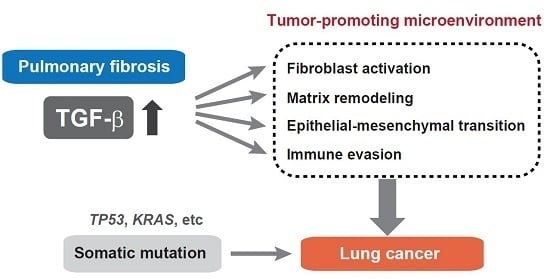
The Role of TGF-β Signaling in Lung Cancer Associated with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Genetic Predispositions to Pulmonary Fibrosis
3. Genomic Features of Lung Cancer That Occurs in Pulmonary Fibrosis
4. Genome-Wide Methylation Profiles of Pulmonary Fibrosis and Lung Cancer
5. Roles of TGF-β in Alveolar Epithelial Cells
6. TGF-β-Mediated Fibroproliferative Reactions in Pulmonary Fibrosis and Lung Cancer
7. Clinical Implications and Future Perspectives
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raghu, G.; Collard, H.R.; Egan, J.J.; Martinez, F.J.; Behr, J.; Brown, K.K.; Colby, T.V.; Cordier, J.F.; Flaherty, K.R.; Lasky, J.A.; et al. An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT statement: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Evidence-based guidelines for diagnosis and management. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 788–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchinson, J.; Fogarty, A.; Hubbard, R.; McKeever, T. Global incidence and mortality of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A systematic review. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richeldi, L.; Collard, H.R.; Jones, M.G. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet 2017, 389, 1941–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lederer, D.J.; Martinez, F.J. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1811–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubbard, R.; Venn, A.; Lewis, S.; Britton, J. Lung cancer and cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. A population-based cohort study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 161, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghu, G.; Amatto, V.C.; Behr, J.; Stowasser, S. Comorbidities in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients: A systematic literature review. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 1113–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Jeune, I.; Gribbin, J.; West, J.; Smith, C.; Cullinan, P.; Hubbard, R. The incidence of cancer in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and sarcoidosis in the UK. Respir. Med. 2007, 101, 2534–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozawa, Y.; Suda, T.; Naito, T.; Enomoto, N.; Hashimoto, D.; Fujisawa, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Inui, N.; Nakamura, H.; Chida, K. Cumulative incidence of and predictive factors for lung cancer in IPF. Respirology 2009, 14, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomassetti, S.; Gurioli, C.; Ryu, J.H.; Decker, P.A.; Ravaglia, C.; Tantalocco, P.; Buccioli, M.; Piciucchi, S.; Sverzellati, N.; Dubini, A.; et al. The impact of lung cancer on survival of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 2015, 147, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micke, P.; Ostman, A. Tumour-stroma interaction: Cancer-associated fibroblasts as novel targets in anti-cancer therapy? Lung Cancer 2004, 45, S163–S175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, A.; Nagase, T. Hippo and TGF-β interplay in the lung field. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2015, 309, L756–L767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reck, M.; Kaiser, R.; Mellemgaard, A.; Douillard, J.Y.; Orlov, S.; Krzakowski, M.; von Pawel, J.; Gottfried, M.; Bondarenko, I.; Liao, M.; et al. Docetaxel plus nintedanib versus docetaxel plus placebo in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (LUME-Lung 1): A phase 3, double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, M.; Derynck, R.; Miyazono, K. TGF-β and the TGF-β family: Context-dependent roles in cell and tissue physiology. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosas, I.O.; Dellaripa, P.F.; Lederer, D.J.; Khanna, D.; Young, L.R.; Martinez, F.J. Interstitial lung disease: NHLBI Workshop on the primary prevention of chronic lung diseases. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2014, 11, S169–S177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosas, I.O.; Ren, P.; Avila, N.A.; Chow, C.K.; Franks, T.J.; Travis, W.D.; McCoy, J.P.J.; May, R.M.; Wu, H.P.; Nguyen, D.M.; et al. Early interstitial lung disease in familial pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 176, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgartner, K.B.; Samet, J.M.; Stidley, C.A.; Colby, T.V.; Waldron, J.A. Cigarette smoking: A risk factor for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 155, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, J.; Malvezzi, M.; Negri, E.; La Vecchia, C.; Boffetta, P. Risk factors for lung cancer worldwide. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 48, 889–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mushiroda, T.; Wattanapokayakit, S.; Takahashi, A.; Nukiwa, T.; Kudoh, S.; Ogura, T.; Taniguchi, H.; Kubo, M.; Kamatani, N.; Nakamura, Y. A genome-wide association study identifies an association of a common variant in TERT with susceptibility to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J. Med. Genet. 2008, 45, 654–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fingerlin, T.E.; Murphy, E.; Zhang, W.; Peljto, A.L.; Brown, K.K.; Steele, M.P.; Loyd, J.E.; Cosgrove, G.P.; Lynch, D.; Groshong, S.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies multiple susceptibility loci for pulmonary fibrosis. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armanios, M.; Blackburn, E.H. The telomere syndromes. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, R.J.; Porte, J.; Braybrooke, R.; Flores, C.; Fingerlin, T.E.; Oldham, J.M.; Guillen-Guio, B.; Ma, S.F.; Okamoto, T.; John, A.E.; et al. Genetic variants associated with susceptibility to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in people of European ancestry: A genome-wide association study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 869–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibold, M.A.; Wise, A.L.; Speer, M.C.; Steele, M.P.; Brown, K.K.; Loyd, J.E.; Fingerlin, T.E.; Zhang, W.; Gudmundsson, G.; Groshong, S.D.; et al. A common MUC5B promoter polymorphism and pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1503–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunninghake, G.M.; Hatabu, H.; Okajima, Y.; Gao, W.; Dupuis, J.; Latourelle, J.C.; Nishino, M.; Araki, T.; Zazueta, O.E.; Kurugol, S.; et al. MUC5B promoter polymorphism and interstitial lung abnormalities. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2192–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldham, J.M.; Ma, S.F.; Martinez, F.J.; Anstrom, K.J.; Raghu, G.; Schwartz, D.A.; Valenzi, E.; Witt, L.; Lee, C.; Vij, R.; et al. TOLLIP, MUC5B, and the response to n-acetylcysteine among individuals with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 192, 1475–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peljto, A.L.; Zhang, Y.; Fingerlin, T.E.; Ma, S.F.; Garcia, J.G.; Richards, T.J.; Silveira, L.J.; Lindell, K.O.; Steele, M.P.; Loyd, J.E.; et al. Association between the MUC5B promoter polymorphism and survival in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. JAMA 2013, 309, 2232–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noth, I.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, S.F.; Flores, C.; Barber, M.; Huang, Y.; Broderick, S.M.; Wade, M.S.; Hysi, P.; Scuirba, J.; et al. Genetic variants associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis susceptibility and mortality: A genome-wide association study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2013, 1, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, C.M.; Fingerlin, T.E.; Schwarz, M.I.; Lynch, D.; Kurche, J.; Warg, L.; Yang, I.V.; Schwartz, D.A. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A genetic disease that involves mucociliary dysfunction of the peripheral airways. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 1567–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, M.G.; Livraghi-Butrico, A.; Fletcher, A.A.; McElwee, M.M.; Evans, S.E.; Boerner, R.M.; Alexander, S.N.; Bellinghausen, L.K.; Song, A.S.; Petrova, Y.M.; et al. Muc5b is required for airway defence. Nature 2014, 505, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Moorsel, C.H.; Van Oosterhout, M.F.; Barlo, N.P.; de Jong, P.A.; Van der Vis, J.J.; Ruven, H.J.; Van Es, H.W.; Van den Bosch, J.M.; Grutters, J.C. Surfactant protein C mutations are the basis of a significant portion of adult familial pulmonary fibrosis in a dutch cohort. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 182, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Kuan, P.J.; Xing, C.; Cronkhite, J.T.; Torres, F.; Rosenblatt, R.L.; DiMaio, J.M.; Kinch, L.N.; Grishin, N.V.; Garcia, C.K. Genetic defects in surfactant protein A2 are associated with pulmonary fibrosis and lung cancer. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 84, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kropski, J.A.; Blackwell, T.S.; Loyd, J.E. The genetic basis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 45, 1717–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armanios, M.Y.; Chen, J.J.; Cogan, J.D.; Alder, J.K.; Ingersoll, R.G.; Markin, C.; Lawson, W.E.; Xie, M.; Vulto, I.; Phillips, J.A.; et al. Telomerase mutations in families with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 1317–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsakiri, K.D.; Cronkhite, J.T.; Kuan, P.J.; Xing, C.; Raghu, G.; Weissler, J.C.; Rosenblatt, R.L.; Shay, J.W.; Garcia, C.K. Adult-onset pulmonary fibrosis caused by mutations in telomerase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7552–7557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alder, J.K.; Chen, J.J.; Lancaster, L.; Danoff, S.; Su, S.C.; Cogan, J.D.; Vulto, I.; Xie, M.; Qi, X.; Tuder, R.M.; et al. Short telomeres are a risk factor for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13051–13056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronkhite, J.T.; Xing, C.; Raghu, G.; Chin, K.M.; Torres, F.; Rosenblatt, R.L.; Garcia, C.K. Telomere shortening in familial and sporadic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 178, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuart, B.D.; Choi, J.; Zaidi, S.; Xing, C.; Holohan, B.; Chen, R.; Choi, M.; Dharwadkar, P.; Torres, F.; Girod, C.E.; et al. Exome sequencing links mutations in PARN and RTEL1 with familial pulmonary fibrosis and telomere shortening. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cogan, J.D.; Kropski, J.A.; Zhao, M.; Mitchell, D.B.; Rives, L.; Markin, C.; Garnett, E.T.; Montgomery, K.H.; Mason, W.R.; McKean, D.F.; et al. Rare variants in RTEL1 are associated with familial interstitial pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 191, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertuch, A.A. The molecular genetics of the telomere biology disorders. RNA Biol. 2016, 13, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, D.H.; Segal, M.; Boyraz, B.; Guinan, E.; Hofmann, I.; Cahan, P.; Tai, A.K.; Agarwal, S. Poly(A)-specific ribonuclease (PARN) mediates 3’-end maturation of the telomerase RNA component. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1482–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barkauskas, C.E.; Cronce, M.J.; Rackley, C.R.; Bowie, E.J.; Keene, D.R.; Stripp, B.R.; Randell, S.H.; Noble, P.W.; Hogan, B.L. Type 2 alveolar cells are stem cells in adult lung. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3025–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alder, J.K.; Barkauskas, C.E.; Limjunyawong, N.; Stanley, S.E.; Kembou, F.; Tuder, R.M.; Hogan, B.L.; Mitzner, W.; Armanios, M. Telomere dysfunction causes alveolar stem cell failure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5099–5104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Povedano, J.M.; Martinez, P.; Flores, J.M.; Mulero, F.; Blasco, M.A. Mice with pulmonary fibrosis driven by telomere dysfunction. Cell Rep. 2015, 12, 286–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masutomi, K.; Possemato, R.; Wong, J.M.; Currier, J.L.; Tothova, Z.; Manola, J.B.; Ganesan, S.; Lansdorp, P.M.; Collins, K.; Hahn, W.C. The telomerase reverse transcriptase regulates chromatin state and DNA damage responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 8222–8227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vannier, J.B.; Sandhu, S.; Petalcorin, M.I.; Wu, X.; Nabi, Z.; Ding, H.; Boulton, S.J. RTEL1 is a replisome-associated helicase that promotes telomere and genome-wide replication. Science 2013, 342, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, T.J.; Brownfield, D.G.; Krasnow, M.A. Alveolar progenitor and stem cells in lung development, renewal and cancer. Nature 2014, 507, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive molecular profiling of lung adenocarcinoma. Nature 2014, 511, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive genomic characterization of squamous cell lung cancers. Nature 2012, 489, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciejowski, J.; de Lange, T. Telomeres in cancer: Tumour suppression and genome instability. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, T.Y.; Cramb, S.M.; Baade, P.D.; Youlden, D.R.; Nwogu, C.; Reid, M.E. The international epidemiology of lung cancer: Latest trends, disparities, and tumor characteristics. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 1653–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karampitsakos, T.; Tzilas, V.; Tringidou, R.; Steiropoulos, P.; Aidinis, V.; Papiris, S.A.; Bouros, D.; Tzouvelekis, A. Lung cancer in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 45, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Incze, J.; Vaughan, C.W.J.; Lui, P.; Strong, M.S.; Kulapaditharom, B. Premalignant changes in normal appearing epithelium in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the upper aerodigestive tract. Am. J. Surg. 1982, 144, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtius, K.; Wright, N.A.; Graham, T.A. An evolutionary perspective on field cancerization. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestri, G.A.; Vachani, A.; Whitney, D.; Elashoff, M.; Porta Smith, K.; Ferguson, J.S.; Parsons, E.; Mitra, N.; Brody, J.; Lenburg, M.E.; et al. A bronchial genomic classifier for the diagnostic evaluation of lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bruin, E.C.; McGranahan, N.; Mitter, R.; Salm, M.; Wedge, D.C.; Yates, L.; Jamal-Hanjani, M.; Shafi, S.; Murugaesu, N.; Rowan, A.J.; et al. Spatial and temporal diversity in genomic instability processes defines lung cancer evolution. Science 2014, 346, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hironaka, M.; Fukayama, M. Pulmonary fibrosis and lung carcinoma: A comparative study of metaplastic epithelia in honeycombed areas of usual interstitial pneumonia with or without lung carcinoma. Pathol. Int. 1999, 49, 1060–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, H.; Ogura, T.; Yokose, T.; Nagai, K.; Nishiwaki, Y.; Esumi, H. p53 gene alteration in atypical epithelial lesions and carcinoma in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Hum. Pathol. 2001, 32, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, T.; Munakata, M.; Ohtsuka, Y.; Nisihara, H.; Nasuhara, Y.; Kamachi-Satoh, A.; Dosaka-Akita, H.; Homma, Y.; Kawakami, Y. Expression and alteration of ras and p53 proteins in patients with lung carcinoma accompanied by idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Cancer 2002, 95, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masai, K.; Tsuta, K.; Motoi, N.; Shiraishi, K.; Furuta, K.; Suzuki, S.; Asakura, K.; Nakagawa, K.; Sakurai, H.; Watanabe, S.I.; et al. Clinicopathological, immunohistochemical, and genetic features of primary lung adenocarcinoma occurring in the setting of usual interstitial pneumonia pattern. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 2141–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohno, T.; Nakaoku, T.; Tsuta, K.; Tsuchihara, K.; Matsumoto, S.; Yoh, K.; Goto, K. Beyond ALK-RET, ROS1 and other oncogene fusions in lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2015, 4, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Duruisseaux, M.; Antoine, M.; Rabbe, N.; Rodenas, A.; Mc Leer-Florin, A.; Lacave, R.; Poulot, V.; Duchêne, B.; Van Seuningen, I.; Cadranel, J.; et al. Lepidic predominant adenocarcinoma and invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma of the lung exhibit specific mucin expression in relation with oncogenic drivers. Lung Cancer 2017, 109, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.K.; Shin, D.H.; Kim, K.B.; Shin, N.; Park, W.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, K.U.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Sol, M.Y.; et al. MUC5AC and MUC5B enhance the characterization of mucinous adenocarcinomas of the lung and predict poor prognosis. Histopathology 2015, 67, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.A.; Kim, D.; Chun, S.M.; Bae, S.; Song, J.S.; Kim, M.Y.; Koo, H.J.; Song, J.W.; Kim, W.S.; Lee, J.C.; et al. Genomic profiles of lung cancer associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J. Pathol. 