1. Introduction
Ever since the pioneering studies of Professor Brånemark, osseointegration of titanium implant fixtures has been recognized as an interfacial event [
1]. The clinical practice of implant dentistry has been based on the intimate apposition of newly formed bone tissue to the titanium surface. A great deal of literature has been devoted to the relationship between titanium surface properties and new bone formation [
2,
3,
4]. The primary physical-chemical variables, titanium oxide surface chemistry, and implant surface topography dictate relevant surface parameters—such as surface charge and wettability—and have been deeply investigated in relation to cellular events leading to peri-implant bone regeneration [
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11]. The understanding of such relationships prompted the clinical evolution of titanium implants from the original turned to present day micro- and nano-rough surfaces [
12,
13,
14].
Parallel to the growth and widespread acceptance of dental implantology, rising knowledge framed relevant interfacial biological events within a broader picture [
15,
16,
17,
18]. Cellular mechanisms leading to new bone formation and soft tissue healing, as well as inflammatory response leading to loss of supporting soft and hard tissue, are mediated by biological molecules and relevant signaling. The presentation of biomolecular cues, rather than the comparatively rough inorganic chemistry of titanium, seems a reasonable highway towards the evolution of better and innovative implant surfaces [
19]. Accordingly, surface engineering of medical devices has long since been involved with the immobilization of a wide range of biomolecules to medical materials surfaces [
20,
21]. Biochemical modification of titanium surfaces (BMTiS) was defined by Puleo and Nancy [
22] as the immobilization of proteins, enzymes, or peptides with the purpose of inducing specific cell and tissue responses using critical organic components of bone to affect tissue response. BMTiS are generally based on surface modification either by peptides, ECM proteins, or polysaccharides, all from animal and vegetal sources [
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33,
34]. Despite a huge number of studies and promising in vitro and pre-clinical results [
35], no practical application exists so far, and clinical performances of present-day dental implants are still dictated by the titanium/host tissue interface and mostly based on stimulation of cell behavior by surface topography.
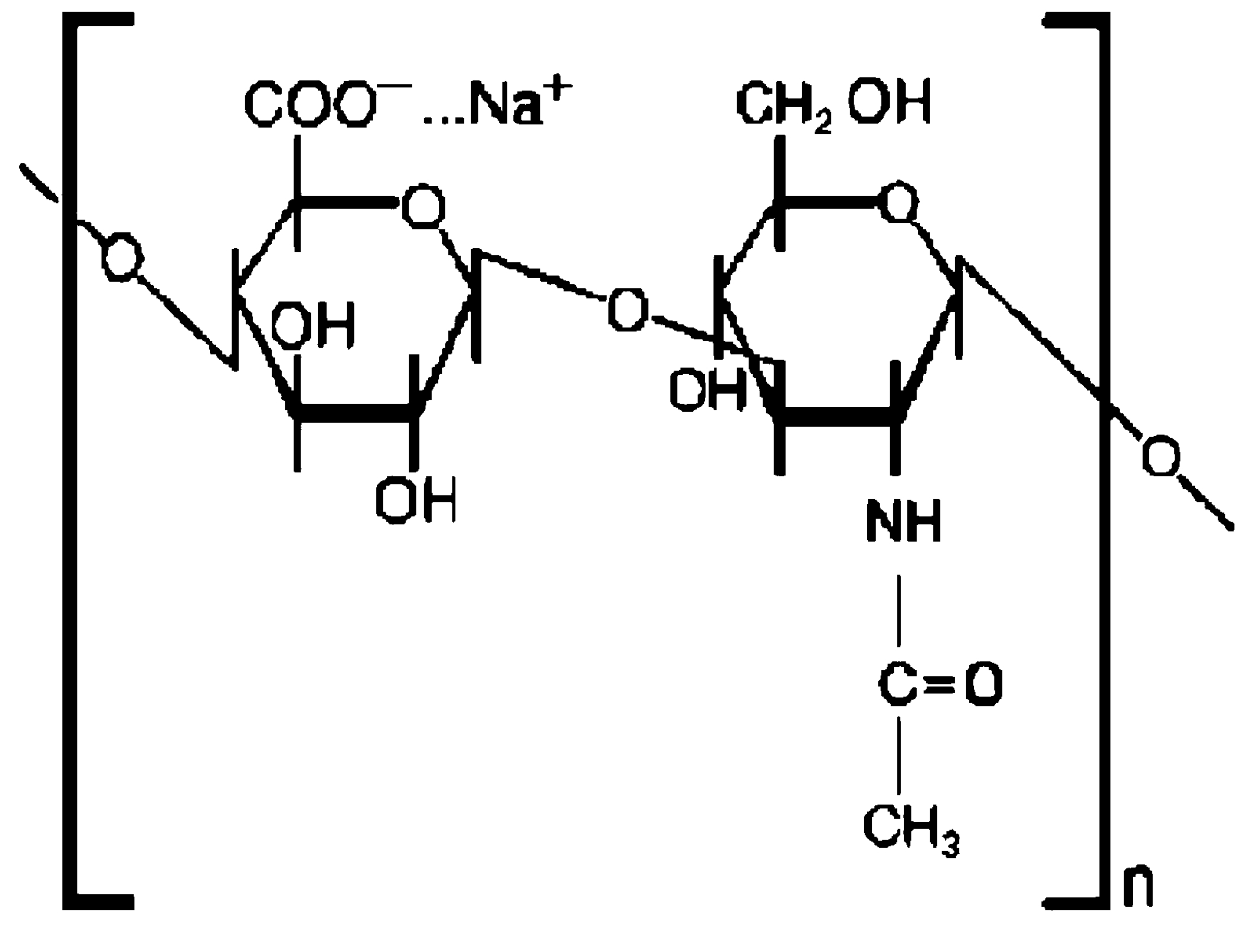
This work presents the results of the first clinical trial involving bio-molecular modification of titanium implant surfaces. Implant fixtures used in the present trial bear a surface nano-layer (a few nm thick) of covalently-linked hyaluronic acid or hyaluronan [while its common acronym is HA, it is indicated as HY in the present paper to avoid any risk of confusion with the widely used inorganic HA (hydroxyapatite)-coatings]. This means that they present a complex macromolecular chemistry and not the relatively simple inorganic chemistry of titanium surfaces at the implant/tissue interface.
HY (
Figure 1) is a linear polysaccharide consisting of the repeating disaccharide unit
N-acetyl-
d-glucosamine-
d-glucuronate linked by β1-4 and β1-3 linkages. It is involved with a huge number of cellular processes [
36,
37,
38,
39].
Contrary to more complex glycosaminoglycans, HY is not sulfated, and it does not occur as part of a proteoglycan linked to a protein carrier. Significant interest in HY as a biomaterial and in biomaterials surface modification exists [
