Structural Determination of Lysosphingomyelin-509 and Discovery of Novel Class Lipids from Patients with Niemann–Pick Disease Type C
Abstract
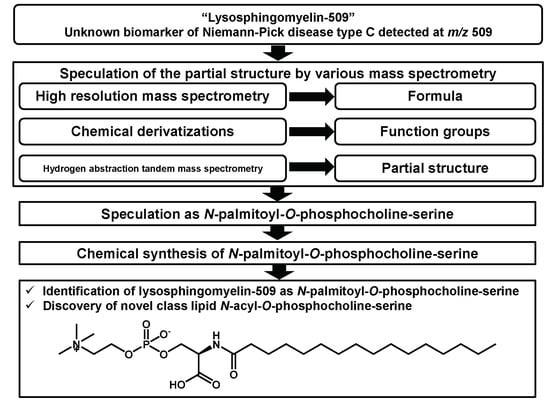
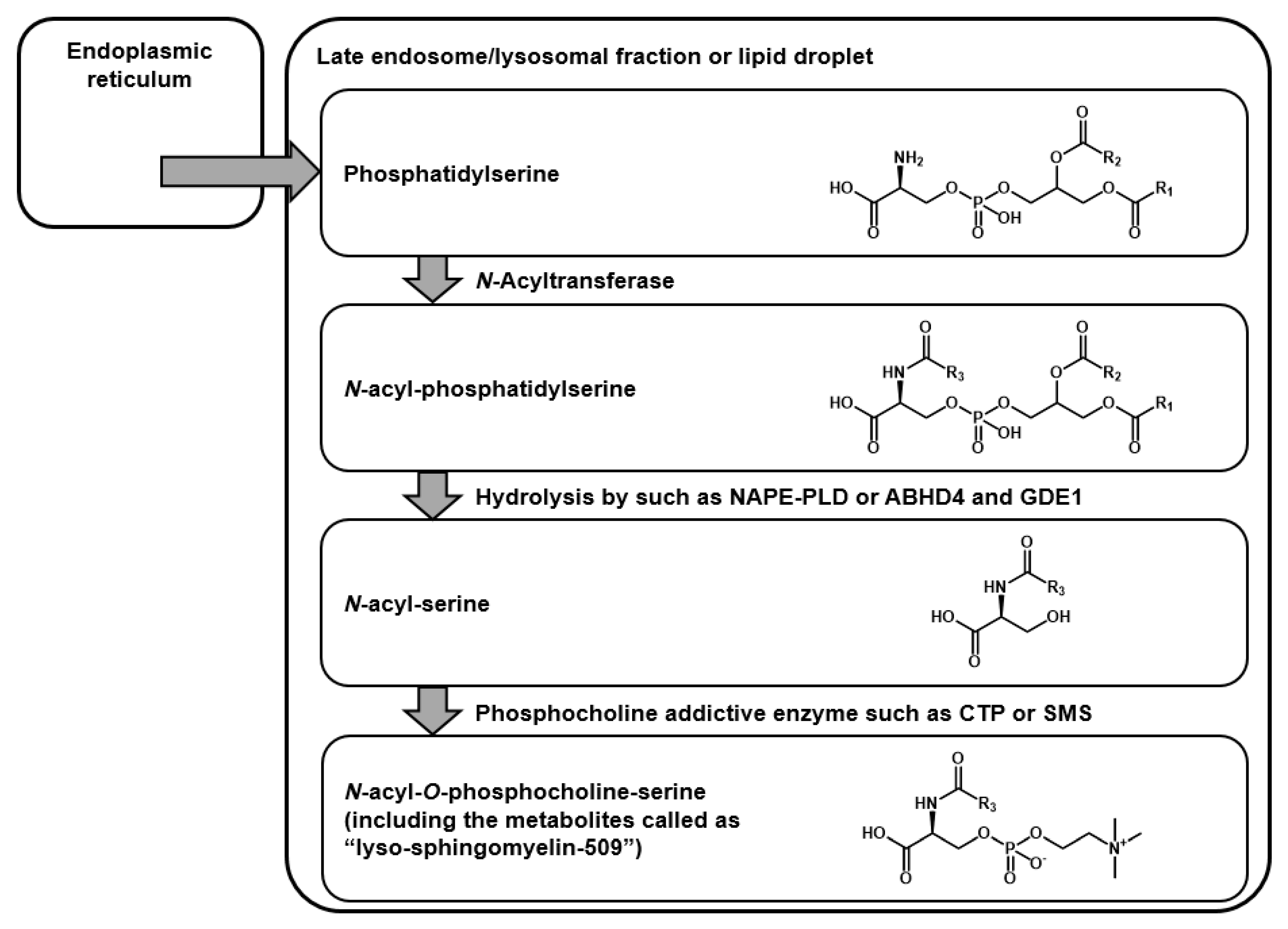
1. Introduction
2. Result and Discussion
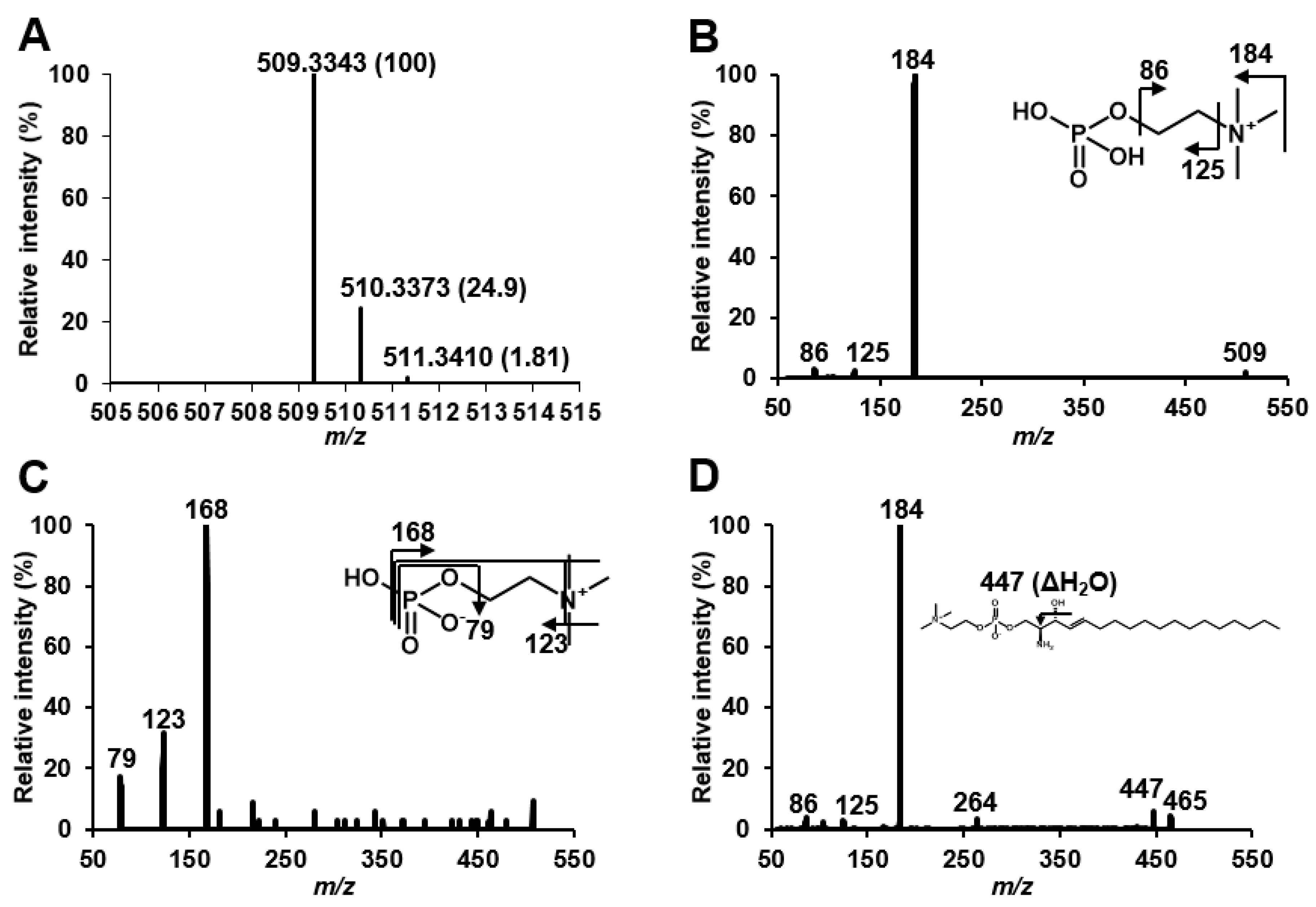
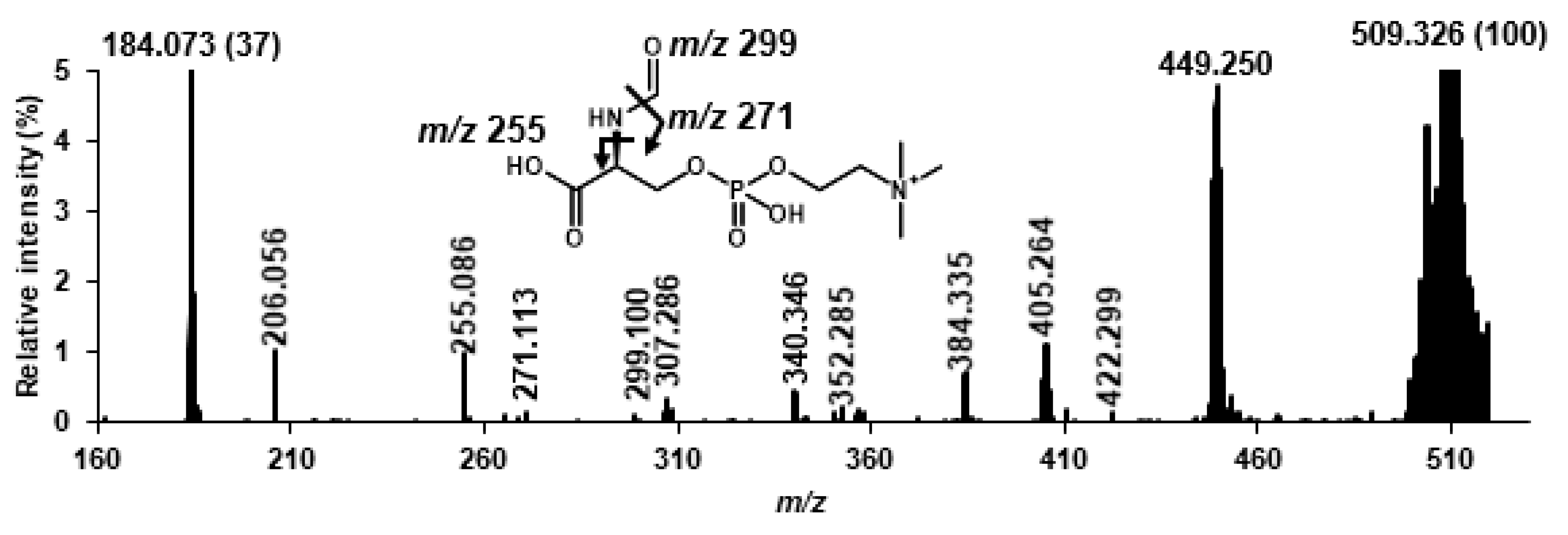
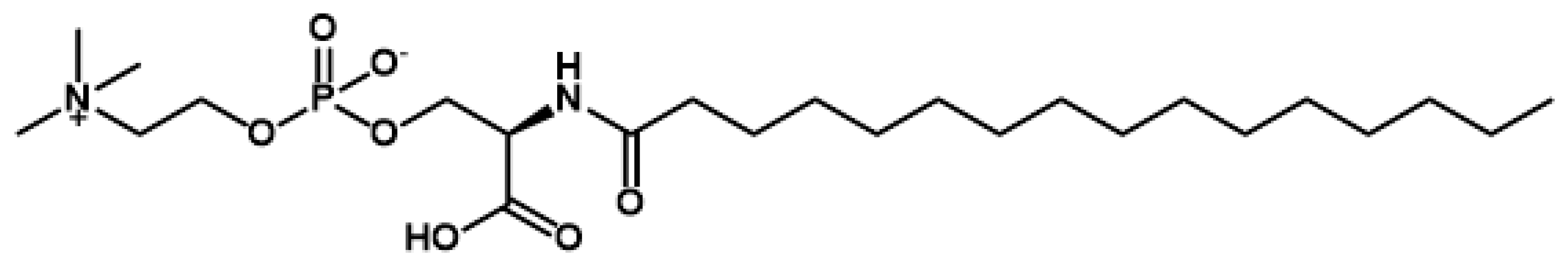
2.1. Structural Speculation of Lyso-SM-509
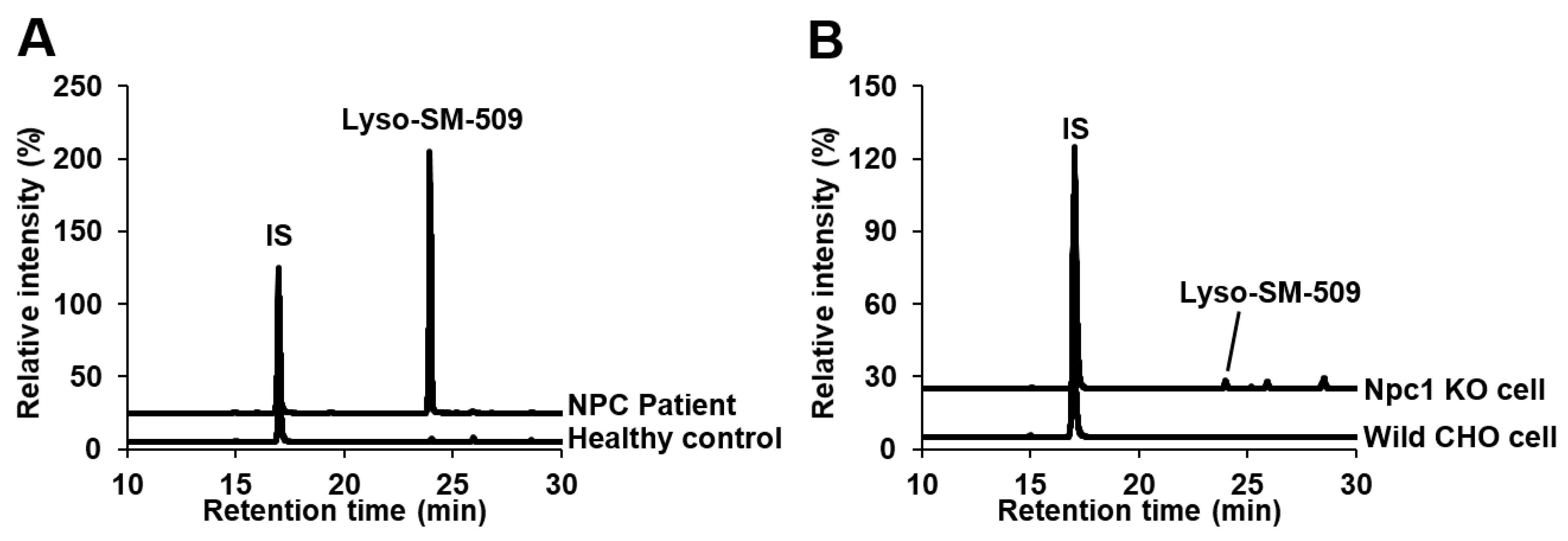
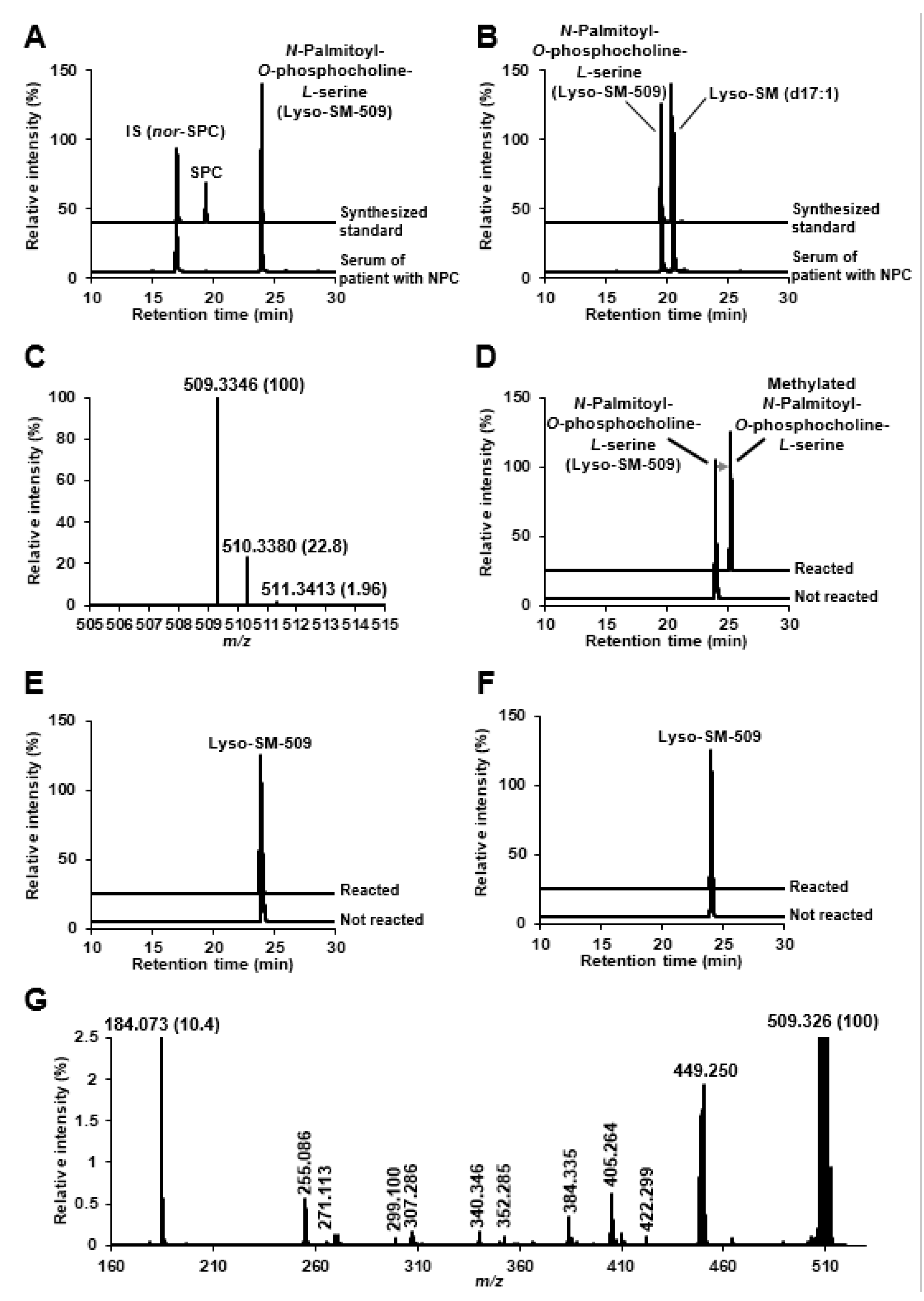
2.2. Identification of Lyso-SM-509
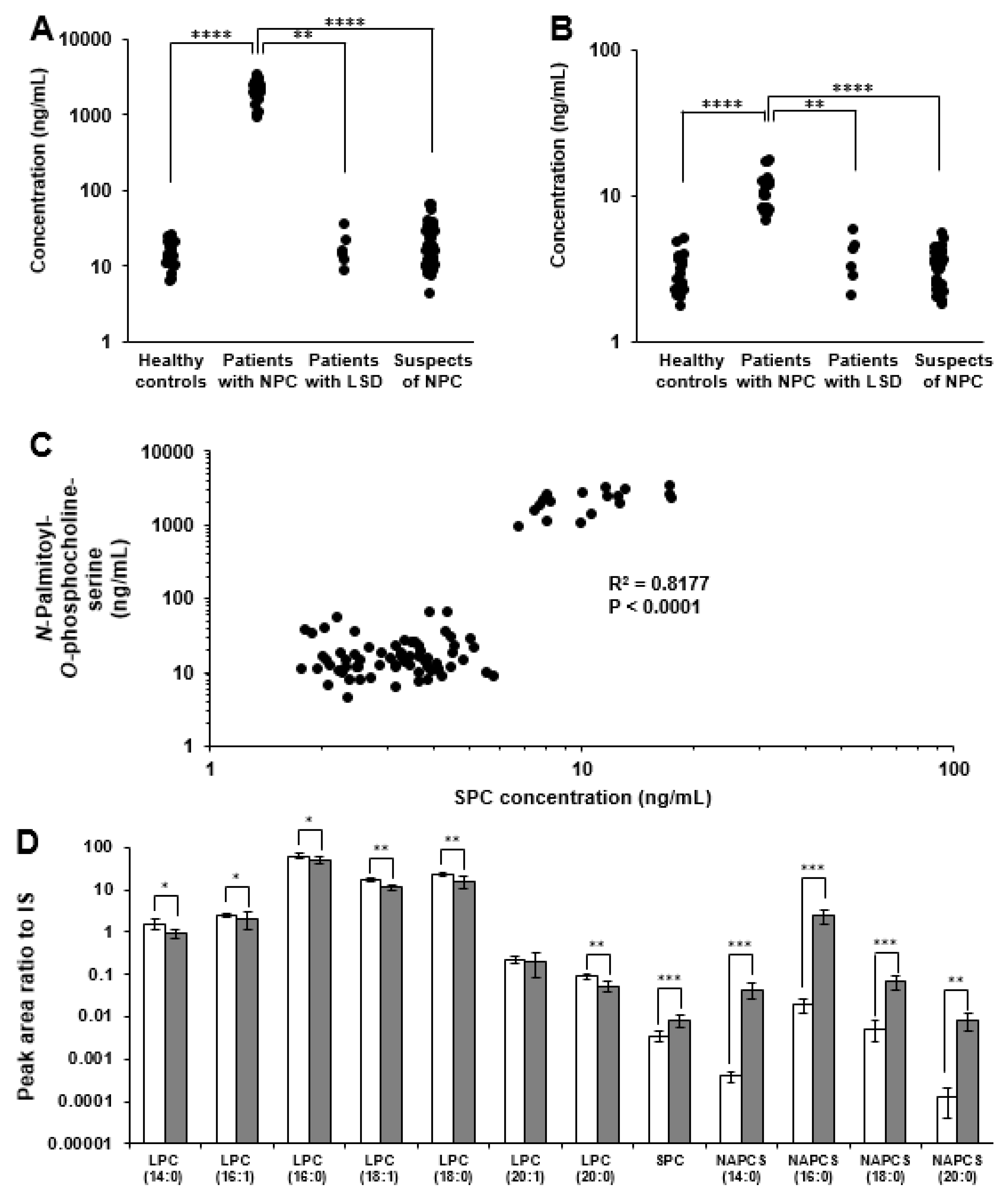
2.3. Analysis of Plasma/Serum Novel Class Lipids
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Structural Speculation of Lyso-SM-509
3.3. Chemical Derivatization for Lyso-SM-509 and SPC
3.4. Chemical Synthesis of N-Palmitoyl-O-Phosphocholine-Serine
3.5. Identification of Lyso-SM-509
3.6. Simultaneous Analysis of N-Palmitoyl-O-Phosphocholine-Serine and SPC in the Serum or Plasma
3.7. Targeted Lipidomics Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CHO | Chinese hamster ovary |
| Lyso-SM | Lysosphingomyelin |
| Lyso-SM-509 | Lysosphingomyelin-509 |
| NBD | 7-Nitro-2,1,3-benzoxadiazole |
| NPC | Niemann–Pick disease type C |
| SPC | Sphingosylphosphocholine |
| SRM | Selected reaction monitoring |
| AcOEt | Ethyl acetate |
| CDCl3 | Chloroform-d |
| CD3OD | Methanol-d4 |
| DCC | N, N’-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide |
| DHB | 2, 5-Dihydroxbenzoic acid |
| Et3N | Triethylamin |
| HOBt | 1-Hydroxybenzotriazole |
| MeOH | Methanol |
| NMM | N-methylmorphorine |
| Ph | Phenyl |
| THF | Tetrahydrofuran |
References
