Ultrafine Particles from Residential Biomass Combustion: A Review on Experimental Data and Toxicological Response
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Characteristics of UFPs Generated by Residential Biomass Combustion
2.1. Ambient Measurements
2.2. Laboratory Scale Experiments
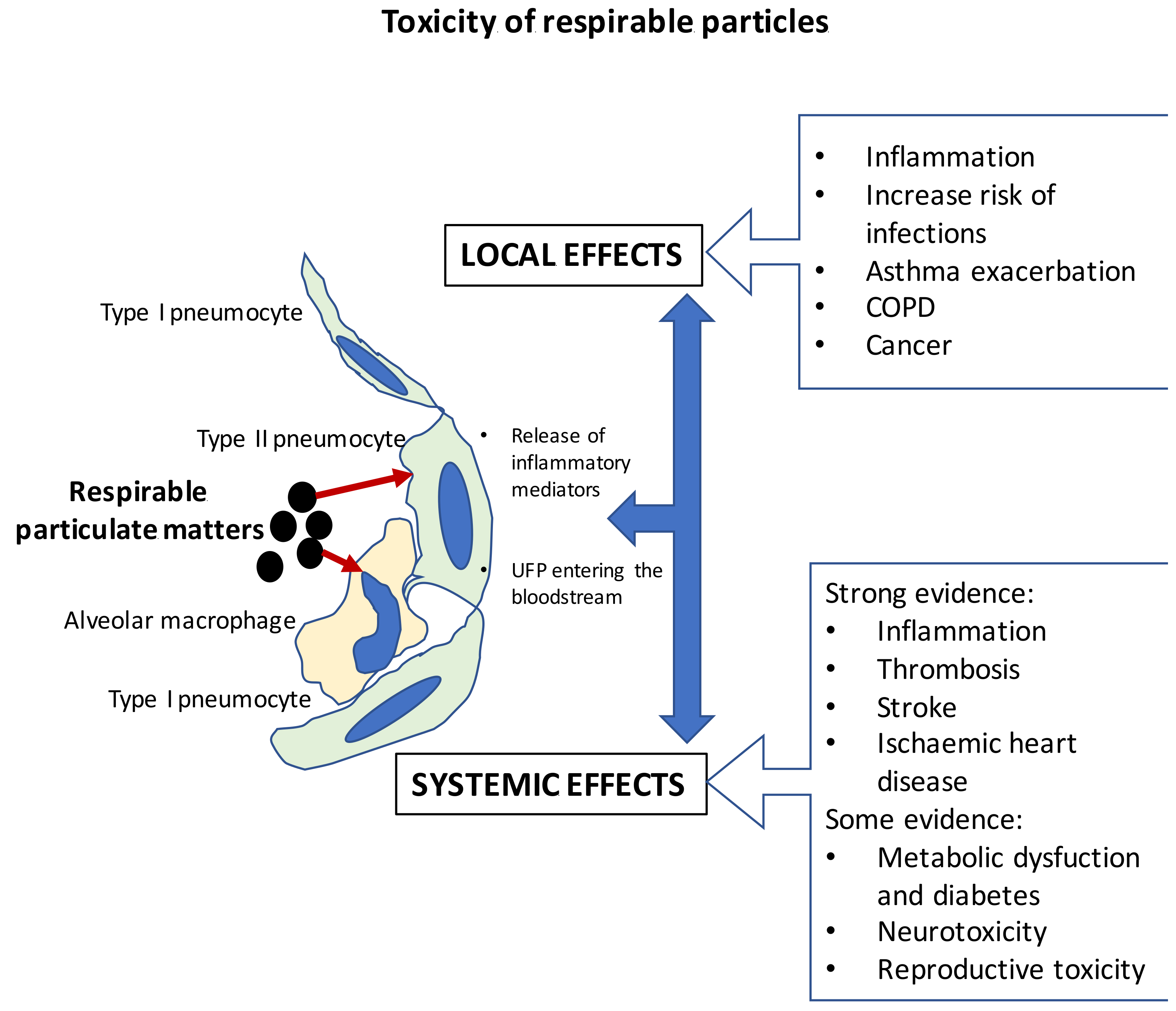
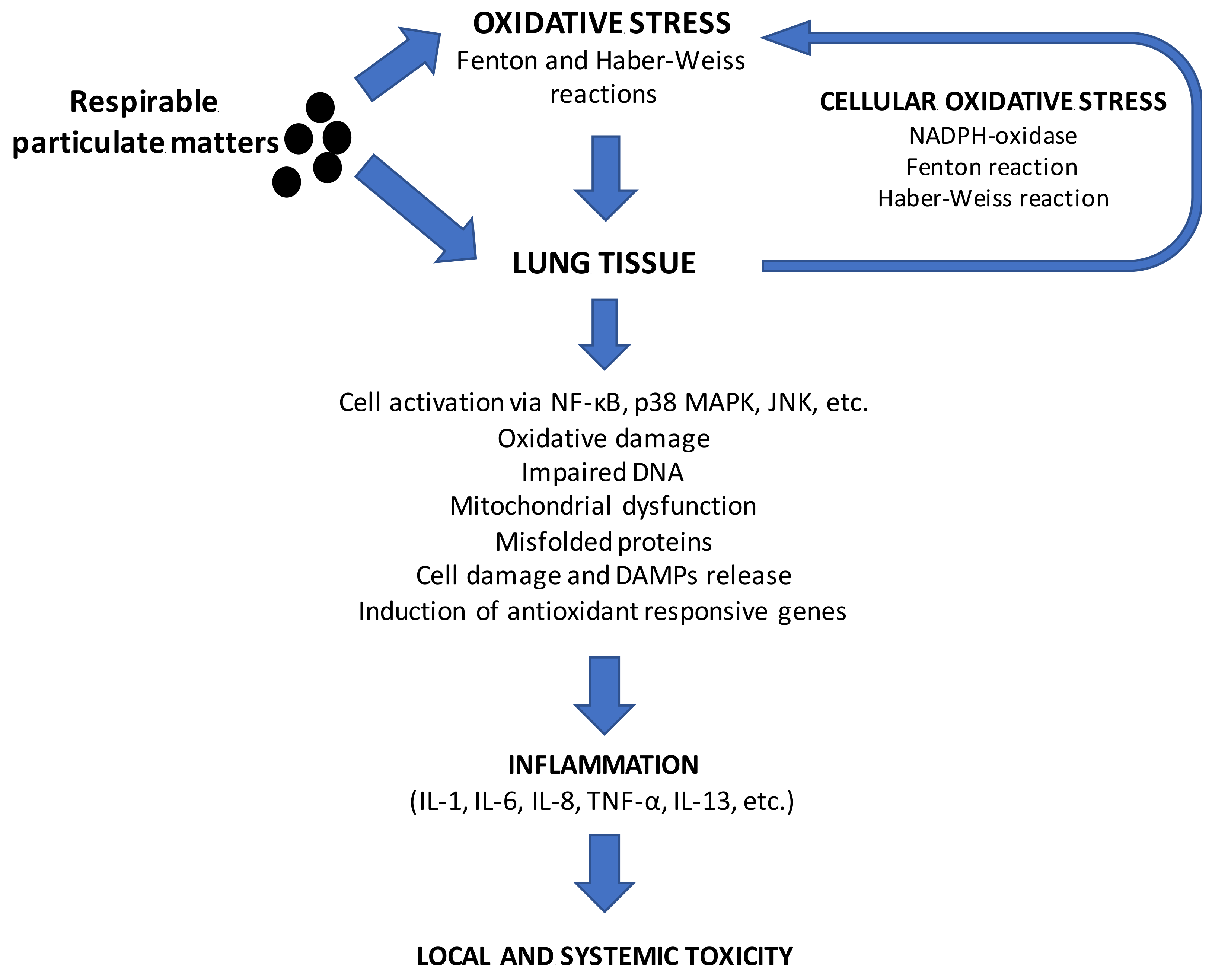
3. Interactions between Particulate Matter Exposure from Biomass and Human Health: In Vivo and In Vitro Effects
Mode of Action
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IL | interleukin |
| PM | particulate matter |
| UFP | ultrafine particles |
References
- Lelieveld, J.; Münzel, T. Air pollution, chronic smoking, and mortality. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 1590–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigsgaard, T.; Forsberg, B.; Annesi-Maesano, I.; Blomberg, A.; Bølling, A.; Boman, C.; Bønløkke, J.; Brauer, M.; Bruce, N.; Héroux, M.E.; et al. Health impacts of anthropogenic biomass burning in the developed world. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 1577–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balmes, J.R. Household air pollution from domestic combustion of solid fuels and health. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 1979–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.R.; Pillarisetti, A. Household Air Pollution from Solid Cookfuels and Its Effects on Health. In Injury Prevention and Environmental Health, 3rd ed.; Mock, C.N., Nugent, R., Kobusingye, O., Smith, K.R., Eds.; The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development/The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; Chapter 7. [Google Scholar]
- Vecchi, R.; Bernardoni, V.; Valentini, S.; Piazzalunga, A.; Fermo, P.; Valli, G. Assessment of light extinction at a European. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 233, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrino, C.; Tofful, L.; Dalla Torre, S.; Sargolini, T.; Canepari, S. Biomass burning contribution to PM10 concentration in Rome (Italy): Seasonal, daily and two-hourly variations. Chemosphere 2019, 222, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muntean, M.; Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Guizzardi, D.; Crippa, M.; Schaaf, E.; Poljanac, M.; Logar, M.; Cristea-Gassler, C. Impact Evaluation of Biomass Used in Small Combustion Activities Sector on Air Emissions: Analyses