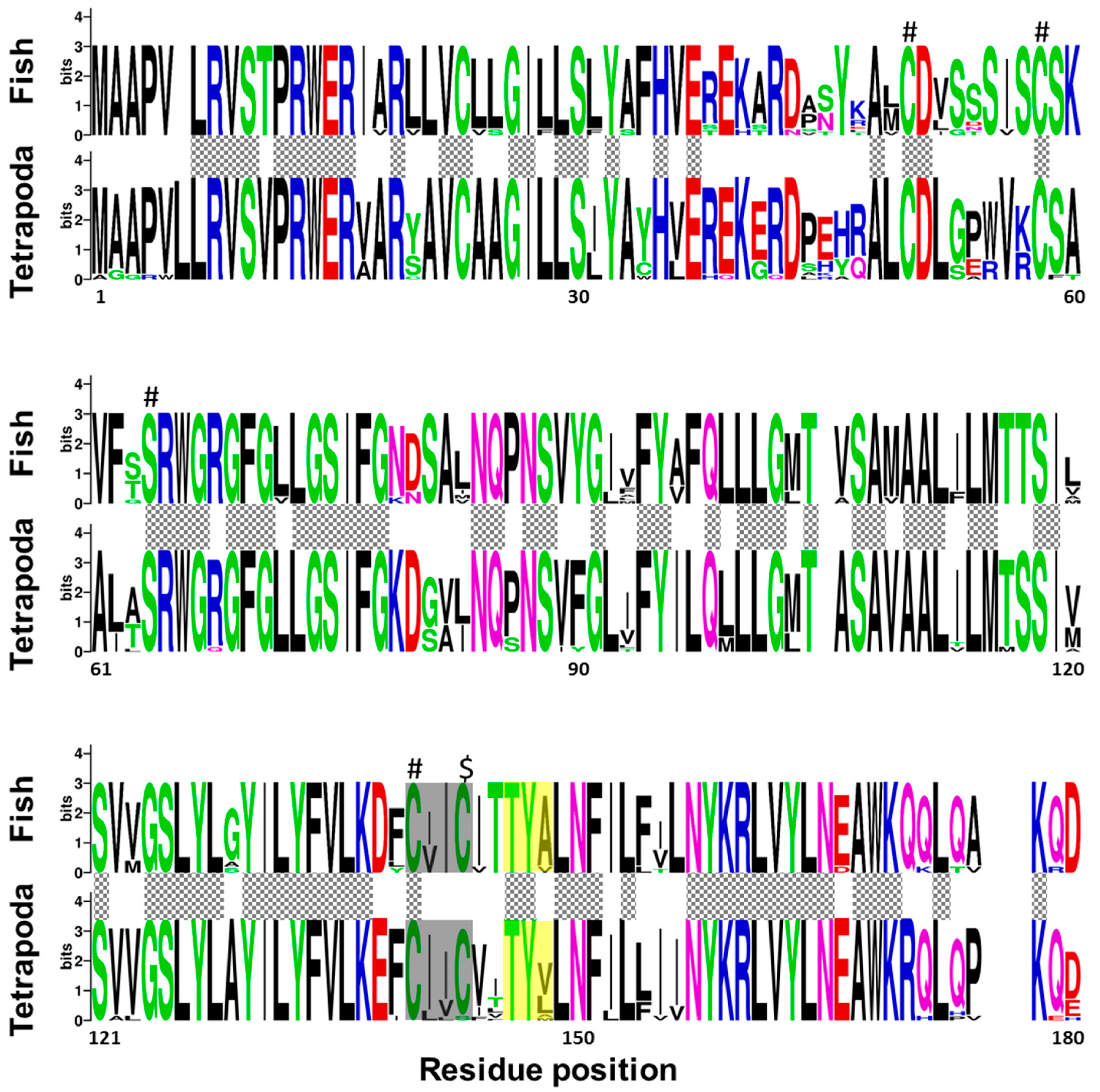
Regarding fish and tetrapod, Vkorc1l1 peptides revealed that 92 amino acid residues were fully conserved between the two taxonomic groups, and 130 among fish species (Figure 3). In contrast to Vkorc1, and although the reported characteristic serine was fully conserved, only three of the four cysteines were fully conserved, being not fully conserved in the last one of the thiol redox (CXXC) site. As for Vkorc1, warfarin binding motif (TYX) was not fully conserved in Vkorc1l1. In contrast to Vkorc1, the third residue of the TYX motive was less variable in fish species.
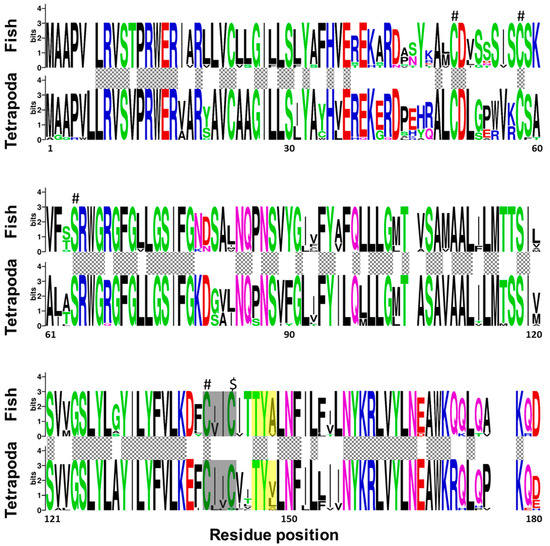
Figure 3.
Conservation of amino acid residues in vitamin K epoxide reductase complex subunit 1 like 1 (Vkorc1l1) between fish and tetrapods. Logos were constructed from isoform-specific alignments of mature peptides. The height of the letters is directly proportional to their frequency. Please, note that: Hashes indicate Vkor active sites (three cysteines and serine); dollar symbol, indicates the non-fully conserved Vkor active site (a cysteine); yellow box, warfarin binding motif (TYX); grey box, the known hydrophobic environment of the thiol redox site of the enzyme; grey squared boxes between alignments, amino acids with full conservation between both taxa: fish and tetrapoda.
2.2. Expression of ssvkorc1 and ssvkorc1l1 During Development and in Adult Tissues
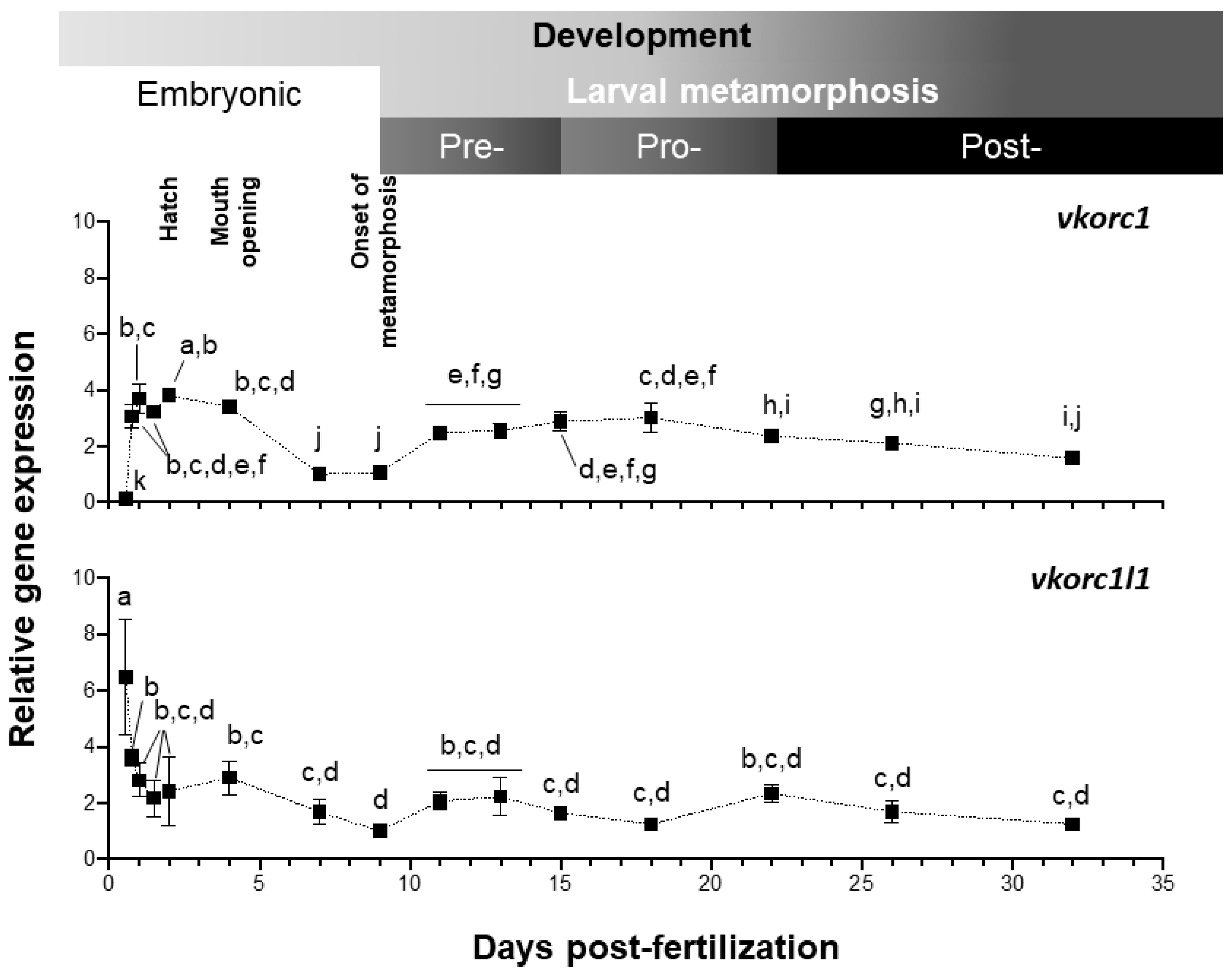
Expression of Senegalese sole vkor genes was evaluated by quantitative PCR (qPCR), from 13.5 h post-fertilization (hpf) embryonic stage, to 32 days post-fertilization (dpf) post-metamorphic juvenile stage (Figure 4). Both genes showed a clearly distinct pattern of expression along larval development. Level of ssvkorc1 expression was the highest (up to 3.8 folds) after hatching (48 hpf), diminished at 7–9 dpf (1.0–1.1 folds), increased through pre- and pro-metamorphosis (up to 3.0 folds) and remained stable during post-metamorphosis (ranging from 1.5 to 2.3 folds). ssvkorc1l1 expression pattern during larval development and metamorphosis showed an initial sharp decrease, from the maximal gene expression at 13.5 hpf (6.5 folds) to a 50% decreased level at 18.5 hpf (3.6 folds). Afterwards, ssvkorc1l1 expression remained constant (between 2.2 and 2.8 folds), decreased to its minimal expression at 9 dpf (1.0 folds), and slightly increased to remain constant during pre-, pro- and post-metamorphosis (around 1.2 to 2.3 folds).