40]. HY in medicine is mostly exploited because of its physical properties (hydration, viscosity, space filling), or by taking advantage of the hydration-promoted ability to reduce non-specific adhesion. Growing knowledge on HY as a key molecule in the regulation of many cellular processes involved with wound healing and tissue regeneration suggests that even more opportunities lie in the exploitation of its specific biological and bioactive properties [
41,
42,
43].
Several literature reports indicate the potential interest of HY in BMTiS. Concerning bone regeneration, since the fifties it has been known that considerable HY is synthesized in the early stages of callus formation during the repair of fractured long bones [
44]. Iwata and Urist [
45] found that large amounts of HY were secreted when implants of decalcified bone underwent remineralization as bone. Bernard and coworkers presented studies aimed at developing “a foundation for the use of HY as a superior carrier for osteotropic substrates, even as HY acts to enhance osteogenesis due to its own molecular structure” [
46]. Their in vitro studies using fetal calvarial cells and bone marrow osteogenic stem cells show that osteogenesis in vitro is significantly enhanced by HY 30–160 kDa, while high Mw HY (550–1300 kDa) shows weak inhibitory effects compared to the control. Zou and coworkers reported that 800 kDa HY added to bone marrow stromal cells cultured in vitro accelerates cell proliferation, increases alkaline phosphatase activity and osteocalcin gene expression, and that HY interacts with BMP-2 to generate direct and specific cellular effects [
47]. Ito and coworkers showed that locally applied 900 kDa HY has a positive effect in bone ingrowth in Titanium fiber mesh implant in rats [
48]. According to Cho, HY shows a positive effect in early bone consolidation in distraction osteogenesis [
49]. HY based scaffolds aid in the regeneration of cartilage and bone defects in tissue engineering applications. The hypothesis of an active role played by local HY delivery upon scaffold degradation was suggested [
50]. Zhao et al. [
51] investigated the role of molecular weight and concentration of HY on the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of rabbit bone marrow-derived stem cells in vitro. Factorial analysis indicated that molecular weight (MW) and concentration had an interactive effect on alkaline phosphatase mRNA expression (
p < 0.05). HY of higher MW and higher concentration promoted bone formation. Regarding the in vivo studies on HY-coated implants, Aebli et al. [
52] did not find bone growth increase in tests involving a sheep model. It should be noted that in the quoted study, the water-soluble HY was simply applied from solution to hydroxyapatite-coated implants without any intervening chemical bond to prevent rapid wash off [
40]. An in vivo study on surface-engineered titanium implants bearing instead of a covalently-linked HY molecular surface layer in a four week rabbit model showed improvement of both bone to implant contact and bone ingrowth by hystomorphometry, while mechanical testing and evaluation of interfacial bone micro-hardness confirmed a faster bone maturation around HY coated implants [
53]. Based on these and other encouraging pre-clinical results, the present study was conducted to investigate the clinical potential of HY covalently-linked implants and to set a starting point for future developments. The main goal was to confirm, in clinical practice and adopting objective clinical evaluation criteria, that “it is possible to do without the titanium surface chemistry”. Once this point is set in routine clinics, pathways to actual exploitation of biomolecular signaling properties in compromised or challenging cases can be explored.
