Biological Properties of Tocotrienols: Evidence in Human Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
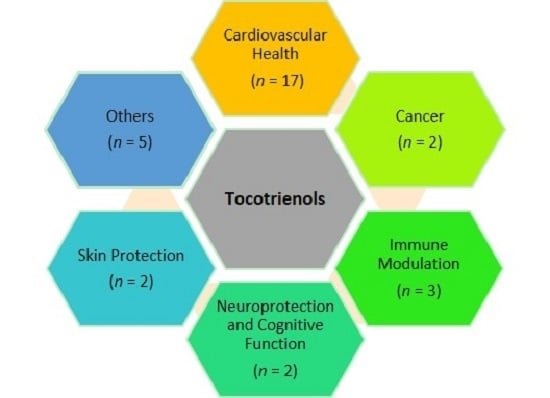
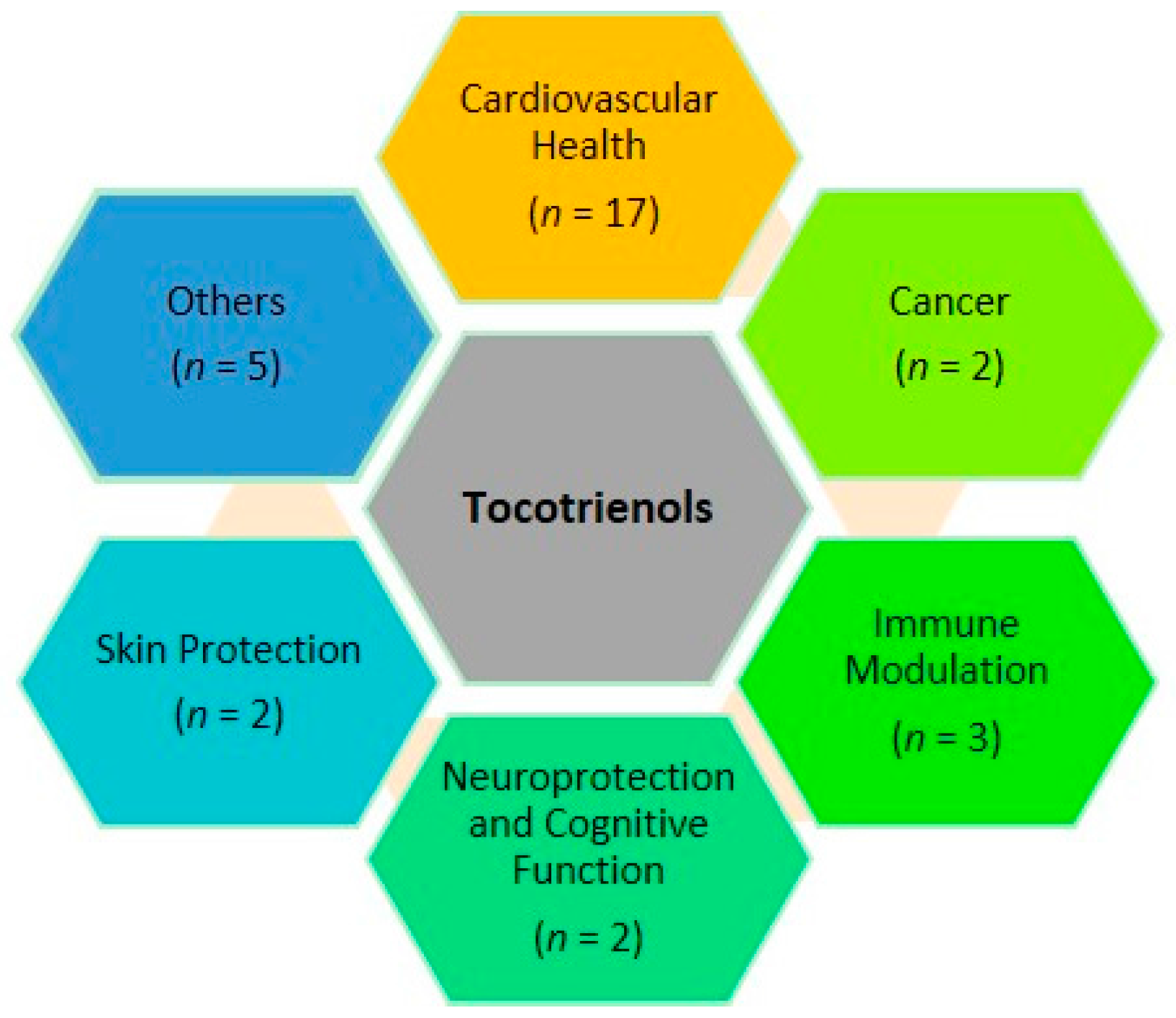
2. Cardiovascular Health
3. Cancer
4. Immune Modulation
5. Neuroprotection and Cognitive Function
6. Skin Protection
7. Other Clinical Effects
8. Pharmacokinetics and Biodistribution
9. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frost and Sullivan. Global Nutraceutical Industry: Investing in Healthy Living. Available online: www.frost.com/prod/servlet/cio/236145272 (accessed on 15 June 2016).