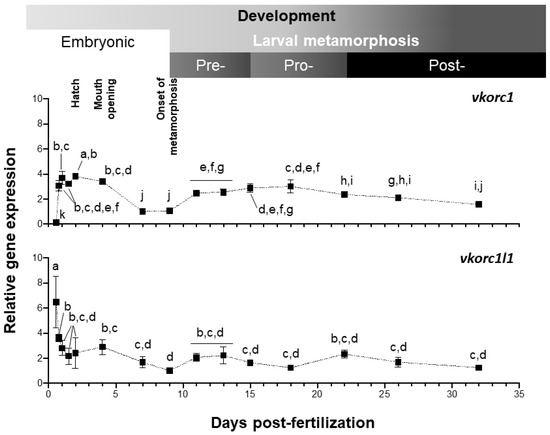
Figure 4.
Relative gene expression of Senegalese sole vitamin K epoxide reductase complex subunit 1 (ssvkorc1) and vkorc1 like 1 (ssvkorc1l1) throughout larval development. Transcript levels of ssvkorc1 (upper image) and ssvkorc1l1 (bottom image) were determined by qPCR and normalized using ubiquitin (ubq) gene expression. Levels at 7 and 9 hours post-fertilization (dpf) were used as reference and set to 1 for ssvkorc1 and ssvkorc1l1, respectively. Different letters over gene expression values denote significant differences among developmental stages (n = 3; one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), Tukey multiple-comparison test; P < 0.05).
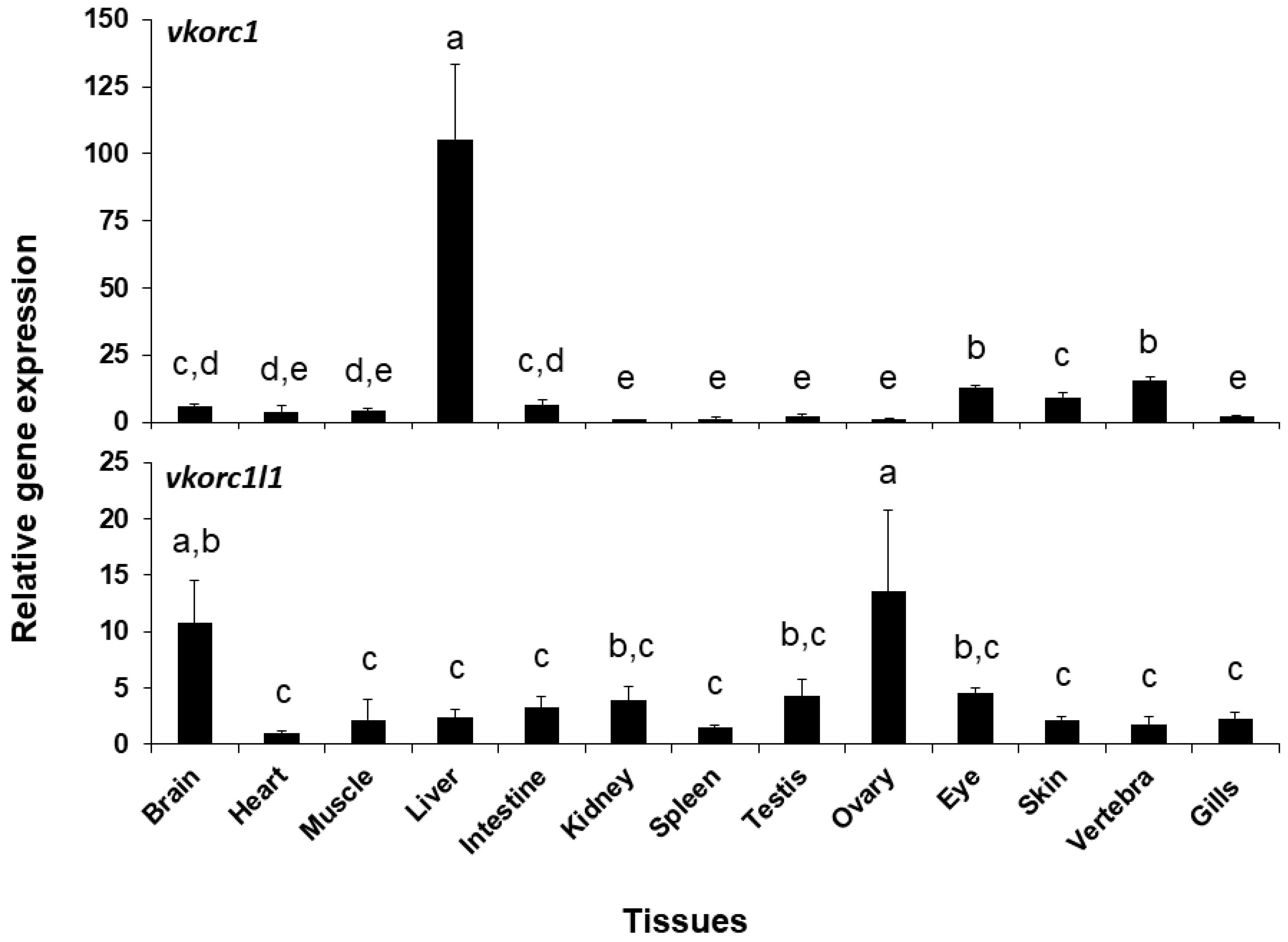
Expression of ssvkorc1 and ssvkorc1l1 was also different depending on the tissue considered (Figure 5). A clearly high expression of ssvkorc1 was found in the liver (105.4 ± 28.1 folds), while it was low in the other tissues (from 1.0 to 13.2 folds). A more homogeneous gene expression pattern was observed for ssvkorc1l1. In this case, highest expression levels were found in brain and ovary tissues (10.7 and 13.5 folds, respectively), while intermediate gene expression values were found in kidney, testis and eye tissues (from 3.8 to 4.6 folds) and lowest in the other explored tissues (from 1.0 to 3.2 folds). A direct comparison of the contribution of both genes (comparing cycle threshold (Ct) values of both genes for each tissue; Table S2) shows that ssvkorc1l1 gene expression levels (Ct values ranging from 33 to 37) are lower than those of ssvkorc1 (with Ct values ranging from 26 to 31) in all tissues unless in the ovary, where both genes might almost equally contribute (Ct values ranging 29–31 and 28–29, respectively).
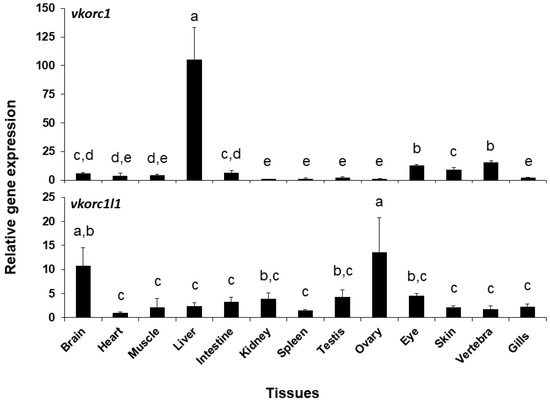
Figure 5.
Relative gene expression of Senegalese sole vitamin K epoxide reductase complex subunit 1 (ssvkorc1) and vkorc1 like 1 (ssvkorc1l1) in adult tissues. Transcript levels of ssvkorc1 (upper image) and ssvkorc1l1 (bottom image) were determined by qPCR and normalized using ubiquitin (ubq) gene expression. Levels in kidney and heart were used as reference and set to 1 for ssvkorc1 and ssvkorc1l1, respectively. Different letters on the top of each bar denote significant differences among tissues (n = 3; one-way ANOVA, Tukey multiple-comparison test; P < 0.05).