- Vanier, M.T. Niemann-Pick type C disease. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2010, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geberhiwot, T.; Moro, A.; Dardis, A.; Ramaswami, U.; Sirrs, S.; Marfa, M.P.; Vanier, M.T.; Walterfang, M.; Bolton, S.; Dawson, C.; et al. Consensus clinical management guidelines for Niemann-Pick disease type C. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2018, 13, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.J.; Abi-Mosleh, L.; Wang, M.L.; Deisenhofer, J.; Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S.; Infante, R.E. Structure of N-terminal domain of NPC1 reveals distinct subdomains for binding and transfer of cholesterol. Cell 2009, 137, 1213–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanier, M.T. Biochemical studies in Niemann-Pick disease. I. Major sphingolipids of liver and spleen. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1983, 750, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, M.C.; Vecchio, D.; Prady, H.; Abel, L.; Wraith, J.E. Miglustat for treatment of Niemann-Pick C disease: a randomised controlled study. Lancet Neurol. 2007, 6, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ory, D.S.; Ottinger, E.A.; Farhat, N.Y.; King, K.A.; Jiang, X.; Weissfeld, L.; Berry-Kravis, E.; Davidson, C.D.; Bianconi, S.; Keener, L.A.; et al. Intrathecal 2-hydroxypropyl-βncyclodextrin decreases neurological disease progression in Niemann-Pick disease, type C1: a non-randomized, open-label, phase 1-2 trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 1758–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, F.D.; Scherrer, D.E.; Lanier, M.H.; Langmade, S.J.; Molugu, V.; Gale, S.E.; Olzeski, D.; Sidhu, R.; Dietzen, D.J.; Fu, R.; et al. Cholesterol oxidation products are sensitive and specific blood-based biomarkers for Niemann-Pick C1 disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010, 2, 56ra81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maekawa, M.; Misawa, Y.; Sotoura, A.; Yamaguchi, H.; Togawa, M.; Ohno, K.; Nittono, H.; Kakiyama, G.; Iida, T.; Hofmann, A.F.; et