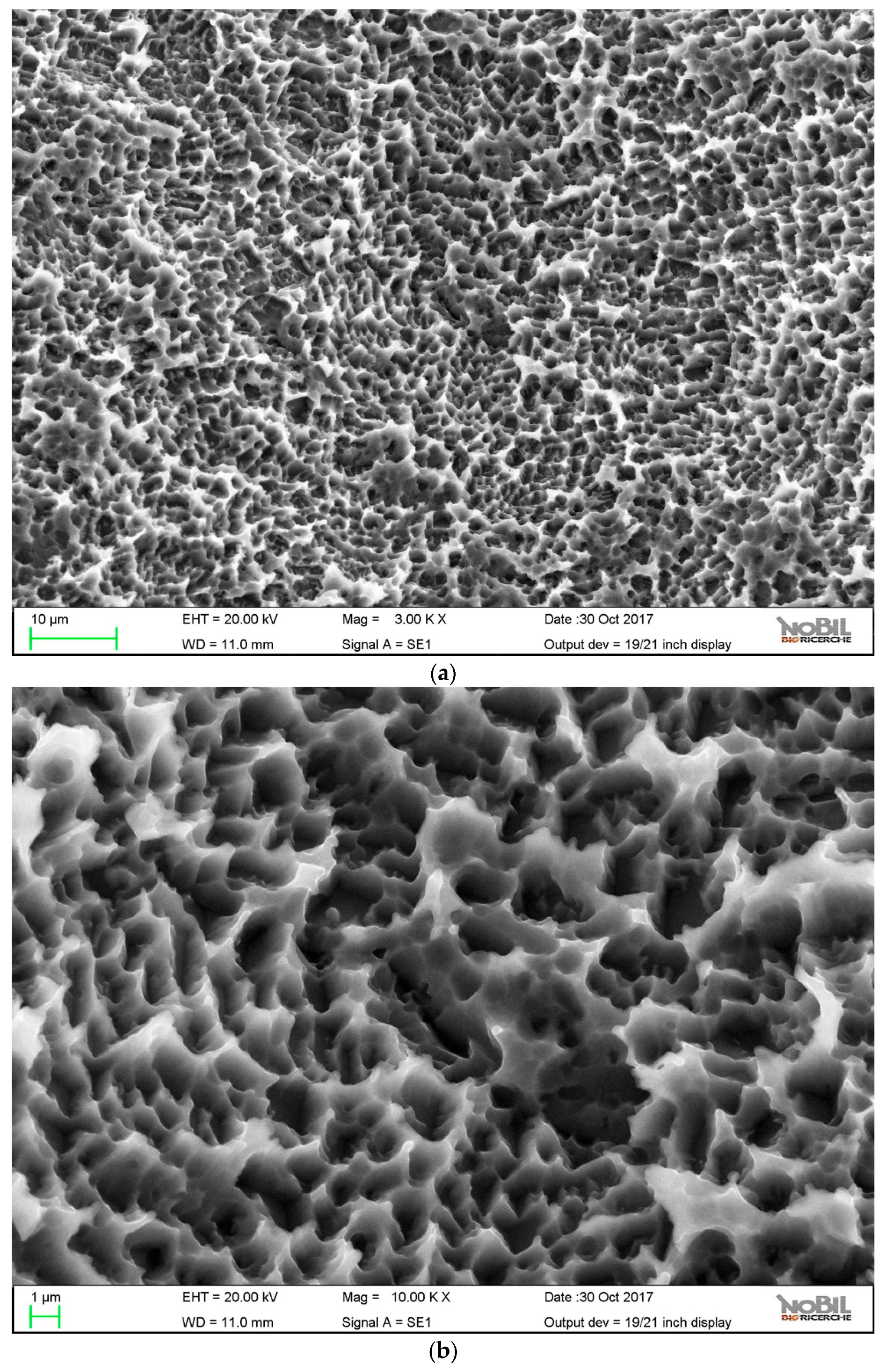
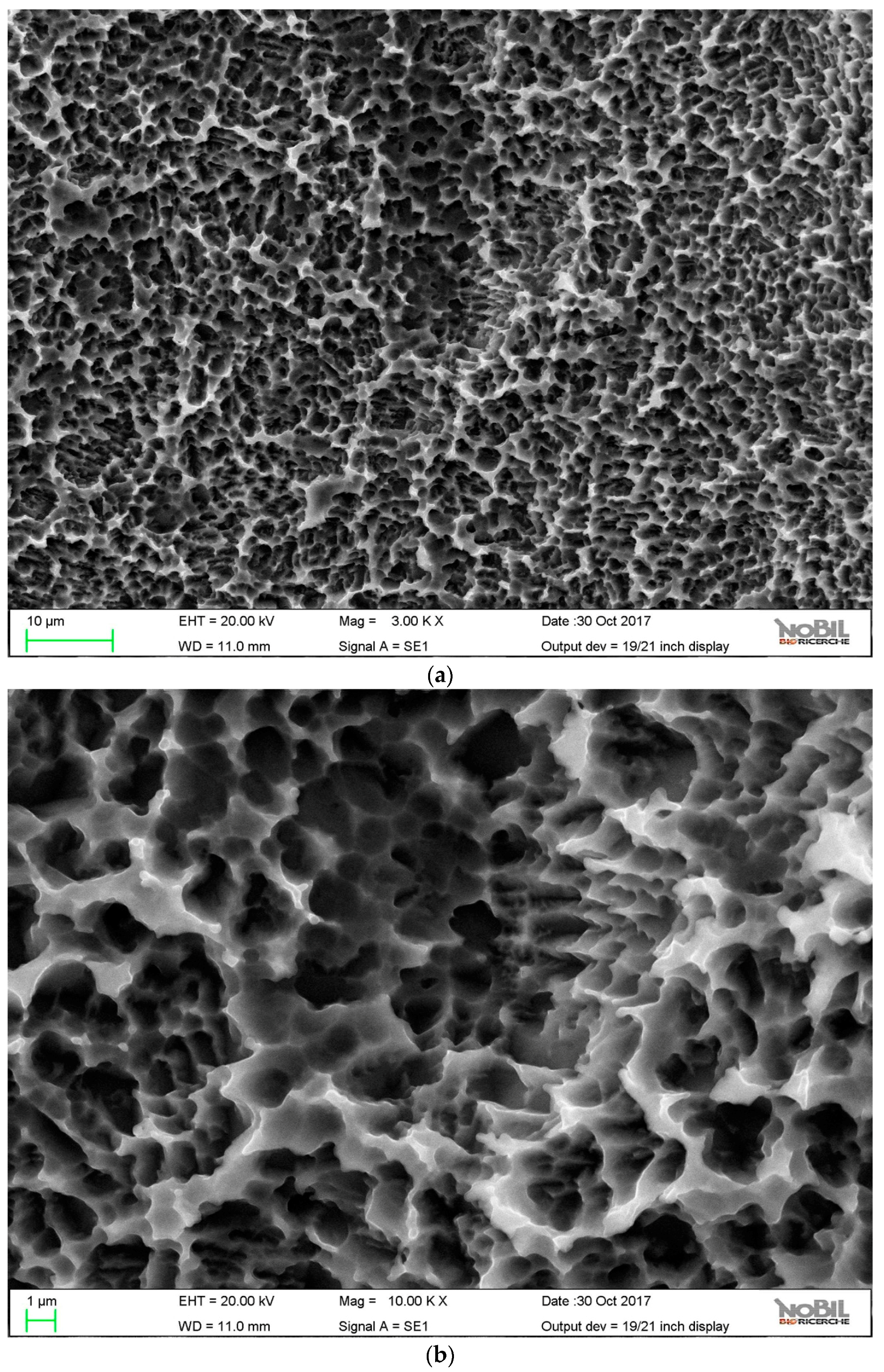
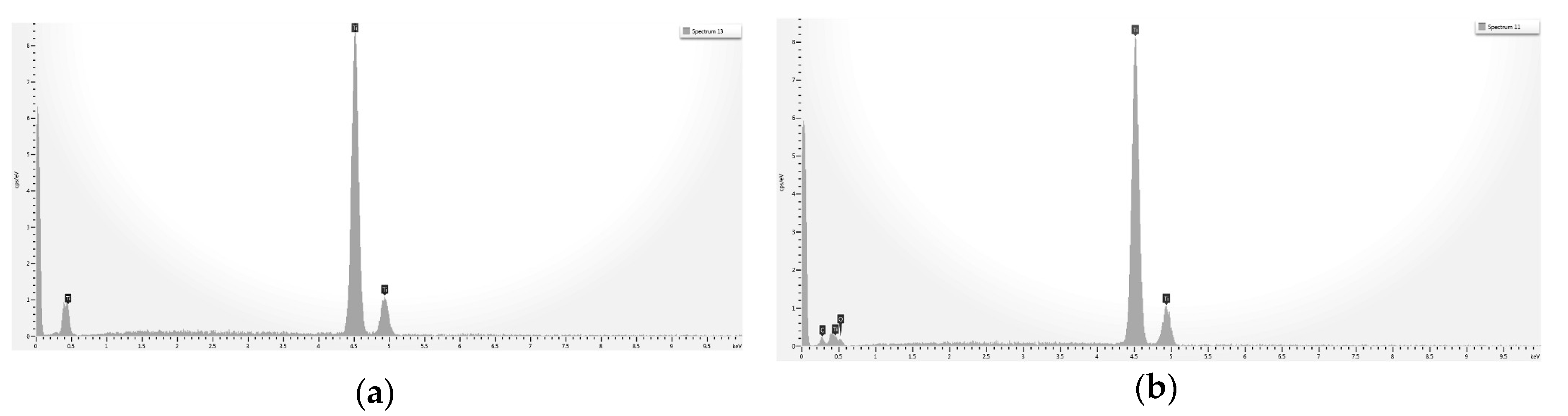
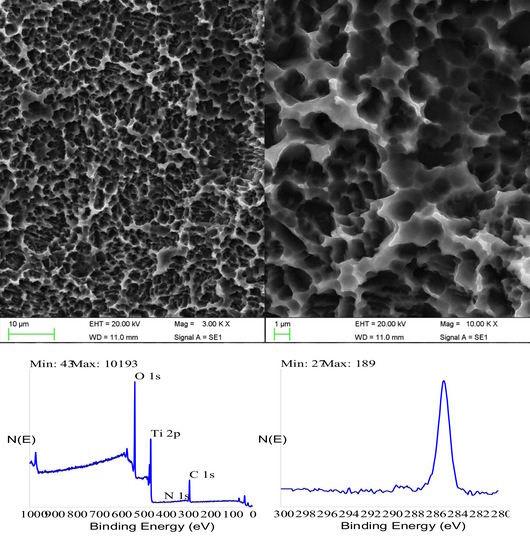
The paper presents first a detailed investigation of HY-coated titanium implants surfaces and relevant uncoated controls by SEM, energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Results of the clinical trial are then presented and discussed.
This split-mouth randomized clinical trial is aimed at assessing the clinical success and marginal bone resorption of dental implants bearing a surface molecular layer of covalently-linked hyaluronan in comparison with traditional sand-blasted and etched titanium implants up to 36 months after loading.
