Mechanisms Underlying Tumor Suppressive Properties of Melatonin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Role of Melatonin during Human Life Stages
3. Evidence That Melatonin Inhibits Cancer Onset
3.1. Direct In Vivo Evidence
3.2. Direct In Vitro Evidence
3.3. Indirect Evidence
4. Evidence That Melatonin Slows Rate of Cancer Progression and Metastasis
4.1. Animal Models
4.2. Cell-Based Models
4.3. Clinical Trials
4.4. Melatonin as A Co-Therapeutic Agent
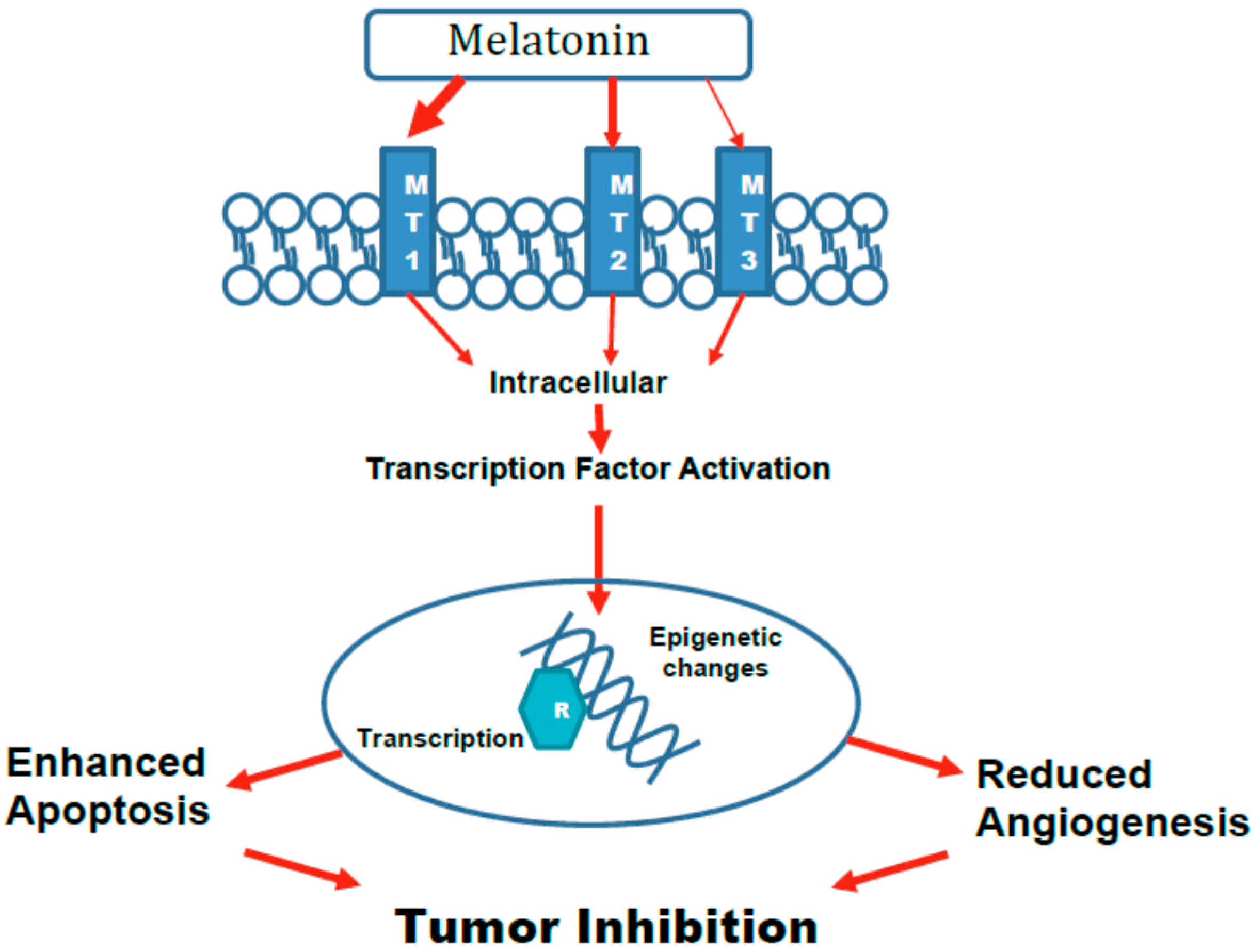
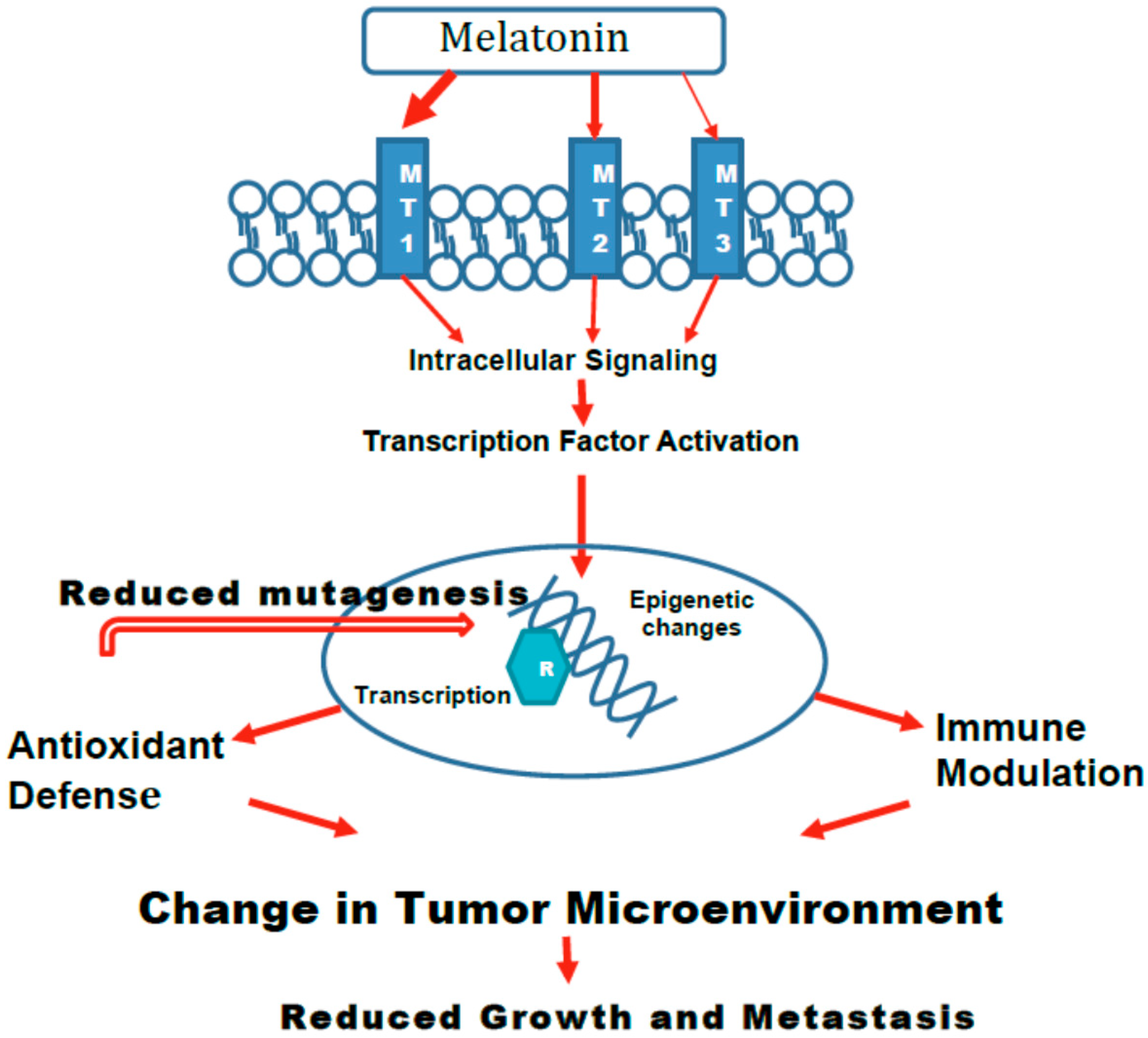
5. Mechanisms
5.1. Epigenetic Changes
5.1.1. Histone Acetylation
5.1.2. Histone and DNA Methylation
5.1.3. miRNA
5.2. Melatonin-Induced Effects on Age-Related Changes in Gene Expression and Immune Modulation
5.3. Activation of Transcription Factors Leading to Altered Gene Expression and Apoptosis
5.4. Angiogenesis
5.5. Role of Various Melatonin Receptors
5.5.1. MT1 and MT2 Receptors
5.5.2. MT3 (Quinone Oxidoreductase) Melatonin Binding Site
5.5.3. RZR/RORα: Retinoid-Related Orphan Nuclear Hormone Receptor
6. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bertrand, P.P.; Polglaze, K.E.; Bertrand, R.L.; Sandow, S.L.; Pozo, M.J. Detection of melatonin production from the intestinal epithelium using electrochemical methods. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 4802–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.X.; Manchester, L.C.; Qin, L.; Reiter, R.J. Melatonin: A mitochondrial targeting molecule involving mitochondrial protection and dynamics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardeland, R.; Cardinali, D.P.; Srinivasan, V.; Spence, D.W.; Brown, G.M.; Pandi-Perumal, S.R. Melatonin-a pleiotropic, orchestrating regulator molecule. Prog. Neurobiol. 2011, 93, 350–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, A.; Sousa, N. Maternal hormonal milieu influence on fetal brain development. Brain Behav. 2018, 8, e00920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Terron, M.P.; Flores, L.J.; Manchester, L.C.; Tan, D.X.; Sugino, N.; Reiter, R.J. Melatonin and pregnancy in the human. Reprod. Toxicol. 2008, 25, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasaki, S.; Nakazawa, K.; Sakai, J.; Kometani, K.; Iwashita, M.; Yoshimura, Y.; Maruyama, T. Melatonin as a local regulator of human placental function. J. Pineal Res. 2005, 39, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazawa, K.; Kanakura, Y.; Kometani, K.; Iwasaki, S.; Yosimura, Y. Study on melatonin in human and rat placental tissue. Trophoblast Res. 1999, 13, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tordjman, S.; Chokron, S.; Delorme, R.; Charrier, A.; Bellissant, E.; Jaafari, N.; Fougerou, C. Melatonin: Pharmacology, functions and therapeutic benefits. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2017, 15, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakatsuki, A.; Okatani, Y.; Shinohara, K.; Ikenoue, N.; Kaneda, C.; Fukaya, T. Melatonin protects fetal rat brain against oxidative mitochondrial damage. J. Pineal Res. 2001, 30, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeh, A. Sleep and melatonin in infants: A preliminary study. Sleep 1997, 20, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gropman, A.L.; Duncan, W.C.; Smith, A.C. Neurologic and developmental features of the Smith-Magenis syndrome (del 17p11.2). Pediatr. Neurol. 2006, 34, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohyama, J. The possible long-term effects of early-life circadian rhythm disturbance on social behavior. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2008, 14, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldonado, M.D.; Pérez-San-Gregorio, M.A.; Reiter, R.J. The role of melatonin in the immune-neuro-psychology of mental disorders. Recent Pat CAN Drug Discov. 2009, 4, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpy, M.J.; Korman, E.; Spielman, A.J.; Glovinsky, P.B. Delayed sleep phase syndrome in adolescents. J. Adolesc. Health Care 1988, 9, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, S.J.; Van Reen, E.; LeBourgeois, M.K.; Acebo, C.; Tarokh, L.; Seifer, R.; Barker, D.H.; Carskadon, M.A. A longitudinal assessment of sleep timing, circadian phase, and phase angle of entrainment across human adolescence. PLoS ONE 2014, 7, e112199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowley, S.J.; Acebo, C.; Carskadon, M.A. Sleep, circadian rhythms, and delayed phase in adolescence. Sleep Med. 2007, 8, 602–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carskadon, M.A.; Acebo, C.; Jenni, O.G. Regulation of adolescent sleep: Implications for behavior. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004, 1021, 276–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onaolapo, O.J.; Onaolapo, A. Melatonin, adolescence, and the brain: An insight into the period-specific influences of a multifunctional signaling molecule. Birth Defects Res. 2017, 109, 1659–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiesner, C.D.; Davoli, V.; Schurger, D.; Prehn-Kristensen, A.; Baving, L. Melatonin secretion during a short nap fosters subsequent feedback learning. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harman, D. Aging: A theory based on free radical and radiation chemistry. J. Gerontol. 1956, 11, 298–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tresguerres, J.A.; Kireev, R.; Forman, K.; Cuesta, S.; Tresguerres, A.F.; Vara, E. Effect of chronic melatonin administration on several physiological parameters from old Wistar rats and SAMP8 mice. Curr. Aging Sci. 2012, 5, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugger, P.; Marktl, W.; Herold, M. Impaired nocturnal secretion of melatonin in coronary heart disease. Lancet 1995, 345, 1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blask, D.E. Melatonin, sleep disturbance and cancer risk. Sleep Med. Rev. 2009, 13, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.Y.; Zhou, J.N.; van Heerikhuize, J.; Hofman, M.A.; Swaab, D.F. Decreased melatonin levels in postmortem cerebrospinal fluid in relation to aging, Alzheimer’s disease, and apolipoprotein E-epsilon4/4 genotype. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1999, 84, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sharman, E.H.; Sharman, K.G.; Bondy, S.C. Extended exposure to dietary melatonin reduces tumor number and size in aged male mice. Exp. Gerontol. 2011, 46, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Meng, X.; Zhang, J.J.; Xu, D.P.; Li, H. Melatonin in the prevention and treatment of cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 39896–39921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, S.M.; Belancio, V.P.; Dauchy, R.T.; Xiang, S.; Brimer, S.; Mao, L.; Hauch, A.; Lundberg, P.W.; Summers, W.; Yuan, L.; et al. Melatonin: An inhibitor of breast cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2015, 22, R183–R204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamarkin, L.; Cohen, M.; Roselle, D.; Reichert, C.; Lippman, M.; Chabner, B. Melatonin inhibition and pinealectomy enhancement of 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene-induced mammary tumors in the rat. Cancer Res. 1981, 41, 4432–4436. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shah, P.N.; Mhatre, M.C.; Kothari, L.S. Effect of melatonin on mammary carcinogenesis in intact and pinealectomized rats in varying photoperiods. Cancer Res. 1984, 44, 3403–3407. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Anisimov, V.N.; Alimova, I.N.; Baturin, D.A.; Popovich, I.G.; Zabezhinski, M.A.; Rosenfeld, S.V.; Manton, K.G.; Semenchenko, A.V.; Yashin, A.I. Dose-dependent effect of melatonin on life span and spontaneous tumor incidence in female SHR mice. Exp. Gerontol. 2003, 38, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, P.; Mirunalini, S.; Dakshayani, K.B.; Pandi-Perumal, S.R.; Trakht, I.; Cardinali, D.P. Prevention by melatonin of hepatocarcinogenesis in rats injected with N-nitrosodiethylamine. J. Pineal Res. 2007, 43, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blask, D.E.; Sauer, L.A.; Dauchy, R.T.; Holowachuk, E.W.; Ruhoff, M.S.; Kopff, H.S. Melatonin inhibition of cancer growth in vivo involves suppression of tumor fatty acid metabolism via melatonin receptor-mediated signal transduction events. Cancer Res. 1999, 15, 4693–4701. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Rabelo, J.F.; Vázquez, R.; Perea, M.D.; Cruz, A.; González, R.; Romero, A.; Muñoz-Villanueva, M.C.; Túnez, I.; Montilla, P.; Muntané, J.; et al. Beneficial properties of melatonin in an experimental model of pancreatic cancer. J. Pineal Res. 2007, 43, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuffa, L.G.; Fioruci-Fontanelli, B.A.; Mendes, L.O.; Fávaro, W.J.; Pinheiro, P.F.; Martinez, M.; Martinez, F.E. Characterization of chemically induced ovarian carcinomas in an ethanol-preferring rat model: Influence of long-term melatonin treatment. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.E.; Kim, S.J.; Youn, J.P.; Hwang, S.Y.; Park, C.S.; Park, Y.S. MicroRNA and gene expression analysis of melatonin-exposed human breast cancer cell lines indicating involvement of the anticancer effect. J. Pineal Res. 2011, 51, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.E.; Kim, S.J.; Yoon, H.J.; Yu, S.Y.; Yang, H.; Jeong, S.I.; Hwang, S.Y.; Park, C.S.; Park, Y.S. Genome-wide profiling in melatonin-exposed human breast cancer cell lines identifies differentially methylated genes involved in the anticancer effect of melatonin. J. Pineal Res. 2013, 54, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sainz, R.M.; Mayo, J.C.; Tan, D.X.; León, J.; Manchester, L.; Reiter, R.J. Melatonin reduces prostate cancer cell growth leading to neuroendocrine differentiation via a receptor and PKA independent mechanism. Prostate 2005, 63, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbajo-Pescador, S.; García-Palomo, A.; Martín-Renedo, J.; Piva, M.; González-Gallego, J.; Mauriz, J.L. Melatonin modulation of intracellular signaling pathways in hepatocarcinoma HepG2 cell line: Role of the MT1 receptor. J. Pineal Res. 2011, 51, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung-Hynes, B.; Reiter, R.J.; Ahmad, N. Sirtuins, melatonin, and circadian rhythms: Building a bridge between aging and cancer. J. Pineal Res. 2010, 48, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schernhammer, E.S.; Schulmeister, K. Melatonin and cancer risk: Does light at night compromise physiologic cancer protection by lowering serum melatonin levels? Br. J. Cancer 2007, 90, 941–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantermann, T.; Roenneberg, T. Is light-at-night a health risk factor or a health risk predictor? Chronobiol. Int. 2009, 2, 1069–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, G.; Yoon, K.A.; Chi, H.; Roh, J.; Kim, J.H. Decreased concentration of serum melatonin in nighttime compared with daytime female medical technologists in South Korea. Chronobiol. Int. 2016, 33, 1305–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, M.; Tranmer, J.; Hung, E.; Korsiak, J.; Day, A.G.; Aronson, K.J. Shift Work, Chronotype, and Melatonin Patterns among Female Hospital Employees on Day and Night Shifts. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2016, 25, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, P.; Bertrand, K.A.; Hart, J.E.; Schernhammer, E.S.; Tamimi, R.M.; Laden, F. Outdoor light at night and breast cancer incidence in the Nurses’ Health Study II. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 087010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papantoniou, K.; Pozo, O.J.; Espinosa, A.; Marcos, J.; Castaño-Vinyals, G.; Basagaña, X.; Juanola Pagès, E.; Mirabent, J.; Martín, J.; Such Faro, P.; et al. Increased and mistimed sex hormone production in night shift workers. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2015, 24, 854–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benabu, J.C.; Stoll, F.; Gonzalez, M.; Mathelin, C. Night work, shift work: Breast cancer risk factor? Gynecol. Obstet. Fertil. 2015, 43, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubatka, P.; Zubor, P.; Busselberg, D.; Kwon, T.K.; Adamek, M.; Petrovic, D.; Opatrilova, R.; Gazdikova, K.; Caprnda, M.; Rodrigo, L.; et al. Melatonin and breast cancer: Evidences from preclinical and human studies. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2018, 122, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirth, M.D.; Andrew, M.E.; Burchfiel, C.M.; Burch, J.B.; Fekedulegn, D.; Hartley, T.A.; Charles, L.E.; Violanti, J.M. Association of shiftwork and immune cells among police officers from the Buffalo Cardio-metabolic occupational police stress study. Chronobiol. Int. 2017, 34, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dycke, K.C.; Rodenburg, W.; van Oostrom, C.T.; van Kerkhof, L.W.; Pennings, J.L.; Roenneberg, T.; van Steeg, H.; van der Horst, G.T. Chronically alternating light cycles Increase breast cancer risk in mice. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 1932–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otálora, B.B.; Madrid, J.A.; Alvarez, N.; Vicente, V.; Rol, M.A. Effects of exogenous melatonin and circadian synchronization on tumor progression in melanoma-bearing C57BL6 mice. J. Pineal Res. 2008, 44, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venegas, C.; García, J.A.; Escames, G.; Ortiz, F.; López, A.; Doerrier, C.; García-Corzo, L.; López, L.C.; Reiter, R.J.