Different Modes of Action of Genetic and Chemical Downregulation of Histone Deacetylases with Respect to Plant Development and Histone Modifications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
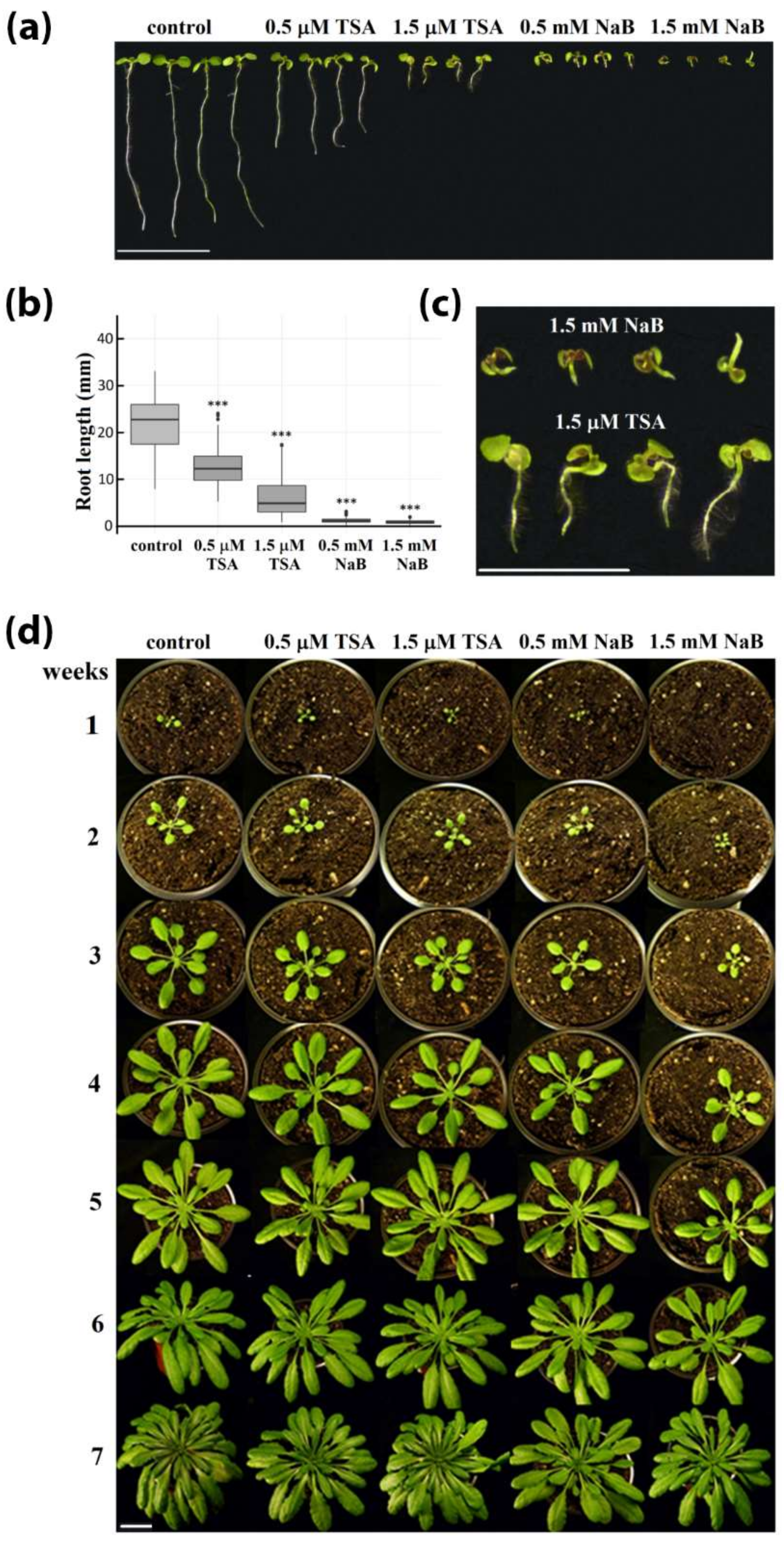
2.1. Strong Phenotype of Seedlings Germinated in the Presence of HDA Inhibitors Is Recovered during Cultivation of Plants in the Soil
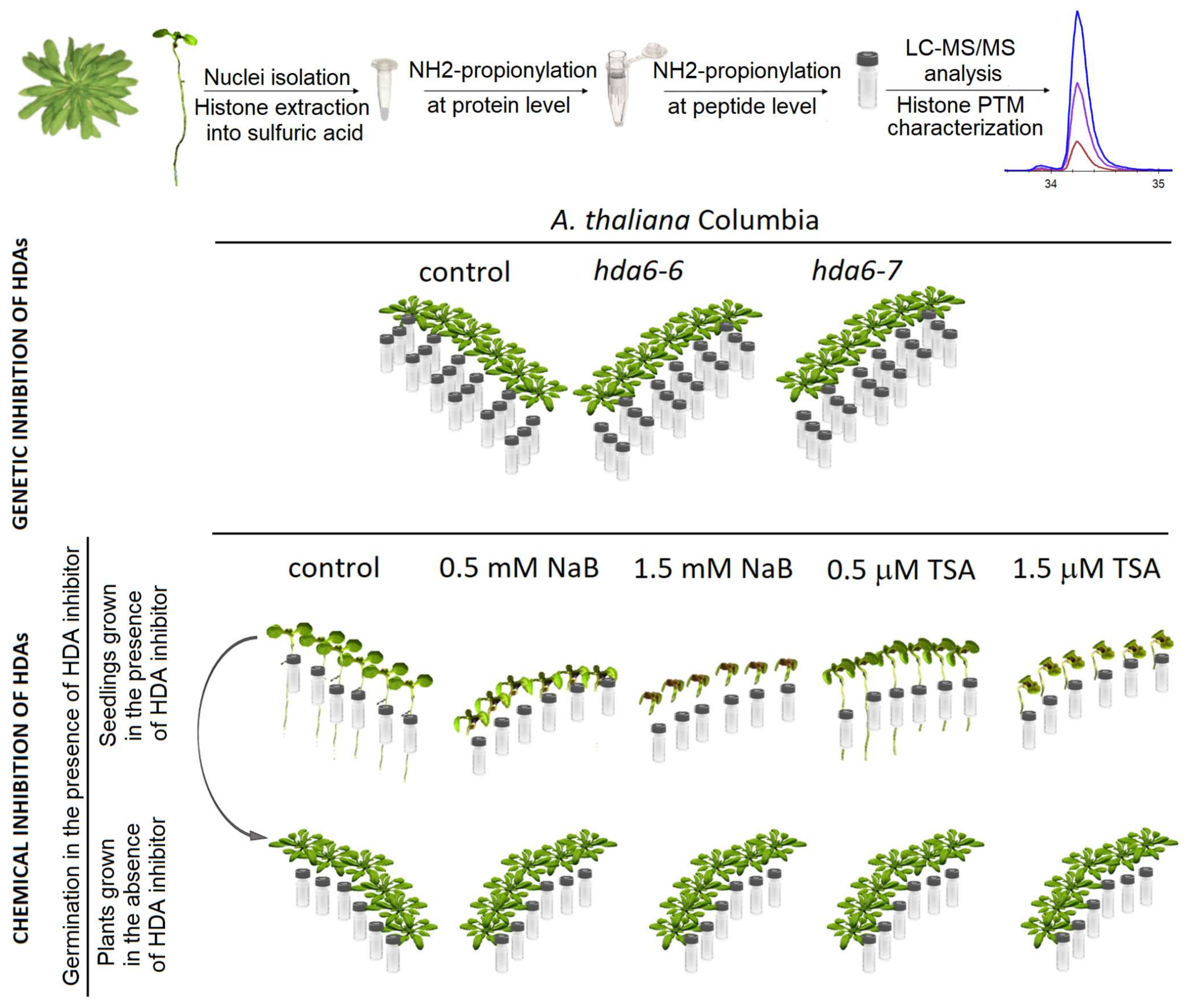
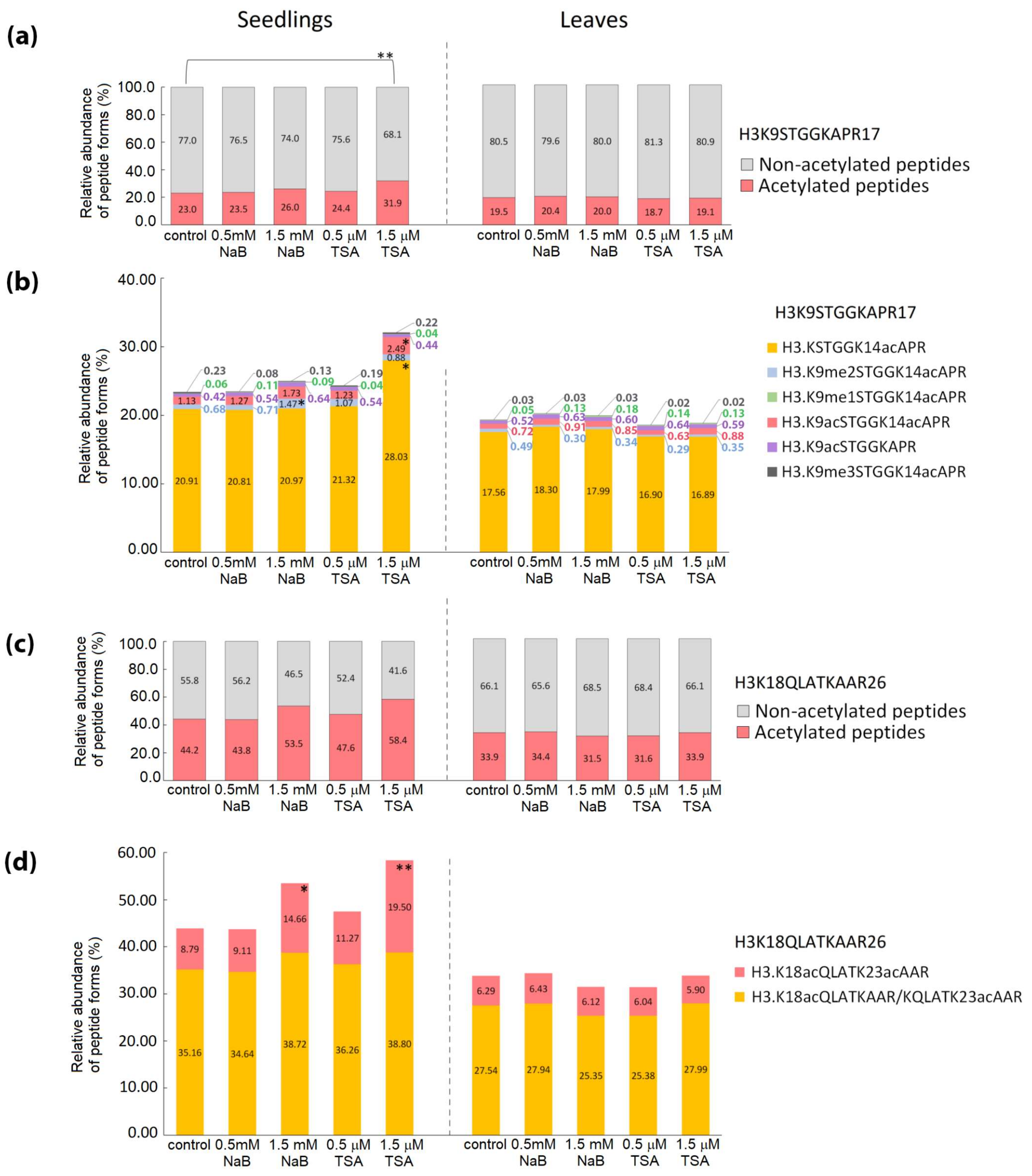
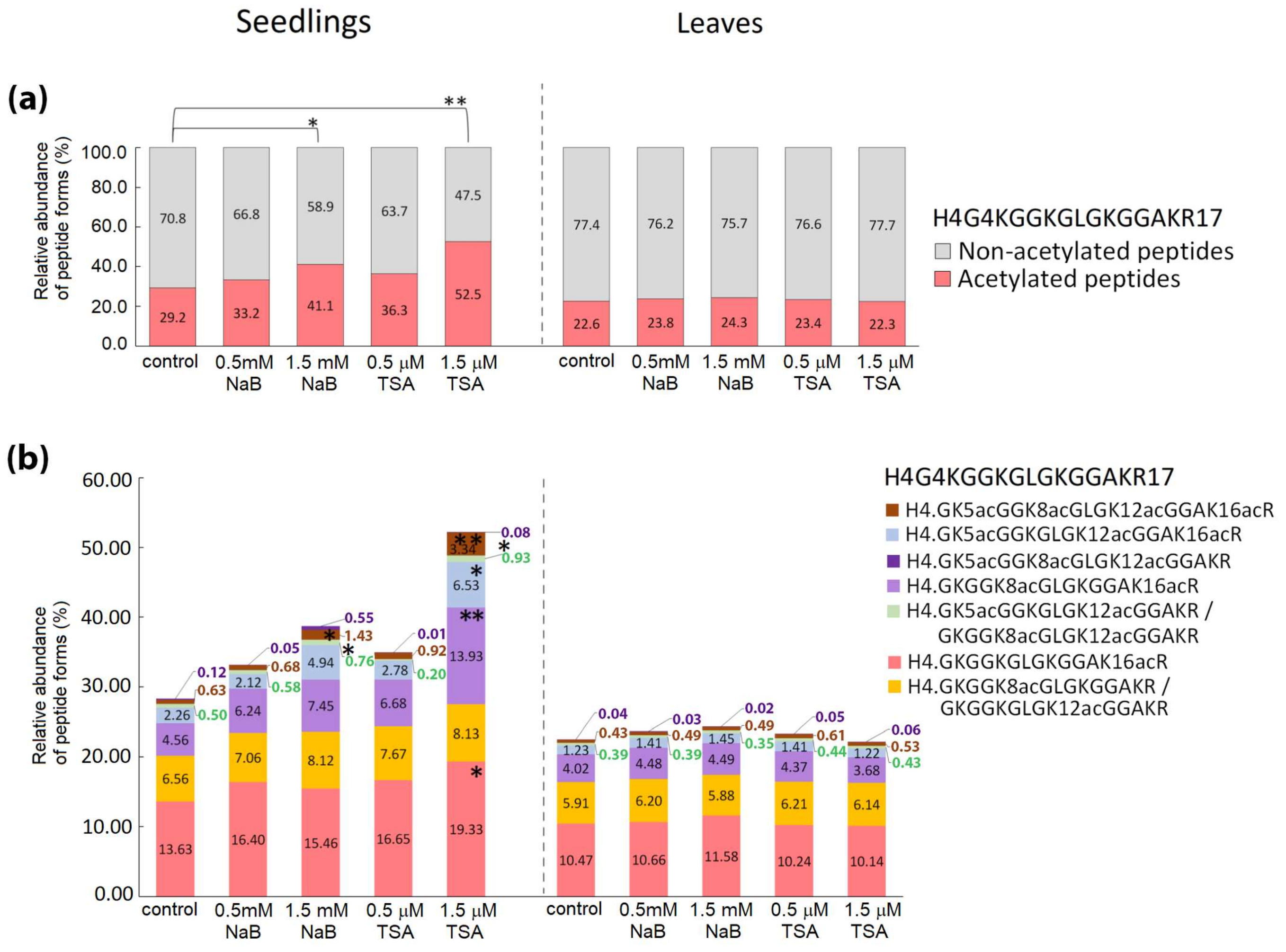
2.2. Distinct Alterations in Histone PTMs Are Hidden under a Mild Phenotype and Vice Versa
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cultivation of Plants, Monitoring of Phenotype
4.2. Histone Isolation and Preparation of Samples for Mass Spectrometry
4.3. Mass Spectrometric Analysis, Database Searches and Quantification of Histone Peptide Forms
4.4. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HAT | Histone acetyltransferase |
| HDA | Histone deacetylase |
| NaB | Sodium butyrate |
| MS | Mass spectrometry |
| PTM | Post-translational modification |
| TSA | Trichostatin A |
References
- Brownell, J.E.; Allis, C.D. Special HATs for special occasions: Linking histone acetylation to chromatin assembly and gene activation. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 1996, 6, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, M.H.; Allis, C.D. Roles of histone acetyltransferases and deacetylases in gene regulation. Bioessays 1998, 20, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.J.; Pikaard, C.S. Epigenetic silencing of RNA polymerase I transcription: A role for DNA methylation and histone modification in nucleolar dominance. Genes Dev. 1997, 11, 2124–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadosh, D.; Struhl, K. Targeted recruitment of the Sin3-Rpd3 histone deacetylase complex generates a highly localized domain of repressed chromatin in vivo. Mol. Cell Biol. 1998, 18, 5121–5127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, Y.Q.; Chen, Q.; Lin, R.N.; Li, Y.Q.; Li, L.; Chen, S.; He, X.J. The HDA19 histone