of Emissions From Alpine, Adriatic-Ionian and Danube Eu Macro-Regions by Using the Edgar Emissions Inventory, EUR 29033 EN; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2017; ISBN 978-92-79-77359-4. JRC109332; Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/jrc/en/publication/impact-evaluation-biomass-used-small-combustion-activities-sector-air-emissions-analyses-emissions (accessed on 10 September 2019). [CrossRef]
- Denier van der Gon, H.A.C.; Bergström, R.; Fountoukis, C.; Johansson, C.; Pandis, S.N.; Simpson, D.; Visschedijk, A.J.H. Particulate emissions from residential wood combustion in Europe –revised estimates and an evaluation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 6503–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amann, M.; Bertok, I.; Cofala, J.; Gyarfas, F.; Zbigniew Klimont, C.-H.; Schöpp, W.; Winiwarter, W. Baseline Scenarios for the Clean Air for Europe (CAFE) Programme; International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis: Laxenburg, Austria, 2005; Available online: http://pure.iiasa.ac.at/id/eprint/7656/ (accessed on 1 August 2019).
- Amann, M. The Final Policy Scenarios of the EU Clean Air Policy Package; International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis: Laxenburg, Austria, 2014; Available online:http://pure.iiasa.ac.at/id/eprint/11153/ (accessed on 1 August 2019).
- Kim, Y.H.; King, C.; Krantz, T.; Hargrove, M.M.; George, I.J.; McGee, J.; Copeland, L.; Hays, M.D.; Landis, M.S.; Higuchi, M.; et al. The role of fuel type and combustion phase on the toxicity of biomass smoke following inhalation exposure in mice. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 1501–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsini, E.; Budello, S.; Marabini, L.; Galbiati, V.; Piazzalunga, A.; Barbieri, P.; Cozzutto, S.; Marinovich, M.; Pitea, D.; Galli, C.L. Comparison of wood smoke PM2.5 obtained from the combustion of FIR and beech pellets on inflammation and DNA damage in A549 and THP-1 human cell lines. Arch. Toxicol. 2013, 87, 2187–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsini, E.; Ozgen, S.; Papale, A.; Galbiati, V.; Lonati, G.; Fermo, P.; Corbella, L.; Valli, G.; Bernardoni, V.; Dell’Acqua, M.; et al. Insights on wood combustion generated proinflammatory ultrafine particles (UFP). Toxicol. Lett. 2017, 15, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.; Joo, H.S.; Lee, K.; Jang, M.; Kim, S.D.; Kim, I.; Borlaza, L.J.S.; Lim, H.; Shin, H.; Chung, K.H.; et al. Differential toxicities of fine particulate matters from various sources. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchetti, S.; Longhin, E.; Bengalli, R.; Avino, P.; Stabile, L.; Buonanno, G.; Colombo, A.; Camatini, M.; Mantecca, P. In vitro lung toxicity of indoor PM10 from a stove fueled with different biomasses. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 1422–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarze, P.E.; Øvrevik, J.; Hetland, R.B.; Becher, R.; Cassee, F.R.; Låg, M.; Løvik, M.; Dybing, E.; Refsnes, M. Importance of size and composition of particles for effects on cells in vitro. Inhal Toxicol. 2007, 19, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualtieri, M.; Grollino, M.G.; Consales, C.; Costabile, F.; Manigrasso, M.; Avino, P.; Aufderheide, M.; Cordelli, E.; Di Liberto, L.; Petralia, E.; et al. Is it the time to study air pollution effects under environmental conditions? A case study to support the shift of in vitro toxicology from the bench to the field. Chemosphere 2018, 207, 552–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sippula, O.; Huttunen, K.; Hokkinen, J.; Kärki, S.; Suhonen, H.; Kajolinna, T.; Kortelainen, M.; Karhunen, T.; Jalava, P.; Uski, O.; et al. Emissions from a fast-pyrolysis bio-oil fired boiler: Comparison of health-related characteristics of emissions from bio-oil, fossil oil and wood. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 888–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naeher, L.P.; Brauer, M.; Lipsett, M.; Zelikoff, J.T.; Simpson, C.D.; Koenig, J.Q.; Smith, K.R. Woodsmoke health effects: A review. Inhal. Toxicol. 2007, 19, 67–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Review of Evidence on Health Aspects of Air Pollution—Revihaap Project Technical Report; WHO Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- DeCarlo, P.F.; Kimmel, J.R.; Trimborn, A.; Northway, M.J.; Jayne, J.T.; Aiken, A.C.; Gonin, M.; Fuhrer, K.; Horvath, T.; Docherty, K.S.; et al. Field-deployable, high-resolution, time-of-flight aerosol mass spectrometer. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 8281–8289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulmala, M.; Petäjä, T.; Ehn, M.; Thornton, J.; Sipilä, M.; Worsnop, D.R.; Kerminen, V.M. Advances on precursor characterization and atmospheric cluster composition in connection with atmospheric New particle formation. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2014, 65, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dall’Osto, M.; Beddows, D.C.S.; Asmi, A.; Poulain, L.; Hao, L.; Freney, E.; Allan, J.D.; Canagaratna, M.; Crippa, M.; Bianchi, F.; et al. Novel insights on new particle formation derived from a pan-european observing system. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manigrasso, M.; Protano, C.; Vitali, M.; Avino, P. Where do ultrafine particles and nano-sized particles come from? J. Alzheimeir’s Dis. 2019, 68, 1371–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, K.; Thomas, W.; Peters, A.; Ries, L.; Obleitner, F.; Schnelle-Kreis, J.; Birmili, W.; Diemer, J.; Fricke, W.; Junkermann, W.; et al. Influences of the 2010 Eyjafjallajökull volcanic plume on air qualityin the northern Alpine region. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 8555–8575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morawska, L.; Ristovski, Z.; Jayaratne, E.R.; Keough, D.U.; Ling, X. Ambient nano and ultrafine particles from motor vehicle emissions: Characteristics, ambient processing and implications on human exposure. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 8113–8138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Morawska, L.; Birmili, W.; Paasonen, P.; Hug, M.; Kulmala, M.; Harrison, R.M.; Norfordj, L.; Britter, R. Ultrafine particles in cities. Environ. Int. 2014, 66, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Pirjola, L.; Ketzel, M.; Harrison, R.M. Nanoparticle emissions from11 non-vehicle exhaust sources – A review. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 67, 252–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacey, B. Measurement of ultrafine particles in airports: A review. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 198, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.M.; Agrawal, H.; Sorooshian, A.; Padró, L.T.; Gates Hersey, S.; Welch, W.A.; Lung, H.; Miller, J.W. Comprehensive simultaneous shipboard and airborne characterization of exhaust from a modern container ship at sea. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 4626–4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. Industrial emissions of nanomaterials and ultrafine particles. Final Report. 2011. Available online: https://publications.europa.eu/en/publication-detail/-/publication/f5002bc6-ddaa-48cb-9033-a9d12574a32e (accessed on 10 September 2019).
