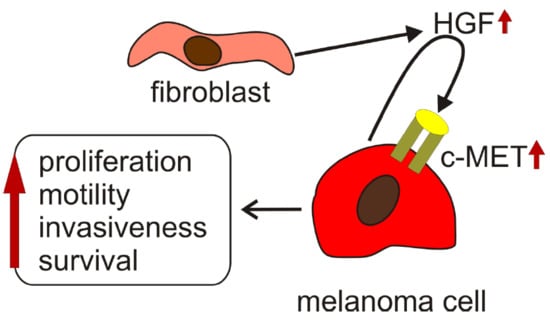
HGF/c-MET Signaling in Melanocytes and Melanoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
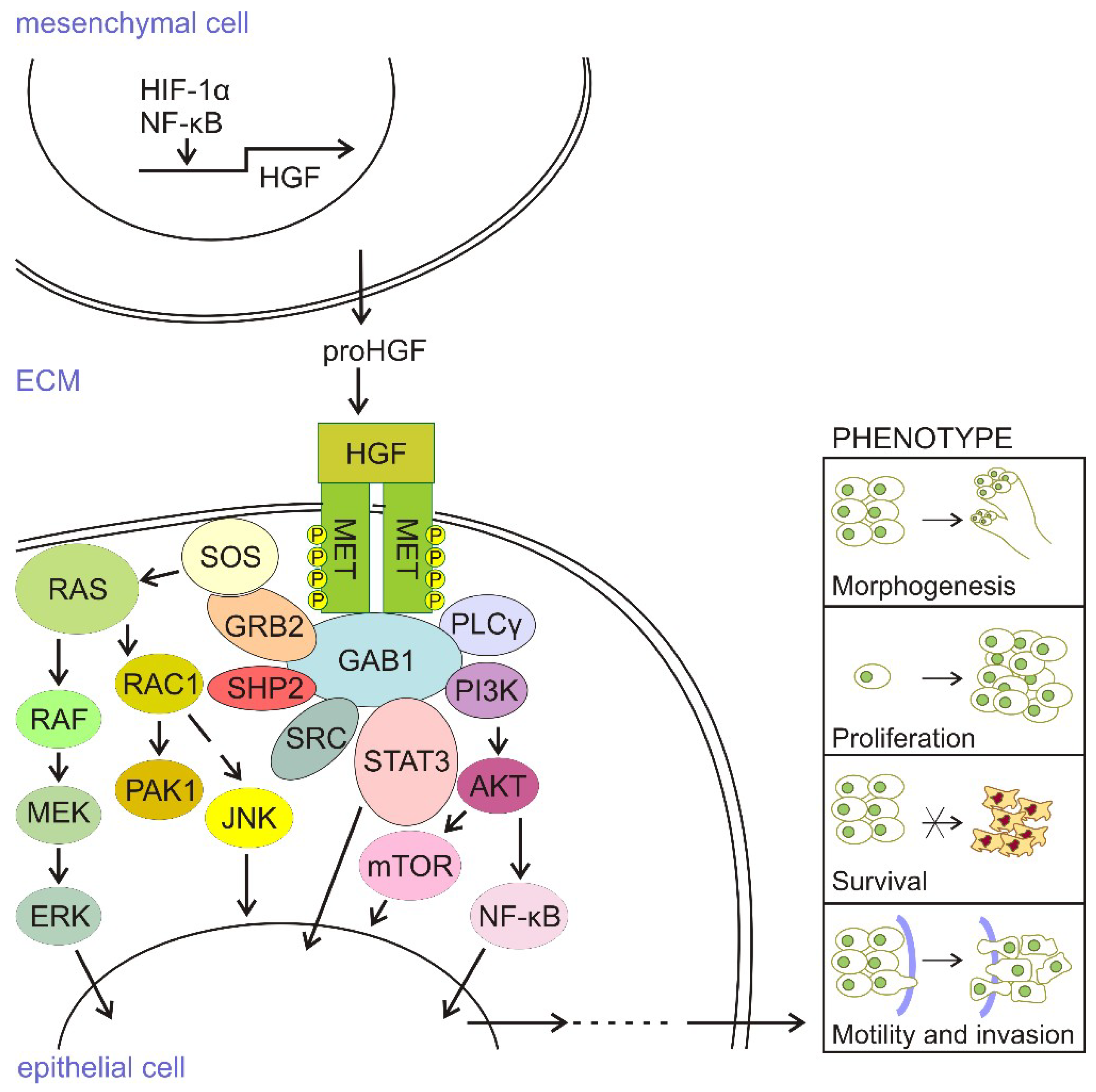
2. HGF/c-MET Signaling in the Skin
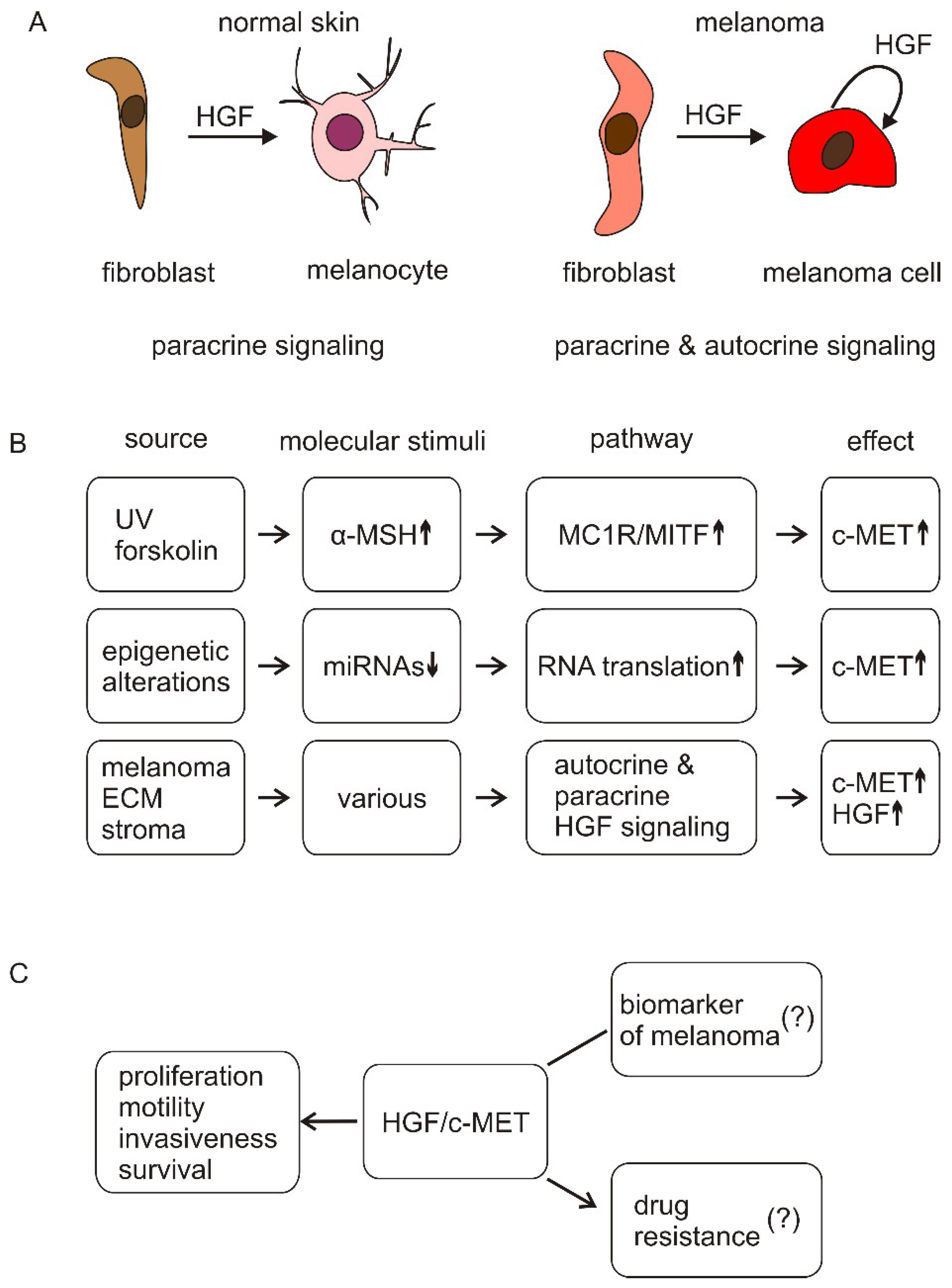
3. HGF/c-MET Signaling in Melanocytes
4. HGF/c-MET Signaling in Melanoma
5. HGF/c-MET Signaling in Melanoma that Is Resistant to Targeted Therapies
6. Preclinical Study Results
7. Clinical Results
8. Targeting HGF/c-MET Signaling in Melanoma
9. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nakamura, T.; Nawa, K.; Ichihara, A.; Kaise, N.; Nishino, T. Purification and subunit structure of hepatocyte growth factor from rat platelets. FEBS Lett. 1987, 224, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Nawa, K.; Ichihara, A. Partial purification and characterization of hepatocyte growth factor from serum of hepatectomized rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1984, 122, 1450–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Nishizawa, T.; Hagiya, M.; Seki, T.; Shimonishi, M.; Sugimura, A.; Tashiro, K.; Shimizu, S. Molecular cloning and expression of human hepatocyte growth factor. Nature 1989, 342, 440–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazawa, K.; Tsubouchi, H.; Naka, D.; Takahashi, K.; Okigaki, M.; Arakaki, N.; Nakayama, H.; Hirono, S.; Sakiyama, O.; Takahashi, K.; et al. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for human hepatocyte growth factor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1989, 163, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashio, K.; Shima, N.; Goto, M.; Itagaki, Y.; Nagao, M.; Yasuda, H.; Morinaga, T. Identity of a tumor cytotoxic factor from human fibroblasts and hepatocyte growth factor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1990, 170, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidner, K.M.; Arakaki, N.; Hartmann, G.; Vandekerckhove, J.; Weingart, S.; Rieder, H.; Fonatsch, C.; Tsubouchi, H.; Hishida, T.; Daikuhara, Y.; et al. Evidence for the identity of human scatter factor and human hepatocyte growth factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 7001–7005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, T.; Hagiya, M.; Shimonishi, M.; Nakamura, T.; Shimizu, S. Organization of the human hepatocyte growth factor-encoding gene. Gene 1991, 102, 213–219. [Google Scholar]
- Bottaro, D.P.; Rubin, J.S.; Faletto, D.L.; Chan, A.M.; Kmiecik, T.E.; Vande Woude, G.F.; Aaronson, S.A. Identification of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor as the c-met proto-oncogene product. Science 1991, 251, 802–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naldini, L.; Vigna, E.; Narsimhan, R.P.; Gaudino, G.; Zarnegar, R.; Michalopoulos, G.K.; Comoglio, P.M. Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) stimulates the tyrosine kinase activity of the receptor encoded by the proto-oncogene c-MET. Oncogene 1991, 6, 501–504. [Google Scholar]
- Uehara, Y.; Minowa, O.; Mori, C.; Shiota, K.; Kuno, J.; Noda, T.; Kitamura, N. Placental defect and embryonic lethality in mice lacking hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor. Nature 1995, 373, 702–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, C.; Bladt, F.; Goedecke, S.; Brinkmann, V.; Zschiesche, W.; Sharpe, M.; Birchmeier, C. Scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor is essential for liver development. Nature 1995, 373, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhownick, N.A.; Neilson, E.G.; Moses, H.L. Stromal fibroblasts in cancer initiation and progression. Nature 2004, 432, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furge, K.A.; Zhang, Y.W.; Vande Woude, G.F. Met receptor tyrosine kinase: Enhanced signaling through adapter proteins. Oncogene 2000, 19, 5582–5589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trusolino, L.; Bertotti, A.; Comoglio, P.M. MET signalling: Principles and functions in development, organ regeneration and cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bladt, F.; Riethmacher, D.; Isenmann, S.; Aguzzi, A.; Birchmeier, C. Essential role for the c-met receptor in the migration of myogenic precursor cells into the limb bud. Nature 1995, 376, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Sakai, K.; Nakamura, T.; Matsumoto, K. Hepatocyte growth factor twenty years on: Much more than a growth factor. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 26, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, T.; Uchiyama, S.; Tanaka, H.; Kataoka, H. Hepatocyte Growth Factor Activator: A Proteinase Linking Tissue Injury with Repair. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.F.; Vande Woude, G.F. HGF/SF-Met signaling in tumor progression. Cell Res. 2005, 15, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noriega-Guerra, H.; Freitas, V.M. Extracellular Matrix Influencing HGF/c-MET Signaling Pathway: Impact on Cancer Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Feng, Q.; Chen, W.