Cholesterol Acceptors Regulate the Lipidome of Macrophage Foam Cells
Abstract
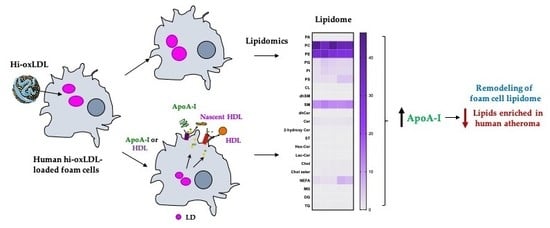
1. Introduction
2. Results
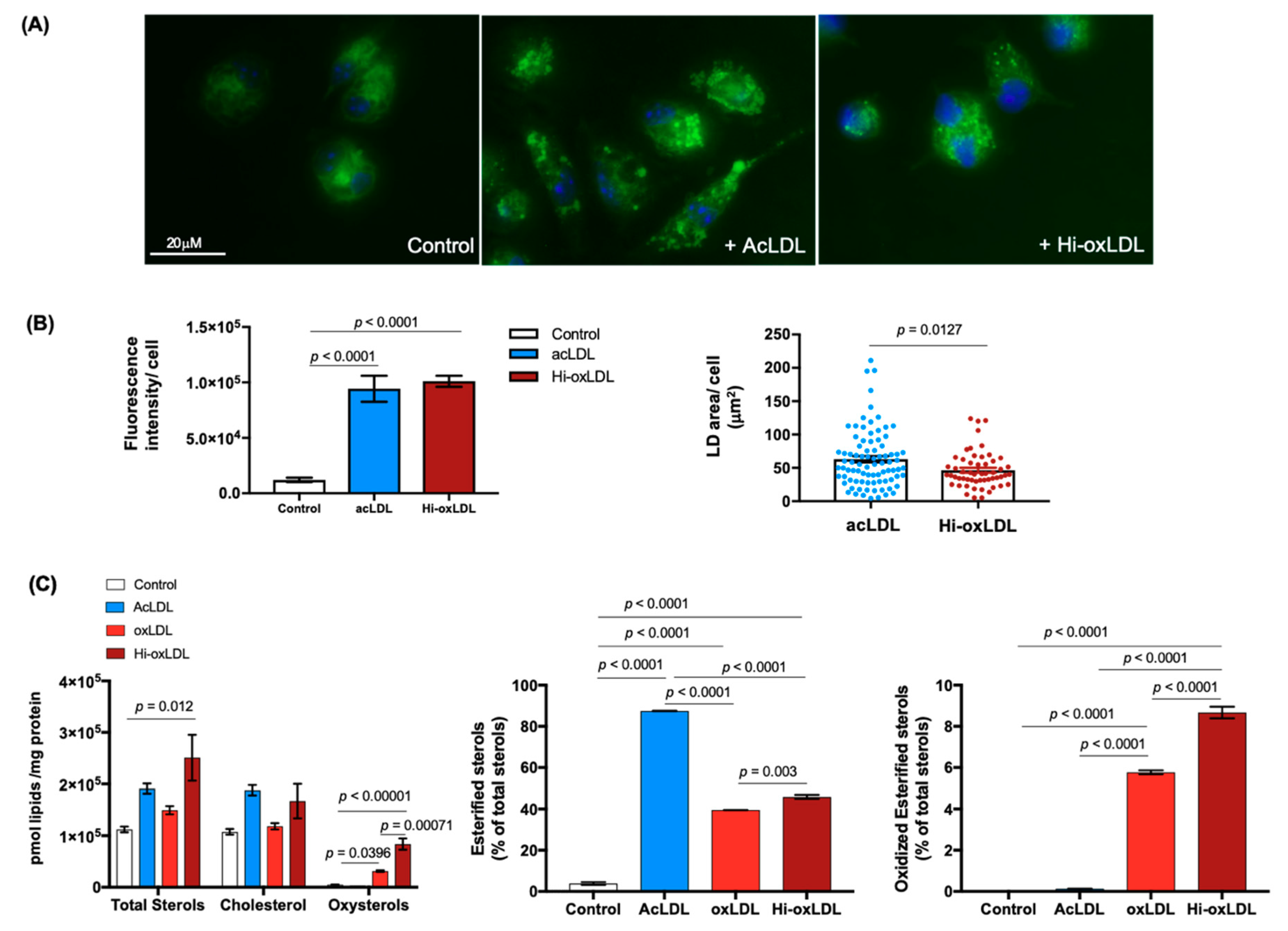
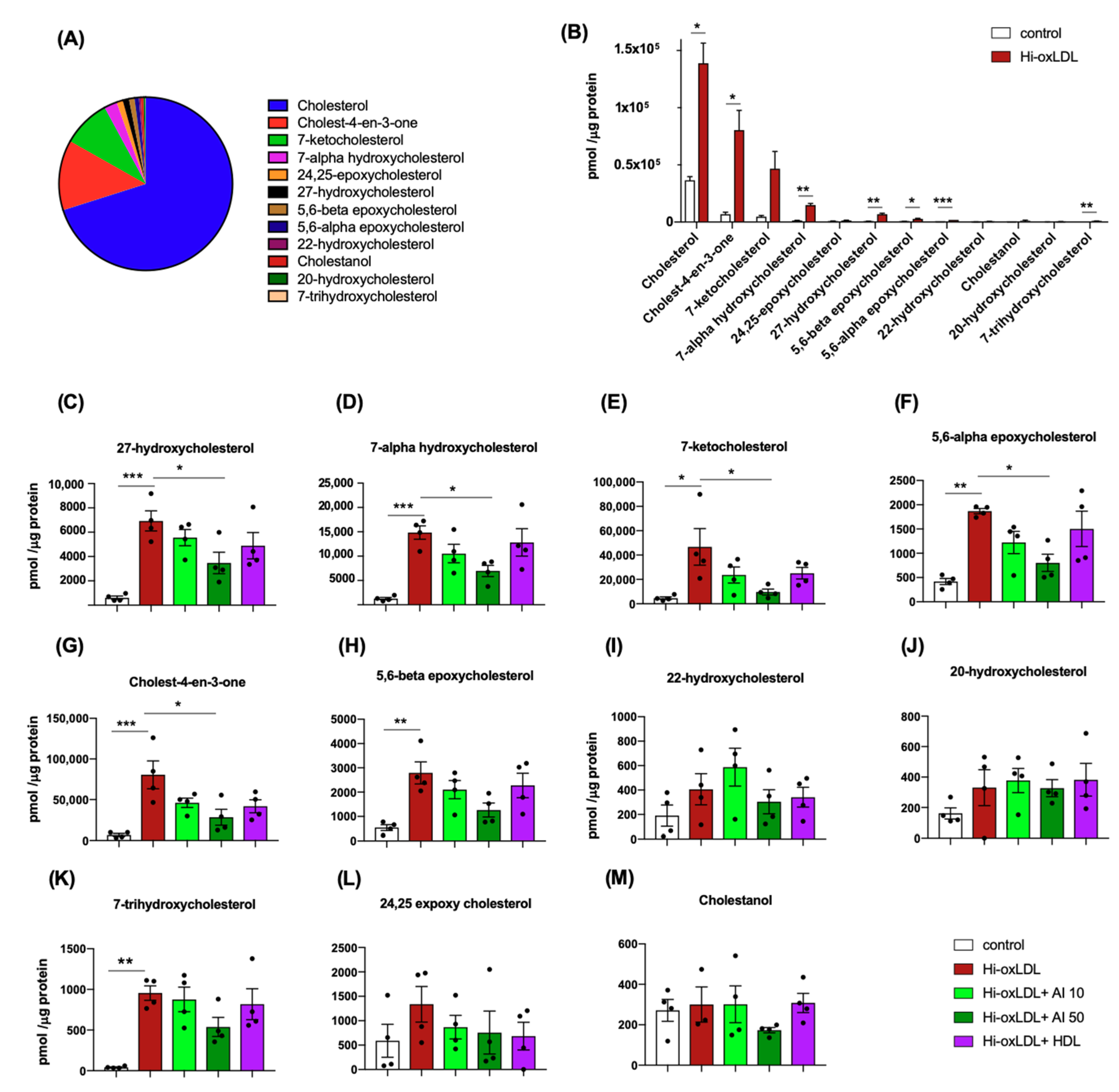
2.1. Highly-Oxidized LDL Loading Increases Intracellular Oxysterols Abundantly Found in Human Atheroma
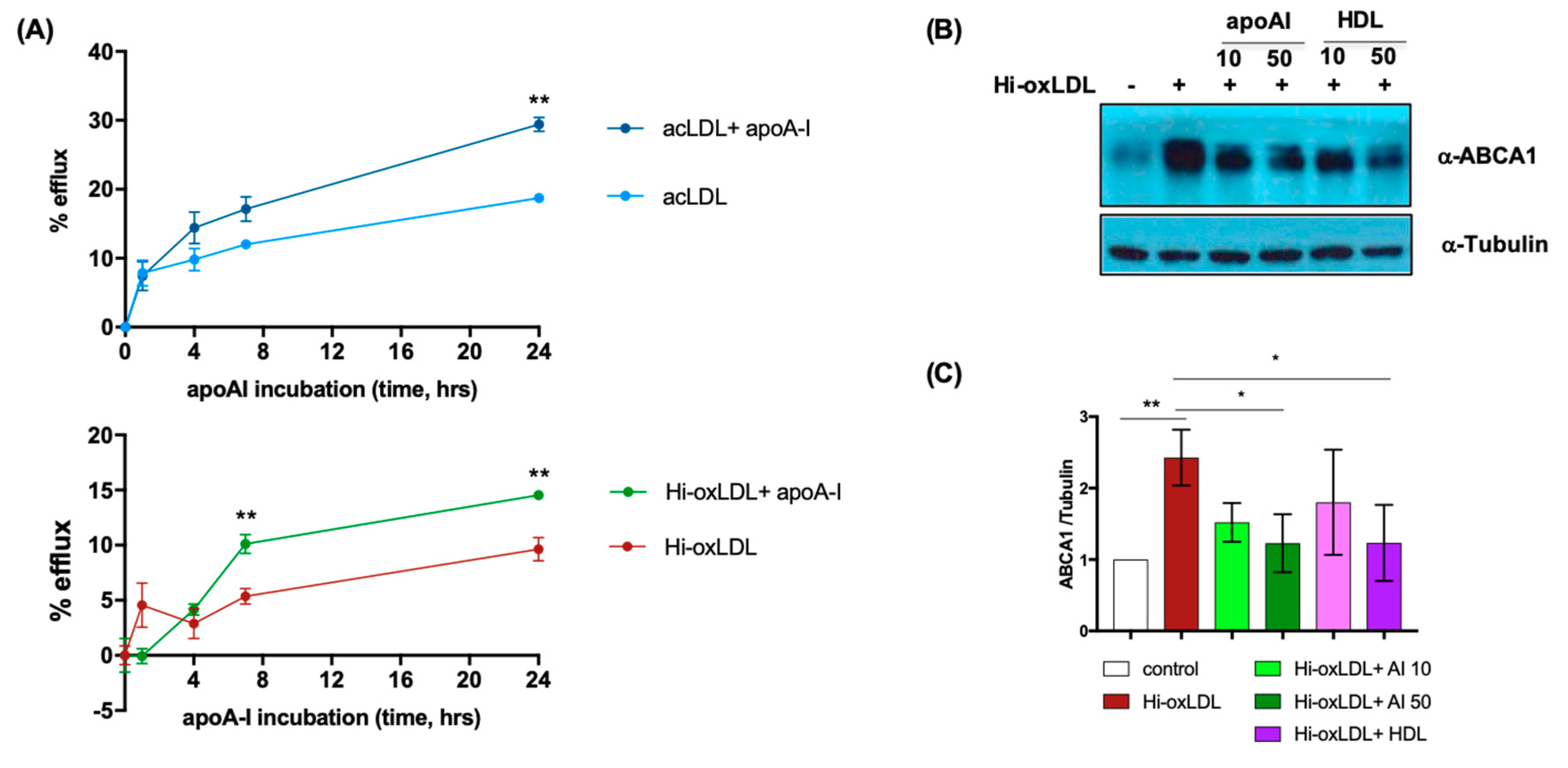
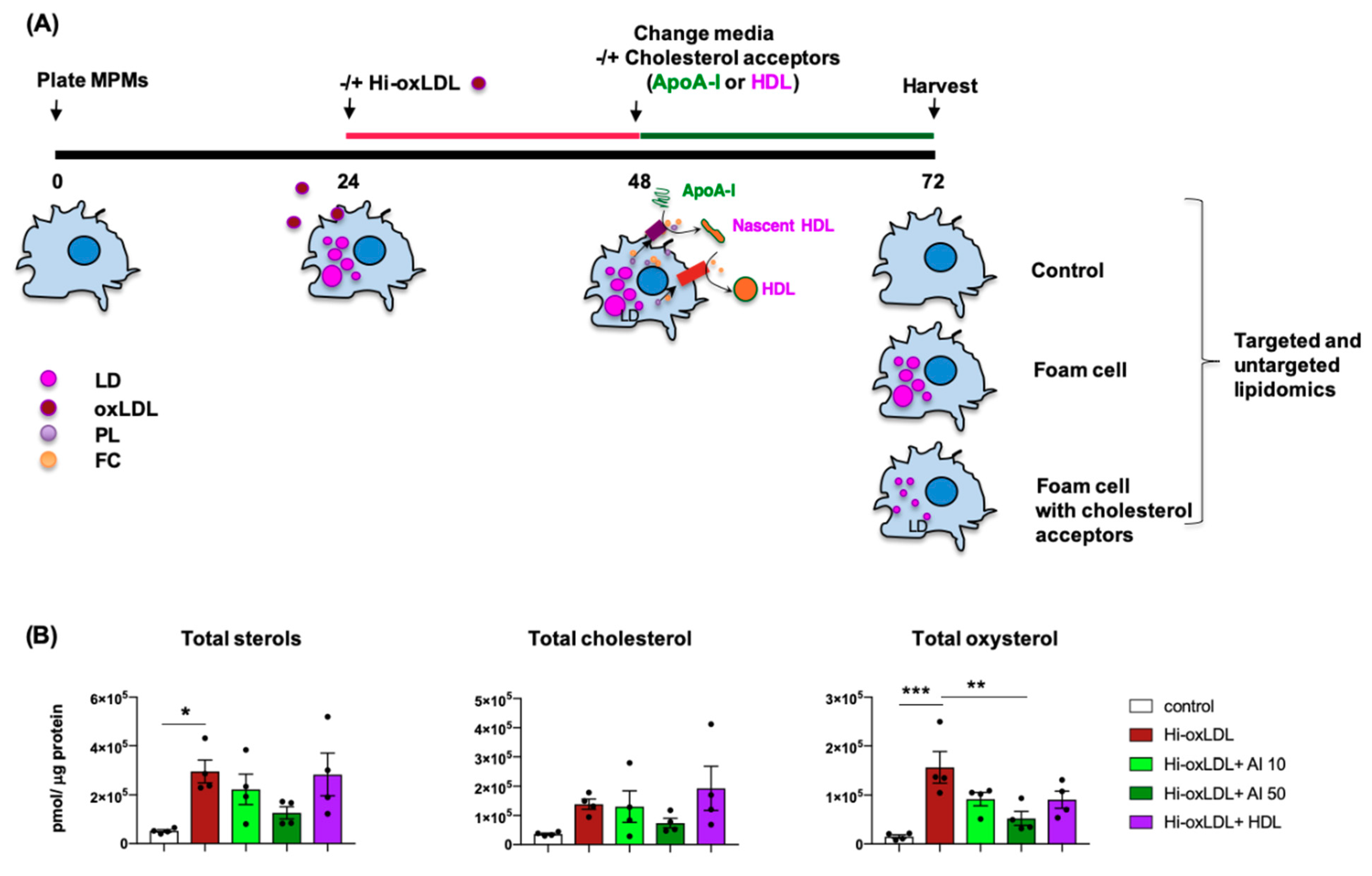
2.2. Lipid-Poor apoA-I Significantly Reduces Oxysterols
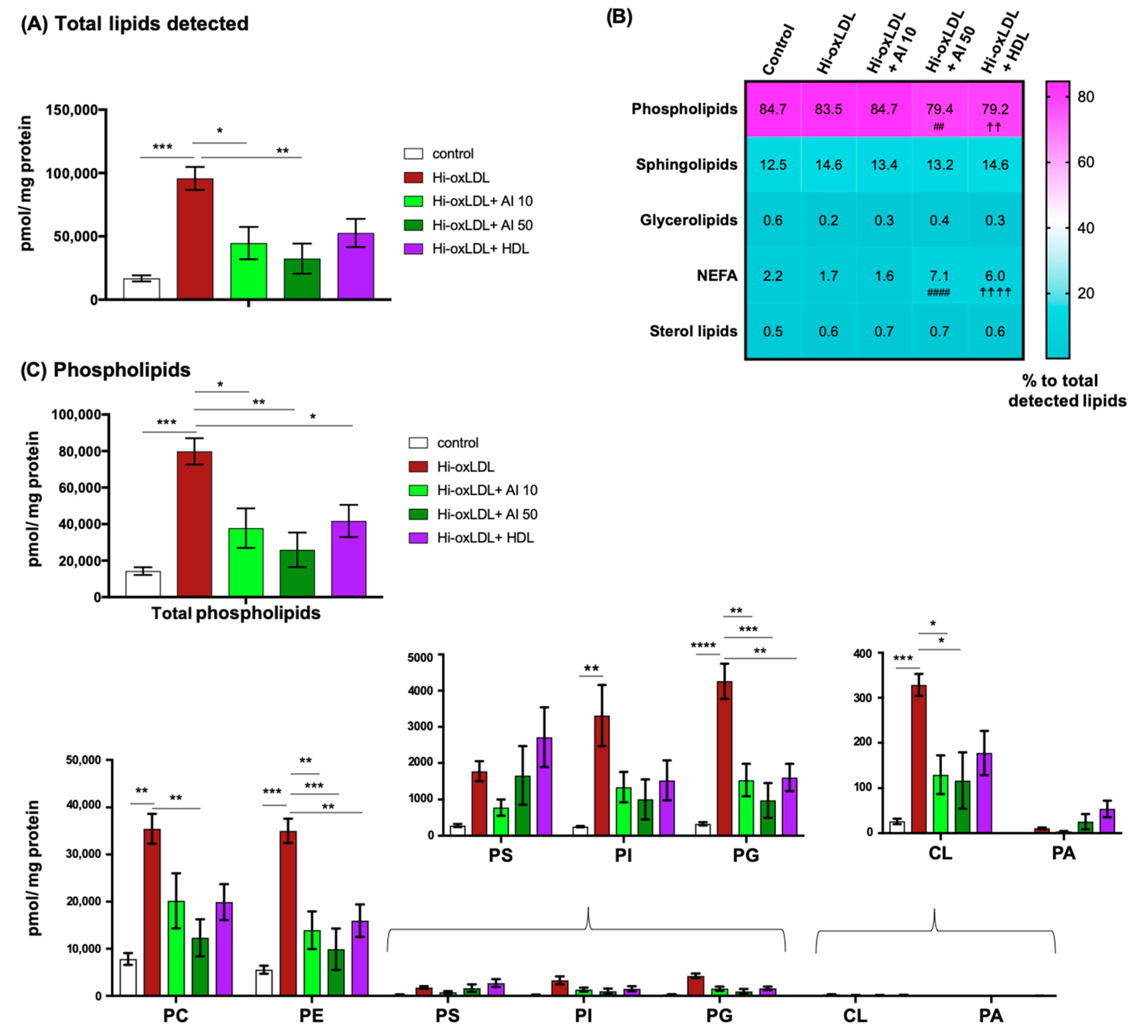
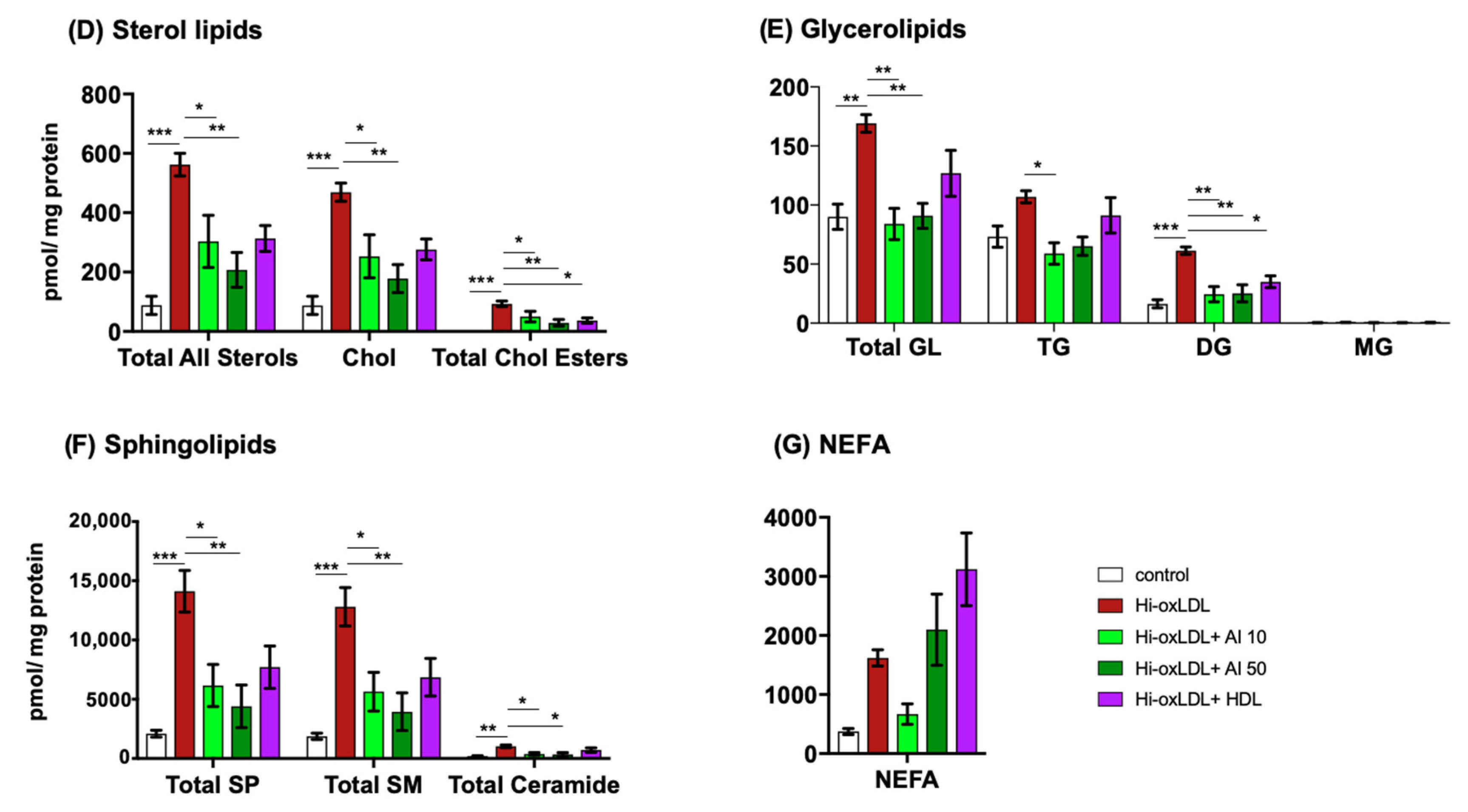
2.3. Major Lipid Categories and Lipid Species Linked to Atherogenesis are Down-Regulated by Cholesterol Acceptors
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Mice
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. Lipid Droplet Staining and Measuring LD Area
4.5. Cholesterol Efflux
4.6. Lipid Extraction
4.7. Global Lipidomics Analysis
4.8. Analysis of Free and Total Sterol Content
4.9. Peak Finding, Analyte Identification, and Quantification
4.10. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HDL | High-density lipoprotein |
| ApoA-I | apolipoprotein A-I |
| CE | Cholesterol ester |
| LDL | Low-density lipoprotein |
| PL | Phospholipids |
| GL | Glycerolipids |
| SL | Sphingolipids |
| ST | Sterol lipids |
| NEFA | Non-esterified fatty acids |
| SM | Sphingomyelins |
| ABCA1 | ATP-binding cassette transporter member 1 |
| ABCG1 | ATP-binding cassette subfamily member G1 |
| OxLDL | Oxidized LDL |
| AcLDL | Acetylated LDL |
| MS | Mass-Spectrometry |
| MPM | Mouse peritoneal macrophage |
| PM | Plasma membrane |
References
- Wang, H.H.; Garruti, G.; Liu, M.; Portincasa, P.; Wang, D.Q. Cholesterol and lipoprotein metabolism and atherosclerosis: Recent advances in reverse cholesterol transport. Ann. Hepatol. 2017, 16, s27–s42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, K.J.; Tabas, I. Macrophages in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Cell 2011, 145, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, S.M.; Defina, L.F.; Leonard, D.; Barlow, C.E.; Radford, N.B.; Willis, B.L.; Rohatgi, A.; McGuire, D.K.; de Lemos, J.A.; Grundy, S.M.; et al. Long-term association of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol with cardiovascular mortality in individuals at low 10-year risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Circulation 2018, 138, 2315–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ference, B.A.; Ginsberg, H.N.; Graham, I.; Ray, K.K.; Packard, C.J.; Bruckert, E.; Hegele, R.A.; Krauss, R.M.; Raal, F.J.; Schunkert, H.; et al. Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. 1. Evidence from genetic, epidemiologic, and clinical studies. A consensus statement from the european atherosclerosis society consensus panel. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 2459–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khera, A.V.; Kathiresan, S. Genetics of coronary artery disease: Discovery, biology and clinical translation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2017, 18, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klarin, D.; Zhu, Q.M.; Emdin, C.A.; Chaffin, M.; Horner, S.; McMillan, B.J.; Leed, A.; Weale, M.E.; Spencer, C.C.A.; Aguet, F.; et al. Genetic analysis in uk biobank links insulin resistance and transendothelial migration pathways to coronary artery disease. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1392–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howson, J.M.M.; Zhao, W.; Barnes, D.R.; Ho, W.K.; Young, R.; Paul, D.S.; Waite, L.L.; Freitag, D.F.; Fauman, E.B.; Salfati, E.L.; et al. Fifteen new risk loci for coronary artery disease highlight arterial-wall-specific mechanisms. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1113–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, J.L.; Ho, Y.K.; Basu, S.K.; Brown, M.S. Binding site on macrophages that mediates uptake and degradation of acetylated low density lipoprotein, producing massive cholesterol deposition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrman, B.; Judith, O.; Keidar, S.; Ben-Yaish, L.; Kaplan, M.; Aviram, M. Increased uptake of ldl by oxidized macrophages is the result of an initial enhanced ldl receptor activity and of a further progressive oxidation of ldl. Free Radic Biol. Med. 1997, 23, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbrecher, U.P.; Parthasarathy, S.; Leake, D.S.; Witztum, J.L.; Steinberg, D. Modification of low density lipoprotein by endothelial cells involves lipid peroxidation and degradation of low density lipoprotein phospholipids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 3883–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankman, L.S.; Gomez, D.; Cherepanova, O.A.; Salmon, M.; Alencar, G.F.; Haskins, R.M.; Swiatlowska, P.; Newman, A.A.; Greene, E.S.; Straub, A.C.; et al. Klf4-dependent phenotypic modulation of smooth muscle cells has a key role in atherosclerotic plaque pathogenesis. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Dubland, J.A.; Allahverdian, S.; Asonye, E.; Sahin, B.; Jaw, J.E.; Sin, D.D.; Seidman, M.A.; Leeper, N.J.; Francis, G.A. Smooth muscle cells contribute the majority of foam cells in apoe (apolipoprotein e)-deficient mouse atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 876–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabas, I.; Lichtman, A.H. Monocyte-macrophages and T cells in atherosclerosis. Immunity 2017, 47, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plakkal Ayyappan, J.; Paul, A.; Goo, Y.H. Lipid droplet-associated proteins in atherosclerosis (review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 4527–4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.Y.; Chang, C.C.; Lu, X.; Lin, S. Catalysis of acat may be completed within the plane of the membrane: A working hypothesis. J. Lipid Res. 2001, 42, 1933–1938. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, M.A.; Liu, J.; Song, B.L.; Li, B.L.; Chang, C.C.; Chang, T.Y. Acyl-coa:Cholesterol acyltransferases (acats/soats): Enzymes with multiple sterols as substrates and as activators. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 151, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Huh, H.Y.; Cadigan, K.M.; Chang, T.Y. Molecular cloning and functional expression of human acyl-coenzyme a:Cholesterol acyltransferase cdna in mutant chinese hamster ovary cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 20747–20755. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, S.; Voogt, J.; Davidson, M.; Glass, A.; Killion, S.; Decaris, J.; Mohammed, H.; Minehira, K.; Boban, D.; Murphy, E.; et al. Measurement of reverse cholesterol transport pathways in humans: In vivo rates of free cholesterol efflux, esterification, and excretion. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2012, 1, e001826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temel, R.E.; Brown, J.M. A new model of reverse cholesterol transport: Enticeing strategies to stimulate intestinal cholesterol excretion. Trends Pharmacol. Sci 2015, 36, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessup, W.; Gelissen, I.C.; Gaus, K.; Kritharides, L. Roles of atp binding cassette transporters a1 and g1, scavenger receptor bi and membrane lipid domains in cholesterol export from macrophages. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2006, 17, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.Y.; Thiam, C.H.; Yeo, K.P.; Bisoendial, R.; Hii, C.S.; McGrath, K.C.; Tan, K.W.; Heather, A.; Alexander, J.S.; Angeli, V. Lymphatic vessels are essential for the removal of cholesterol from peripheral tissues by sr-bi-mediated transport of hdl. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martel, C.; Li, W.; Fulp, B.; Platt, A.M.; Gautier, E.L.; Westerterp, M.; Bittman, R.; Tall, A.R.; Chen, S.H.; Thomas, M.J.; et al. Lymphatic vasculature mediates macrophage reverse cholesterol transport in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.H.; Goo, Y.H.; Choi, M.; Saha, P.K.; Oka, K.; Chan, L.C.; Paul, A. Enhanced atheroprotection and lesion remodelling by targeting the foam cell and increasing plasma cholesterol acceptors. Cardiovasc. Res. 2016, 109, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenson, R.S.; Brewer, H.B., Jr.; Ansell, B.J.; Barter, P.; Chapman, M.J.; Heinecke, J.W.; Kontush, A.; Tall, A.R.; Webb, N.R. Dysfunctional hdl and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2016, 13, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camont, L.; Lhomme, M.; Rached, F.; Le Goff, W.; Negre-Salvayre, A.; Salvayre, R.; Calzada, C.; Lagarde, M.; Chapman, M.J.; Kontush, A. Small, dense high-density lipoprotein-3 particles are enriched in negatively charged phospholipids: Relevance to cellular cholesterol efflux, antioxidative, antithrombotic, anti-inflammatory, and antiapoptotic functionalities. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 2715–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Capelleveen, J.C.; Bochem, A.E.; Boekholdt, S.M.; Mora, S.; Hoogeveen, R.C.