Alteration of GABAergic Input Precedes Neurodegeneration of Cerebellar Purkinje Cells of NPC1-Deficient Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
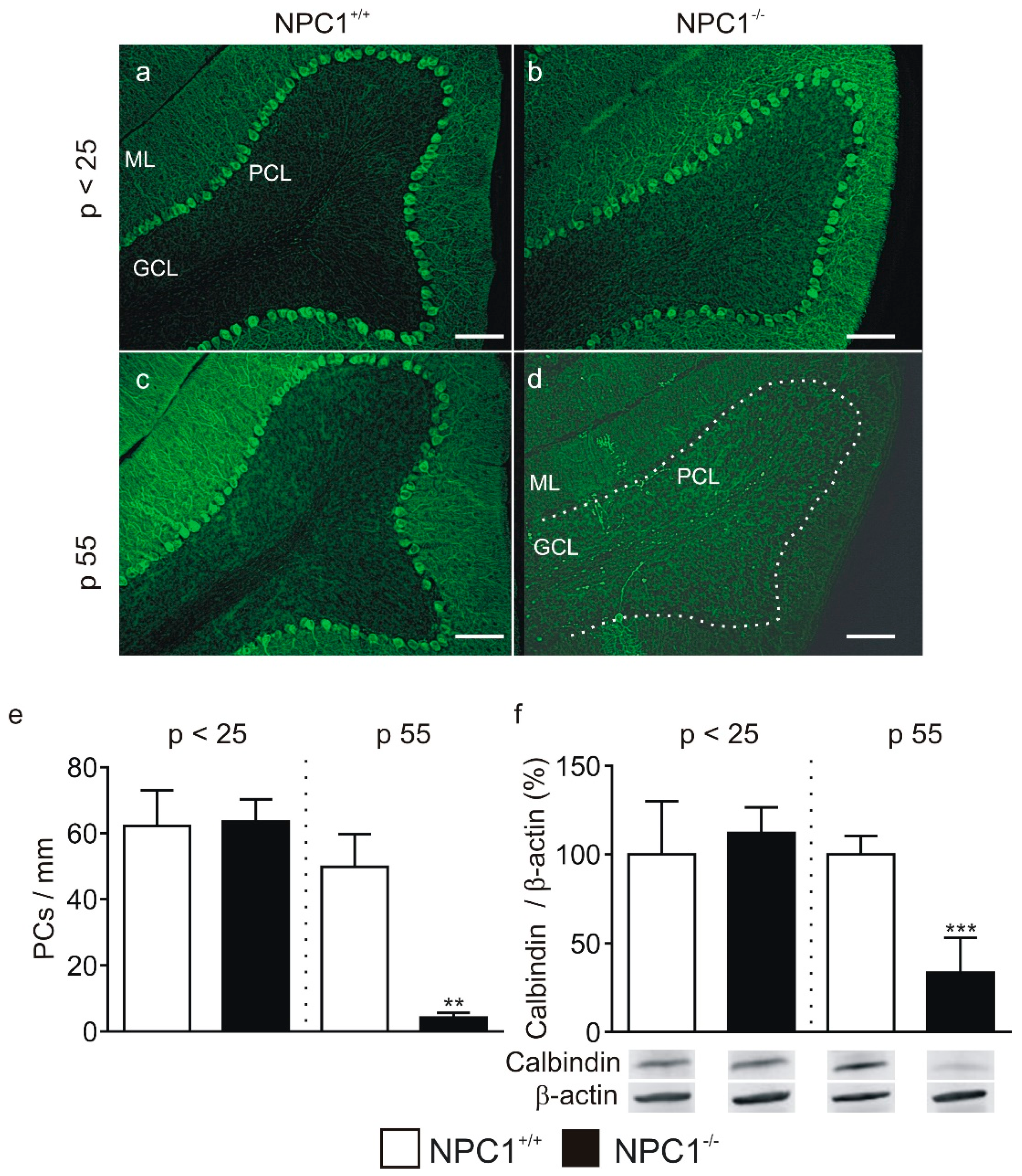
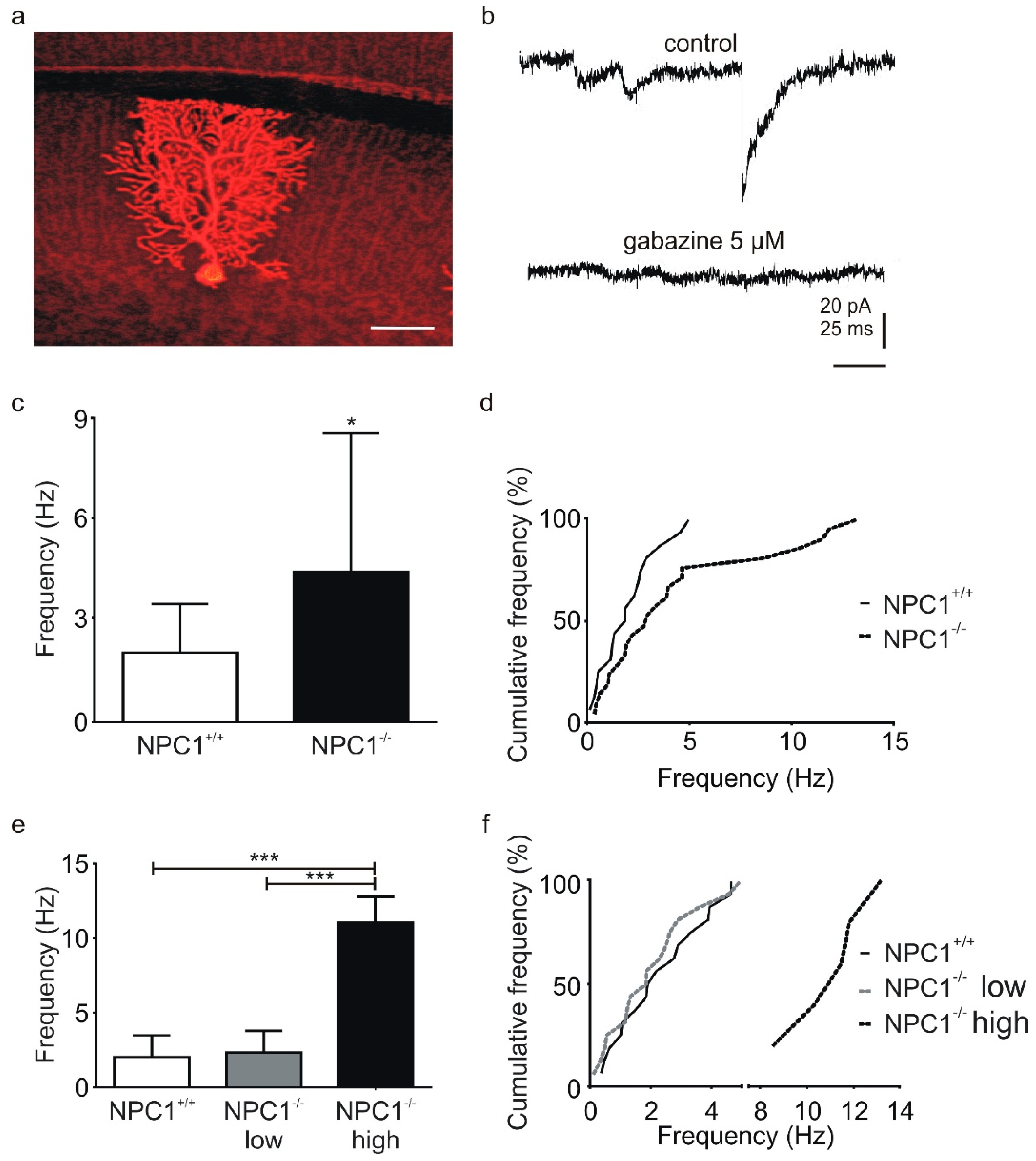
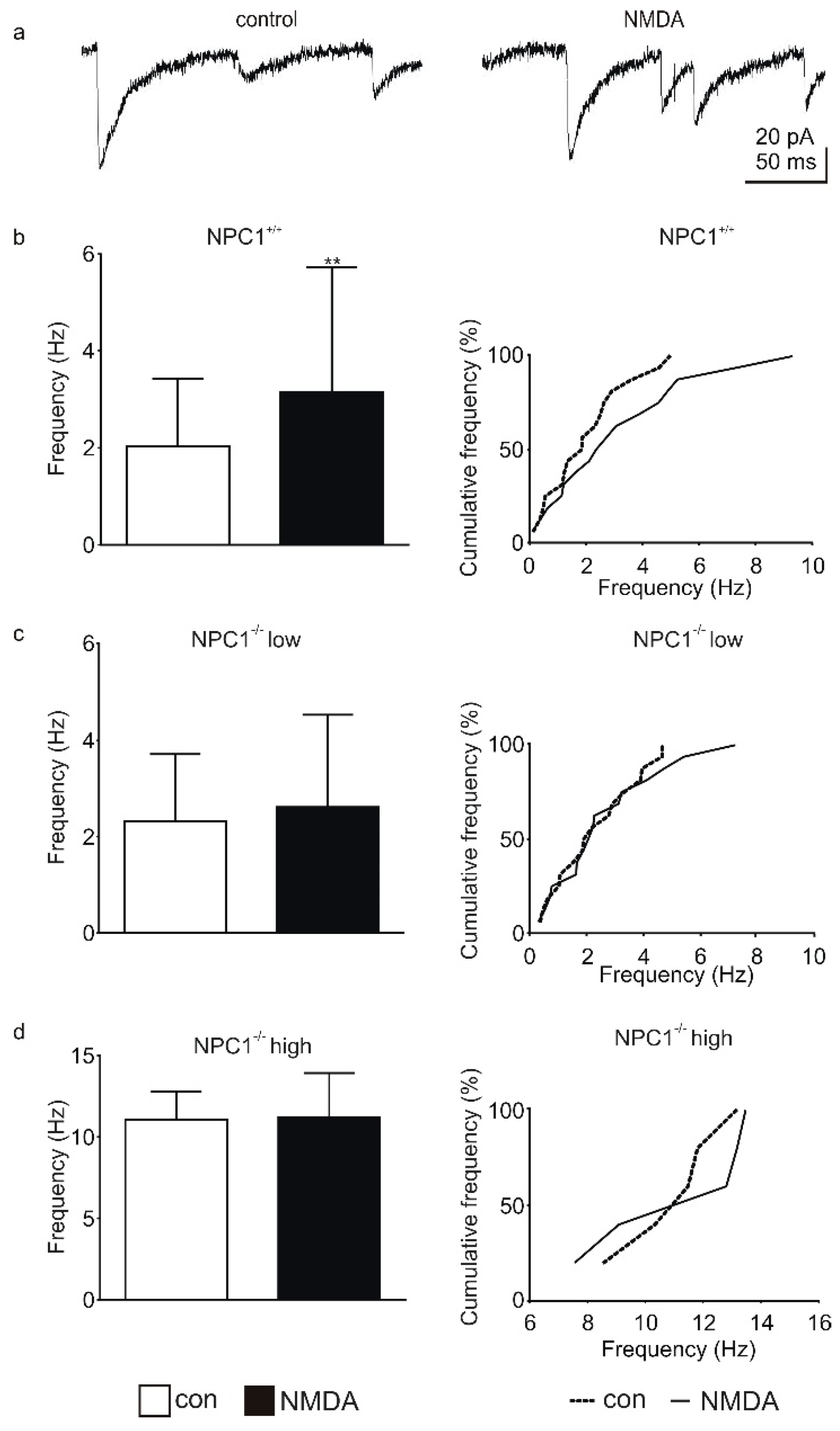
2.1. GABAergic Input to Purkinje Cells Is Altered in NPC1−/− Mice
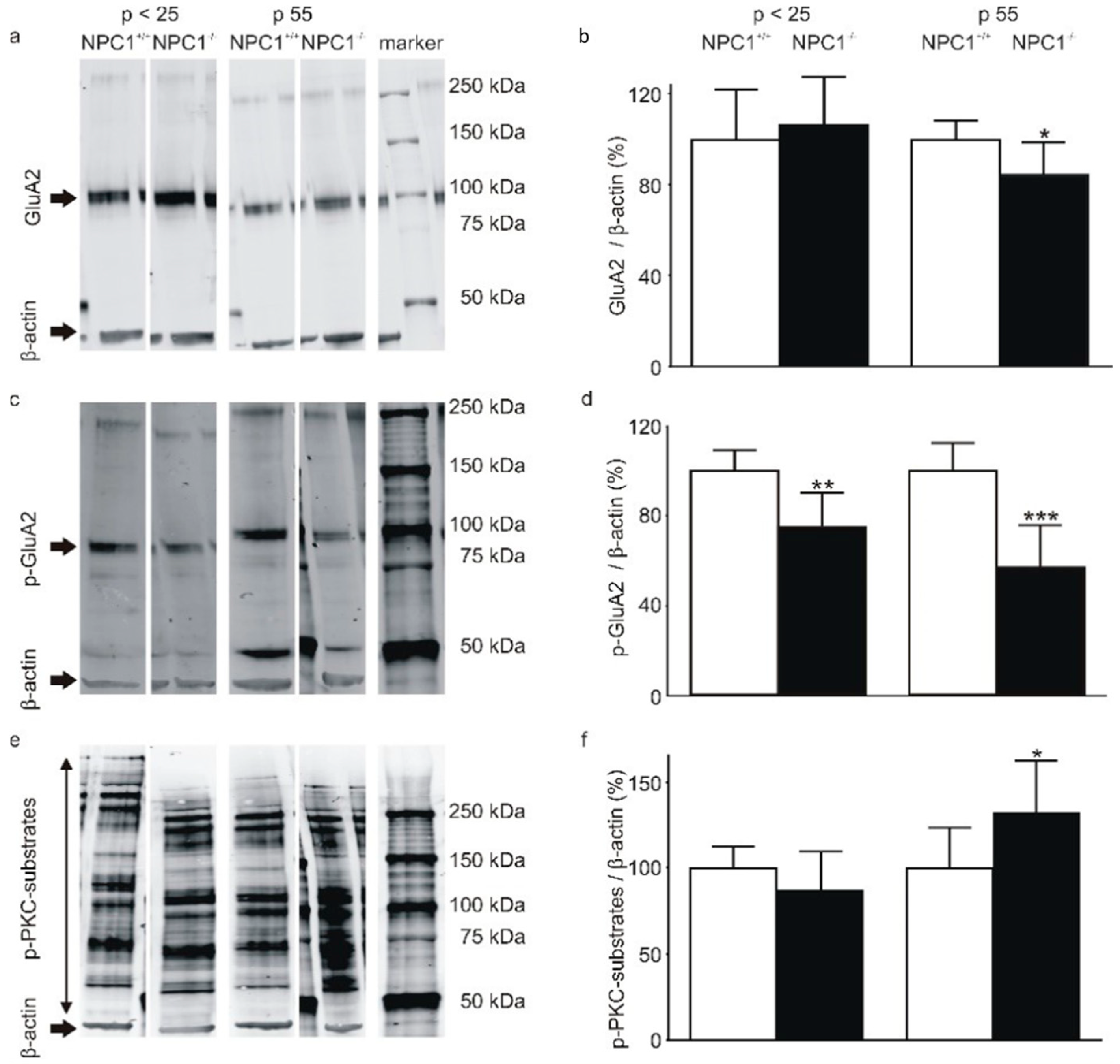
2.2. The AMPA-Receptor Subunit GluA2 Is Hypophosphorylated in the Cerebella of NPC1−/− Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Housing
4.2. Preparation of Cerebellar Slices
4.3. Patch Clamp Recordings
4.4. Sample Preparation for Western Blot Analysis
4.5. Immunocytochemistry
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patterson, M.C.; Clayton, P.; Gissen, P.; Anheim, M.; Bauer, P.; Bonnot, O.; Dardis, A.; Dionisi-Vici, C.; Klünemann, H.-H.; Latour, P.; et al. Recommendations for the detection and diagnosis of Niemann-Pick disease type C. Neurol. Clin. Pract. 2017, 7, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanier, M.T. Niemann-Pick disease type C. Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 2010, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarna, J.R.; Larouche, M.; Marzban, H.; Sillitoe, R.V.; Rancourt, D.E.; Hawkes, R. Patterned Purkinje cell degeneration in mouse models of Niemann-Pick type C disease. J. Comp. Neurol. 