MicroRNA Biogenesis Pathway Genes Are Deregulated in Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. MiRNA Biogenesis Pathway is Significantly Deregulated in Primary Tumor and Metastatic Tissue of CRC
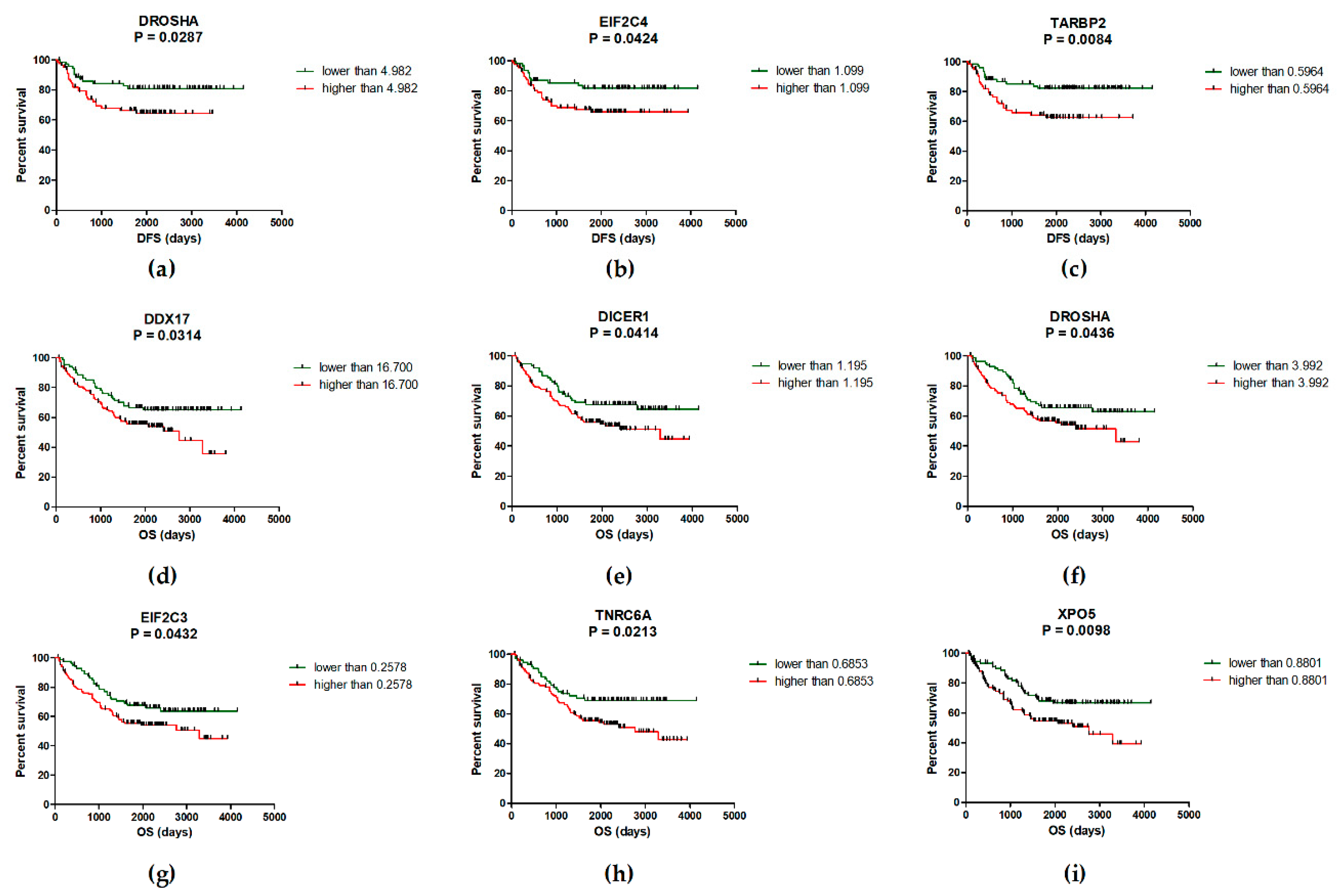
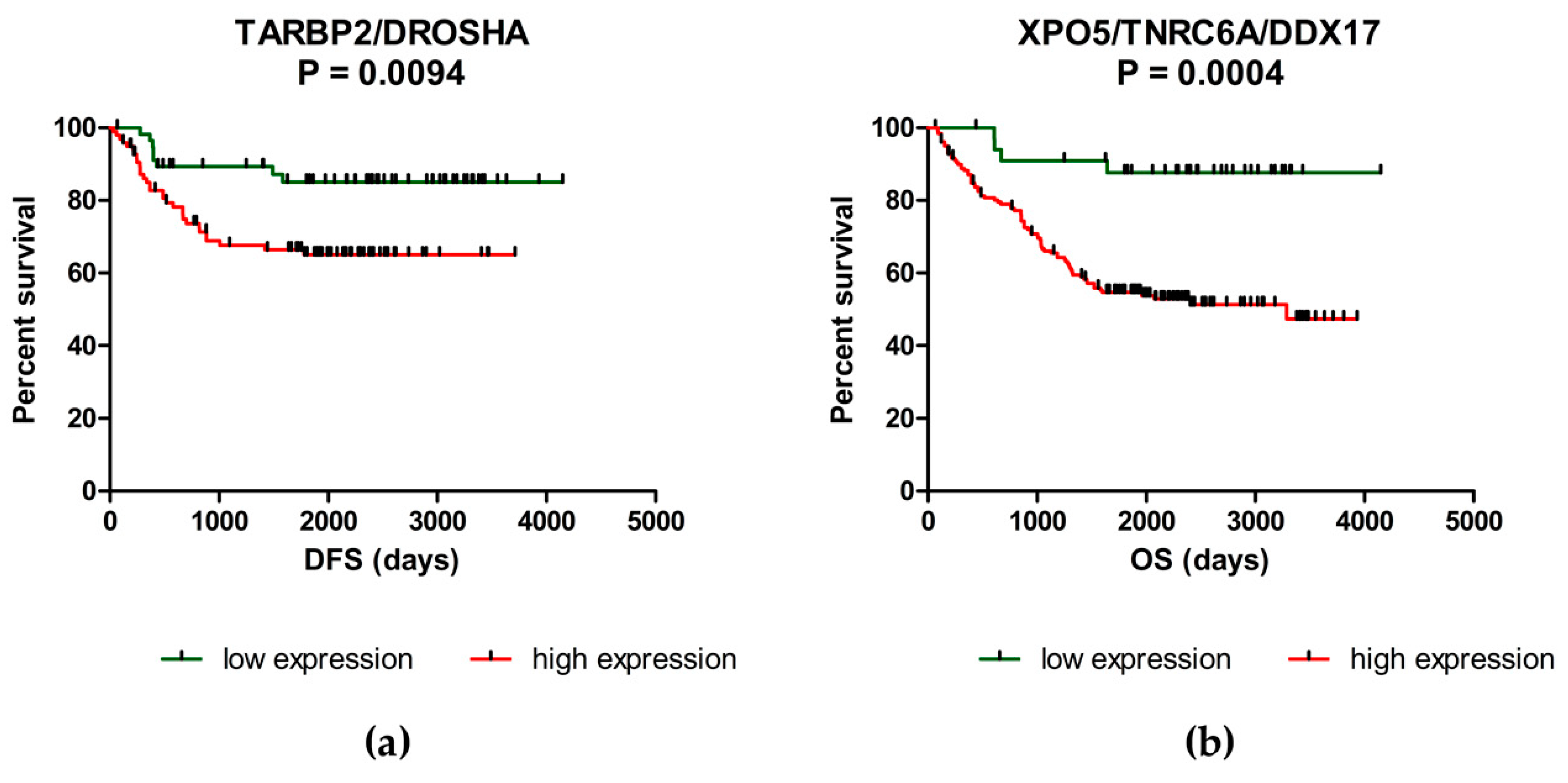
2.2. Deregulation of miRNA Biogenesis Pathway May Influence the Survival of CRC Patients
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients and Tissue Samples
4.2. Tissue Samples Preparation and Total RNA Isolation
4.3. Reverse Transcription and RT-qPCR
4.4. Data Normalization and Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| miRNAs | microRNAs |
| POLR2/3 | RNA polymerase II/III |
| pri-miRNAs | primary microRNAs |
| RNase | ribonuclease |
| DGCR8 | DiGeorge syndrome critical region 8 |
| XPO5 | exportin 5 |
| TARBP2 | TAR RNA binding protein 2 |
| PACT | kinase R-activating protein |
| miRISC | miRNA-induced silencing complex |
| TNRC6 | trinucleotide repeat containing 6 |
| ADAR1/B1 | adenosine deaminase, RNA specific/B1 |
| BRCA1/2 | breast cancer genes 1/2 |
| LIN28A/B | Lin-28 homolog A/B |
| CRC | colorectal cancer |
| OS | overall survival |
| DFS | disease-free survival |
| LNP | lymph node positivity |
| CEA | carcinoembryonic antigen |
| NM | normal mucosa |
| n | number of patients |
| TT | tumor tissue |
| MT | metastatic tissue |
| FC | fold change |
| n. e. | non-expressed |
| n. a. | not applicable |
| NEAT1 | nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1 |
| SD | standard deviation |
| PMM1 | phosphomannomutase 1 |
References
- Lee, R.C.; Feinbaum, R.L.; Ambros, V.; The, C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 1993, 75, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, R.C.; Farh, K.K.-H.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, J.J.; Legesse-Miller, A.; Coller, H.A. A search for conserved sequences in coding regions reveals that the let-7 microRNA targets Dicer within its coding sequence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 14879–14884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytle, J.R.; Yario, T.A.; Steitz, J.A. Target mRNAs are repressed as efficiently by microRNA-binding sites in the 5’ UTR as in the 3’ UTR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 9667–9672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Roosbroeck, K.; Calin, G.A. Cancer Hallmarks and MicroRNAs: The Therapeutic Connection. Adv. Cancer Res. 2017, 135, 119–149. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, A.; Griffiths-Jones, S.; Ashurst, J.L.; Bradley, A. Identification of Mammalian microRNA Host Genes and Transcription Units. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1902–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, M.; Han, J.; Yeom, K.-H.; Lee, S.; Baek, S.H.; Kim, V.N. MicroRNA genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II. Embo J. 2004, 23, 4051–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borchert, G.M.; Lanier, W.; Davidson, B.L. RNA polymerase III transcribes human microRNAs. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2006, 13, 1097–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, R.I.; Yan, K.-P.; Amuthan, G.; Chendrimada, T.; Doratotaj, B.; Cooch, N.; Shiekhattar, R. The Microprocessor complex mediates the genesis of microRNAs. Nature 2004, 432, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fareh, M.; Yeom, K.-H.; Haagsma, A.C.; Chauhan, S.; Heo, I.; Joo, C. TRBP ensures efficient Dicer processing of precursor microRNA in RNA-crowded environments. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Hur, I.; Park, S.-Y.; Kim, Y.-K.; Suh, M.R.; Kim, V.N. The role of PACT in the RNA silencing pathway. Embo J. 2006, 25, 522–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noland, C.L.; Doudna, J.A. Multiple sensors ensure guide strand selection in human RNAi pathways. RNA 2013, 19, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khvorova, A.; Reynolds, A.; Jayasena, S.D. Functional siRNAs and miRNAs exhibit strand bias. Cell 2003, 115, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizarbe, M.A.; Calle-Espinosa, J.; Fernández-Lizarbe, E.; Fernández-Lizarbe, S.; Robles, M.Á; Olmo, N.; Turnay, J. Colorectal Cancer: From the Genetic Model to Posttranscriptional Regulation by Noncoding RNAs. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-S.; Maurin, T.; Robine, N.; Rasmussen, K.D.; Jeffrey, K.L.; Chandwani, R.; Papapetrou, E.P.; Sadelain, M.; O’Carroll, D.; Lai, E.C. Conserved vertebrate mir-451 provides a platform for Dicer-independent, Ago2-mediated microRNA biogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 15163–15168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruby, J.G.; Jan, C.H.; Bartel, D.P. Intronic microRNA precursors that bypass Drosha processing. Nature 2007, 448, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, K.; Lai, E.C. Endogenous small interfering RNAs in animals. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, M.S.; Ono, M. From snoRNA to miRNA: Dual function regulatory non-coding RNAs. Biochimie 2011, 93, 1987–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Song, Y.; Shi, X.; Liu, J.; Xiong, S.; Chen, W.; Fu, Q.; Huang, Z.; Gu, N.; Zhang, R. The landscape of miRNA editing in animals and its impact on miRNA biogenesis and targeting. Genome Res. 2018, 28, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, S.; Amano, A. BRCA1 regulates microRNA biogenesis via the DROSHA microprocessor complex. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 197, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piskounova, E.; Polytarchou, C.; Thornton, J.E.; Hagan, J.P.; LaPierre, R.J.; Pothoulakis, C.; Iliopoulos, D.; Gregory, R.I. Oncogenic Lin28A and Lin28B inhibit let-7 microRNA biogenesis by distinct mechanisms. Cell 2011, 147, 1066–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garibaldi, F.; Falcone, E.; Trisciuoglio, D.; Colombo, T.; Lisek, K.; Walerych, D.; Del Sal, G.; Paci, P.; Bossi, G.; Piaggio, G.; et al. Mutant p53 inhibits miRNA biogenesis by interfering with the microprocessor complex. Oncogene 2016, 35, 3760–3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fearon, E.R. Molecular genetics of colorectal cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2011, 6, 479–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faber, C.; Horst, D.; Hlubek, F.; Kirchner, T. Overexpression of Dicer predicts poor survival in colorectal cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2011, 47, 1414–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Song, M.L.; Min, H.; Hwang, I.; Baek, S.K.; Kwon, T.K.; Park, J.-W. miRNA biogenesis-associated RNase III nucleases Drosha and Dicer are upregulated in colorectal adenocarcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 4379–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papachristou, D.J.; Korpetinou, A.; Giannopoulou, E.; Antonacopoulou, A.G.; Papadaki, H.; Grivas, P.; Scopa, C.D.; Kalofonos, H.P. Expression of the ribonucleases Drosha, Dicer, and Ago2 in colorectal carcinomas. Virchows Arch. 2011, 459, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.-H.; Lin, L.-J.; Hung, L.-Y.; Chen, P.-S. Role of Dicer in regulating oxaliplatin resistance of colon cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 506, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliou, M.S.; da Silva-Diz, V.; Carmona, F.J.; Ramalho-Carvalho, J.; Heyn, H.; Villanueva, A.; Muñoz, P.; Esteller, M. Impaired DICER1 function promotes stemness and metastasis in colon cancer. Oncogene 2014, 33, 4003–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigeyasu, K.; Okugawa, Y.; Toden, S.; Boland, C.R.; Goel, A. Exportin-5 functions as an oncogene and a potential therapeutic target in colorectal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 1312–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullany, L.E.; Herrick, J.S.; Wolff, R.K.; Slattery, M.L. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms within MicroRNAs, MicroRNA Targets, and MicroRNA Biogenesis Genes and Their Impact on Colorectal Cancer Survival. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2017, 56, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramassone, A.; Pagotto, S.; Veronese, A.; Visone, R. Epigenetics and MicroRNAs in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratnadiwakara, M.; Mohenska, M.; Änkö, M.-L. Splicing factors as regulators of miRNA biogenesis—links to human disease. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 79, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Gregory, R.I. MicroRNA biogenesis pathways in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, C.E.; Cuatrecasas, M.; Castells, A.; Sepulveda, A.R.; Lee, J.S.; Rustgi, A.K. LIN28B promotes colon cancer progression and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 4260–4268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Pan, G.; Liu, X.; Huang, J.; Jiang, Z.; Zhu, X.; Gan, X.; Xu, Q.; Tan, N. High expression of ALDOA and DDX5 are associated with poor prognosis in human colorectal cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 1799–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.; Rossow, K.L.; Grande, J.P.; Janknecht, R. Involvement of RNA helicases p68 and p72 in colon cancer. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 7572–7578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Jiang, M.; Han, Y.; Liu, H.; Chu, Y.; Liu, H.; Cao, J.; Hou, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, B.; et al. O-GlcNAcylation promotes colorectal cancer progression by regulating protein stability and potential catcinogenic function of DDX5. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 1354–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Causevic, M.; Hislop, R.G.; Kernohan, N.M.; Carey, F.A.; Kay, R.A.; Steele, R.J.; Fuller-Pace, F.V. Overexpression and poly-ubiquitylation of the DEAD-box RNA helicase p68 in colorectal tumours. Oncogene 2001, 20, 7734–7743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Lee, J.-H.; Park, J.W.; Kwon, T.K.; Baek, S.K.; Hwang, I.; Kim, S. An essential microRNA maturing microprocessor complex component DGCR8 is up-regulated in colorectal carcinomas. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 14, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincenzi, B.; Zoccoli, A.; Schiavon, G.; Iuliani, M.; Pantano, F.; Dell’aquila, E.; Ratta, R.; Muda, A.O.; Perrone, G.; Brunelli, C.; et al. Dicer and Drosha expression and response to Bevacizumab-based therapy in advanced colorectal cancer patients. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 1501–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Yu, C.; Gao, H.; Li, Y. Argonaute proteins: Potential biomarkers for human colon cancer. Bmc Cancer 2010, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-X.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Zhang, B.-F.; Yang, C.-Q.; Gao, H.-J. Study on the clinical significance of Argonaute2 expression in colonic carcinoma by tissue microarray. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2013, 6, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Faggad, A.; Kasajima, A.; Weichert, W.; Stenzinger, A.; Elwali, N.E.; Dietel, M.; Denkert, C. Down-regulation of the microRNA processing enzyme Dicer is a prognostic factor in human colorectal cancer. Histopathology 2012, 61, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Han, P.; He, Y.; Zhao, C.; Wang, G.; Yang, W.; Shan, M.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, C.; Weng, M.; et al. Lin28A enhances chemosensitivity of colon cancer cells to 5-FU by promoting apoptosis in a let-7 independent manner. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 7657–7665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, C.E.; Wang, L.; Winograd, R.; Madison, B.B.; Mongroo, P.S.; Johnstone, C.N.; Rustgi, A.K. LIN28B fosters colon cancer migration, invasion and transformation through let-7-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Oncogene 2011, 30, 4185–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, M.; Wu, G.; Hou, X.; Hou, N.; Liang, L.; Jia, G.; Shuai, P.; Luo, B.; Wang, K.; Li, G. LIN28B promotes colon cancer migration and recurrence. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.H.; Sui, H.M.; Liu, Y.X.; Xiao, Z.Q.; Zheng, P.; Chen, L.; Yao, S.; Xing, C.; et al. A signature for induced pluripotent stem cell-associated genes in colorectal cancer. Med. Oncol. 2013, 30, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Tian, J. LIN28B promotes the progression of colon cancer by increasing B-cell lymphoma 2 expression. Biomed. Pharm. 2018, 103, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michlewski, G.; Cáceres, J.F. Post-transcriptional control of miRNA biogenesis. RNA 2019, 25, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Weng, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Ni, S.; Tan, C.; Xu, M.; Sun, H.; Liu, C.; Wei, P.; et al. The lncRNA NEAT1 activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling and promotes colorectal cancer progression via interacting with DDX5. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pong, S.K.; Gullerova, M. Noncanonical functions of microRNA pathway enzymes – Drosha, DGCR8, Dicer and Ago proteins. Febs Lett. 2018, 592, 2973–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.; Khan, Z.; Uddin, Y.; Mustafa, S.; Shaukat, I.; Pan, J.; Höti, N. Evaluating the Oncogenic and Tumor Suppressor Role of XPO5 in Different Tissue Tumor Types. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2018, 19, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Swahari, V.; Nakamura, A.; Deshmukh, M. The paradox of dicer in cancer. Mol Cell Oncol 2016, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Li, W.-F.; Wu, X.; Zhang, H.-C.; Chen, L.; Zhang, P.-Y.; Liu, L.-Y.; Ma, D.; Chen, T.; Zhou, L.; et al. Dicer regulates non-homologous end joining and is associated with chemosensitivity in colon cancer patients. Carcinogenesis 2017, 38, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.J.; Yang, D.D.; Na, S.; Sandusky, G.E.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, G. Dicer Is Required for Embryonic Angiogenesis during Mouse Development. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 9330–9335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuehbacher, A.; Urbich, C.; Zeiher, A.M.; Dimmeler, S. Role of Dicer and Drosha for Endothelial MicroRNA Expression and Angiogenesis. Circ. Res. 2007, 101, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Getz, G.; Miska, E.A.; Alvarez-Saavedra, E.; Lamb, J.; Peck, D.; Sweet-Cordero, A.; Ebert, B.L.; Mak, R.H.; Ferrando, A.A.; et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 2005, 435, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.; Cheng, Y.Y.; Blenkiron, C.; Reid, G. Exploring Mechanisms of MicroRNA Downregulation in Cancer. MicroRNA 2017, 6, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volinia, S.; Calin, G.A.; Liu, C.-G.; Ambs, S.; Cimmino, A.; Petrocca, F.; Visone, R.; Iorio, M.; Roldo, C.; Ferracin, M.; et al. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2257–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Israel, A.; Sharan, R.; Ruppin, E.; Galun, E. Increased MicroRNA Activity in Human Cancers. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.-S.; Rossi, J.J. Molecular mechanisms of Dicer: Endonuclease and enzymatic activity. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 1603–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berdiel-Acer, M.; Berenguer, A.; Sanz-Pamplona, R.; Cuadras, D.; Sanjuan, X.; Paules, M.J.; Santos, C.; Salazar, R.; Moreno, V.; Capella, G.; et al. A 5-gene classifier from the carcinoma-associated fibroblast transcriptomic profile and clinical outcome in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 6437–6452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vychytilova-Faltejskova, P.; Merhautova, J.; Machackova, T.; Gutierrez-Garcia, I.; Garcia-Solano, J.; Radova, L.; Brchnelova, D.; Slaba, K.; Svoboda, M.; Halamkova, J.; et al. MiR-215-5p is a tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer targeting EGFR ligand epiregulin and its transcriptional inducer HOXB9. Oncogenesis 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | NM # (n = 239) | TT # (n = 239) | MT # (n = 17) | FC (NM vs. TT) p-value (n = 239) | FC (NM vs. MT) p-value (n = 17) | Stage p-value | Grade p-value | Location p-value | Size p-value | LNP p-value | CEA p-value | CA19-9 p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADAR | 2.37 (1.43–6.78) | 6.72 (3.31–18.97) | 4.06 (1.64–5.65) | 2.84 p < 0.0001 | 2.03 p = 0.2763 | p = 0.2652 | p = 0.3613 | p = 0.0060 | p = 0.0004 | p = 0.0900 | p = 0.1515 | p = 0.9743 |
| ADARB1 | 0.15 (0.06–0.45) | 0.27 (0.12–0.78) | 0.32 (0.23–0.43) | 1.80 p < 0.0001 | 2.29 p = 0.0884 | p = 0.4729 | p = 0.1934 | p = 0.0967 | p = 0.0118 | p = 0.2357 | p = 0.2186 | p = 0.5291 |
| DDX5 | 10.37 (5.86–19.84) | 18.98 (11.35–37.92) | 15.82 (10.03–27.11) | 1.83 p < 0.0001 | 1.52 p = 0.0294 | p = 0.8801 | p = 0.1473 | p = 0.0929 | p = 0.0075 | p = 0.4623 | p = 0.1383 | p = 0.2262 |
| DDX17 | 16.66 (7.85–55.75) | 20.75 (11.78–75.89) | 16.61 (10.99–23.14) | 1.25 p < 0.0001 | 1.13 p = 0.2977 | p = 0.3977 | p = 0.1484 | p = 0.0619 | p = 0.0018 | p = 0.2857 | p = 0.4826 | p = 0.9357 |
| DDX20 | 0.53 (0.30–1.27) | 1.58 (0.87–4.61) | 1.79 (1.38–2.26) | 2.98 p < 0.0001 | 2.95 p = 0.0092 | p = 0.3402 | p = 0.0021 | p = 0.0520 | p = 0.0001 | p = 0.5983 | p = 0.2669 | p = 0.1066 |