3. Discussion
In the present clinical trial, a widely adopted microrough titanium surface and the same surface further modified by a covalently-linked nanolayer of hyaluronan were compared in terms of clinical success in routine clinical practice.
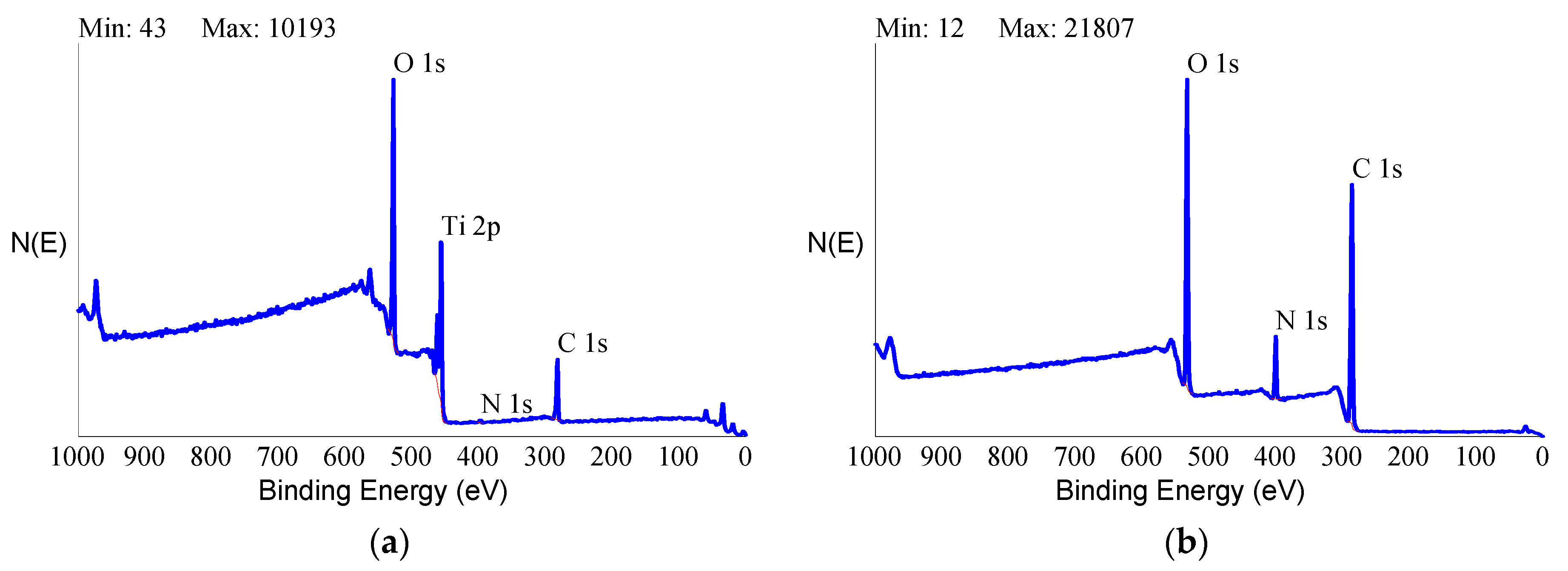
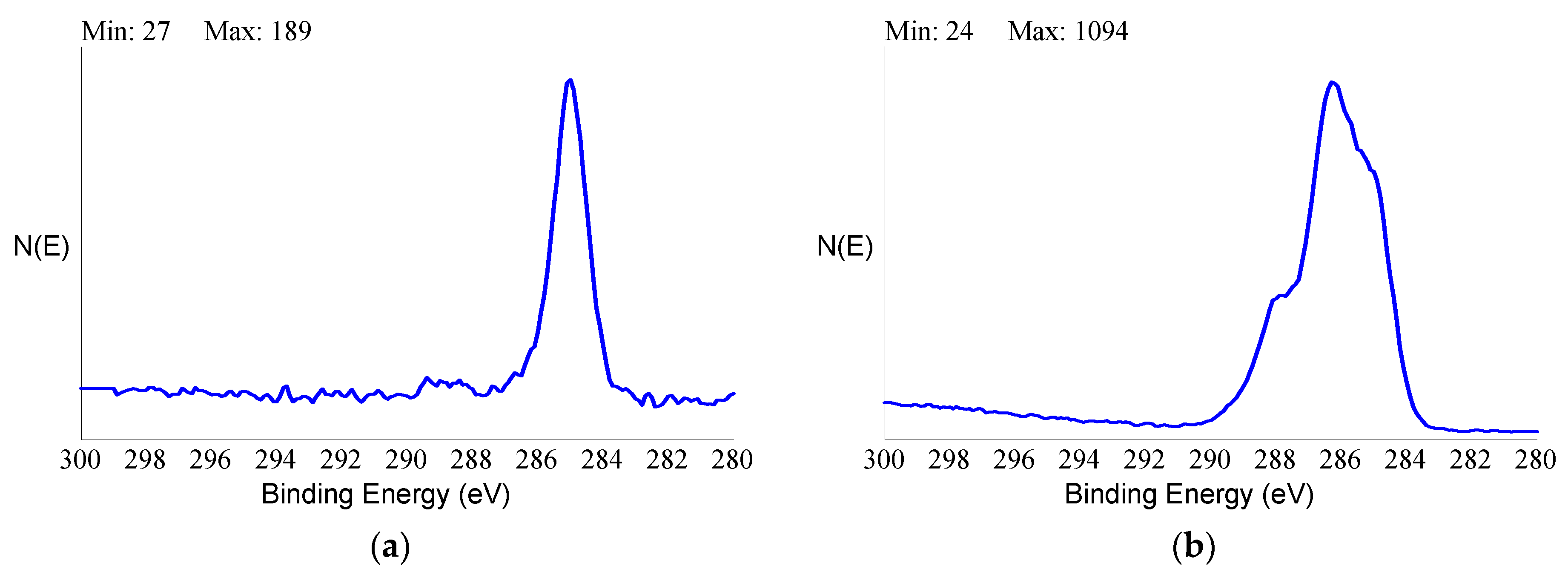
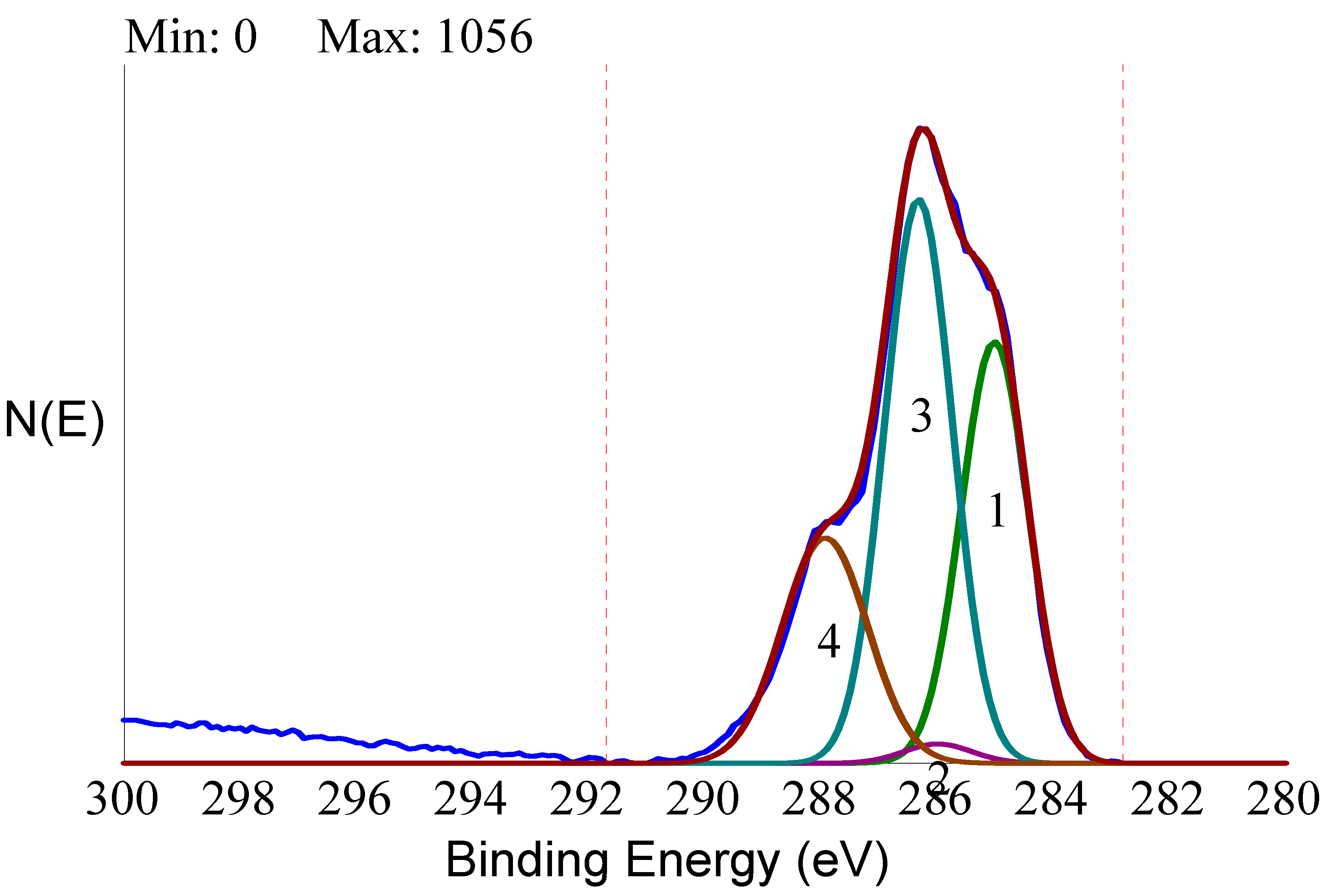
Analytical data confirmed the exquisitely superficial nature of the surface modification process that was adopted. The analytical signal captured in EDX analysis stemmed from a surface volume that was a few micrometers deep [
60]. Thus, within the EDX sampling depth, the signal by the nanometers-thick HY surface layer was diluted within the micrometer-thick