2.3. Expression of ssvkorc1 and sskorc1l1 under Different Physiological Conditions
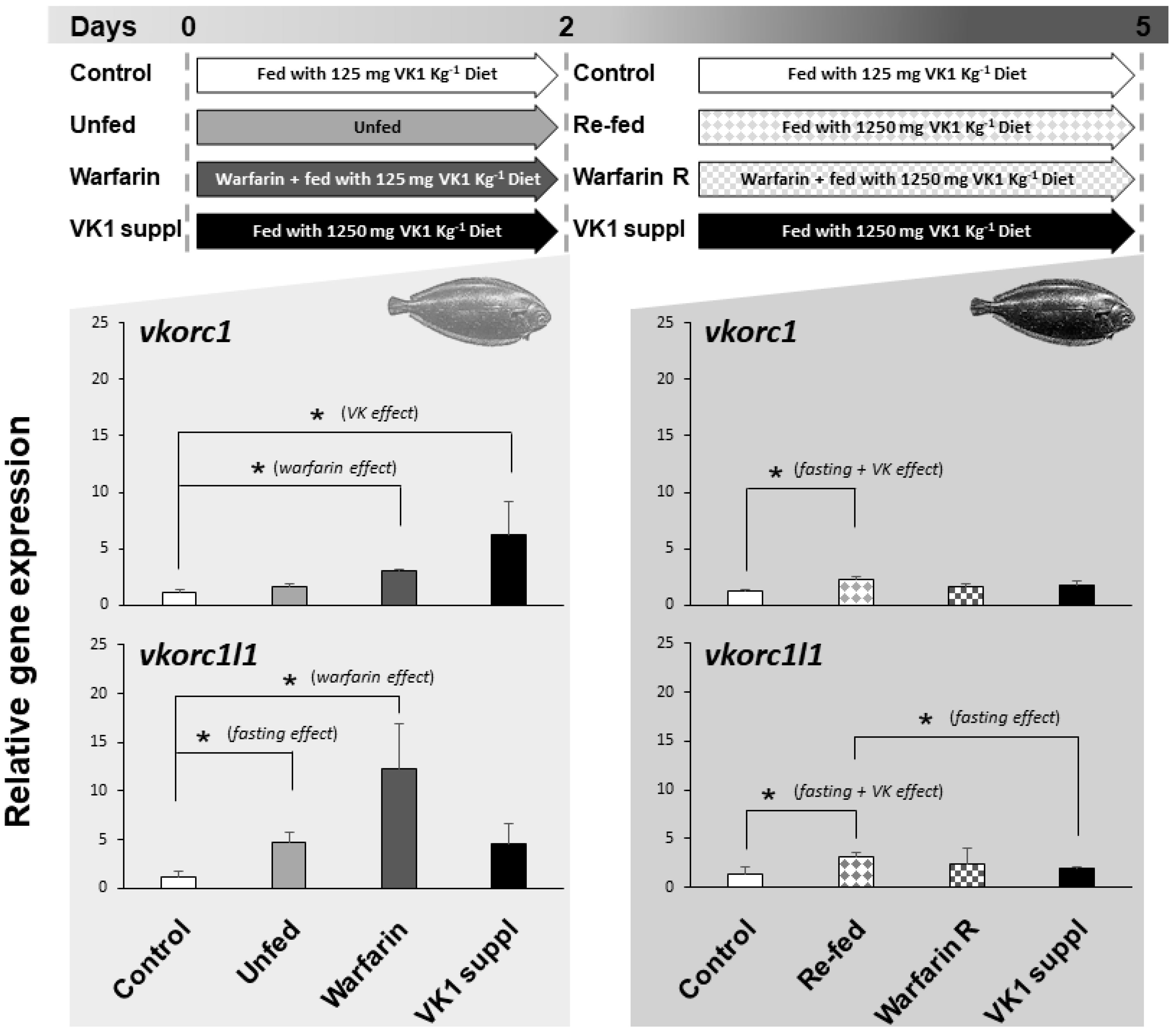
The expression of ssvkorc1 and ssvkorc1l1 in whole Senegalese sole early juveniles, reared under relevant physiological conditions, and found in the natural environment and/or specific to fish farming environment (fasting, re-feeding, presence of emerging contaminants or supplementation of VK), was evaluated (Figure 6). Expression of ssvkorc1 in early juveniles unfed for two days did not show significant differences with control fish (fish fed with 125 mg kg−1 dry weight (DW) of phylloquinone (VK1); 125VK1 diet), ranging 1.2 ± 0.2 to 1.6 ± 0.3 folds. Nevertheless, juveniles fasted for two days and then re-fed for three days with a feed supplemented with VK1 (1250 mg kg−1 DW of VK1; 1250VK1 diet)—compiling fasting and VK effects—showed an increased ssvkorc1 expression (2.2 ± 0.3 folds) compared to control fish (fed with 125VK1 diet). In contrast, ssvkorc1l1 expression was up-regulated (4.8 ± 0.9 folds) in unfed juveniles during two days compared to the control group. Furthermore, when unfed fish were re-fed for three days with 1250VK1 diet, ssvkorc1l1 expression was significantly higher (3.2 ± 0.4 folds) than that of fish fed 125VK1 diet (Control) and 1250VK1 diet (VK1 suppl) over five days.
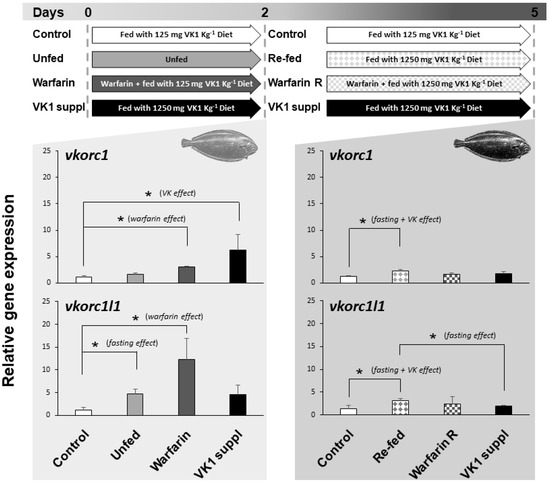
Figure 6.
Experimental design and relative gene expression of Senegalese sole vitamin K epoxide reductase complex subunit 1 (ssvkorc1) and vkorc1 like 1 (ssvkorc1l1) in juveniles cultured under different physiological conditions. Top image: experimental design indicating the physiological conditions to which Senegalese sole juveniles were subjected, from zero to two days and from two to five days. Grey shadow graphs: mean and standard deviations values of ssvkorc1 (upper image) and ssvkorc1l1 (bottom image) transcript levels at two and five sampling days. Transcript levels were determined by qPCR and normalized using ubiquitin (ubq) gene expression levels. Levels in Control group were used as reference and set to 1. Left side of the graphs: juveniles fed with 125VK1 diet (Control), kept unfed (Unfed), exposed to 25 mg L−1 of warfarin while fed with 125VK1 diet (Warfarin), or fed with 1250VK1 diet (VK1 suppl) for two days. Right side of the graphs: juveniles fed with 125VK1 diet for five days (Control), fed with 1250VK1 diet for three days after being kept unfed for two days (Re-fed), fed with 1250VK1 diet for three days while being exposed to 25 mg L−1 of warfarin (Warfarin R), or fed with 1250VK1 diet (VK1 suppl) for five days of experiment. At two days all Experimental groups were compared to Control group, while at five days all experimental groups were compared to Control and VK1 suppl group. Asterisks on the top denote significant differences between the two experimental groups compared (n = 3; Student’s t-test; P < 0.05). Text in brackets indicates the effect studied within each comparison.
When juveniles fed 125VK1 diet were exposed for two days to 25 mg L−1 of warfarin (Warfarin group), a rodenticide commonly used worldwide that induces VK deficiency, gene expression of ssvkorc1 (3.0 ± 0.1 folds) and ssvkorc1l1 (12.2 ± 4.6 folds) was significantly increased. After these two days, continued warfarin exposure but feeding with 1250VK1 diet led expression of ssvkorc1 and ssvkorc1l1 to reach levels not significantly different from either Control or VK1 supplied groups at five days.
Finally, expression of ssvkorc1 and ssvkorc1l1 in juveniles fed with 1250VK1 diet (10 times more VK1 than the Control diet) showed a different regulation throughout time. While ssvkorc1 expression was up-regulated (6.2 folds) after two days, it returned to basal levels after five days (1.8 ± 0.3 versus 1.2 ± 0.2 folds in Control group). The tendency for ssvkorc1l1 expression was similar after two days (an increase of 4.5 ± 2.1 folds versus 1.2 ± 0.5 folds in the Control group), although differences were not significantly different. After five days of feeding with 1250VK1 diet, expression was also unaltered (1.9 ± 0.2 versus 1.4 ± 0.7 folds in Control group).
3. Discussion
Vitamin K (VK) is an essential micronutrient that vertebrates do not synthesize, thus they depend on dietary sources to obtain the required daily amounts. Nowadays, VK is known to be required for blood coagulation [49,50], skeletal tissue [21] and redox [23,51] homeostasis, sphingolipid [52] and glucose metabolism [53], neural development and cognitive capacities [52,54,55,56], pathological calcification and inflammation [57,58,59], angiogenesis [60], and reproduction [61,62,63]. Studies in fish also suggest that VK is required for blood coagulation [16,64], skeletal development and skeletal tissues homeostasis [15,17,18], redox homeostasis [18], sphingolipid metabolism [14], brain development and cognitive capacities [19], pathological calcification and inflammation [16], and reproduction [14,16,65], reinforcing the idea of a well conserved function of VK throughout vertebrate evolution [26,66]. Nevertheless, the identification and characterization of the different molecular pathways where VK acts in vertebrates development and physiology, particularly how they respond to relevant physiological conditions, still needs to be determined in order to identify potential suitable biomarkers of VK nutritional status [67,68,69].