| DGCR8 | 0.70 (0.42–1.28) | 1.45 (0.83–2.75) | 1.89 (1.38–2.24) | 2.07 p < 0.0001 | 2.35 p = 0.0261 | p = 0.9808 | p = 0.0077 | p = 0.0900 | p = 0.0086 | p = 0.1624 | p = 0.5286 | p = 0.2024 |
| DICER1 | 1.09 (0.61–1.94) | 1.70 (0.93–3.01) | 2.73 (1.83–3.17) | 1.56 p < 0.0001 | 2.34 p = 0.0080 | p = 0.1826 | p = 0.0177 | p = 0.1101 | p = 0.0080 | p = 0.0075 | p = 0.4460 | p = 0.6283 |
| DROSHA | 2.39 (1.27–4.19) | 4.95 (2.65–9.59) | 6.33 (4.86–10.01) | 2.07 p < 0.0001 | 2.65 p = 0.0033 | p = 0.7477 | p = 0.0309 | p = 0.0212 | p = 0.0078 | p = 0.1891 | p = 0.7143 | p = 0.2388 |
| EIF2C1 | 0.63 (0.37–1.06) | 1.26 (0.64–2.05) | 1.72 (1.24–2.14) | 2.00 p < 0.0001 | 2.95 p = 0.0021 | p = 0.2571 | p = 0.0059 | p = 0.0484 | p = 0.0008 | p = 0.6534 | p = 0.1351 | p = 0.3017 |
| EIF2C2 | 1.07 (0.68–1.95) | 3.75 (2.57–7.33) | 2.71 (2.06–4.56) | 3.50 p < 0.0001 | 2.46 p = 0.0179 | p = 0.7145 | p < 0.0001 | p = 0.3883 | p = 0.0422 | p = 0.1497 | p = 0.7964 | p = 0.6398 |
| EIF2C3 | 0.13 (0.06–0.27) | 0.31 (0.16–0.63) | 0.50 (0.34–0.74) | 2.38 p < 0.0001 | 3.58 p = 0.0004 | p = 0.0018 | p = 0.0928 | p = 0.4038 | p = 0.0015 | p = 0.1236 | p = 0.1549 | p = 0.6630 |
| EIF2C4 | 0.74 (0.45–1.38) | 1.31 (0.74–2.37) | 3.11 (2.44–3.92) | 1.77 p < 0.0001 | 3.12 p = 0.0004 | p = 0.8931 | p = 0.0661 | p = 0.0097 | p = 0.0153 | p = 0.9047 | p = 0.4678 | p = 0.3493 |
| GEMIN4 | 0.17 (0.10–0.29) | 0.63 (0.32–1.36) | 0.71 (0.47–1.03) | 3.71 p < 0.0001 | 2.47 p = 0.0045 | p = 0.2558 | p = 0.0058 | p = 0.0656 | p = 0.0031 | p = 0.2672 | p = 0.9761 | p = 0.7838 |
| LIN28A | 0.59 (0.09–2.38) | 0.22 (0.02–1.11) | 2.95 (1.30–5.40) | 0.37 p < 0.0001 | 2.92 p = 0.8498 | p = 0.0215 | p = 0.0140 | p = 0.0568 | p = 0.8374 | p = 0.0186 | p = 0.9569 | p = 0.8718 |
| POLR2A | 1.62 (0.95–3.05) | 2.54 (1.31–4.89) | 1.47 (1.20–1.76) | 1.57 p < 0.0001 | 1.37 p = 0.8498 | p = 0.5469 | p = 0.4252 | p = 0.0642 | p = 0.0201 | p = 0.2857 | p = 0.9378 | p = 0.2024 |
| TARBP2 | 0.20 (0.12–0.39) | 0.59 (0.35–1.18) | 0.34 (0.29–0.47) | 2.95 p < 0.0001 | 2.37 p = 0.2763 | p = 0.3238 | p = 0.0036 | p = 0.0324 | p = 0.0044 | p = 0.1779 | p = 0.5850 | p = 0.5504 |
| TNRC6A | 0.70 (0.39–1.45) | 1.08 (0.49–2.15) | 1.78 (1.16–3.47) | 1.54 p < 0.0001 | 1.81 p = 0.0138 | p = 0.2170 | p = 0.0021 | p = 0.0885 | p = 0.0736 | p = 0.0526 | p = 0.3585 | p = 0.8718 |
| XPO5 | 0.23 (0.12–0.42) | 1.17 (0.59–2.41) | 1.33 (1.07–2.27) | 5.09 p < 0.0001 | 7.82 p = 0.0003 | p = 0.5897 | p = 0.0183 | p = 0.8636 | p = 0.0002 | p = 0.8314 | p = 0.3712 | p = 0.3017 |
| Gene Combination | Condition | Median DFS | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| EIF2C4/TARBP2/DROSHA # | High level of 1-3 genes Low level of all three genes | 58.3 months 78.5 months | 0.0209 |
| EIF2C4/TARBP2 | High level of one/both genes Low level of one/both genes | 58.3 months 78.5 months | 0.0343 |