al. LC/ESI-MS/MS analysis of urinary 3β-sulfooxy-7β-N-acetylglucosaminyl-5-cholen-24-oic acid and its amides: New biomarkers for the detection of Niemann-Pick type C disease. Steroids 2013, 78, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzacuva, F.; Mills, P.; Mills, K.; Camuzeaux, S.; Gissen, P.; Elena-Raluca, N.; Wassif, C.; Vruchte, D.; Porter, F.D.; Maekawa, M.; et al. Identification of novel bile acids as biomarkers for the early diagnosis of Niemann-Pick C disease. FEBS Lett. 2016, 590, 1651–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welford, R.W.; Garzotti, M.; Lourenço, C.M.; Mengel, E.; Marquardt, T.; Reunart, J.; Amraoui, Y.; Kolb, S.A.; Morand, O.; Groenen, P. Plasma lysosphingomyelin demonstrates great potential as a diagnostic biomarker for Niemann-Pick disease type C in a retrospective study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giese, A.K.; Mascher, H.; Grittner, U.; Eichler, S.; Kramp, G.; Lukas, J.; Vruchte, D.; Eisa, N.; Cortina-Borja, M.; Porter, F.D.; et al. A novel, highly sensitive and specific biomarker for Niemann-Pick type C1 disease. Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 2015, 10, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidhu, R.; Mondjinou, Y.; Qian, M.; Song, H.; Kumar, A.B.; Hong, X.; Hsu, F.F.; Dietzen, D.J.; Yanjanin, N.M.; Porter, F.D.; et al. N-acyl-O-phosphocholineserines: structure of a novel class lipid that are biomarkers for Niemann-Pick C1 disease. J. Lipid Res. 2019, 60, 1410–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higaki, K.; Ninomiya, H.; Sugimoto, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Taniguchi, M.; Niwa, H.; Pentchev, P.G.; Vanier, M.T.; Ohno, K. Isolation of NPC1-deficient Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants by gene trap mutagenesis. J. Biochem. 