3.1. ssvkorc1 and ssvkorc1l1 are Orthologous to Vertebrate Vkors
Up to date, Vkor orthologues have been detected in different taxa of eukaryotic organisms, being Vkorc1 and Vkorc1l1 paralogues that probably originated through a duplication event occurring at the base of the vertebrate split from other metazoans [66]. While Goodstadt and Ponting [70] were the first to identify the four conserved cysteines and a conserved serine/threonine as residues likely required for the enzymatic activity of Vkorc1, by comparing Vkorc1 sequences from 37 species of archaea, eubacteria, plants, invertebrates and vertebrates, we and others further confirmed the conservation of these five residues in other species [65,66]. Here, we have cloned two vkor-related transcripts in Senegalese sole (ssvkorc1 and ssvkorc1l1, respectively), and confirmed that related peptides are orthologous to vertebrate Vkorc1 and Vkorc1l1 through phylogenetic analysis. Senegalese sole Vkorc1 and Vkorc1l1 showed the characteristic cysteine and serine conserved residues, the four transmembrane domains, the thiol redox site and the warfarin binding motif characteristic of Vkors. In addition, we have identified the presence of highly conserved residues not only among fish species, but also when comparing sequences from fish and tetrapod taxa, and evidenced a higher amino acid residue conservation in Vkorc1l1 than in Vkorc1. Conserved residues have been associated with the VK 2,3-epoxide to VK quinone, and VK quinone to VK quinol reduction (the above-mentioned four cysteines and the serine), the transmembrane helices, and the putative functional residues essential for quinone substrate reduction or substrate binding and specificity [66,71]. In this sense, some of the residues reported to be important in K vitamers binding with human Vkorc1 [71] were fully conserved in fish species. For instance, residues F55, N80 and F87 (but not F83 and L112), involved in VK1 MK-4 and MK-7 binding, and residues A115 and G116 for MK-7 binding, were conserved. We also confirmed the higher conservation of the warfarin binding motif (TYX) in fish Vkorc1l1 proteins, with most species exhibiting the fully conserved form (TYA motif) in human and mouse Vkorc1, as previously reported in zebrafish (Danio rerio) Vkors [65]. Research studies on protein sequence analysis and functional characterization of Vkors in fish species are scarce compared to the extensive effort made in mammals, [72,73,74,75] and more recently in birds [76]. Taking into account the relevant roles of Vkorc1 and Vkorc1l1 in recycling VK, and thus on vertebrate development and physiology, it may be highly relevant for the aquaculture industry to identify single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in vkors from important species (including Senegalese sole), toward the selection of breeders with lower VK nutritional requirements and/or more efficient VK recycling. The present research work providing the cDNA sequences might also be used for the recombinant production of ssVkorc1 and ssVkorc1l1 in in vitro systems, to assess their function and characterize their ability to bind and recycle different K vitamers. This would certainly help to identify the most suitable source of VK (or the best combination) to be included in the diets for each particular fish species.
3.2. ssvkorc1 and ssvkorc1l1 Distinct Gene Expression Patterns May Reflect Their Functional Specialization
The exploration of the gene expression values of Senegalese sole vkors, by means of qPCR, might be a suitable approach to get insights into the nutritional requirements of VK along its ontogenetic development, and in different tissues/organs. The potential effects of organ size being variable along the larval development (and thus, the portion of its RNA with respect to the total RNA) on the interpretations performed using a whole-body RNA extraction protocol might not be neglected. Nevertheless, the higher expression of ssvkorc1 and ssvkorc1l1 during embryonic development (from 18.5 hpf to 2 dpf and from 13.5 to 24 hpf, respectively) is consistent with the expression profile of both genes in zebrafish [65], suggesting that VK is actively recycled during fish endotrophic development, due to the lack of new dietary incomes of VK. These high values are also consistent with a higher developmental and physiological impact of VK deficiency, induced by warfarin exposure during zebrafish embryogenesis [18], than during larval development and/or adult stages [16,17]. These results are clearly in line with the most known consequences of VK deficiency: the preterm death by excessive bleeding and abnormal skeletal development in newborns [13,77,78,79]. Furthermore, increased gene expression of ssvkorc1 from post-fertilization to mouth opening, in parallel with a decreased expression of ssvkorc1l1, is in agreement with the restricted capacity of Vkorc1l1 in supporting VKDP carboxylation in liver and bone only during the mammalian pre- and perinatal periods in the absence of Vkorc1 [27]. A second peak of expression was observed for ssvkorc1 during pre- and pro-metamorphosis. When Senegalese sole larvae initiate hormonal and morphological transformations in order to adapt their body to a benthonic way of life, a stressful condition that correlates with reduced feed intake [45,80], an increased VK recycling through Vkorc1 might help to sustain VKDPs hepatic γ-carboxylation.
Vertebrate genomes contain two Vkors, Vkorc1 and its paralog Vkorc1l1 [26]. Upon gene duplication, one of the paralogs can evolve a new function, a process known as neofunctionalization. In this regard, patterns of ssvkorc1 and ssvkorc1l1 expression were also different in the adult tissues selected in this work. Highest and almost exclusive ssvkorc1 expression in liver is consistent with expression data reported for vkorc1 in mouse liver [24], and functional data showing that Vkorc1 is the main isoform responsible for recycling VK epoxide originated from hepatic γ-carboxylation of hemostasis-related VKDPs [25]. Vkorc1l1 has been recently shown to support in vivo VKDP carboxylation in liver and bone during the pre- and perinatal periods in the absence of Vkorc1 [27,28], suggesting a partial redundancy between both Vkors. In line with this, ssvkorc1 and ssvkorc1l1 were here found to be expressed in both tissues (liver and vertebra). High expression of ssvkorc1l1 in brain is in agreement with previous reports, showing high expression in fish and rodent brains [24,65,81], and the proposed role of VK in brain development and homeostasis [19,52]. High expression of ssvkorc1l1 observed in ovary further supports a central role of VK in reproduction [14,82], and is in agreement with the VK nutritional requirement proposed for offspring development [83]. The tissue gene expression patterns here reported suggest an urgent need for determining the VK nutritional requirements for the normal development and functioning of neural and reproductive systems, most probably with K2 vitamers.
3.3. Expression of ssvkorc1 and ssvkorc1l1 is Differentially Regulated under Relevant Physiological Conditions
In general, and in contrast to the other fat-soluble vitamins, vertebrates seemed to have a low VK nutritional requirement [10]. Recommended dietary levels are in the order of 20,000 to 50,000 international units (IU) kg−1 for vitamin A, 240 to 1,300,000 IU VD3 kg−1 for vitamin D, and 25 to 3000 mg α-tocopherol kg−1 for vitamin E, depending on the fish species considered [10], while suggested optimal dietary levels for VK in juveniles are 1.5–20 mg VK3 kg−1 (reviewed in [11]). In fact, lower requirements might probably be due to the VK recycling system in hepatic and extra-hepatic tissues, through the conserved action of Vkorc1 and Vkorc1l1 along evolution [26].
Although no severe deformities (scoliosis, lordosis and/or kyphosis) were reported in Senegalese sole larvae when VK content in the commercial emulsion used to enrich Artemia was increased (up to 250 mg kg−1), a lower incidence of skeletal deformities per specimen, particularly at the caudal fin region, was observed [15]. Although those deformities of the caudal fin were small, they are largely accepted to be the source of the severe deformities encountered in the caudal fin (e.g., vertebral compression and/or fusion) in Senegalese sole at later stages, thus suggesting the former authors a slightly better osteological development when increased dietary VK content was offered to the larvae. In the same study, VK1 dietary supplementation for 40 days was associated with a lower expression of ssvkorc1. Here, expression of ssvkorc1 increased when sole juveniles normally fed a diet containing 125 mg VK1 kg−1 were given a diet containing 10 times more VK1 for two days, but returned to basal (Control) values when the feeding schedule with supplemented VK1 diet was extended to five days. This result supports the hypothesis that VK recycling through ssVkorc1 and VK metabolism is regulated, and progressively adapts to altered VK1 dietary intake. In a short-term exposure (two days feeding), higher dietary VK content might lead to higher availability of VK, more γ-carboxylation reactions of VKDPs, and thus more VK epoxide. Similar to warfarin exposure, higher VK epoxide accumulation might require more VK recycling in order to avoid alterations of the redox status, resulting in an induction of higher expression of vkorc1. In a longer-term situation, different regulatory steps might be activated (e.g., blocking/reducing dietary VK assimilation at intestine through NPC1L1, or increased hydroxylation of VK1 by CYP4F2; reviewed in [10]) reducing the VK availability, and a lower expression of vkorc1 might be restored. This was previously observed in Senegalese sole larvae fed increasing levels of VK for more than 30 days [15], and here after 5 days continuous feeding a diet containing 1250 mg kg−1. In contrast, expression of ssvkorc1l1 remained unchanged in both conditions regardless of VK1 dietary intake, suggesting that a controlled metabolism and transport of K vitamers (VK1, VK2 metabolites, including menaquinone-4 and -7 (MK-4 and MK-7, respectively), and VK3) to extra-hepatic tissues might occur. Unfortunately, our understanding of how VK1 is absorbed at the intestinal lumen, transported or partially metabolized to VK3, and progressively prenylated to MK-4 by UbiA prenyltransferase domain-containing protein 1 (Ubiad1), is still limited (reviewed in [13]). Nevertheless, while VK1 is known to be preferentially retained in the liver to assist γ-carboxylation of clotting factors, VK2 has to be redistributed through circulation in order to be available for extra-hepatic tissues [84]. Moreover, while the low absorption efficiency of K vitamers from the diet (between 5% and 20% for VK1 and 55% for VK2 [85,86]) suggests a very high efficiency of hepatic VK recycling during the synthesis of blood clotting factors, it is still questioned whether similar efficiency is obtained in other tissues (e.g., bone and vessel wall), where the vkorc1l1 may recycle VK epoxides resulting from the extra-hepatic γ-carboxylation of VKDPs. Previous studies indicated that chemically induced VK deficiency (through warfarin exposure) leads to arterial calcification that could be rescued through VK2, but not VK1, dietary supplementation [87]. These observations reinforce the notion that fulfilling VK dietary requirements for normal development and physiological status may require both VK1 and VK2 sources. In any case, present and previous results [15,19], on how the two main VK pathways respond to increased/decreased dietary VK levels in the short/long term, suggest that evaluating gene expression of ssvkorc1 or sspxr, but not ssvkorc1l1, might be suitable and reliable biomarkers of nutritional VK1 intake.