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D. Extrapineal melatonin: Analysis of its subcellular distribution and daily fluctuations. J. Pineal Res. 2012, 52, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dauchy, R.T.; Xiang, S.; Mao, L.; Brimer, S.; Wren, M.A.; Yuan, L.; Anbalagan, M.; Hauch, A.; Frasch, T.; Rowan, B.G.; et al. Circadian and melatonin disruption by exposure to light at night drives intrinsic resistance to tamoxifen therapy in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 4099–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, S.; Dauchy, R.T.; Hauch, A.; Mao, L.; Yuan, L.; Wren, M.A.; Belancio, V.P.; Mondal, D.; Frasch, T.; Blask, D.E.; et al. Doxorubicin resistance in breast cancer is driven by light at night-induced disruption of the circadian melatonin signal. J. Pineal Res. 2015, 59, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Z.W.; Liu, T.; Li, Y.; Chen, P.; Peng, X.; Ma, C.; Zhang, W.J.; Li, P.D. Melatonin suppresses thyroid cancer growth and overcomes radioresistance via inhibition of p65 phosphorylation and induction of ROS. Redox Biol. 2018, 16, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borin, T.F.; Arbab, A.S.; Gelaleti, G.B.; Ferreira, L.C.; Moschetta, M.G.; Jardim-Perassi, B.V.; Iskander, A.S.; Varma, N.R.; Shankar, A.; Coimbra, V.B.; et al. Melatonin decreases breast cancer metastasis by modulating Rho-associated kinase protein-1 expression. J. Pineal Res. 2016, 60, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.M.; Lin, W.Y.; Shen, C.C.; Pan, H.C.; Keh-Bin, W.; Chen, Y.C.; Jan, Y.J.; Lai, D.W.; Tang, S.C.; Tien, H.R.; et al. Melatonin set out to ER stress signaling thwarts epithelial mesenchymal transition and peritoneal dissemination via calpain-mediated C/EBPβ and NFκB cleavage. J. Pineal Res. 2016, 60, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.W.; Lee, L.M.; Lee, W.J.; Chu, C.Y.; Tan, P.; Yang, Y.C.; Chen, W.Y.; Yang, S.F.; Hsiao, M.; Chien, M.H. Melatonin inhibits MMP-9 transactivation and renal cell carcinoma metastasis by suppressing Akt-MAPKs pathway and NF-κB DNA-binding activity. J. Pineal Res. 2016, 60, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Wang, Z.; Hu, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, C.; Yang, H.; Wang, H.; Fang, Z.; Wu, L.; Chen, X. The melatonin-MT1 receptor axis modulates tumor growth in PTEN-mutated gliomas. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 496, 1322–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves Ndo, N.; Colombo, J.; Lopes, J.R.; Gelaleti, G.B.; Moschetta, M.G.; Sonehara, N.M.; Hellmén, E.; Zanon Cde, F.; Oliani, S.M.; Zuccari, D.A. Effect of melatonin in epithelial mesenchymal transition markers and invasive properties of breast cancer stem cells of canine and human cell lines. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Gui, S.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, Y. Melatonin inhibits the migration of human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cell lines involving JNK/MAPK pathway. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhelev, Z.; Ivanova, D.; Bakalova, R.; Aoki, I.; Higashi, T. Synergistic cytotoxicity of melatonin and new-generation anticancer drugs against leukemia lymphocytes but not normal lymphocytes. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelaleti, G.B.; Borin, T.F.; Maschio-Signorini, L.B.; Moschetta, M.G.; Jardim-Perassi, B.V.; Calvinho, G.B.; Facchini, M.C.; Viloria-Petit, A.M.; de Campos Zuccari, D.A.P. Efficacy of melatonin, IL-25 and siIL-17B in tumorigenesis-associated properties of breast cancer cell lines. Life Sci. 2017, 183, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.J.; Um, S.J. SIRT1: Roles in aging and cancer. BMB Rep. 2008, 41, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayo, J.C.; Sainz, R.M.; González Menéndez, P.; Cepas, V.; Tan, D.X.; Reiter, R.J. Melatonin and sirtuins: A “not-so unexpected” relationship. J. Pineal Res. 2017, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, E.; Wu, P.; Seely, D.; Guyatt, G. Melatonin in the treatment of cancer: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials and meta-analysis. J. Pineal Res. 2005, 39, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lissoni, P.; Brivio, F.; Fumagalli, L.; Messina, G.; Vigoré, L.; Parolini, D.; Colciago, M.; Rovelli, F. Neuroimmunomodulation in medical oncology: Application of psychoneuroimmunology with subcutaneous low-dose IL-2 and the pineal hormone melatonin in patients with untreatable metastatic solid tumors. Anticancer Res. 2008, 28, 1377–1381. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lissoni, P. Biochemotherapy with standard chemotherapies plus the pineal hormone melatonin in the treatment of advanced solid neoplasms. Pathol. Biol. (Paris) 2007, 55, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lissoni, P.; Chilelli, M.; Villa, S.; Cerizza, L.; Tancini, G. Five years survival in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with chemotherapy alone or chemotherapy and melatonin: A randomized trial. J. Pineal Res. 2003, 35, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seely, D.; Wu, P.; Fritz, H.; Kennedy, D.A.; Tsui, T.; Seely, A.J.; Mills, E. Melatonin as adjuvant cancer care with and without chemotherapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomov, B.; Popov, D.; Tomova, R.; Vladov, N.; Den Otter, W.; Krastev, Z. Therapeutic response of untreatable hepatocellular carcinoma after application of the immune modulators IL-2, BCG and melatonin. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 4531–4535. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Onseng, K.; Johns, N.P.; Khuayjarernpanishk, T.; Subongkot, S.; Priprem, A.; Hurst, C.; Johns, J. Beneficial effects of adjuvant melatonin in minimizing oral mucositis complications in head and neck cancer patients receiving concurrent chemoradiation. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2017, 23, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund Rasmussen, C.; Klee Olsen, M.; Thit Johnsen, A.; Petersen, M.A.; Lindholm, H.; Andersen, L.; Villadsen, B.; Groenvold, M.; Pedersen, L. Effects of melatonin on physical fatigue and other symptoms in patients with advanced cancer receiving palliative care: A double-blind placebo-controlled crossover trial. Cancer 2015, 121, 3727–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, S.G.; Melan, M.A.; Latimer, J.J.; Witt-Enderby, P.A. Melatonin and breast cancer: Cellular mechanisms, clinical studies and future perspectives. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2009, 11, e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norsa, A.; Martino, V. Somatostatin, retinoids, melatonin, vitamin D, bromocriptine, and cyclophosphamide in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients with low performance status. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2006, 21, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Bella, G.; Leci, J.; Ricchi, A.; Toscano, R. Recurrent glioblastoma multiforme (grade IV—WHO 2007): A case of complete objective response—Concomitant administration of somatostatin/octreotide, retinoids, Vit E, Vit D3, Vit C, melatonin, D2 R agonists (Di Bella Method). Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 2015, 36, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Allis, C.D.; Jenuwein, T. The molecular hallmarks of epigenetic control. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkmaz, A.; Reiter, R.J. Epigenetic regulation: A new research area for melatonin? J. Pineal Res. 2008, 44, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, C.M.; Lin, C.W.; Yang, J.S.; Yang, W.E.; Su, S.C.; Yang, S.F. Melatonin inhibits TPA-induced oral cancer cell migration by suppressing matrix metalloproteinase-9 activation through the histone acetylation. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 21952–21967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.Y.; Li, W.M.; Zhou, L.L.; Lu, Q.N.; He, W. Melatonin induces apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells through HDAC4 nuclear import mediated by CaMKII inactivation. J. Pineal Res. 2015, 58, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Niles, L.P. Epigenetic mechanisms of melatonin action in human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2015, 402, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.Y.; Lin, C.K.; Tsao, C.H.; Hsieh, C.C.; Lin, G.J.; Ma, K.H.; Shieh, Y.S.; Sytwu, H.K.; Chen, Y.W. Melatonin exerts anti-oral cancer effect via suppressing LSD1 in patient-derived tumor xenograft models. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 33756–33769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwimmer, H.; Metzer, A.; Pilosof, Y.; Szyf, M.; Machnes, Z.M.; Fares, F.; Harel, O.; Haim, A. Light at night and melatonin have opposite effects on breast cancer tumors in mice assessed by growth rates and global DNA methylation. Chronobiol. Int. 2014, 31, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín, V.; Sanchez-Sanchez, A.M.; Herrera, F.; Gomez-Manzano, C.; Fueyo, J.; Alvarez-Vega, M.A.; Antolín, I.; Rodriguez, C. Melatonin-induced methylation of the ABCG2/BCRP promoter as a novel mechanism to overcome multidrug resistance in brain tumour stem cells. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 2005–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, F.; Ferraiuolo, M.; Santoro, R.; Sacconi, A.; Goeman, F.; Pallocca, M.; Pulito, C.; Korita, E.; Fanciulli, M.; Muti, P.; et al. Multitargeting activity of miR-24 inhibits long-term melatonin anticancer effects. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 20532–20548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, E.J.; Won, G.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.H. Upregulation of miRNA3195 and miRNA374b mediates the anti-angiogenic properties of melatonin in hypoxic PC-3 prostate cancer cells. J. Cancer 2015, 6, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Huang, Q.; Zhu, H. Melatonin inhibits the proliferation of gastric cancer cells through regulating the miR-16-5p- and Smad3 Pathway. DNA Cell Biol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Lu, Z.; Ji, C.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lei, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.T.; Li, X. Melatonin inhibits proliferation and invasion via repression of miRNA-155 in glioma cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 93, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poland, G.A.; Ovsyannikova, I.G.; Kennedy, R.B.; Lambert, N.D.; Kirkland, J.L. A systems biology approach to the effect of aging, immunosenescence and vaccine response. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2014, 29, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, L.; Pawelec, G. As we age: Does slippage of quality control in the immune system lead to collateral damage? Ageing Res. Rev. 2015, 23, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharman, E.H.; Bondy, S.C.; Sharman, K.Z.; Lahiri, D.; Cotman, C.; Perreau, V.M. Effects of melatonin and age on gene expression in mouse CNS using microarray analysis. Neurochem. Int. 2007, 50, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yancik, R.; Ries, L.A. Cancer in older persons: An international issue in an aging world. Semin. Oncol. 2004, 31, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondy, S.C. Melatonin: Beneficial Aspects and Underlying Mechanisms. In Melatonin: Medical Uses and Role in Health and Disease; Correia, L., Meyers, G., Eds.; Nova Press: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 277–294. ISBN 978-1-53612-987-8. [Google Scholar]
- Sharman, E.H.; Sharman, K.G.; Bondy, S.C. Melatonin causes gene expression in aged animals to respond to inflammatory stimuli in a manner differing from that of young animals. Curr. Aging Sci. 2008, 1, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chovancova, B.; Hudecova, S.; Lencesova, L.; Babula, P.; Rezuchova, I.; Penesova, A.; Grman, M.; Moravcik, R.; Zeman, M.; Krizanova, O. Melatonin-Induced Changes in Cytosolic Calcium Might be Responsible for Apoptosis Induction in Tumour Cells. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 44, 763–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, L.J.; Yu, H.Q.; Fan, L.L.; Li, X.Q.; Wang, F.; Liu, J.T.; Zhong, F.; Zhang, C.J.; Wei, W.; Wang, H.; et al. Melatonin, a novel selective ATF-6 inhibitor, induces human hepatoma cell apoptosis through COX-2 downregulation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 986–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Hoffmann, K.; Gao, C.; Petrulionis, M.; Herr, I.; Schemmer, P. Melatonin promotes sorafenib-induced apoptosis through synergistic activation of JNK/c-jun pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Pineal Res. 2017, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, C.; Yu, W.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Feng, X.; Hao, J.; Zhang, K.; et al. Melatonin synergizes the chemotherapeutic effect of 5-fluorouracil in colon cancer by suppressing PI3K/AKT and NF-κB/iNOS signaling pathways. J. Pineal Res. 2017, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivedi, P.P.; Jena, G.B.; Tikoo, K.B.; Kumar, V. Melatonin modulated autophagy and Nrf2 signaling pathways in mice with colitis-associated colon carcinogenesis. Mol. Carcinog. 