2003, 456, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftus, S.K. Murine Model of Niemann-Pick C Disease: Mutation in a Cholesterol Homeostasis Gene. Science 1997, 277, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, M.E.; Klein, A.D.; Scott, M.P. Complement is dispensable for neurodegeneration in Niemann-Pick disease type C. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voikar, V.; Rauvala, H.; Ikonen, E. Cognitive deficit and development of motor impairment in a mouse model of Niemann-Pick type C disease. Behav.Brain Res. 2002, 132, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Repa, J.J.; Valasek, M.A.; Beltroy, E.P.; Turley, S.D.; German, D.C.; Dietschy, J.M. Molecular, Anatomical, and Biochemical Events Associated with Neurodegeneration in Mice with Niemann-Pick Type C Disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2005, 64, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.-L.; Su, L.-D.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.-X.; Shen, Y. Cerebellar long-term depression is deficient in Niemann-Pick type C disease mice. Cerebellum. 2011, 10, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporali, P.; Bruno, F.; Palladino, G.; Dragotto, J.; Petrosini, L.; Mangia, F.; Erickson, R.P.; Canterini, S.; Fiorenza, M.T. Developmental delay in motor skill acquisition in Niemann-Pick C1 mice reveals abnormal cerebellar morphogenesis. Acta. Neuropathol. Commun. 