2018, 244, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horie, M.; Kaczkowski, B.; Ohshima, M.; Matsuzaki, H.; Noguchi, S.; Mikami, Y.; Lizio, M.; Itoh, M.; Kawaji, H.; Lassmann, T.; et al. Integrative CAGE and DNA methylation profiling identify epigenetically regulated genes in NSCLC. Mol. Cancer Res. 2017, 15, 1354–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Chen, X.; Hong, Q.; Deng, Z.; Ma, H.; Xin, Y.; Fang, Y.; Ye, H.; Wang, R.; Zhang, C.; et al. Meta-analyses of gene methylation and smoking behavior in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djureinovic, D.; Hallström, B.M.; Horie, M.; Mattsson, J.S.; La Fleur, L.; Fagerberg, L.; Brunnström, H.; Lindskog, C.; Madjar, K.; Rahnenführer, J.; et al. Profiling cancer testis antigens in non-small-cell lung cancer. JCI Insight 2016, 1, e86837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, Y.Y.; Ambalavanan, N.; Halloran, B.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Crossman, D.K.; Bray, M.; Zhang, K.; Thannickal, V.J.; Hagood, J.S. Altered DNA methylation profile in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, I.V.; Pedersen, B.S.; Rabinovich, E.; Hennessy, C.E.; Davidson, E.J.; Murphy, E.; Guardela, B.J.; Tedrow, J.R.; Zhang, Y.; Singh, M.K.; et al. Relationship of DNA methylation and gene expression in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 1263–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabinovich, E.I.; Kapetanaki, M.G.; Steinfeld, I.; Gibson, K.F.; Pandit, K.V.; Yu, G.; Yakhini, Z.; Kaminski, N. Global methylation patterns in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, W.E.; Cheng, D.S.; Degryse, A.L.; Tanjore, H.; Polosukhin, V.V.; Xu, X.C.; Newcomb, D.C.; Jones, B.R.; Roldan, J.; et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress enhances fibrotic remodeling in the lungs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 10562–10567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Ibarra, G.H.; Kaminski, N. Fibrosis: Lessons from OMICS analyses of the human lung. Matrix Biol. 2018, 68, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolahian, S.; Fernandez, I.E.; Eickelberg, O.; Hartl, D. Immune mechanisms in pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 55, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broekelmann, T.J.; Limper, A.H.; Colby, T.V.; McDonald, J.A. Transforming growth factor β1 is present at sites of extracellular matrix gene expression in human pulmonary fibrosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 6642–6646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coker, R.K.; Laurent, G.J.; Jeffery, P.K.; du Bois, R.M.; Black, C.M.; McAnulty, R.J. Localisation of transforming growth factor beta1 and beta3 mRNA transcripts in normal and fibrotic human lung. Thorax 2001, 56, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.G.; Cho, S.J.; Kang, M.J.; Chapoval, S.P.; Lee, P.J.; Noble, P.W.; Yehualaeshet, T.; Lu, B.; Flavell, R.A.; Milbrandt, J.; et al. Early growth response gene 1-mediated apoptosis is essential for transforming growth factor beta1-induced pulmonary fibrosis. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 200, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sime, P.J.; Xing, Z.; Graham, F.L.; Csaky, K.G.; Gauldie, J. Adenovector-mediated gene transfer of active transforming growth factor-beta1 induces prolonged severe fibrosis in rat lung. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 100, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, R.M.; Mineo-Kuhn, M.M.; Kramer, C.M.; Finkelstein, J.N. Growth factors alter neonatal type II alveolar epithelial cell proliferation. Am. J. Physiol. 1994, 266, L17–L22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, B.C.; Liebler, J.M.; Luby-Phelps, K.; Nicholson, A.G.; Crandall, E.D.; du Bois, R.M.; Borok, Z. Induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in alveolar epithelial cells by transforming growth factor-beta1: Potential role in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 166, 1321–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kage, H.; Borok, Z. EMT and interstitial lung disease: A mysterious relationship. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2012, 18, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Mizuno, T.; Sridharan, A.; Du, Y.; Guo, M.; Tang, J.; Wikenheiser-Brokamp, K.A.; Perl, A.T.; Funari, V.A.; Gokey, J.J.; et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing identifies diverse roles of epithelial cells in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. JCI Insight 2016, 1, e90558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brabletz, T.; Kalluri, R.; Nieto, M.A.; Weinberg, R.A. EMT in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horie, M.; Saito, A.; Mikami, Y.; Ohshima, M.; Morishita, Y.; Nakajima, J.; Kohyama, T.; Nagase, T. Characterization of human lung cancer-associated fibroblasts in three-dimensional in vitro co-culture model. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 423, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, A.; Suzuki, H.I.; Horie, M.; Ohshima, M.; Morishita, Y.; Abiko, Y.; Nagase, T. An integrated expression profiling reveals target genes of TGF-β and TNF-α possibly mediated by microRNAs in lung cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micke, P.; Ostman, A. Exploring the tumour environment: Cancer-associated fibroblasts as targets in cancer therapy. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets 2005, 9, 1217–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horie, M.; Saito, A.; Noguchi, S.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Ohshima, M.; Morishita, Y.; Suzuki, H.I.; Kohyama, T.; Nagase, T. Differential knockdown of TGF-β ligands in a three-dimensional co-culture tumor-stromal interaction model of lung cancer. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navab, R.; Strumpf, D.; Bandarchi, B.; Zhu, C.Q.; Pintilie, M.; Ramnarine, V.R.; Ibrahimov, E.; Radulovich, N.; Leung, L.; Barczyk, M.; et al. Prognostic gene-expression signature of carcinoma-associated fibroblasts in non-small cell lung cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 7160–7165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanouchi, H.; Fujita, J.; Yoshinouchi, T.; Hojo, S.; Kamei, T.; Yamadori, I.; Ohtsuki, Y.; Ueda, N.; Takahara, J. Measurement of hepatocyte growth factor in serum and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in patients with pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Med. 1998, 92, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, Q.; Yamada, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Matsumoto, I.; Oda, M.; Watanabe, G.; Kayano, Y.; Nishioka, Y.; Sone, S.; et al. Crosstalk to stromal fibroblasts induces resistance of lung cancer to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 6630–6638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, A.B.; Huh, C.G.; Becker, D.; Geiser, A.; Lyght, M.; Flanders, K.C.; Roberts, A.B.; Sporn, M.B.; Ward, J.M.; Karlsson, S. Transforming growth factor beta 1 null mutation in mice causes excessive inflammatory response and early death. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 770–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shull, M.M.; Ormsby, I.; Kier, A.B.; Pawlowski, S.; Diebold, R.J.; Yin, M.; Allen, R.; Sidman, C.; Proetzel, G.; Calvin, D.; et al. Targeted disruption of the mouse transforming growth factor-β1 gene results in multifocal inflammatory disease. Nature 1992, 359, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.O.; Sanjabi, S.; Flavell, R.A. Transforming growth factor-beta controls development, homeostasis, and tolerance of T cells by regulatory T cell-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Immunity 2006, 25, 455–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariathasan, S.; Turley, S.J.; Nickles, D.; Castiglioni, A.; Yuen, K.; Wang, Y.; Kadel Iii, E.E.; Koeppen, H.; Astarita, J.L.; Cubas, R.; et al. TGFβ attenuates tumour response to PD-L1 blockade by contributing to exclusion of T. cells. Nature 2018, 554, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tauriello, D.V.F.; Palomo-Ponce, S.; Stork, D.; Berenguer-Llergo, A.; Badia-Ramentol, J.; Iglesias, M.; Sevillano, M.; Ibiza, S.; Cañellas, A.; Hernando-Momblona, X.; et al. TGFβ drives immune evasion in genetically reconstituted colon cancer metastasis. Nature 2018, 554, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flavell, R.A.; Sanjabi, S.; Wrzesinski, S.H.; Licona-Limón, P. The polarization of immune cells in the tumour environment by TGFbeta. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 554–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horowitz, J.C.; Osterholzer, J.J.; Marazioti, A.; Stathopoulos, G.T. “Scar-cinoma”: Viewing the fibrotic lung mesenchymal cell in the context of cancer biology. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 47, 1842–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotta, K.; Kiura, K.; Takigawa, N.; Yoshioka, H.; Harita, S.; Kuyama, S.; Yonei, T.; Fujiwara, K.; Maeda, T.; Aoe, K.; et al. Comparison of the incidence and pattern of interstitial lung disease during erlotinib and gefitinib treatment in Japanese Patients with non-small cell lung cancer: The Okayama Lung Cancer Study Group experience. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, A.; Kishi, K.; Yoshimura, K. A nationwide survey concerning lung surgery for lung cancer associated with idiopathic interstitial pneumonia. Nihon. Kokyuki. Gakkai. Zasshi. 2011, 49, 148–150. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Teramukai, S.; Kondo, H.; Watanabe, A.; Ebina, M.; Kishi, K.; Fujii, Y.; Mitsudomi, T.; Yoshimura, M.; Maniwa, T.; et al. Impact and predictors of acute exacerbation of interstitial lung diseases after pulmonary resection for lung cancer. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 147, 1604–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, T.E.J.; Bradford, W.Z.; Castro-Bernardini, S.; Fagan, E.A.; Glaspole, I.; Glassberg, M.K.; Gorina, E.; Hopkins, P.M.; Kardatzke, D.; Lancaster, L.; et al. A phase 3 trial of pirfenidone in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2083–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richeldi, L.; du Bois, R.M.; Raghu, G.; Azuma, A.; Brown, K.K.; Costabel, U.; Cottin, V.; Flaherty, K.R.; Hansell, D.M.; Inoue, Y.; et al. Efficacy and safety of nintedanib in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2071–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, S.D.; Albera, C.; Bradford, W.Z.; Costabel, U.; Glaspole, I.; Glassberg, M.K.; Kardatzke, D.R.; Daigl, M.; Kirchgaessler, K.U.; Lancaster, L.H.; et al. Effect of pirfenidone on mortality: Pooled analyses and meta-analyses of clinical trials in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richeldi, L.; Cottin, V.; du Bois, R.M.; Selman, M.; Kimura, T.; Bailes, Z.; Schlenker-Herceg, R.; Stowasser, S.; Brown, K.K. Nintedanib in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Combined evidence from the TOMORROW and INPULSIS® trials. Respir. Med. 2016, 113, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horie, M.; Saito, A.; Ohshima, M.; Suzuki, H.I.; Nagase, T. YAP and TAZ modulate cell phenotype in a subset of small cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 1755–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyashita, N.; Horie, M.; Suzuki, H.I.; Yoshihara, M.; Djureinovic, D.; Persson, J.; runnström, H.; Lindskog, C.; Elfving, H.; Micke, P.; et al. An integrative analysis of transcriptome and epigenome features of ASCL1-positive lung adenocarcinomas. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1676–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, T.; Tamiya, M.; Tamiya, A.; Nakahama, K.; Taniguchi, Y.; Shiroyama, T.; Isa, S.I.; Nishino, K.; Kumagai, T.; Kunimasa, K.; et al. Analysis of early death in japanese patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer treated with nivolumab. Clin. Lung Cancer 2018, 19, e171–e176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saito, A.; Horie, M.; Micke, P.; Nagase, T. The Role of TGF-β Signaling in Lung Cancer Associated with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3611. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113611
Saito A, Horie M, Micke P, Nagase T. The Role of TGF-β Signaling in Lung Cancer Associated with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(11):3611. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113611
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaito, Akira, Masafumi Horie, Patrick Micke, and Takahide Nagase. 2018. "The Role of TGF-β Signaling in Lung Cancer Associated with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 11: 3611. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113611
APA StyleSaito, A., Horie, M., Micke, P., & Nagase, T. (2018). The Role of TGF-β Signaling in Lung Cancer Associated with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(11), 3611. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113611