2001, 129, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, H.; Shimabukuro, Y.; Asakawa, D.; Yamauchi, S.; Sekiya, S.; Iwamoto, S.; Wada, M.; Tanaka, K. Structural analysis of phospholipid using hydrogen abstraction dissociation and oxygen attachment dissociation in tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 7230–7238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Summer, L.W.; Amberg, A.; Barrett, D.; Beale, M.H.; Beger, R.; Daykin, C.A.; Fan, T.W.M.; Fiehn, O.; Goodacre, R.; Griffin, J.L.; et al. Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis. Metabolomics 2007, 3, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Te Vruchte, D.; Speak, A.O.; Wallom, K.L.; Eisa, N.A.; Smith, D.A.; Hendriksz, C.J.; Simmons, L.; Lachmann, R.H.; Cousins, A.; Hartung, R.; et al. Relative acidic compartment volume as a lysosomal storage disorder-associated biomarker. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 1320–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leventis, P.A.; Grinstein, S. The distribution and function of phosphatidylserine in cellular membranes. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2010, 39, 407–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Z.; Li, S.; Smith, D.C.; Shaw, W.A.; Raetz, C.R.H. Identification of N-acylphosphatidylserine molecules in eukaryotic cells. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 14500–14513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, M.; Tsuboi, K.; Okamoto, Y.; Hidaka, M.; Uyama, T.; Tsutsumi, T.; Tanaka, T.; Ueda, N.; Tokumura, A. Peripheral tissue levels and molecular species compositions of N-acyl-phosphatidylethanolamine and its metabolites in mice lacking N-acyl-phosphatidylethanolamine-specific phospholipase D. J. Biochem. 