For animal health and development, fasting is one of the most drastic conditions determining their survival and growth potential. In this regard, although a one day fasting increases weaning success in Senegalese sole larvae, it also increases the incidence of skeletal deformities up to 88%, particularly at the neural arch, pleural and caudal vertebrae [88]. Here, a short fasting period of two days did not alter the expression levels of ssvkorc1, but it increased the expression of ssvkorc1l1, suggesting that extra-hepatic (but not the hepatic) γ-carboxylation of VKDPs, related to arterial uncalcification (Mgp; [89]) and bone mineralization (Bgp; [90]), may be compromised. Consequently, increased expression of both sskvors after three days re-feeding with a VK1 (1250VK) rich diet might be in line with: (i) increased dietary VK1 supplementation in the case of ssvkorc1, and a still unrecovered situation on extra-hepatic VK status regarding ssvkorc1l1 gene expression, even when fed a VK1 rich diet; or (ii) the reported period of metabolic adjustments directed toward the physiological condition restoration after a fasting period [91]. Furthermore, similar transcriptional regulation of ssvkorc1l1 and sspxr genes under fasting and re-feeding conditions (present study and [19]) evidenced a higher impact of fasting on specific roles of VK, particularly the transcriptional activation of Pxr signaling pathways and the extra-hepatic γ-carboxylation of VKDPs.
Warfarin is an anticoagulant drug commonly used at low doses for prevention and treatment of arterial and venous thromboembolic disorders in humans [92], but at high doses as a rodenticide, causing lethal hemorrhages in rats and mice, as well as other organisms including fish and birds [93,94]. Thus, it is considered an emerging contaminant negatively impacting the natural environment [95]. A recent review highlighted that the aquatic environment experiences a greater risk of anticoagulant rodenticide exposure than previously thought [96]. We and others have characterized and quantified the effects of warfarin exposure during fish embryogenesis, larval development and at adult stages [16,17,94], as well as described the particular molecular pathways altered in a global context [18]. We previously demonstrated that sspxr expression was altered upon warfarin exposure, but returned to normal values upon dietary VK1 supplementation [19]. A similar effect was observed for ssvkorc1 and ssvkorc1l1 under the same conditions, although ssvkorc1l1 showed a higher up-regulation. Two different studies using in vitro cell culture models indicated that, in mammals, Vkorc1l1 is less sensitive to warfarin than Vkorc1 [24,27,28]. Although this might be in contradiction with our expression data, it is in agreement with the higher conservation of the warfarin binding (TYA) motif in ssVkorc1l1 than in ssVkorc1. Altered expression of sspxr, ssvkorc1 and ssvkorc1l1 upon warfarin exposure suggests that the known functions of VK—i.e., an activator of gene transcription and co-factor of hepatic and extra-hepatic Ggcx enzyme—may be affected upon anticoagulant exposure. Our data not only evidence the action of anticoagulants on VK-related gene expression; they highlight the risks that their presence in aquatic environments (in the water, sediment and/or organisms [97]) poses to aquatic animals, in particular to fish.
In conclusion, based on present and previous results, a combined analysis of pxr, vkorc1 and vkorc1l1 expression may be the best approach to assess the overall VK physiological status in Senegalese sole, while analysis of pxr and vkorc1 expression should be sufficient to evaluate VK1 intake. Moreover, based on vkors gene expression profiles during larval development and at adult tissues, Senegalese sole might have higher dietary VK requirements during embryogenesis, pre- and pro-metamorphosis, and for proper gametogenesis than during juvenile stages. Therefore, future research efforts should be placed on determining VK content in embryos, live preys and inert diets (for weaning and breeding), and correlate them with important production traits such as survival, growth, quality and welfare, as well as with molecular data on VK pathways. Only with this approach we will be able to fine-tune the VK content in diets to promote Senegalese sole aquaculture.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
Fish facilities and persons in charge of animal experimentation were all accredited by the Portuguese National Authority for Animal Health (DGAV; permit 0421/000/000, 19 April 2016), and all experimental procedures involving animals followed the Animal Research: Reporting In Vivo Experiments (ARRIVE) guidelines, the European Directive 2010/63/EU, the related guidelines (European Commission, 2014) and the Portuguese legislation (Decreto-Lei 113/2013) for animal experimentation and welfare.
4.2. Rearing and Sampling Senegalese Sole Larvae and Juveniles
Senegalese sole eggs were obtained from natural spawning of fish broodstock at the Aquaculture Research Station of Pilot Fishing Station (EPPO)/ Instituto Português do Mar e da Atmosfera (IPMA) (Olhão, Portugal) and transferred to the fish facilities at the Centre of Marine Sciences (CCMAR), University of Algarve (Faro, Portugal). After thermal, light and chemical acclimatization, eggs were incubated in a semi-closed water recirculating system equipped with mechanical and biological filters, protein skimmer and a ultra violet (UV) sterilizer. After hatching, larvae were randomly distributed into four 100 L cylindro-conical tanks at a density of 95 larvae L−1. After settlement (21 days post-fertilization; dpf), post-larvae were transferred to 3-L flat bottom plastic trays (120 larvae per tray). Environmental parameters were: water temperature at 19.9 ± 1.2°C, water salinity at 36.9 ± 1.2 g L−1, dissolved oxygen saturation at 97.6% ± 4.9 %, a 12 h light/12 h dark photoperiod and 900 lux light intensity at water surface.
Larvae were progressively fed three times a day with live preys: rotifers (Brachionus rotundiformis) from 4 to 12 dpf, Artemia nauplii (AF strain; INVE, Salt Lake, Utah, USA) from 8 to 12 dpf and Artemia metanauplii (EG strain; INVE, Salt Lake, Utah, USA) enriched with Red PepperTM (Bernaqua, Olen, Belgium), supplemented with 250 mg VK1 kg−1 (as described in [15]) from 11 to 19 dpf. The same Artemia metanauplii, but immediately frozen after enrichment, were provided to the larvae from 20 dpf until the end of the experiment (32 dpf).
Fish previously euthanized with an overdose of tricaine methanesulfonate (MS-222, Sigma-Aldrich, Madrid, Spain) were sampled and washed with sterile distilled water. Embryonic samples were collected at 13.5, 18.5, 24, 36 (hatching) and 48 hours post-fertilization (hpf), while larval and juvenile samples were collected at 4, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 18, 22, 26 and 32 dpf. A total of 60 eggs, up to 20 larvae and 5 juveniles, depending on their size, were collected per replicate, kept in TRI-Reagent (Ambion, Alcobendas, Spain) and stored at −80 °C until processed for RNA extraction.
4.3. Maintenance of Adult Senegalese Sole and Tissues Sampling
Adult fish from Aquaculture Research Station of EPPO/IPMA were transferred to the fish facilities of the CCMAR. After thermal, light and chemical acclimatization, and 15 days of maintenance in a semi-closed water recirculating system, fish were sacrificed and spleen, eye, brain, testis, ovaries, muscle, bone, skin, liver, heart, kidney, gills and intestine were sampled. Pools of tissues from 3 adults were placed in 10 volumes of TRI-Reagent and stored at −80 °C until processed.
4.4. Exposure of Senegalese Sole Juveniles to Different Physiological Conditions
RNA samples of Senegalese sole juveniles were obtained from an experiment conducted for a previous publication [19]. In brief, specimens aged 57 dpf (with 80 ± 7 mg wet weight (WW) and 14.91 ± 1.79 mm of standard length) grown under standard rearing procedures were distributed into 4 experimental flat bottom plastic trays (40 specimens per tray), and further cultured under the environmental conditions previously described. Juveniles were initially fed with 125 mg kg−1 DW VK1 inert diet (125VK1 diet) at 3% WW during 5 days, then: (i) fed with 125VK1 diet for 5 days (Control group); (ii) fasting during 2 days (Unfed group) and re-fed for 3 days with VK1 supplemented diet (1250 mg kg−1 DW, 1250VK1 diet; Re-fed group); (iii) fed with 125VK1 diet and exposed to 25 mg L−1 of warfarin (3-(α-acetonylbenzyl)-4-hydroxycoumarin sodium salt; Sigma-Aldrich, Madrid, Spain) during 2 days (Warfarin group) and re-fed for 3 days with 1250VK1 diet while still exposed to warfarin (Warfarin rescue group); or (iv) fed with 1250VK1 diet for 5 days (VK1 suppl group). Individual fish were sampled in triplicate from each experimental group at 2 and 5 days after each treatment initiated, euthanized with an overdose of MS-222, washed with sterile distilled water and stored in TRI-Reagent at −80 °C until RNA extraction.
4.5. RNA Isolation and Construction of Senegalese sole cDNA Library
RNA from larval and juvenile stages, and adult fish, tissues was prepared as described below. Aliquots of each RNA were pooled (to a total amount of 2 μg) and used to construct a cDNA library using the Marathon cDNA amplification kit (Clontech, Mountain View, CA, USA). Total RNA was converted into cDNA with oligo-(dT) and a special adaptor containing the two primers, AP1 and AP2, was attached to both ends of the cDNAs according to the manufacturer instructions. These marathon cDNA libraries were used as a template for the PCR reaction.
4.6. cDNA Partial and Full-Length Amplification through 3′- and 5′-RACE
Degenerated primers used to amplify internal cDNA fragments of Senegalese sole ssvkorc1 and ssvkorc1l1 were designed in regions conserved among fish vkor sequences retrieved from GenBank and SoleaDB databases using on-site Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST) facilities. cDNA fragments of ssvkorc1 and ssvkorc1l1 were used to design gene-specific primers to amplify cDNA ends by RACE-PCR following the manufacturer instructions, and later the full-length cDNAs. PCR fragments were cloned in pCR2.1-TOPO TA cloning vector (Invitrogen, Alcobendas, Spain) and sequenced using CCMAR sequencing facilities. Gene-specific primers for the quantification of ssvkorc1 and ssvkorc1l1 relative gene expression by qPCR were designed. The sequences of the primers used in this work are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Designed primers for initial amplification of Senegalese sole vkors cDNA sequences, full-length amplifications and relative gene expression.