analytical layer, and the resulting spectrum contained convoluted contributions from the underlying Ti implant and the overlying HY molecules in roughly a 1000:1 ratio. As a consequence, the elements composing the surface layer were barely detectable. For this reason, a more surface-sensitive analytical technique, namely XPS, was conducted to fully appreciate the biomolecular modification of the HY-coated implants. Contrary to EDX analysis, the physics of photoelectrons escaped from solids endowed XPS with just a few nanometers of sampling depth, consequently providing chemical information on the outermost atomic layers of materials [
58]. For this reason, XPS was extensively used in the surface analysis of dental implants [
7,
61,
62,
63].
Despite the widely different surface chemistry, objective optimal healing was observed for both groups, and no differences were detected in the clinical outcome for all tested parameters. Far from being uneventful, the described results suggested some important reflections. From a chemical-physical point of view, it would be difficult to imagine two more different surface structures—the titanium surface (in particular, the outermost few nanometers of oxidized titanium) presented a hard, impervious interface to the host tissue, whose chemical behavior was controlled by titanium oxide interfacial chemistry, as widely described in many scientific papers [
7,
8,
61]. On the contrary, the HY-coated implant aqueous interface was diffuse, soft, and hydrated [
64]. Its chemistry stemmed from the molecular details of the
N-acetyl-
d-glucosamine-
d-glucuronate repeating unit. Shortly, one of them (the control arm) belonged to inorganic chemistry. The HY-coated surface belonged instead to organic biomacromolecular chemistry. Despite being two worlds apart, no significant difference was detected in the tested clinical variables, and both of them led to successful osseointegration and clinical success. The first significant reflection from the data of the present work is that the titanium surface chemistry is not necessary to achieve a clinically satisfactory load-bearing capacity by a titanium dental implant.