2017, 162, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rooden, E.J.; Van Esbroeck, A.C.M.; Baggelaar, M.P.; Deng, H.; Florea, B.I.; Marques, A.R.A.; Ottenhoff, R.; Boot, R.G.; Overkleeft, H.S.; Aerts, J.M.F.G.; et al. Chemical proteomic analysis of serine hydrolase activity in Niemann-Pick type C mouse brain. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 440. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, P.L. Accumulation of N-acylphosphatidylserines and N-acylserines in the frontal cortex in schizophrenia. Neurotransmitter (Houst) 2014, 1, e263. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arnold, R.S.; Cornell, R.B. Lipid regulation of CTP: phosphocholine cytidyltransferase: electrostatic, hydrophobic, and synergistic interactions of anionic phospholipids and diacylglycerol. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 9917–9924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huitema, K.; van den Dikkenberg, J.; Brouwers, J.F.; Holthuis, J.C. Identification of a family of animal sphingomyelin synthases. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zollinger, M.; Sayer, C.; Dannecker, R.; Schuler, W.; Sedrani, R. The macrolide everolimus forms an unusual metabolite in animals and humans: Identification of a phosphocholine ester. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2008, 36, 1457–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuo, X.; Cantone, J.L.; Wang, Y.; Leet, J.E.; Drexler, D.M.; Yeung, K.S.; Huang, X.S.; Eastman, K.J.; Parcella, K.E.; Mosure, K.W.; et al. Phosphocholine conjugation: An unexpected in vivo conjugation pathway associated with hepatitis C NS5B inhibitors featuring a bicycle[1.1.1]pentane. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2016, 44, 1332–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deodato, F.; Boenzi, S.; Taurisano, R.; Semeraro, M.; Sacchetti, E.; Carrozzo, R.; Dionisi-Vici, G. The impact of biomarkers analysis in the diagnosis of Niemann-Pick C disease and acid sphingomyelinase deficiency. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 486, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorink-Moret, M.; Goorden, S.M.I.; van Kuilenburg, A.B.P.; Wijburg, F.A.; Ghauharali-van der Vlugt, J.M.M.; Beers-Stet, F.S.; Zoetekouw, A.; Kulik, W.; Hollak, C.E.M.; Vaz, F.M. Rapid screening for lipid storage disorders using biochemical markers. Expert center data and review of the literature. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2018, 123, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas, F.; Garcia-Ruiz, C.; Fernandez-Checa, J.C. Intracellular cholesterol trafficking and impact in neurodegeneration. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pol, A.; Gross, S.P.; Parton, R.G. Biogenesis of the multifunctional lipid droplet: Lipids, proteins, and sites. J. Cell. Biol. 2014, 204, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plemel, J.R.; Michaels, N.J.; Weishaupt, N.; Caprariello, A.V.; Keough, M.B.; Rogers, J.A.; Yukseloglu, A.; Lim, J.; Patel, V.V.; Rawji, K.S.; et al. Mechanisms of lysophosphatidylcholine-induced demyelination: A primary lipid disrupting myelinopathy. Glia 2018, 66, 327–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, C.R.; Lu, Y.C.; Jiann, B.P.; Chang, H.T.; Wang, J.L.; Chen, W.C.; Huang, J.K. Novel effect of N-palmitoyl-L-serine phosphoric acid on cytosolic Ca2+ levels in human osteoblasts. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2003, 93, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pentchev, P.G.; Comly, M.E.; Kruth, H.S.; Vanier, M.T.; Wenger, D.A.; Patel, S.; Brady, R.O. A defect in cholesterol esterification in Niemann-Pick disease (type C) patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 8247–8251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreau, J.P.; Dubacq, J.P. Adaptation of a macro-scale method to the micro-scale fatty acid methyl transesterification of biological lipid extracts. J. Chroromatogr. 