4.7. Sequences Collection and Phylogenetic Reconstruction
Vitamin K epoxide reductase (Vkors) protein sequences (54 in total; Table S1) were retrieved from GenBank database using on-site BLASTP tool with position-specific iterated BLAST (PSI-BLAST; [98]) algorithm. Sequences were aligned using MUSCLE software [99] and alignments were fed to MEGA version X to construct a molecular phylogeny [48]. Maximum Likelihood tree was created using a JTT model and a gamma distribution with site rate variation, and gaps were considered as partial deletion. For branching support, 500 bootstrap replications were analyzed. Vkors percentage identity matrixes were calculated using MUSCLE software. Sequence of the sea squirt (Ciona intestinalis) Vkor (NP_001073142) was used as outgroup.
4.8. Multiple sequence Alignment and Construction of Sequence Logos
Fish and tetrapod sequences for Vkorc1 and Vkorc1l1 were aligned using T-Coffee facilities [100]. Sequence alignments were improved by manual adjustments and fed to the Weblogo facilities [101] to construct taxon- and protein-specific sequence logos, where the height of each letter is directly proportional to its conservation, i.e., the more conserved residues are represented as larger characters.
4.9. RNA Extraction and qPCR Amplification
Total RNA was extracted from samples stored in TRI-Reagent following manufacturer instructions and purified using the High Pure RNA Isolation kit (Roche Applied Science, Alcobendas, Spain). RNA integrity was confirmed using Experion Automated Electrophoresis system (Bio-Rad, Alcobendas, Spain) and quantity was determined using NanoDrop spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, Alcobendas, Spain). Total RNA (1 µg) was reverse-transcribed for 1 h at 37 °C, using M-MLV reverse transcriptase (Invitrogen, Alcobendas, Spain), oligo-d(T) universal primer (5’-ACGCGTCGACCTCGAGATCGATG(T)13-3’) and RNase OUT (Invitrogen, Alcobendas, Spain). All quantitative real time PCR (qPCR) reactions were performed in triplicates using SsoFast EVAgreen Supermix (Bio-Rad), 0.25 μM of isoform-specific primers (Table 1) and 1:10 dilution of reverse transcribed RNA, in the StepOnePlus Real-Time PCR system (Applied Biosystems, Alcobendas, Spain). PCR amplification was as follows: an initial denaturation step of 1 min at 95 °C and 40 cycles of amplification (5 s at 95 °C and 10 s at 65 °C). A calibrator sample (cDNA pooled from all samples) was included in each qPCR plate [102]. Efficiency of amplification was between 96% and 104% for all primer sets. Levels of gene expression were calculated using the ΔΔCt comparative method and normalized using ubiquitin (ubq) RNA levels, a known reference gene for accurate normalization in qPCR studies with Senegalese sole [103]. Gene expression at 7 and 9 dpf for relative expression during development, while kidney and heart for relative expression in adult tissues were set to 1 and used as reference samples, for ssvkorc1 and ssvkorc1l1, respectively.
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Results are given as mean and standard deviation. All data were checked for normality (Kolmogorov–Smirnov test) and homoscedasticity of variance (Bartlett’s test). Significant differences in gene expression were detected by one-way ANOVA or Student’s t-test. When significant differences were detected by one-way ANOVA, the Tukey multiple-comparison test was used to detect differences among experimental groups. Differences were considered to be significant when P < 0.05. Statistical analysis was done using Prims 5.0 (GraphPad Software, Inc.; San Diego, CA, USA).
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary materials can be found at https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/21/10/3489/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.F; methodology, V.L. and I.F.; formal analysis, S.B., C.M. and I.F.; investigation, I.F.; resources, V.L., P.J.G. and I.F.; writing—original draft preparation, S.B. and I.F.; writing—review and editing, S.B., V.L., P.J.G. and I.F.; funding acquisition, V.L., P.J.G. and I.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology (FCT) through the project UIDB/04326/2020 (CCMAR) and the postdoctoral grant SFRH/BPD/82049/2011; the European Maritime and Fisheries Fund (EMFF/FEAMP) through the National Operational Programme MAR2020 (grant ALGASOLE-16-02-01-FMP-0058); the MET2VI project (Ref. RTI2018-099029-A-I00) funded by the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) - Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades (MICIU) - Agencia Estatal de Investigación of the Spanish Government. I.F. acknowledges the funding from the MICIU and the European Social Fund, “The European Social Fund invests in your future” through the Ramón y Cajal (Ref. RYC2018-025337-I) contract from the Plan Estatal de Investigación Científica y Técnica e Innovación 2017-2020.
Acknowledgments
Authors are gratefully to Tiago Rocha for the excellent technical work and help during gene cloning and sampling procedures.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| BGP | Bone gla protein |
| BLAST | Basic Local Alignment Search Tool |
| bp | base pairs |
| cDNA | Complementary Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| DW | dry weight |
| GCCX | γ-glutamyl carboxylase (Ggcx) |
| hpf | hours post-fertilization |
| JTT | Jones-Taylor-Thornton |
| MEGA | Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis |
| MGP | Matrix gla protein |
| MK-4 | Menaquinone 4 |
| MK-7 | Menaquinone 7 |
| M-MLV | Moloney Murine Leukemia Virus |
| M-MLV | Moloney Murine Leukemia Virus |
| MUSCLE | MUltiple Sequence Comparison by Log-Expectation |
| no | number |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| PSI-BLAST | Position Specific Iterated Basic Local Alignment Search Tool |
| PXR | Pregnane X receptor |
| qPCR | Quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| RACE | Rapid Amplification of cDNA Ends |
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid |
| SNPs | Single nucleotide polymorphisms |
| UBQ | Ubiquitin |
| UBUAD1 | UbiA prenyltransferase domain-containing protein 1 |
| VK1 | Vitamin K1 - phylloquinone |
| VK2 | Vitamin K2 - menaquinone |
| VK3 | Vitamin K3 - menadione |
| VK | Vitamin K |
| VKDPs | Vitamin K dependent proteins |
| VKOR | Vitamin K epoxide reductase |
| VKORC1 | Vitamin K epoxide reductase complex subunit 1 |
| VKORC1L1 | Vitamin K epoxide reductase complex subunit 1 like protein 1 |
| VKORS | Vitamin K epoxide reductases |
References
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2018—Meeting the Sustainable Development Goals; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nation: Rome, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Transforming our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Sustainable Development Knowledge Platform. (n.d.). Available online: https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/post2015/transformingourworld/publication (accessed on 5 April 2020).
- Calder, P.C. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and inflammatory processes: Nutrition or pharmacology? Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 75, 645–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tibbetts, S.M. Microalgal Biotechnology; IntechOpen: Halifax, NS, Canada, 2018; pp. 151–175. [Google Scholar]
- Romanelli, C.; Cooper, H.D.; de Souza Dias, B.F. The integration of biodiversity into One Health. Rev. Sci. Tech. Off. Int. Epiz. 2014, 33, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Summers, J.K.; Smith, L.M.; Fulford, R.S.; de Jesus Crespo, R. Ecosystem Services and Global Ecology; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; pp. 145–168. [Google Scholar]
- Halver, J.E.; Hardy, R.W. Fish Nutrition, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2003; pp. 1–824. [Google Scholar]
- Lall, S.P.; Dumas, A. Feed and Feeding Practices in Aquaculture; Woodhead Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 53–109. [Google Scholar]
- Holt, G.J. Larval Fish Nutrition; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 1–435. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández, I.; Gavaia, P.; Darias, M.J.; Gisbert, E. Emerging Issues in Fish Larvae Research; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 159–208. [Google Scholar]
- Krossøy, C.; Waagbø, R.; Ørnsrud, R. Vitamin K in fish nutrition. Aquac. Nutr. 2011, 17, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearer, M.J.; Newman, P. Recent trends in the metabolism and cell biology of vitamin K with special reference to vitamin K cycling and MK-4 biosynthesis. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 345–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shearer, M.J.; Okano, T. Key Pathways and Regulators of Vitamin K Function and Intermediary Metabolism. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2018, 38, 127–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, I.; Fernandes, J.M.O.; Roberto, V.P.; Kopp, M.; Oliveira, C.; Riesco, M.F.; Dias, J.; Cox, C.J.; Leonor Cancela, M.; Cabrita, E.; et al. Circulating small non-coding RNAs provide new insights into vitamin K nutrition and reproductive physiology in teleost fish. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2019, 1863, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, N.; Fernández, I.; Wulff, T.; Hamre, K.; Cancela, L.; Conceicao, L.E.; Gavaia, P.J. Dietary supplementation with vitamin k affects transcriptome and proteome of Senegalese sole, improving larval performance and quality. Mar. Biotechnol. (N.Y.) 2014, 16, 522–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, I.; Santos, A.; Cancela, M.L.; Laize, V.; Gavaia, P.J. Warfarin, a potential pollutant in aquatic environment acting through Pxr signaling pathway and gamma-glutamyl carboxylation of vitamin K-dependent proteins. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 194, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardeira, J.; Gavaia, P.J.; Fernández, I.; Cengiz, I.F.; Moreira-Silva, J.; Oliveira, J.M.; Reis, R.L.; Cancela, M.L.; Laize, V. Quantitative assessment of the regenerative and mineralogenic performances of the zebrafish caudal fin. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granadeiro, L.; Dirks, R.P.; Ortiz-Delgado, J.B.; Gavaia, P.J.; Sarasquete, C.; Laize, V.; Cancela, M.L.; Fernández, I. Warfarin-exposed zebrafish embryos resembles human warfarin embryopathy in a dose and developmental-time dependent manner—From molecular mechanisms to environmental concerns. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 181, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, C.; Roberto, V.P.; Granadeiro, L.; Trindade, M.; Gavaia, P.J.; Laize, V.; Cancela, M.L.; Fernández, I. The xenobiotic sensor PXR in a marine flatfish species (Solea senegalensis): Gene expression patterns and its regulation under different physiological conditions. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 130, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabb, M.M.; Sun, A.; Zhou, C.; Grun, F.; Errandi, J.; Romero, K.; Pham, H.; Inoue, S.; Mallick, S.; Lin, M.; et al. Vitamin K2 regulation of bone homeostasis is mediated by the steroid and xenobiotic receptor SXR. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 43919–43927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azuma, K.; Casey, S.C.; Ito, M.; Urano, T.; Horie, K.; Ouchi, Y.; Kirchner, S.; Blumberg, B.; Inoue, S. Pregnane X receptor knockout mice display osteopenia with reduced bone formation and enhanced bone resorption. J. Endocrinol. 2010, 207, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldenburg, J.; Marinova, M.; Müller-Reible, C.; Watzka, M. Vitamin K; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2008; pp. 35–62. [Google Scholar]