2016, 55, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santofimia-Castaño, P.; Clea Ruy, D.; Garcia-Sanchez, L.; Jimenez-Blasco, D.; Fernandez-Bermejo, M.; Bolaños, J.P.; Salido, G.M.; Gonzalez, A. Melatonin induces the expression of Nrf2-regulated antioxidant enzymes via PKC and Ca2+ influx activation in mouse pancreatic acinar cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 87, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahiri, D.K.; Ge, Y.W.; Sharman, E.H.; Bondy, S.C. Age-related changes in serum melatonin in mice: Higher levels of combined melatonin and 6-hydroxymelatonin sulfate in the cerebral cortex than serum, heart, liver and kidney tissues. J. Pineal Res. 2004, 36, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Moreno, C.; Dorfman, S.E.; Lichtenstein, A.H.; Martin, A. Dietary fat type affects vitamins C and E and biomarkers of oxidative status in peripheral and brain tissues of golden Syrian hamsters. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewczuk, B.; Ziółkowska, N.; Prusik, M.; Przybylska-Gornowicz, B. Diurnal profiles of melatonin synthesis-related indoles, catecholamines and their metabolites in the duck pineal organ. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 12604–12630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janjetovic, Z.; Jarrett, S.G.; Lee, E.F.; Duprey, C.; Reiter, R.J.; Slominski, A.T. Melatonin and its metabolites protect human melanocytes against UVB-induced damage: Involvement of NRF2-mediated pathways. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goradel, N.H.; Asghari, M.H.; Moloudizargari, M.; Negahdari, B.; Haghi-Aminjan, H.; Abdollahi, M. Melatonin as an angiogenesis inhibitor to combat cancer: Mechanistic evidence. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 335, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, A.; González-González, A.; Alonso-González, C.; Menéndez-Menéndez, J.; Martínez-Campa, C.; Cos, S. Melatonin inhibits angiogenesis in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells by downregulation of VEGF. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 2433–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maschio-Signorini, L.B.; Gelaleti, G.B.; Moschetta, M.G.; Borin, T.F.; Jardim-Perassi, B.V.; Lopes, J.R.; Lacerda, J.Z.; Roela, R.A.; Bordin, N.A.; Corrêa, L.A.; et al. Melatonin regulates angiogenic and inflammatory proteins in MDA-MB-231 cell line and in co-culture with cancer-associated fibroblasts. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 1474–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.Y.; Chuang, W.L. High therapeutic concentration of prazosin up-regulates angiogenic IL6 and CCL2 genes in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2012, 66, 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osanai, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Otsu, M.; Izawa, T.; Sakai, K.; Iwashita, M. Ramelteon, a selective MT1/T2 receptor agonist, suppresses the proliferation and invasiveness of endometrial cancer cells. Hum. Cell. 2017, 30, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourboulia, D.; Stetler-Stevenson, W.G. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs): Positive and negative regulators in tumor cell adhesion. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2010, 20, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winczyk, K.; Fuss-Chmielewska, J.; Lawnicka, H.; Pawlikowski, M.; Karasek, M. Luzindole but not 4-phenyl-2-propionamidotetralin (4P-PDOT) diminishes the inhibitory effect of melatonin on murine Colon 38 cancer growth in vitro. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 2009, 30, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cutando, A.; López-Valverde, A.; De Vicente, J.; Gimenez, J.L.; Carcía, I.A.; De Diego, R.G. Action of melatonin on squamous cell carcinoma and other tumors of the oral cavity. Oncol. Lett. 2014, 7, 923–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, J.R.; Maschio, L.B.; Jardim-Perassi, B.V.; Moschetta, M.G.; Ferreira, L.C.; Martins, G.R.; Gelaleti, G.B.; De Campos Zuccari, D.A. Evaluation of melatonin treatment in primary culture of canine mammary tumors. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 311–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girgert, R.; Hanf, V.; Emons, G.; Gründker, C. Membrane-bound melatonin receptor MT1 down-regulates estrogen responsive genes in breast cancer cells. J. Pineal Res. 2009, 47, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, S.M.; Cheng, C.; Yuan, L.; Mao, L.; Jockers, R.; Dauchy, B.; Blask, D.E. Age-related decline in melatonin and its MT1 receptor are associated with decreased sensitivity to melatonin and enhanced mammary tumor growth. Curr. Aging Sci. 2013, 6, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suofu, Y.; Li, W.; Jean-Alphonse, F.G.; Jia, J.; Khattar, N.K.; Li, J.; Baranov, S.V.; Leronni, D.; Mihalik, A.C.; He, Y.; et al. Dual role of mitochondria in producing melatonin and driving GPCR signaling to block cytochrome c release. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E7997–E8006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pariente, R.; Bejarano, I.; Espino, J.; Rodríguez, A.B.; Pariente, J.A. Participation of MT3 melatonin receptors in the synergistic effect of melatonin on cytotoxic and apoptotic actions evoked by chemotherapeutics. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2017, 80, 985–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, R.M.; Reiter, R.J.; Schlabritz-Loutsevitch, N.; Ostrom, R.S.; Slominski, A.T. Melatonin membrane receptors in peripheral tissues: Distribution and functions. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 351, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Xiong, F.; Wang, X.; Qi, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, H. Nuclear receptor retinoid-related orphan receptor alpha promotes apoptosis but is reduced in human gastric cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 11105–11113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, J.A.; Volt, H.; Venegas, C.; Doerrier, C.; Escames, G.; López, L.C.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D. Disruption of the NF-κB/NLRP3 connection by melatonin requires retinoid-related orphan receptor-α and blocks the septic response in mice. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 3863–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Navarro, A.; González-Puga, C.; Escames, G.; López, L.C.; López, A.; López-Cantarero, M.; Camacho, E.; Espinosa, A.; Gallo, M.A.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D. Cellular mechanisms involved in the melatonin inhibition of HT-29 human colon cancer cell proliferation in culture. J. Pineal Res. 2007, 43, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.X.; Liu, H.; Xu, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, R.X. Melatonin downregulates nuclear receptor RZR/RORγ expression causing growth-inhibitory and anti-angiogenesis activity in human gastric cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liljevald, M.; Rehnberg, M.; Söderberg, M.; Ramnegård, M.; Börjesson, J.; Luciani, D.; Krutrök, N.; Brändén, L.; Johansson, C.; Xu, X.; et al. Retinoid-related orphan receptor γ (RORγ) adult induced knockout mice develop lymphoblastic lymphoma. Autoimmun. Rev. 2016, 15, 1062–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.H.; Li, Y.H.; Zhao, Y.S.; Zhai, Y.Z.; Zhang, L.C. Anti-aging effects of melatonin on the myocardial mitochondria of rats and associated mechanisms. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuffa, L.G.; Alves, M.S.; Martinez, M.; Camargo, I.C.; Pinheiro, P.F.; Domeniconi, R.F.; Júnior, L.A.; Martinez, F.E. Apoptosis is triggered by melatonin in an in vivo model of ovarian carcinoma. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2016, 23, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bondy, S.C.; Campbell, A. Mechanisms Underlying Tumor Suppressive Properties of Melatonin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082205
Bondy SC, Campbell A. Mechanisms Underlying Tumor Suppressive Properties of Melatonin. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(8):2205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082205
Chicago/Turabian StyleBondy, Stephen C., and Arezoo Campbell. 2018. "Mechanisms Underlying Tumor Suppressive Properties of Melatonin" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 8: 2205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082205
APA StyleBondy, S. C., & Campbell, A. (2018). Mechanisms Underlying Tumor Suppressive Properties of Melatonin. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(8), 2205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082205