-D.; Wang, Y.-D. HGF/c-MET: A Promising Therapeutic Target in the Digestive System Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, S.; Bhola, N.E.; Grandis, J.R. HGF/Met Signaling in Head and Neck Cancer: Impact on the Tumor Microenvironment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 4005–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, K.; Umitsu, M.; De Silva, D.M.; Roy, A.; Bottaro, D.P. Hepatocyte growth factor/MET in cancer progression and biomarker discovery. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendinelli, P.; Maroni, P.; Matteucci, E.; Desiderio, M.A. Epigenetic regulation of HGF/Met receptor axis is critical for the outgrowth of bone metastasis from breast carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takada, N.; Yano, Y.; Matsuda, T.; Otani, S.; Osugi, H.; Higashino, M.; Kinoshita, H.; Fukushima, S. Expression of immunoreactive human hepatocyte growth factor in human esophageal squamous cell carcinomas. Cancer Lett. 1995, 97, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boromand, N.; Hasanzadeh, M.; ShahidSales, S.; Farazestanian, M.; Gharib, M.; Fiuji, H.; Behboodi, N.; Ghobadi, N.; Hassanian, S.M.; Ferns, G.A.; et al. Clinical and prognostic value of the C-Met/HGF signaling pathway in cervical cancer. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 4490–4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, S.; Ojima, H.; Tsuda, H.; Hashimoto, J.; Morizane, C.; Ikeda, M.; Ueno, H.; Tamura, K.; Shimada, K.; Kanai, Y.; et al. Clinical impact of c-Met expression and its gene amplification in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 18, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.T.; Wu, J.R.; Cheng, C.C.; Wu, W.S. The Therapeutic Targeting of HGF/c-Met Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Alternative Approaches. Cancers 2017, 9, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abounader, R.; Laterra, J. Scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor in brain tumor growth and angiogenesis. Neuro Oncol. 2005, 7, 436–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Herdt, M.J.; Baatenburg de Jong, R.J. HGF and c-MET as potential orchestrators of invasive growth in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 2516–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, L.; Enders, J.; Thomas, S.M. Activated HGF-c-Met Axis in Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers 2017, 9, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquini, G.; Giaccone, G. C-MET inhibitors for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2018, 27, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seneviratne, D.; Ma, J.; Tan, X.; Kwon, Y.K.; Muhammad, E.; Melhem, M.; DeFrances, M.C.; Zarnegar, R. Genomic instability causes HGF gene activation in colon cancer cells, promoting their resistance to necroptosis. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Bradley, R.; Kang, L.; Koeman, J.; Ascierto, M.L.; Worschech, A.; De Giorgi, V.; Wang, E.; Kefene, L.; Su, Y.; et al. Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) autocrine activation predicts sensitivity to MET inhibition in glioblastoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lengyel, E.; Prechtel, D.; Resau, J.H.; Gauger, K.; Welk, A.; Lindemann, K.; Salanti, G.; Richter, T.; Knudsen, B.; Vande Woude, G.F.; et al. C-Met overexpression in node-positive breast cancer identifies patients with poor clinical outcome independent of Her2/neu. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 113, 678–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Renzo, M.F.; Poulsom, R.; Olivero, M.; Comoglio, P.M.; Lemoine, N.R. Expression of the Met/hepatocyte growth factor receptor in human pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.H.; Cheng, C.Y.; Su, T.; Fu, X.Q.; Guo, H.; Li, T.; Tse, A.K.; Kwan, H.Y.; Yu, H.; Yu, Z.L. Quercetin inhibits HGF/c-Met signaling and HGF-stimulated melanoma cell migration and invasion. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoker, M.; Gherardi, E.; Perryman, M.; Gray, J. Scatter factor is a fibroblast-derived modulator of epithelial cell mobility. Nature 1987, 327, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imokawa, G.; Yada, Y.; Morisaki, N.; Kimura, M. Biological characterization of human fibroblast-derived mitogenic factors for human melanocytes. Biochem. J. 1998, 330, 1235–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Tajima, H.; Nakamura, T. Hepatocyte growth factor is a potent stimulator of human melanocyte DNA synthesis and growth. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1991, 176, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, M.; Zhang, G.; Zarnegar, R.; Michalopoulos, G.; Myoken, Y.; McKeehan, W.L.; Stevens, J.L. Hepatocyte growth factor/hepatopoietin A stimulates the growth of rat kidney proximal tubule epithelial cells (RPTE), rat nonparenchymal liver cells, human melanoma cells, mouse keratinocytes and stimulates anchorage-independent growth of SV-40 transformed RPTE. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1991, 174, 331–337. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, C.; Tsuboi, R.; Shi, C.-M.; Rubin, J.S.; Ogawa, H. Comparative study of hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor and keratinocyte growth factor effects on human keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1995, 104, 958–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCawley, L.J.; O’Brien, P.; Hudson, L.G. Epidermal growth factor (EGF)- and scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor (SF/HGF)-mediated keratinocyte migration is coincident with induction of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9. J. Cell Physiol. 1998, 176, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohda, E.; Matsunaga, T.; Kataoka, H.; Takebe, T.; Yamamoto, I. Induction of hepatocyte growth factor in human skin fibroblasts by epidermal growth factor, platelet-derived growth factor and fibroblast growth factor. Cytokine 1994, 6, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohda, E.; Nagao, T.; Yamamoto, I. Stimulation of hepatocyte growth factor production in human fibroblasts by the protein phosphatase inhibitor okadaic acid. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2000, 60, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, Y.; Sotani, T.; Nagao, T.; Horio, T.; Yamamoto, I.; Gohda, E. Induction by staurosporine of hepatocyte growth factor production in human skin fibroblasts independent of protein kinase inhibition. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 66, 1797–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Okazaki, H.; Nakamura, T. Up-regulation of hepatocyte growth factor gene expression by interleukin-1 in human skin fibroblasts. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1992, 188, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takami, Y.; Motoki, T.; Yamamoto, I.; Gohda, E. Synergistic induction of hepatocyte growth factor in human skin fibroblasts by the inflammatory cytokines interleukin-1 and interferon-gamma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 327, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, Y.; Hiramatsu, K.; Hamauzu, R.; Motoki, T.; Miyazaki, M.; Uto, H.; Tsubouchi, H.; Tanaka, S.; Gohda, E. Mitogen-activated protein kinases-dependent induction of hepatocyte growth factor production in human dermal fibroblasts by the antibiotic polymyxin B. Cytokine 2012, 60, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Worthen, C.A.; Quan, T. Cell-size-dependent upregulation of HGF expression in dermal fibroblasts: Impact on human skin connective tissue aging. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2017, 88, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitoh, K.; Takahashi, H.; Sawada, N.; Parsons, P.G. Detection of the c-met proto-oncogene product in normal skin and tumours of melanocytic origin. J. Pathol. 1994, 174, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Itami, S.; Yoshikawa, K.; Tabata, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Nakamura, T. Neutralization of hepatocyte growth factor leads to retarded cutaneous wound healing associated with decreased neovascularization and granulation tissue formation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 120, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, G.; Menrad, A.; Gherardi, E.; Merlino, G.; Welker, P.; Handjiski, B.; Roloff, B.; Paus, R. Involvement of hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor and met receptor signaling in hair follicle morphogenesis and cycling. FASEB J. 2000, 14, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Nakamura, T. Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) as a tissue organizer for organogenesis and regeneration. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 239, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmielowiec, J.; Borowiak, M.; Morkel, M.; Stradal, T.; Munz, B.; Werner, S.; Wehland, J.; Birchmeier, C.; Birchmeier, W. c-Met is essential for wound healing in the skin. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 177, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, K.; Price, P.; Harding, K.G.; Jiang, W.G. The molecular and clinical impact of hepatocyte growth factor, its receptor, activators, and inhibitors in wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2006, 14, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.F.; Duan, H.F.; Wu, C.T.; Zhang, D.J.; Deng, Y.; Yin, H.L.; Han, B.; Gong, H.C.; Wang, H.W.; Wang, Y.L. HGF accelerates wound healing by promoting the dedifferentiation of epidermal cells through β1-integrin/ILK pathway. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 470418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, Y.; Ngo Thai Bich, V.; Furuya, M.; Hasegawa, H.; Takahashi, S.; Katagiri, N.; Hongu, T.; Funakoshi, Y.; Ohbayashi, N.; Kanaho, Y. The small G protein Arf6 expressed in keratinocytes by HGF stimulation is a regulator for skin wound healing. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagi, Z.; Hieronymus, T. The Impact of the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Regulator Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor/Met on Skin Immunity by Modulating Langerhans Cell Migration. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, T.; Imado, T.; Kitano, S.; Sano, H. Hepatocyte growth factor ameliorates dermal sclerosis in the tight-skin mouse model of scleroderma. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, R161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurz, S.M.; Diebold, S.S.; Hieronymus, T.; Gust, T.C.; Bartunek, P.; Sachs, M.; Birchmeier, W.; Zenke, M. The impact of c-met/scatter factor receptor on dendritic cell migration. Eur. J. Immunol. 2002, 32, 1832–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.H.; Birchmeier, C.; Zenke, M.; Hieronymus, T. The HGF receptor/Met tyrosine kinase is a key regulator of dendritic cell migration in skin immunity. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 1699–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilchrest, B.A.; Park, H.Y.; Eller, M.S.; Yaar, M. Mechanisms of ultraviolet light-induced pigmentation. Photochem. Photobiol. 1996, 63, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Pelling, J.C. UV-B/A irradiation of mouse keratinocytes results in p53-mediated WAF1. CIP1 expression. Oncogene 1995, 10, 1955–1960. [Google Scholar]
- Eller, M.S.; Maeda, T.; Magnoni, C.; Atwal, D.; Gilchrest, B.A. Enhancement of DNA repair in human skin cells by thymidine dinucleotides: Evidence for a p53-mediated mammalian SOS response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 12627–12632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mildner, M.; Eckhart, L.; Lengauer, B.; Tschachler, E. Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor inhibits UVB induced apoptosis of human keratinocytes via the PI-3-kinase pathway. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1999, 113, 1136–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noonan, F.P.; Otsuka, T.; Bang, S.; Anver, M.R.; Merlin, G. Accelerated Ultraviolet Radiation-induced Carcinogenesis in Hepatocyte Growth Factor/Scatter Factor Transgenic Mice. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 3738–3743. [Google Scholar]
- Brenner, M.; Degitz, K.; Besch, R.; Berking, C. Differential expression of melanoma-associated growth factors in keratinocytes and fibroblasts by ultraviolet A and ultraviolet B radiation. Br. J. Dermatol. 2005, 153, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mildner, M.; Mlitz, V.; Gruber, F.; Wojta, J.; Tschachler, E. Hepatocyte growth factor establishes autocrine and paracrine feedback loops for the protection of skin cells after UV irradiation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 2637–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Hashimoto, K.; Yoshikawa, K.; Nakamura, T. Marked stimulation of growth and motility of human keratinocytes by hepatocyte growth factor. Exp. Cell Res. 1991, 196, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halaban, R.; Rubin, J.S.; Funasaka, Y.; Cobb, M.; Boulton, T.; Faletto, D.; Rosen, E.; Chan, A.; Yoko, K.; White, W.; et al. Met and hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor signal transduction in normal melanocytes and melanoma cells. Oncogene 1992, 7, 2195–2206. [Google Scholar]
- Takayama, H.; La Rochelle, W.J.; Anver, M.; Bockman, D.E.; Merlino, G. Scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor as a regulator of skeletal muscle and neural crest development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 5866–5871. [Google Scholar]
- Kos, L.; Aronzon, A.; Takayama, H.; Maina, F.; Ponzetto, C.; Merlino, G.; Pavan, W. Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor-MET signaling in neural crest-derived melanocyte development. Pigment Cell Res. 1999, 12, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuret, L.; Flori, E.; Denoyelle, C.; Bille, K.; Busca, R.; Picardo, M.; Bertolotto, C.; Ballotti, R. Up-regulation of MET expression by alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone and MITF allows hepatocyte growth factor to protect melanocytes and melanoma cells from apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 14140–14147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larribere, L.; Khaled, M.; Tartare-Deckert, S.; Busca, R.; Luciano, F.; Bille, K.; Valony, G.; Eychene, A.; Auberger, P.; Ortonne, J.P.; et al. PI3K mediates protection against TRAIL-induced apoptosis in primary human melanocytes. Cell Death Differ. 2004, 11, 1084–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, M.L.; Czyz, M. MITF in melanoma: Mechanisms behind its expression and activity. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 1249–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soong, J.; Scott, G. Plexin B1 inhibits MET through direct association and regulates Shp2 expression in melanocytes. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, E.; Dottorini, T.; Sarkozy, A.; Tiller, G.E.; Esposito, G.; Pizzuti, A.; Dallapiccola, B. A novel PTPN11 mutation in LEOPARD syndrome. Hum. Mutat. 2003, 21, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natali, P.G.; Nicotra, M.R.; Di Renzo, M.F.; Prat, M.; Bigotti, A.; Cavaliere, R.; Comoglio, P.M. Expression of the c-Met/HGF receptor in human melanocytic neoplasms: Demonstration of the relationship to malignant melanoma tumour progression. Br. J. Cancer 1993, 68, 746–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, J.; Reis-Filho, J.S.; Silva, P.; Lopes, J.M. Expression of c-met tyrosine kinase receptor is biologically and prognostically relevant for primary cutaneous malignant melanomas. Oncology 2003, 65, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, S.R.; Persons, D.L.; Sosman, J.A.; Bobadilla, D.; Bedell, V.; Smith, D.D.; Wolman, S.R.; Tuthill, R.J.; Moon, J.; Sondak, V.K.; et al. Detection of copy number alterations in metastatic melanoma by a DNA fluorescence in situ hybridization probe panel and array comparative genomic hybridization: A southwest oncology group study (S9431). Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 2927–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, I.; Botton, T.; Talevich, E.; Shain, A.H.; Sparatta, A.J.; de la Fouchardiere, A.; Mully, T.W.; North, J.P.; Garrido, M.C.; Gagnon, A.; et al. Activating MET kinase rearrangements in melanoma and Spitz tumours. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Recio, J.A.; Merlino, G. Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor activates proliferation in melanoma cells through p38 MAPK, ATF-2 and cyclin D1. Oncogene 2002, 21, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsuka, T.; Takayama, H.; Sharp, R.; Celli, G.; LaRochelle, W.J.; Bottaro, D.P.; Ellmore, N.; Vieira, W.; Owens, J.W.; Anver, M.; et al. c-Met autocrine activation induces development of malignant melanoma and acquisition of the metastatic phenotype. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 5157–5167. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ferraro, D.; Corso, S.; Fasano, E.; Panieri, E.; Santangelo, R.; Borrello, S.; Giordano, S.; Pani, G.; Galeotti, T. Pro-metastatic signaling by c-Met through RAC-1 and reactive oxygen species (ROS). Oncogene 2006, 25, 3689–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, D.W.; Nam, H.S.; Cho, M.K. Expression of the c-Met Proteins in Malignant Skin Cancers. Ann. Dermatol. 2011, 23, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenessey, I.; Keszthelyi, M.; Kramer, Z.; Berta, J.; Adam, A.; Dobos, J.; Mildner, M.; Flachner, B.; Cseh, S.; Barna, G.; et al. Inhibition of c-Met with the specific small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor SU11274 decreases growth and metastasis formation of experimental human melanoma. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2010, 10, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.H.; Jeffers, M.; Bellacosa, A.; Mitsuuchi, Y.; Vande Woude, G.F.; Testa, J.R. Anti-apoptotic signaling by hepatocyte growth factor/Met via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, C.; Grimm, E.A.; Woodman, S.E. Simultaneous inhibition of the HGF/MET and Erk1/2 pathways affect uveal melanoma cell growth and migration. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e83957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, C.; Guldberg, P. Growth factors rescue cutaneous melanoma cells from apoptosis induced by knockdown of mutated (V 600 E) B-RAF. Oncogene 2005, 24, 6292–6302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stella, M.C.; Trusolino, L.; Pennacchietti, S.; Comoglio, P.M. Negative feedback regulation of Met-dependent invasive growth by Notch. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 3982–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Putnam, A.J.; Miranti, C.K.; Gustafson, M.; Wang, L.M.; Vande Woude, G.F.; Gao, C.F. Overexpression of sprouty 2 inhibits HGF/SF-mediated cell growth, invasion, migration, and cytokinesis. Oncogene 2004, 23, 5193–5202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Q.; Chen, S.; You, Z.; Yang, F.; Carey, T.E.; Saims, D.; Wang, C.Y. Hepatocyte growth factor inhibits anoikis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells by activation of ERK and Akt signaling independent of NFkappa B. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 25203–25208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; DeFrances, M.C.; Dai, Y.; Pediaditakis, P.; Johnson, C.; Bell, A.; Michalopoulos, G.K.; Zarnegar, R. A mechanism of cell survival: Sequestration of Fas by the HGF receptor Met. Mol. Cell 2002, 9, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Schaider, H.; Satyamoorthy, K.; Hanakawa, Y.; Hashimoto, K.; Herlyn, M. Downregulation of E-cadherin and Desmoglein 1 by autocrine hepatocyte growth factor during melanoma development. Oncogene 2001, 20, 8125–8135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaggioli, C.; Deckert, M.; Robert, G.; Abbe, P.; Batoz, M.; Ehrengruber, M.U.; Ortonne, J.P.; Ballotti, R.; Tartare-Deckert, S. HGF induces fibronectin matrix synthesis in melanoma cells through MAP kinase-dependent signaling pathway and induction of Egr-1. Oncogene 2005, 24, 1423–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recio, J.A.; Merlino, G. Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor induces feedback up-regulation of CD44v6 in melanoma cells through Egr-1. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 1576–1582. [Google Scholar]
