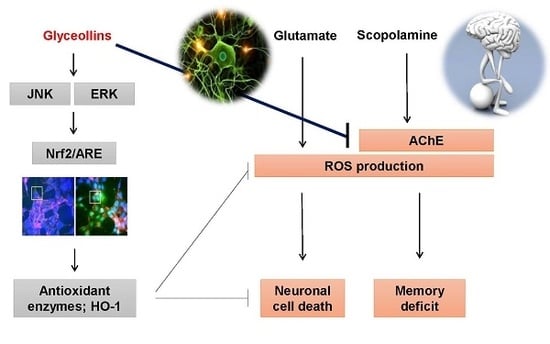
Soybean-Derived Phytoalexins Improve Cognitive Function through Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
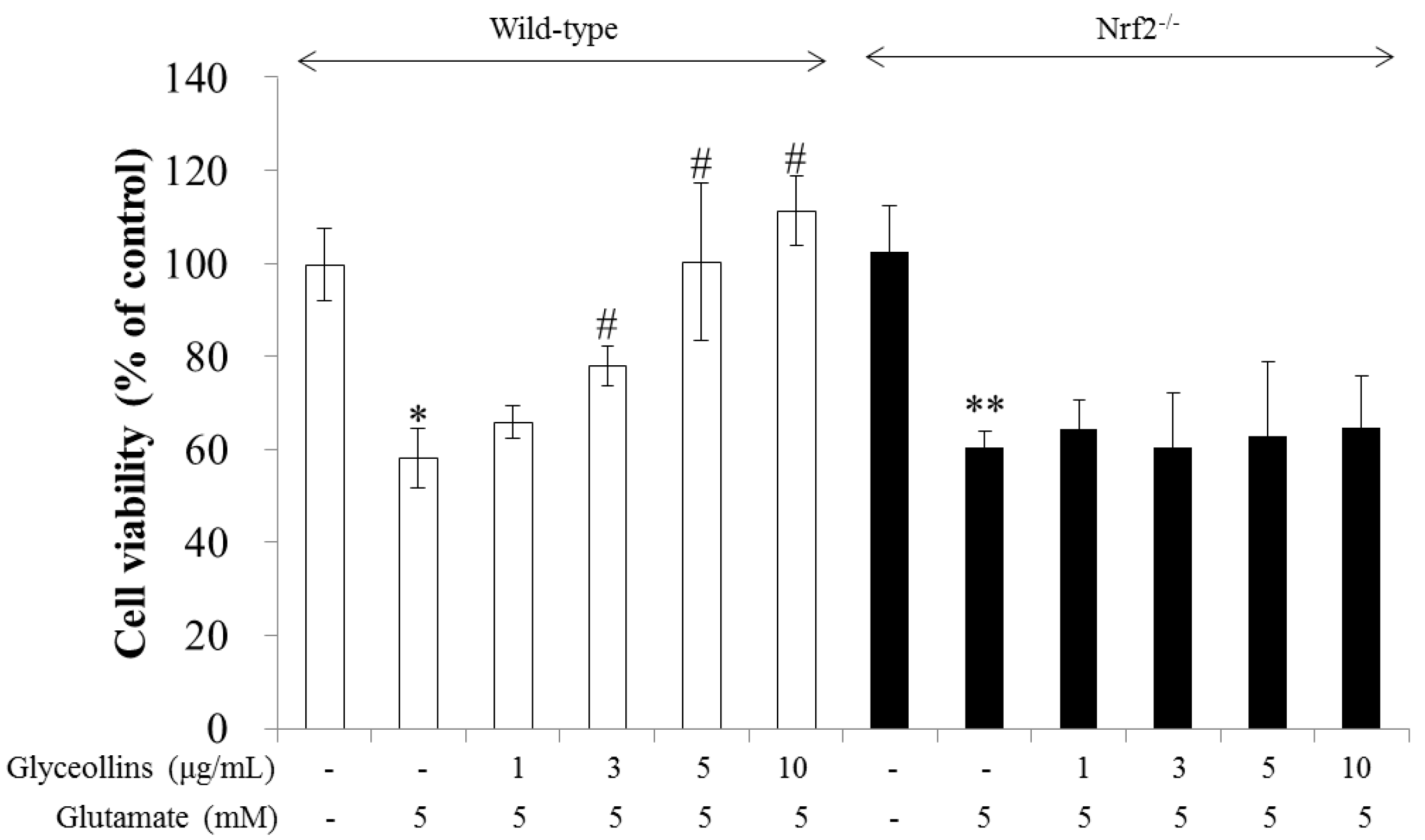
2.1. Effect of Glyceollins on Glutamate-Induced Cytotoxicity in Primary Cortical Neurons Isolated from Nrf2 Wild-Type and Knockout Mice
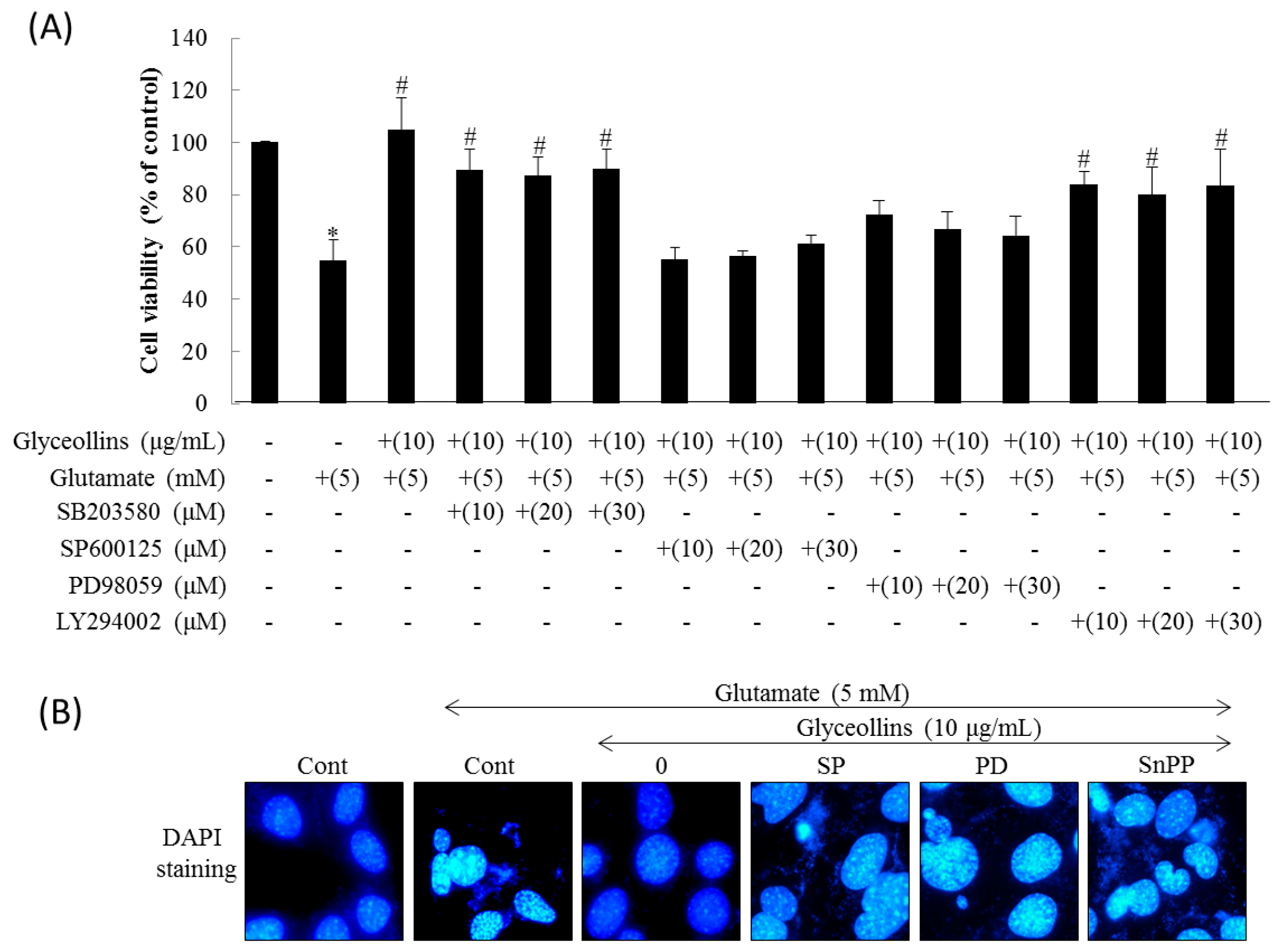
2.2. Effect of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK), PI3K, Nrf2, and HO-1 on the Attenuation of Glutamate-Induced Oxytosis by Glyceollins
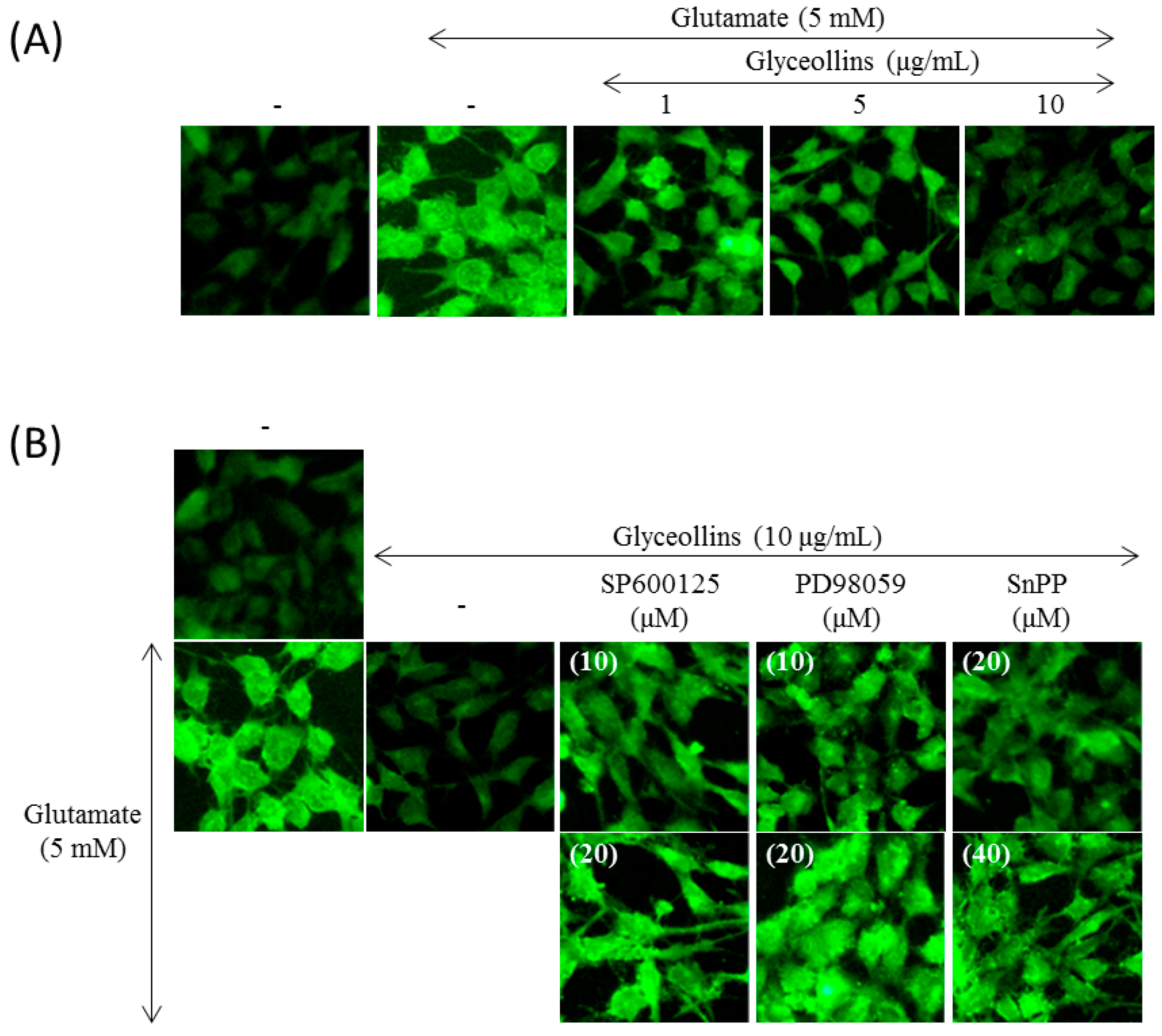
2.3. Suppression of Intracellular ROS (Reactive Oxygen Species) Level by Glyceollins
2.4. Effect of MAPK and HO-1 Inhibitors on Glyceollins-Mediated Suppression of ROS Production
2.5. Stimulation of Nuclear Translocation of Nrf2 and HO-1 Expression by Glyceollins
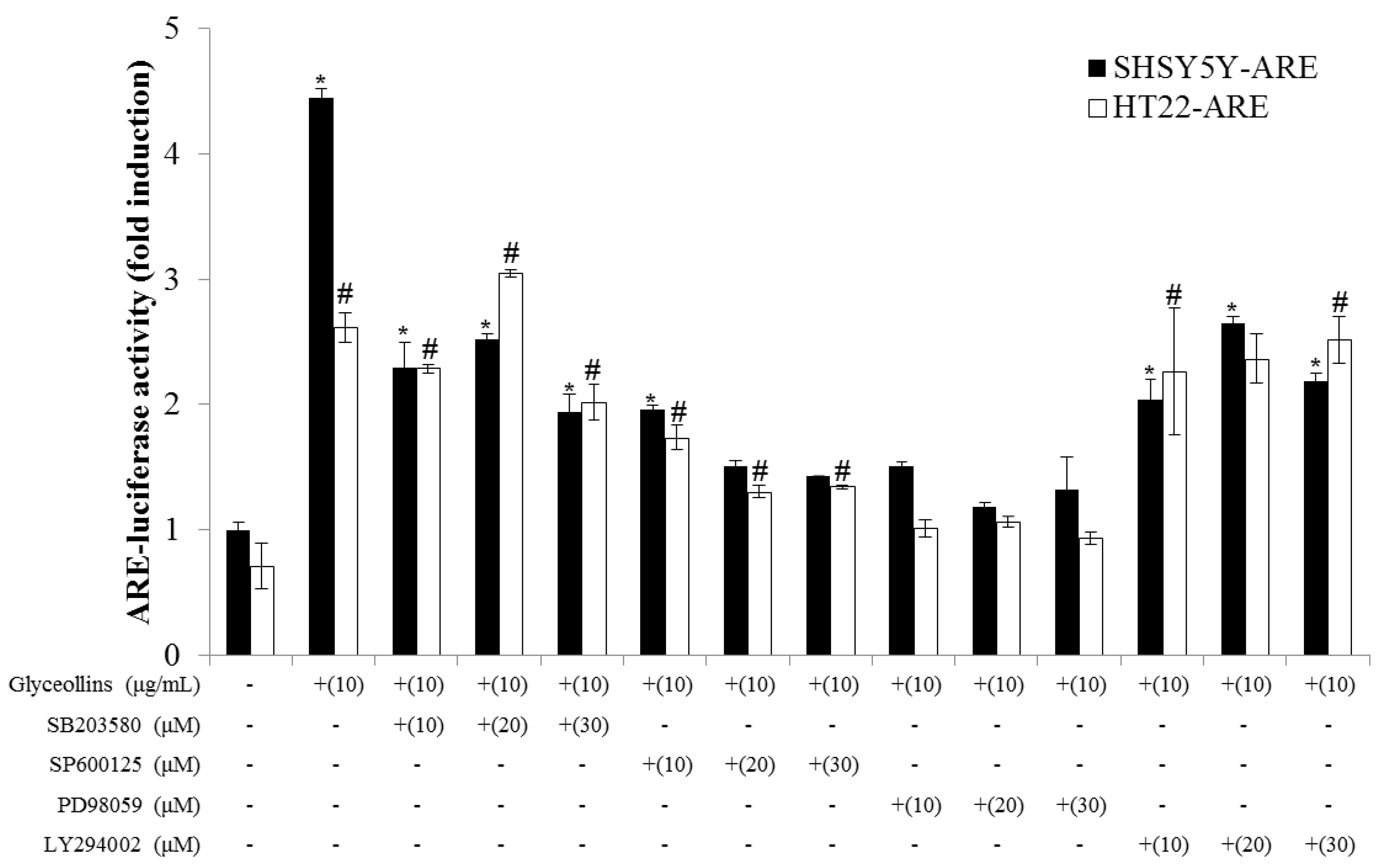
2.6. Effect of MAPK Inhibitors on ARE-Mediated Transcriptional Activation by Glyceollins
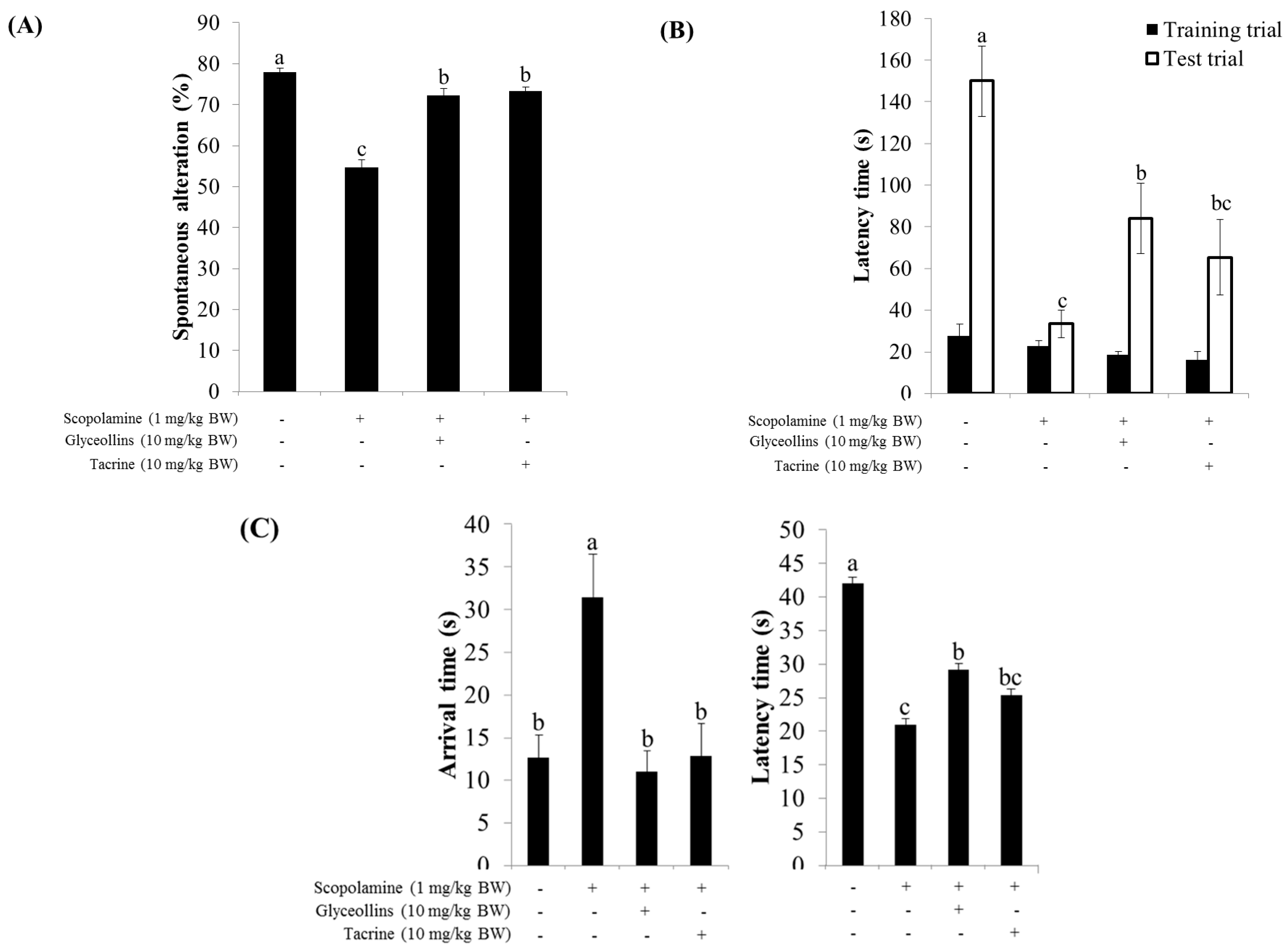
2.7. Improvement of Cognitive Function by Glyceollin Treatment of Scopolamine-Induced Mouse Model of Amnesis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Chemicals
4.2. Preparation of Glyceollins
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. Isolation of Cortical Neurons
4.5. Oxytosis Assay
4.6. DAPI Staining