| EIF2C4/DROSHA | High level of one/both genes Low level of one/both genes | 57.5 months 78.5 months | 0.0224 |
| TARBP2/DROSHA | High level of one/both genes Low level of one/both genes | 57.5 months 77.7 months | 0.0094 |
| Gene Combination | Condition | Median OS | p-Value |
| XPO5/TNRC6A/DDX17/ DICER1/EIF2C3/DROSHA * | High level of 3–6 genes Low level of 4–6 genes | 51.5 months 73.6 months | 0.0020 |
| XPO5/TNRC6A | High level of one/both genes Low level of one/both genes | 52.3 months 71.1 months | 0.0024 |
| XPO5/TNRC6A/DDX17 | High level of 1–3 genes Low level of all three genes | 52.1 months 78.9 months | 0.0004 |
| Characteristics | Number of Patients (n) |
|---|---|
| Number | n = 239 |
| Age (mean ± SD) *, years | 75 ± 11 |
| Sex, number (%) | |
| Male | 131 (55) |
| Female | 108 (45) |
| TNM stage, number (%) | |
| Stage I | 41 (17) |
| Stage II | 77 (32) |
| Stage III | 55 (23) |
| Stage IV | 66 (28) |
| Grade, number (%) | |
| Grade 1 | 64 (27) |
| Grade 2 | 119 (50) |
| Grade 3 | 52 (22) |
| Unknown | 4 (1) |
| Location, number (%) | |
| Distal | 142 (59) |
| Proximal | 96 (40) |
| Unknown | 1 (1) |
| Tumor size, number (%) | |
| < 50 mm | 157 (66) |
| ≥ 50 mm | 54 (23) |
| Unknown | 28 (11) |
| Pre-CEA levels †, number (%) | |
| < 5 ng · mL −1 | 70 (29) |
| ≥ 5 ng · mL −1 | 68 (29) |
| Unknown | 101 (42) |
| Pre-CA19-9 levels ‡, number (%) | |
| < 27 U · mL −1 | 110 (46) |
| ≥ 27 U · mL −1 | 28 (12) |
| Unknown | 101 (42) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vychytilova-Faltejskova, P.; Svobodova Kovarikova, A.; Grolich, T.; Prochazka, V.; Slaba, K.; Machackova, T.; Halamkova, J.; Svoboda, M.; Kala, Z.; Kiss, I.; et al. MicroRNA Biogenesis Pathway Genes Are Deregulated in Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4460. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20184460
Vychytilova-Faltejskova P, Svobodova Kovarikova A, Grolich T, Prochazka V, Slaba K, Machackova T, Halamkova J, Svoboda M, Kala Z, Kiss I, et al. MicroRNA Biogenesis Pathway Genes Are Deregulated in Colorectal Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(18):4460. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20184460
Chicago/Turabian StyleVychytilova-Faltejskova, Petra, Alena Svobodova Kovarikova, Tomas Grolich, Vladimir Prochazka, Katerina Slaba, Tana Machackova, Jana Halamkova, Marek Svoboda, Zdenek Kala, Igor Kiss, and et al. 2019. "MicroRNA Biogenesis Pathway Genes Are Deregulated in Colorectal Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 18: 4460. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20184460
APA StyleVychytilova-Faltejskova, P., Svobodova Kovarikova, A., Grolich, T., Prochazka, V., Slaba, K., Machackova, T., Halamkova, J., Svoboda, M., Kala, Z., Kiss, I., & Slaby, O. (2019). MicroRNA Biogenesis Pathway Genes Are Deregulated in Colorectal Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(18), 4460. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20184460