- Riffault, V.; Arndt, J.; Marris, H.; Mbengue, S.; Setyan, A.; Alleman, L.Y.; Deboudt, K.; Flament, P.; Augustin, P.; Delbarre, H.; et al. Fine and ultrafine particles in the vicinity of industrial activities: A review. Environ. Sci. Techn. 2015, 45, 2305–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Camacho, R.; Rodriguez, S.; De la Rosa, J.D.; Sanchez de la Campa, A.M.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X.; Gonzalez-Castanedo, Y.; Garcia-Orellana, I.; Nava, S. Ultrafine particle and fine trace metal (As, Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn) pollution episodes induced by industrial emissions in Huelva, SW Spain. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 61, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.M.; Harrison, R.M. Emission of ultrafine particles from the incineration of municipal solid waste: A review. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 140, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonanno, G.; Ficco, G.; Stabile, L. Size distribution and number concentration of particles at the stack of a municipal waste incinerator. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonanno, G.; Stabile, L.; Avino, P.; Belluso, E. Chemical, dimensional and morphological ultrafine particle characterization from a waste-to-energy plant. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 2253–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, P.; Delgado-Saborit, J.M.; Harrison, R.M. A review of chemical and physical characterisation of atmospheric metallic nanoparticles. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 94, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernuschi, S.; Giugliano, M.; Ozgen, S.; Consonni, S. Number concentration and chemical composition of ultrafine and nanoparticles from WTE (waste to energy) plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 420, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morawska, L.; Ayoko, G.A.; Bae, G.N.; Buonanno, G.; Chao, C.Y.H.; Clifford, S.; Fu, S.C.; Hänninen, O.; He, C.; Isaxon, C.; et al. Airborne particles in indoor environment of homes, schools, offices and aged care facilities: The main routes of exposure. Environ. Intern. 2017, 108, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manigrasso, M.; Vitali, M.; Protano, C.; Avino, P. Temporal evolution of ultrafine particles and of alveolar deposited surface area from main indoor combustion and non-combustion sources in a model room. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, J.S.; Koppmann, R.; Eck, T.F.; Eleuterio, D.P. A review of biomass burning emissions part II: Intensive physical properties of biomass burning particles. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 799–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, J.S.; Eck, T.F.; Christopher, S.A.; Koppmann, R.; Dubovik, O.; Eleuterio, D.P.; Holben, B.N.; Reid, E.A.; Zhang, J. A review of biomass burning emissions part III: Intensive optical properties of biomass burning particles. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 827–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinds, W.C. Aerosol Technology: Properties, Behavior, and Measurement of Airborne Particles, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Corsini, E.; Vecchi, R.; Marabini, L.; Fermo, P.; Becagli, S.; Bernardoni, V.; Caruso, D.; Corbella, L.; Dell’Acqua, M.; Galli, C.L.; et al. The chemical composition of ultrafine particles and associated biological effects at an alpine town impacted by wood burning. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 587–588, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Lee, M.L.; Eatough, D.J. Review of recent advances in detection of organic markers in fine particulate matter and their use for source apportionment. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2010, 60, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozgen, S.; Becagli, S.; Bernardoni, V.; Caserini, S.; Caruso, D.; Corbella, L.; Dell’Acqua, M.; Fermo, P.; Gonzalez, R.; Lonati, G.; et al. Analysis of the chemical composition of ultrafine particles from two domestic solid biomass fired room heaters under simulated real-world use. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 150, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, M.; Kuhlbusch, T.A.J.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A.; Harrison, R.M.; Hopke, P.K.; Winiwarter, W.; Vallius, M.; Szidat, S.; Prévôt, A.S.H.; et al. Source apportionment of particulate matter in Europe: A review of methods and results. J. Aerosol Sci. 2008, 39, 827–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belis, C.A.; Favez, O.; Mircea, M.; Diapouli, E.; Manousakas, M.I.; Vratolis, S.; Gilardoni, S.; Paglione, M.; Decesari, S.; Mocnik, G.; et al. European Guide on Air Pollution Source Apportionment with Receptor Models—Revised Version; EUR 29816 EN; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2019; ISBN 978-92-76-09001-4. JRC117306; Available online:https://source-apportionment.jrc.ec.europa.eu/downloads.aspx (accessed on 10 September 2019). [CrossRef]