4.7. Establishment of Antioxidant Response Element (ARE) Construct Transfected Stable Cell Lines
4.8. Antioxidant Response Element (ARE)–Reporter Gene Assay
4.9. Determination of Intracellular ROS Level
4.10. Western Blot Analysis
4.11. Animal Behavioral Tests
4.12. AChE Activity Assay
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barnham, K.J.; Masters, C.L.; Bush, A.I. Neurodegenerative diseases and oxidative stress. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Suh, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.; Joo, Y.C.; Kim, J.S. Antioxidant activity of glyceollins derived from soybean elicited with Aspergillus sojae. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 11633–11638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; di Luccio, E.; Kong, A.N.; Kim, J.S. Nrf2-mediated induction of phase 2 detoxifying enzymes by glyceollins derived from soybean exposed to Aspergillus sojae. Biotechnol. J. 2011, 6, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Lim, J.S.; Kim, W.K.; Kim, J.S. Soyabean glyceollins: Biological effects and relevance to human health. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2012, 71, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, M.; Li, L.; Iwamoto, N.; Nakajima-Takagi, Y.; Kaneko, H.; Nakayama, Y.; Eguchi, M.; Wada, Y.; Kumagai, Y.; Yamamoto, M. The antioxidant defense system Keap1-Nrf2 comprises a multiple sensing mechanism for responding to a wide range of chemical compounds. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, K.; Chiba, T.; Takahashi, S.; Ishii, T.; Igarashi, K.; Katoh, Y.; Oyake, T.; Hayashi, N.; Satoh, K.; Hatayama, I.; et al. An Nrf2/small Maf heterodimer mediates the induction of phase II detoxifying enzyme genes through antioxidant response elements. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 236, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schipper, H.M.; Song, W.; Zukor, H.; Hascalovici, J.R.; Zeligman, D. Heme oxygenase-1 and neurodegeneration: Expanding frontiers of engagement. J. Neurochem. 2009, 110, 469–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schipper, H.M. Heme oxygenase-1: Role in brain aging and neurodegeneration. Exp. Gerontol. 2000, 35, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linker, R.A.; Lee, D.H.; Ryan, S.; van Dam, A.M.; Conrad, R.; Bista, P.; Zeng, W.; Hronowsky, X.; Buko, A.; Chollate, S.; et al. Fumaric acid esters exert neuroprotective effects in neuroinflammation via activation of the Nrf2 antioxidant pathway. Brain 2011, 134 Pt 3, 678–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, J.; Fang, L.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, W.; An, L. Neuroprotective effects of sulforaphane on cholinergic neurons in mice with Alzheimer’s disease-like lesions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 14396–14410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romeo, L.; Intrieri, M.; D’Agata, V.; Mangano, N.G.; Oriani, G.; Ontario, M.L.; Scapagnini, G. The major green tea polyphenol, (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate, induces heme oxygenase in rat neurons and acts as an effective neuroprotective agent against oxidative stress. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2009, 28, 492S–499S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Lim, S.S.; Park, I.S.; Lim, J.S.; Seo, J.Y.; Kim, J.S. Neuroprotective effects of dehydroglyasperin C through activation of heme oxygenase-1 in mouse hippocampal cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 5583–5589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoh, T.; Okamoto, S.I.; Cui, J.; Watanabe, Y.; Furuta, K.; Suzuki, M.; Tohyama, K.; Lipton, S.A. Activation of the Keap1/Nrf2 pathway for neuroprotection by electrophilic [correction of electrophillic] phase II inducers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukui, K.; Omoi, N.O.; Hayasaka, T.; Shinnkai, T.; Suzuki, S.; Abe, K.; Urano, S. Cognitive impairment of rats caused by oxidative stress and aging, and its prevention by vitamin E. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2002, 959, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Yuan, X.; Pan, Z.; Shen, G.; Kim, J.H.; Yu, S.; Khor, T.O.; Li, W.; Ma, J.; Kong, A.N. Mechanism of action of isothiocyanates: The induction of ARE-regulated genes is associated with activation of ERK and JNK and the phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of Nrf2. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2006, 5, 1918–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, R.; Chen, C.; Mo, Y.Y.; Hebbar, V.; Owuor, E.D.; Tan, T.H.; Kong, A.N. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways induces antioxidant response element-mediated gene expression via a Nrf2-dependent mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 39907–39913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klinkenberg, I.; Blokland, A. The validity of scopolamine as a pharmacological model for cognitive impairment: A review of animal behavioral studies. Neurosci. Biobehav. R. 2010, 34, 1307–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pushpalatha, B.; Venumadhav, N.; Swathi, M.; Raju, A.B. Neuroprotective effect of resveratrol against scopolamine-induced cognitive impairment and oxidative stress in rats. Arch. Biol. Sci. 2013, 65, 1381–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Hu, J.F.; Li, J.; Yang, Z.; Xin, X.L.; Wang, J.; Ding, J.; Geng, M.Y. Effect of acidic oligosaccharide sugar chain on scopolamine-induced memory impairment in rats