1978, 151, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, J.S.; Schenk, G.H. Acid-catalyzed acetylation of organic hydroxyl groups. Anal. Chem. 1959, 31, 1808–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, R.; Miyoshi, Y.; Negishi, E.; Kaneko, T.; Mita, M.; Lindner, W.; Hamase, K. Enantioselective two-dimensional high-performance liquid chromatographic determination of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid and its analogues in mammals and bivalves. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1269, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, C.; Akita, T.; Mita, M.; Ide, T.; Hamase, K. Development of an online two-dimensional high-performance liquid chromatographic system in combination with tandem mass spectrometric detection for enantiomeric analysis of free amino acids in human physiological fluid. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1570, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.A.; Chung, H.M.; Park, J.S.; Choi, W.; Min, J.; Park, N.H.; Kim., K.H.; Jhon, G.J.; Han, S.Y. Synthesis of novel lysophosphatidylcholine analogues using serine as chiral template. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 68, 10162–10165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, M.; Rattery, B.; Nuhn, P. Synthesis of enantiomerically pure, sn-1 modified sn-2-deoxy-2-amido-glycero-3-phospholipids. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2000, 107, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bioanalytical Method Validation: Guidance for Industry. Available online: http://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/bioanalytical-method-validation-guidance-industry (accessed on 27 June 2018).