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Ridker, P.M.; Sun, W.; Barter, P.J.; Tall, A.R.; et al. Association of high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol versus apolipoprotein a-i with risk of coronary heart disease: The european prospective investigation into cancer-norfolk prospective population study, the atherosclerosis risk in communities study, and the women’s health study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Lee-Rueckert, M.; Escola-Gil, J.C.; Kovanen, P.T. Hdl functionality in reverse cholesterol transport--challenges in translating data emerging from mouse models to human disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1861, 566–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, S.; Stein, J.H.; Jorgensen, N.W.; McClelland, R.L.; Tascau, L.; Shrager, S.; Heinecke, J.W.; Yvan-Charvet, L.; Tall, A.R. Cholesterol mass efflux capacity, incident cardiovascular disease, and progression of carotid plaque. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quehenberger, O.; Armando, A.M.; Brown, A.H.; Milne, S.B.; Myers, D.S.; Merrill, A.H.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Jones, K.N.; Kelly, S.; Shaner, R.L.; et al. Lipidomics reveals a remarkable diversity of lipids in human plasma. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 3299–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, A.; Rudnitskaya, A.; Blackburn, G.J.; Mohd Fauzi, N.; Pitt, A.R.; Spickett, C.M. A comparison of five lipid extraction solvent systems for lipidomic studies of human ldl. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 1812–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegemann, C.; Drozdov, I.; Shalhoub, J.; Humphries, J.; Ladroue, C.; Didangelos, A.; Baumert, M.; Allen, M.; Davies, A.H.; Monaco, C.; et al. Comparative lipidomics profiling of human atherosclerotic plaques. Circ. Cardiovasc Genet. 2011, 4, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upston, J.M.; Niu, X.; Brown, A.J.; Mashima, R.; Wang, H.; Senthilmohan, R.; Kettle, A.J.; Dean, R.T.; Stocker, R. Disease stage-dependent accumulation of lipid and protein oxidation products in human atherosclerosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2002, 160, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plat, J.; Theuwissen, E.; Husche, C.; Lutjohann, D.; Gijbels, M.J.; Jeurissen, M.; Shiri-Sverdlov, R.; van der Made, I.; Mensink, R.P. Oxidised plant sterols as well as oxycholesterol increase the proportion of severe atherosclerotic lesions in female ldl receptor+/- mice. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 111, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umetani, M.; Ghosh, P.; Ishikawa, T.; Umetani, J.; Ahmed, M.; Mineo, C.; Shaul, P.W. The cholesterol metabolite 27-hydroxycholesterol promotes atherosclerosis via proinflammatory processes mediated by estrogen receptor alpha. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowri, H.; Chinen, K.; Ohkuma, S.; Takano, T. Peroxidized lipids isolated by hplc from atherosclerotic aorta. Biochem. Int. 1986, 12, 347–352. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, K.L.; Wilkins, G.M.; Fussell, B.; Ballantine, J.A.; Taylor, S.E.; Mitchinson, M.J.; Leake, D.S. Production of oxidized lipids during modification of low-density lipoprotein by macrophages or copper. Biochem. J. 1994, 304, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folcik, V.A.; Nivar-Aristy, R.A.; Krajewski, L.P.; Cathcart, M.K. Lipoxygenase contributes to the oxidation of lipids in human atherosclerotic plaques. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 96, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, S.; Raghavamenon, A.; Garelnabi, M.O.; Santanam, N. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 610, 403–417. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.D.; Kiss, R.S.; Franklin, V.; McBride, H.M.; Whitman, S.C.; Marcel, Y.L. Different cellular traffic of ldl-cholesterol and acetylated ldl-cholesterol leads to distinct reverse cholesterol transport pathways. J. Lipid Res. 2007, 48, 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.X.; Tabas, I. Lipoproteins activate acyl-coenzyme a:Cholesterol acyltransferase in macrophages only after cellular cholesterol pools are expanded to a critical threshold level. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 17040–17048. [Google Scholar]
- Vorkas, P.A.; Shalhoub, J.; Isaac, G.; Want, E.J.; Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E.; Davies, A.H. Metabolic phenotyping of atherosclerotic plaques reveals latent associations between free cholesterol and ceramide metabolism in atherogenesis. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 1389–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goo, Y.H.; Son, S.H.; Kreienberg, P.B.; Paul, A. Novel lipid droplet-associated serine hydrolase regulates macrophage cholesterol mobilization. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, H.; Hoang, A.; Sviridov, D. Cholesterol efflux assay. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, e3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.C. Molecular mechanisms of cellular cholesterol efflux. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 24020–24029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswaran, A.; Laffitte, B.A.; Joseph, S.B.; Mak, P.A.; Wilpitz, D.C.; Edwards, P.A.; Tontonoz, P. Control of cellular cholesterol efflux by the nuclear oxysterol receptor lxr alpha. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 12097–12102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lydic, T.A.; Goo, Y.H. Lipidomics unveils the complexity of the lipidome in metabolic diseases. Clin. Transl. Med. 2018, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmschrodt, C.; Becker, S.; Schroter, J.; Hecht, M.; Aust, G.; Thiery, J.; Ceglarek, U. Fast lc-ms/ms analysis of free oxysterols derived from reactive oxygen species in human plasma and carotid plaque. Clin. Chim. Acta 2013, 425, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, P.M.; Tabas, I. Free cholesterol loading of macrophages is associated with widespread mitochondrial dysfunction and activation of the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 42468–42476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scull, C.M.; Tabas, I. Mechanisms of er stress-induced apoptosis in atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 2792–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahy, E.; Subramaniam, S.; Murphy, R.C.; Nishijima, M.; Raetz, C.R.; Shimizu, T.; Spener, F.; van Meer, G.; Wakelam, M.J.; Dennis, E.A. Update of the lipid maps comprehensive classification system for lipids. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, S9–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.D.; Le Goff, W.; Settle, M.; Brubaker, G.; Waelde, C.; Horwitz, A.; Oda, M.N. Abca1 mediates concurrent cholesterol and phospholipid efflux to apolipoprotein a-i. J. Lipid Res. 2004, 45, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna, J.; Garcia-Seisdedos, D.; Alcazar, A.; Lasuncion, M.A.; Busto, R.; Pastor, O. Quantitative lipidomic analysis of plasma and plasma lipoproteins using maldi-tof mass spectrometry. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2015, 189, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Meer, G. Cellular lipidomics. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 3159–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lee, M.; Fairn, G.D. Phospholipid subcellular localization and dynamics. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 6230–6240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, J.J.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Mohammadyani, D.; Kapralov, A.A.; Anthonymuthu, T.S.; Qu, F.; Amoscato, A.A.; Sparvero, L.J.; Tyurin, V.A.; Planas-Iglesias, J.; et al. Known unknowns of cardiolipin signaling: The best is yet to come. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2017, 1862, 8–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, S.S.; He, Q.; Janczy, J.R.; Elliott, E.I.; Zhong, Z.; Olivier, A.K.; Sadler, J.J.; Knepper-Adrian, V.; Han, R.; Qiao, L.; et al. Mitochondrial cardiolipin is required for nlrp3 inflammasome activation. Immunity 2013, 39, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duewell, P.; Kono, H.; Rayner, K.J.; Sirois, C.M.; Vladimer, G.; Bauernfeind, F.G.; Abela, G.S.; Franchi, L.; Nunez, G.; Schnurr, M.; et al. Nlrp3 inflammasomes are required for atherogenesis and activated by cholesterol crystals. Nature 2010, 464, 1357–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spann, N.J.; Garmire, L.X.; McDonald, J.G.; Myers, D.S.; Milne, S.B.; Shibata, N.; Reichart, D.; Fox, J.N.; Shaked, I.; Heudobler, D.; et al. Regulated accumulation of desmosterol integrates macrophage lipid metabolism and inflammatory responses. Cell 2012, 151, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Shim, D.; Lee, J.S.; Zaitsev, K.; Williams, J.W.; Kim, K.W.; Jang, M.Y.; Seok Jang, H.; Yun, T.J.; Lee, S.H.; et al. Transcriptome analysis reveals nonfoamy rather than foamy plaque macrophages are proinflammatory in atherosclerotic murine models. Circ. Res. 2018, 123, 1127–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusminski, C.M.; Shetty, S.; Orci, L.; Unger, R.H.; Scherer, P.E. Diabetes and apoptosis: Lipotoxicity. Apoptosis 2009, 14, 1484–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabas, I. Consequences of cellular cholesterol accumulation: Basic concepts and physiological implications. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerome, W.G. Advanced atherosclerotic foam cell formation has features of an acquired lysosomal storage disorder. Rejuvenation Res. 2006, 9, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, S.; Merida, I. Diacylglycerol, when simplicity becomes complex. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2007, 32, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bismuth, J.; Lin, P.; Yao, Q.; Chen, C. Ceramide: A common pathway for atherosclerosis? Atherosclerosis 2008, 196, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Fischman, D.A.; Steck, T.L. Selective solubilization of proteins and phospholipids from red blood cell membranes by nonionic detergents. J. Supramol. Struct. 1973, 1, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Liu, K.; Jiang, D.; Fang, D. Codetermination of sphingomyelin and cholesterol in cellular plasma membrane in sphingomyelin-depletion-induced cholesterol efflux. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 1501–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agmon, E.; Stockwell, B.R. Lipid homeostasis and regulated cell death. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2017, 39, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, A.J.; Westerterp, M.; Yvan-Charvet, L.; Tall, A.R. Anti-atherogenic mechanisms of high density lipoprotein: Effects on myeloid cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1821, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajani, S.; Curley, S.; McGillicuddy, F.C. Unravelling hdl-looking beyond the cholesterol surface to the quality within. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tits, L.J.; Stienstra, R.; van Lent, P.L.; Netea, M.G.; Joosten, L.A.; Stalenhoef, A.F. Oxidized ldl enhances pro-inflammatory responses of alternatively activated m2 macrophages: A crucial role for kruppel-like factor 2. Atherosclerosis 2011, 214, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.C.; Hu, Y.W.; Sha, Y.H.; Gao, J.J.; Ma, X.; Li, S.F.; Zhao, J.Y.; Qiu, Y.R.; Lu, J.B.; Huang, C.; et al. Ox-ldl upregulates il-6 expression by enhancing nf-kappab in an igf2-dependent manner in thp-1 macrophages. Inflammation 2015, 38, 2116–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongstra-Bilen, J.; Zhang, C.X.; Wisnicki, T.; Li, M.K.; White-Alfred, S.; Ilaalagan, R.; Ferri, D.M.; Deonarain, A.; Wan, M.H.; Hyduk, S.J.; et al. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein loading of macrophages downregulates tlr-induced proinflammatory responses in a gene-specific and temporal manner through transcriptional control. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 2149–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yin, Y.; Zhou, Z.; He, M.; Dai, Y. Oxldl-induced il-1 beta secretion promoting foam cells formation was mainly via cd36 mediated ros production leading to nlrp3 inflammasome activation. Inflamm. Res. 2014, 63, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabas, I.; Bornfeldt, K.E. Macrophage phenotype and function in different stages of atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 653–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tall, A.R.; Yvan-Charvet, L. Cholesterol, inflammation and innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goo, Y.H.; Son, S.H.; Yechoor, V.K.; Paul, A. Transcriptional profiling of foam cells reveals induction of guanylate-binding proteins following western diet acceleration of atherosclerosis in the absence of global changes in inflammation. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e002663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staprans, I.; Pan, X.M.; Rapp, J.H.; Grunfeld, C.; Feingold, K.R. Oxidized cholesterol in the diet accelerates the development of atherosclerosis in ldl receptor- and apolipoprotein e-deficient mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2000, 20, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manicke, N.E.; Nefliu, M.; Wu, C.; Woods, J.W.; Reiser, V.; Hendrickson, R.C.; Cooks, R.G. Imaging of lipids in atheroma by desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 8702–8707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lydic, T.A.; Busik, J.V.; Reid, G.E. A monophasic extraction strategy for the simultaneous lipidome analysis of polar and nonpolar retina lipids. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 1797–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delekta, P.C.; Lydic, T.A.; Hammer, N.D. Isolation of lipoprotein particles from chicken egg yolk for the study of bacterial pathogen fatty acid incorporation into membrane phospholipids. J. Vis. Exp. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machacek, M.; Saunders, H.; Zhang, Z.; Tan, E.P.; Li, J.; Li, T.; Villar, M.T.; Artigues, A.; Lydic, T.; Cork, G.; et al. Elevated o-glcnacylation enhances pro-inflammatory th17 function by altering the intracellular lipid microenvironment. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 8973–8990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lydic, T.A.; Townsend, S.; Adda, C.G.; Collins, C.; Mathivanan, S.; Reid, G.E. Rapid and comprehensive ’shotgun’ lipidome profiling of colorectal cancer cell derived exosomes. Methods 2015, 87, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clasquin, M.F.; Melamud, E.; Rabinowitz, J.D. LC-MS data processing with maven: A metabolomic analysis and visualization engine. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2012. Available online: https://currentprotocols.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/0471250953.bi1411s37 (accessed on 1 March 2012).
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paul, A.; Lydic, T.A.; Hogan, R.; Goo, Y.-H. Cholesterol Acceptors Regulate the Lipidome of Macrophage Foam Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3784. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153784
Paul A, Lydic TA, Hogan R, Goo Y-H. Cholesterol Acceptors Regulate the Lipidome of Macrophage Foam Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(15):3784. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153784
Chicago/Turabian StylePaul, Antoni, Todd A. Lydic, Ryan Hogan, and Young-Hwa Goo. 2019. "Cholesterol Acceptors Regulate the Lipidome of Macrophage Foam Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 15: 3784. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153784
APA StylePaul, A., Lydic, T. A., Hogan, R., & Goo, Y.-H. (2019). Cholesterol Acceptors Regulate the Lipidome of Macrophage Foam Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(15), 3784. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153784