- Kannappan, R.; Gupta, S.C.; Kim, J.H.; Aggarwal, B.B. Tocotrienols fight cancer by targeting multiple cell signaling pathways. Genes Nutr. 2012, 7, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, E.R.; Pastor-Barriuso, R.; Dalal, D.; Riemersma, R.A.; Appel, L.J.; Guallar, E. Meta-analysis: High-dosage vitamin E supplementation may increase all-cause mortality. Ann. Intern. Med. 2005, 142, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meydani, M. Vitamin E and atherosclerosis: beyond prevention of LDL oxidation. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 366S–368S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Parker, R.A.; Pearce, B.C.; Clark, R.W.; Gordon, D.A.; Wright, J.J. Tocotrienols regulate cholesterol production in mammalian cells by post-transcriptional suppression of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 11230–11238. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khor, H.T.; Chieng, D.Y.; Ong, K.K. Tocotrienols inhibit liver HMG CoA reductase activity in the guinea pig. Nutr. Res. 1995, 15, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.A.; Qureshi, N.; Wright, J.J.; Shen, Z.; Kramer, G.; Gapor, A.; Chong, Y.H.; de Witt, G.; Ong, A.S.H.; Peterson, D.M. Lowering of serum cholesterol in hypercholesterolemic humans by tocotrienols (palmvitee). Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1991, 53, 1021S–1026S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, A.A.; Bradlow, B.A.; Salser, W.A.; Brace, L.D. Novel tocotrienols of rice bran modulate cardiovascular disease risk parameters of hypercholesterolemic humans. J. Nutr. Biochem. 1997, 8, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.A.; Sami, S.A.; Salser, W.A.; Khan, F.A. Synergistic effect of tocotrienol-rich fraction (TRF 25) of rice bran and lovastatin on lipid parameters in hypercholesterolemic humans. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2001, 12, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.A.; Sami, S.A.; Salser, W.A.; Khan, F.A. Dose-dependent suppression of serum cholesterol by tocotrienol-rich fraction (TRF 25) of rice bran in hypercholesterolemic humans. Atherosclerosis 2002, 161, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, K.H.; Wong, J.W.; Lim, A.B.; Ng, B.H.; Choy, W.P. Effect of mixed-tocotrienols in hypercholesterolemic subjects. Funct. Food Health Dis. 2011, 1, 106–117. [Google Scholar]
- Wahlqvist, M.L.; Krivokuca-Bogetic, Z.; Lo, C.S.; Hage, B.; Smith, R.; Lukito, W. Differential serum responses of tocopherols and tocotrienols during vitamin supplementation in hypercholesterolaemic individuals without change in coronary risk factors. Nutr. Res. 1992, 12, S181–S201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensink, R.P.; van Houwelingen, A.C.; Kromhout, D.; Hornstra, G. A vitamin E concentrate rich in tocotrienols had no effect on serum lipids, lipoproteins, or platelet function in men with mildly elevated serum lipid concentrations. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 69, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rasool, A.H.; Yuen, K.H.; Yusoff, K.; Wong, A.R.; Rahman, A.R. Dose dependent elevation of plasma tocotrienol levels and its effect on arterial compliance, plasma total antioxidant status, and lipid profile in healthy humans supplemented with tocotrienol rich vitamin E. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2006, 52, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasool, A.H.G.; Rahman, A.R.A.; Yuen, K.H.; Wong, A.R. Arterial compliance and vitamin E blood levels with a self emulsifying preparation of tocotrienol rich vitamin E. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2008, 31, 1212–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, S.F.; Ibahim, J.; Makpol, S.; Hamid, N.A.A.; Latiff, A.A.; Zakaria, Z.; Mazlan, M.; Yusof, Y.A.M.; Karim, A.A.; Ngah, W.Z.W. Tocotrienol rich fraction supplementation improved lipid profile and oxidative status in healthy older adults: A randomized controlled study. Nutr. Metab. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.T.; Khor, H.T.; Low, W.H.; Ali, A.; Gapor, A. Effect of a palm-oil-vitamin E concentrate on the serum and lipoprotein lipids in humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1991, 53, 1027S–1030S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baliarsingh, S.; Beg, Z.H.; Ahmad, J. The therapeutic impacts of tocotrienols in type 2 diabetic patients with hyperlipidemia. Atherosclerosis 2005, 182, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daud, Z.A.M.; Tubie, B.; Sheyman, M.; Osia, R.; Adams, J.; Tubie, S.; Khosla, P. Vitamin E tocotrienol supplementation improves lipid profiles in chronic hemodialysis patients. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2013, 9, 747–761. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tomeo, A.C.; Geller, M.; Watkins, T.R.; Gapor, A.; Bierenbaum, M.L. Antioxidant effects of tocotrienols in patients with hyperlipidemia and carotid stenosis. Lipids 1995, 30, 1179–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.W.; Loh, H.S.; Ting, K.N.; Bradshaw, T.D.; Zeenathul, N.A. Cytotoxicity and apoptotic activities of α-, β-and δ-tocotrienol isomers on human cancer cells. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, S.; Parinandi, N.L.; Kotha, S.R.; Roy, S.; Rink, C.; Bibus, D.; Sen, C.K. Nanomolar vitamin E α-tocotrienol inhibits glutamate-induced activation of phospholipase A2 and causes neuroprotection. J. Neurochem. 2010, 112, 1249–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustad, V.A.; Smith, C.A.; Ruey, P.P.; Edens, N.K.; DeMichele, S.J. Supplementation with 3 compositionally different tocotrienol supplements does not improve cardiovascular disease risk factors in men and women with hypercholesterolemia. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 76, 1237–1243. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zaiden, N.; Yap, W.N.; Ong, S.; Xu, C.H.; Teo, V.H.; Chang, C.P.; Zhang, X.W.; Nesaretnam, K.; Shiba, S.; Yap, Y.L. Gamma delta tocotrienols reduce hepatic triglyceride synthesis and VLDL secretion. J. Atheroscler Thromb. 2010, 17, 1019–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Byrne, D.; Grundy, S.; Packer, L.; Devaraj, S.; Baldenius, K.; Hoppe, P.P.; Kraemer, K.; Jialal, I.; Traber, M.G. Studies of LDL oxidation following α-, γ-, or δ-tocotrienyl acetate supplementation of hypercholesterolemic humans. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2000, 29, 834–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesaretnam, K.; Meganathan, P.; Veerasenan, S.D.; Selvaduray, K.R. Tocotrienols and breast cancer: The evidence to date. Genes Nutr. 2012, 7, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesaretnam, K.; Selvaduray, K.R.; Razak, G.A.; Veerasenan, S.D.; Gomez, P.A. Effectiveness of tocotrienol-rich fraction combined with tamoxifen in the management of women with early breast cancer: A pilot clinical trial. Breast Cancer Res. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Springett, G.M.; Husain, K.; Neuger, A.; Centeno, B.; Chen, D.T.; Hutchinson, T.Z.; Lush, R.M.; Sebti, S.; Malafa, M.P. A Phase I Safety, Pharmacokinetic, and Pharmacodynamic Presurgical Trial of Vitamin E δ-tocotrienol in Patients with Pancreatic Ductal Neoplasia. EBioMedicine 2015, 2, 1987–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radhakrishnan, A.K.; Lee, A.L.; Wong, P.F.; Kaur, J.; Aung, H.; Nesaretnam, K. Daily supplementation of tocotrienol-rich fraction or α-tocopherol did not induce immunomodulatory changes in healthy human volunteers. Br. J. Nutr. 2009, 101, 810–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahalingam, D.; Radhakrishnan, A.K.; Amom, Z.; Ibrahim, N.; Nesaretnam, K. Effects of supplementation with tocotrienol-rich fraction on immune response to tetanus toxoid immunization in normal healthy volunteers. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 65, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jubri, Z.; Latif, A.A.; Top, A.G.M.; Ngah, W.Z.W. Perturbation of cellular immune functions in cigarette smokers and protection by palm oil vitamin E supplementation. J. Nutr. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, V.; Rink, C.; Gordillo, G.M.; Khanna, S.; Gnyawali, U.; Roy, S.; Shneker, B.; Ganesh, K.; Phillips, G.; More, J.L.; et al. Oral tocotrienols are transported to human tissues and delay the progression of the model for end-stage liver disease score in patients. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopalan, Y.; Shuaib, I.L.; Magosso, E.; Ansari, M.A.; Bakar, M.R.A.; Wong, J.W.; Khan, N.A.K.; Liong, W.C.; Sundram, K.; Ng, B.H.; et al. Clinical investigation of the protective effects of palm vitamin E tocotrienols on brain white matter. Stroke 2014, 45, 1422–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.L.; Foong, S.C.; Foong, W.C.; Yusuff, Y.; Chettiar, S.M. Tocotrienol-rich fractions (TRF) supplementation in school-going children with Attention Deficit/Hyperactive Disorder (ADHD): A randomized controlled trial. BMC Nutr. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrelli, V.F.; Lauriola, M.M.; Pigatto, P.D. Clinical evaluation of photoprotective effect by a topical antioxidants combination (tocopherols and tocotrienols). J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2012, 26, 1449–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoo, T.L.; Halim, A.S.; Zakaria, Z.; Saad, A.M.; Wu, L.Y.; Lau, H.Y. A prospective, randomised, double-blinded trial to study the efficacy of topical tocotrienol in the prevention of hypertrophic scars. J. Plast Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2011, 64, e137–e145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heng, E.C.; Karsani, S.A.; Rahman, M.A.; Hamid, N.A.A.; Hamid, Z.; Ngah, W.Z.W. Supplementation with tocotrienol-rich fraction alters the plasma levels of Apolipoprotein AI precursor, Apolipoprotein E precursor, and C-reactive protein precursor from young and old individuals. Eur. J. Nutr. 2013, 52, 1811–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, S.F.; Hamid, N.A.A.; Latiff, A.A.; Zakaria, Z.; Mazlan, M.; Yusof, Y.A.M.; Karim, A.A.; Ibahim, J.; Hamid, Z.; Ngah, W.Z.W. Reduction of DNA damage in older healthy adults by Tri E® Tocotrienol supplementation. Nutrition 2008, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magosso, E.; Ansari, M.A.; Gopalan, Y.; Shuaib, I.L.; Wong, J.W.; Khan, N.A.K.; Bakar, M.R.A.; Ng, B.H.; Yuen, K.H. Tocotrienols for normalisation of hepatic echogenic response in nonalcoholic fatty liver: A randomised placebo-controlled clinical trial. Nutr. J. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, Y.L.; Ming, L.; How, C.B.; Hay, Y.K.; Nesaretnam, K.; Kim-Tiu, T.; Selvaduray, K.R.; Meganathan, P.; Fu, J.-Y. Safety assessment of tocotrienol supplementation in subjects with metabolic syndrome: A randomised control trial. J. Oil Palm Res. 2016, 28, 34–43. [Google Scholar]
- Mahdy, Z.A.; Siraj, H.H.; Khaza’ai, H.; Mutalib, M.S.A.; Azwar, M.H.; Wahab, M.A.; Dali, A.Z.H.M.; Jaafar, R.; Ismail, N.A.M.; Jamil, M.A.; et al. Does palm oil vitamin E reduce the risk of pregnancy induced hypertension? Acta Medica 2013, 56, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, S.P.; Yuen, K.H.; Wong, J.W. Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of α-, γ-and δ-tocotrienols under different food status. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2001, 53, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, S.P.; Yuen, K.H. Influence of lipolysis and droplet size on tocotrienol absorption from self-emulsifying formulations. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 281, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairus, S.; Nor, R.M.; Cheng, H.M.; Sundram, K. Postprandial metabolic fate of tocotrienol-rich vitamin E differs significantly from that of α-tocopherol. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 84, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fairus, S.; Nor, R.M.; Cheng, H.M.; Sundram, K. α-tocotrienol is the most abundant tocotrienol isomer circulated in plasma and lipoproteins after postprandial tocotrienol-rich vitamin E supplementation. Nutr. J. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loganathan, R.; Selvaduray, K.R.; Nesaretnam, K.; Radhakrishnan, A.K. Tocotrienols promote apoptosis in human breast cancer cells by inducing poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase cleavage and inhibiting nuclear factor κ-B activity. Cell Prolif. 2013, 46, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvaduray, K.R.; Radhakrishnan, A.K.; Kutty, M.K.; Nesaretnam, K. Palm tocotrienols decrease levels of pro-angiogenic markers in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) and murine mammary cancer cells. Genes Nutr. 2012, 7, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meganathan, P.; Jabir, R.S.; Fuang, H.G.; Bhoo-Pathy, N.; Choudhury, R.B.; Taib, N.A.; Nesaretnam, K.; Chik, Z. A new formulation of gamma delta Tocotrienol has superior bioavailability compared to existing Tocotrienol-Rich Fraction in healthy human subjects. Sci. Rep. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.-Y.; Che, H.L.; Tan, D.M.Y.; Teng, K.T. Bioavailability of tocotrienols: Evidence in human studies. Nutr. Metab. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meganathan, P.; Fu, J.-Y. Biological Properties of Tocotrienols: Evidence in Human Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1682. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111682
Meganathan P, Fu J-Y. Biological Properties of Tocotrienols: Evidence in Human Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(11):1682. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111682
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeganathan, Puvaneswari, and Ju-Yen Fu. 2016. "Biological Properties of Tocotrienols: Evidence in Human Studies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 11: 1682. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111682
APA StyleMeganathan, P., & Fu, J.-Y. (2016). Biological Properties of Tocotrienols: Evidence in Human Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(11), 1682. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111682