- Bernardoni, V.; Elser, M.; Valli, G.; Valentini, S.; Bigi, A.; Fermo, P.; Piazzalunga, A.; Vecchi, R. Size-segregated aerosol in a hot-spot pollution urban area: Chemical composition and three-way source apportionment. Environ. Poll. 2017, 231, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulbrich, I.M.; Canagaratna, M.R.; Cubison, M.J.; Zhang, Q.; Ng, N.L.; Aiken, A.C.; Jimenez, J.L. Three-dimensional factorization of size-resolved organic aerosol mass spectra from Mexico City. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 195–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Xue, W.; Sowlat, M.H.; Sioutas, C.; Lolinco, A.; Hasson, A.; Kleeman, M.J. Seasonal and Annual Source Appointment of Carbonaceous Ultrafine Particulate Matter (PM0.1) in Polluted California Cities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwayama, T.; Ruehl, C.R.; Kleeman, M.J. Daily Trends and Source Apportionment of Ultrafine Particulate Mass (PM0.1) over an Annual Cycle in a Typical California City. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 13957–13966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleeman, M.J.; Riddle, S.G.; Robert, M.A.; JAkober, C.A.; Fine, P.M.; Hays, M.D.; Schauer, J.J.; Hannigan, M.P. Source apportionment of fine (PM1.8) and ultrafine (PM0.1) airborne particulate matter during a severe winter pollution episode. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Pitz, M.; Schnelle-Kreis, J.; Diemer, J.; Reller, A.; Zimmermann, R.; Soentgen, J.; Stoelzel, M.; Wichmann, H.-E.; Peters, A.; et al. Source apportionment of ambient particles: Comparison of positive matrix factorization analysis applied to particle size distribution and chemical composition data. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 1849–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krecl, P.; Hedberg Larsson, E.; Ström, J.; Johansson, C. Contribution of residential wood combustion and other sources to hourly winter aerosol in Northern Sweden determined by positive matrix factorization. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 3639–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, L.S.; Leckner, B.; Gustavsson, L.; Cooper, D.; Tullina, C.; Potter, A. Emission characteristics of modern and old-type residential boilers fired with wood logs and wood pellets. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 4183–4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tissari, J.; Lyyranen, J.; Hytonen, K.; Sippula, O.; Tapper, U.; Frey, A.; Saarnio, K.; Pennanen, A.S.; Hillamo, R.; Salonen, R.O.; et al. Fine particle and gaseous emissions from normal and smouldering wood combustion in a conventional masonry heater. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 7862–7873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torvela, T.; Tissari, J.; Sippula, O.; Kaivosoja, T.; Leskinen, J.; Virén, A.; Lähde, A.; Jokiniemi, J. Effect of wood combustion conditions on the morphology of freshly emitted fine particles. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 87, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.S.; Sim, S.Y.; Bae, M.S.; Schauer, J.J. Size distribution of water-soluble components in particulate matter emitted from biomass burning. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 73, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilli, A.; Bengalli, R.; Longhin, E.; Capasso, L.; Proverbio, M.C.; Forcato, M.; Bicciato, S.; Gualtieri, M.; Battaglia, C.; Camatini, M. Transcirptional profiling of human bronchial epithelial cell BEAS-2B exposed to diesel and biomass ultrafine particles. BMC Genomics 2018, 19, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleeman, M.J.; Robert, M.A.; Riddle, S.G.; Fine, P.M.; Hays, M.D.; Schauer, J.J.; Hannigan, M.P. Size distribution of trace organic species emitted from biomass combustion and meat charbroiling. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 3059–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salthammer, T.; Schripp, T.; Wientzek, S.; Wensing, M. Impact of operating wood-burning fireplace ovens on indoor air quality. Chemosphere 2014, 103, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, R.L.; Jensen, O.M.; Afshari, A.; Bergsøe, N.C. Wood-burning stoves in low-carbon dwellings. Energy Build. 2013, 59, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gennaro, G.; Dambruoso, P.R.; Di Gilio, A.; Di Palma, V.; Marzocca, A.; Tutino, M. Discontinuous and Continuous Indoor Air Quality Monitoring in Homes with Fireplaces or Wood Stoves as Heating System. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Household air pollution and health; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland; Available online:https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/household-air-pollution-and-health (accessed on 20 August 2019).