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maekawa, M.; Jinnoh, I.; Matsumoto, Y.; Narita, A.; Mashima, R.; Takahashi, H.; Iwahori, A.; Saigusa, D.; Fujii, K.; Abe, A.; et al. Structural Determination of Lysosphingomyelin-509 and Discovery of Novel Class Lipids from Patients with Niemann–Pick Disease Type C. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5018. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20205018
Maekawa M, Jinnoh I, Matsumoto Y, Narita A, Mashima R, Takahashi H, Iwahori A, Saigusa D, Fujii K, Abe A, et al. Structural Determination of Lysosphingomyelin-509 and Discovery of Novel Class Lipids from Patients with Niemann–Pick Disease Type C. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(20):5018. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20205018
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaekawa, Masamitsu, Isamu Jinnoh, Yotaro Matsumoto, Aya Narita, Ryuichi Mashima, Hidenori Takahashi, Anna Iwahori, Daisuke Saigusa, Kumiko Fujii, Ai Abe, and et al. 2019. "Structural Determination of Lysosphingomyelin-509 and Discovery of Novel Class Lipids from Patients with Niemann–Pick Disease Type C" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 20: 5018. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20205018
APA StyleMaekawa, M., Jinnoh, I., Matsumoto, Y., Narita, A., Mashima, R., Takahashi, H., Iwahori, A., Saigusa, D., Fujii, K., Abe, A., Higaki, K., Yamauchi, S., Ozeki, Y., Shimoda, K., Tomioka, Y., Okuyama, T., Eto, Y., Ohno, K., T Clayton, P., ... Mano, N. (2019). Structural Determination of Lysosphingomyelin-509 and Discovery of Novel Class Lipids from Patients with Niemann–Pick Disease Type C. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(20), 5018. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20205018