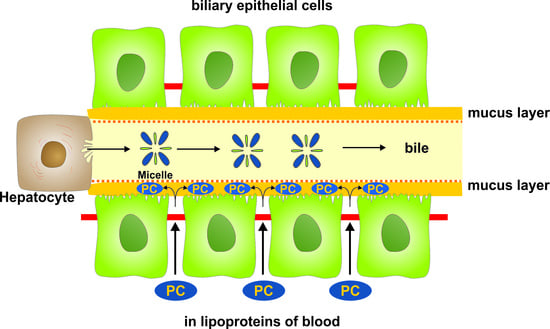
Phosphatidylcholine Passes by Paracellular Transport to the Apical Side of the Polarized Biliary Tumor Cell Line Mz-ChA-1
Abstract
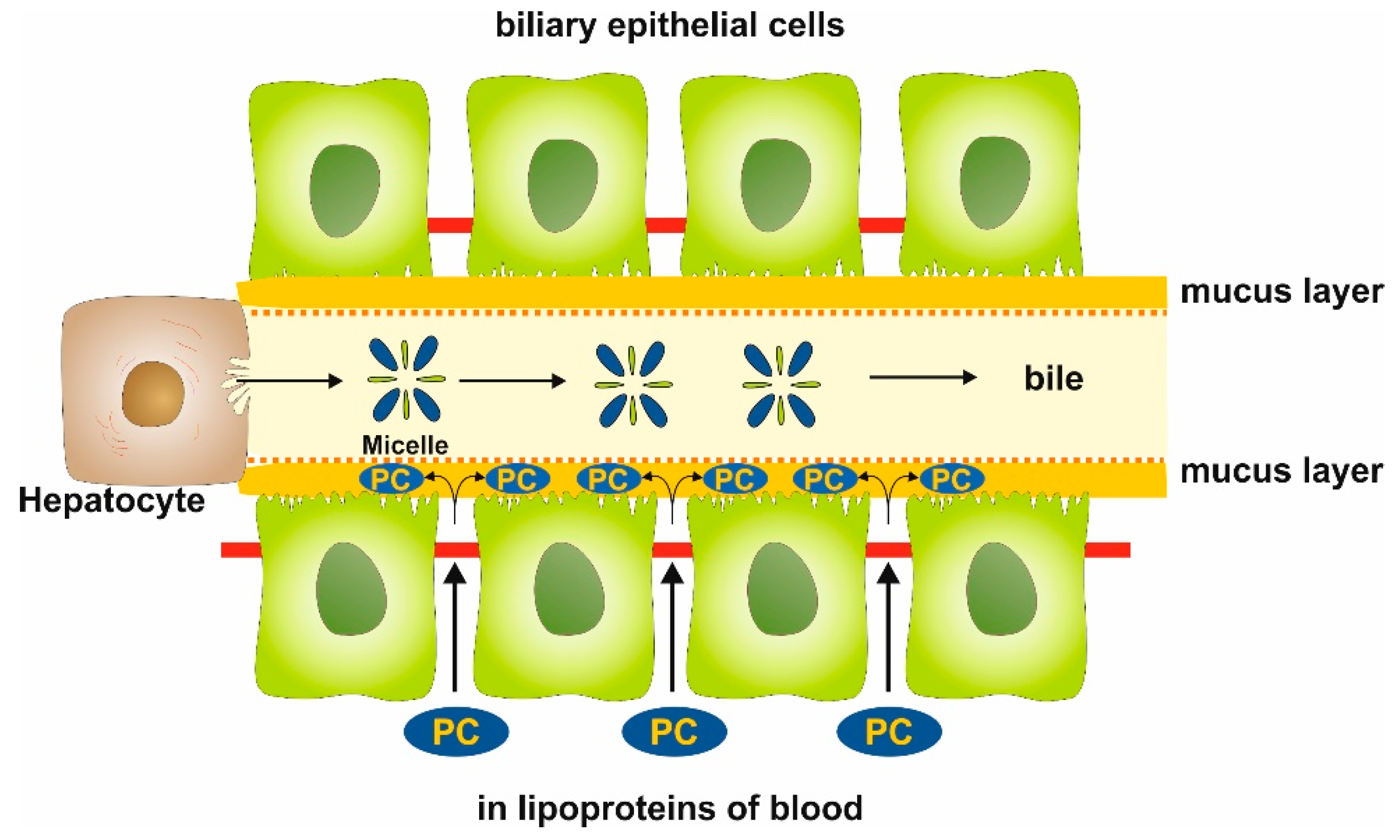
1. Introduction
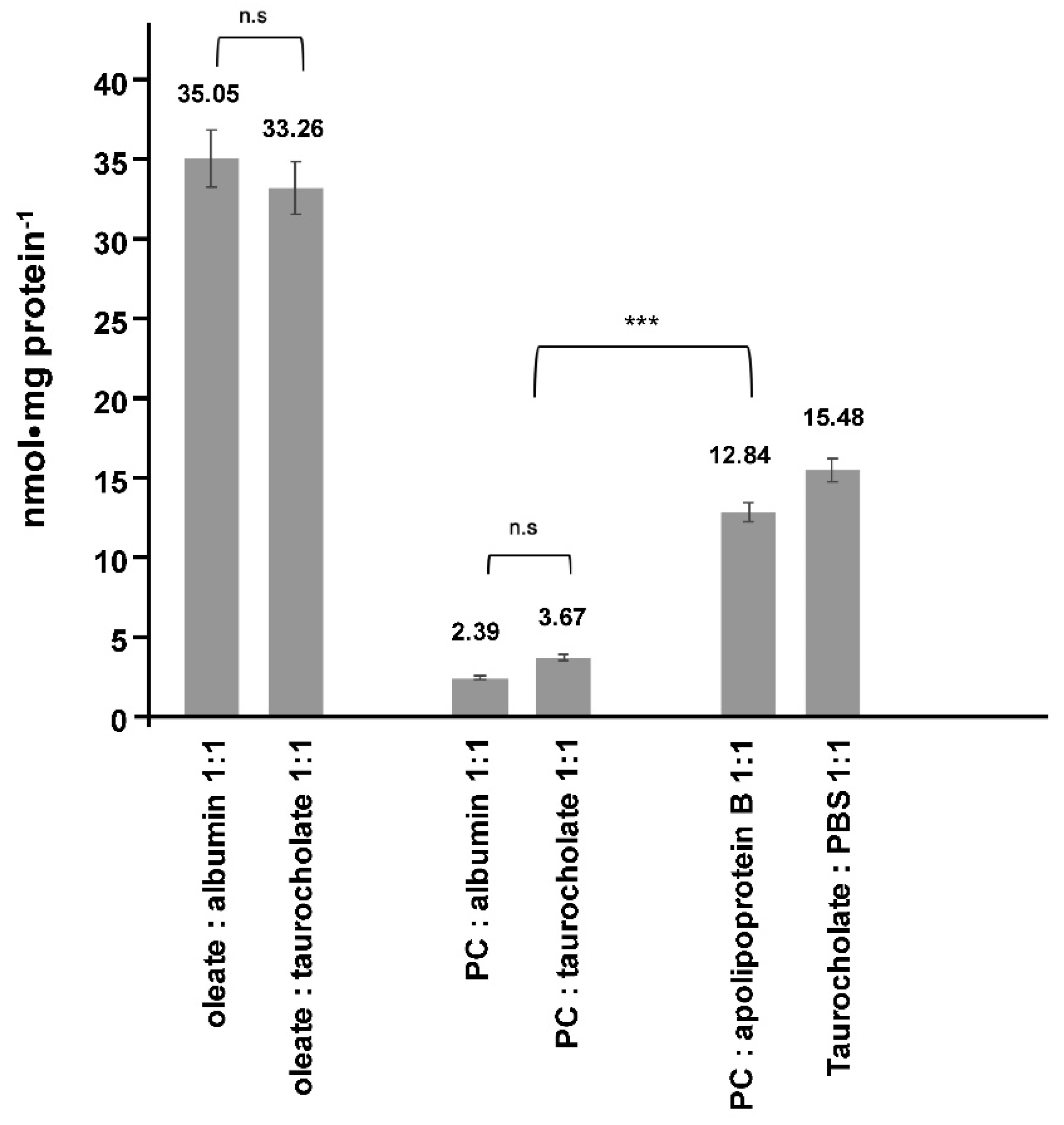
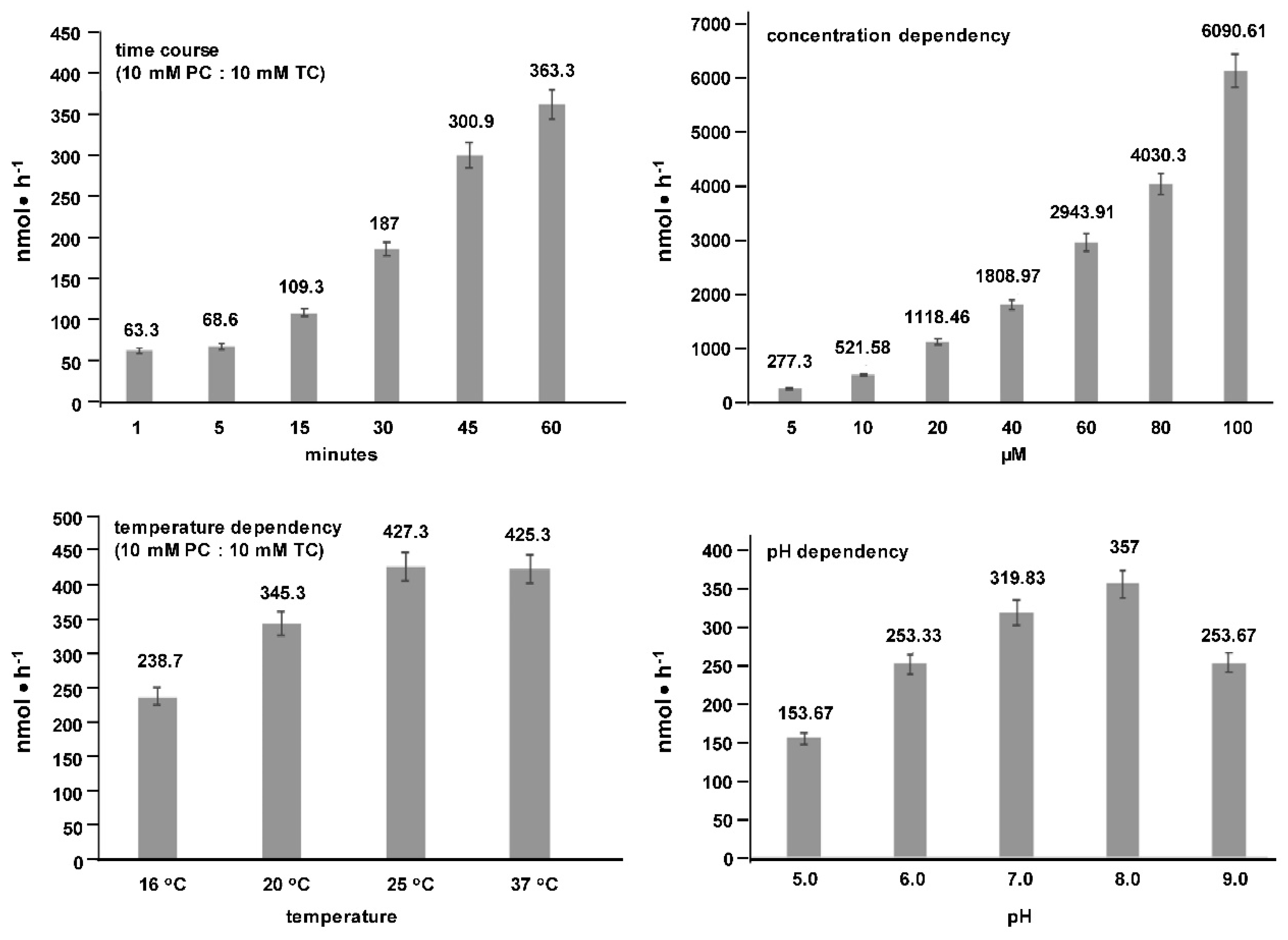
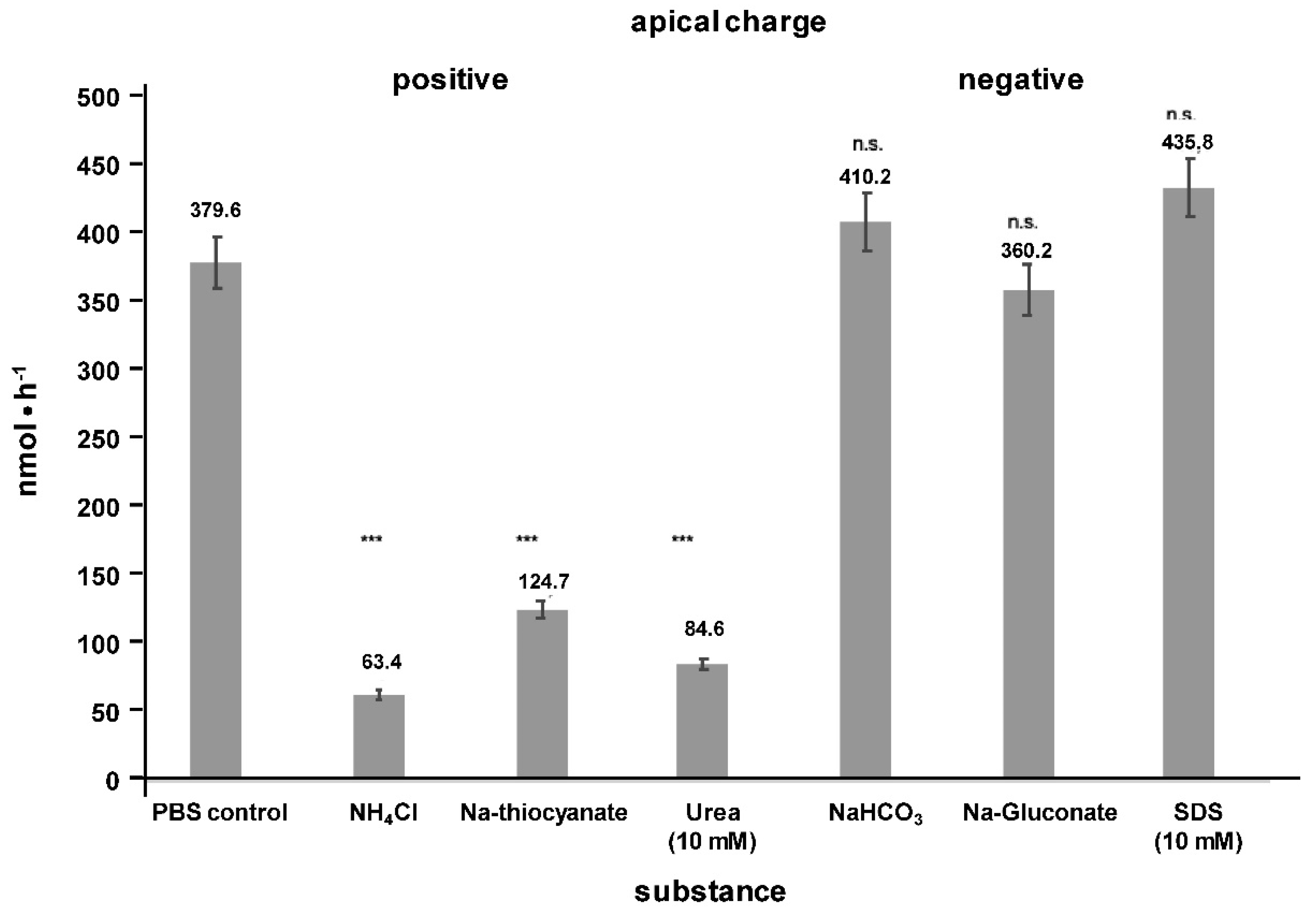
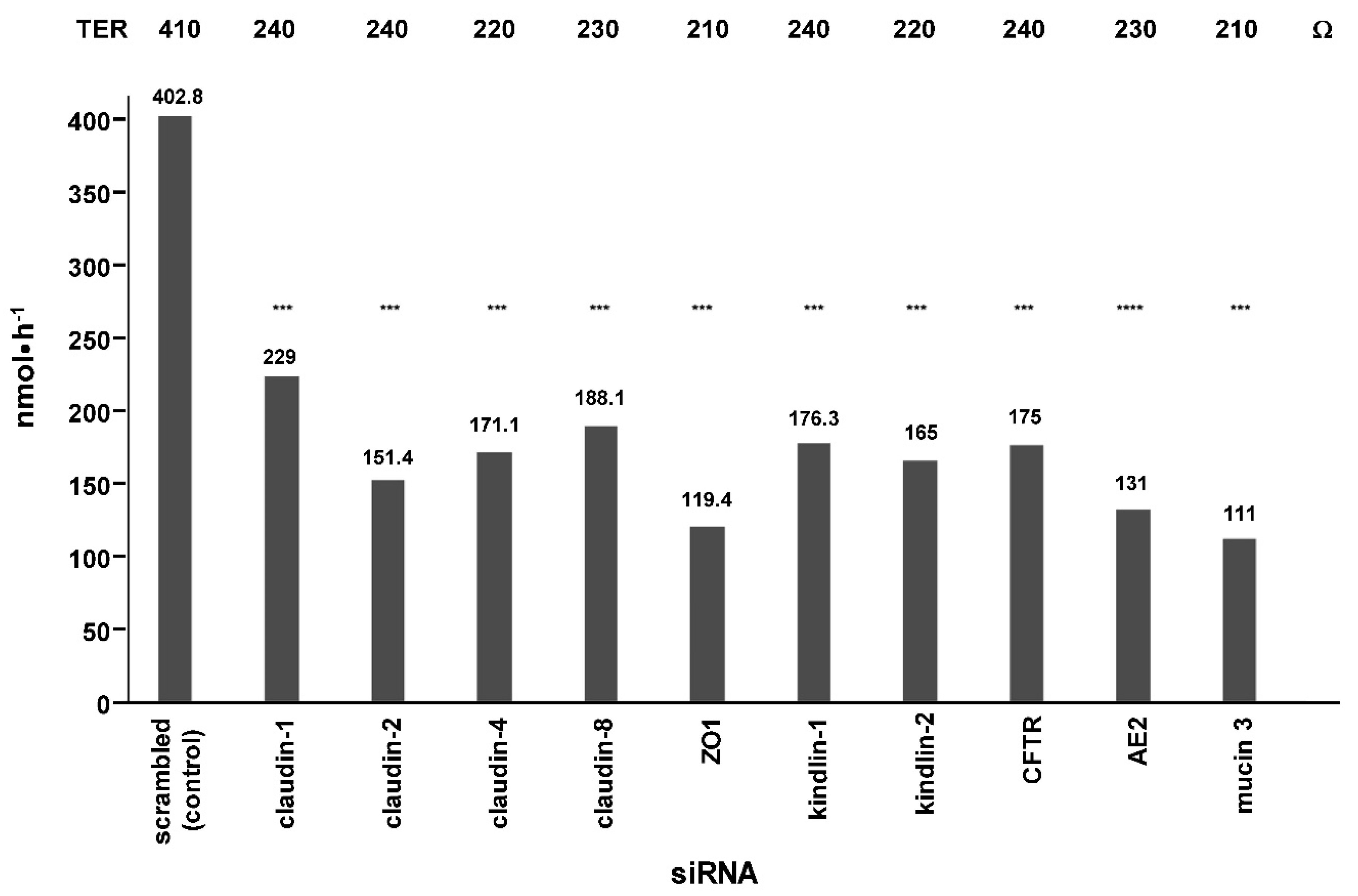
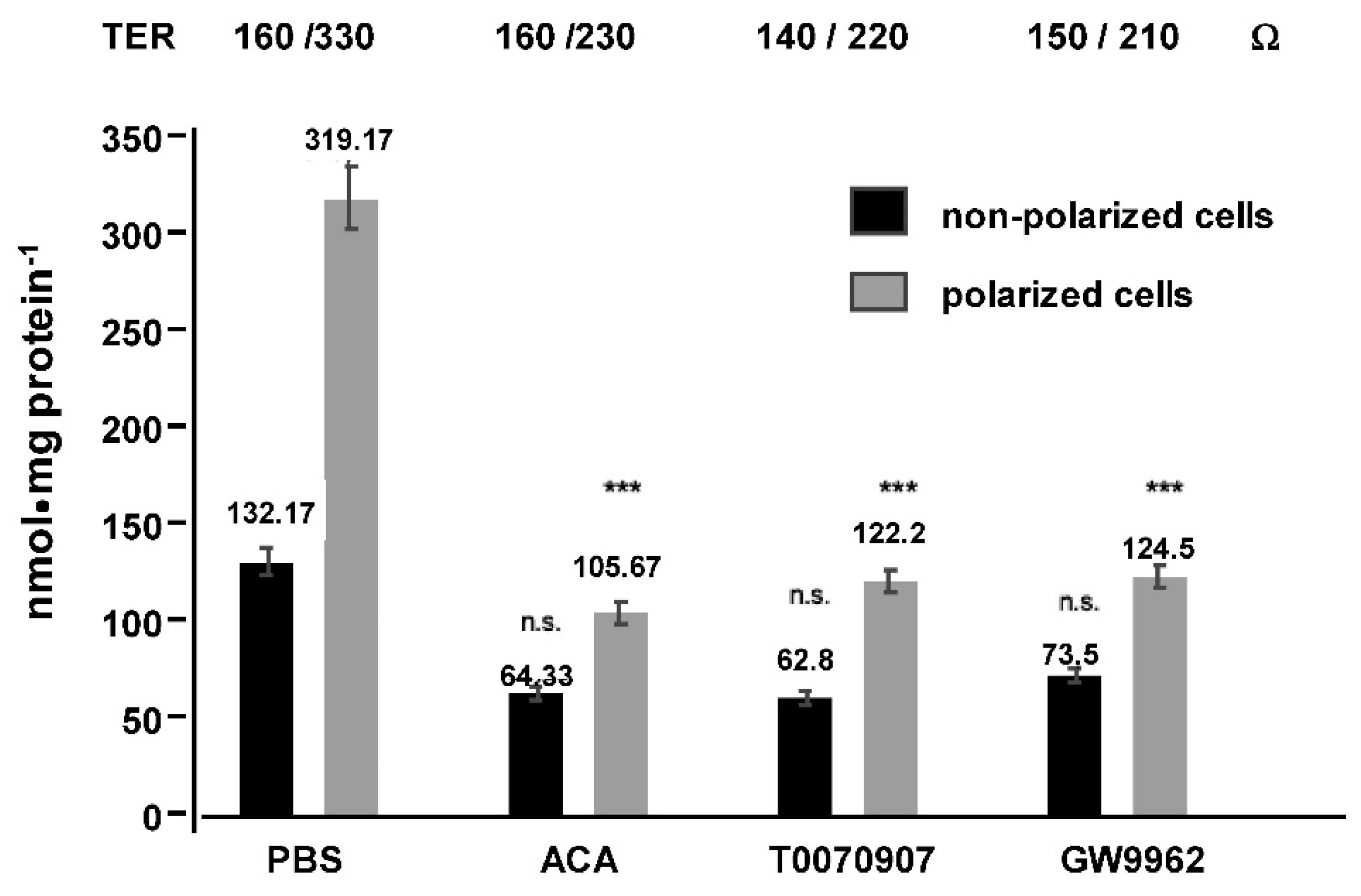
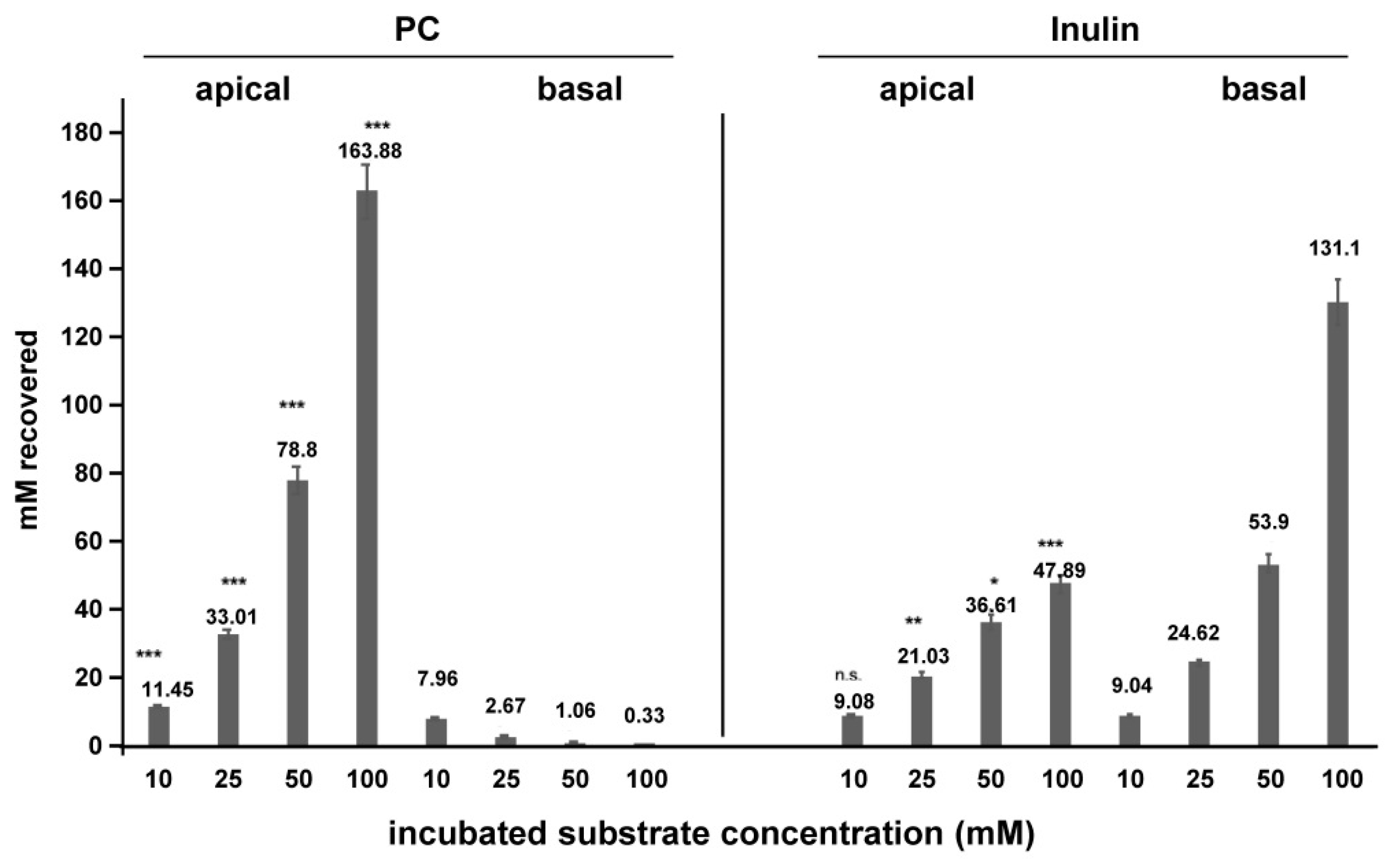
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture Transport Studies
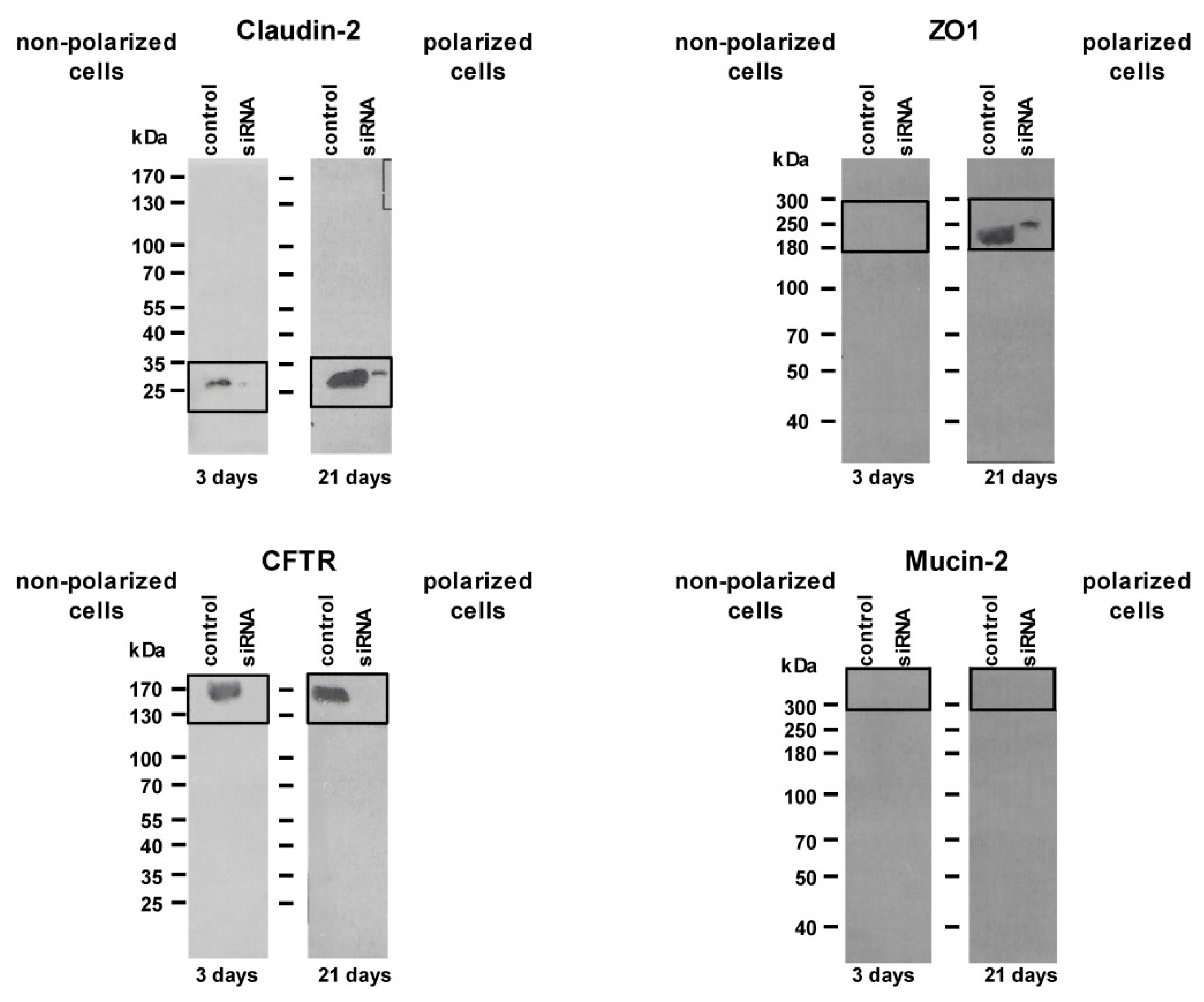
4.2. siRNA Knockdown Experiments
4.3. Immunoblot Analysis
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACA | acetaldehyde |
| AE2 | anion exchange protein 2 |
| ApoB | apolipoprotein B |
| CFTR | cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator |
| LPC | lysophosphatidylcholine |
| PBS | phosphate-buffered saline |
| PC | phosphatidylcholine |
| PSC | primary sclerosing cholangitis |
| SM | sphingomyelin |
| TER | transepithelial resistance |
| TC | taurocholate |
| TJ | tight junction(s) |