and its related mechanisms. Neurosci. Lett. 2005, 374, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mhillaj, E.; Catino, S.; Miceli, F.M.; Santangelo, R.; Trabace, L.; Cuomo, V.; Mancuso, C. Ferulic acid improves cognitive skills through the activation of the heme oxygenase system in the rat. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Suh, H.J.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kang, S.C.; Park, S.; Kim, J.S. Antifungal activity of glyceollins isolated from soybean elicited with aspergillus sojae. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 9483–9487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromley-Brits, K.; Deng, Y.; Song, W. Morris water maze test for learning and memory deficits in Alzheimer’s disease model mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.V.; Kim, H.Y.; Ehrlich, H.Y.; Choi, S.Y.; Kim, D.J.; Kim, Y. Amelioration of Alzheimer’s disease by neuroprotective effect of sulforaphane in animal model. Amyloid 2013, 20, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, K.; Tanaka, T.; Han, D.; Senzaki, K.; Kameyama, T.; Nabeshima, T. Protective effects of idebenone and α-tocopherol on β-amyloid-(1-42)-induced learning and memory deficits in rats: Implication of oxidative stress in β-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity in vivo. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1999, 11, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.Y.; Lim, S.S.; Kim, J.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, J.S. Alantolactone and isoalantolactone prevent amyloid β25-35—Induced toxicity in mouse cortical neurons and scopolamine—Induced cognitive impairment in mice. Phytother. Res. 2017, 31, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V., Jr.; Feather-Stone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seo, J.Y.; Kim, B.R.; Oh, J.; Kim, J.-S. Soybean-Derived Phytoalexins Improve Cognitive Function through Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010268
Seo JY, Kim BR, Oh J, Kim J-S. Soybean-Derived Phytoalexins Improve Cognitive Function through Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(1):268. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010268
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeo, Ji Yeon, Bo Ram Kim, Jisun Oh, and Jong-Sang Kim. 2018. "Soybean-Derived Phytoalexins Improve Cognitive Function through Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 1: 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010268
APA StyleSeo, J. Y., Kim, B. R., Oh, J., & Kim, J.-S. (2018). Soybean-Derived Phytoalexins Improve Cognitive Function through Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(1), 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010268