The previous point could be interpreted as a no-effect of surface chemistry on osseointegration. As long as the implant surface is inert and no disturbance is introduced in the bone healing mechanism—that is, as long as no toxic or irritating compounds are released in the evolving new bone matrix independent from specific details of surface chemistry—clinically effective osseointegration will occur. If this is the case, no advancement is expected by BMTiS over conventional surfaces, and the sole opportunity to direct tissue response is through surface topography.
The last sentence falls short when compared to existing scientific evidence gathered from animal data, which shows direct effects of interfacial chemistry on bone healing in terms of peri-implant bone volume, bone to implant contact, or gene expression by peri-implant bone cells [
35,
53,
65,
66]. In the present clinical trial, a patient’s selection and surgery addressed comparatively routine clinical practice. The control arm, involving a state-of-the-art doubly acid etched microrough surface, obviously provided optimal healing and clinical success. Endpoint variables aimed at general clinical evidence expectedly confirmed that both the well-known titanium interfacial chemistry and the biologically relevant HY molecular cued direct cellular events involved with peri-implant tissue healing towards proper clinical response.
HY is a key molecule in many tissue regeneration processes; it is involved with most of the mammalian cells’ healing mechanisms [
67,
68,
69] in a concentration and size-dependent way. The permanent linking of HY to materials surfaces avoids quick wash-off of the water soluble HY and aims at providing these regenerative properties at the peri-implant interface, as confirmed by several in vivo evidences. It is not clear yet how surface-immobilized HY compares with HY in solution in terms of the effect of the hindered conformational freedom on the multiple ligand-receptor interactions required to trigger a biological response [
40]. It would be of interest to check the stimulation of bone tissue regeneration at machined interfaces of hybrid implants, the effect on soft tissue healing in the transmucosal section of tissue level implants, or the control of inflammatory responses of periodontal patients [
70] and relevant clinical implications. The positive evidence supplied by the present clinical trial in standard practice opens the path to comprehensive investigation of the merits of BMTiS in clinical implantology by further finely-targeted clinical trials.
A last observation involves the relationship of present results with in vitro investigation of dental implant surfaces. A widely adopted approach involves the “adhesion and growth” paradigm, meaning that prospective surface structures are screened in terms of effects on adhesion and growth of osteoblast cells—the faster and more extensive the surface colonization by cells, the better the properties. Against this view, HY-coated surfaces are notoriously anti-adhesive in vitro [
64,
71], meaning that they prevent cell adhesion of a number of cell lines, including osteoblasts. Several applications of HY-coated surfaces are based on tissue-anti-adhesive properties. In vitro tests of present clinically successful HY-coated implants would provide unsatisfactory results if judged according to the “adhesion and growth” paradigm. Yet, clinical evidence as supplied by the present trial indicates that they are fit for the intended use. Far from being inconsistent, this evidence simply indicates the complexity of the peri-implant environment as opposed to the comparatively simple biological environment of in vitro tests. In clinics, osteoblasts do not adhere and grow onto the implant surface. Rather, they come to a complex peri-implant milieu after the blood clot and relevant blood cells, inflammatory cells, and the sequela of cytokine and growth factors are released in the initial stage of inflammation and healing [
72]. Rather than the direct effect of the interfacial HY (or of any surface-linked biomolecular layer) on osteoblasts, it is the effect of molecular signaling on the evolution of the peri-implant biochemical environment that directs clinical outcome and that holds the potential merits of BMTiS in clinics.
In summary, the clinical trial did not record any significant difference between the HY- and the C-group in terms of clinical success and marginal bone resorption. In the present study, for the first time in clinics (to the author’s knowledge), dental implants with a biomolecular nanolayer on the surface showed a behavior similar to the commercial pure titanium one. This study presents the limits to having a follow up limited to 36 months. The duration of the follow up was chosen because in this span of time, the HY layer should be completely integrated within the newly formed interfacial tissue. Further studies should be conducted to evaluate the long-term success of HY-implants. Present data build up the ethical basis for the investigation into the merits of HY-coated implants in more challenging and compromised cases where signaling and regenerative properties encoded within the HY molecular structure could play a role that is presently not supplied by the comparatively rough titanium surface chemistry.