- Westhofen, P.; Watzka, M.; Marinova, M.; Hass, M.; Kirfel, G.; Muller, J.; Bevans, C.G.; Muller, C.R.; Oldenburg, J. Human vitamin K 2,3-epoxide reductase complex subunit 1-like 1 (VKORC1L1) mediates vitamin K-dependent intracellular antioxidant function. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 15085–15094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammed, A.; Matagrin, B.; Spohn, G.; Prouillac, C.; Benoit, E.; Lattard, V. VKORC1L1, an enzyme rescuing the vitamin K 2,3-epoxide reductase activity in some extrahepatic tissues during anticoagulation therapy. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 28733–28742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rishavy, M.A.; Hallgren, K.W.; Wilson, L.A.; Usubalieva, A.; Runge, K.W.; Berkner, K.L. The vitamin K oxidoreductase is a multimer that efficiently reduces vitamin K epoxide to hydroquinone to allow vitamin K-dependent protein carboxylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 31556–31566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldenburg, J.; Watzka, M.; Bevans, C.G. VKORC1 and VKORC1L1: Why do Vertebrates Have Two Vitamin K 2,3-Epoxide Reductases? Nutrients 2015, 7, 6250–6280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacombe, J.; Rishavy, M.A.; Berkner, K.L.; Ferron, M. VKOR paralog VKORC1L1 supports vitamin K-dependent protein carboxylation in vivo. JCI Insight 2018, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacombe, J.; Ferron, M. VKORC1L1, An Enzyme Mediating the Effect of Vitamin K in Liver and Extrahepatic Tissues. Nutrients 2018, 10, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campinho, M.A.; Silva, N.; Martins, G.G.; Anjos, L.; Florindo, C.; Roman-Padilla, J.; Garcia-Cegarra, A.; Louro, B.; Manchado, M.; Power, D.M. A thyroid hormone regulated asymmetric responsive centre is correlated with eye migration during flatfish metamorphosis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louro, B.; Marques, J.P.; Manchado, M.; Power, D.M.; Campinho, M.A. Sole head transcriptomics reveals a coordinated developmental program during metamorphosis. Genomics 2020, 112, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, C.; Martins, M.; Diniz, M.S.; Costa, M.H.; Caeiro, S.; Costa, P.M. May sediment contamination be xenoestrogenic to benthic fish? A case study with Solea senegalensis. Mar. Environ. Res. 2014, 99, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solé, M.; Mananos, E.; Blazquez, M. Vitellogenin, sex steroid levels and gonadal biomarkers in wild Solea solea and Solea senegalensis from NW Mediterranean fishing grounds. Mar. Environ. Res. 2016, 117, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morais, S.; Aragão, C.; Cabrita, E.; Conceição, L.E.C.; Constenla, M.; Costas, B.; Dias, J.; Duncan, N.; Engrola, S.; Estevez, A.; et al. New developments and biological insights into the farming of Solea senegalensis reinforcing its aquaculture potential. Rev. Aquac. 2016, 8, 227–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Cueto, J.A.; Mañanós-Sánchez, E.; Sánchez-Vázquez, F.J. The Biology of Sole; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 1–404. [Google Scholar]
- Anguis, V.; Cañavate, J.P. Spawning of captive Senegal sole (Solea senegalensis) under a naturally fluctuating temperature regime. Aquaculture 2005, 243, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carazo, I.; Chereguini, O.; Martín, I.; Huntingford, F.; Duncan, N. Reproductive ethogram and mate selection in captive wild Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis). Span. J. Agric. Res. 2016, 14, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauvigne, F.; Fatsini, E.; Duncan, N.; Olle, J.; Zanuy, S.; Gomez, A.; Cerda, J. Plasma levels of follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones during the reproductive cycle of wild and cultured Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2016, 191, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riesco, M.F.; Valcarce, D.G.; Martinez-Vazquez, J.M.; Martin, I.; Calderon-Garcia, A.A.; Gonzalez-Nunez, V.; Robles, V. Male reproductive dysfunction in Solea senegalensis: New insights into an unsolved question. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2019, 31, 1104–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavaia, P.J.; Dinis, M.T.; Cancela, M.L. Osteological development and abnormalities of the vertebral column and caudal skeleton in larval and juvenile stages of hatchery-reared Senegal sole (Solea senegalensis). Aquaculture 2002, 211, 305–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, I.; Pimentel, M.S.; Ortiz-Delgado, J.B.; Hontoria, F.; Sarasquete, C.; Estévez, A.; Zambonino-Infante, J.L.; Gisbert, E. Effect of dietary vitamin A on Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis) skeletogenesis and larval quality. Aquaculture 2009, 295, 250–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, I.; Gisbert, E. Senegalese sole bone tissue originated from chondral ossification is more sensitive than dermal bone to high vitamin A content in enrichedArtemia. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2010, 26, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losada, A.P.; de Azevedo, A.M.; Barreiro, A.; Barreiro, J.D.; Ferreiro, I.; Riaza, A.; Quiroga, M.I.; Vázquez, S. Skeletal malformations in Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis Kaup, 1858): Gross morphology and radiographic correlation. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2014, 30, 804–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Azevedo, A.M.; Losada, A.P.; Ferreiro, I.; Riaza, A.; Vazquez, S.; Quiroga, M.I. New insight on vertebral anomalies in cultured Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis, Kaup) at early stages of development. J. Fish Dis. 2017, 40, 987–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, I.; Ortiz-Delgado, J.B.; Darias, M.J.; Hontoria, F.; Andree, K.B.; Manchado, M.; Sarasquete, C.; Gisbert, E. Vitamin A Affects Flatfish Development in a Thyroid Hormone Signaling and Metamorphic Stage Dependent Manner. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, I.; Granadeiro, L.; Darias, M.J.; Gavaia, P.J.; Andree, K.B.; Gisbert, E. Solea senegalensis skeletal ossification and gene expression patterns during metamorphosis: New clues on the onset of skeletal deformities during larval to juvenile transition. Aquaculture 2018, 496, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geffen, A.J.; van der Veer, H.W.; Nash, R.D.M. The cost of metamorphosis in flatfishes. J. Sea Res. 2007, 58, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, S.Q.; Gascuel, O. An improved general amino acid replacement matrix. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 1307–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.; Sun, H.; Raymond, R.M., Jr.; Furie, B.C.; Furie, B.; Bronstein, M.; Kaufman, R.J.; Westrick, R.; Ginsburg, D. Fatal hemorrhage in mice lacking gamma-glutamyl carboxylase. Blood 2007, 109, 5270–5275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkner, K.L. Vitamin K; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2008; pp. 131–156. [Google Scholar]
- Sidorova, Y.A.; Perepechaeva, M.L.; Pivovarova, E.N.; Markel, A.L.; Lyakhovich, V.V.; Grishanova, A.Y. Menadione Suppresses Benzo(alpha)pyrene-Induced Activation of Cytochromes P450 1A: Insights into a Possible Molecular Mechanism. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferland, G. Vitamin K, an emerging nutrient in brain function. Biofactors 2012, 38, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karsenty, G.; Ferron, M. The contribution of bone to whole-organism physiology. Nature 2012, 481, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chouet, J.; Ferland, G.; Feart, C.; Rolland, Y.; Presse, N.; Boucher, K.; Barberger-Gateau, P.; Beauchet, O.; Annweiler, C. Dietary Vitamin K Intake Is Associated with Cognition and Behaviour among Geriatric Patients: The CLIP Study. Nutrients 2015, 7, 6739–6750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soutif-Veillon, A.; Ferland, G.; Rolland, Y.; Presse, N.; Boucher, K.; Feart, C.; Annweiler, C. Increased dietary vitamin K intake is associated with less severe subjective memory complaint among older adults. Maturitas 2016, 93, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirota, Y.; Suhara, Y. New Aspects of Vitamin K Research with Synthetic Ligands: Transcriptional Activity via SXR and Neural Differentiation Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schurgers, L.J.; Uitto, J.; Reutelingsperger, C.P. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylation of matrix Gla-protein: A crucial switch to control ectopic mineralization. Trends Mol. Med. 2013, 19, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, J.K.; Grzybowska-Chlebowczyk, U.; Landowski, P.; Szaflarska-Poplawska, A.; Klincewicz, B.; Adamczak, D.; Banasiewicz, T.; Plawski, A.; Walkowiak, J. Prevalence and correlates of vitamin K deficiency in children with inflammatory bowel disease. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheiber, D.; Veulemans, V.; Horn, P.; Chatrou, M.L.; Potthoff, S.A.; Kelm, M.; Schurgers, L.J.; Westenfeld, R. High-Dose Menaquinone-7 Supplementation Reduces Cardiovascular Calcification in a Murine Model of Extraosseous Calcification. Nutrients 2015, 7, 6991–7011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghiri, M.A.; Asatourian, A.; Ershadifar, S.; Moghadam, M.M.; Sheibani, N. Vitamins and regulation of angiogenesis: [A, B1, B2, B3, B6, B9, B12, C, D, E, K]. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 38, 180–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirakawa, H.; Ohsaki, Y.; Minegishi, Y.; Takumi, N.; Ohinata, K.; Furukawa, Y.; Mizutani, T.; Komai, M. Vitamin K deficiency reduces testosterone production in the testis through down-regulation of the Cyp11a a cholesterol side chain cleavage enzyme in rats. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1760, 1482–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, A.; Shirakawa, H.; Takumi, N.; Minegishi, Y.; Ohashi, A.; Howlader, Z.H.; Ohsaki, Y.; Sato, T.; Goto, T.; Komai, M. Menaquinone-4 enhances testosterone production in rats and testis-derived tumor cells. Lipids Health Dis. 2011, 10, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harshman, S.G.; Fu, X.; Karl, J.P.; Barger, K.; Lamon-Fava, S.; Kuliopulos, A.; Greenberg, A.S.; Smith, D.; Shen, X.; Booth, S.L. Tissue Concentrations of Vitamin K and Expression of Key Enzymes of Vitamin K Metabolism Are Influenced by Sex and Diet but Not Housing in C57Bl6 Mice. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 1521–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Zhang, W.; Lin, S.; Xu, W.; Mai, K. Effects of dietary vitamin K on growth performances, blood coagulation time and menaquinone-4 (MK-4) concentration in tissues of juvenile large yellow croakerPseudosciaena crocea. Aquac. Res. 2015, 46, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, I.; Vijayakumar, P.; Marques, C.; Cancela, M.L.; Gavaia, P.J.; Laize, V. Zebrafish Vitamin K epoxide reductases: Expression in vivo, along extracellular matrix mineralization and under phylloquinone and warfarin in vitro exposure. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 41, 745–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bevans, C.G.; Krettler, C.; Reinhart, C.; Watzka, M.; Oldenburg, J. Phylogeny of the Vitamin K 2,3-Epoxide Reductase (VKOR) Family and Evolutionary Relationship to the Disulfide Bond Formation Protein B (DsbB) Family. Nutrients 2015, 7, 6224–6249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harshman, S.G.; Saltzman, E.; Booth, S.L. Vitamin K: Dietary intake and requirements in different clinical conditions. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2014, 17, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shea, M.K.; Booth, S.L. Concepts and Controversies in Evaluating Vitamin K Status in Population-Based Studies. Nutrients 2016, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turck, D.; Bresson, J.L.; Burlingame, B.; Dean, T.; Fairweather-Tait, S.; Heinonen, M.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H.J.; Naska, A.; et al. Dietary reference values for vitamin K. EFSA J. 2017, 15, 4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodstadt, L.; Ponting, C.P. Vitamin K epoxide reductase: Homology, active site and catalytic mechanism. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2004, 29, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatron, N.; Hammed, A.; Benoit, E.; Lattard, V. Structural Insights into Phylloquinone (Vitamin K1), Menaquinone (MK4, MK7), and Menadione (Vitamin K3) Binding to VKORC1. Nutrients 2019, 11, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Lange, L.A.; Li, X.; Susswein, L.; Bryant, B.; Malone, R.; Lange, E.M.; Huang, T.-Y.; Stafford, D.W.; Evans, J.P. Polymorphisms in the VKORC1 gene are strongly associated with warfarin dosage requirements in patients receiving anticoagulation. J. Med. Genet. 2006, 43, 740–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czogalla, K.J.; Watzka, M.; Oldenburg, J. Structural Modeling Insights into Human VKORC1 Phenotypes. Nutrients 2015, 7, 6837–6851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rost, S.; Pelz, H.-J.; Menzel, S.; MacNicoll, A.D.; León, V.; Song, K.-J.; Jäkel, T.; Oldenburg, J.; Clemens, R.; Müller, C.R. Novel mutations in the VKORC1 gene of wild rats and mice—A response to 50 years of selection pressure by warfarin? BMC Genet. 2009, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mooney, J.; Lynch, M.R.; Prescott, V.V.; Clegg, T.; Loughlin, M.; Hannon, B.; Moore, C.; Faulkner, R. VKORC1 sequence variants associated with resistance to anticoagulant rodenticides in Irish populations of Rattus norvegicus and Mus musculus domesticus. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, S.M.M.; Morita, A.; Ikenaka, Y.; Kawai, Y.K.; Watanabe, K.P.; Ishii, C.; Mizukawa, H.; Yohannes, Y.B.; Saito, K.; Watanabe, Y.; et al. Avian interspecific differences in VKOR activity and inhibition: Insights from amino acid sequence and mRNA expression ratio of VKORC1 and VKORC1L1. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 228, 108635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.G.; Pauli, R.M.; Wilson, K.M. Maternal and fetal sequelae of anticoagulation during pregnancy. Am. J. Med. 1980, 68, 122–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.W. Fetal warfarin syndrome. Chang Gung Med. J. 2004, 27, 691–695. [Google Scholar]
- Mehndiratta, S.; Suneja, A.; Gupta, B.; Bhatt, S. Fetotoxicity of warfarin anticoagulation. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2010, 282, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro Cañavate, J.; Zerolo, R.; Fernández-Díaz, C. Feeding and development of Senegal sole (Solea senegalensis) larvae reared in different photoperiods. Aquaculture 2006, 258, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caspers, M.; Czogalla, K.J.; Liphardt, K.; Muller, J.; Westhofen, P.; Watzka, M.; Oldenburg, J. Two enzymes catalyze vitamin K 2,3-epoxide reductase activity in mouse: VKORC1 is highly expressed in exocrine tissues while VKORC1L1 is highly expressed in brain. Thromb. Res. 2015, 135, 977–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyaolu, A.O.; Oremosu, A.A.; Osinubi, A.A.; Vermeer, C.; Daramola, A.O. Warfarin-induced vitamin K deficiency affects spermatogenesis in Sprague-Dawley rats. Andrologia 2019, 51, e13416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udagawa, M. The Effect of Parental Vitamin K Deficiency on Bone Structure in Mummichog Fundulus heteroclitus. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2004, 35, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, M.; Petsophonsakul, P.; Akbulut, A.C.; Pavlic, A.; Bohan, F.; Anderson, E.; Maresz, K.; Kramann, R.; Schurgers, L. Vitamin K: Double Bonds beyond Coagulation Insights into Differences between Vitamin K1 and K2 in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gijsbers Birgit, L.M.G.; Jie Kon-Siong, G.; Vermeer, C. Effect of food composition on vitamin K absorption in human volunteers. Br. J. Nutr. 1996, 76, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koivu-Tikkanen Terhi, J.; Schurgers Leon, J.; Thijssen Henk, H.W.; Vermeer, C. Intestinal, hepatic, and circulating vitamin K levels at low and high intakes of vitamin K in rats. Br. J. Nutr. 2000, 83, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Spronk, H.M.; Soute, B.A.; Schurgers, L.J.; Thijssen, H.H.; De Mey, J.G.; Vermeer, C. Tissue-specific utilization of menaquinone-4 results in the prevention of arterial calcification in warfarin-treated rats. J. Vasc. Res. 2003, 40, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engrola, S.; Conceição, L.E.C.; Gavaia, P.J.; Cancela, M.L.; Dinis, M.T. Effect of pre-weaning feeding regime on weaning performance of Senegalese sole, Solea senegalensis (Kaup, 1858). Isr. J. Aquac. 2005, 57, 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Bjørklund, G.; Svanberg, E.; Dadar, M.; Card, D.J.; Chirumbolo, S.; Harrington, D.J.; Aaseth, J. The role of matrix gla protein (MGP) in vascular calcification. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 27, 1647–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boskey Adele, L.; Gadaleta, S.; Gundberg, C.; Doty, S.B.; Ducy, P.; Karsenty, G. Fourier transform infrared microspectroscopic analysis of bones of osteocalcin-deficient mice provides insight into the function of osteocalcin. Bone 1998, 23, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Jimenez, A.; Cardenete, G.; Hidalgo, M.C.; Garcia-Alcazar, A.; Abellan, E.; Morales, A.E. Metabolic adjustments of Dentex dentex to prolonged starvation and refeeding. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 38, 1145–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevans, C.G.; Krettler, C.; Reinhart, C.; Tran, H.; Kossmann, K.; Watzka, M.; Oldenburg, J. Determination of the warfarin inhibition constant Ki for vitamin K 2,3-epoxide reductase complex subunit-1 (VKORC1) using an in vitro DTT-driven assay. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 4202–4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.P.; Saengtienchai, A.; Tanaka, K.D.; Ikenaka, Y.; Ishizuka, M. Comparison of warfarin sensitivity between rat and bird species. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010, 152, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigt, S.; Huebler, N.; Strecker, R.; Braunbeck, T.; Broschard, T.H. Developmental effects of coumarin and the anticoagulant coumarin derivative warfarin on zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Reprod. Toxicol. 2012, 33, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lao, W.; Gan, J. Enantioselective degradation of warfarin in soils. Chirality 2012, 24, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regnery, J.; Friesen, A.; Geduhn, A.; Göckener, B.; Kotthoff, M.; Parrhysius, P.; Petersohn, E.; Reifferscheid, G.; Schmolz, E.; Schulz, R.S.; et al. Rating the risks of anticoagulant rodenticides in the aquatic environment: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 17, 215–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotthoff, M.; Rudel, H.; Jurling, H.; Severin, K.; Hennecke, S.; Friesen, A.; Koschorreck, J. First evidence of anticoagulant rodenticides in fish and suspended particulate matter: Spatial and temporal distribution in German freshwater aquatic systems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 7315–7325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notredame, C.; Higgins, D.G.; Heringa, J. T-Coffee: A novel method for fast and accurate multiple sequence alignment. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 302, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crooks, G.E.; Hon, G.; Chandonia, J.M.; Brenner, S.E. WebLogo: A sequence logo generator. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1188–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derveaux, S.; Vandesompele, J.; Hellemans, J. How to do successful gene expression analysis using real-time PCR. Methods 2010, 50, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Infante, C.; Matsuoka, M.P.; Asensio, E.; Canavate, J.P.; Reith, M.; Manchado, M. Selection of housekeeping genes for gene expression studies in larvae from flatfish using real-time PCR. BMC Mol. Biol. 2008, 9, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).