| UC | ulcerative colitis |
| ZO1 | Zonula Occludens-1 |
References
- Stremmel, W.; Staffer, S.; Gan-Schreier, H.; Wannhoff, A.; Bach, M.; Gauss, A. Phosphatidylcholine passes through lateral tight junctions for paracellular transport to the apical side of the polarized intestinal tumor cell-line CaCo2. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1861 Pt A, 1161–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stremmel, W.; Staffer, S.; Schneider, M.J.; Gan-Schreier, H.; Wannhoff, A.; Stuhrmann, N.; Gauss, A.; Wolburg, H.; Mahringer, A.; Swidsinski, A.; et al. Genetic mouse models with intestinal-specific tight junction deletion resemble an ulcerative colitis phenotype. J. Crohns. Colitis 2017, 11, 1247–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehehalt, R.; Wagenblast, J.; Erben, G.; Lehmann, W.D.; Hinz, U.; Merle, U.; Stremmel, W. Phosphatidylcholine and lysophosphatidylcholine in intestinal mucus of ulcerative colitis patients. A quantitative approach by nanoElectrospray-tandem mass spectrometry. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 39, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, A.; Schönfeld, U.; Welsch, T.; Kadmon, M.; Funke, B.; Gotthardt, D.; Zahn, A.; Autschbach, F.; Kienle, P.; Zharnikov, M.; et al. Reduced hydrophobicity of the colonic mucosal surface in ulcerative colitis as a hint at a physicochemical barrier defect. Int. J. Colorectal. Dis. 2011, 26, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saich, R.; Chapman, R. Primary sclerosing cholangitis, autoimmune hepatitis and overlap syndromes in inflammatory bowel disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smit, J.J.; Schinkel, A.H.; Oude Elferink, R.P.; Groen, A.K.; Wagenaar, E.; van Deemter, L.; Mol, C.A.; Ottenhoff, R.; van der Lugt, N.M.; van Roon, M.A.; et al. Homozygous disruption of the murine mdr2 P-glycoprotein gene leads to a complete absence of phospholipid from bile and to liver disease. Cell 1993, 75, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oude Elferink, R.P.; Paulusma, C.C. Function and pathophysiological importance of ABCB4 (MDR3 P-glycoprotein). Pflug. Arch. 2007, 453, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauss, A.; Ehehalt, R.; Lehmann, W.D.; Erben, G.; Weiss, K.H.; Schaefer, Y.; Kloeters-Plachky, P.; Stiehl, A.; Stremmel, W.; Sauer, P.; et al. Biliary phosphatidylcholine and lysophosphatidylcholine profiles in sclerosing cholangitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 5454–5463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knuth, A.; Gabbert, H.; Dippold, W.; Klein, O.; Sachsse, W.; Bitter-Suermann, D.; Prellwitz, W.; Meyer zum Buschenfelde, K.H. Biliary adenocarcinoma. Characterisation of three new human tumor cell lines. J. Hepatol. 1985, 1, 579–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, N.; Todoroki, T.; Kawamoto, T.; Yoshida, S.; Kashiwagi, H.; Fukao, K.; Ohno, T.; Watanabe, T. The invasion potentials of human biliary tract carcinoma cell lines: Correlation between invasiveness and morphologic characteristics. Int. J. Oncol. 1998, 13, 1269–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braconi, C.; Swenson, E.; Kogure, T.; Huang, N.; Patel, T. Targeting the IL-6 dependent phenotype can identify novel therapies for cholangiocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrumpf, E.; Tan, C.; Karlsen, T.H.; Sponheim, J.; Björkström, N.K.; Sundnes, O.; Alfsnes, K.; Kaser, A.; Jefferson, D.M.; Ueno, Y.; et al. The biliary epithelium presents antigens to and activates natural killer T cells. Hepatology 2015, 62, 1249–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onori, P.; Wise, C.; Gaudio, E.; Franchitto, A.; Francis, H.; Carpino, G.; Lee, V.; Lam, I.; Miller, T.; Dostal, D.E.; et al. Secretin inhibits cholangiocarcinoma growth via dysregulation of the cAMP-dependent signaling mechanisms of secretin receptor. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zach, S.; Birgin, E.; Rückert, F. Primary cholangiocellular carcinoma cell lines. J. Stem Cell Res. Transpl. 2015, 2, 1013. [Google Scholar]
- Tietz, P.S.; Marinelli, R.A.; Chen, X.M.; Huang, B.; Cohn, J.; Kole, J.; McNiven, M.A.; Alper, S.; LaRusso, N.F. Agonist-induced coordinated trafficking of functionally related transport proteins for water and ions in cholangiocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 20413–20419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Vilar, J.; Hill, R.L. The structure and assembly of secreted mucins. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 31751–31754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, P.A.; Lan, T.; Rao, A. Bile acid transporters. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 2340–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunagan, M.; Chaudhry, K.; Samak, G.; Rao, R.K. Acetaldehyde disrupts tight junctions in Caco-2 cell monolayers by a protein phosphatase 2A-dependent mechanism. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 303, G1356–G1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogasawara, N.; Kojima, T.; Go, M.; Ohkuni, T.; Koizumi, J.; Kamekura, R.; Masaki, T.; Murata, M.; Tanaka, S.; Fuchimoto, J.; et al. PPARγ agonists upregulate the barrier function of tight junctions via a PKC pathway in human nasal epithelial cells. Pharm. Res. 2010, 61, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| siRNA | Sense Oligo | Antisense Oligo |
|---|---|---|
| scrambled | 5′-gaugggaccuggccaguga-3′[dT][dT] | 5′-ucacuggccaggucccauc-3′[dT][dT] |
| claudin-1 | 5′-cagucaaugccagguacga-3′[dT][dT] | 5′-ucguaccuggcauugacug-3′[dT][dT] |
| claudin-2 | 5′-gacacuaccacuggaucgu-3′[dT][dT] | 5′-acgauccagugguaguguc-3′[dT][dT] |
| claudin-4 | 5′-gaccaucugggagggccua-3′[dT][dT] | 5′-uaggcccucccagaugguc-3′[dT][dT] |
| claudin-8 | 5′gguucaagcaucuacucuu-3′[dT][dT] | 5′-aagaguagaugcuugaacc-3′[dT][dT] |
| mucin 2 | 5′-gcaacauuaccgucugcaa-3′[dT][dT] | 5′-uugcagacgguaauguugc-3′[dT][dT] |
| mucin 3 | 5′-ccaaacuacucuuacuaca-3′[dT][dT] | 5′-uguaguaagaguaguuugg-3′[dT][dT] |
| CFTR | 5′-gaacacauaccuucgauau-3′[dT][dT] | 5′-auaucgaagguauguguuc-3′[dT][dT] |
| AE2 | 5′-gagaucuucgccuucuuga-3′[dT][dT] | 5′-ucaagaaggcgaagaucuc-3′[dT][dT] |
| ZO1 | 5′-gagaugaacgggcuacgcu-3′[dT][dT] | 5′-agcguagcccguucaucuc-3′[dT][dT] |
| kindlin-1 | 5′-ggacauuacugauaucccu-3′[dT][dT] | 5′-agggauaucaguaaugucc-3′[dT][dT] |
| kindlin-2 | 5′-gugugaauagaaauacugu-3′[dT][dT] | 5′-acaguauuucuauucacac-3′[dT][dT] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stremmel, W.; Staffer, S.; Weiskirchen, R. Phosphatidylcholine Passes by Paracellular Transport to the Apical Side of the Polarized Biliary Tumor Cell Line Mz-ChA-1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4034. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20164034
Stremmel W, Staffer S, Weiskirchen R. Phosphatidylcholine Passes by Paracellular Transport to the Apical Side of the Polarized Biliary Tumor Cell Line Mz-ChA-1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(16):4034. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20164034
Chicago/Turabian StyleStremmel, Wolfgang, Simone Staffer, and Ralf Weiskirchen. 2019. "Phosphatidylcholine Passes by Paracellular Transport to the Apical Side of the Polarized Biliary Tumor Cell Line Mz-ChA-1" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 16: 4034. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20164034
APA StyleStremmel, W., Staffer, S., & Weiskirchen, R. (2019). Phosphatidylcholine Passes by Paracellular Transport to the Apical Side of the Polarized Biliary Tumor Cell Line Mz-ChA-1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(16), 4034. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20164034