- Wong, G.W.; Brunekreef, B.; Ellwood, P.; Anderson, H.R.; Asher, M.I.; Crane, J.; Lai, C.K. ISAAC Phase Three Study Group. Cooking fuels and prevalence of asthma: A global analysis of phase three of the International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC). Lancet Respir. Med. 2013, 1, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumpter, C.; Chandramohan, D. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the associations between indoor air pollution and tuberculosis. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2013, 18, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, F.J.; Fussell, J.C. Linking ambient particulate matter pollution effects with oxidative biology and immune responses. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2015, 1340, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azike, J.E. A review of the history, epidemiology and treatment of squamous cell carcinoma of the scrotum. Rare Tumors 2009, 1, e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tena, A.F.; Clarà, P.C. Deposition of inhaled particles in the lungs. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2012, 48, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.V.; Ondracek, J.; Zdímal, V.; Schwarz, J.; Delgado-Saborit, J.M.; Harrison, R.M. Physical properties and lung deposition of particles emitted from five major indoor sources. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2017, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linehan, S.A.; Martinez-Pomares, L.; Gordon, S. Mannose receptor and scavenger receptor: Two macrophage pattern recognition receptors with diverse functions in tissue homeostasis and host defense. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2000, 479, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yue, H.; Wei, W.; Yue, Z.; Lv, P.; Wang, L.; Ma, G.; Su, Z. Particle size affects the cellular response in macrophages. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 41, 650–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarieiro Lefol Nani, L.; Guarieiro Lefol Nani, A. Vehicle Emissions: What Will Change with Use of Biofuel? Biofuels—Economy, Environment and Sustainability, Zhen Fang, IntechOpen. Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/books/biofuels-economy-environment-and-sustainability/vehicle-emissions-what-will-change-with-use-of-biofuel- (accessed on 1 August 2019). [CrossRef]
- Kurmi, O.P.; Dunster, C.; Ayres, J.G.; Kelly, F.J. Oxidative potential of smoke from burning wood and mixed biomass fuels. Free Radic. Res. 2013, 47, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrella, B.; Naumova, E.N.; Cepeda, M.; Voortman, T.; Katsikis, P.D.; Drexhage, H.A. Effects of Air Pollution on Lung Innate Lymphoid Cells: Review of In Vitro and In Vivo Experimental Studies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamra, G.B.; Guha, N.; Cohen, A.; Laden, F.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; Samet, J.M.; Vineis, P.; Forastiere, F.; Saldiva, P.; Yorifuji, T.; et al. Outdoor particulate matter exposure and lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 906–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Pan, B.; Wu, J.; Chen, E.; Chen, L. Relationship between exposure to PM2.5 and lung cancer incidence and mortality: A meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 43322–43331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC working group on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans. Household use of solid fuels and high-temperature frying: Evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans. IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum. 2010, 95, 1–430. [Google Scholar]
- Harada, A.; Sekido, N.; Akahoshi, T.; Wada, T.; Mukaida, N.; Matsushima, K. Essential involvement of interleukin-8 (IL-8) in acute inflammation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1994, 56, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.F. Inflammatory mediators in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Curr. Drug Targets Inflamm. Allergy 2005, 4, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marabini, L.; Ozgen, S.; Turacchi, S.; Aminti, S.; Arnaboldi, F.; Lonati, G.; Fermo, P.; Corbella, L.; Valli, G.; Bernardoni, V.; et al. Ultrafine particles (UFPs) from domestic wood stoves: Genotoxicity in human lung carcinoma A549 cells. Mutag. Res. 2017, 820, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henneman, L.R.F.; Choirat, C.; Zigler, A.C.M. Accountability assessment of health improvements in the United States associated with reduced coal emissions between 2005 and 2012. Epidemiology 2019, 30, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Boraschi, D. Endotoxin contamination: A key element in the interpretation of nanosafety studies. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 269–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoda, Y.; Tamura, K.; Shima, M. Airborne endotoxin concentrations in indoor and outdoor particulate matter and their predictors in an urban city. Indoor Air 2017, 27, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, D.; Bruce, N.; Dherani, M.; Jagoe, K.; Rehfuess, E. Real-life effectiveness of ‘improved’ stoves and clean fuels in reducing PM2.5 and CO: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Int. 2017, 101, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Corsini, E.; Marinovich, M.; Vecchi, R. Ultrafine Particles from Residential Biomass Combustion: A Review on Experimental Data and Toxicological Response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4992. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20204992
Corsini E, Marinovich M, Vecchi R. Ultrafine Particles from Residential Biomass Combustion: A Review on Experimental Data and Toxicological Response. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(20):4992. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20204992
Chicago/Turabian StyleCorsini, Emanuela, Marina Marinovich, and Roberta Vecchi. 2019. "Ultrafine Particles from Residential Biomass Combustion: A Review on Experimental Data and Toxicological Response" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 20: 4992. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20204992
APA StyleCorsini, E., Marinovich, M., & Vecchi, R. (2019). Ultrafine Particles from Residential Biomass Combustion: A Review on Experimental Data and Toxicological Response. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(20), 4992. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20204992