2016, 4, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Yang, F.; Rabenstein, M.; Wang, Z.; Frech, M.J.; Wree, A.; Bräuer, A.U.; Witt, M.; Gläser, A.; Hermann, A.; et al. Stimulation of mGluR1/5 Improves Defective Internalization of AMPA Receptors in NPC1 Mutant Mouse. Cereb. Cortex. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabenstein, M.; Peter, F.; Joost, S.; Trilck, M.; Rolfs, A.; Frech, M.J. Decreased calcium flux in Niemann-Pick type C1 patient-specific iPSC-derived neurons due to higher amount of calcium-impermeable AMPA receptors. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 83, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.J.; Lachamp, P. The activation of excitatory glutamate receptors evokes a long-lasting increase in the release of GABA from cerebellar stellate cells. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 9332–9339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudolph, R.; Jahn, H.M.; Courjaret, R.; Messemer, N.; Kirchhoff, F.; Deitmer, J.W. The inhibitory input to mouse cerebellar Purkinje cells is reciprocally modulated by Bergmann glial P2Y1 and AMPA receptor signaling. Glia. 2016, 64, 1265–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.J.; Zukin, R.S. Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors in synaptic plasticity and neuronal death. Trends Neurosci. 2007, 30, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, P.G.R.; Henley, J.M. AMPA Receptor Cell Biology/Trafficking. In Encyclopedia of Neuroscience; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 295–302. ISBN 9780080450469. [Google Scholar]
- Henley, J.M.; Wilkinson, K.A. Synaptic AMPA receptor composition in development, plasticity and disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2016, 17, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, M.; Chen, F.W.; Tamari, F.; Wang, R.; Ioannou, Y.A. Endosomal lipid accumulation in NPC1 leads to inhibition of PKC, hypophosphorylation of vimentin and Rab9 entrapment. Biol. Cell 2009, 101, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamari, F.; Chen, F.W.; Li, C.; Chaudhari, J.; Ioannou, Y.A. PKC activation in Niemann pick C1 cells restores subcellular cholesterol transport. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, F.; Rost, S.; Rolfs, A.; Frech, M.J. Activation of PKC triggers rescue of NPC1 patient specific iPSC derived glial cells from gliosis. Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 2017, 12, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivas, O.; Tiscione, S.A.; Dixon, R.E.; Ory, D.S.; Dickson, E.J. Niemann-Pick Type C Disease Reveals a Link between Lysosomal Cholesterol and PtdIns(4,5)P2 That Regulates Neuronal Excitability. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 2636–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasser, C.R.; Ertunc, M.; Liu, X.; Kavalali, E.T. Cholesterol-dependent balance between evoked and spontaneous synaptic vesicle recycling. J. Physiol. (Lond) 2007, 579, 413–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitroi, D.N.; Pereyra-Gómez, G.; Soto-Huelin, B.; Senovilla, F.; Kobayashi, T.; Esteban, J.A.; Ledesma, M.D. NPC1 enables cholesterol mobilization during long-term potentiation that can be restored in Niemann-Pick disease type C by CYP46A1 activation. EMBO Rep. 2019, e48143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Arcangelo, G.; Grossi, D.; de Chiara, G.; de Stefano, M.C.; Cortese, G.; Citro, G.; Rufini, S.; Tancredi, V.; Merlo, D.; Frank, C. Glutamatergic neurotransmission in a mouse model of Niemann-Pick type C disease. Brain Res. 2011, 1396, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, N.; Saito, N.; Seki, T. Molecular pathophysiology of neurodegenerative disease caused by γPKC mutations. World J. Biol. Psychiatry. 2011, 12, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabenstein, M.; Peter, F.; Rolfs, A.; Frech, M.J. Impact of Reduced Cerebellar EAAT Expression on Purkinje Cell Firing Pattern of NPC1-deficient Mice. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abcam. Available online: http://www.abcam.com/protocols/ihc-for-brain-slice-sections-video-protocol (accessed on 18 December 2017).
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rabenstein, M.; Murr, N.; Hermann, A.; Rolfs, A.; Frech, M.J. Alteration of GABAergic Input Precedes Neurodegeneration of Cerebellar Purkinje Cells of NPC1-Deficient Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6288. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20246288
Rabenstein M, Murr N, Hermann A, Rolfs A, Frech MJ. Alteration of GABAergic Input Precedes Neurodegeneration of Cerebellar Purkinje Cells of NPC1-Deficient Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(24):6288. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20246288
Chicago/Turabian StyleRabenstein, Michael, Nico Murr, Andreas Hermann, Arndt Rolfs, and Moritz J. Frech. 2019. "Alteration of GABAergic Input Precedes Neurodegeneration of Cerebellar Purkinje Cells of NPC1-Deficient Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 24: 6288. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20246288
APA StyleRabenstein, M., Murr, N., Hermann, A., Rolfs, A., & Frech, M. J. (2019). Alteration of GABAergic Input Precedes Neurodegeneration of Cerebellar Purkinje Cells of NPC1-Deficient Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(24), 6288. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20246288





