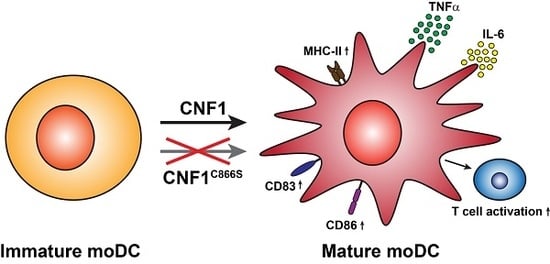
The Bacterial Toxin CNF1 Induces Activation and Maturation of Human Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
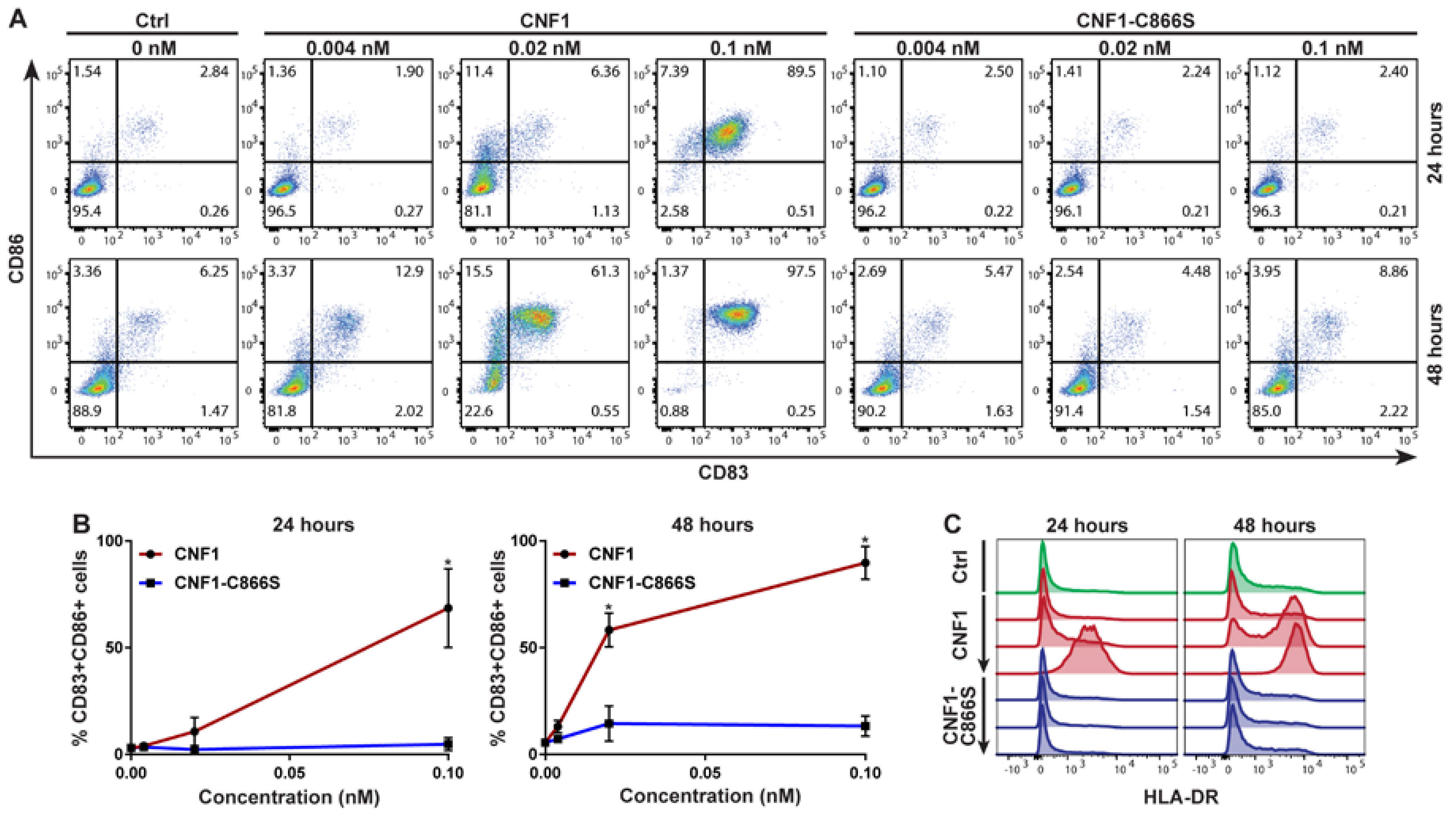
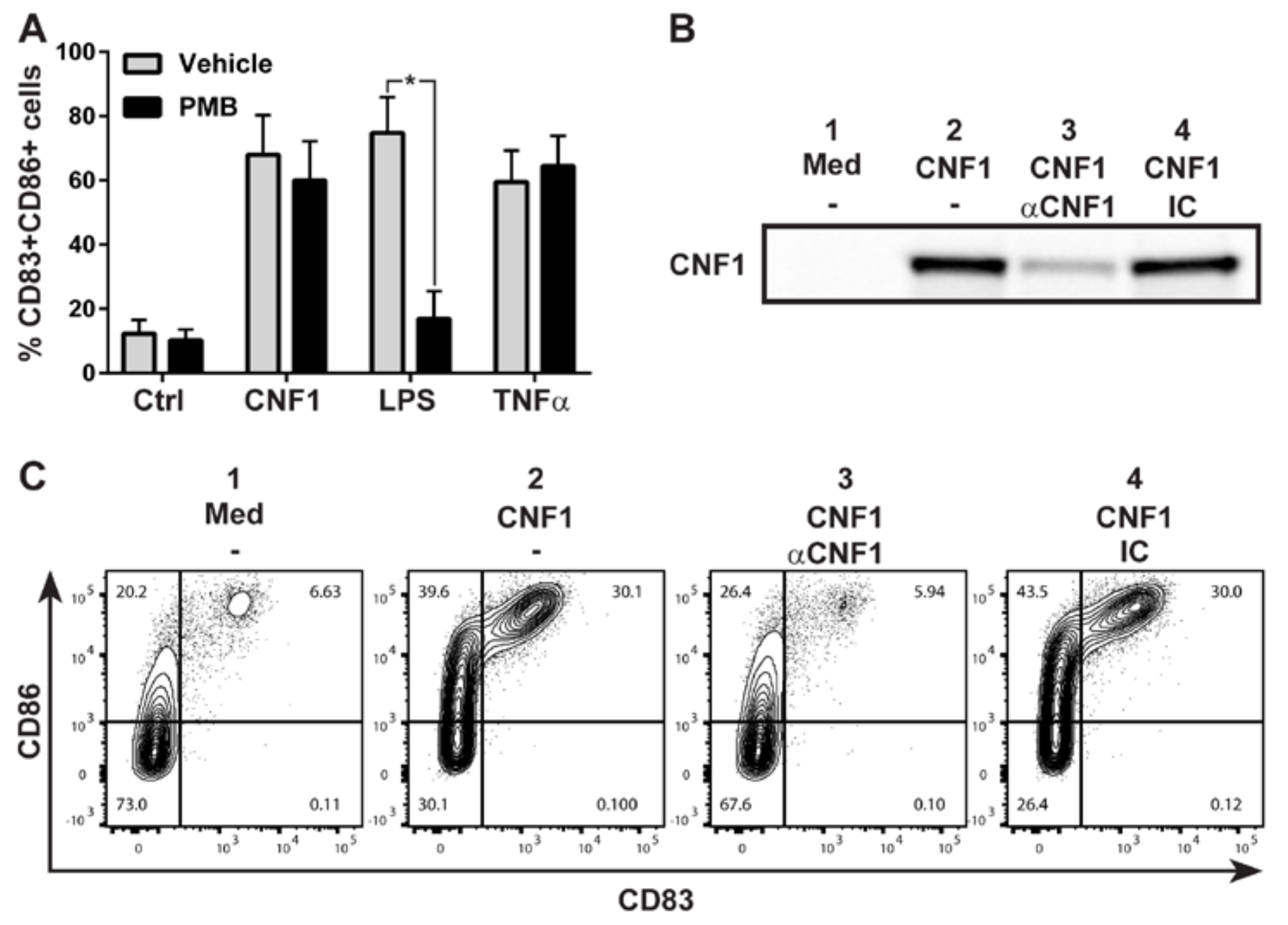
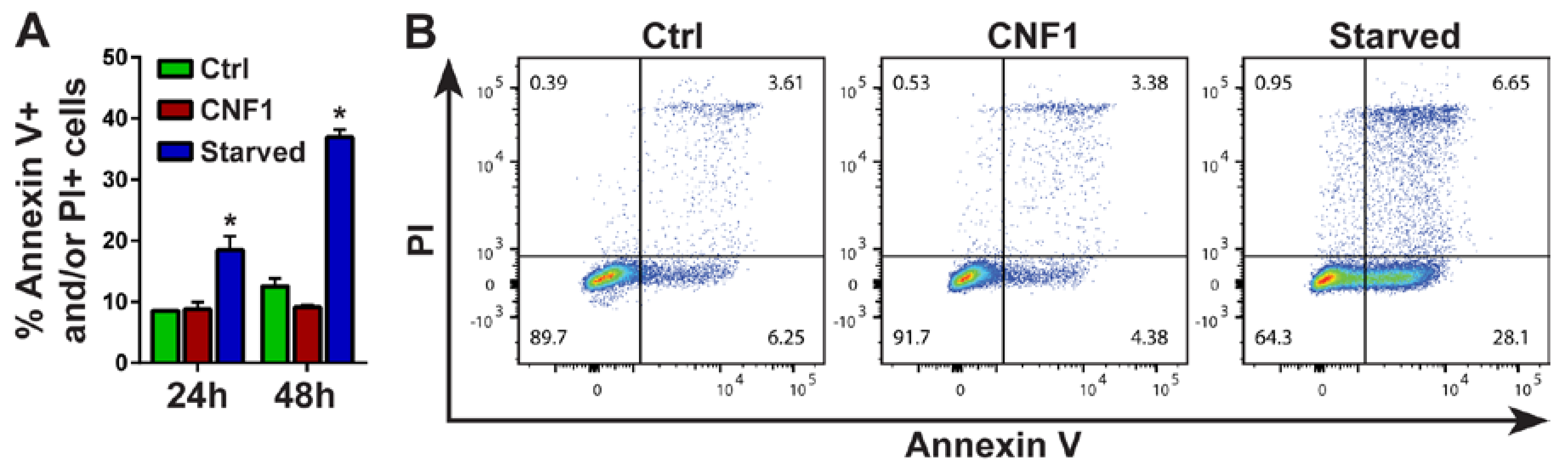
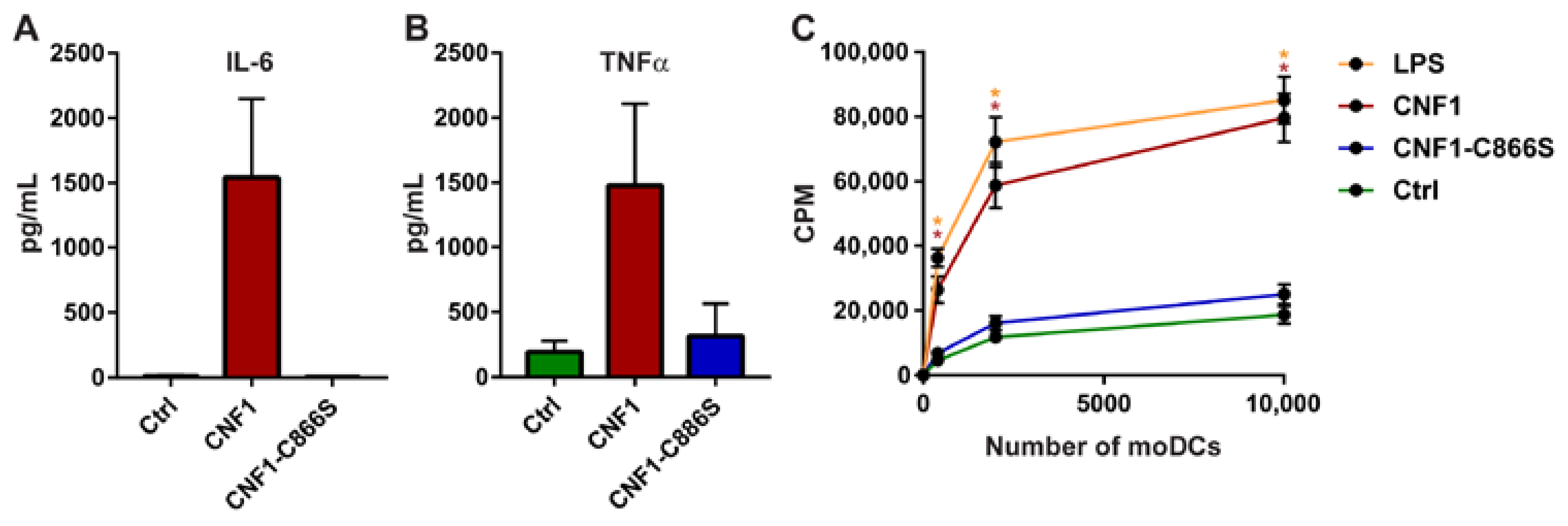
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Purification of CNF1 and CNF1-C866S
4.2. Purification of PBMCs and Generation of Immature moDCs
4.3. Flow Cytometry
4.4. CNF1 Depletion
4.5. ELISA
4.6. moDC-Induced Proliferation of Allogenic Naïve CD4+ T Cells
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CNF1 | Cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1 |
| DCs | Dendritic cells |
| MAMPs | Microbe-associated molecular patterns |
| moDCs | Monocyte-derived DCs |
| PMB | Polymyxin B |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| cDCs | Classical DCs |
| PBMCs | Peripheral blood mononuclear cells |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| TNFα | Tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| PBS | Phosphate buffered saline |
| PI | Propidium iodide |
| MHC | Major histocompatibility complex |
References
- Wang, M.H.; Kim, K.S. Cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1 contributes to Escherichia coli meningitis. Toxins 2013, 5, 2270–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petkovsek, Z.; Elersic, K.; Gubina, M.; Zgur-Bertok, D.; Starcic, E.M. Virulence potential of Escherichia coli isolates from skin and soft tissue infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 1811–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knust, Z.; Schmidt, G. Cytotoxic necrotizing factors (CNFs)—A growing toxin family. Toxins 2010, 2, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.W.; Hong, S.J.; Kim, K.J.; Goti, D.; Stins, M.F.; Shin, S.; Dawson, V.L.; Dawson, T.M.; Kim, K.S. 37-kDa laminin receptor precursor modulates cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1-mediated RhoA activation and bacterial uptake. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 16857–16862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, A.C.; Krishnan, S.; Prasadarao, N.V. The effects of cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1 expression in the uptake of Escherichia coli K1 by macrophages and the onset of meningitis in newborn mice. Virulence 2016, 7, 806–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piteau, M.; Papatheodorou, P.; Schwan, C.; Schlosser, A.; Aktories, K.; Schmidt, G. Lu/BCAM adhesion glycoprotein is a receptor for Escherichia coli Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 (CNF1). PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1003884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reppin, F.; Cochet, S.; El, N.W.; Fritz, G.; Schmidt, G. High affinity binding of Escherichia coli Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 (CNF1) to Lu/BCAM adhesion glycoprotein. Toxins 2017, 10, E3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falzano, L.; Fiorentini, C.; Donelli, G.; Michel, E.; Kocks, C.; Cossart, P.; Cabanie, L.; Oswald, E.; Boquet, P. Induction of phagocytic behaviour in human epithelial cells by Escherichia coli cytotoxic necrotizing factor type 1. Mol. Microbiol. 1993, 9, 1247–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrino, S.; Visvikis, O.; Doye, A.; Boyer, L.; Stefani, C.; Munro, P.; Bertoglio, J.; Gacon, G.; Mettouchi, A.; Lemichez, E. The E3 ubiquitin-ligase HACE1 catalyzes the ubiquitylation of active Rac1. Dev. Cell 2011, 21, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rippere-Lampe, K.E.; Lang, M.; Ceri, H.; Olson, M.; Lockman, H.A.; O’Brien, A.D. Cytotoxic necrotizing factor type 1-positive Escherichia coli causes increased inflammation and tissue damage to the prostate in a rat prostatitis model. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 6515–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rippere-Lampe, K.E.; O’Brien, A.D.; Conran, R.; Lockman, H.A. Mutation of the gene encoding cytotoxic necrotizing factor type 1 (CNF(1)) attenuates the virulence of uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 3954–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, Y.C.; Rasmussen, S.B.; Grande, K.K.; Conran, R.M.; O’Brien, A.D. Hemolysin of uropathogenic Escherichia coli evokes extensive shedding of the uroepithelium and hemorrhage in bladder tissue within the first 24 hours after intraurethral inoculation of mice. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 2978–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.A.; Weingarten, R.A.; Russo, L.M.; Ventura, C.L.; O’Brien, A.D. Antibodies against hemolysin and cytotoxic necrotizing factor type 1 (CNF1) reduce bladder inflammation in a mouse model of urinary tract infection with toxigenic uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 1661–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munro, P.; Flatau, G.; Anjuere, F.; Hofman, V.; Czerkinsky, C.; Lemichez, E. The Rho GTPase activators CNF1 and DNT bacterial toxins have mucosal adjuvant properties. Vaccine 2005, 23, 2551–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munro, P.; Flatau, G.; Lemichez, E. Intranasal immunization with tetanus toxoid and CNF1 as a new mucosal adjuvant protects BALB/c mice against lethal challenge. Vaccine 2007, 25, 8702–8706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, G.; Ferrua, B.; Munro, P.; Boyer, L.; Mathal, N.; Gillet, D.; Marty, P.; Lemichez, E. Immunoadjuvant properties of the Rho activating factor CNF1 in prophylactic and curative vaccination against Leishmania infantum. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer, L.; Magoc, L.; Dejardin, S.; Cappillino, M.; Paquette, N.; Hinault, C.; Charriere, G.M.; Ip, W.K.; Fracchia, S.; Hennessy, E.; et al. Pathogen-derived effectors trigger protective immunity via activation of the Rac2 enzyme and the IMD or Rip kinase signaling pathway. Immunity 2011, 35, 536–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diabate, M.; Munro, P.; Garcia, E.; Jacquel, A.; Michel, G.; Obba, S.; Goncalves, D.; Luci, C.; Marchetti, S.; Demon, D.; et al. Escherichia coli alpha-hemolysin counteracts the anti-virulence innate immune response triggered by the Rho GTPase activating toxin CNF1 during bacteremia. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer, L.; Lemichez, E. Switching Rho GTPase activation into effective antibacterial defenses requires the caspase-1/IL-1beta signaling axis. Small GTPases 2015, 6, 186–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dalod, M.; Chelbi, R.; Malissen, B.; Lawrence, T. Dendritic cell maturation: Functional specialization through signaling specificity and transcriptional programming. EMBO J. 2014, 33, 1104–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worbs, T.; Hammerschmidt, S.I.; Forster, R. Dendritic cell migration in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 30–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, P.; Palucka, A.K.; Pascual, V.; Banchereau, J. Dendritic cells and cytokines in human inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2008, 19, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuart, L.M.; Paquette, N.; Boyer, L. Effector-triggered versus pattern-triggered immunity: How animals sense pathogens. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duff, G.W.; Atkins, E. The inhibitory effect of polymyxin B on endotoxin-induced endogenous pyrogen production. J. Immunol. Methods 1982, 52, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, A.; Travaglione, S.; Fiorentini, C. Escherichia coli cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1 (CNF1): Toxin biology, in vivo applications and therapeutic potential. Toxins 2010, 2, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, K.; Albrekt, A.S.; Nelissen, I.; Santegoets, S.; de Gruijl, T.D.; Gibbs, S.; Lindstedt, M. Transcriptional profiling of human dendritic cell populations and models—Unique profiles of in vitro dendritic cells and implications on functionality and applicability. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e52875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, K.V.; Sutherland, R.M.; Zhan, Y.; Lew, A.M. Heterogeneity, functional specialization and differentiation of monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2017, 95, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, M.B.; Strobl, H.; Schuler, G.; Romani, N. GM-CSF Monocyte-derived cells and Langerhans cells as part of the dendritic cell family. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munro, P.; Flatau, G.; Doye, A.; Boyer, L.; Oregioni, O.; Mege, J.L.; Landraud, L.; Lemichez, E. Activation and proteasomal degradation of rho GTPases by cytotoxic necrotizing factor-1 elicit a controlled inflammatory response. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 35849–35857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falzano, L.; Quaranta, M.G.; Travaglione, S.; Filippini, P.; Fabbri, A.; Viora, M.; Donelli, G.; Fiorentini, C. Cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1 enhances reactive oxygen species-dependent transcription and secretion of proinflammatory cytokines in human uroepithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 4178–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malorni, W.; Quaranta, M.G.; Straface, E.; Falzano, L.; Fabbri, A.; Viora, M.; Fiorentini, C. The Rac-activating toxin cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1 oversees NK cell-mediated activity by regulating the actin/microtubule interplay. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 4195–4202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemichez, E.; Aktories, K. Hijacking of Rho GTPases during bacterial infection. Exp. Cell Res. 2013, 319, 2329–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keestra, A.M.; Winter, M.G.; Auburger, J.J.; Frassle, S.P.; Xavier, M.N.; Winter, S.E.; Kim, A.; Poon, V.; Ravesloot, M.M.; Waldenmaier, J.F.; et al. Manipulation of small Rho GTPases is a pathogen-induced process detected by NOD1. Nature 2013, 496, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keestra, A.M.; Baumler, A.J. Detection of enteric pathogens by the nodosome. Trends Immunol. 2014, 35, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krejsgaard, T.; Willerslev-Olsen, A.; Lindahl, L.M.; Bonefeld, C.M.; Koralov, S.B.; Geisler, C.; Wasik, M.A.; Gniadecki, R.; Kilian, M.; Iversen, L.; et al. Staphylococcal enterotoxins stimulate lymphoma-associated immune dysregulation. Blood 2014, 124, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gall-Mas, L.; Fabbri, A.; Namini, M.R.J.; Givskov, M.; Fiorentini, C.; Krejsgaard, T. The Bacterial Toxin CNF1 Induces Activation and Maturation of Human Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1408. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051408
Gall-Mas L, Fabbri A, Namini MRJ, Givskov M, Fiorentini C, Krejsgaard T. The Bacterial Toxin CNF1 Induces Activation and Maturation of Human Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(5):1408. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051408
Chicago/Turabian StyleGall-Mas, Laura, Alessia Fabbri, Martin R. J. Namini, Michael Givskov, Carla Fiorentini, and Thorbjørn Krejsgaard. 2018. "The Bacterial Toxin CNF1 Induces Activation and Maturation of Human Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 5: 1408. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051408
APA StyleGall-Mas, L., Fabbri, A., Namini, M. R. J., Givskov, M., Fiorentini, C., & Krejsgaard, T. (2018). The Bacterial Toxin CNF1 Induces Activation and Maturation of Human Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(5), 1408. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051408