- Makowiecka, A.; Simiczyjew, A.; Nowak, D.; Mazur, A.J. Varying effects of EGF, HGF and TGFβ on formation of invadopodia and invasiveness of melanoma cell lines of different origin. Eur. J. Histochem. 2016, 60, 2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajos-Michniewicz, A.; Duechler, M.; Czyz, M. MiRNA in melanoma-derived exosomes. Cancer Lett. 2014, 347, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peinado, H.; Alečković, M.; Lavotshkin, S.; Matei, I.; Costa-Silva, B.; Moreno-Bueno, G.; Hergueta-Redondo, M.; Williams, C.; García-Santos, G.; Ghajar, C.; et al. Melanoma exosomes educate bone marrow progenitor cells toward a pro-metastatic phenotype through MET. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, E.; Sakai, K.; Nishiuchi, T.; Imamura, R.; Sato, H.; Matsumoto, K. Different growth and metastatic phenotypes associated with a cell-intrinsic change of Met in metastatic melanoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 70779–70793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barisione, G.; Fabbi, M.; Gino, A.; Queirolo, P.; Orgiano, L.; Spano, L.; Picasso, V.; Pfeffer, U.; Mosci, C.; Jager, M.J.; et al. Potential Role of Soluble c-Met as a New Candidate Biomarker of Metastatic Uveal Melanoma. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2015, 133, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hügel, R.; Muendlein, A.; Volbeding, L.; Drexel, H.; Richtig, E.; Wehkamp, U.; Painsi, C.; Lange-Asschenfeldt, B.; Hauschild, A.; Egberts, F. Serum levels of hepatocyte growth factor as a potential tumor marker in patients with malignant melanoma. Melanoma Res. 2016, 26, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straussman, R.; Morikawa, T.; Shee, K.; Barzily-Rokni, M.; Qian, Z.R.; Du, J.; Davis, A.; Mongare, M.M.; Gould, J.; Frederick, D.T.; et al. Tumour micro-environment elicits innate resistance to RAF inhibitors through HGF secretion. Nature 2012, 487, 500–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wozniak, M.; Mielczarek, A.; Czyz, M. miRNAs in Melanoma: Tumor Suppressors and Oncogenes with Prognostic Potential. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 3136–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermeking, H. The miR-34 family in cancer and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2010, 17, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Tetteh, P.W.; Merz, P.R.; Dickes, E.; Abukiwan, A.; Hotz-Wagenblatt, A.; Holland-Cunz, S.; Sinnberg, T.; Schittek, B.; Schadendorf, D.; et al. miR-137 inhibits the invasion of melanoma cells through downregulation of multiple oncogenic target genes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 768–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Bian, G.; Meng, Z.; Dang, G.; Shi, D.; Mi, S. MiR144 inhibits uveal melanoma cell proliferation and invasion by regulating c-met expression. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124428. [Google Scholar]
- Volpe, V.O.; Klufas, D.M.; Hegde, U.; Grant-Kels, J.M. The new paradigm of systemic therapies for metastatic melanoma. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 77, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsh, S.J.; Rizos, H.; Scolyer, R.A. Long GV Resistance to combination BRAF and MEK inhibition in metastatic melanoma: Where to next? Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 62, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Leite de Oliveira, R.; Huijberts, S.; Bosdriesz, E.; Pencheva, N.; Brunen, D.; Bosma, A.; Song, J.Y.; Zevenhoven, J.; Los-de Vries, G.T.; et al. An Acquired Vulnerability of Drug-Resistant Melanoma with Therapeutic Potential. Cell 2018, 173, 1413–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teh, J.L.F.; Aplin, A.E. Playing the Melanoma Endgame. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 4629–4630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandner, J.M.; Haass, N.K. Melanoma’s connections to the tumour microenvironment. Pathology 2013, 45, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Haass, N.K. Microenvironment-Driven Dynamic Heterogeneity and Phenotypic Plasticity as a Mechanism of Melanoma Therapy Resistance. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, T.R.; Fridlyand, J.; Yan, Y.; Penuel, E.; Burton, L.; Chan, E.; Peng, J.; Lin, E.; Wang, Y.; Sosman, J.; et al. Widespread potential for growth-factor-driven resistance to anticancer kinase inhibitors. Nature 2012, 487, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergani, E.; Vallacchi, V.; Frigerio, S.; Deho, P.; Mondellini, P.; Perego, P.; Cassinelli, G.; Lanzi, C.; Testi, M.A.; Rivoltini, L.; et al. Identification of MET and SRC activation in melanoma cell lines showing primary resistance to PLX4032. Neoplasia 2011, 13, 1132–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jubb, A.M.; Ribas, A.; Sosman, J.A.; McArthur, G.A.; Yan, Y.; Rost, S.; Zhao, S.; Koeppen, H. Impact of MET expression on outcome in BRAF(V600E/K) advanced melanoma. Histopathology 2013, 63, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezcano, C.; Lee, C.W.; Larson, A.R.; Menzies, A.M.; Kefford, R.F.; Thompson, J.F.; Mihm, M.C., Jr.; Ogino, S.; Long, G.V.; Scolyer, R.A.; et al. Evaluation of stromal HGF immunoreactivity as a biomarker for melanoma response to RAF inhibitors. Mod. Pathol. 2014, 27, 1193–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalesna, I.; Osrodek, M.; Hartman, M.L.; Rozanski, M.; Sztiller-Sikorska, M.; Niewinna, K.; Nejc, D.; Czyz, M. Exogenous growth factors bFGF, EGF and HGF do not influence viability and phenotype of V600EBRAF melanoma cells and their response to vemurafenib and trametinib in vitro. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corso, S.; Giordano, S. Cell-autonomous and non-cell-autonomous mechanisms of HGF/MET-driven resistance to targeted therapies: From basic research to a clinical perspective. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 978–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lito, P.; Pratilas, C.A.; Joseph, E.W.; Tadi, M.; Halilovic, E.; Zubrowski, M.; Huang, A.; Wong, W.L.; Callahan, M.K.; Merghoub, T.; et al. Relief of profound feedback inhibition of mitogenic signaling by RAF inhibitors attenuates their activity in BRAFV600E melanomas. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 668–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.K.; Hollingshead, M.G.; Weiner, J.; Navas, T.; Evrard, Y.A.; Khin, S.A.; Ji, J.J.; Zhang, Y.; Borgel, S.; Pfister, T.D.; et al. Pharmacodynamic Response of the MET/HGF Receptor to Small-Molecule Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Examined with Validated, Fit-for-Clinic Immunoassays. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 3683–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, D.R.; Pinto, P.A.; Cecchi, F.; Reilly, J.; Semerjian, A.; Rabe, D.C.; Gupta, G.; Choyke, P.L.; Bottaro, D.P. Tumor and Plasma Met Levels in Non-Metastatic Prostate Cancer. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, A.; Kluger, H.M.; Kurzrock, R.; Schimmoller, F.; Weitzman, A.L.; Samuel, T.A.; Moussa, A.H.; Gordon, M.S.; Shapiro, G.I. Phase II randomised discontinuation trial of the MET/VEGF receptor inhibitor cabozantinib in metastatic melanoma. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 116, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surriga, O.; Rajasekhar, V.K.; Ambrosini, G.; Dogan, Y.; Huang, R.; Schwartz, G.K. Crizotinib, a c-Met inhibitor, prevents metastasis in a metastatic uveal melanoma model. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 2817–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puri, N.; Ahmed, S.; Janamanchi, V.; Tretiakova, M.; Zumba, O.; Krausz, T.; Jagadeeswaran, R.; Salgia, R. c-Met is a potentially new therapeutic target for treatment of human melanoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 2246–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etnyre, D.; Stone, A.L.; Fong, J.T.; Jacobs, R.J.; Uppada, S.B.; Botting, G.M.; Rajanna, S.; Moravec, D.N.; Shambannagari, M.R.; Crees, Z.; et al. Targeting c-Met in melanoma: Mechanism of resistance and efficacy of novel combinatorial inhibitor therapy. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2014, 15, 1129–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucerova, L.; Demkova, L.; Skolekova, S.; Bohovic, R.; Matuskova, M. Tyrosine kinase inhibitor SU11274 increased tumorigenicity and enriched for melanomainitiating cells by bioenergetic modulation. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, F.; Engst, S.; Yamaguchi, K.; Yu, P.; Won, K.-A.; Mock, L.; Lou, T.; Tan, J.; Li, C.; Tam, D.; et al. Inhibition of tumor cell growth, invasion, and metastasis by EXEL-2880 (XL880, GSK1363089), a novel inhibitor of HGF and VEGF receptor tyrosine Kinases. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 8009–8016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, C.; Ellerhorst, J.A.; Ekmekcioglu, S.; Greene, V.R.; Davies, M.A.; Grimm, E.A. Association of Activated c-met with NRAS-mutated human melanomas: A possible avenue for targeting. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; He, C.; Liu, L.; Ma, N.; Chen, X.; Zheng, D.; Qiu, G.H. PHA665752 inhibits the HGF-stimulated migration and invasion of cells by blocking PI3K/AKT pathway in uveal melanoma. Neoplasma 2017, 64, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjei, A.A.; Schwartz, B.; Garmey, E. Early Clinical Development of ARQ 197, a Selective, Non–ATP-Competitive Inhibitor Targeting MET Tyrosine Kinase for the Treatment of Advanced Cancers. Oncologist 2011, 16, 788–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puzanov, I.; Sosman, J.; Santoro, A.; Saif, M.W.; Goff, L.; Dy, G.K.; Zucali, P.; Means-Powell, J.A.; Ma, W.W.; Simonelli, M.; et al. Phase 1 trial of tivantinib in combination with sorafenib in adult patients with advanced solid tumors. Investig. New Drugs 2015, 33, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basilico, C.; Pennacchietti, S.; Vigna, E.; Chiriaco, C.; Arena, S.; Bardelli, A.; Valdembri, D.; Serini, G.; Michieli, P. Tivantinib (ARQ197) displays Cytotoxic activity that is independent of its ability to bind MET. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2381–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, T. Safety of quercetin for clinical application (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2005, 16, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.H.; Tse, A.K.; Kwan, H.Y.; Yu, H.; Cheng, C.Y.; Su, T.; Fong, W.F.; Yu, Z.L. Quercetin exerts anti-melanoma activities and inhibits STAT3 signaling. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 87, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, Z.; Donovan, M.G.; Branco, G.M.; Limesand, K.H.; Burd, R. Quercetin as an Emerging Anti-Melanoma Agent: A Four-Focus Area Therapeutic Development Strategy. Front. Nutr. 2016, 3, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.M.; Kang, J.H.; Yun, M.; Lee, S.B. Quercetin inhibits the poly(dA:dT)-induced secretion of IL-18 via down-regulation of the expressions of AIM2 and pro-caspase-1 by inhibiting the JAK2/STAT1 pathway in IFN-γ-primed human keratinocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöffski, P.; Gordon, M.; Smith, D.C.; Kurzrock, R.; Daud, A.; Vogelzang, N.J.; Lee, Y.; Scheffold, C.; Shapiro, G.I. Phase II randomised discontinuation trial of cabozantinib in patients with advanced solid tumours. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 86, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, M.S.; Kluger, H.M.; Shapiro, G.; Kurzrock, R.; Edelman, G.; Samuel, T.A.; Moussa, A.H.; Ramies, D.A.; Laird, A.D.; Schimmoller, F.; et al. Activity of cabozantinib (XL184) in metastatic melanoma: Results from a phase II randomized discontinuation trial (RDT). J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 8531. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, K.; Nakamura, T. Hepatocyte growth factor and the Met system as a mediator of tumor-stromal interactions. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradbury, J. A two-pronged approach to the clinical use of HGF. Lancet 1998, 351, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Name of Inhibitor | Designed/Assessed Activity | Type of Experiments | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| CabozantinibXL184 BMS-907351 | Inhibitor of c-MET | Clinical trial | NCT00940225 [123,138,139] |
| Crizotinib PF-02341066 | Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-competitive inhibitor of catalytic activity of c-MET | Preclinical in vivo clinical trial (uveal melanoma) | [103,124] NCT02223819 (ongoing) |
| Foretinib EXEL-2880 | ATP-competitive inhibitor of c-MET | Preclinical in vitro Preclinical in vivo | [128] |
| PHA-665752 | Inhibitor of Y1234 and Y1235 in catalytic region of c-MET | Preclinical in vitro | [129,130] |
| SU11274 | Selective inhibitor of Y1234 and Y1235 in catalytic region of c-MET | Preclinical in vitro Preclinical in vivo | [86,115,125,126,127] |
| Tivantinib ARQ 197 | Non-ATP-competitive inhibitor of c-MET; binding to dephosphorylated c-MET | Preclinical in vitro Preclinical in vivo Clinical trial | [126,131,132,133] NCT00827177 |
| E7050 | ATP-competitive inhibitor of c-MET | Clinical trial | NCT01433991 |
| Quercetin | Inhibitor of c-MET phosphorylation and dimerization | Preclinical in vitro Preclinical in vivo | [36,135] |
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Czyz, M. HGF/c-MET Signaling in Melanocytes and Melanoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123844
Czyz M. HGF/c-MET Signaling in Melanocytes and Melanoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(12):3844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123844
Chicago/Turabian StyleCzyz, Malgorzata. 2018. "HGF/c-MET Signaling in Melanocytes and Melanoma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 12: 3844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123844
APA StyleCzyz, M. (2018). HGF/c-MET Signaling in Melanocytes and Melanoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(12), 3844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123844