deacetylase complex is involved in the regulation of flowering time in a photoperiod-dependent manner. Plant J. 2019, 98, 448–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Kikuchi, A.; Kamada, H. The Arabidopsis histone deacetylases HDA6 and HDA19 contribute to the repression of embryonic properties after germination. Plant Physiol. 2008, 146, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Chen, Z.J. Blocking histone deacetylation in Arabidopsis induces pleiotropic effects on plant gene regulation and development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Liu, X.B.; Lin, J.C.; Liu, X.Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Xin, M.M.; Yao, Y.Y.; Peng, H.R.; Zhou, D.X.; Ni, Z.F.; et al. Histone acetyltransferase GCN5 contributes to cell wall integrity and salt stress tolerance by altering the expression of cellulose synthesis genes. Plant J. 2019, 97, 587–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, R.; Muller, A.; Napoli, C.A.; Selinger, D.A.; Pikaard, C.S.; Richards, E.J.; Bender, J.; Mount, D.W.; Jorgensen, R.A. Analysis of histone acetyltransferase and histone deacetylase families of Arabidopsis thaliana suggests functional diversification of chromatin modification among multicellular eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 5036–5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.J.; Seto, E. Collaborative spirit of histone deacetylases in regulating chromatin structure and gene expression. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2003, 13, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murfett, J.; Wang, X.J.; Hagen, G.; Guilfoyle, T.J. Identification of arabidopsis histone deacetylase HDA6 mutants that affect transgene expression. Plant Cell 2001, 13, 1047–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aufsatz, W.; Mette, M.F.; van der Winden, J.; Matzke, M.; Matzke, A.J. HDA6, a putative histone deacetylase needed to enhance DNA methylation induced by double-stranded RNA. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 6832–6841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Earley, K.; Lawrence, R.J.; Pontes, O.; Reuther, R.; Enciso, A.J.; Silva, M.; Neves, N.; Gross, M.; Viegas, W.; Pikaard, C.S. Erasure of histone acetylation by Arabidopsis HDA6 mediates large-scale gene silencing in nucleolar dominance. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 1283–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.C.; Yu, C.W.; Duan, J.; Luo, M.; Wang, K.C.; Tian, G.; Cui, Y.H.; Wu, K.Q. HDA6 Directly Interacts with DNA Methyltransferase MET1 and Maintains Transposable Element Silencing in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2012, 158, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Probst, A.V.; Fagard, M.; Proux, F.; Mourrain, P.; Boutet, S.; Earley, K.; Lawrence, R.J.; Pikaard, C.S.; Murfett, J.; Furner, I.; et al. Arabidopsis histone deacetylase HDA6 is required for maintenance of transcriptional gene silencing and determines nuclear organization of rDNA repeats. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 1021–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.T.; Luo, M.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wu, K.Q. Involvement of Arabidopsis histone deacetylase HDA6 in ABA and salt stress response. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 3345–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Hu, Q.; Wu, Z.J.; Wang, H.; Han, S.M.; Jin, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Z.F.; Jiang, J.F.; Shen, Y.; et al. HISTONE DEACETYLASE 6 represses pathogen defence responses in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Environ. 2017, 40, 2972–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.W.; Liu, X.C.; Luo, M.; Chen, C.Y.; Lin, X.D.; Tian, G.; Lu, Q.; Cui, Y.H.; Wu, K.Q. HISTONE DEACETYLASE6 Interacts with FLOWERING LOCUS D and Regulates Flowering in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnin, M.S.; Donigian, J.R.; Cohen, A.; Richon, V.M.; Rifkind, R.A.; Marks, P.A.; Breslow, R.; Pavletich, N.P. Structures of a histone deacetylase homologue bound to the TSA and SAHA inhibitors. Nature 1999, 401, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cousens, L.S.; Gallwitz, D.; Alberts, B.M. Different Accessibilities in Chromatin to Histone Acetylase. J. Biol. Chem. 1979, 254, 1716–1723. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, B.; Yang, C.P.; Li, S.J. Identification of genes regulated by histone acetylation during root development in Populus trichocarpa. BMC Genom. 2016, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Earley, K.W.; Shook, M.S.; Brower-Toland, B.; Hicks, L.; Pikaard, C.S. In vitro specificities of Arabidopsis co-activator histone acetyltransferases: Implications for histone hyperacetylation in gene activation. Plant J. 2007, 52, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagano, A.; Araujo, S.D.; Macovei, A.; Dondi, D.; Lazzaroni, S.; Balestrazzi, A. Metabolic and gene expression hallmarks of seed germination uncovered by sodium butyrate in Medicago truncatula. Plant Cell Environ. 2019, 42, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledvinová, D.; Mikulášek, K.; Kuchaříková, H.; Brabencová, S.; Fojtová, M.; Zdráhal, Z.; Lochmanová, G. Filter-Aided Sample Preparation Procedure for Mass Spectrometric Analysis of Plant Histones. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, C.; Yu, C.W.; Chaikam, V. HDA6 is required for jasmonate response, senescence and flowering in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Lv, S.; Zhang, C.; Yang, C. Histone deacetylases and their functions in plants. Plant Cell Rep. 2013, 32, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, M.; Matsui, A.; Tanaka, M.; Nakamura, T.; Abe, T.; Sako, K.; Sasaki, T.; Kim, J.M.; Ito, A.; Nishino, N.; et al. The Distinct Roles of Class I and II RPD3-Like Histone Deacetylases in Salinity Stress Response. Plant Physiol. 2017, 175, 1760–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartl, M.; Füßl, M.; Boersema, P.J.; Jost, J.O.; Kramer, K.; Bakirbas, A.; Sindlinger, J.; Plöchinger, M.; Leister, D.; Uhrig, G.; et al. Lysine acetylome profiling uncovers novel histone deacetylase substrate proteins in Arabidopsis. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2017, 13, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Činčárová, L.; Lochmanová, G.; Nováková, K.; Šultesová, P.; Konečná, H.; Fajkusová, L.; Fajkus, J.; Zdráhal, Z. A combined approach for the study of histone deacetylase inhibitors. Mol. Biosyst. 2012, 8, 2937–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Varghese, D.S.; Gillam, M.C.; Peyton, M.; Modi, B.; Schiltz, R.L.; Girard, L.; Martinez, E.D. Differential response of cancer cells to HDAC inhibitors trichostatin A and depsipeptide. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 106, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krämer, O.H.; Zhu, P.; Ostendorff, H.P.; Golebiewski, M.; Tiefenbach, J.; Peters, M.A.; Brill, B.; Groner, B.; Bach, I.; Heinzel, T.; et al. The histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid selectively induces proteasomal degradation of HDAC2. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 3411–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marks, P.A.; Xu, W.S. Histone deacetylase inhibitors: Potential in cancer therapy. J. Cell Biochem. 2009, 107, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.R.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.L.; Li, L.C.; Chen, W.Q.; Xu, Z.H.; Bai, S.N. Histone acetylation affects expression of cellular patterning genes in the Arabidopsis root epidermis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 14469–14474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.H.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Si, J.P. Chromatin-Based Regulation of Plant Root Development. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vizcaíno, J.A.; Csordas, A.; Del-Toro, N.; Dianes, J.A.; Griss, J.; Lavidas, I.; Mayer, G.; Perez-Riverol, Y.; Reisinger, F.; Ternent, T.; et al. 2016 update of the PRIDE database and its related tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 11033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitchison, J. The Statistical-Analysis of Compositional Data. J. Roy. Stat. Soc. B Met. 1982, 44, 139–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hron, K.; Templ, M.; Filzmoser, P. Imputation of missing values for compositional data using classical and robust methods. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2010, 54, 3095–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing, R Foundation for Statistical Computing: 2018. Available online: http:// www.R-project.org (accessed on 15 May 2019).

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lochmanová, G.; Ihnatová, I.; Kuchaříková, H.; Brabencová, S.; Zachová, D.; Fajkus, J.; Zdráhal, Z.; Fojtová, M. Different Modes of Action of Genetic and Chemical Downregulation of Histone Deacetylases with Respect to Plant Development and Histone Modifications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5093. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20205093
Lochmanová G, Ihnatová I, Kuchaříková H, Brabencová S, Zachová D, Fajkus J, Zdráhal Z, Fojtová M. Different Modes of Action of Genetic and Chemical Downregulation of Histone Deacetylases with Respect to Plant Development and Histone Modifications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(20):5093. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20205093
Chicago/Turabian StyleLochmanová, Gabriela, Ivana Ihnatová, Hana Kuchaříková, Sylva Brabencová, Dagmar Zachová, Jiří Fajkus, Zbyněk Zdráhal, and Miloslava Fojtová. 2019. "Different Modes of Action of Genetic and Chemical Downregulation of Histone Deacetylases with Respect to Plant Development and Histone Modifications" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 20: 5093. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20205093
APA StyleLochmanová, G., Ihnatová, I., Kuchaříková, H., Brabencová, S., Zachová, D., Fajkus, J., Zdráhal, Z., & Fojtová, M. (2019). Different Modes of Action of Genetic and Chemical Downregulation of Histone Deacetylases with Respect to Plant Development and Histone Modifications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(20), 5093. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20205093




